NEET Chemistry MCQs
NEET Chemistry For Aldehydes Ketones And Carboxylic Acids Multiple Choice Questions
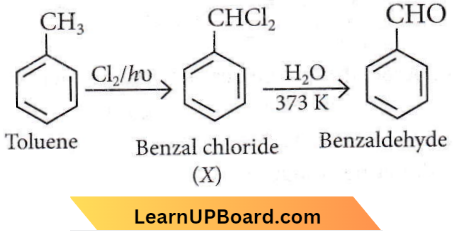
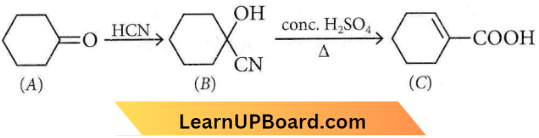
Question 1. The intermediate compound X in the following chemical reaction is
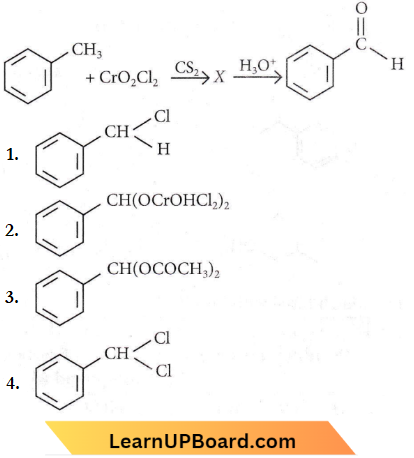
Answer: 2
Question 2. Identify compound X in the following sequence of reactions:
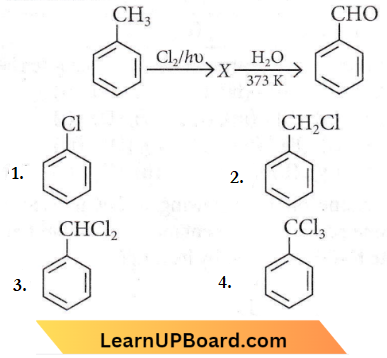
Answer: 3
NEET chemistry MCQs
Question 3. Reaction by which benzaldehyde cannot be prepared
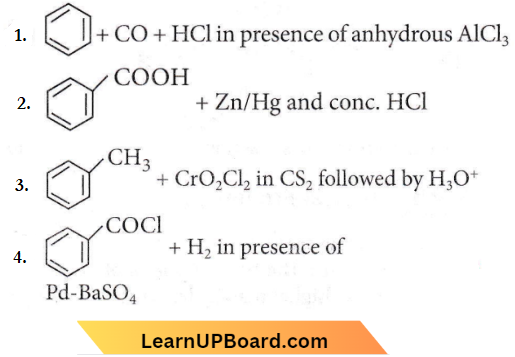
Answer: 2
Clemmensen reduction in the presence of Zn-Hg and con. HCl reduces aldehydes and ketones to -CH2 group but the carboxylic acid group remains unaffected.
Question 4. Consider the following reaction.
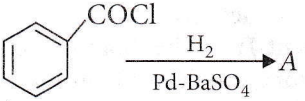
The product A is
Answer: 1
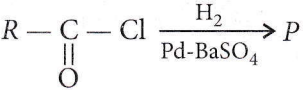
It is Rosenmund’s reduction.
Question 5. Which one of the following can be oxidised to the corresponding carbonyl compound?
- 2-Hydroxypropane
- Ortho-Nitrophenol
- Phenol
- 2-Methyl-2-hydroxy-propane
Answer: 1. 2-Hydroxypropane
Read and Learn More NEET MCQs with Answers
Question 6. In the following reaction, product P is
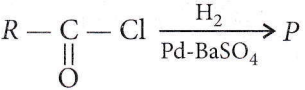
- RCH2OH
- RCOOH
- RCHO
- RCH3
Answer: 3. RCHO
This is Rosenmund reduction
Question 7. Which alkene on ozonolysis gives CH3CH2CHO and CH3COCH3?
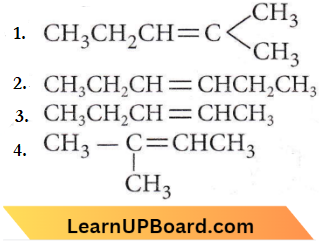
Answer: 1
Question 8. 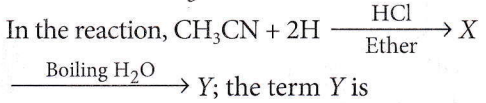
- Acetaldehyde
- Ethanolamine
- Acetone
- Dimethylamine.
Answer: 1. Acetaldehyde
Question 9. Ketones [RCOR1] where R = R1 = alkyl group. It can be obtained in one step by
- Oxidation of tertiary alcohol
- Reaction of acid halide with alcohols
- Hydrolysis of esters
- Oxidation of primary alcohol.
Answer: 1. Oxidation of tertiary alcohol
A tertiary alcohol is difficult to oxidise. But when it is treated with an acidic oxidising agent under some conditions, it is oxidised to ketone and then to acids. Both the ketone and acid contain a lesser number of carbon atoms than the starting alcohol.
Question 10. The oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde by chromyl chloride is called
- Etard reaction
- Riemer-Tiemann reaction
- Wurtz reaction
- Cannizzaro’s reaction.
Answer: 1. Etard reaction
The oxidation of toluene (C6H5CH3) with chromyl chloride (CrO2Cl2) in CCl4 or CS2 to give benzaldehyde is called the Etard reaction. In this reaction, the chromyl chortle first forms a brown complex, which is separated and then decomposed with H2O to give benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO).
Question 11. Given below are two statements:
- Statement-1: The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are higher than hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses because of weak molecular association in aldehydes and ketones due to dipole-dipole interactions.
- Statement 2: The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are lower than the alcohols of similar molecular masses due to the absence of H-bonding. In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
- Both statement-1 and statement-2 are correct.
- Both statement-1 and statement-2 are incorrect.
- Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect.
- Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct.
Answer: 1. Both statement 1 and statement 2 are correct.
Both the given statements are correct.
Question 12. Identify the product (A) in the following reaction
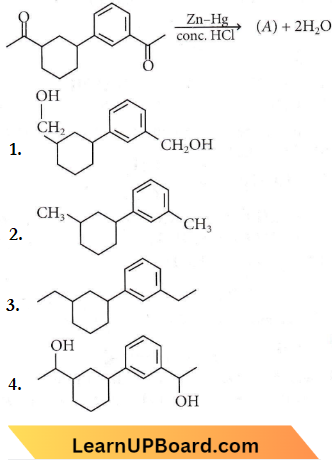
Answer: 3
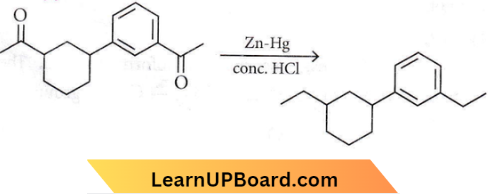
This is the Ciemmensen reduction reaction.
Question 13. Identify the product [D] obtained in the following sequence of reactions.
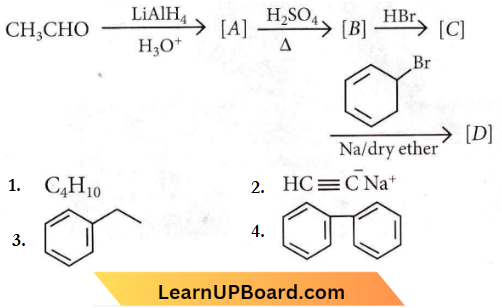
Answer: 3
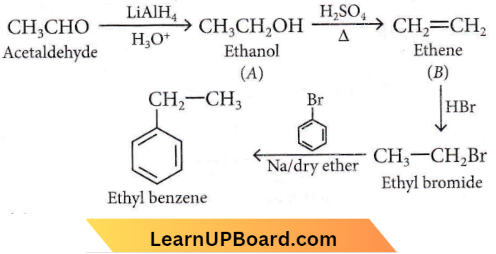
NEET organic chemistry questions
Question 14. Identify the major product obtained in the following reaction.
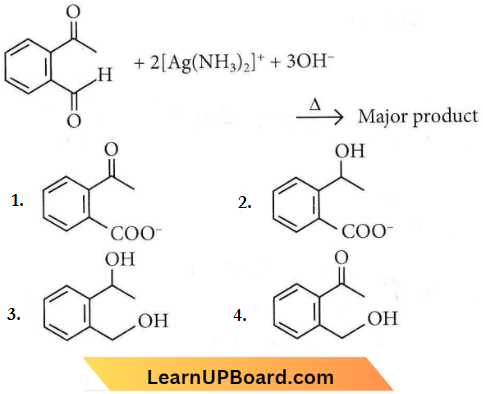
Answer: 1
Question 15. Match the List 1 with List 2.
