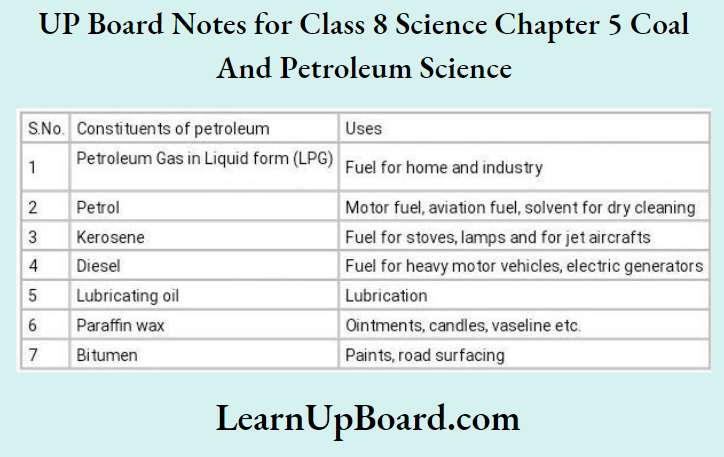
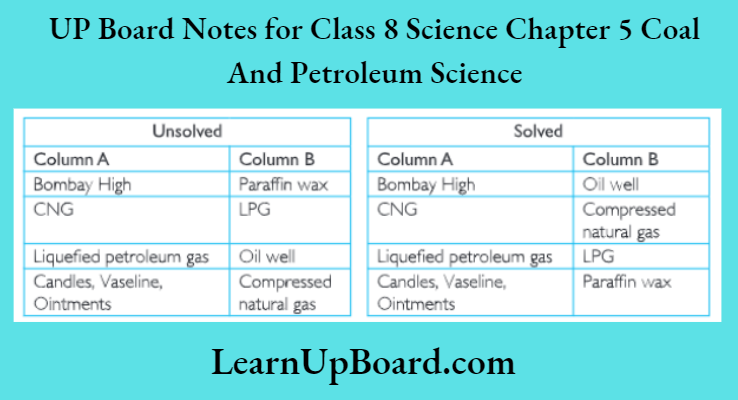
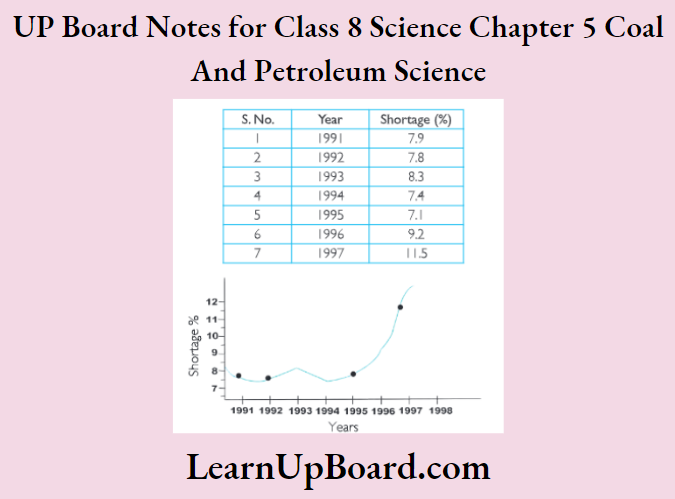
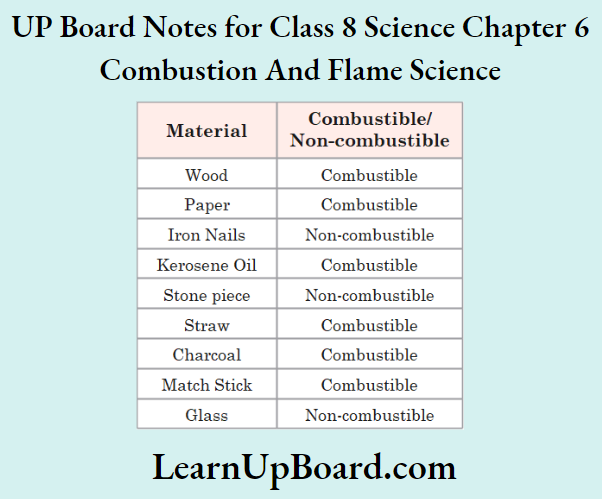
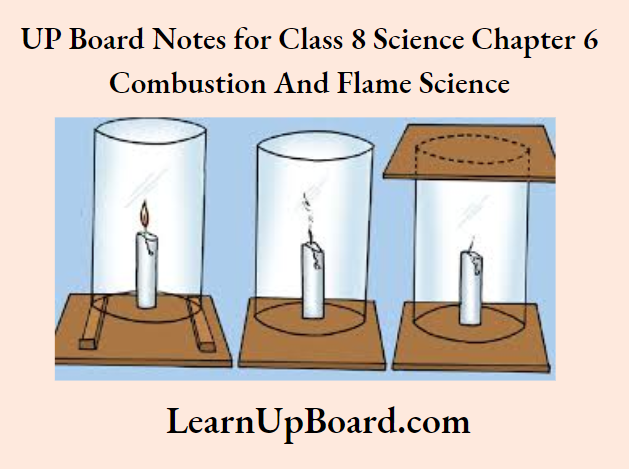
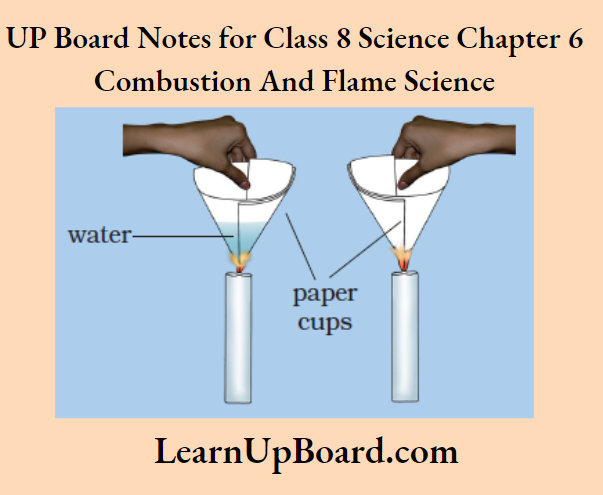
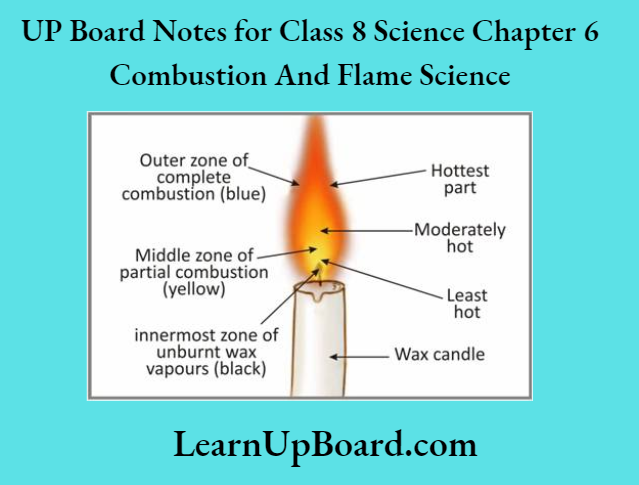
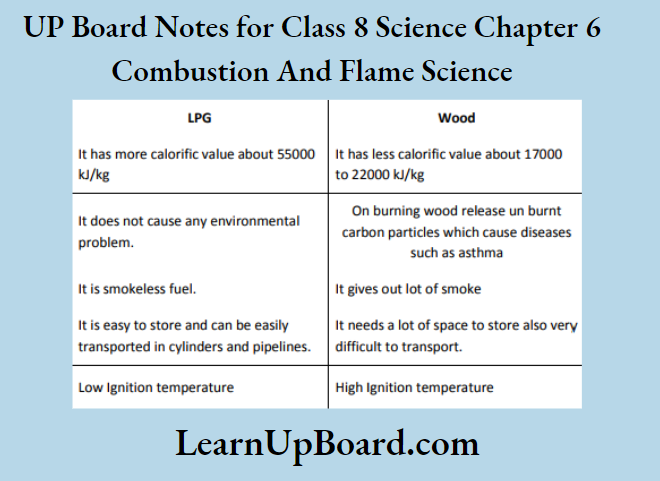
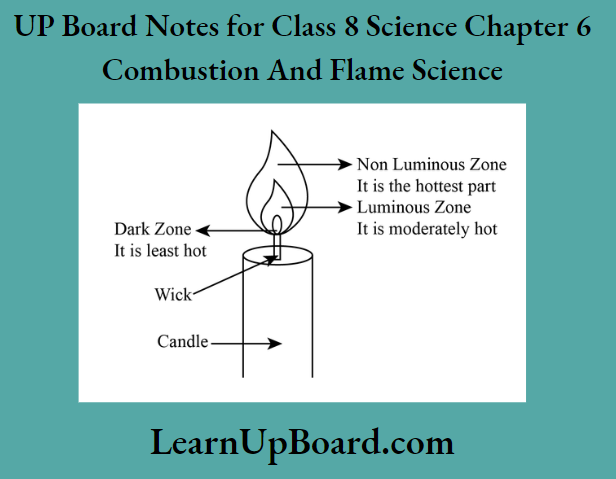
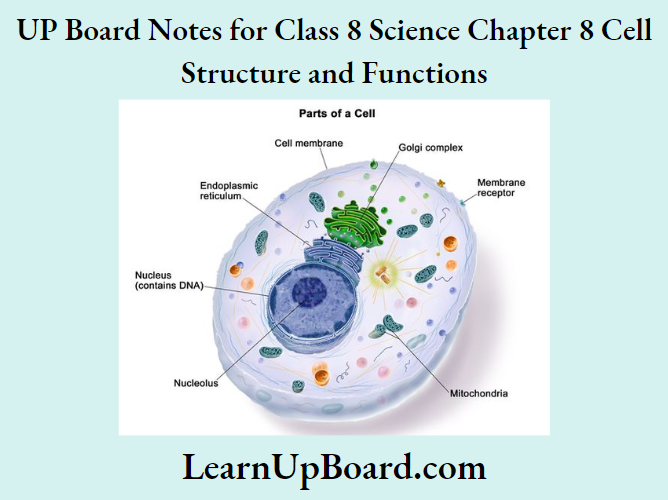
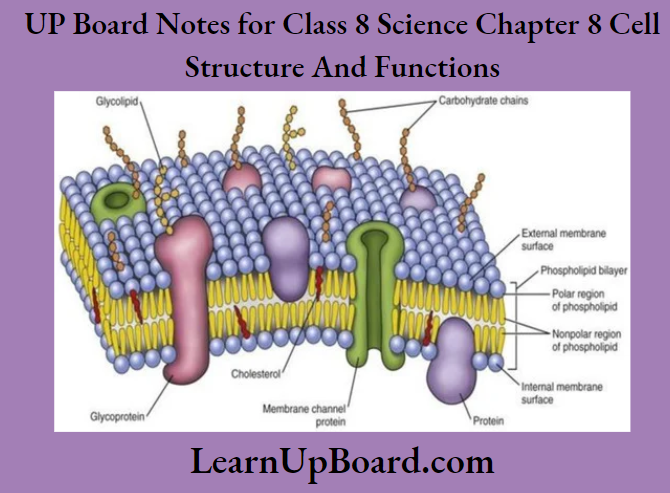
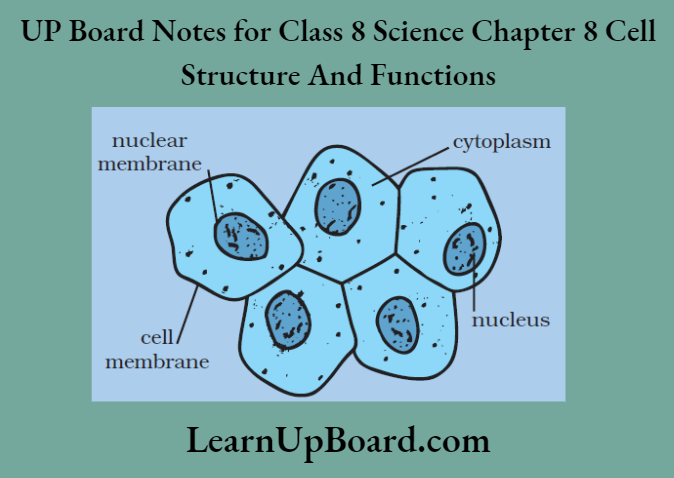
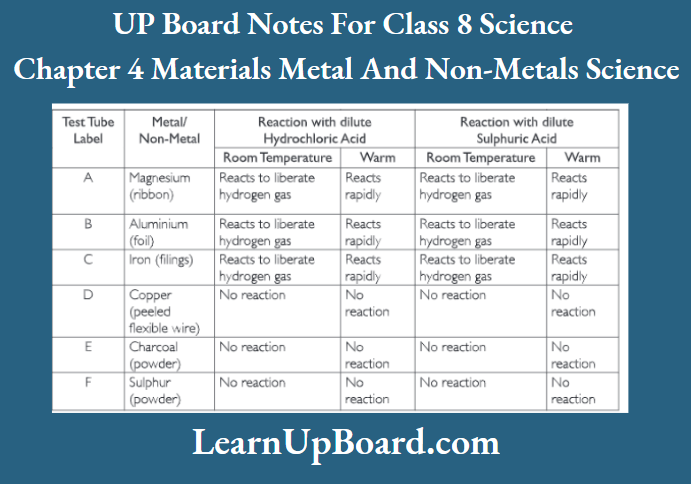
