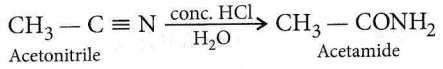NEET Chemistry MCQs
NEET Chemistry For Amines Multiple Choice Questions
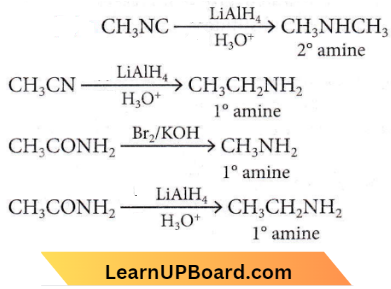
Question 1. Which of the following reactions will not give primary amine as the product?
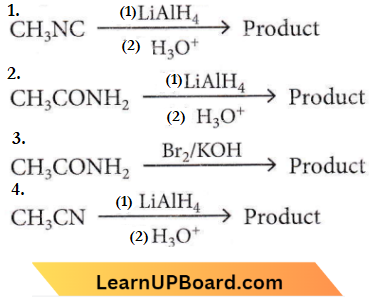
Answer: 1
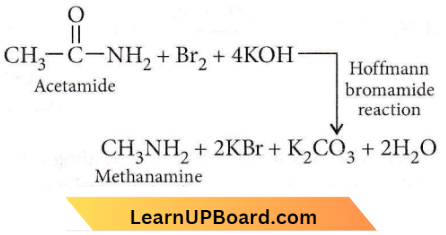
Question 2. Which of the following reactions is appropriate for converting acetamide to methanamine?
- Hoffmann hypobromamide reaction
- Stephens reaction
- Gabriel phthalimide synthesis
- Carbylamine reaction
Answer: 1. Hoffmann hypobromite reaction
Question 3. The method by which aniline cannot be prepared is
- Degradation of benzamide with bromine in alkaline solution
- Reduction of nitrobenzene with H2/Pd in ethanol
- Potassium salt of phthalimide treated with chlorobenzene followed by hydrolysis with aqueous NaOH solution
- Hydrolysis of phenyhsocyamde with acidic solution
Answer: 3. Potassium salt of phthalimide treated with chlorobenzene followed by hydrolysis with aqueous NaOH solution
Aniline cannot be prepared by this method because aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction with potassium phthalimide under mild conditions.
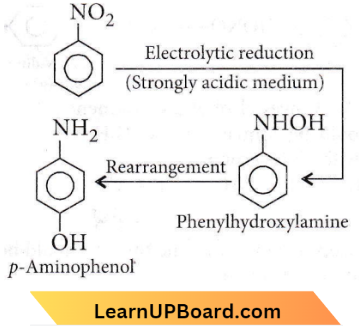
Question 4. The electrolytic reduction of nitrobenzene in a strongly acidic medium produces
- Azobenzene
- Aniline
- P-aminophenol
- Azoxybenzene.
Answer: 3. P-aminophenol
NEET Chemistry MCQs
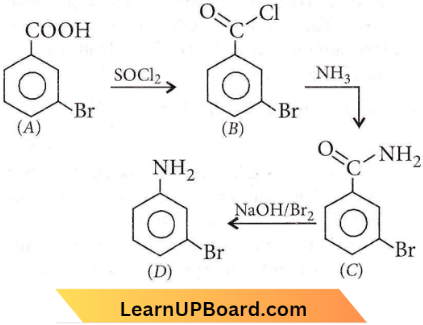
Question 5. In a set of reactions m-bromobenzoic acid gave a product D. Identify the product D.
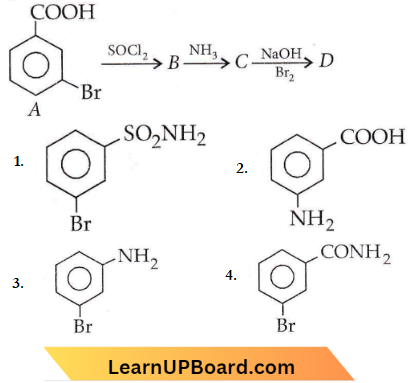
Answer: 3
Question 6. Acetamide is treated with the following reagents separately. Which one of these would yield methyl amine?
- NaOH-Br2
- Sodalime
- Hot conc.H2SO4
- PCl5
Answer: 1. NaOH-Br2
⇒ \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CONH}_2+4 \mathrm{NaOH}+\mathrm{Br}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{NH}_2+2 \mathrm{NaBr}+\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{CO}_3+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
This reaction is called the Hoffmann Bromamide degradation reaction.
Read and Learn More NEET MCQs with Answers
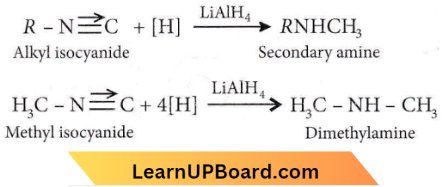
Question 7. Which one of the following on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride yields a secondary amine?
- Methyl isocyanide
- Acetamide
- Methyl cyanide
- Nitroethane
Answer: 1. Methyl isocyanide
Alkyl isocyanide on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride forms a secondary amine-containing methyl as one of the acyl groups.
