Important Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 11- Organisms And Populations Very Short Questions and Answers
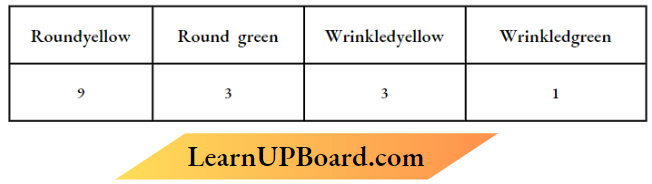
Question 1. Win do cattle and goats generally not browse on Caiotropis plants growing in an abandoned field? Give any one reason.
Answer: Caiotropis produces highly poisonous cardiac glycosides so cattle or goats never browse on this plant.
OR
Give two reasons as to why a weed such as Caiotropis flourishes in abandoned fields,
Answer: Dry hairy seeds help in dissemination or are not grazed by animals as they produce poisonous substances.
Important Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 11- Organisms And PopulationsShort Question And Answers
Question 1.
1. Observe the schematic representation given above and answer the following questions :
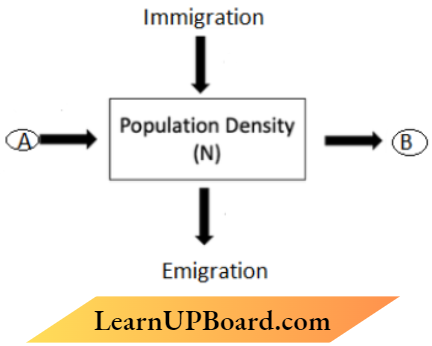
biology most important questions
- Identify A and B.
- Calculate the growth rate of bacteria in a curd sample, where I million bacteria increased to two million, within one hour.
Answer: A – Mortality B – Natality
The per cent growth or birth rate per individual
- A – Mortality B – Natality
- The per cent growth or birth rate per individual
= \(\frac{\text { Final population }- \text { Initial population }}{\text { Initial population }} \times 100\)
= \( \frac{2 \text { Million }-1 \text { Million }}{1 \text { Million }} \times 100\)
= \(\frac{1}{1} \times 100=100 \%\)
Read and Learn More Important Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter Wise
2. Identify the type of pyramid given above. Write (lie identifying feature based on which of you identified it.
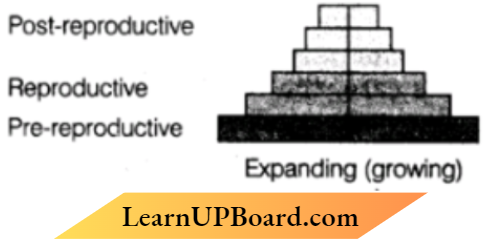
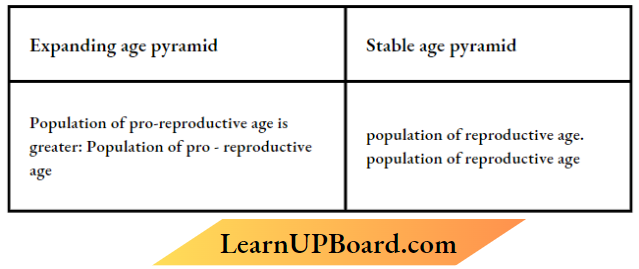
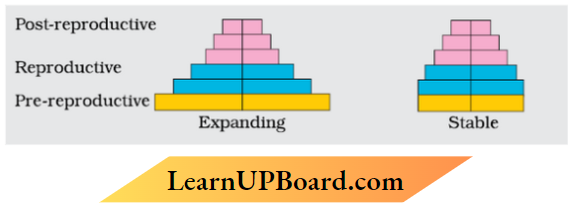
Answer: The given pyramid is expanding. The population of pre-reproductive is higher than the post-reproductive population, which makes the expanding pyramid of population.
Question 2. Explain the pollination mechanism involved in the co-evolution of the two species, namely Ophrys (orchid) and its insect pollinator bees (& bumble bees).
Answer:
- Orchids show a bewildering diversity of floral patterns many of which have evolved to attract the right pollinator insect (bees and bumblebees) and ensure guaranteed pollination by it
- The Mediterranean orchid Ophrys employs ‘sexual deceit’ to get pollination done by a species of bee. One petal of its flower bears an uncanny resemblance to the female of the bee in size, colour and markings.
- The male bee is attracted to what it perceives as a female, ‘pseudocopulates’ with the flower, and during that process is dusted with pollen from the flower When this same bee pseudocopulates’ with another flower, it transfers pollen to it and thus, pollinates the flower, so we can see how co-evolution operates.
- If the female bee’s colour patterns change even slightly for any reason during evolution, pollination success will be reduced unless the orchid flower co-evolves to maintain the resemblance of its petal to the female bee
“important topics of biology class 12 “
Question 3.Given below an equation describing the growth pattern of a population: dN/dt = rN
- Mention the type of growth in the model or growth pattern of the population described by the given equation.
- What does V in the equation signify?
- Mention the type of growth curve that will be obtained if the population density (N) is plotted against time (t).