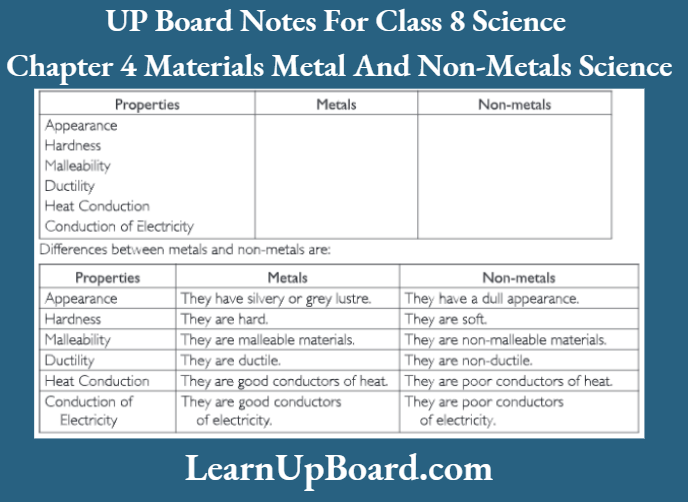
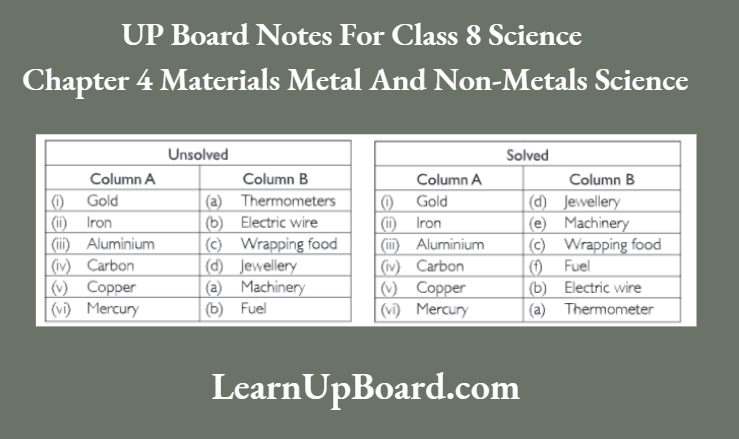
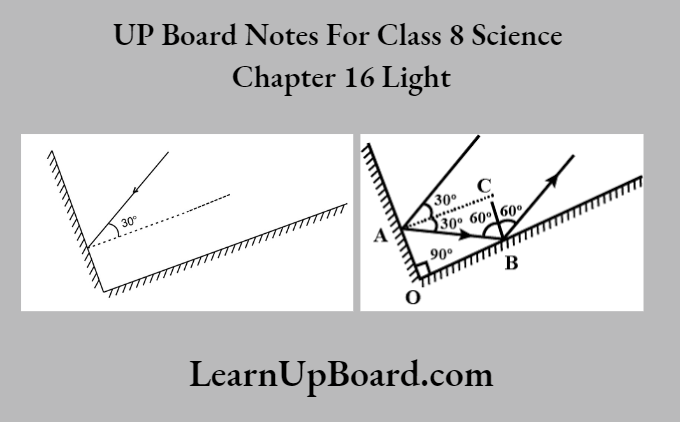
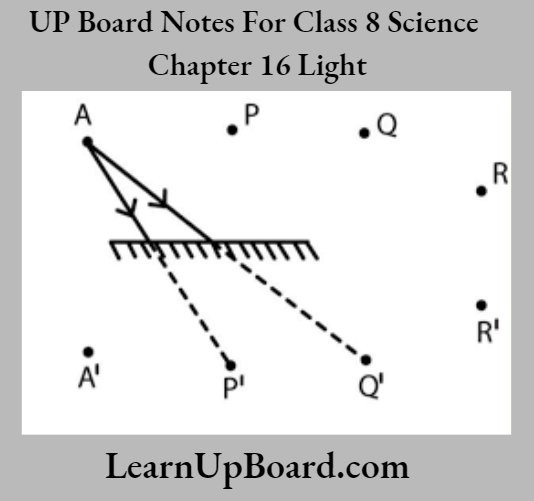
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation Of Plants And Animals Chapter In A Nutshell
- The flora and fauna of a place together form the biodiversity of a place.
- The cutting down of trees on a large scale for various purposes is called deforestation.
- Deforestation occurs due to both natural and man-made causes.
- One of the major causes of deforestation is the use of trees in the paper industry.
- It takes about 17 full-grown trees to produce one tonne of paper. Thus, we should save, reuse, and recycle paper.
- Deforestation has various adverse effects on the environment.
- The restocking of forests by planting new trees is called reforestation.
- IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) has created five categories for the conservation of biodiversity. These categories are extinct, endangered, vulnerable, rare, and critically endangered species.
- Red Data Book is a source that keeps a record of all endangered plants and animals.
- The government lays down rules, methods, and policies to protect and conserve forests and animals.
- Various protected areas like sanctuaries, national parks, and biosphere reserves are earmarked for conservation of biodiversity.
- The Forest Conservation Act, 1927, and Wildlife Protection Act, of 1972 deal with the conservation of forests and wild animals respectively. The main aim of these acts is to preserve and conserve our biodiversity.