Question 8. In a set of reactions propionic acid yielded a compound D. \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{COOH}\) \(\underrightarrow{\mathrm{SOCl}_2}\) B \(\underrightarrow{\mathrm{NH}_3}\) C KOH/Br2 D. The structure of D would be
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{NH}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{NH}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CONH}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{NHCH}_3\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{NH}_2\)
In a set of reactions propionic acid yielded a compound D. \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{COOH}\) \(\underrightarrow{\mathrm{SOCl}_2}\) B \(\underrightarrow{\mathrm{NH}_3}\) C KOH/Br2 D.
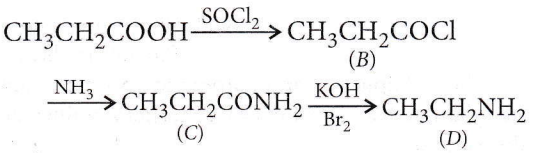
Question 9. Electrolytic reduction of nitrobenzene in a weakly acidic medium gives
- N-phenylhydroxylamine
- Nitrosobenzene
- Aniline
- p-hydroxyproline
Answer: 3. Aniline
Electrolytic reduction of nitrobenzene in a weakly acidic medium gives aniline but in the strongly acidic medium, it gives aminophenol through the acid-catalysed rearrangement of the initially formed phenylhydroxylamine.

NEET chemistry MCQs
Question 10. Intermediates formed during the reaction of RCONH with Br2 and KOH are
- RCONHBr and RNCO
- RNHCOBr and RNCO
- RNH – Br and RCONHBr
- RCONBr2
Answer: 1. RCONHBr and RNCO
The reaction, RCONH2 + Br2 + KOH→ RNH2 is known as Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction. The mechanism of the reaction is
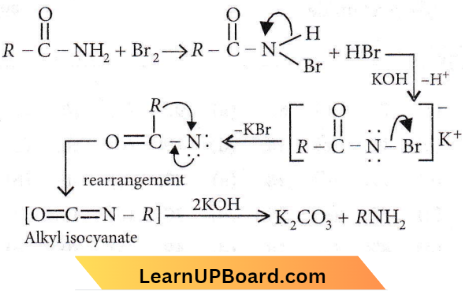
This reaction is used to descend the series, i.e., for preparing a lower homologue from a higher one.
Question 11. Amides may be converted into amines by a reaction named after
- Hoffmann
- Claisen
- Perkin
- Kekule.
Answer: 1. Hoffmann

This reaction is called the Hoffmannbromamide degradation reaction.
Question 12. Indicate which nitrogen compound amongst the following would undergo Hoffmann reaction (i.e. reaction with Br2 and strong KOH) to furnish the primary amine (R-NH2).
- \(\mathrm{RCONHCH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{RCOONH}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{RCONH}_2\)
- \(R-\mathrm{CO}-\mathrm{NHOH}\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{RCONH}_2\)
The amide (-CONH2) group is converted into a primary amino group (-NH2) by the Hoffman bromamide degradation reaction.
⇒ \(R \mathrm{CONH}_2+\mathrm{Br}_2+4 \mathrm{KOH}\) \(\underrightarrow{^{\Delta}}\) \(\underset{1^{\circ} \text { amine }}{R-\mathrm{NH}_2} +2 \mathrm{KBr}\) + \(\mathrm{K}_2 \mathrm{CO}_3+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
NEET chemistry MCQs
Question 13. Given below are two statements:
- Statement-1: Primary aliphatic amines react with HNO2 to give unstable diazonium salts.
- Statement-2: Primary aromatic amines react with HNO2 to form diazonium salts which are stable even above 300 K.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
- Both statement-1 and statement-2 are correct.
- Both statement-1 and statement-2 are incorrect.
- Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect.
- Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct.
Answer: 3. Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect.
Primary aliphatic amines react with nitrous to form aliphatic diazonium salts which are unstable while aromatic amines react with nitrous acid at low temperatures (273-275 K) to form diazonium salts, a very important class of compounds used for the synthesis of a variety of aromatic compounds.
Question 14. Identify the compound that will react with Hinsberg’s reagent to give a solid which dissolves in alkali.
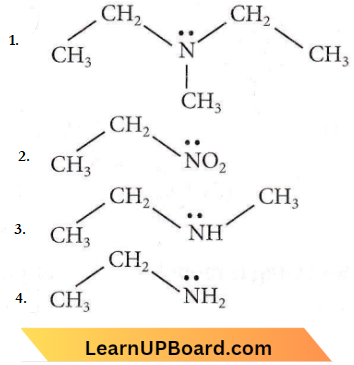
Answer: 4
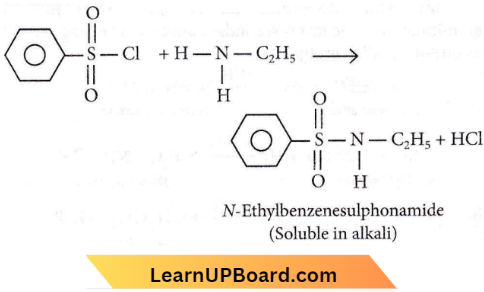
Benzene sulphonyl chloride (C6H5SO2Cl)2 which is also known as Hinsberg’s reagent, reacts with primary amines to form sulphonamides. The hydrogen attached to nitrogen in sulphonamide is strongly acidic due to the presence of a strong electron-withdrawing sulphonyl group. Hence, it is soluble in alkali.
