NEET Biology For Plant Kingdom Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Seedless tracheophytes are
- Bryophyta
- Pteridophyta
- Gymnosperms
- Angiosperms
Answer: 2. Pteridophyta
Question 2. Algae were grouped into how many kingdoms according to Whittaker?
- Two
- Three
- One
- Four
Answer: 2. Three
Question 3. Hcterotrichous nature of thallus is found in
- Fimaria
- Fritschiella and Ectocarpous
- Stigeoclonium and Coleochaete
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
NEET Biology MCQ
Question 4. Thick-walled perennating sexual spore is
- Zygote
- Zoospore
- Hypnospore
- Zygospore
Answer: 4. Zygospore
Question 5. Gulf weed belongs to the class
- Chlorophyceae
- Dirlophyceae
- Phaeophyceac
- Rhodophvceae
Answer: 3. Phaeophyceac
Question 6. The thallus organization of Volvox is
- Multicellular and coccoid
- Colonial and non-flagellate
- Unicellular
- Colonial and motile
Answer: 4. Colonial and motile
Question 7. The hydroxyproline nature of the cell wall is found in
- Chlamydomonas
- Ulothrix
- Spirogyra
- Chlorella
Answer: 1. Chlamydomonas
Question 8. The gametophytic plant body is non-vascular in
- Algae and liverworts
- Mosses and ferns
- Gymnosperms and angiosperms
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 9. Brown algae are quite common in
- Freshwater habitats
- Tropical seawater
- Temperate seawater
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 3. Temperate seawater
NEET Biology MCQ
Question 10. Chloroplast with many pyrenoids is the feature of
- Chlamydomonas
- Sargassum
- Batrachospermum
- Spirogyra
Answer: 4. Spirogyra
Question 11. Algae with Floridian starch as reserve food material are also characterized by
- Presence of chlorophyll b
- Stacked thylakoids
- Nonsulphated hydrocolloids
- Non-flagellate nature
Answer: 4. Non-flagellate nature
Question 12. In the haplontic life cycle of many algae,
- Sporophytic generation is represented by one-celled zygote
- The free-living sporophyte is present
- Meiosis is involved in gamete formation
- Diploid spore forms gametophyte
Answer: 1. Sporophytic generation is represented by one-celled zygote
Question 13. Red snow is caused by
- Zoospores of Chlamydomonas
- Hypnospores of C. brauni
- Aplanospores of C. media
- Hypnospores of C. nivalis
Answer: 4. Hypnospores of C. nivalis
Question 14. Thallus is flattened, leaf-like, and anchors to the rocks with the help of holdfast in
- Laminaria
- Polysiphonia
- Batrachospermum
- Ectocarpus
Answer: 1. Laminaria
Question 15. Hundred zygospores alternate with empty cells in Spirogyra in conjugation. The total number of daughter filaments formed will be
- Scalariform, 400
- Lateral, 100
- Lateral, 400
- Scalariform, 100
Answer: 2. Lateral, 100
NEET Biology MCQ
Question 16. Algin is a hydrocolloid, obtained from the cell wall of
- Macrocystis and Porphyridium
- Mastigocladus and Laminaria
- Microcystis and Nereocystis
- Macrocystis and Fucus
Answer: 4. Macrocystis and Fucus
Question 17. A parasitic algae is
- Porphyra
- Sargassum
- Laminaria
- Cephaleuros
Answer: 4. Cephaleuros
Question 18. An edible red algae is
- Focus
- Sargassum
- Acetabularia
- Porphyra
Answer: 4. Porphyra
” plant kingdom mcq for neet”
Question 19. A floating brown algae that covers thousands of hectares of sea in the Atlantic Ocean is
- Focus
- Nereocystis
- Sargassum
- Dictyota
Answer: 3. Sargassum
Question 20. Motile flagellated asexual spore is
- Zygote
- Zygospore
- Aplanospore
- Zoospore
Answer: 4. Zoospore
Question 21. Laminarin starch is a reserve product characteristic of
- Green algae
- Blue-green algae
- Red algae
- Brown algae
Answer: 4. Brown algae
Question 22. Which of the following is a red alga that is not red?
- Nemalion
- Polysiphonia
- Gelidium
- Batrachospermum
Answer: 4. Batrachospermum
NEET Biology MCQ
Question 23. The color of brown algae is due to
- Carotene
- Fucoxanthin
- Phycoerythrin
- Phycocyanin
Answer: 2. Fucoxanthin
Question 24. The alga Chara is called stonewort because its plant body is encrusted with
- Calcium bicarbonate
- Calcium carbonate
- Calcium chloride
- Calcium oxalate
Answer: 2. Calcium carbonate
Question 25. In Chlorophyceae, the flagella are
- Tinsel type
- Whiplash type
- Whiplash and tinsel-type
- Basal tinsel, apical whiplash type
Answer: 2. Whiplash type
Question 26. Irish moss belongs to
- Mosses
- Bryophytes
- Red algae
- Lichens
Answer: 3. Red algae
Question 27. Which of the following are useful for curing goiter?
- Sea kelps
- Diatoms
- Red algae
- Porphyra
Answer: 1. Sea kelps
Question 28. Which of the following statements is correct regarding spermatophyte?
- Gymnosperms are homosporous.
- Microspore which develops into male gametophytes is highly reduced.
- The development of pollen grains occurs in megasporangia.
- The male and female cones are borne on the same tree in Cycas.
Answer: 2. Microspore which develops into male gametophytes is highly reduced.
Question 29. Meiosis occurs in green algae inside
- Gametangia
- Zygote
- Sporangia
- Zygospore
Answer: 4. Zygospore
Question 30. Non-motile gametes are characteristically found in
- Chrysophyta
- Rhodophyta
- Phaeophyta
- Chlorophyta
Answer: 2. Rhodophyta
Question 31. Flagella are of equal length and smooth in Chlamydomonas. This condition can be referred to as
- Isokont and pleuronematic
- Heterokont and acronematic
- Isokont and acronematic
- Heterokont and pleuronematic
Answer: 3. Isokont and acronematic
Question 32. The female sex organ in red algae is flask-shaped and is known as
- Trichogyne
- Carpogonium
- Spermatium
- Archegonium
Answer: 2. Carpogonium
NEET Biology MCQ
Question 33. Non-vascular archegoniates are
- Thallophyta
- Pteridophyta
- Bryophyta
- Gymnosperms
Answer: 3. Bryophyta
Question 34. Antheridial branch and archegonial branch are found in the same plant body of
- Hornworts
- Seaweeds
- Liverworts
- Cotton moss
Answer: 4. Cotton moss
Question 35. What is the chromosome number in calyptra, perichaetial cells, columella, and protonema if the endothecium cell contains 20 chromosomes?