- According to you, will the resource availability be limited or unlimited for (his type of growth in a given population?
Answer:
- Exponential growth
- The r in this equation is called the ‘intrinsic rate of natural increase’
- Logistic Growth Curve
- The resource availability will be limited for this type of growth in a given population
Question 4. Describe the two basic processes which contribute to an increase in the population density of an area.
Answer:
Natality and Immigration contribute to an increase in population density.
- Natality refers to the number of births during a given period in the population that are added to the initial density.
- Immigration is the number of individuals of fee same that have come into the habitat from elsewhere during the period under consideration.
Question 5. Explain commensalism with the help of an example from the animal world.
Answer: Commensalism is the interaction in which one species benefits and the other is neither harmed nor benefited.
- An example of commensalism is the interaction between a sea anemone that has stinging tentacles and the clown fish that lives among them.
- The fish gets protection from predators which stay away from the stinging tentacles. The anemone does not appear to derive any benefit from hosting the clownfish.
“class 12 biology chapter 2 important questions pdf download “
Question 6. Why do some organisms enter into diapause while some others into aestivation? Give one example of each of such organisms.
Answer:
- Diapause: To avoid unfavourable conditions, Example-Zooplankton
- Aestivation: To avoid summer-related problems or to avoid heat/desiccation, for Example, Snail Fish.
Question 7. If in a population of size ‘N’, the birth rate is represented as it and the death rate as ‘d’ the increase or decrease in ‘N’ during a unit period ‘t’ will he :
⇒\(\frac{d N}{d T}=(b-d) \times N\)
The equation given above can also be represented as :
⇒\(\frac{d N}{d T}=r \times N\)
What does V represent? Write any one significance of calculating V for any population.
Answer:
r = intrinsic rate of natural increase, it is an important parameter for assessing the impacts of any biotic or abiotic factor on population growth.
Question 8. Explain (the role played by predators in a community.
Answer:
- Acting as ‘conduits’ for energy transfer across trophic levels, predators play important roles. They keep prey populations under control.
- Predators also help in maintaining species diversity in a community, by reducing the intensity of competition among competing prey species.
previous year question paper class 12 biology chapter wise
Question 9. Explain the difference between commensalism and mutualism types of interactions, with the help of a suitable example of each.
Answer:
- Mutualism – Both the interacting species are benefitted example Uehen or Mycorrhizae or Fig And Wasp
- Commensalism – One species benefits and the other does not benefit from loss example orchid gunving on a mango branch or a barnacle on the back of a whale or cattle egret And grazing cattle.
Question 10. The graph given below shows the different types of growth curves of different species.
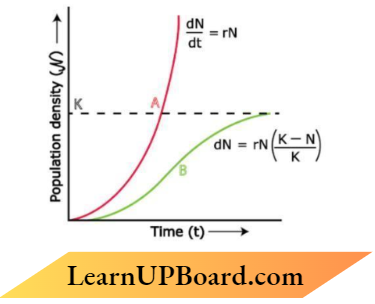
Answer the questions :
- Name the type of growth curve ‘as shown in the graph.
- State one reason the growth equation ‘b’ is said to be logistic.
- what is ‘K’ representing in the equation ⇒\(\frac{\mathrm{dN}}{\mathrm{dt}}=\mathrm{rN}\left[\frac{\mathrm{K}-\mathrm{N}}{\mathrm{K}}\right]\) given along the logistic curve?
Answer:
- Exponential or geometries or T-shaped
- Resources for the growth of most animal populations are finite and become limiting sooner or later
- Carrying capacity.
Question 11. Differentiate between an ’Expanding age pyramid’ and a ’Stable age pyramid’. Substantiate your answer with diagrams.
Answer:
Question 12. Explain with the help of an example each any three ways the ecologists use to measure the population density of different organisms rather than by calculating their absolute number.
Answer:
- By measuring the per cent cover or biomass which may be more meaningful, in cases like in an area where a large number of Parthenium is there but only one banyan tree densities of microorganisms in a culture medium ”
- Measuring relative densities instead of absolute densities of organisms, eg the number of fish caught per trap in a lake is good enough to estimate population size.
By estimating the population size indirectly without actually seeing or counting them, e.g counting tiger population in national parks based on their pug marks or faecal pellets
“12th biology important questions 2023 “
Question 13. Explain the logistic growth pattern of a population. Why do population growth patterns of all organisms ultimately follow it?
Answer:
- A population growing in a habitat with limited resources, shows a lag phase, followed by phases of acceleration and deceleration and finally an asymptote when the population density reaches the carrying capacity,.
- A plot of population density about time results in sigmoid curve Since resources for growth of most organisms are finite, and become limiting sooner or later the logistic growth pattern is ultimately followed.
Question 14. Explain with the help of two examples how certain plants have evolved morphological and chemical defences against primary consumers such as cows and goats.
Answer:
Plants have evolved an astonishing variety of morphological and chemical defences against herbivores.
- Thorns (Acacia, Cactus)are the most common morphological means of defence Many plants produce and store chemicals that make the herbivore sick when they are eaten, inhibit feeding or digestion, disrupt its reproduction or even kill it.