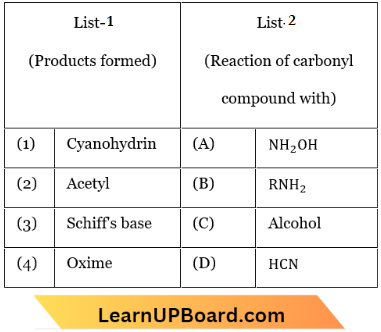
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- 1-C, 2-D, 3-B, 4-A
- 1-B, 2-C, 3-D, 4-A
- 1-A, 2-C, 3-B, 4-D
- 1-D, 2-C, 3-B, 4-A
Answer: 4. 1-C, 2-D, 3-B, 4-A
- Aldehydes react with HCN to give cyanohydrin.
- Aldehydes react with alcohol to form acetal.
- Aldehydes react with amine to give Schifft base.
- Aldehydes react with NH2OH to give oxime.
Question 16. Which one of the following is not formed when acetone reacts with 2-pentanone in the presence of dilute NaOH followed by heating?
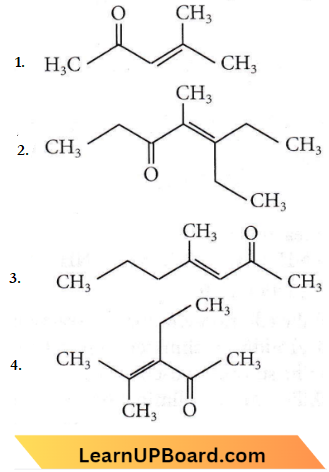
Answer: 2
When acetone reacts with 2-pentanone in the presence of dii. NaOH, the following products are formed
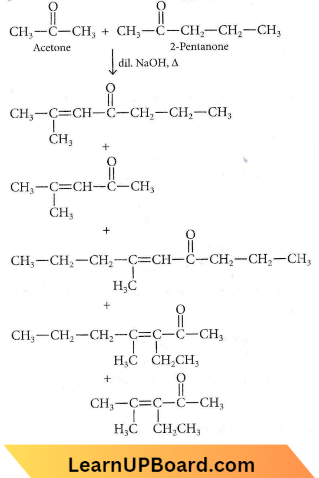
NEET organic chemistry questions
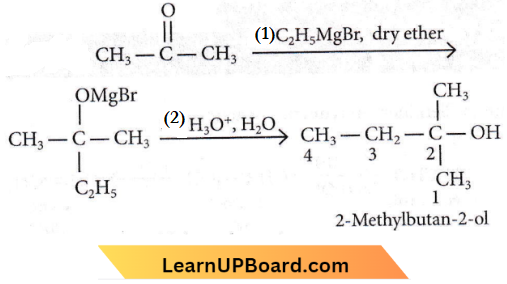
Question 17. What is the IUPAC name of the organic compound formed in the following chemical reaction?
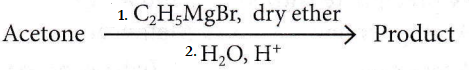
- 2-Methylbutan-2-ol
- 2-Methylpropan-2-ol
- Pentan-2-ol
- Pentan-3-ol
Answer: 1. 2-Methylbutan-2-ol
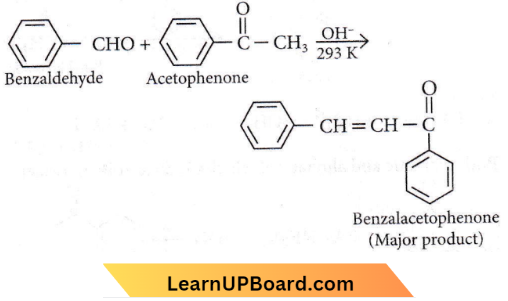
Question 18. The reaction between benzaldehyde and acetophenone in the presence of dilute NaOH is known as
- Aldol condensation
- Cannizzaros reaction
- Cross Cannizzaros reaction
- Cross Aldol condensation.
Answer: 4. Cross Aldol condensation.
Cross aldol condensation
Question 19. Consider the reactions,
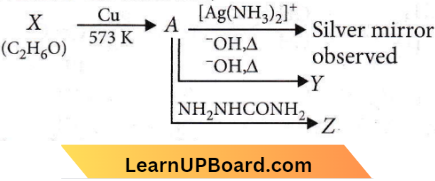
Identify A, X, Y and Z.
- A-Methoxymethane, X-Ethanol, Y-Ethanoic acid, Z-Semicarbazide.
- A-Ethanal, X-Ethanol, Y-But-2-enal, Z-Semicarbazone.
- A-Ethanol, X-Acetaldehyde, Y-Butanone, Z- Hydrazone.
- A-Methoxymethane, X-Ethanoic acid, Y-Acetate ion, Z-Hydrazine.
Answer: 2. A-Ethanal, X-Ethanol, Y-But-2-enal, Z-Semicarbazone.
Since A gives a silver mirror test, it must be an aldehyde and aldehydes are formed by oxidation of 1° alcohols’ Thus, ‘X’ is a 1° alcohol, i.e., CH3CH2OH.
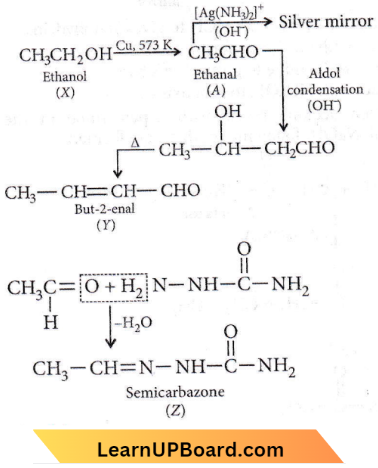
Question 20. Of the following, which is the product formed when cyclohexanone undergoes aldol condensation followed by heating?
Answer: 1
Question 21. The correct structure of the product ‘A’ formed in the reaction
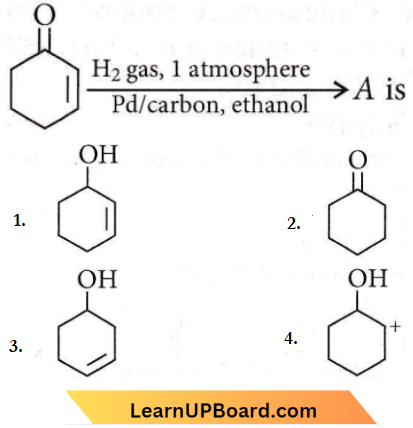
Answer: 2
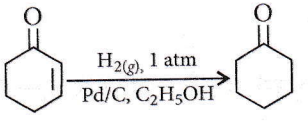
C = C bond is reduced faster than C = O bond with H2(Pd-C).
Question 22. Which of the following reagents would distinguish ds-cyclopenta-1,2-diol from the trans-isomer?
- MnO2
- Aluminium isopropoxide
- Acetone
- Ozone
Answer: 3. Acetone
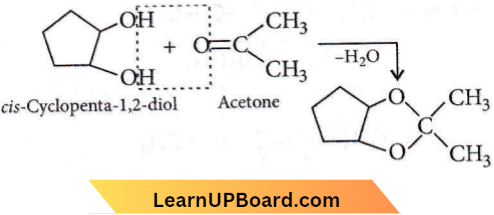
Trans-isomer does not react with acetone
Question 23. The correct statement regarding a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon is
- A carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon rapidly equilibrates with its corresponding enol and this process is known as carbonylation
- A carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon rapidly equilibrates with its corresponding enol and this process is known as keto-enol tautomerism
- A carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon never equilibrates with its corresponding enol
- A carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon rapidly equilibrates with its corresponding enol and this process is known as aldehyde-ketone equilibration.
Answer: 2. A carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon rapidly equilibrates with its corresponding enol and this process is known as keto-enol tautomerism
Keto-enol tautomerism
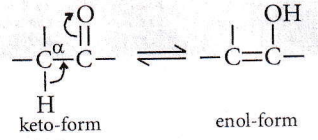
Question 24. The product formed by the reaction of an aldehyde with a primary amine is
- Carboxylic acid
- Aromatic acid
- Schiff’sbase
- Ketone.
Answer: 3. Schiff’sbase
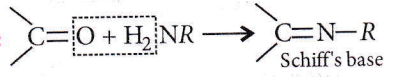
Question 25. Reaction of a carbonyl compound with one of the following reagents involves nucleophilic addition followed by elimination of water. The reagent is
- Hydrazine in the presence of a feebly acidic solution
- Hydrocyanic acid
- Sodium hydrogen sulphite
- A Grignard reagent.
Answer: 1. Hydrazine in the presence of a feebly acidic solution
Carbonyl compounds react with ammonia derivatives in the weakly acidic medium as follows
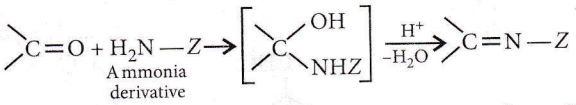
Question 26. Which one is most reactive towards nucleophilic addition reaction?