Amines NEET MCQs
Question 15. Which of the following amines will give the carbylamine test?
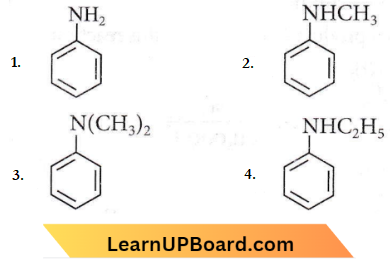
Answer: 1
Aliphatic and aromatic primary amines give an arylamine test. Secondary and tertiary amines do not show this reaction.
Question 16. The correct order of the basic strength of methyl-substituted amines in an aqueous solution is
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{NH}_2>\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_2 \mathrm{NH}>\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \mathrm{~N}\)
- \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_2 \mathrm{NH}>\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{NH}_2>\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \mathrm{~N}\)
- \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \mathrm{~N}>\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{NH}_2>\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_2 \mathrm{NH}\)
- \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \mathrm{~N}>\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_2 \mathrm{NH}>\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{NH}_2\)
Answer: 2. \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_2 \mathrm{NH}>\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{NH}_2>\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \mathrm{~N}\)
The basicity of amines in an aqueous solution depends on the stability of the ammonium cation or conjugate acid formed by accepting a proton from water which in turn depends on the + I-effect of alkyl group, the extent of hydrogen bonding and the steric factor. AII these factors are favourable for 2° amines. Therefore, 2° amines are the strongest bases.
If the alkyl group is small i.e., CH3 then there is no steric hindrance to H-bonding. Thus, the stability due to hydrogen bonding predominates over the stability due to the +I-effect of the -CH3, group and hence primary amine is a stronger base than 3°amine. Hence, the overall decreasing basic strength for methylamines in an aqueous solution is (CH3)2NH > CH3NH2 > (CH3)3N
Quetsion 17. The amine that reacts with Hinsberg’s reagent to give an alkali-insoluble product is
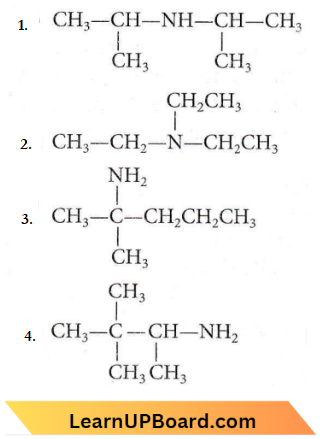
Answer: 1
Secondary amines on reaction with Hinsberg’s reagent give N, N-divinylbenzene sulphonamide which does not contain any hydrogen atom attached to the N atom, it is not acidic and hence, insoluble in alkali. Tertiar,v amines do not react with Hinsberg’s reagent. Primary antine gives products which are soluble in alkali.
Question 18. Nitration of aniline in a strongly acidic medium also gives m-nitroaniline because
- In spite of substituents nitro group always goes to only the m-position
- In electrophilic substitution reactions amino group is meta-directive
- In the absence of substituents nitro group always goes to the m-position
- In an acidic (strong) medium aniline is present as an anilinium ion.
Answer: 4. In an acidic (strong) medium aniline is present as an anilinium ion.
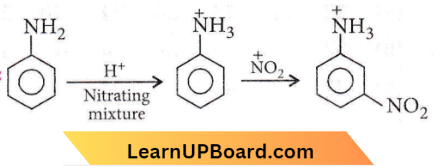
The reason for the formation of an unexpected amount of m-nitroaniline is that under strongly acidic conditions of nitration, most of the aniline is converted into anilinium ion and since, -NH3 is a m-directing group, therefore, a large amount of m-nitroaniline is also obtained.
Amines NEET MCQs
Question 19. The correct increasing order of basic strength for the following compounds is
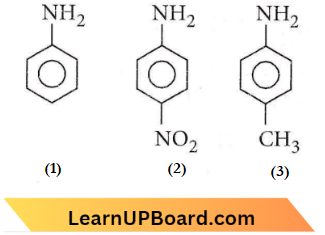
- 3<1<2
- 3<2<1
- 2<1<3
- 2<3<1
Answer: 3. 2<1<3
+I effect of the substituted group increases the basic strength while -I effect of the substituent decreases the basic strength of aniline.
Question 20. The correct statement regarding the basicity of arylamines is
- Arylamines are generally more basic than alkylamines because of the aryl group
- Arylamines are generally more basic than alkylamines because the nitrogen atom in arylamines is sp-hybridised
- Arylamines are generally less basic than alkylamines because the nitrogen lone-pair electrons are delocalised by interaction with the aromatic ring π electron system
- Arylamines are generally more basic than alkylamines because the nitrogen lone-pair electrons are not delocalised by interaction with the aromatic ring π-electron system.