- 10,10, 20, and 10. respectively
- 10, 20, 20, and 10, respectively
- 20, 10. 20, and 10, respectively
- 10, 10, 20, and 10, respectively
Answer: 1. 10,10, 20, and 10. respectively
Question 36. Which one of the following is homosporous with exosmotic embryogeny?
- All pteridophytes
- Bryophytes and gymnosperms
- Angiosperms
- All bryophytes
Answer: 4. All bryophytes
Question 37. Algae, bryophytes, and pteridophytes resemble with each other in which one of the following features?
- Gametophytic plant body
- Dependence on water for fertilization
- Heteromorphic alternation of generation
- Presence of embryo
Answer: 2. Dependence on the water for fertilization
Question 38. Find the correct match.
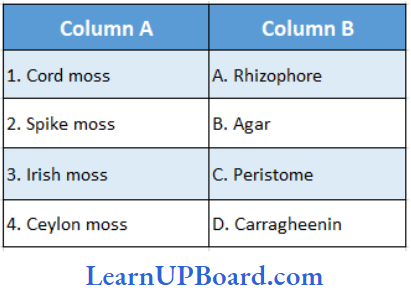
- (1) → (A), (2) → (B), (3) → (C), (4) → (D)
- (1) → (C), (2) → (B), (3) → (D), (4) → (A)
- (1) → (C), (2) → (A), (3) → (B), (4) →(D)
- (1) →(C), (2) (A), (3) → (D), (4) → (B)
Answer: 4. (1) → (C), (2) → (A), (3) → (D), (4) → (B)
NEET Biology MCQ
Question 39. Bryophytes are not characterized by
- Sporophyte parasitic over gametophyte
- Independent gametophyte
- Absence of vascular tissues
- Independent sporophyte
Answer: 4. Independent sporophyte
Question 40. Which of the following is a heterotrophic bryophyte?
- Cryptothallus
- Riccia
- Dawsonia
- Sphaerocarpiis
Answer: 1. Cryptothallus
Question 41. In Funaria, the number of peristome teeth in the exostome is
- 32
- 64
- 16
- 8
Answer: 3. 16
Question 42. Rhizoids of mosses are
- Unicellular and pigmented
- Multicellular and pigmented
- Unicellular and non-pigmented
- Multicellular and non-pigmented
Answer: 4. Multicellular and non-pigmented
Question 43. In Funaria, calyptra is derived from
- Antheridium
- Columella
- Capsule
- Archegonium
Answer: 4. Archegonium
Question 44. In Funaria, the following is not connected with spore dispersal
- Seta
- Peristome
- Annulus
- Foot
Answer: 4. Foot
Biology MCQs with answers
Question 45. Cliloroplasts are present in the spores of
- Rhizopus
- Funaria
- Yeast
- Dryopteris
Answer: 2. Funaria
Question 46. Stomata having pores bounded by a single ring-shaped guard cell are found in
- Capsule of Funaria
- Leaf of fern
- Pinnule of Cycas
- All of these
Answer: 1. Capsule of Funaria
Question 47. Conducting tissue is not found in
- Mosses
- Liverworts
- Cycas
- Ferns
Answer: 2. Liverworts
Question 48. Stems and leaves of bryophytes are
- Analogous to vascular plants
- Homologous to vascular plants
- Analogous to algae thallus
- None of these
Answer: 1. Analogous to vascular plants
Question 49. Non-vascular embryophyte with leaves is
- Riccia
- Porella
- Selaginella
- Macrocystis
Answer: 2. Porella
plant kingdom mcq with answers
Question 50. Aquatic weed Salvinia also called the sorrow of Kashmir, is
- Heterosporous water fern
- Homosporous water fern
- Member of bryophyte
- Both (1) and (3)
Answer: 1. Heterosporous water fern
Question 51. Mitospores are totally absent in
- Chlorophyceae
- Phaeophyceae
- Fungi
- Bryophytes
Answer: 4. Bryophytes
Question 52. Which is a member of Bryopsida?
- Maidenhair moss
- Irish moss
- Reindeer moss
- All of these
Answer: 1. Maiden hair moss
Biology MCQs with answers
Question 53. Which group of plantae represents gametophytic plant body with dependent sporophyte?
- Algae and bryophytes
- Bryophytes and pteridophytes
- Liverworts and mosses
- Ferns and cycades
Answer: 3. Liverworts and mosses
Question 54. The life cycle of cord moss is
- Haplontic
- Haplo-diplontic
- Diplontic
- Haplo-haplontic
Answer: 2. Haplo-diplontic
Question 55. Heterosporous pteridophyte with eusporangiate type of sporangium is
- Pteris and Adiantum
- Equisetum and Selaginella
- Dryopteris and Azolla
- Marsilea and Pteris
Answer: 2. Equisetum and Selaginella
Question 56. In Little Club Moss, the embryo develops from the part of the zygote, and the rest is used to form a suspensor. This mode of development is called
- Exoscopic
- Endoscopic
- Meroblastic
- Holoblastic
Answer: 3. Meroblastic
Question 57. The shedding of male gametophyte in Selaginella occurs at a 13-celled stage which consists of
- 8 jacket cells, 1 generative cell, and 4 androgenic cells
- 9 jacket cells and 4 androgenic cells
- 12 jacket cells and 1 male gamete
- 8 jacket cells, 1 urothelial cell, and 4 androgenic cells
Answer: 4. 8 jacket cells, 1 urothelial cell, and 4 androgenic cells
Question 58. Find the correct statement for the prothallus of fern.
- Monoecious, protandrous with multicellular rhizoids
- Monoecious, protandrous with unicellular rhizoids
- Dioecious, with unicellular rhizoids
- Monoecious, protandrous with apical antheridia, and basal archegonia on the ventral surface
Answer: 2. Monoecious, protandrous with unicellular rhizoids
Question 59. Pteridophytes are divided into how many classes?