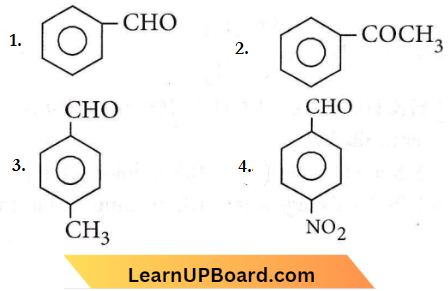
Answer: 4
Aromatic aldehydes are more reactive than alkyl aryl ketones. The electron withdrawing group (-NO2) increases the reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reactions whereas the electron donating group (-CH3) decreases the reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reactions.
Therefore, the order is
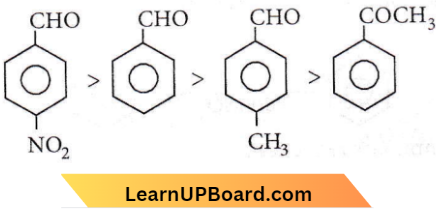
NEET organic chemistry questions
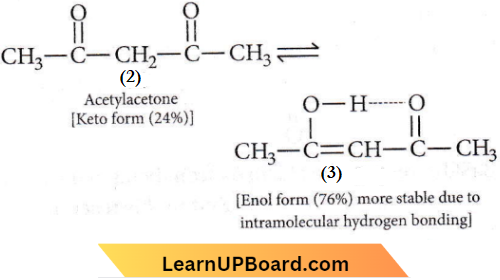
Question 27. The order of stability of the following tautomeric compounds is
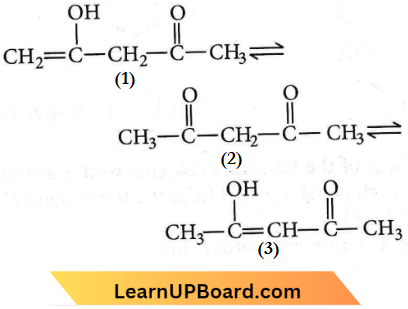
- 2>1>3
- 2>3>1
- 1>2>3
- 3>2>1
Answer: 4. 3>2>1
Question 28. Predict the products in the given reaction.
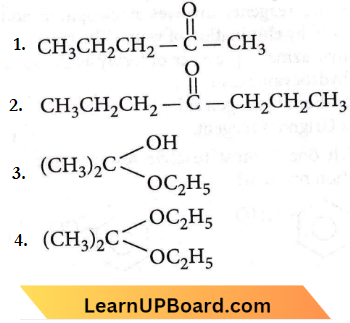
Answer: 3
Aldehyde having no α,-hydrogen atoms on heating with concentrated alkali solution (50%) undergoes Cannizzaro’s reaction.
Question 29. Acetone is treated with excess ethanol in the presence of hydrochloric acid. Hie product obtained is
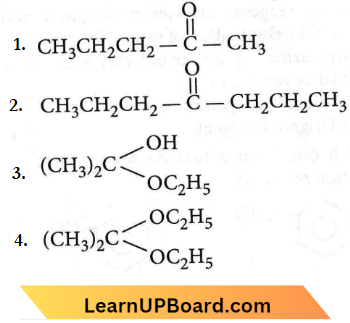
Answer: 4
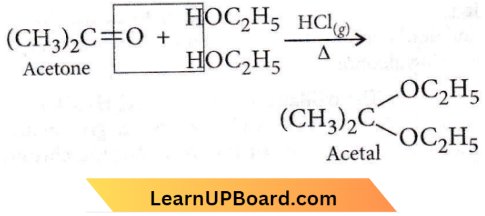
Question 30. CH3CHO and C6H5CH2CHO can be distinguished chemically by
- Benedict’s test
- Iodoform test
- Tollens’ reagent test
- Fehling’s solution test.
Answer: 2. Iodoform test
Acetaldehyde acetone and methyl ketones having CH3CO- group undergo a haloform reaction. Thus CH3CHO will give a yellow precipitate with I2 and NaOH but C6H5CH2CHO will not.
NEET organic chemistry questions
Question 31. Consider the reaction RCHO + NH2NH2 → RCH=N — NH2 What sort of reaction is it?
- Electrophilic addition-elimination reaction
- Free radical addition-elimination reaction
- Electrophilic substitution-elimination reaction
- Nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction
Answer: 4. Nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction
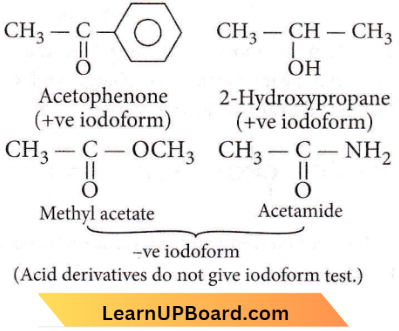
Question 32. Which of the following compounds will give a yellow precipitate with iodine and alkali?
- Acetophenone
- Methyl acetate
- Acetamide
- 2-Hydroxypropane
Answer: 1. Acetophenone and 4. 2-Hydroxypropane
This example shows the iodoform reaction.
The compound with  the group will give a yellow precipitate of iodoform (CH3) when reacting with iodine and alkali.
the group will give a yellow precipitate of iodoform (CH3) when reacting with iodine and alkali.
Question 33. Clemmensen reduction of a ketone is carried out in the presence of which of the following?
- Glycol with KOH
- Zn-Hg with HCl
- LiAIH4
- H2 and Pt as catalyst
Answer: 2. Zn-Hg with HCl
The Carbonyl group is reduced to -CH2 group when treated with amalgamated zinc and conc. HCI. This process is called Clemmensent reduction.
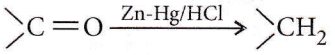
Question 34. The order of reactivity of phenyl magnesium bromide (PhMgBr) with the following compounds :
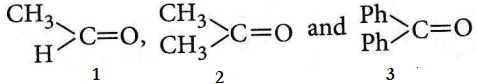
- 3>2>1
- 2>1>3
- 1>3>2
- 1>2>3
Answer: 4. 1>2>3
The greater the number of alkyl/phenyl groups attached to the carbonyl groups lower its reactivity 1 > 2 > 3. +R-effect is stronger than +I-effect
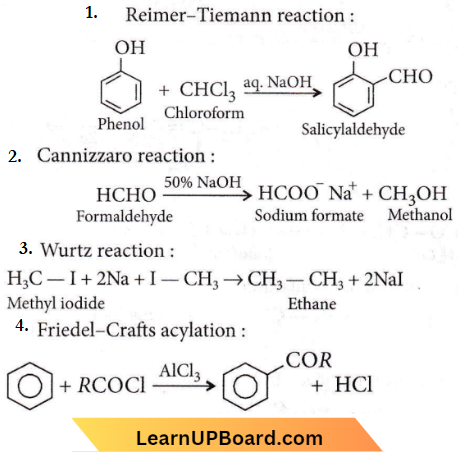
Question 35. Which of the following reactions will not result in the formation of carbon-carbon bonds?
- Reimer-Tiemann reaction
- Cannizzaro reaction
- Wurtz reaction
- Friedel-Crafts acylation
Answer: 2. Cannizzaro reaction
From the above examples, it is evident that C-C bond formation does not take place in the Cannizzaro reaction.
NEET chemistry practice questions
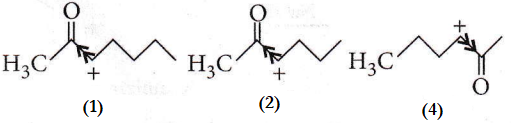
Question 36. Which one of the following compounds will be most readily dehydrated?
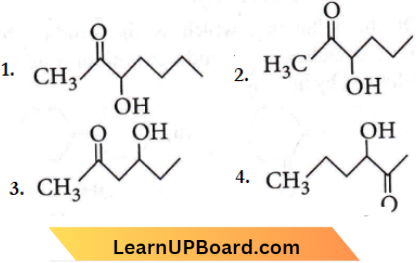
Answer: 3
The ease of dehydration of the given compounds can be explained on the basis of the stability of the carbocation formed. In the case of options (1), (2) and (4), a secondary carbocation is formed but the presence of an electron-withdrawing ![]() group adjacent to the positively charged carbon, intensifies the charge and hence, destabilises the species.
group adjacent to the positively charged carbon, intensifies the charge and hence, destabilises the species.
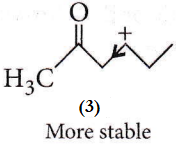
However, in the case of option (3), a secondary carbocation is formed, but the electron-withdrawing ![]() group is present farther away, as a result, the effect of this group is diminished and hence, the carbocation is relatively more stable
group is present farther away, as a result, the effect of this group is diminished and hence, the carbocation is relatively more stable
Question 37. The following compounds are given,

Which of the above compound(s), on being warmed with iodine solution and NaOH, will give iodoform?