- You must have seen the weed Caloiropisgrowing in abandoned fields The plant produces highly poisonous cardiac glycosides and that is why you never see any cattle or goats browsing on this plant.
- A wide variety of chemical substances that we extract from plants on a commercial scale (nicotine, caffeine, quinine, strychnine, opium, etc.) are produced by them actually as defences against grazers and browsers
Important Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 11- Organisms and Populations Long Question And Answers
Question 1. Study the age pyramids; A’, ‘B’ and ‘c’ Of the human population given below the questions that follow :
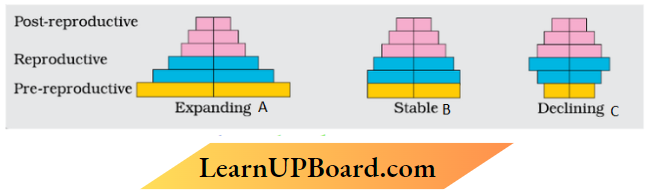
- Identify pyramids ‘B’ and ‘C’
- Write the basis on which the above pyramids are plotted.
Answer:
- B-Stable population
- C- Declining population
- Age Distribution of male and female human population
Question 2.
1. Compare, giving reasons, the (J-shaped and S-shaped) models of population growth of a species.
Answer:
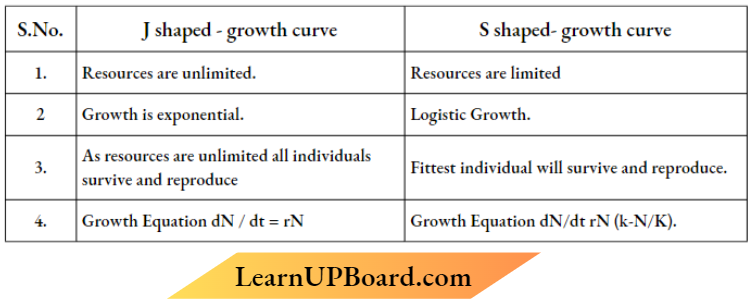
Question 3. Explain “fitness of a species” as mentioned by Darw in.
Answer: When resources are limited. Competition occurs between individuals, the fittest will survive, and reproduce to leave more progeny
Important Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 11- Organisms and Populations Case Study-Based Question And Answers
Question 1. Read the following passage and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
- Acacia plants are particularly common in drier tropical and subtropical environments in the world.
- The swollen thorn acacias, form obligate mutualisms with Pseudomyrmex.
- A species of ants restricted to the New World Swollen thorn acacias show several characteristics related to their obligate association with ants, including enlarged thorns with a soft, easily excavated pith; year-round leaf production, enlarged foliar nectaries; and leaflet tips modified into concentrated food sources called Beltian bodies.
- The thorns provide living space, while the foliar nectaries provide a source of sugar and liquid.
- Beltian bodies are a source of oils and protein. Resident ants vigorously guard these resources against encroachment by nearly all comers, including other plants.
1. The association between the genus of Acaci and species of ants depict population interactions, known as :
- Competition
- Amensalism
- Mutualism
- Predation
Answer: 1. Mutualism
“important topics of biology class 12 “
2. In exchange for food and shelter, ants protect Acacias from the attacks of:
- Fungi
- Bacteria
- Herbivores
- Carnivores
Answer: 3. Herbivores
3. The above interaction suggests that the relationship between the two species is an example of:
- Competitive release
- Competitive exclusion
- Co-evolution
- Resource partitioning
Answer: 3. Co-evolution
4. The removal of resident ants from the Acacias will lead to :
- Reduced growth of Acacias
- Increased growth of Acacias
- Reduced population of ant species
- Increased population of ant species
Choose the correct alternative from the above statements :
- Only 1 is true
- 1 and 3 are true
- 3 and 4 are true
- 1 and 4 are true
Answer: 2. 1 and 3 are true
5. Given below is a graphical representation of ants and the Acacia shoots with an abundance of herbivorous insects :
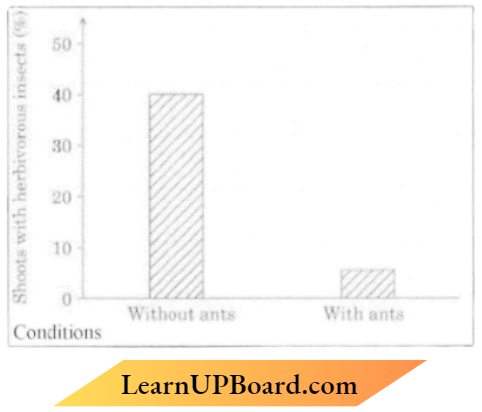
The conclusion drawn from the above data is :
- Acacia shoots will have higher rates of growth with resident ant species.
- Acacia shoots will have a neutral effect on growth with or without resident ant species
- Acacia shoots will have higher rates of growth without resident ant species.
- Growth of Acacia shoots is independent of resident ant species
Answer: 3. Acacia shoots will have higher rates of growth without resident ant species.

 (Polarity, Nucleotide sequence)
(Polarity, Nucleotide sequence)