Answer: 3. Arylamines are generally less basic than alkylamines because the nitrogen lone-pair electrons are delocalised by interaction with the aromatic ring π-electron system
In arytrarnines, one pair of electrons on a nitrogen atom is delocalised over the benzene ring and, thus, not available for donation. So, arylamines are less basic than alkylamines
Question 21. On hydrolysis of a “compound”, two compounds are obtained. One of which on treatment with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid gives a product which does not respond to the iodoform test. The second one reduces Tollens’ reagent and Fehling’s solution. The “compound” is
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{NC}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CN}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{ON}=\mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CON}\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_2\)
Answer: 1
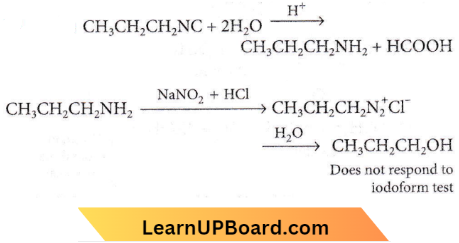
HCOOH reduces Tollens’reagent and Fehling’s solution.
NEET organic chemistry questions
Question 22. Some reactions of amines are given. Which one is not correct?
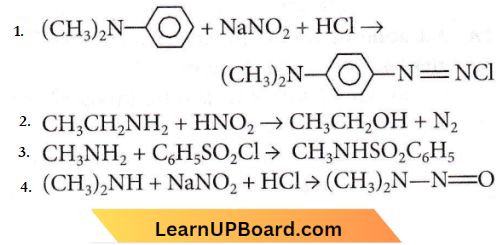
Answer: 1
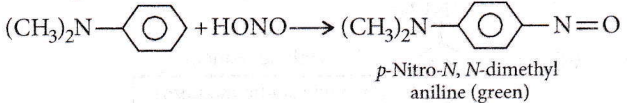
Aromatic tertiary amines undergo electrophilic substitution with nitrosonium ion at the p-position of the phenyl ring to form green-coloured nitrosamines.
Quesion 23. An organic compound (C3H9N) (A), when treated with nitrous acid, gave an alcohol and N2 gas was evolved. (A) on warming with CHCl3 and caustic potash gave (C) which on reduction gave isopropylmethylamine. Predict the structure of (A).
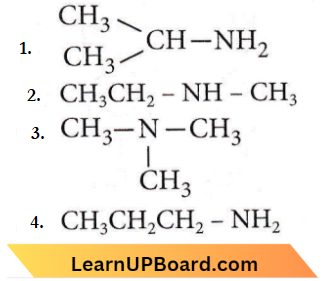
Answer: 1
As A gives alcohol on treatment with nitrous acid thus, it should be primary amine. C3H9N has two possible structures with -NH2 group.
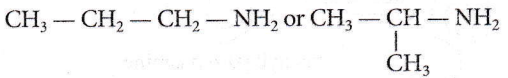
As it gives isopropylmethylamine thus, it should be isopropyl amine, not n-propyl amine.
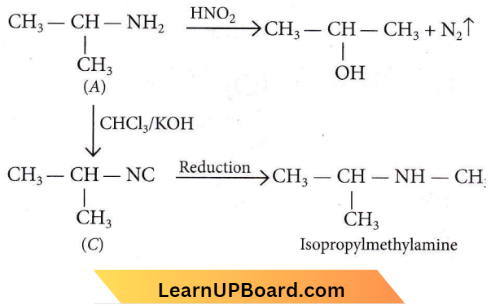
NEET organic chemistry questions
Question 24. Which of the following compounds is most basic?
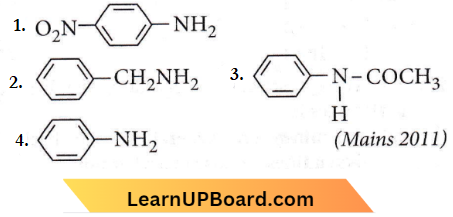
Answer: 2
In benzylamine, the electron pair present on the nitrogen is not delocalised with the benzene ring.
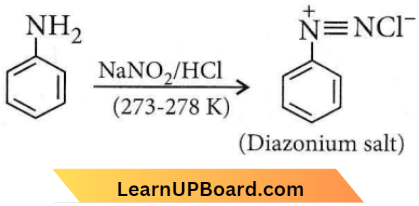
Question 25. Which of the following statements about primary amines is false?
- Alkyl amines are stronger bases than aryl amines.
- Alkyl amines react with nitrous acid to produce alcohols.
- Aryl amines react with nitrous acid to produce phenols.
- Alkyl amines are stronger bases than ammonia.
Answer: 3. Aryl amines react with nitrous acid to produce phenols.
Aryl amines react with nitrous acid to produce diazonium salts.
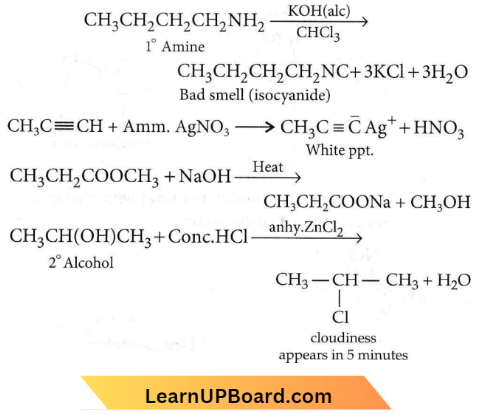
Question 26. Match the compounds given in List 1 with their characteristic reactions given in List 2. Select the correct option.