- 1, 3 and 4
- Only 2
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 2
Answer: 3. 1, 2 and 3
Compounds with 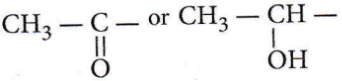 give positive iodoform hence, (1), (2) and (3) will give positive iodoform not (4).
give positive iodoform hence, (1), (2) and (3) will give positive iodoform not (4).
Question 38. Acetophenone when reacted with a base, C2H5ONa, yields a stable compound which has the structure
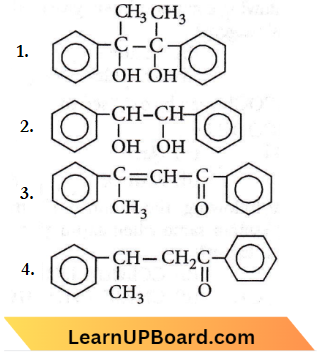
Answer: 3
The first step is a simple condensation reaction. The last step is an example of the E1cB mechanism and the leaving group is hydroxide, which is unusual. Still, this step manages to take place owing to the stability incorporated therein the product, which is a conjugated carbonyl compound.
Question 39. A strong base can abstract an α-hydrogen from
- Ketone
- Alkane
- Alkene
- Amine.
Answer: 1. Ketone
The base (OH–) ion removes one of the α-hydrogen atoms (which is somewhat acidic) from aldehydes and ketones to form a carbanion or the enolate ion. The acidity of a-hydrogen is due to resonance stabilization of enolate anion.
NEET chemistry practice questions
Question 40. Reduction of aldehydes and ketones into hydrocarbons using zinc amalgam and cone. HCl is called
- Cope reduction
- Dow reduction
- Wolff-Kishner reduction
- Clemmensen reduction.
Answer: 4. Clemmensen reduction.
Aldehydes and ketones are converted to alkanes when treated with zinc amalgam and conc. HCl. This is known as Clemmensen reduction. Here ![]() group is reduced to
group is reduced to ![]() the group.
the group.
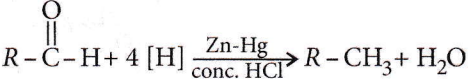
Question 41. Which one of the following on treatment with 50% aqueous sodium hydroxide yields the corresponding alcohol and acid?
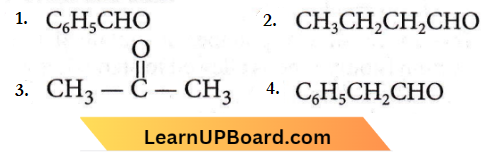
Answer: 1
Aldehydes which do not have α-H atoms, in the presence of 50% NaOH or 50% KOH undergo a disproportionation reaction to produce alcohol and sodium salt of the acid. This reaction is known as Cantizzaro reaction. C6H5CHO containing no α-H atom undergoes the Canrtizzaro reaction to produce benzyl alcohol and sodium benzoate.
⇒ \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{CHO}\) \(\underrightarrow{50 \% \mathrm{NaOH}}\) \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{OH}+\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{COONa}\)
Question 42. The product formed in aldol condensation is
- A beta-hydroxy aldehyde or a beta-hydroxy ketone
- An alpha-hydroxy aldehyde or ketone
- An alpha, beta-unsaturated ester
- A beta-hydroxy acid.
Answer: 1. A beta-hydroxy aldehyde or a beta-hydroxy ketone
The aldehydes or ketones containing α-H atom in the presence of dilute alkali undergo a self-condensation reaction to form β-hydroxyaldehyde or β-hydroxyketone. This reaction is known as aldol condensation.
Question 43. Nucleophilic addition reaction will be most favoured in
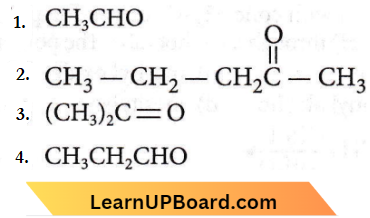
Answer: 1
NEET chemistry practice questions
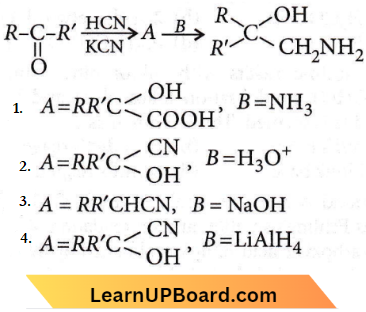
Question 44. A carbonyl compound reacts with hydrogen cyanide to form cyanohydrin which on hydrolysis forms a racemic mixture of a-hydroxy acid. The carbonyl compound is
- Formaldehyde
- Acetaldehyde
- Acetone
- Diethyl ketone.
Answer: 2
Given
A carbonyl compound reacts with hydrogen cyanide to form cyanohydrin which on hydrolysis forms a racemic mixture of a-hydroxy acid.
Question 45. The major organic product formed from the following reaction:
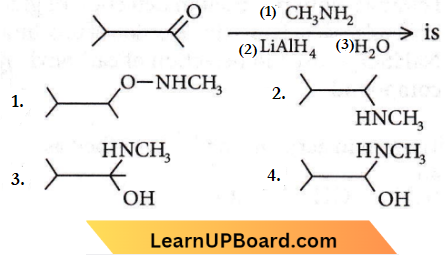
Answer: 2
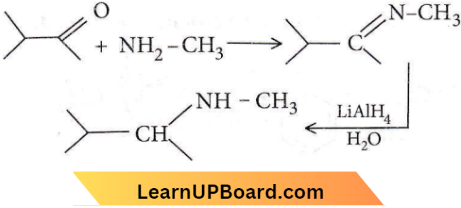
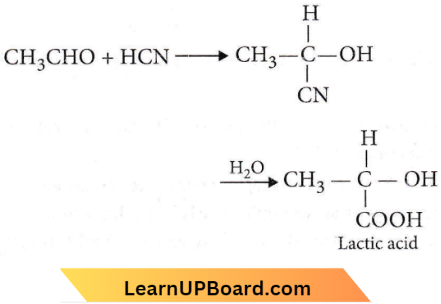
Question 46. In this reaction, an asymmetric centre is generated. The acid obtained would be
⇒ \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CHO}+\mathrm{HCN}\rightarrow \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}(\mathrm{OH}) \mathrm{CN}\) \(\underrightarrow{\mathrm{HOH}}\) \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}(\mathrm{OH}) \mathrm{COOH}\)
An asymmetric centre is generated. The acid obtained would be
- D-isomer
- L-isomer
- 50% D + 50% L-isomer
- 20% D + 80% L-isomer.
Answer: 3. 50% D + 50% L-isomer
Lactic acid (CH3CH(OH)COOH) is an optically active compound due to the presence of an asymmetric carbon atom. It exists, in D- and L-form, the ratio of which is found to be (1: 1), i.e., a racemic mixture is obtained.
NEET chemistry chapter-wise questions
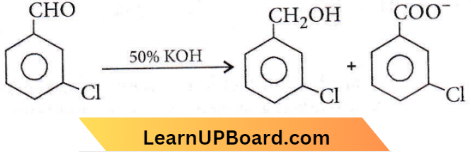
Question 47. When m-chlorobenzaldehyde is treated with 50% KOH solution, the product(s) obtained is (are)
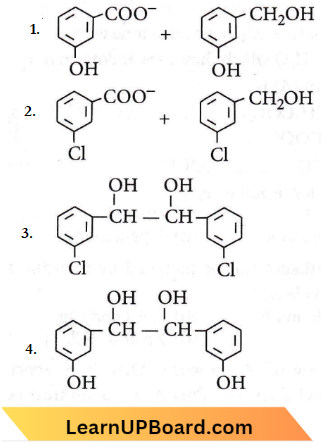
Answer: 2
The above reaction is known as Cannizzaro’s reaction.
Question 48. A and B in the following reactions are
Answer: 4
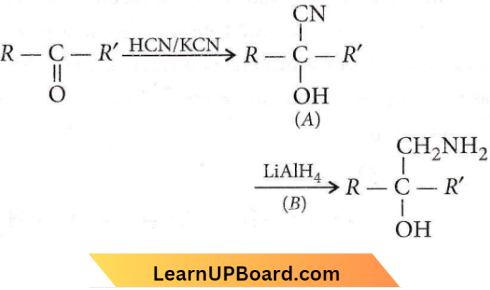
Aldehydes ketones carboxylic acids NEET MCQs
Question 49. 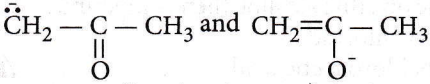 are
are
- Resonating structures
- Tautomers
- Geometrical isomers
- Optical isomers.
Answer: 1. Resonating structures
They are resonating forms because the position of the atomic nuclei remains the same and only electron redistribution has occurred.
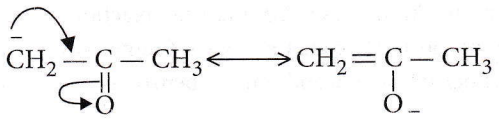
Question 50. Which of the following is incorrect?
- FeCl3 is used in the detection of phenol.
- Fehling solution is used in the detection of glucose.