- Two
- Three
- Pour
- Six
Answer: 3. Pour
Question 60. Rootless pteridophytes with rhizoids are included in
- Sphenopsida
- Psilopsida
- Pteropsida
- Lycopsida
Answer: 2. Psilopsida
Question 61. The dominant photosynthetic phase in the life cycle of Pteridophyta is equivalent to the
- The gametophytic phase of Bryophyta
- Sporophytic phase of bryophyta
- The gametophytic phase of Pteridophyta
- The gametophytic phase of gymnosperm
Answer: 1. Gametophytic phase of Bryophyta
Question 62. In pteridophytes, reduction division occurs when
- Prothallus is formed
- Sex organs are formed
- Spores are formed
- Gametes are formed
Answer: 3. Spores are formed
Biology MCQs with answers
Question 63. Fern sperms (antherozoids) are
- Multiflagellated
- Pentaflagellated
- Biflagellated
- Non-flagellated
Answer: 1. Multiflagellated
Question 64. The evolutionary advanced features of Selaginella are
- Heterospory
- Endosporic development of gametophyte
- Reduced gametophyte
- Localization of sporangium-bearing appendages in strobila
- Unisexual gametophytes
- Fertilization with the help of water
- All are correct.
- All except (6) are correct.
- All except (5) and (6) are correct.
- All except (3) are correct.
Answer: 2. Endosporic development of gametophyte
Question 65. When the gametophyte development occurs within spore, it is known as
- Exosporic
- Endospores
- Episporic
- None of these
Answer: 2. Endosporic
Question 66. In Selaginella’s life cycle, generative tissue of female gametophytes makes
- Androgenic cells
- Prothallial cell diaphragm
- Diaphragm
- Archegonia
Answer: 4. Archegonia
Question 67. Equisetum, commonly called horsetail or scouring rush and exceptional pteridophyte, i.e., xylem with vessels, possesses the character of
- Heterosporous
- Autotrophic gametophyte
- Biflagellate spermatozoid
- Unjointed stem
Answer: 2. Autotrophic gametophyte
Question 68. Venation in fern leaves is
- Unicostate
- Reticulate
- Furcate
- Parallel
Answer: 3. Furcate
Question 69. If the number of chromosomes in the foot of an embryo is 8, what should be the number in its spore?
- 4
- 8
- 16
- 23
Answer: 1. 4
Question 70. Type of stele without pith
- Solenostele
- Siphonostele
- Protostele
- Dictyostele
Answer: 3. Protostele
Question 71. The sporangia of eusporangiate ferns
- Possess a single layer of wall cells
- Produce very few spores
- Originate from a group of initial cells
- Dehisce at the region of a well-defined stomium
Answer: 3. Originate from a group of initial cells
Question 72. Spores with elaters are characteristic of
- Lycopodium
- Equisetum
- Adiantum
- Marchantia
Answer: 2. Equisetum
Biology MCQs with answers
Question 73. In the archegonium of Dryopteris, the number of neck canal cells is/are
- 4
- 2
- 1
- 6-10
Answer: 3. 1
Question 74. Vascular cryptogams are
- Bryophyta
- Pteridophyta
- Gymnosperms
- Angiospenns
Answer: 2. Pteridophyta
Question 75. Maidenhair fem is
- Adiantum
- Dryopteris
- Cyathaea
- Alsophila
Answer: 1. Adiantum
Question 76. The endosperm of gymnosperm is ontogenetically similar to angiosperms
- Endosperm
- Embryo sac
- Archegonium
- Megasporangia
Answer: 2. Embryo sac
Question 77. Which group of plantae represents the smallest group with perennial plants only?
- Pteridophyta
- Angiosperms
- Bryophyta
- Gymnosperms
Answer: 4. Gymnosperms
Question 78. Monkey’s puzzle is a common name for
- Araucaria imbricate
- Cycas revolute
- Pinus longifolia
- Gnetum anemone
Answer: 1. Araucaria embricata
Question 79. Living fossils of gymnosperms are
- Cycas
- Metasequoia
- Ginkgo biloba
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 80. Endospermic, perispermic, polycotyledonous, and winged seeds having members of Plantae also show
- Sulfur shower
- Largest ovule
- Double fertilization
- Placentation
Answer: 1. Sulfur shower
Question 81. Which character is found in gymnosperms?
- Annuals
- Herbaceous
- Climber and trailing shrub
- Ovary
Answer: 3. Climber and trailing shrub
Biology MCQs with answers
Question 82. Pollination occurs in Pinus at
- Two-celled stage
- Three-celled stage
- Four-celled stage
- Five-celled stage
Answer: 3. Four-celled stage
Question 83. Polyxylic and mano xylic wood is present in
- Pinus
- Cycas
- Ginkgo
- Gnetum
Answer: 2. Cycas
Question 84. Which one of the following groups acts as the connecting link between gymnosperms and angiosperms?
- Ginkgoales
- Cycadales
- Coniferales
- Gnetales
Answer: 4. Gnetales
Question 85. Phanerogams without wombs are
- Angiosperms
- Bryophytes
- Ferns
- Gymnosperms
Answer: 4. Gymnosperms
Question 86. Fruits are not produced in gymnosperms because they are
- Without pollination
- Without fertilization
- Seedless plants
- Without any ovary
Answer: 4. Without any ovary
Question 87. Which one constitutes the dominant vegetation in colder regions?
- Monocots
- Dicots
- Legumes
- Gymnosperms
Answer: 4. Gymnosperms
Biology MCQs with answers
Question 88. In gymnosperms, pollination takes place through
- Insects
- Wind
- Bats
- Birds
Answer: 2. Wind
Question 89. Of the following, the false character with respect to Pinus is
- Resin canals in needles
- Tracheids with bordered pits
- Bracts and ovuliferous scales
- Embryo with two cotyledons
Answer: 4. Embryo with two cotyledons
Question 90. Maidenhair tree is
- Ginkgo biloba
- Gnetum
- Ephedra
- Welwitschia
Answer: 1. Ginkgo biloba
Question 91. Edible seeds are obtained from
- Mangifera indica
- Pinus gerardiana
- P. roxburghii
- Dalbergia sissoo
Answer: 1. Mangifera indica
NEET Biology practice mcq questions with solution
Question 92. Diploxylic vascular bundles are found in
- Pteris
- Selaginella
- Funaria
- Cycas
Answer: 4. Cycas
Question 93. Circinate ptyxis is found in
- Pteris
- Dryopteris
- Cycas
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 94. Transfusion tissue replaces the veins in
- Cycas
- Ferns
- Pinus
- Both Pinus and Cycas
Answer: 4. Both Pinus and Cycas
” class 11 biology chapter 3 mcq”
Question 95. Find the correct match.