- Migratory birds fly to faraway areas during a particular time of the year because of inhospitable climatic conditions in their habitat.
Read and Learn More UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation Of Plants And Animals Important Terms And Definitions
Biodiversity: All the living organisms of an ecosystem are together referred to as biodiversity.
Desertification: Desertification is the process by which fertile land loses fertility and gets converted into desert as a result of deforestation.
Ecosystem: An ecosystem is an interactive system in which all biotic and abiotic components interact with each other as well as with the environment.
Endangered Species: The species in danger of extinction due to rapid decline in their number and change in their habitat are called endangered species.
Endemic Species: The species unique to a particular habitat are called endemic species.
Extinct Species: A species is called an extinct species when the last existing member of the species dies.
Fauna: All the plant species found in a particular habitat are referred to as fauna.
Flora: All the animal species found in a particular habitat are referred to as flora.
Migration: Migration is the regular or systematic movement of a group of organisms in search of suitable temporary shelter.
Species: A group of a population capable of interbreeding is called a species.
Deforestation
Answer.
Deforestation
A major threat to the survival of plants and animals on the Earth is deforestation. Deforestation has adverse effects on the food chains. Deforestation results in increased levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. This results in an increase in the temperature of the Earth and consequently leads to global warming. A decrease in the number of trees and forests results in decreased rainfall. This disturbs the water cycle which leads to drought. Deforestation is also responsible for the change in the physical properties like nutrient content, texture, etc. of the soil. Deforestation exposes the topsoil to agents like wind and water that are responsible for soil erosion. Deforestation also affects the water-holding capacity of the soil.
Human beings are the main cause of deforestation. Forests are cleared to use land for the cultivation of crops, the construction of houses, roads, factories, etc. Forest fire and drought are some natural causes of deforestation.
Hence, reforestation must be practiced to retain the green wealth for future generations.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation Of Plants And Animals Activity 1
Aim: To list the causes of deforestation and classify them as natural and man-made
Observation:

Conclusion:
Deforestation occurs due to both natural and man-made causes.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals Activity 2
Aim: To list various effects of deforestation on animals
Observation: Effects of deforestation on animals are:
1. Loss of habitat
2. Shortage of food
3. Disturbance of food chain
4. Increased risk of natural calamities and hunters
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals Objective Type Questions
A. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Habitat destruction is a major threat to biodiversity.
- Forests are mostly cut for their leaves.
- Deforestation ruins the ecology of a region and destroys a large portion of the life forms that live there.
- Forests shelter a variety of plants and animals.
- Forest conservation is the management of rivers to save the environment.
Answers:
- True
- False
- True
- True
- False
B. Fill in the blanks.
- The large-scale cutting of trees and clearing of forests is called_______
- Deforestation reduces the amount of water in the soil and lowers the______
- Depletion of forests leads to a decrease in_______fertility.
- If all plants in a forest are cut, it will lead to soil______
- Establishing a new forest on land that had been deforested earlier is called_____
Answer:
- Deforestation
- Water table
- Soil
- Erosion
- Afforestation
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation Of Plants And Animals Short Answer Type Questions
A. What do you mean by desertification?
Answer.
Desertification:
Soil erosion exposes the lower, hard and rocky layers. This soil has less humus and is less fertile. Gradually the fertile land gets converted into deserts. It is called desertification.
Loss of Biodiversity
Answer.
Loss of Biodiversity
The huge variety of flora and fauna on the earth is termed as biodiversity. Some of the major causes of loss of biodiversity are deforestation, land degradation and overexploitation of resources. Some species of plants and animals are found exclusively in a particular geographical area. Such species are called endemic species. The destruction of habitat or introduction of new species may affect the natural habitat of an endemic species IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural resources) evaluates the status of threat to a species based on available information. It has identified five categories of animals and plants that need protection. A Red Data Book is a record of all threatened species of plants and animals.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation Of Plants And Animals Objective Type Questions
A. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- The IUCN Red List has information about species that do not exist.
- Endangered animals are not seen on the earth anymore.
Answers: 1. False 2. False
B. Fill in the blanks.
- Red data book is a list of______species.
- The species found only in a particular area is known as______
Answers: 1. Threatened 2. Endemic species
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation Of Plants And Animals Multiple Choice Questions.
1. What are critically endangered species?
- Species having an extremely high risk of becoming extinct.
- Species with high chances of moving into the endangered category.
- Species with huge populations.
- Species that do not exist anymore.
Answer: 1. (1) Species having an extremely high risk of becoming extinct
2. The species that exist in small numbers are called_______
- Threatened species
- Rare species
- Endangered species
- Critically Endangered
Answer.(2) Rare species
3. Which of the following bird have become extinct?
- Dodo
- Pigeon
- Bat
- Gesse
Answer.(1) Dodo
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation Of Plants And Animals Short Answer Type Questions
A. What is biodiversity conservation?
Answer.