- Tollens reagent is used in the detection of unsaturation.
- NaHSO3 is used in the detection of carbonyl compounds.
Answer: 3. Tollens reagent is used in the detection of unsaturation.
Tollens reagent is a solution of ammoniacal silver nitrate and is used for the detection of -CHO group. Aldehydes reduce Tollens reagent and get oxidised to convert Ag+ ions to Ag powder which forms the silver-coloured mirror in the test tube. So, this test is also known as the silver mirror test.
⇒ \(R-\mathrm{CHO}+\left[\mathrm{Ag}\left(\mathrm{NH}_3\right)_2\right]^{+} \rightarrow R-\mathrm{COO}^{-}+\mathrm{Ag}\)
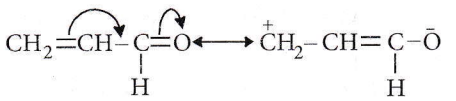
Question 51. Polarisation in acrolein can be described as
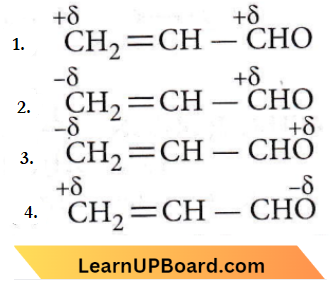
Answer: 4
O-atom is more electronegative than C-atom, therefore O-atom bears a partial -ve charge and C-atom to which it is attached bears a partial +ve charge.
Question 52. The first product of the reaction between PCHO and NH2NH2 is
- \(\mathrm{RCH}=\mathrm{NNH}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{RCH}=\mathrm{NH}\)
- \(\mathrm{RCH}_2 \mathrm{NH}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{RCON}_3\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{RCH}=\mathrm{NNH}_2\)
It is a simple condensation reaction which proceeds with the elimination of water.
![]()
Aldehydes ketones carboxylic acids NEET MCQs
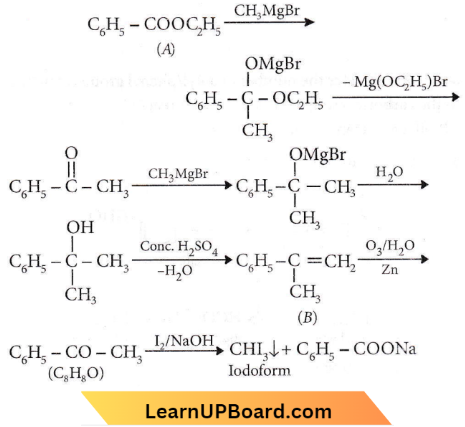
Quetsion 53. An ester (A) with the molecular formula, C9H10O2 was treated with an excess of CH3MgBr and the complex so formed, was treated with H2SO4 to give an olefin(B). Ozonolysis of (B) gave a ketone with molecular formula C8H8O which shows +ve iodoform test. The structure of (A) is
- \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{CCH}_2 \mathrm{COC}_6 \mathrm{H}_5\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{COOC}_6 \mathrm{H}_5\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{COOC}_2 \mathrm{H}_5\)
- \(p-\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{CO}-\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_4-\mathrm{COCH}_3\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{COOC}_2 \mathrm{H}_5\)
An ester (A) with the molecular formula, C9H10O2 was treated with an excess of CH3MgBr and the complex so formed, was treated with H2SO4 to give an olefin(B). Ozonolysis of (B) gave a ketone with molecular formula C8H8O which shows +ve iodoform test.
Question 54. The iodoform test is not given by
- Ethanal
- Ethanol
- 2-Pentanone
- 3-Pentanone.
Answer: 4. 3-Pentanone.
Compounds containing  group show iodoform test.
group show iodoform test.
So iodoform test is not given by 3-pentanone.
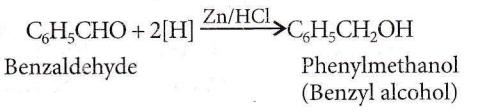
Question 55. Phenylmethanol can be prepared by reducing the benzaldehyde with
- CH3Br and Na
- CH3I and Mg
- CH3Br
- Zn and HCl
Answer: 4. Zn and HCl
Aldehydes ketones carboxylic acids NEET MCQs
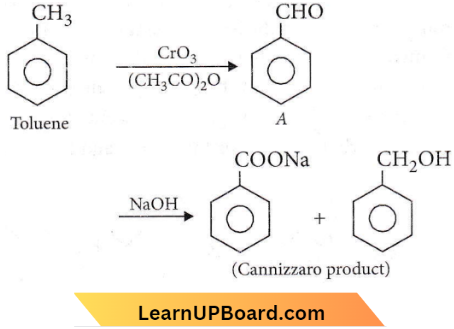
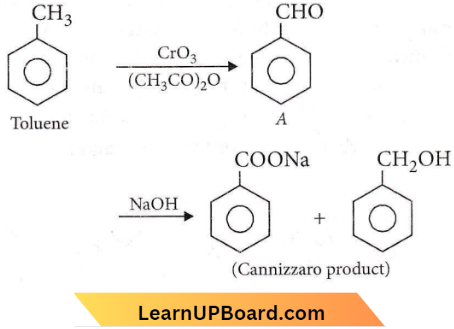
Question 56. The oxidation of toluene with CrO3 in the presence of (CH3CO)2O gives a product A, which on treatment with aqueous NaOH produces
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{COONa}\)
- 2,4-diacetyl toluene
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{CHO}\)
- \(\left(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{CO}\right)_2 \mathrm{O}\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{COONa}\)
Question 57. When aniline reacts with the oil of bitter almonds (C6H5CHO) condensation takes place and a benzal derivative is formed. This is known as
- Schiffs base
- Benedicts reagent
- Millon’sbase
- Schiff’s reagent
Answer: 1. Schiff base
Benzaldehyde reacts with primary aromatic amines to form Schiff’s base (Benzylidene aniline)
Question 58. Compound A has a molecular formula C2Cl3OH. It reduces Fehling’s solution and on oxidation, it gives a monocarboxylic acid B. If A is obtained by the action of chlorine on ethyl alcohol, then compound A is
- Methyl chloride
- Monochloroacetic acid
- Chloral
- Chloroform
Answer: 3. Chloral
Compound A has a molecular formula C2Cl3OH. It reduces Fehling’s solution and on oxidation, it gives a monocarboxylic acid B. If A is obtained by the action of chlorine on ethyl alcohol,
The compound ‘A’ reduces Fehling’s solution thus, it must have a free -CHO group.
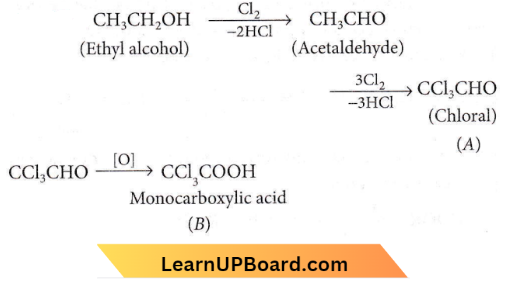
Thus, the compound A is chloral.
Aldehydes ketones carboxylic acids MCQs
Question 59. Which of the following compounds will undergo self-aldol condensation in the presence of cold dilute alkali?
- \(\mathrm{CH} \equiv \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{CHO}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_2=\mathrm{CHCHO}\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{CHO}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CHO}\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CHO}\)
Since CH3CH2CHO has an α-hydrogen atom, therefore it will undergo aldol condensation in the presence of cold dilute alkali.
Question 60. Which of the following compounds will give a positive test with Tollens reagent?
- Acetic acid
- Acetone
- Acetamide
- Acetaldehyde
Answer: 4. Acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde reduces Toiiens’ reagent to the silver mirror.
Question 61. (CH3)2C = CHCOCH3 can be oxidised to (CH3)2C = CHCOOH by
- Chromic acid
- NaOI
- Cu at 300°C
- KMnO4
Answer: 2. NaOI
⇒ \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_2 \mathrm{C}=\mathrm{CHCOCH}_3\) \(\underrightarrow{\mathrm{NaOI}}\) \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_2 \mathrm{C}=\mathrm{CHCOOH}+\mathrm{CHI}_3\)
(NaOH + I2)/NaOI is the most suitable reagent for the given reaction.
Question 62. In which of the following, the number of carbon atoms does not remain the same when carboxylic acid is obtained by oxidation?
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COCH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{CCl}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CHO}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{OH}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CHO}\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COCH}_3\)
Ketones on oxidation give carboxylic acids with lesser number of carbon atoms i.e \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COCH}_3\) \(\underrightarrow{[\mathrm{O}]}\) \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}+\mathrm{CO}_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
Aldehydes ketones carboxylic acids MCQs
Question 63. Acetaldehyde reacts with
- Electrophiles only
- Nucleophiles only
- Free radicals only
- Both electrophiles and nucleophiles.