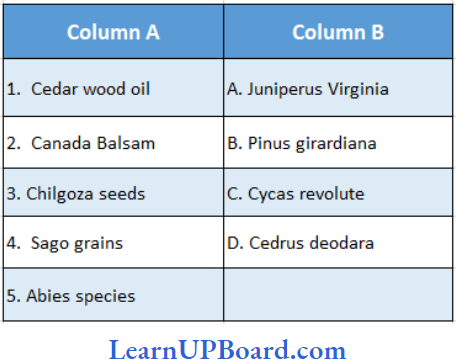
- (1) → (A), (2) → (E), (3) → (B), (4) → (C)
- (1) → (A), (2) → (E), (3) → (C), (4) → (B)
- (1) → (C), (2) → (E), (3) → (A), (4) → (B)
- (1) → (A), (2) → (E), (3) → (B), (4) → (D)
Answer: 1. (1) → (A), (2) → (E), (3) → (B), (4) → (C)
Question 96. Carpels are equivalent to
- Microsporophylls
- Megasporophylls
- Megasporangia
- Embryo sac
Answer: 2. Megasporophylls
Question 97. Vessels are present in the xylem of which tracheophytes?
- Angiosperms
- Gymnosperms
- Pteridophytes
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 1. Angiosperms
Question 98. A marine angiosperm is
- Hydrilla
- Utricularia
- Potamogeton
- Zostera
Answer: 4. Zostera
Question 99. Biennials are characterized by
- Bearing flowers for two seasons
- Forming aerial stem and flowering in the second year
- Flowering in the first year and forming fruits in the second year
- Forming storage organs in the first year and reproductive organs or flowers in the second year
Answer: 4. Forming storage organs in the first year and reproductive organs or flowers in the second year
Question 100. Flowering plants are more successful than other members of the plant world because
- They are large and have a good vascular tissue system
- They carry out a variety of pollination mechanism
- The protected plant embryo can survive in the period of unfavorable conditions
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 101. The father of taxonomy described plants in his book
- 480, Historia Plantarum
- 340, Historia Naturalis
- 18000, Historia Generalis Plantarum
- 5900, Species Plantarum
Answer: 4. 5900, Species Plantarum
Question 102. The basis of a dendrogram is
- Phenetics
- Taximetrics
- Numerical taxonomy
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 103. Huxley is considered to be the founder of
- Classical systematic
- New systematic
- Phylogenetic system of classification
- Artificial system of classification
Answer: 2. New systematic
NEET Biology practice mcq questions with solution
Question 104. The classification of plants and animals on the basis of chromosome number is called
- Cytotaxonomy
- Biochemical systematics
- Taxonomy
- Numerical taxonomy
Answer: 1. Cytotaxonomy
Question 105. The sequencing in DNA and the chemical nature of proteins have been used as the basis of classification by
- Cytotaxonomist
- Karyotaxonomist
- Chemotaxonomist
- α-taxonomist
Answer: 3. Chemotaxonomist
Question 106. The term α-taxonomy was introduced by
- John Ray
- Hutchinson
- Bassey
- Turril
Answer: 4. Turril
Question 107. The sexual system of classification is
- Artificial system
- Based on stamens characters
- Based on corolla and carpels characters
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 108. The Linnaeus system of classification contains
- 4 classes of plants
- 8 classes of plants
- 16 classes of plants
- 24 classes of plants
Answer: 4. 24 classes of plants
Question 109. Classification based on several characters is
- Natural
- Artificial
- Classical
- Phylogenetic
Answer: 1. Natural
Question 110. The natural system of classification was proposed by
- Engler and Prantl
- Bentham and Hooker
- Carolus Linnaeus
- Julian Huxley
Answer: 2. Bentham and Hooker
Question 111. Bentham and Hooker’s classification is
- Classification of taxa based on actual examination
- Artificial system of classification
- Phylogenetic system of classification
- Based on evolution
Answer: 1. Classification of taxa based on actual examination
Question 112. In Bentham and Hooker’s system, the term “cohort” has been used. It is similar to which rank in today’s classification.
- Class
- Family
- Order
- Sub-family
Answer: 3. Order
Question 113. Which one of the following classifications is best suited for the identification of seed plants?
- Bentham and Hooker’s classification
- Engler and Prantl’s classification
- Hutchinson’s classification
- Takhtajan’s classification
Answer: 1. Bentham and Hooker’s classification
” class 11 biology chapter 3 mcqs”
Question 114. Which is the most advanced among the following?
- Cycadaceae
- Gnetaceae
- Coniferae
- Cryptogamae
Answer: 2. Gnetaceae
NEET Biology practice mcq questions with solution
Question 115. Which is not true about the series Heteromerae in Bentham and Hooker’s system?
- Always carpellary condition
- Ovary usually superior
- Stamens are as many as corolla lobe
- It includes three cohorts
Answer: 1. Always carpellary condition
Question 116. Who is not associated with the artificial system of classification?
- Pliny
- Theophrastus
- Hutchinson
- Linnaeus
Answer: 3. Hutchinson
Question 117. The evolutionary history of an organism is known as
- Phylogeny
- Ontogeny
- Phycology
- Mycology
Answer: 1. Phylogeny
Question 118. Angiosperms (dicotyledons) were distinguished into Ar- chichlamydeae and Metachlamydeae by
- Candolle
- Cronquist
- Hutchinson
- Engler and Prantl
Answer: 4. Engler and Prantl
Question 119. “Taxonomy without phylogeny may be likened to bones without flesh” is a statement supported by
- Oswald Tippo
- Bentham and Hooker
- Takhtajan
- John Hutchinson
Answer: 3. Takhtajan
Question 120. Select the cladistic system of classification in which di¬cots are more primitive than monocots
- Horizontal system
- Hutchinson system
- Bentham and Hooker’s system
- Engler and Prantl’s system
Answer: 2. Hutchinson system
Question 121. Trabeculae are present in the
- Capsule of Funaria
- Ovule of gymnosperm
- Sporangia of a fern
- Ovule of angiosperm
Answer: 1. Capsule of Funaria
Question 122. Engler and Prantl published a phylogenetic system in the monograph
- Die Naturlichen Pflanzen
- Historia Plantarum
- Species Plantarum
- Genera Plantarum
- Origin of Species
Answer: 1. Die Naturlichen Pflanzen
Question 123. Dominant generation in bryophytes is
- Capsule
- Sporophyte
- Gametophyte
- Seta
Answer: 3. Gametophyte
NEET Biology practice mcq questions with solution
Question 124. Which of the following plants has high water reten¬tion capacity and is used to provide moisture to plants?