Biodiversity Conservation
Biodiversity is protection and scientific management of biodiversity so as to maintain it at its optimum level and derive sustainable benefits for present as well as future generations.
Conservation of Forest and Wildlife
Answer.
Conservation of Forest and Wildlife
The Government of India has created some protected areas such as national parks, wildlife sanctuaries and biosphere reserves to protect flora and fauna and their habitats.
National parks are protected land areas preserved in natural conditions to provide natural habitat to wildlife. An example of a national park is Jim Corbett national park, Uttarakhand.
Wildlife sanctuary is an area where only animals are protected and their capturing and killing is strictly prohibited. However permission for collection of minor forest products, harvesting of timber and
cultivation is granted.
A biosphere reserve is a large protected area for the conservation of wildlife, plant and animal resources. The main aim of the biosphere reserves is to conserve biodiversity, maintain ecological balance, and maintain the culture of that particular area. A biosphere reserve may contain National Parks and Sanctuaries. For example, Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve includes Satpura National Park, Bori Sanctuary and Pachmarhi Wildlife Sanctuary.
Zoological park also referred to as a ‘zoo’, is a place where animals are protected by keeping them in special enclosures and cages for public exhibition. Botanical garden is a place where a wide variety of plants are cultivated for scientific, educational, and ornamental purposes. It often includes a library, a herbarium, greenhouses and an arboretum.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation Of Plants And Animals Objective Type Questions
A. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Kanha National Park is in Madhya Pradesh.
- A biosphere reserve is an international designation for conservation.
Answers: 1. True 2. False
B. Multiple-Choice Questions
1. Which of the following biosphere reserves is a part of MAB program?
- Nokrek
- Pachmarhi
- Nanda Devi
- Bori
Answers. (3) Nanda Devi
2. Wildlife protection act was enacted in which year?
- 1967
- 1970
- 1992
- 1972
Answers. (4) 1972
3. Where is Jaldapara Sanctuary located in India?
- (West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Andhra Pradesh
Answers: (4) Andhra Pradesh
C. Fill in the blanks.
- Jim Corbett National Park is situated in_____
- Gir Sanctuary is located in_______ and is famous for_______
Answer: 1. Uttrakhand 2. Gujarat, lion
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation Of Plants And Animals Short Answer Type Questions
A. List some important national parks in India.
Some important national parks in India are:
- Kanha National Park, Madhya Pradesh
- Betla National Park, Jharkhand
- Tadoba National Park, Maharashtra
- Simplipal National Park, Orissa
B. Name at least seven wild animals of Khangchendzonga National Park, which face the danger of extinction.
Answer. Wild animals of Khangchendzonga National Park which face extinction are snow leopard, clouded
leopard, marbled cat, Himalayan black bear, red panda, Tibetian wild ass, blue sheep, serow, goral, takin, musk deer, and green pigeon.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation Of Plants And Animals Textbook Exercises
1. Fill in the blanks.
- A place where animals are protected in an artificial habitat is called a______
- Species found only in a particular area are known as_______
- Migratory birds fly to faraway places because of_______changes.
Answer: (1) Zoo (2) Endemic species (3) Climatic
2. Differentiate between the following:
- Wildlife sanctuary and biosphere reserve
- Zoo and wildlife sanctuary
- Endangered and extinct species
- Flora and fauna
(a) Differences between Wildlife sanctuary and Biosphere reserve are:
Wildlife Sanctuary
A wildlife sanctuary is an area where only animals are protected and their capturing and killing is strictly prohibited.
Biosphere Reserve
A biosphere reserve is a large protected area for the conservation of wildlife, plant, and animal resources.
(b) Differences between Zoo and Wildlife sanctuaries are:
Zoo
A zoological park also referred to as a ‘zoo’, is a place where animals are protected by keeping them in special enclosures and cages for public exhibition.
Wildlife Sanctuary
A wildlife sanctuary is an area where only animals are protected and their capturing and killing is strictly prohibited.
(c) Differences between endangered and extinct species are:
Endangered Species
The species in danger of extinction due to rapid decline in their number and change in their habitat are called endangered species.
Extinct Species
A species is called an extinct species when the last existing member of the species dies.
(d) Differences between flora and fauna are:
Flora
All the plant species found in a particular habitat are referred to a flora.
Fauna
All the animal species found in a particular are referred to a flora.
3. Discuss the effect of deforestation on the following.
- Wild animals
- Environment
- Villages (Rural areas)
- Cities (Urban areas)
- Earth
- The next generation
Answer.
- Deforestation destroys the natural habitat of wild animals and thus, they can become endangered.
