NEET Biology Notes PDF Free Download
NEET Biology Notes For Major Abiotic Factors
NEET Biology Notes For Temperature
Ecologically, it is the most relevant factor as temperature variation affects the enzyme kinetics, basal metabolic activities, and physiological functions of organisms. So, thermal tolerance de- cides to a large extent the geographical distribution of different species.
NEET Biology Notes For Stenothermal
Such organisms live in areas where the temperature is uniform throughout the year. These organisms cannot tolerate temperature variation.
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Notes
NEET Biology Notes For Eurythermal
Such organisms can tolerate large changes in temperature. These organisms are classified into four temperature groups on the basis of their occurrence in different climatic zones.
- Megatherms: High temperature throughout the year as found in a tropical zone.
- Mesotherms: They are adapted to winters and high summer temperatures. These organisms live in subtropical zone.
- Microtherms: They live in temperate areas where the winter temperature is low but the summer temperature is moderate.
- Hekistotherms: These organisms are adapted to a brief period of summer below 10°C and a long snowy winter period. This condition occurs in arctic or alpine zone.
Some effects of temperature are defined as under:
- Bergman’s rule: Warm-blooded animals (birds and mammals) have a larger body size in cold climate than in hotter areas..
- Allen’s rule: Extremities (legs, ears, tail, and mouth) of warm-blooded animals become smaller in colder areas as compared to the animals of warmer areas.
- Renton’s rule: In a colder climate, birds possess narrow and acuminate wings as compared to broader wings of birds found in warmer areas.
- Jordan’s rule: As the temperature is lowered, some fishes possess a larger size with a larger number of vertebrae.
NEET Biology Notes For Thermoperiodicity
Thermoperiodicity or thermoperiodism is the response of living organisms to regular changes of temperature. It is of two types: diurnal and seasonal.
- Diurnal thermoperiodicity: It is the response of organisms to daily changes of temperature. Generally, the day-time temperature is higher while the night-time temperature is lower.
- Seasonal thermoperiodicity: It is the response of organisms to seasonal changes in temperature. Along with photoperiodicity, it controls the growth of plants.
NEET Biology Notes For Thermal Stratification in Lakes
The occurrence of different temperatures in different horizontal layers as in a forest or a deep water body is called thermal stratification. A deep-water body, such as a lake, has three temperature strata: epilimnion, metalimnion, and hypolimnion.
- Epilimnion: It is the upper stratum in the water body. Epilimnion is warmer during summer and cooler during winter.
- Metalimnion: It is a short transitional zone between epilimnion and hypolimnion. The middle part of metalimnion is called thermocline. It is the area of maximum temperature changes.
- Hypolimnion: It is the lower stratum of a water body with lesser temperature fluctuations.
class 12 organisms and population notes
NEET Biology Notes For Water
Water is an important component of protoplasm, which is a general solvent. Water is also present over more than 71% surface of the earth as oceans, lakes, rivers, ice caps, and glaciers. The seawater has a high percentage of salt content (3.5%). Water present on land is called fresh water. Its salt content is low-less than 0.5%. The salt concentration (measured as salinity in parts per thousand) is less than 5% in inland water, 30-35% in the sea, and more than 100% in some hypersaline lagoons.
The regular movement of water among various regions and components of biosphere, viz., aquatic systems, air, and land, constitutes a water cycle. Water comes over land and water bodies as precipitation or rainfall. The total global rainfall is 4.46 G. Precipitation comes from water vapors present in the air. At any time, the atmosphere contains only 0.13 G of water vapors (1 G or genogram
Animals found in coastal water are called neritic and those found in open water are termed pelagic. Pelagic organisms are plankton (if microscopic), neuston (if macroscopic and found on the surface), and nekton (if actively swimming). Organisms found at the bottom of water bodies are called benthos.
NEET Biology Notes For Light
Light has a wide range of spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum is a complete range of oscillating waves that travel together through space at a speed of 3 x 105 km/s. At 83 km above the surface of the earth, solar radiation carries an energy equivalent to 2 cal/cm2/min. This value is called solar constant.
Shortwave radiations are cosmic rays (with a wavelength less than 10-5 nm), gamma rays (103-105 nm), X-rays (10-1–10-2 nm), and UV rays (100-400 nm).
All shortwave radiation is extremely harmful. Most of them are trapped in the ionosphere and mesosphere. UV rays are also harmful.