Answer: 2. Nucleophiles only
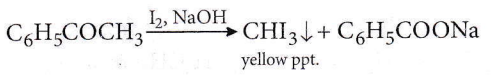
Question 64. The reagent which can be used to distinguish acetophenone from benzophenone is
- 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine
- Aqueous solution of NaHSO3
- Benedict reagent
- I2 and NaoH
Answer: 4. I2 and NaoH
Acetophenone reacts with NaOH and I2 to give yellow ppt. of CHI3 but benzophenone (C6H5COC6H5) does not. Hence, it can be used to distinguish between them.
Question 65. The above-shown polymer is obtained when a carbonyl compound is allowed to stand. It is a white solid. The polymer is
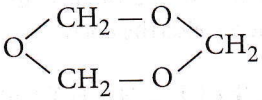
- Trioxane
- Formose
- Paraformaldehyde
- Metaldehyde.
Answer: 1. Trioxane
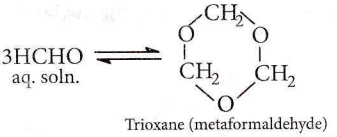
Question 66. The given compound describes a condensation polymer which can be obtained in two ways: either by treating 3 molecules of acetone (CH3COCH3) with cone. H2SO4 or passing propyne (CH3C ≡ CH) through a red hot tube. The polymer is
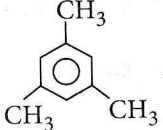
- Phorone
- Mesityl oxide
- Deacetonyl alcohol
- Mesitylene.
Answer: 4. Mesitylene.
The given compound describes a condensation polymer which can be obtained in two ways: either by treating 3 molecules of acetone (CH3COCH3) with cone. H2SO4 or passing propyne (CH3C ≡ CH) through a red hot tube.
Acetone forms mesitylene ( 1, 3, 5- trimethylbenzene) on distillation with conc. H2SO4.
Aldehydes ketones carboxylic acids MCQs
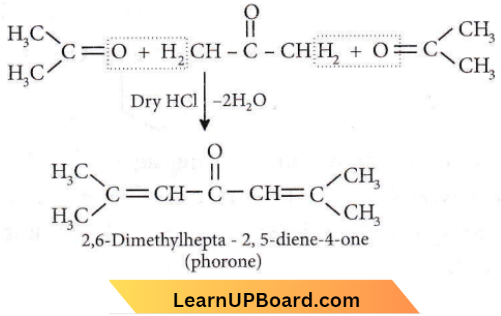
Question 67. This polymer (B) is obtained when acetone is saturated with hydrogen chloride gas, B can be
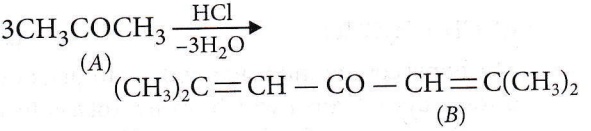
- Phorone
- Formose
- Diacetone alcohol
- Mesityl oxide.
Answer: 1. Phorone
Question 68. If formaldehyde and KOH are heated, then we get
- Methane
- Methyl alcohol
- Ethyl formate
- Acetylene.
Answer: 2. Methyl alcohol
⇒ \(\mathrm{HCHO}+\mathrm{KOH}\) \(\underrightarrow{50 \% \mathrm{KOH}}\) \(\mathrm{HCOOK}+\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{OH}\)
The above reaction is called as Canrizzards reaction.
Question 69. Formalin is an aqueous solution of
- Fluorescein
- Formic acid
- Formaldehyde
- Furfuraldehyde.
Answer: 3. Formaldehyde
The formula is an aqueous solution of 40% HCHO.
Question 70. Complete the following reaction:
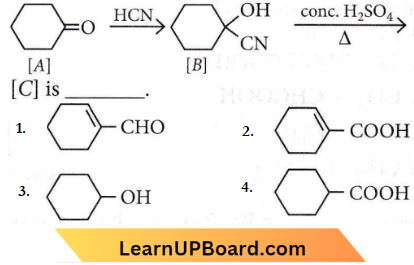
Answer: 2
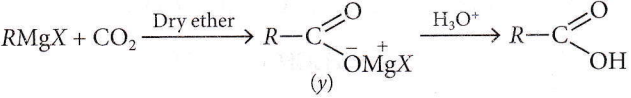
Question 71. What is Y in the above reaction?
- \(\mathrm{RCOO}^{-} \mathrm{Mg}^{+} \mathrm{X}\)
- \(R_3 \mathrm{CO}^{-} \mathrm{Mg}^{+} X\)
- \(\mathrm{RCOO}^{-} \mathrm{X}^{+}\)
- \((\mathrm{RCOO})_2 \mathrm{Mg}\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{RCOO}^{-} \mathrm{Mg}^{+} \mathrm{X}\)
Question 72. The reaction that does not give benzoic acid as the major product is
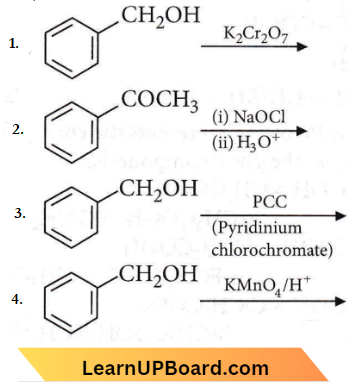
Answer: 3
PCC (Pyridium chlorochromate) stops oxidation at the aldehyde stage, thereby preventing the further oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylic acids.
Aldehydes ketones carboxylic acids questions
Question 73. Which one of the following esters gets hydrolysed most easily under alkaline conditions?
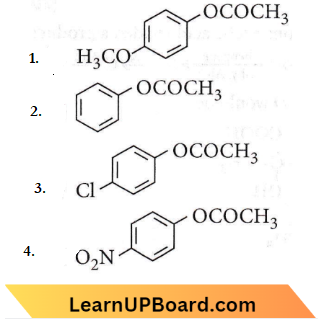
Answer: 4
Electron-withdrawing groups increase the reactivity towards nucleophilic substitution reaction and -NO2 is a strong electron-withdrawing group.
Question 74. Consider the following compounds
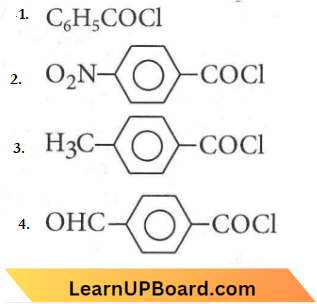
The correct decreasing order of their reactivity towards hydrolysis is
- 1>2>3>4
- 4>2>1>3
- 2>4<>1>3
- 2>4>3>1
Answer: 3. 2>4<>1>3
Question 75. 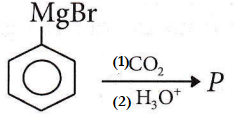
In the above reaction product P is
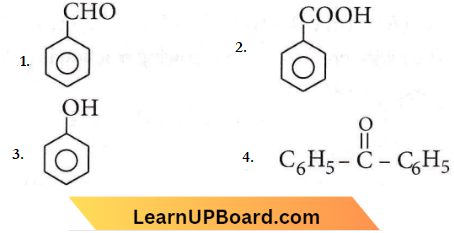
Answer: 2
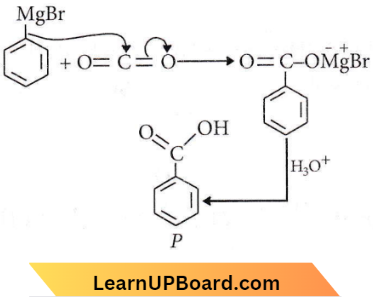
The product (P) is benzoic acid.
Aldehydes ketones carboxylic acids questions
Question 76. Which of the following compounds gives benzoic acid on hydrolysis?
- Chlorobenzene
- Benzoyl chloride
- Chlorophenol
- Chlorotoluene
Answer: 2. Benzoyl chloride
⇒ \(\begin{aligned}
\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{COCl}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{COOH}+\mathrm{HCl} \\
\text { Benzoyl chloride } \quad \text { Benzoic acid }
\end{aligned}\)
Question 77. Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular mass. It is due to their
- Formation of intramolecular H-bonding
- Formation of carboxylate ion
- More extensive association of carboxylic acid via van der Waals’ forces of attraction
- Formation of intermolecular H-bonding.
Answer: 4. Formation of intermolecular H-bonding.
