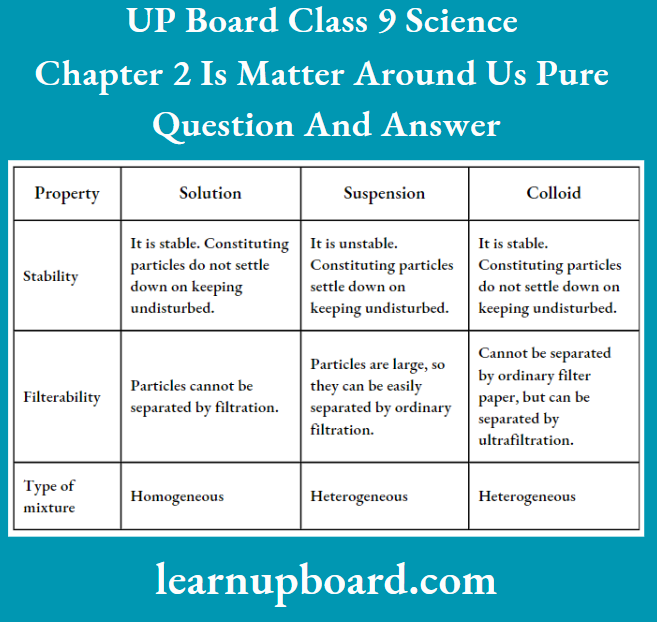
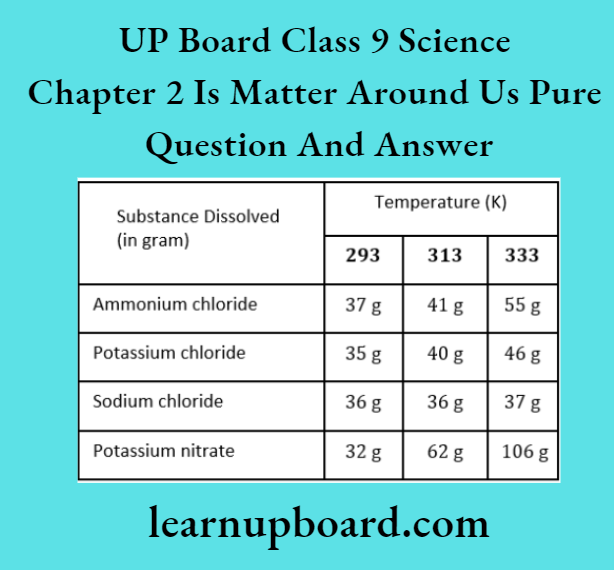
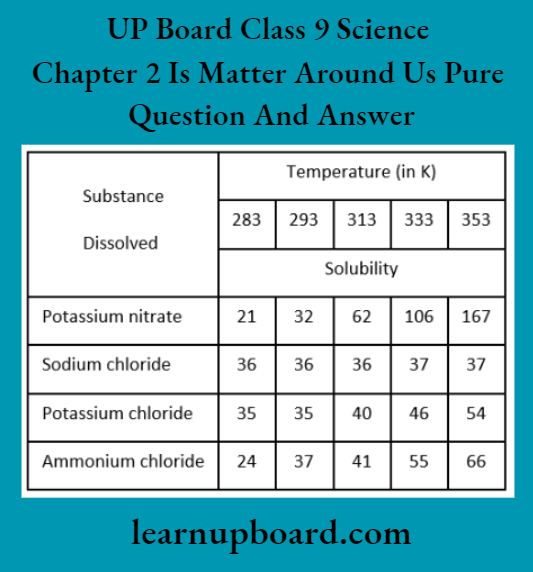
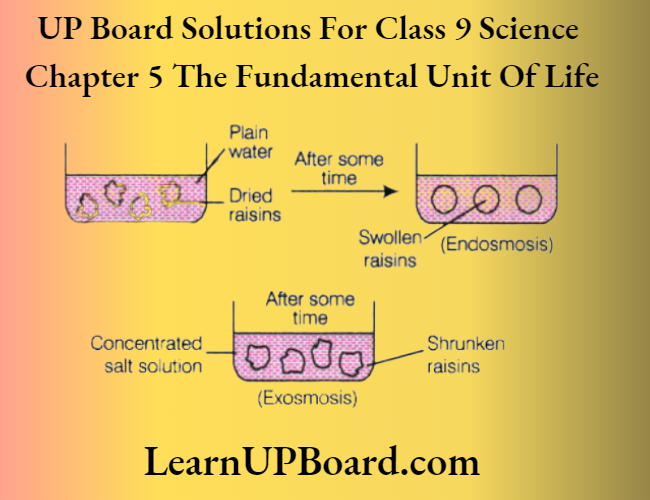
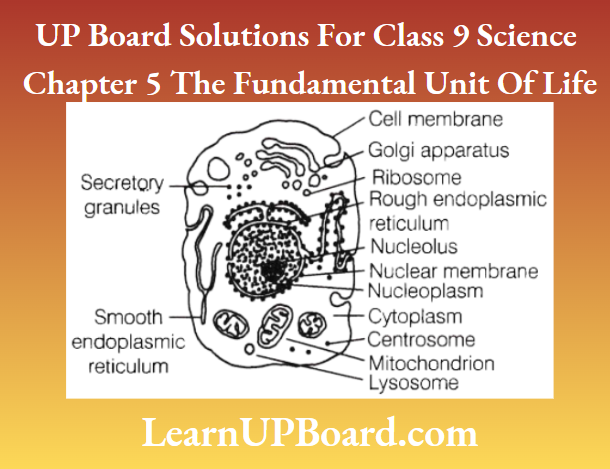
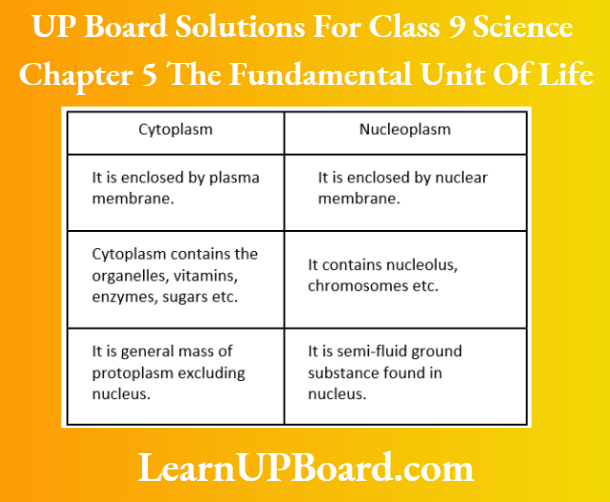