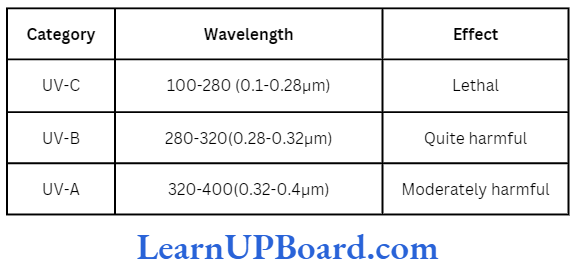
UV-C and half of UV-B radiations are absorbed by the ozone layer of the stratosphere. A large amount of the rest is dissipated by the particles of troposphere; only a small amount reaches the earth.
Light affects photosynthesis, growth, reproduction, movement, stratification, photoperiodism, and phenology in plants, whereas it affects migration, reproduction, development, pigmentation, locomotion, and the period of activity in animals.
NEET Biology Notes For Light Zonation Of Lakes
- Littoral zone: It is exposed to wave action and is highly productive.
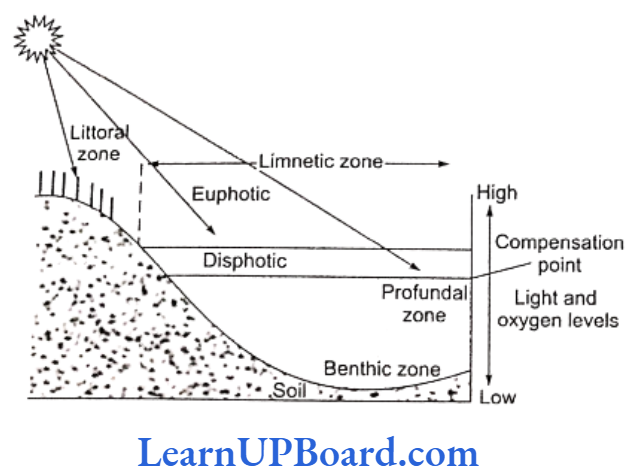
- Limnetic zone: It is an open water body.
- Euphotic zone: This zone receives maximum light above the light compensation point.
- Disphotic zone: This zone receives diffused light at or below the light compensation point. It is also known as the twilight zone.
- Profundal (dark, abyssal) zone: It has no light.
- Benthic zone: It lies at the bottom of the sea.
NEET Biology Notes For Soil
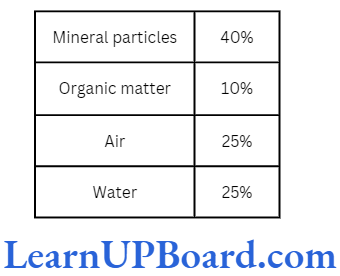
Soil Composition
Soil consists of four components: two solid and two nonsolid. The solid components are mineral particles and organic matter. The nonsolid components are air and water. A fifth component of variable nature is soil organisms.
Chief characteristics of soil are studied with the help of a soil profile. The type of soil profile depends upon the climate and vegetation of the area. The smallest three-dimensional volume of the soil required to study the profile is called pedon. Most soils possess three-four horizons and a number of subhorizons. A soil horizon is a horizontal layer approximately parallel to the soil surface that possesses distinctive properties which are unlike the ones present in adjoining regions. In general, a profile consists of O, A, B, C, and R horizons.
- Weathering: It is the breaking of rocks into fine particles as present on the soil. Weathering occurs by the following methods:
- Physical weathering: It is caused by alternate heating and cooling, alternate wetting and drying, and action of frost, snow, rain, and wind.
- Chemical weathering: Oxidation, reduction, carbonation, and solubilization are performed to break the rock.
- Biological weathering: It is caused by lichens, mosses, and other organisms.
- Humification: It is addition of organic matter or humus to a weathered rock. Humification is essential to starting biological activity and nutritional cycling. Humus is a dark-colored amorphous substance. It is slightly acidic and colloidal and is a reservoir of nutrients. The main functions of humus are biogeochemical cycling, preventing soil from compaction, helping in the formation of soil crumbs, and improving the aeration and water-holding capacity of the soil. It also makes the soil spongy, therefore, rendering it easy for penetration by roots.
- Eluviation and illuviation: The two processes bring about transport and deposition of materials in the soil. Eluviation is washing down of materials from the upper strata of soil and helping in enriching the different layers of soil with minerals. Illuviation is deposition of minerals in the lower strata of soil.
- Mineral matter: It consists of inorganic substances present as particles of different sizes and composition.
- Gravel: It is made of fine pebbles with a size of 2-10 mm.
- Sand: It consists of grains of quartz or silicon dioxide (SiO2). Size varies from 0.02-2.0 mm. Sand is chemically inert. It allows quick percolation of rain or irrigation water. Aeration is good.
- Silt: It is formed of fine grains of quartz. The size is 0.002-0.02 mm. It is chemically inert.