- Sphagnum
- Botrychilum
- Mars ilea
- March Antia
Answer: 1. Sphagnum
Question 125. If in Funaria, the leaf has eight chromosomes, the structure with 16 chromosomes will be
- Protonema
- Rhizoids
- Capsule and seta
- All above
Answer: 3. Capsule and seta
Question 126. Leptoids and hydroids are the vascular supply of
- Hornworts
- Irish mosses
- Liverworts
- Pteridophytes
Answer: 3. Liverworts
Question 127. Moss peat is used as a packing material for sending flowers and live plants to distant places because
- It serves as a disinfectant
- It is easily available
- It is hygroscopic
- It reduces transpiration
Answer: 3. It is hygroscopic
Question 128. In a moss, the sporophyte
- Manufactures food for itself as well as for the gametophyte
- Is partially parasitic on the gametophyte
- Produces gametes that give rise to the gametophyte
- Arises from a spore produced from the gametophyte
Answer: 2. Is partially parasitic on the gametophyte
Question 129. Bryophytes are exceptional, as
- They produce spores
- Their sporophytic stage grows on gametophyte
- They do not require water for fertilization
- Their gametophyte stage grows on sporophyte
Answer: 2. Their sporophytic stage grows on gametophyte
Question 130. Which of the following is the amphibian of the plant kingdom?
- Pteridophyte
- Bryophyte
- Cycas
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 131. Flagellated male gametes are present in all three of which one of the following sets?
- Zygnema, Saprolegnia, and Hydrilla
- Fucus, Marsilea, and Calotropis
- Riccia, Dry op ter is, and Cycas
- Anthoceros, Funaria, and Spirogyra
Answer: 3. Riccia, Dry op ter is, and Cycas
Question 132. The plant classification proposed by C. Linnaeus was artificial because it was based on
- Few morphological characters
- Diverse evolutionary tendencies
- Adaptive anatomical characters
- Physiological traits together with morphological characters
Answer: 1. Few morphological characters
NEET Biology practice mcq questions with solution
Question 133. In which of the following, gametes are produced by mitrotic division?
- Pteridophytes
- Algae
- Gymnosperms
- Angiosperms
Answer: 2. Algae
Question 134. Which one of the following is heterosporous?
- Dryopteris
- Salvinia
- Adiantum
- Equisetum
Answer: 2. Salvinia
Question 135. Four rows and six rows of NCC are found, respectively, in
- Bryophytes and Pteridophytes
- Pteridophytes and gymnosperms
- Gymnosperms and angiosperms
- Pteridophytes and bryophytes
Answer: 4. Pteridophytes and bryophytes
Question 136. Peat is formed from
- Funaria
- Sphagnum
- Mosses
- Liverworts
Answer: 2. Sphagnum
Question 137. Liverworts, hornworts, and mosses together constitute
- Pteridophytes
- Lichens and Plantae
- Bryophyta
- Bryopsida
Answer: 2. Lichens and Plantae
Question 138. Protonemma is a characteristic feature of
- Fern
- Marchantia
- Moss
- Cycas
Answer: 3. Moss
Question 139. Bryophytes resemble algae in the following aspects.
- Filamentous body, pressure of vascular tissues, and autotrophic nutrition
- Differentiation of plant body into root, stem, and autotrophic nutrition
- Thallus-like plant body, pressure of roots, and autotrophic nutrition
- Thallus-like plant body, lack of vascular tissues, and autotrophic nutrition
Answer: 4. Thallus-like plant body, lack of vascular tissues, and autotrophic nutrition
Question 140. Sphagnum is commonly used as packing material for the trans-shipment of living material due to its
- Capacity to hold water
- Easy availability
- Nature as it can grow anywhere
- All the above
Answer: 1. Capacity to hold water
Question 141. A dominant gametophytic phase alternated by multicellular dependent sporophytic phase material for transshipment of living occurs in
- Chlamydomonas
- Politrichum
- Asian
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Politrichum
Question 142. Which of the following plants do not produce seeds?
- Ficus and Funaria
- Fern and Funaria
- Chlamydomonas and Ficus
- Punica and Pinus
Answer: 2. Fern and Funaria
Question 143. Algae that form motile colonies are
- Volvox
- Nostoc
- Spirogyra
- Chlamydomonas
Answer: 1. Volvox
NEET Biology MCQ With Solutions
Question 144. Auxospore formation is seen in
- Nostoc
- Yeast
- Diatoms
- Agaricus
Answer: 3. Diatoms
Question 145. Which of the following is a flagellated algae?
- Chlamydomonas
- Ulothrix
- Saccharomyces
- Agaricus
Answer: 1. Chlamydomonas
Question 146. Which of the following is coenocytic?
- Vaucheria
- Centuria
- Chlamydomonas
- Pseudomonas
Answer: 1. Vaucheria
Question 147. Auxospores and oocysts are formed, respectively, by
- Several diatoms and few cyanobacteria
- Several cyanobacteria and several diatoms
- Some diatoms and several cyanobacteria
- Some cyanobacteria and many diatoms
Answer: 3. Some diatoms and several cyanobacteria
Question 148. Alga which is a parasite of the tea plant is
- Cephaleuros
- Ulva
- Oedogonium
- Vaucheria
Answer: 1. Cephaleuros
Question 149. The largest alga is
- Microcystis
- Macrocytis
- Red alga
- Blue-green algae
Answer: 2. Macrocytis
Question 150. A triphasic life cycle is present
- Red algae
- Brown algae
- Diatoms
- Dinoflagellates
Answer: 2. Brown algae
Question 151. Alginic acid is obtained from
- Blue-green algae
- Red algae
- Green algae
- Brown algae
Answer: 2. Green algae
Question 152. In Chlamydomonas, meiosis occurs in
- Gamete
- Zygote
- Sporogonium
- Zoospore
Answer: 2. Zygote
NEET Biology MCQ With Solutions
Question 153. The zoospores of Ulothrix are
- Quadriflagellated
- Biflagellated
- Monoflagellated
- Alagellated
Answer: 1. Quadriflagellated
Question 154. Kelps are
- Freshwater algae
- Marine algae
- Terrestrial
- Amphibious
Answer: 2. Marine algae
Question 155. Which of the following is not correctly matched?
- Chlamydomonas—Unicellular flagellated alga
- Laminaria—Flattened leaf-like thallus
- Chlorella—Filamentous non flagellated
- Spirogyra—Filamentous structure
- Volvox—Colonial non-flagellated
Answer: 5. Volvox—Colonial non-flagellated
Question 156. Agar-agar which is commonly used in micro-biological studies and culture media is obtained from
- Gelidium
- Laminaria
- Polysiphonia
- Batrachospremum
Answer: 1. Gelidium
Question 157. From which of the following algae, agar is commercially extracted?
- Gracilaria
- Focus
- Sargassum
- Gelidium
- Turk inari
- (3) and (5)
- (2) and (3)
- (4) and (5)
- (1) and (2)
- (1) and (4)
Answer: 5. (1) and (4)
Question 158. Match column 1 with column 2 option.
