NEET Biology Notes PDF Free Download
NEET Biology Notes For Fungi Zygomycetes
- Common Name: Conjugation fungi.
- Cell Wall: Chitinous
- Mycelium: Coenocytic
- Sexual Reproduction: Gametangial copulation
- Sexual Spore: Zygospore Motile stage is absent.
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Notes
NEET Biology Notes For Life Cycle Of Rhizopus
Rhizopus grows on carbohydrate-rich medium. It is a saprophyte with an absorptive mode of nutrition.
The mycelium contains two types of vegetative hyphae, which arise from definite points called apparent nodes or holdfasts. The two types of hyphae are stoloniferous and rhizoidal in the asexual phase the mycelium produces a third type of hyphae called sporangiophore.
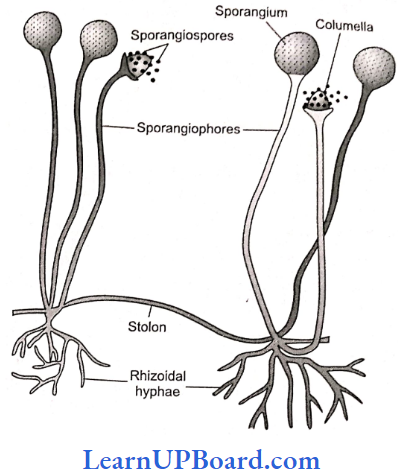
A dome-shaped partition or columella separates the spore-bearing part from the rest of the sporangiophore. During sexual reproduction, a fourth type of hyphae arises. They are called as zygospores.
- Life Cycle Of Rhizopus Asexual Reproduction: Mycelium can multiply asexually by means of three types of mitospores: sporangiospores, chlamydospores, and oidia. Oidia formation occurs when the hyphae get submerged in sugary fermentation. Chlamydospores are produced under unfavorable conditions while sporangiospores are formed in favorable environments.
- Life Cycle Of Rhizopus Sexual Reproduction: Most of the species of Rhizopus are heterothallic, but a few (for example, R. sexualis) are homothallic. The phenomenon of heterothallism was discovered by Blakeslee in R. stolonifer. Heterothallism results in greater variations and it is a device to prevent inbreeding.
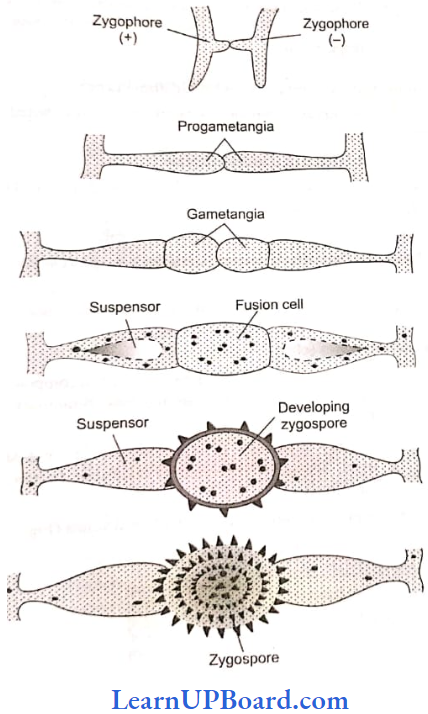
Sexual Reproduction occurs by conjugation. In heterothallic species, mycelia are morphologically similar but genetically different. They are designated as plus (+) and minus (-). The presence of both types of mycelia stimulates (through trisporic acid) each other to produce special subaerial hyphae called zy- gophores.
The two types of zygophores come in contact and produce gametangia at the tips of club-shaped branches. The common wall between the gametangia dissolves. Their protoplasts function as gametes. They fuse to form a diploid zygote- spore. The wall of the mature zygospore is five-layered (two in exosporium and three in endosporium).
NEET Biology Notes For Zygomycetes
Zygospore germinates under favorable conditions. Its diploid nuclei divide meiotically to produce haploid nuclei. Only one haploid nucleus remains functional. It multiplies repeatedly to produce multinucleate conditions.
Importance Of Zygomycetes:
- Ramysin antibiotic is produced by Mucor Armenians.
- The growth of Mucor arrhizus removes heavy metal contamination of water.
- Fumaric acid is obtained from R. stolonifer and citric acid is obtained from Mucor.
- Rhizopus species produces soft rot or leak disease in sweet potatoes, apple, and strawberries.
- Ahsidia corymhifera causes bronchomycosis.
NEET Biology Notes For Ascomycetes (Sac Fungi)
- Plant body is unicellular (for example, yeast) or mycelial (for example, Penicillium, Aspergillus).
- Mycelium is branched, septate, generally monokaryotic (for example, Penicillium) or dikaryotic (shorter phase).
- The simple septal pore is present in mycelia, which may get partially plugged by membrane-bound bodies and a crystalline structure called worn bodies.
- Asexual reproduction takes place by the formation of conidia.
- Sexual reproduction occurs by (1) gametangial contact (for example, Pyronemd), (2) conjugation (for example, yeast),
- somatization (for example, Ascoholus), (4) homogamy (for example, Peziza), or (5) autogamy.
- Each ascus lias four to eight ascospores arranged either in linear order (for example, Neurospora) or unorderly (for example, yeast).
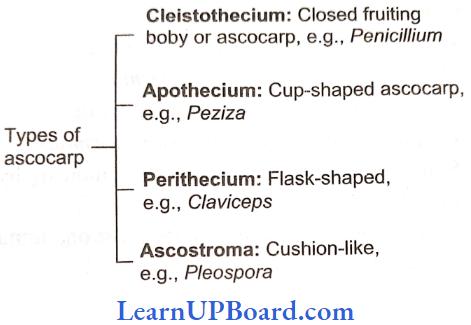
- Asci are aggregated into fructifications called ascocarps. It is surrounded by a peridium of vegetative hyphae and internal contents collectively called centrum.