- Clay: It is made of Al, Fe, and Si. The size is less than 0.002 mm. Clay particles are chemically active and have fine interspaces that can hold abundant water, but aeration is poor.
- Soil air: It is the air present in macropores with a size between 20 and 50 μm. A good soil should have 25% air by volume. Soil air is required for the respiration of roots and several microorganisms. Soil air is richer in CO2 and poorer in O2.
- Soil porosity: It is the percentage of interspaces present per unit dry weight of soil. The value of soil porosity is 30% in sandy soil, 45% in loam soil, and 50% in clay soil. There are two types of soil pores: micropores and macropores. Micropores are small sized interspaces having a diameter of 20 μm or less. These hold water by capillarity. Macropores are interspaces with a size of more than 20 μm.
Residual soils develop in situ. Transported soils are brought from other places through gravity (colluvial), running water (deposited on flood plains and called alluvial), wind (colian or acolian), and glacier (glacial soil).
Soil Types:
- Red soils: These are acidic laterite soils which are deficient in lime, magnesium, phosphorus, and potassium but rich in organic matter, iron, and aluminum. These soils support tea, coffee, rubber, cardamom, areca nut, and paddy plantation.
- Black soils: Also called black cotton soils, locally known as regular, these soils have dark brown or black color from organic matter, clay/hydrated iron, aluminum silicate, and undifferentiated B-horizon (A-C soil).
- Terai/Bhabar soils: These soils are mostly colluvial and highly productive.
Soil Texture:
There are three main types of soil textures.
- Sandy soils: These soils contain about 80% or more of sand, the remaining being silt and clay. Sandy soils are porous and loose. Their water-holding capacity is poor and there is little chemical nutrition.