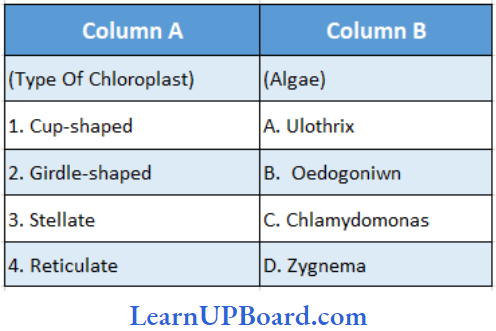
- (1) → (B), (2) → (D), (3) → (C), (4) → (A)
- (1) → (C), (2) → (A), (3) → (D), (4) → (B)
- (1) → (B), (2) → (D), (3) → (B), (4) → (A)
- (1) → (D), (2) → (C), (3) → (A), (4) → (B)
- (1) → (D), (2) → (C), (3) → (A), (4) → (B)
Answer: 2. (1) → (C), (2) → (A), (3) → (D), (4) → (B)
Question 159. If you are asked to classify various algae into distinct groups, which of the following characters you should choose?
- Nature of stored food materials in the cell
- Structural organization of thallus
- Chemical composition of cell wall
- Types of pigments present in the cell
Answer: 4. Types of pigments present in the cell
NEET Biology MCQ With Solutions
Question 160. All algae have
- Chlorophyll-a and chlorophyll-b
- Chlorophyll-b and carotenes
- Chlorophyll-a and carotenes
- Phycobilins and carotenes
- Chlorophyll-a, chlorophyll-b, carotenes
Answer: 3. Chlorophyll-a and carotenes
Question 161. The edible green alga rich in protein is
- Porphyra
- Chlorella
- Laminaria
- Chondrus crispus
Answer: 2. Chlorella
Question 162. Consider the following statements regarding the major pigments and stored food in the different groups of algae and select the correct options given.
- In Chlorophyceae, the stored food material in starch, and the major pigments are chlorophyll-a and chlorophyll-b.
- In Phaeophyceae, laminarin is the stored food and major pigments are chlorophyll-a and chlorophyll-b.
- In Rhodophyceae, floridean starch is the stored food and the major pigments are chlorophyll-a, chloro-phyll-d, and phycoerythrin.
- (1) is correct, but (2) and (3) are wrong.
- (1) and (2) are correct, but (3) is wrong.
- (1) and (3) are correct, but (2) is wrong.
- (2) is correct, but (1) and (3) are wrong
- (3) is correct, but (1) and (2) are wrong.
Answer: 5. (3) is correct, but (1) and (2) are wrong
Question 163. Sex organs of algae and fungi are
- Antheridium oogonia
- Carpogonia and ascogonia
- Zygospore and akinetes
- Heterocyst and archegonia
Answer: 1. Antheridium oogonia
Question 164. Pyerenoids are commonly found in
- Red algae
- Green algae
- Brown algae
- Blue-green algae
Answer: 2. Green algae
Question 165. Which pigments is not found in red algae?
- Chlorophyll-a
- Phycocyanin
- Chlorophyll-b
- Phycoerythrin
Answer: 2. Phycocyanin
Question 166. The nutrition of Protista is
- Phagotrophic
- Saprotrophic
- Autotrophic
- All above
Answer: 4. All above
Question 167. Match the following and choose the correct combination from the options given.
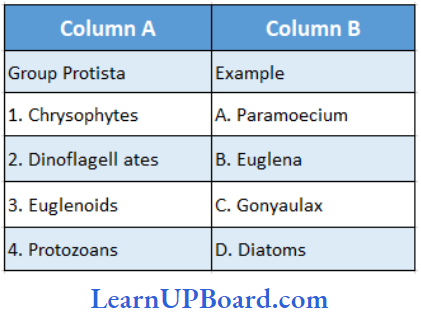
- (1) → (A), (2) → (C), (3) → (B), (4) → (D)
- (1) → (A), (2) → (D), (3) → (C), (4) → (B)
- (1) → (D), (2) → (B), (3) → (C), (4) → (A)
- (1) → (B), (2) → (D), (3) → (A), (4) → (B)
- (1) → (D), (2) → (C), (3) →(B), (4) → (A)
Answer: 1. (1) → (A), (2) → (C), (3) → (B), (4) → (D)
Question 168. Which of the following correctly represents the type of life cycle patterns from the options given?
- Diplontic, Haplodiplontic, Haplontic
- Haplodiplontic, Haplontic, Diplontic
- Haplontic, Diplontic, Haplodiplontic
- Diplontic, Haplontic, Haplodiplontic
- Haplontic, Haplodiplontic, Diplontic
Answer: 4. Diplontic, Haplontic, Haplodiplontic
Question 169. Gracilaria and Gelidium are important sources of
- Carrageenan jelly
- Iodine
- Agar
- Vitamin B
Answer: 3. Agar
Question 170. Laminaria and Fucus belong to
- Chlorophyceae
- Rhodophyceae
- Paeophyceae
- Cyanophyceae
Answer: 3. Paeophyceae
Question 171. Monascus purpura is a yeast used commercially in the production of
- Streptokinase for removing clots from the blood ves¬sels.
- Citric acid
- Blood cholesterol-lowering statins
- Ethanol
Answer: 3. Blood cholesterol-lowering statins
NEET Biology MCQ With Solutions
Question 172. Which one of the following is correctly matched?
- Ginger—Sucker
- Chlamydomonas—Conidia
- Yeast—Zoospores
- Onion—Bulb
Answer: 4. Onion—Bulb
Question 173. Which of the following is characteristic of ferns?
- Leafy gametophyte
- Circinate vernation
- Mycorrhizal roots
- Coralloid roots
Answer: 2. Circinate vernation
Question 174. Vascular cryptogams are
- Pteridophytes
- Angiosperms
- Mosses
- Algae
Answer: 1. Pteridophytes
Question 175. Microspores of massulae in Azolla are found in
- Indicium
- Sporangium
- Antheridium
- Archcgonoum
Answer: 2. Sporangium
Question 176. First vascular plant is
- Thallophyta
- Bryophyta
- Pteridophyta
- Spermatophyta
Answer: 3. Pteridophyta
Question 177. Fronds are
- Leaves of ferns
- Leaves of Cycas
- Moss roots
- The reproductive structure of ferns
Answer: 1. Leaves of ferns
Question 178. In pteridophytes, phloem is without
- Sieve cells
- Sieve tubes
- Companion cells
- Bast fibers
Answer: 3. Companion cells
Question 179. Independent alternation of generation is found in
- Fern
- Cycas
- Onion
- Lotus
Answer: 1. Fern
Question 180. Which of the following is called the resurrection plant?