- Deforestation decreases the level of oxygen in the atmosphere. The rainfall and fertility of soil also decrease due to deforestation. As a result, there are increased chances of natural calamities like floods and drought.
- Most of the agriculture is done in rural areas. Deforestation leads to a change in soil properties, which in turn affects the agriculture.
- In cities, there are many factories and automobiles. Deforestation further pollutes the environment and hence, the life in cities will not be healthy for living.
- Deforestation leads to an increase in the temperature of the earth causing global warming. Less trees would result in more soil erosion.
- Deforestation leads to climatic changes which has a great effect on the next generation. So, the next generation would not be as prosperous as the previous one.
4. What will happen if
- we go on cutting trees?
- the habitat of an animal is disturbed?
- the top layer of soil is exposed?
Answer.
- If we go on cutting trees continuously, rainfall and fertility of the soil will decrease. Hence, there are increased chances of natural calamities such as floods and drought. If the habitat of an animal is disturbed, some of the species will not get appropriate food and shelter and with the passage of time, they will come under the category of endangered species.
- If the top layer of the soil is exposed, the soil will have less humus and will become less fertile. Gradually, the land will convert into desert. This is called desertification.
5. Answer in brief
- Why should we conserve biodiversity?
- Protected forests are also not completely safe for wild animals. Why?
- Some tribals depend on the jungle. How?
- What are the causes and consequences of deforestation?
- What is a Red Data Book?
- What do you understand by the term migration?
Answer.
- We should conserve biodiversity to save flora and fauna from extinction.
- Protected forests are also not completely safe for wild animals because people living in the neighbourhood encroach upon them and harm them.
- Certain tribes depend on jungle for food, shelter and fuel.
- Human beings are the main cause of deforestation. Forests are cleared to use land for the cultivation of crops, construction of houses, roads, factories etc. Forest fire and drought are some natural causes of deforestation. Deforestation has adverse affects on the food chains. Deforestation results in increased levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. This results in the increase in temperature of the Earth and consequently leads to global warming. Decrease in the number of trees and forests results in decreases rainfall. This disturbs the water cycle which leads to drought. Deforestation is also responsible for the change in the physical properties like nutrient content, texture, etc. of the soil. Deforestation exposes the top soil to agents like wind and water that are responsible for soil erosion. Deforestation also affects the water holding capacity of the soil.
- Red Data Book is a record of all threatened species of plants and animals. It is published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural resources (IUCN), which is now known as World Conservation Union (WCU). The red-listing assessment is a simple logical process to determine the status of threat to a species based on available information.
- The seasonal, mass movement of animals from one place to another to escape from extreme cold, to breed or to find food is called migration.
6. In order to meet the ever-increasing demand in factories and for shelter, trees are being continually cut. Is it justified to cut trees for such projects? Discuss and prepare a brief report.
Answer. It is not justified to cut trees for such projects.
When trees are cut down, the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere goes up, which results in the increase in temperature and consequently leads to global warming. Trees bring rain. So, the decrease in number of trees results in decreasing rainfall. Cutting down of trees is also responsible for the change in physical properties like nutrient content, texture of the soil.
7. How can you contribute to the maintenance of green wealth of your locality? Make a list of actions to be taken by you.
Answer.
For maintenance of green wealth in our locality, we shoul
- Grow more and more trees on both sides of the road.
- Discourage the cutting of trees.
- Maintain greenery in the parks of our locality.
- Water the plants in our locality regularly
- Convince other people to plant new trees.
- Take out rallies to create awareness among people.
- Coordinate with local authorities for proper help.
8. Explain how deforestation leads to reduced rainfall.
Answer. Trees lose water by the process of transpiration. This water contributes a lot towards atmospheric moisture. Thus, green plants have major contribution in precipitation and rainfall pattern. So,\ deforestation leads to reduced rainfall.
9. Find out about the national parks in your state. Identify and show their locations in the outline map of India.
Some of the national parks of India are marked on the map

10. Why should paper be saved? Prepare a list of ways by which you can save paper.
Answer. By wasting paper products, we waste forests. The more paper we use, the more trees we need to cut down to feed our insatiable appetite for paper. In order to reduce deforestation, we must learn to recycle used paper, efficiently and economically.
Ways by which paper can be saved are:
- Collect used paper and recycle it.
- Use both sides of a paper for writing.
- Spread awareness about the importance of paper.
- Use paper intelligently.
- Old envelopes can also be used for doing the rough work.
- Schools should encourage online submission of reports and assignments so that papers can be saved.
- Don’t take a printout unless it is absolutely necessary.