- Clay soils: These are soils having 40-50% clay, the rest being silt. Sand is little. Clay soils have abundant capillary pores; therefore, their water-holding capacity is high. Inorganic nutrients are available in good quantity. However, aeration is poor.
- Loam soils: These soils contain 20% clay, 40% sand, and 40% silt. These have good mineral nutrition, aeration, and hydration. Therefore, loam soils are the best for plant growth.
Soil pH:
Soil pH determines the type of soil microorganisms, the solubility of different minerals, and the type of plants which will grow on it. In alkaline soils (pH above 7), there is reduced availability of Zn, Mn, Cu, and Fe. In acidic soils, there is an abundance of Fe, Mn, and Al but deficiency of Ca, Mg, and K. Certain soils possess excess of salts, especially of Na and Mg. These are called saline soils. Salinity increases with excessive irrigation. Another category of infertile soil is alkali soil.
NEET Biology Notes For Topography
Topography, i.e., surface configuration of an area (physical features like hills, plains, or slopes), also influences the distribution of organisms. For example, the center and edge of a pond or a stream, the top side and underside of a rock, and the north and south face of a ridge or a mountain are usually inhabited by different species of organisms,

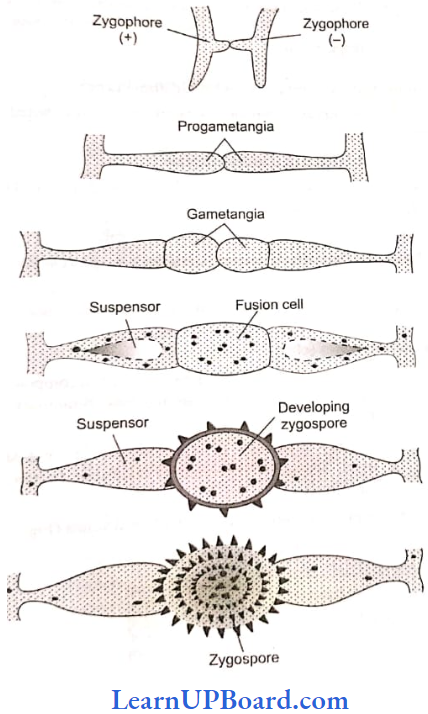
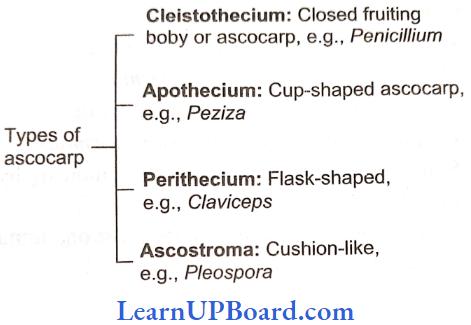
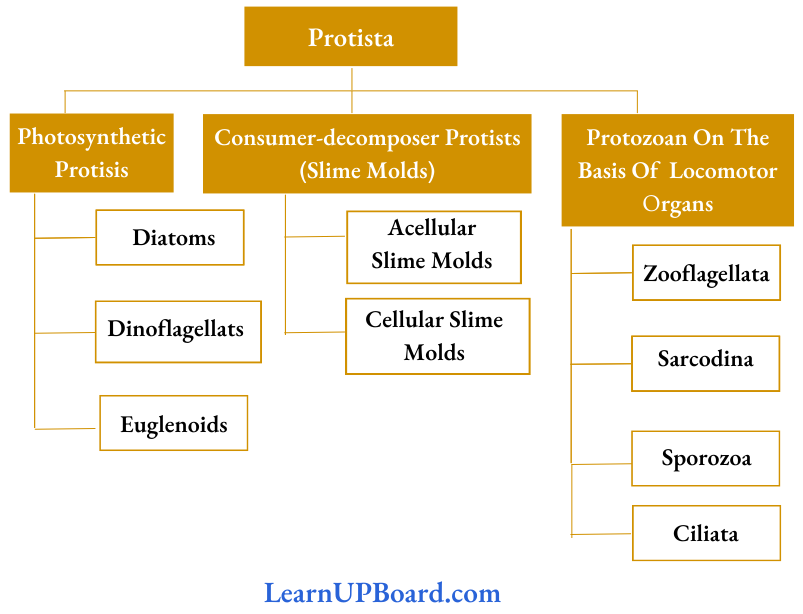
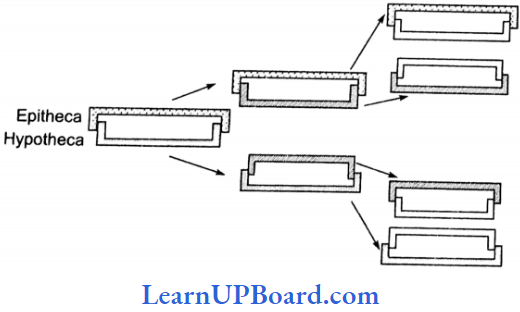
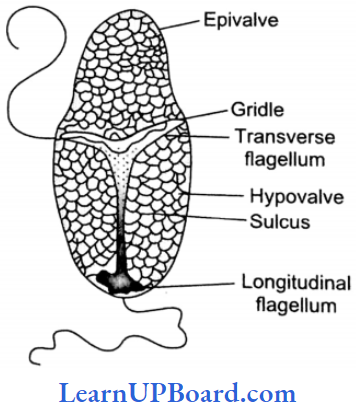
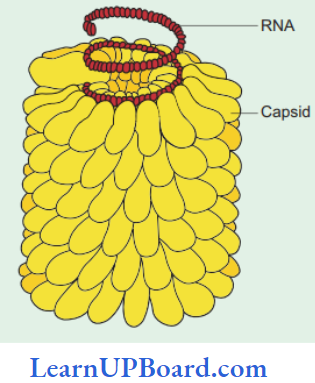
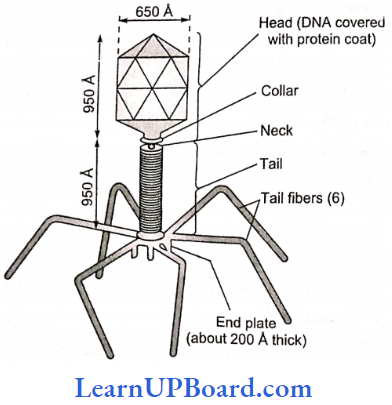
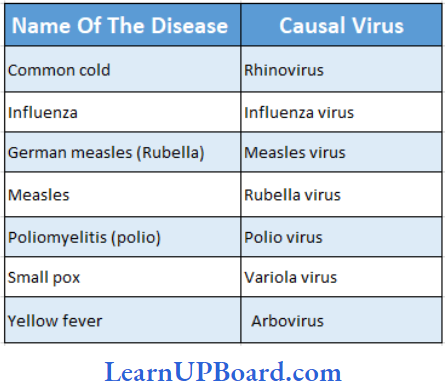
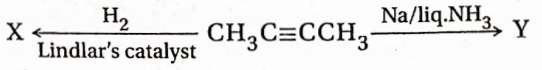
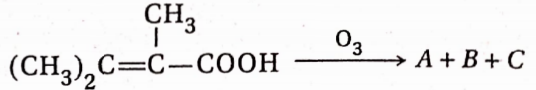 , A, B, C in the above reaction are respectively—
, A, B, C in the above reaction are respectively—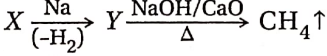 In this reaction, X and Y are-
In this reaction, X and Y are-