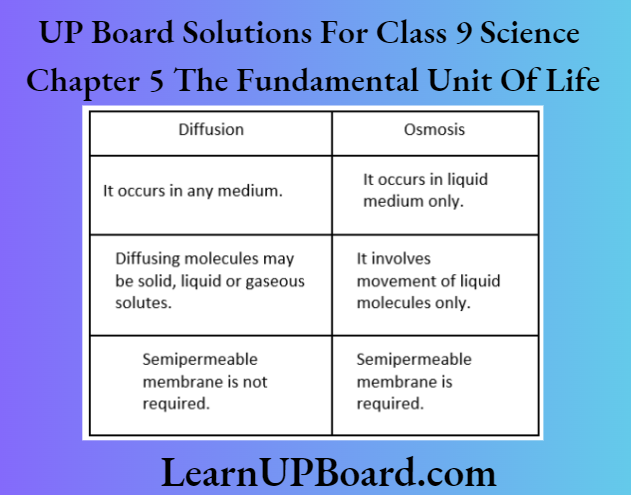
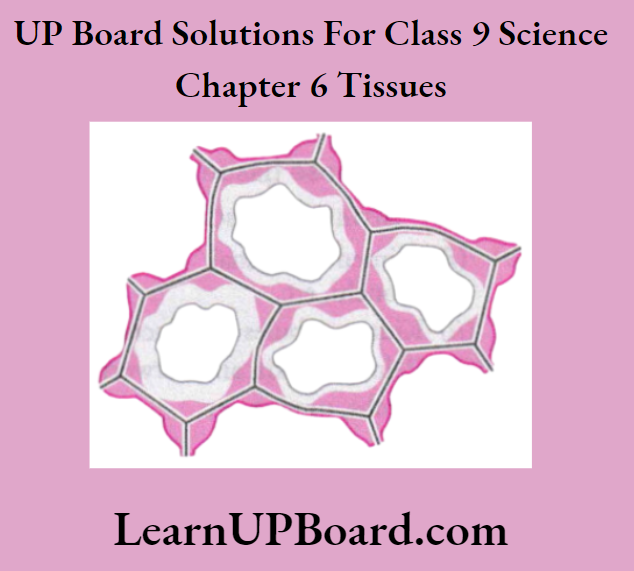
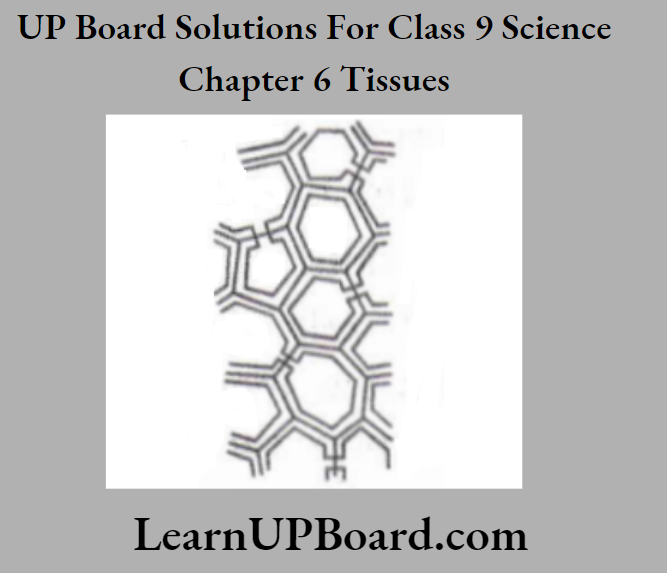
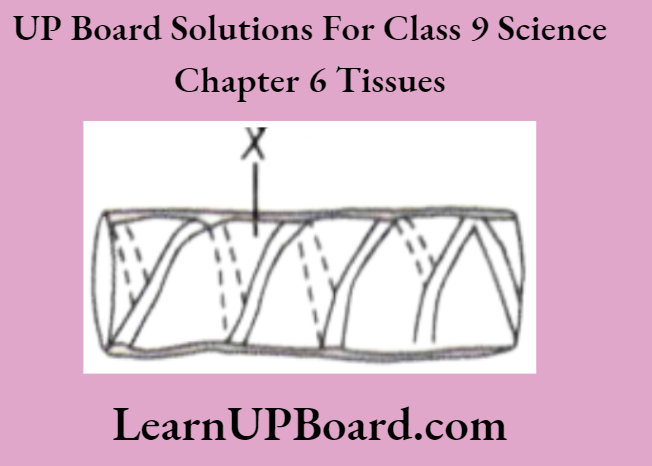
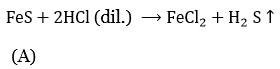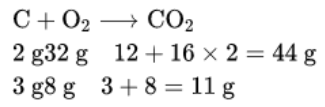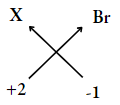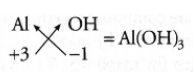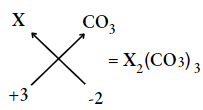UP Board Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms And Molecules Question And Answers
Question 1.