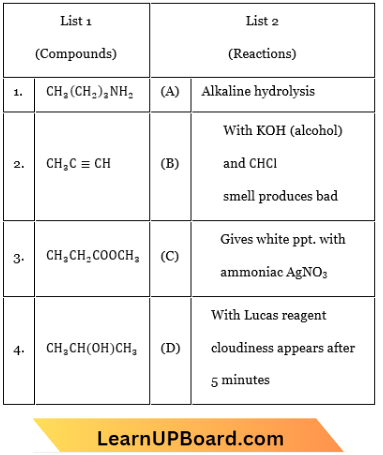
- 1-B, 2-A, 3-D, 4-C
- 1-C, 2-B, 3-A, 4-D
- 1-B, 2-C, 3-A, 4-D
- 1-D, 2-C, 3-A, 4-D
Answer: 3. 1-B, 2-C, 3-A, 4-D
NEET organic chemistry questions
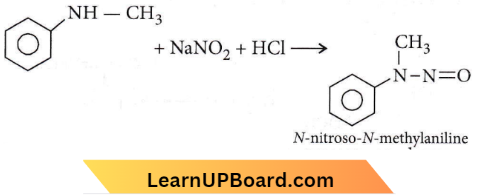
Question 27. Predict the product.
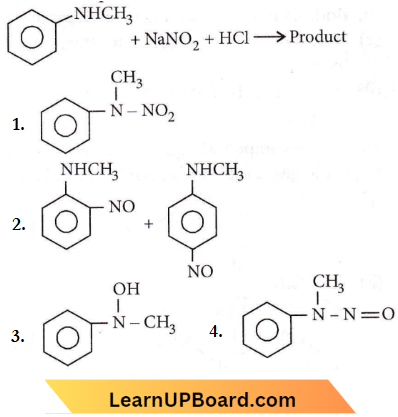
Answer: 4
2° aliphatic and aromatic amines react with nitrous acid to form N-nitrosamine.
Question 28. Which of the following is more basic than aniline?
- Benzylamine
- Diphenylamine
- Triphenylamine
- p-Nitroaniline
Answer: 1. Benzylamine
Any group which when present on a benzene ring has electron-withdrawing nature (-NO2,-CN,-SO3H, -COOH, -CI, -C6H5 etc) decreases the basicity of aniline example, aniline is more basic than nitroaniline, Lone pair of electrons are more delocalised in diphenylamine and triphenylamine, thus these are less basic than aniline.
In benzylamine the electron pair present on nitrogen is not delocalised with the benzene ring hence, it is more basic than aniline.
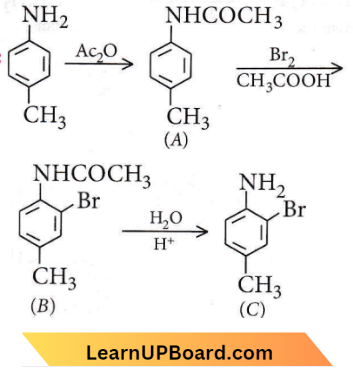
Question 29. The final product C, obtained in this reaction, would be
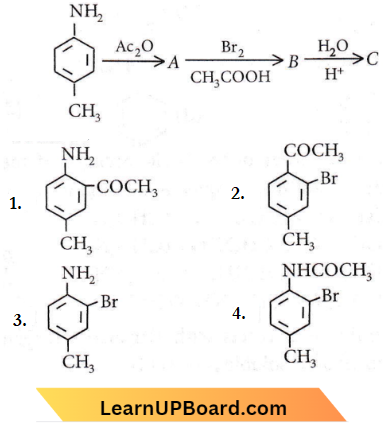
Answer: 3
Question 30.
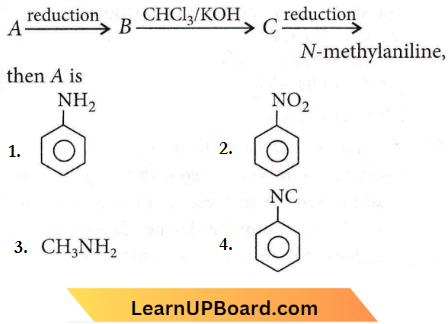
NEET organic chemistry questions
Answer: 2
‘C’ must be an isocyanide and it is obtained from a 1° amine by arylamine reaction (CHCI3 + KOH). Further 1o amine can be obtained by the reduction of nitro compound so ‘A’ is nitrobenzene.
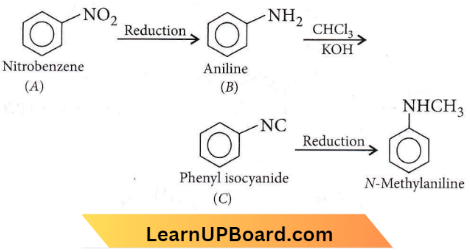
Question 31. Phenyl isocyanides are prepared by which of the following reaction?