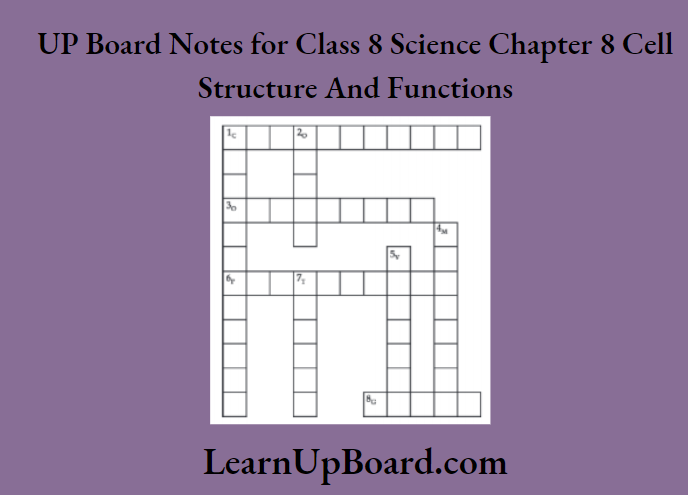
11. Complete the word puzzle.
Down:
- Species on the verge of extinction.
- A book carrying information about endangered species.
- Consequence of deforestation.
Across
- Species which have vanished.
- Species found only in a particular habitat.
- Variety of plants, animals, and micro-organisms found in an area.
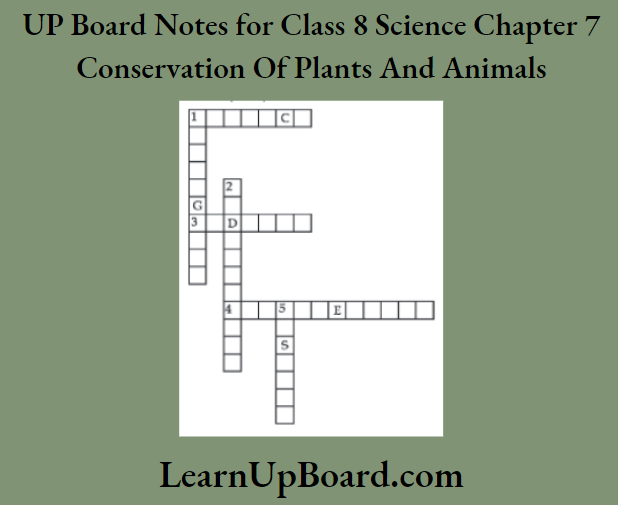
Down:
1. Endangered
2. Red data book
5. Deserts
Across:
1. Extinct
3. Endemic
4. Biodiversity
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants And Animals Hots corner
A. People living in hilly areas are cutting down a lot of trees for their daily needs and agricultural purposes. After a few years they face a lot of landslides in their area. What do you think is the reason behind it?
Answer. Cutting down of trees on a large scale is one of the main reasons behind the landslides. The roots of the trees hold the soil. As a result of deforestation, the soil gets loose and runs off during heavy rain resulting in landslides.
B. Suppose in a forest the number of carnivorous animals suddenly increases than the number of herbivore animals. What will be the consequences?
Answer. If the number of carnivorous animals increases as compared to the number of herbivore animals, then there will be a shortage of food for the carnivores and soon they will die due to hunger. There will be a bloom of plants also.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants And Animals Practice exercise
A. Fill in the blanks.
- The Indian Giant Squirrel is_______ fauna.
- A species with a very small population on the earth is called_______species
- ______ is a protected area where only animals are protected.
- Project Tiger was launched in India in the year_______
- A_______ is much larger than a national park or a sanctuary.
Answers:
- Endemic
- Rare
- Wildlife Sanctuary
- 1973
- Biosphere Reserve
B. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Deforestation results in desertification.
- Deforestation has disastrous effects on the biodiversity of a place.
- Siberian cranes come to India during winter.
- Man is not responsible for deforestation.
- Climatic changes do not affect biodiversity.
Answer:
- True
- True
- True
- False
- False
C. Answer the following in one word.
- Asiatic lion and pink pigeon belong to which IUCN category?
- Which form of wood is used to make paper?
- Name an extinct flightless bird.
- Which term is used for species that are likely to become endangered shortly?
- Which bird covers the longest migration distance?
Answer:
- Endangered
- Pulp
- Dodo
- Vulnerable
- Arctic tern
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation Of Plants And Animals Short Answer Questions
1. Write a short note on biosphere reserve.
Answer.
Biosphere Reserve
The concept of a Biosphere Reserve has been evolved by the Man and Biosphere (MBA) program of UNESCO. In a biosphere reserve, multiple land use is allowed by designating various zones such as core, buffer zone, and manipulation zone. In a biosphere reserve, wild population, traditional lifestyle of tribals, and varied domesticated plant and animal genetic resources are protected.
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe.
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 8 Cell: Structure and Functions
- Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Chapter 11 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 12 Friction
- Chapter 13 Sound
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water