- Selaginella lipidophyla
- Gingko aloha
- Cedrus deodara
- Sequoia sempervivums
Answer: 1. Selaginclla lipidophyla
Question 181. Female gametophyte in heterosporous ferns is
- Archegonium
- Prothallus
- Gymnosperm
- Angiosperm
Answer: 4. Angiosperm
Question 182. In which group will you place a plant that reproduces by means of spores, has vascular supply, and diploid sporophytic phase as a dominant phase?
- Bryophyte
- Pteridophyta
- Gymnosperm
- Angiosperm
Answer: 2. Pteridophyta
Question 183. Which pteridophyta is called as horse tail?
- Equisetum
- Lycopodium
- Mars ilea
- Selaginella
Answer: 1. Equisetum
Question 184. Which of the following is present in association with Azolla?
- Anabaena
- Nostoc
- Clostridium
- Azotobacter
Answer: 1. Anabaena
Question 185. The dehiscence of sporangia of fern occurs through
- Annulus
- Stomium
- Elaters
- Sori
Answer: 1. Annulus
Question 186. In a fern prothallus, the following occurs.
- Self-fertilization
- Cross-fertilization
- Conjugation
- Isogamv
Answer: 2. Cross-fertilization
Question 187. The Sporophytes in Ncphrolepis is _____ and the spores are
- Diploid, haploid
- Haploid, haploid
- Haploid, diploid
- Diploid, diploid
Answer: 1. Diploid, haploid
Question 188. One of the following is a pteridophyte.
- Cycas
- Sphagnum
- Nephrolepis
- All above
Answer: 3. Nephrolepis
Question 189. Which one has the maximum number of chromosomes?
- Marsilea
- Equisetum
- Ophioglossum
- Lycopodium
Answer: 3. Ophioglossum
Question 190. Indusium is found in
- Algae
- Fronds
- Moss
- Cycas
Answer: 2. Fronds
Question 191. One of the following differentiates pteridophytes from mosses.
- Prothallus
- Homosporous spores
- Haplontic life cycle
- All above
Answer: 1. Prothallus
Question 192. Which one of the following is called maiden hair fern?
- Dryopteris
- Pteris
- Adiantum
- Lycopodium
- Selaginella
Answer: 3. Dryopteris
Question 193. Walking fern belongs to the genus
- Adiantum
- Dryopteris
- Peter is
- Mars ilea
Answer: 1. Adiantum
Question 194. In the prothallus of a vascular cryptogam, the antherozoids and egg mature at different times. At a result,
- There is a high degree of sterility.
- One can conclude that the plant is apomictic.
- Self-fertilization is prevented.
- There is no change in the success rate of fertilization.
Answer: 3. Self-fertilization is prevented.
Question 195. Pick up the wrongly matched pair
- Equisetum—Horsetail
- Psilotum—Whisk fern
- Selaginella—Peat moss
- Dryopteris—Male shield fern
Answer: 3. Selaginella—Peat moss
Question 196. Match the following with the correct combination.
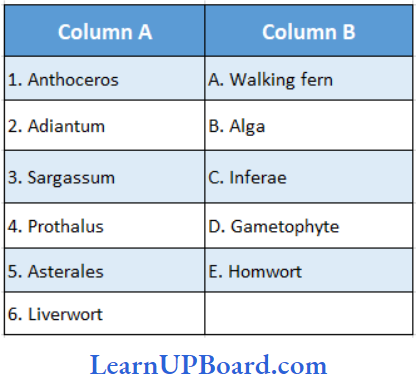
- (1) → (F), (2) → (E), (3) → (A), (4) → (C), (5) → (D)
- (1) → (E), (2) → (D), (3) → (C), (4) → (B), (5) → (A)
- (1) → (E), (2) → (A), (3) → (B), (4) → (D), (5)→ (C)
- (1) → (C), (2) → (B), (3) → (A), (4) → (E), (5) → (D)
Answer: 3. (1) → (E), (2) → (A), (3) → (B), (4) → (D), (5) → (C)
Question 197. Which of the following has medicinal value and is a pteridophyte?
- Lycopodium
- Adiantum
- Gnetum
- Dryopteris
Answer: 1. Lycopodium
Question 198. Seed habit originated in certain
- Bryophytes
- Ferns
- Angiosperms
- Gymnosperm
Answer: 4. Gymnosperm
Question 199. Circinafe vernation is seen in
- Equisteum, Nephrolepis, Psilotum
- Nephrolepis, Adiantum, Pteris
- Lycopodium, Nephrolepis
- Psilotum, Nephrolepis, Adiantum
Answer: 2. Nephrolepis, Adiantum, Pteris
Question 200. Petiole and reacts in ferns are covered with small hairs called
- Spurs
- Ramenta
- Fronds
- Ligule
- Rhizoids
Answer: 4. Rhizoids
Question 201. Which one of the following is a vascular cryptogam?
- Marchantia
- Cedras
- Equisetum
- Ginkgo
Answer: 3. Equisetum
Question 202. Fertile leaves of ferns are called
- Sporophylls
- Posophylls
- Mesophylls
- Cataphylls
Answer: 1. Sporophylls
Question 203. Top-shaped multifoliate male gametes and the mature seed which bears only one embryo with two cotyledons are characteristic features of
- Polypetalous angiosperms
- Gamopetalous angiosperms
- Conifers
- Cycads
Answer: 4. Cycads
Question 204. Match items in Column A with those in Column B.
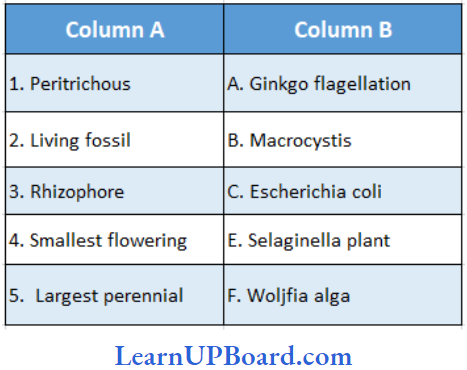
- (1) → (B), (2) → (A), (3) → (C), (4) → (D), (5) → (E)
- (1) → (E), (2) → (C), (3) → (B), (4) → (E). (5) → (A)
- (1) → (A), (2) → (B), (3) → (E), (4) → (C), (5) → (B)
- (1) → (C), (2) → (A), (3) → (D), (4) → (E), (5) → (B)
Answer: 4. (1) → (C), (2) → (A), (3) → (D), (4) → (E), (5) → (B)
Question 205. Angiosperms and gymnosperms resemble in having
- Vessel in wood
- Mode of fertilization
- Sessile and oblong leaflets
- Sessile endosperm
Answer: 3. Sessile and oblong leaflets
Question 206. Leaflet in Cycas is
- Sessile and linear
- Sessile and lanceolate
- Sessile and oblong
- Sessile anti obturate
Answer: 2. Sessile and lanceolate
Question 207. Ephedra and Gnetum are similar in having
- Pollination mechanism
- Double fertilization
- Winged pollen
- Heteromorph genes
Answer: 1. Pollination mechanism
Question 208. Which of the following statements is wrong about gymnosperms?