- Reimer-Tiemann reaction
- Carbylamine reaction
- Rosenmunds reaction
- Wurtz reaction
Answer: 2. Carbylamine reaction
⇒ \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5-\mathrm{NH}_2+\mathrm{CHCl}_3+3 \mathrm{KOH} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5-\mathrm{NC}+3 \mathrm{KCl}+3 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
The above reaction is called the arylamine reaction, which is a specific reaction of 1-amine.
NEET chemistry practice questions
Question 32. The compound obtained by heating a mixture of ethylamine and chloroform with ethanolic potassium hydroxide (KOH) is
- An amide
- An amide and nitro compound
- An ethyl isocyanide
- An alkyl halide.
Answer: 3. An ethyl isocyanide
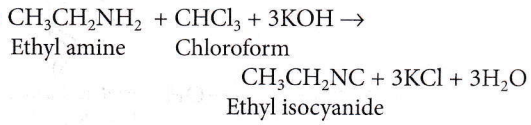
Question 33. An aniline on nitration gives
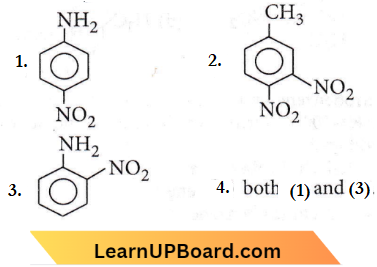
Answer: 4
As NO+2 electrophile can attack both ortho and para positions, therefore both (1) and (3) products will be obtained
NEET chemistry practice questions
Question 34. The action of nitrous acid on an aliphatic primary amine gives
- Secondary amine
- Nitro alkane
- Alcohol
- Alkyl nitrite.
Answer: 3. Alcohol
R-NH2 + HNO2 → ROH + N2 + H2O
Question 35. Which one of the following orders is wrong, with respect to the property indicated?
- Benzoic acid > phenol > cyclohexanol (add strength)
- Aniline > cyclohexylamine > benzamide (basic strength)
- Formic acid > acetic acid > propanoic acid (acid strength)
- Fluoroacetic acid > chloroacetic acid > bromoacetic acid (acid strength)
Answer: 2. Aniline > cyclohexylamine > benzamide (basic strength)
Basic strength decreases as, cyclohexylamine > aniline > benzamide.
Lesser basicity in aniline and benzamide is due to the participation of a lone pair of electrons of -NH2 group in resonance.
NEET chemistry practice questions
Question 36. For the arylamine reaction, we need hot alcoholic KOH and
- Any primary amine and chloroform
- Chloroform and silver powder
- A primary amine and an alkyl halide
- A monoalkylamine and trichloromethane.
Answer: 1. Any primary amine and chloroform
In arylamine reaction, primary amines on heating with chloroform in the presence of alcoholic KOH form isocyanides (or carbylamines). It is used to distinguish 1° amines from 2° and 3° amines.
⇒ \(R-\mathrm{NH}_2+\mathrm{CHCl}_3+3 \mathrm{KOH} \rightarrow R \mathrm{NC}+3 \mathrm{KCl}+3 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
Question 37. Which of the following will be the most stable diazonium salt RN+2+X–?