Question 78. The weight (g) of two moles of the organic compound, which is obtained by heating sodium ethanoate with sodium hydroxide in the presence of calcium oxide is
- 30
- 18
- 16
- 32
Answer: 4. 32
This is the Kolbe electrolysis reaction. The weight of two moles of methane is 32 g
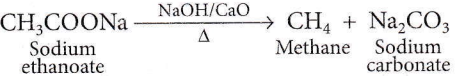
Question 79. Match List 1 with List 2
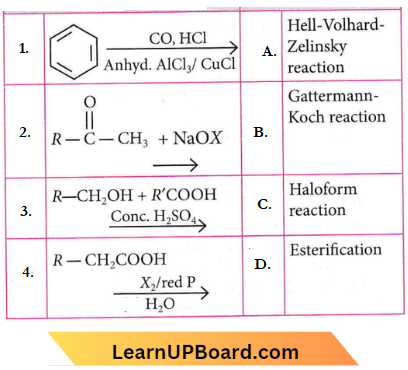
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
- 1-B, 2-C, 3-C, 4-A
- 1-D, 2-A, 3-B, 4-C
- 1-C, 2-B, 3-A, 4-D
- 1-A, 2-D, 3-C, 4-B
Answer: 1. 1-B, 2-C, 3-C, 4-A
Question 80. The major product of the following reaction is
Answer: 3
Aldehydes ketones carboxylic acids questions
Question 81. The correct order of strengths of the carboxylic acids
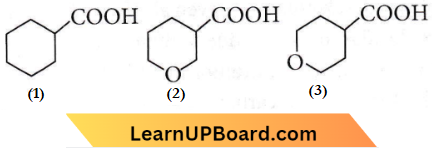
Answer: 2
Acidic strength ∝ – I effect
As oxygen is more electron withdrawing (2) and (3) show greater – I effect than (1). Thus, (1) is the least acidic. Out of (2) and (3), (2) is more acid than (3) as the distance of O increases from the -COOH group and acidic strength decreases
Quetsion 82. The correct order of decreasing acid strength of trichloroacetic acid (A), trifluoroacetic acid (B), acetic acid (C) and formic acid (D) is
- B>A>D>C
- B>D>C>A
- A> B>C>D
- A> C>B>D
Answer: 1. B>A>D>C
As the -I effect increases, the -COOH group becomes more electron deficient and the tendency to lose H+ ions increases ie., acid strength increases. As the +I effect increases acid strength decreases.
Thus, the correct order of acid strength is
Question 83. Which one of the following is most reactive towards electrophilic reagents?
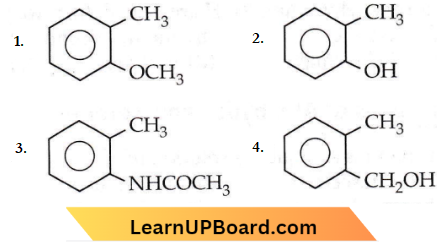
Answer: 4
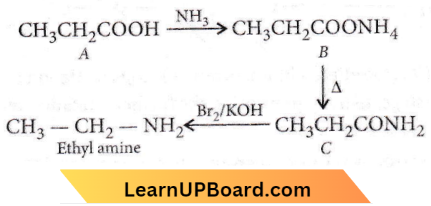
Question 84. An organic compound A on treatment with NH3 gives B, which on heating gives C. C when treated with Br2 in the presence of KOH produces ethyl amine. Compound A is
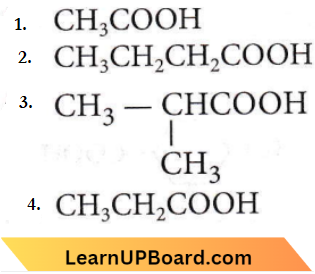
Answer: 4
The compound will be CH3CH2COOH
Aldehydes ketones carboxylic acids questions
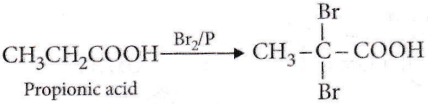
Question 85. Propionic acid with Br2/P yields a dibromo product. Its structure would be
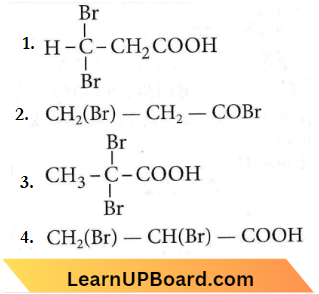
Answer: 3
This is Hell-Volhard-Zelinksy reavtion. In this reaction, acids containing α-H react with X2/red P giving a product in which the hydrogens are substituted by X.
Carboxylic acids NEET questions
Question 86. Which of the following represents the correct order of the acidity in the given compounds?
- \(\mathrm{FCH}_2 \mathrm{COOH}>\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}\)> \(\mathrm{BrCH}_2 \mathrm{COOH}>\mathrm{ClCH}_2 \mathrm{COOH}\)
- \(\mathrm{BrCH}_2 \mathrm{COOH}>\mathrm{ClCH}_2 \mathrm{COOH}\) > \(\mathrm{FCH}_2 \mathrm{COOH}>\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}\)
- \(\mathrm{FCH}_2 \mathrm{COOH}>\mathrm{ClCH}_2 \mathrm{COOH}\) > \(\mathrm{BrCH}_2 \mathrm{COOH}>\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}>\mathrm{BrCH}_2 \mathrm{COOH}\)>\(\mathrm{ClCH}_2 \mathrm{COOH}>\mathrm{FCH}_2 \mathrm{COOH}\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{FCH}_2 \mathrm{COOH}>\mathrm{ClCH}_2 \mathrm{COOH}\) > \(\mathrm{BrCH}_2 \mathrm{COOH}>\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}\)
Question 87. In a set of reactions acetic add yielded a product D.
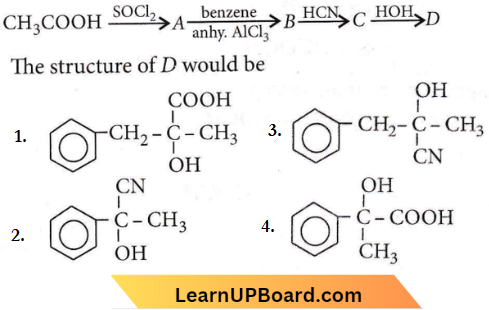
The structure of D would be COOH
Answer: 4
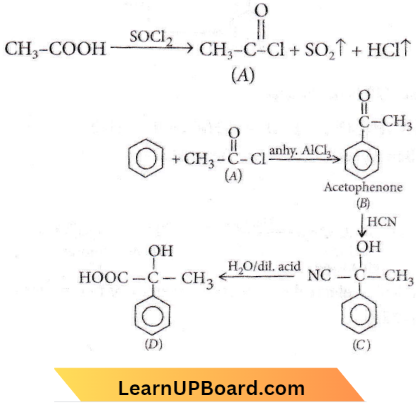
Quetsion 88. The – OH group of an alcohol or the – COOH group of a carboxylic acid can be replaced by – Cl using
- Phosphorus pentachloride
- Hypochlorous acid
- Chlorine
- Hydrochloric acid.
Answer: 1. Phosphorus pentachloride
⇒ \(\mathrm{ROH}+\mathrm{PCl}_5 \rightarrow \mathrm{RCl}+\mathrm{POCl}_3+\mathrm{HCl}\)
RCOOH+\(\mathrm{PCl}_5 \rightarrow R \mathrm{ROCl}+\mathrm{POCl}_3+\mathrm{HCl}\)
Question 89. Which one of the following orders of acid strength is correct?
- RCOOH > ROH > HOH > HC ≡ CH
- RCOOH > HOH > ROH > HC ≡ CH
- RCOOH > HOH > HC ≡ CH > ROH
- RCOOH > HC ≡ CH > HOH > ROH
Answer: 2. RCOOH > HOH > ROH > HC ≡ CH
Carboxylic acid is much stronger than water and alcohol. Since the carboxylate ion after the removal of the proton is stabilised by resonating structures. The -OH in alcohols is almost neutral. Acetylene is also the weakest acid among the given examples.
Carboxylic acids NEET questions
Question 90. In a set of the given reactions, acetic acid yielded a product C.
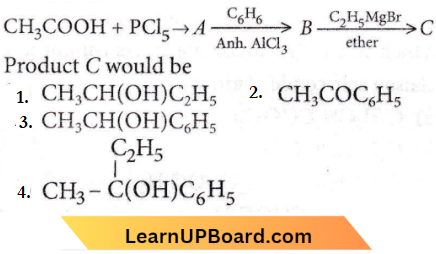
Answer: 4
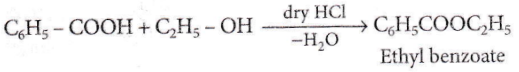
Question 91. Ethyl benzoate can be prepared from benzoic acid by using
- Ethyl alcohol
- Ethyl alcohol and dry HCl
- Ethyl chloride
- Sodium ethoxide.
Answer: 2. Ethyl alcohol and dry HCl
Ethyl benzoate can be prepared by heating benzoic acid with alcohol in the presence of dry HCI or conc H2SO4. The reaction is called as esterification reaction.
Question 92. Reduction by LiAlH4 of the hydrolyzed product of an ester gives
- Two alcohols
- Two aldehydes
- One acid and one alcohol
- Two acids.
Answer: 1. Two alcohols
The reduction of the hydrolyzed product of ester by LiAlH4 produces two alcohols.
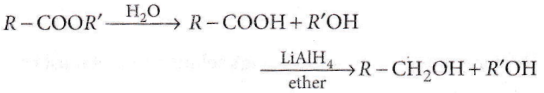
Question 93. Which one of the following compounds will react with the NaHCO3 solution to give sodium salt and carbon dioxide?