- They have naked seeds.
- They are perennial,
- Their xylem consists of vessels.
- They are xerophytic.
Answer: 3. Their xylem consists of vessels.
Question 209. Coralloid roots of Cycas has
- Anabaena
- Nostoc
- Mycorrhizae
- Rhizopus
Answer: 1. Anabaena
Question 210. The integument of the Cycas ovule is hard on account of
- Testa
- Tegmen
- Sclerotesta
- Sarcotesta
Answer: 3. Sclerotesta
Question 211. Cycas is dicotyledonous, yet not placed under a doctor’s lens because
- It looks like a palm tree.
- It has compound leaves.
- Its ovules are naked.
- It bears megasporophylls.
Answer: 3. Its ovules are naked.
Question 212. From which of the following plants is a medicine for respiratory disorders obtained?
- Bambusa
- Sesamutn
- Ephedra
- Pinns
Answer: 3. Ephedra
Question 213. Cholgoza pinus is
- Pinus girardiana
- Pinus rox Burgi
- Pinus wallichiana
- Pinus mercuric
Answer: 1. Pinus girardiana
Question 214. In gymnosperms, the pollen chamber represents
- A cavity in the ovule in which pollen grains are stored after pollination.
- An opening in the megagametophyte through which the pollen tube approaches the egg.
- The microsporangium in which pollen grain develops.
- A cell in the pollen grain in which the sperms are formed.
Answer: 1. A cavity in the ovule in which pollen grains are stored after pollination.
Question 215. Which of the following gymnosperm is a bushy trailing shrub?
- Ephedra
- Cycas
- Pinus
- Aurocaria
- Cednis
Answer: 1. Ephedra
Question 216. Conifers differ from grasses in the
- Formation of endosperm before fertilization
- Production of seeds from ovules
- Lack of xylem tracheids
- Absence of pollen tubes
Answer: 4. Absence of pollen tubes
Question 217. In Pinus, many embryos are formed from a single zygote, which is known as
- Simple polyembryony
- Cleavage polyembryony
- Polyspermy
- Apogamy
Answer: 2. Simple polyembryony
Question 218. In Pinus, the male cone bears a large number of
- Ligules
- Anthers
- Microsporophylls
- Megasporophylls
Answer: 3. Microsporophylls
Question 219. Which among the following is a living fossil gymnosperm?
- Pinus roxburghii
- Medullosa noei
- Ginkgo biloba
- Abiespindrow
Answer: 3. Ginkgo biloba
Question 220. Cycas has an embryo with two cotyledons yet it is not classified in dicots because
- It looks like a palm.
- Its ovules are naked,
- It has compound leaves.
- It bears megasporophyll.
Answer: 2. Its ovules are naked,
Question 221. In which one of the following, male and female gametophytes do not have free-living independent existence?
- Pten’s
- Funaria
- Polytrichurn
- Cairns
Answer: 4. Cairns
Question 222. Turpentine oil is extracted from
- Angiosperms
- Pinus
- Oak
- Citrus plants
Answer: 2. Pinus
Question 223. The largest ovule is present in
- Cycas
- Pinus
- Wolffia
- Rafflesia
Answer: 1. Cycas
Question 224. Resin and turpentine are products of
- Teak
- Oak
- Eucalyptus
- Pine
Answer: 4. Pine
Question 225. Pinus seeds are
- Naked and campylotropus
- Naked and anatropous
- Naked and orthotropus
- Covered and orthotropous
Answer: 3. Naked and orthotropous
Question 226. Which of the following statements are true or false?
- The trimerous condition of floral whorl is characteristic of dicotyledons.
- Adiant Inn is also called a walking fern.
- In gymnosperms. the vascular system consists of a xylem without vessels and a phloem without companion cells.
- Riccia and Marchantia are liver worts.
- (1) and (2) are true and (3) and (4) are false.
- (1) and (3) are true and (2) and (4) are false.
- (1) and (4) are true and (2) and (3) are false.
- (2), (3), and (4) are true and (1) is false.
Answer: 4. (2), (3), and (4) are true and (1) is false.
Question 227. The sieve tubes and companion cells are exceptional features of
- Gymnospenns
- Angiosperms
- Ferns
- Pteridophytes
Answer: 2. Angiosperms
Question 228. In angiosperms double fertilization means
- Fusion of egg cell with male gamete
- Fusion of secondary nucleus with male gamete
- Both above
- None above
Answer: 3. Both above
Question 229. Typical embryosac of angiosperms is
- Tetranucleated
- Eight-nucleated and seven celled
- Tetranucleated and seven celled
- Tetranucleated and tetra celled
Answer: 2. Eight-nucleated and seven celled
Question 230. Male gametes in angiosperms are formed by the division of
- Generative cell
- Vegetative cell
- Microspore mother cell
- Microspore
Answer: 1. Generative cell
Question 231. Which of the following is a rootless aquatic plant in which a portion of the leaf forms a tiny sac for trapping insects?
- Nepenthes
- Drosera
- Utricularia
- Dionaea
- Answer: 3. Utricularia
Question 232. Which one of the following contains xylem vessels?
- Bryophyta
- Pteridophyta
- Gymnosperms
- Angiosperms
Answer: 4. Angiosperms
Question 233. Gymnosperms are also called softwood spermatophytes because they lack
- Phloem fibers
- Thick-walled tracheids
- Xylem fibers
- Cambium
Answer: 3. Xylem fibers
Question 234. Which one of the following is a correct statement?
- In gymnosperms, female gametophytes is free-living.
- Antheridiophores and archegoniophores are present in pteridophytes.
- The origin of seed habit can be traced in pteridophytes.
- Pteridophyte gametophyte has a protonemal and leafy stage.
Answer: 3. The origin of seed habit can be traced in pteridophytes.