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{~N}_2^{+} \mathrm{X}^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{~N}_2^{+} X^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{~N}_2^{+} \mathrm{X}^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{~N}_2^{+} \mathrm{X}\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{~N}_2^{+} X^{-}\)
Aromatic diazonium salts are more stable due to the dispersal of the positive charge in the benzene ring
Question 38. Identify the product in the following reaction
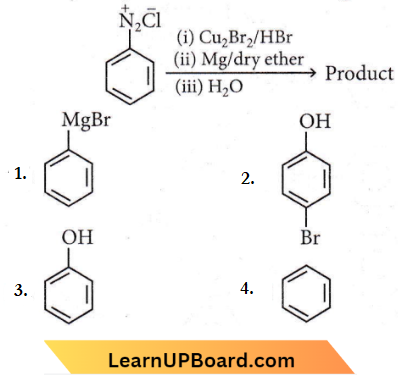
NEET chemistry chapter-wise questions
Answer: 4
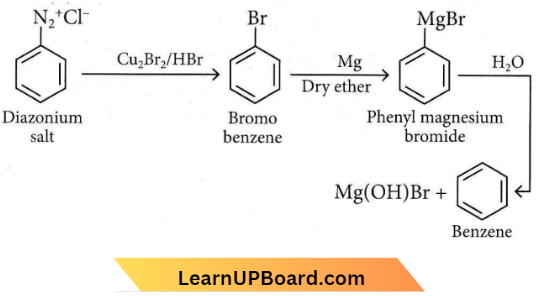
Question 39. The product formed from the following reaction sequence is
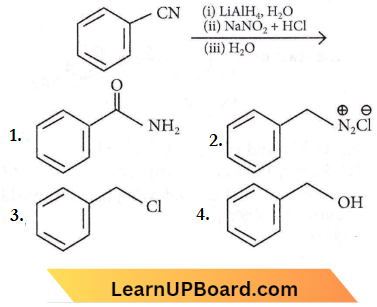
Answer: 4
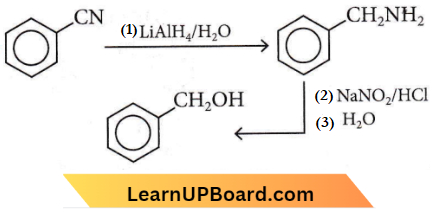
NEET chemistry chapter-wise questions
Question 40. The reagent in ‘R’ in the given sequence of a chemical reaction is
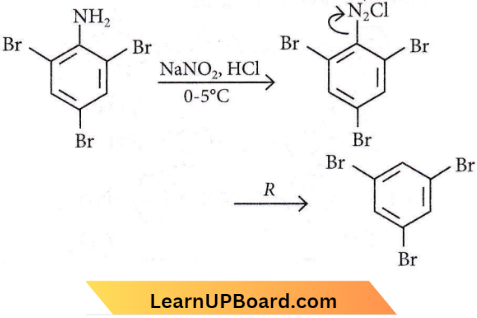
- CuCN/KCN
- H2O
- CH3CH2OH
- HI
Answer: 3. CH3CH2OH
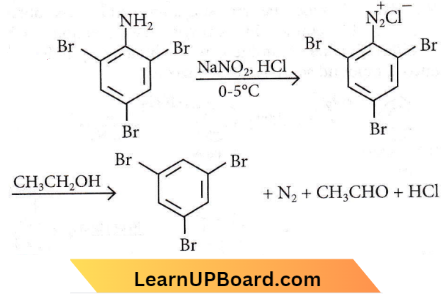
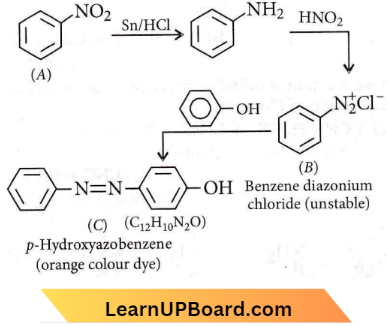
Question 41. A given nitrogen-containing aromatic compound ‘A’ reacts with Sn/HCl, followed by HNO2 to give an unstable compound ‘If. ‘If, on treatment with phenol, forms a beautiful coloured compound ‘C with the molecular formula C12H10N2O. The structure of compound ‘A’ is
Answer: 2
A given nitrogen-containing aromatic compound ‘A’ reacts with Sn/HCl, followed by HNO2 to give an unstable compound ‘If. ‘If, on treatment with phenol, forms a beautiful coloured compound ‘C with the molecular formula C12H10N2O.
Question 42. In the following reaction, the product (A) is
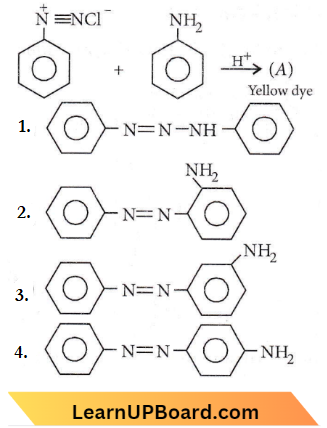
Amines objective questions NEET
Answer: 4
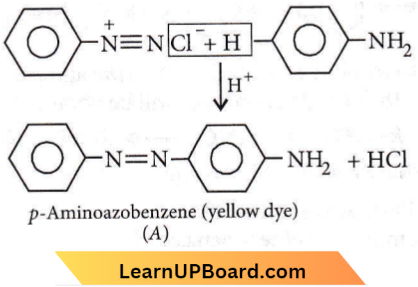
Question 43. In the reaction A is
- \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{PO}_2\) and \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{H}^{+} \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{HgSO}_4 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{Cu}_2 \mathrm{Cl}_2\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{PO}_2\) and \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{PO}_2 \text { and } \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \text { reduces the }-\stackrel{+}{\mathrm{N}} 2 \mathrm{Cl}^{-} \text {to }-\mathrm{H} \text {. }\)
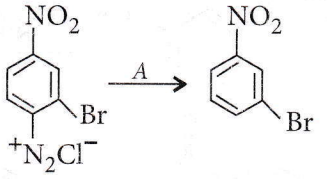
Question 44. Anline in a set of the following reactions yielded a coloured product Y.
Amines objective questions NEET
Answer: 1
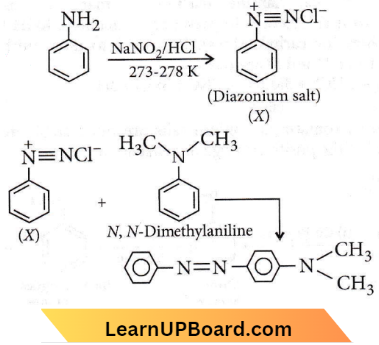
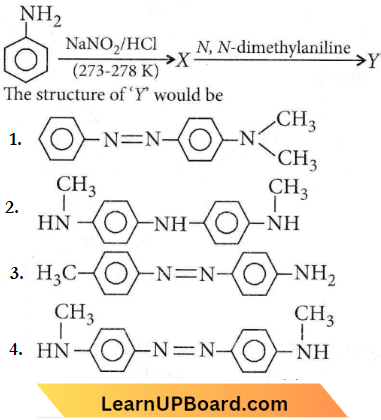
Quetsion 45. Aniline in a set of the following reactions yielded a coloured product D.