- Acetic acid
- n-Hexanol
- Phenol
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 1. Acetic acid
NaHCO3 is weakly basic so it can the acid CH3COOH. While phenol is weakly acidic and r-hexanol is neutral, they do not react with NaHCO3.
⇒ \(\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{COOH}+\mathrm{NaHCO}_3 \rightarrow \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COONa}+\mathrm{CO}_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
Aldehydes and ketones MCQs
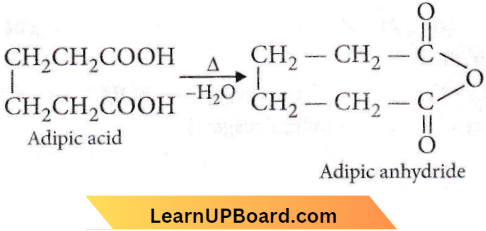
Question 94. Which one of the following products is formed when adipic acid is heated?
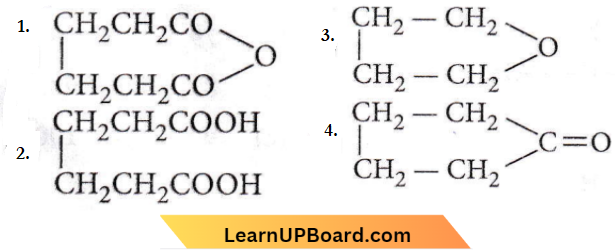
Answer: 1
Question 95. An acyl halide is formed when PCl5 reacts with an
- Amide
- Ester
- Acid
- Alcohol.
Answer: 3. Acid
⇒\(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}+\mathrm{PCl}_5 \rightarrow \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COCl}+\mathrm{POCl}_3+\mathrm{HCl}\)
Question 96. Benzoic acid gives benzene on being heated with X and phenol gives benzene on being heated with Y. Therefore, X and Y are respectively
- Soda-lime and copper
- Zn dust and NaOH
- Zn dust and soda-lime
- Soda-lime and zinc dust.
Answer: 4. Soda-lime and zinc dust.
⇒ \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{COOH}\) \(\underrightarrow{\text { Soda-lime }(X)}\) \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_6+\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{CO}_3\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{OH}\) \(\underrightarrow{\mathrm{Zn} \text { dust }(Y)}\) \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_6+\mathrm{ZnO}\).
Aldehydes and ketones MCQs
Question 97. A is a lighter phenol and B is an aromatic carboxylic acid. Separation of a mixture of A and B can be carried out easily by using a solution of
- Sodium hydroxide
- Sodium sulphate
- Calcium chloride
- Sodium bicarbonate.
Answer: 4. Sodium bicarbonate.
Carboxylic acids dissolve in NaHCO3 but phenols do not.
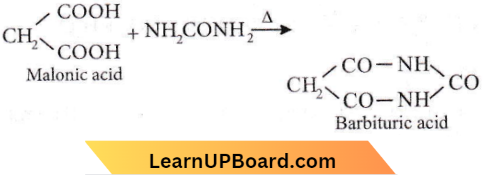
Question 98. The compound formed when malonic acid is heated with urea is
- Cinnamic acid
- Butyric acid
- Barbituric acid
- Crotonic acid.
Answer: 3. Barbituric acid
Question 99. Among the following the strongest acid is
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{ClCH}_2 \mathrm{COOH}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{ClCOOH}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{COOH}\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{ClCOOH}\)
The strongest acid is CH2ClCOOH as -I effect of CI atom decreases with the increase in distance.
Question 100. Which of the following is the correct decreasing order of acidic strength of
- Methanoic acid
- Ethanoic acid
- Propanoic acid
- Butanoic acid
- 1>2>3>4
- 2>3>4>1
- 1>4>3>2
- 4>1>3>2
Answer: 1. 1>2>3>4
+I effect of the alkyl group increases from CH3 to CH3CH2 to CH3CH2CH2 to CH3CH2CH2CH2 resulting in a decrease of acid character. Therefore, the order is (1) > (2) > (3) > (4).
Question 101. The product formed in the following chemical reaction is
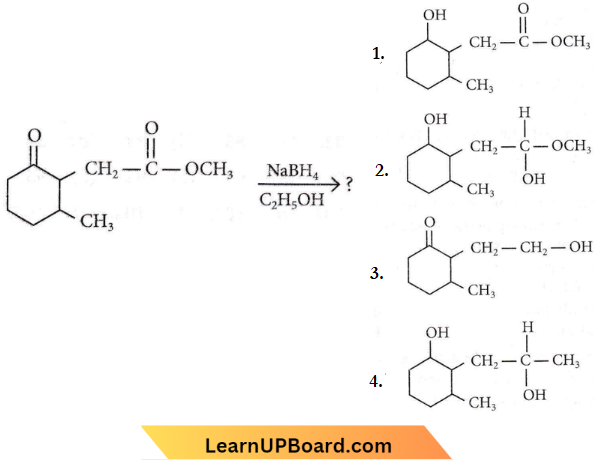
Answer: 1
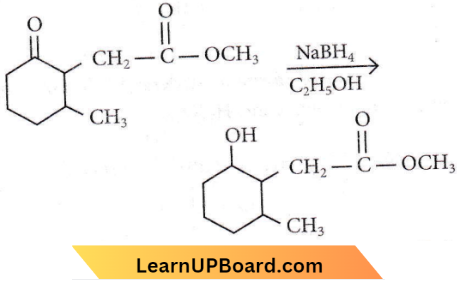
NaBH4 is a less powerful reducing agent than LiAlH4. It is only powerful enough to reduce aldehydes, ketones and acid chlorides to alcohols. Ester amides acids and nitrites are not reduced.
Aldehydes and ketones MCQs
Question 102. Match the compounds given in List 1 with List 2 and select the suitable option using the codes given below.
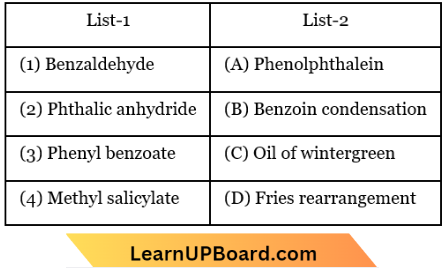
- 1-D, 2-A, 3-C, 4-B
- 1-D, 2-B, 3-B, 4-A
- 1-B, 2-C, 3-D, 4-A
- 1-B, 2-A, 3-D, 4-C
Answer: 4. 1-B, 2-A, 3-D, 4-C
Question 103. Among the given compounds, the most susceptible to nucleophilic attack at the carbonyl group is
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOCH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CONH}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOCOCH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COCl}\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COCl}\)
NEET chemistry chapter-wise questions
CH3COCI is most susceptible to nucleophilic attack. The susceptibility of a substrate towards nucleophilic attack depends on how well a leaving group is attached to it. Cl– is a weak base and therefore, a good leaving group
Question 104. The relative reactivities of acyl compounds towards nucleophilic substitution are in the order of
- Acid anhydride > amide > ester > acyl chloride
- Acyl chloride > ester > acid anhydride > amide
- Acyl chloride > acid anhydride > ester > amide
- Ester > acyl chloride > amide > acid anhydride.
Answer: 3. Acyl chloride > acid anhydride > ester > amide
Question 105. Self-condensation of two moles of ethyl acetate in the presence of sodium ethoxide yields
- Ethyl propionate
- Ethyl butyrate
- Acetoacetic ester
- Methyl acetoacetate.
Answer: 3. Acetoacetic ester
Ethyl acetate undergoes Claisen condensation in the presence of sodium ethoxide involving an α-hydrogen atom in which two molecules of ethyl acetate combine together to form an acetoacetic ester.
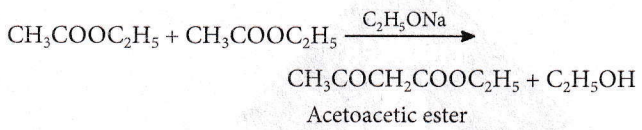
Question 106. Which one of the following esters cannot undergo Claisen self-condensation?
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{COOC}_2 \mathrm{H}_5\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{COOC}_2 \mathrm{H}_5\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{COOC}_2 \mathrm{H}_5\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_{11} \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{COOC}_2 \mathrm{H}_5\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{COOC}_2 \mathrm{H}_5\)
The esters having active methylene group (-CH2-), show Claisen condensation reaction. As C6H5 – COOC2H5 has no α-hydrogen atom or active methylene group, it cannot undergo Claisen condensation reaction.
NEET chemistry chapter-wise questions
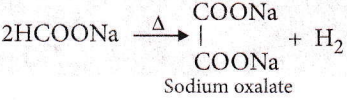
Question 107. Sodium formate on heating yields
- Oxalic acid and H2
- Sodium oxalate and H2
- CO2 and NaOH
- Sodium oxalate
Answer: 2. Sodium oxalate and H2