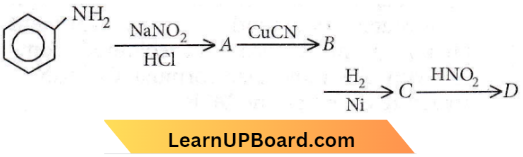
The structure of the product D would be
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{NHOH}\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{NHCH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{NH}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{OH}\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{OH}\)
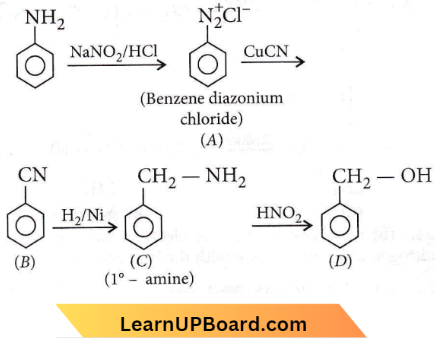
Question 46. Aniline is reacted with bromine water and the resulting product is treated with an aqueous solution of sodium nitrite in the presence of dilute hydrochloric acid. The compound so formed is converted into a tetrafluoroborate which is subsequently heated to dry. The final product is
- p-bromoaniline
- p-bromofluorobenzene
- 1, 3, 5-tribromobenzene
- 2, 4, 6-tribromofluorobenzene
Answer: 4. 2, 4, 6-tribromofluorobenzene
Amines objective questions NEET
Aniline reacts with bromine water and the resulting product is treated with an aqueous solution of sodium nitrite in dilute hydrochloric acid. The compound so formed is converted into a tetrafluoroborate which is subsequently heated to dry.
Question 47. Which one of the following nitro compounds do not react with nitrous acid?
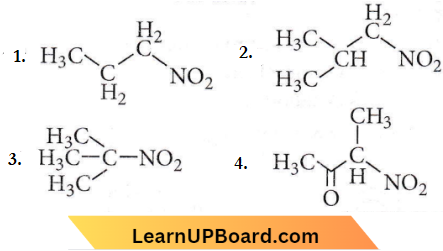
Answer: 3
Tertiary nitroalkanes do not react with nitrous acid as they do not contain cr-hydrogen atoms.
Amines objective questions NEET
Question 48. Nitrobenzene on reaction with cone. HNO3/H2SO4 at 80-100°C forms which one of the following products?
- 1,4-Dinitrobenzene
- 1,2,4-Trinitrobenzene
- 1, 2-Dinitrobenzene
- 1, 3-Dinitrobenzene
Answer: 4. 1, 3-Dinitrobenzene
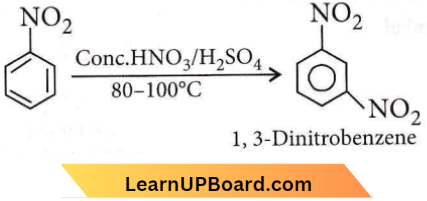
Question 49. What is the product obtained in the following reaction?
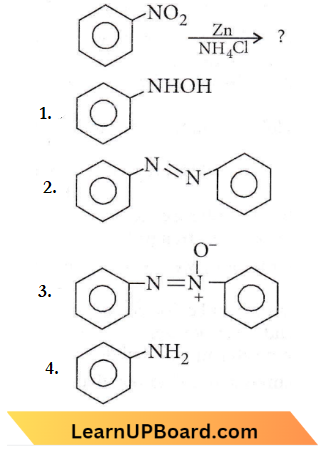
Answer: 1
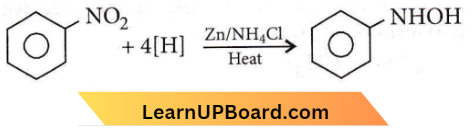
Amines practice questions NEET
Question 50. Product ‘P in the above reaction is
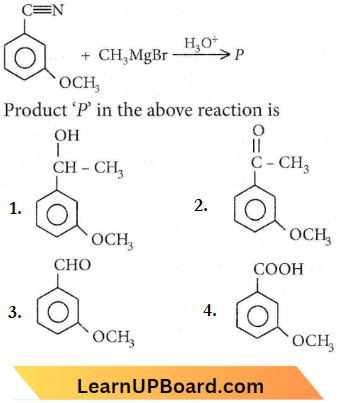
Answer: 2
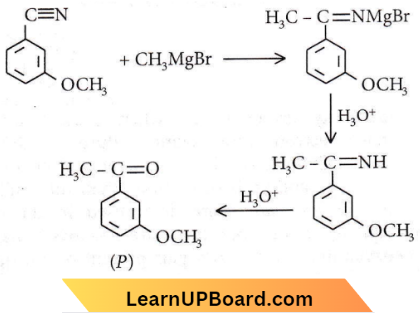
Amines practice questions NEET
Question 51. Which product is formed, when acetonitrile is hydrolyzed partially with cold concentrated HCl?
- Methyl cyanide
- Acetic anhydride
- Acetic acid
- Acetamide
Answer: 4. Acetamide