- Explain why the number of atoms in one mole of hydrogen gas is double the number of atoms in one mole of helium gas.
- Explain atomic mass unit.
- How many atoms are present in
- MnO2 molecule
- CO molecule?
Answer:
- Hydrogen gas exists as a diatomic molecule, i.e. each hydrogen gas molecule (H2) has two atoms. While helium gas exists as a monoatomic particle that is its atoms exist individually.
- Thus, one mole of hydrogen gas has a double number of atoms as compared to one mole of helium gas.
- The unit of mass equivalent to the twelfth part of the mass of the C-12 isotope of carbon is called atomic mass unit (amu) or unified mass (u).
- In the MnO2 molecule, three atoms are present: one manganese atom and two oxygen atoms.
- In a CO molecule, two atoms are present: one carbon atom and one oxygen atom.
Question 1. A 0.24 g sample of a compound of oxygen and boron was found by analysis to contain 0.096 g of boron and 0.144 g of oxygen. Calculate the percentage composition of the compound by weight.
Answer:
Given
A 0.24 g sample of a compound of oxygen and boron was found by analysis to contain 0.096 g of boron and 0.144 g of oxygen.
Mass of the compound = 0.24 g,
Mass of boron = 0.096 g
Mass of oxygen = 0.l44g
Percentage of boron = \(\frac{\text { Mass of boron }}{\text { Mass of compound }} \times 100\)
⇒ \(=\frac{0.096 \mathrm{~g}}{0.240 \mathrm{~g}} \times 100=40 \%\)
Percentage of oxygen =\(\frac{\text { Mass of oxygen }}{\text { Mass of compound }} \times 100\)
⇒ \(\frac{0.144 \mathrm{~g}}{0.240 \mathrm{~g}} \times 100=60 \%\)
Alternative method
Percentage of oxygen = 100 – a percentage of boron
= 100-40=60%
Read and Learn More Class 9 Science Solutions
Question 2. Calculate the molecular masses of H2, O2, Cl2, CO2, CH4, C2H6, C2H4, NH3, CH3OH
Answer:
Given
H2, O2, Cl2, CO2, CH4, C2H6, C2H4, NH3, CH3OH
1. The molecular mass of H2 (hydrogen)
= Atomic mass of hydrogen × 2 =1 × 2 = 2 u
2. The molecular mass of O2 (oxygen)
= Atomic mass of oxygen × 2 = 16 × 2 = 32 u
3. The molecular mass of Cl2 (chlorine)
Atomic mass of chlorine × 2 = 35.5 × 2 = 71 u
4. The molecular mass of CO2 (carbon dioxide)
= (Atomic mass of carbon x 1) + (Atomic mass of oxygen × 2)
= 12 × 1 + (16 × 2) = 12 + 32 = 44 u
5. The molecular mass of CH4 (methane)
= (Atomic mass of carbon × 1) +(Atomic mass of hydrogen × 4) =12 × 1 +(1 × 4) =12 +4 = 16 u
6. The molecular mass of C2H6 (ethane)
= (Atomic mass of carbon × 2) + (Atomic mass of hydrogen × 6)
= (12 × 2)+ (1 × 6) = 24 + 6 =30 u
7. The molecular mass of C2H4 (ethene)
= (Atomic mass of carbon × 2) + (Atomic mass of hydrogen × 4)
= (12 × 2) + (1 × 4) = 24 + 4 = 28 u
8. The molecular mass of NH3 (ammonia)
= (Atomic mass of nitrogen × 1) + (Atomic mass of hydrogen × 3)
= (14 × 1) + (1 × 3)
= 14 + 3 =17u
9. Molecular mass of CH3OH (methanol or methyl alcohol) = (Atomic mass of carbon × 1) + (Atomic mass ,of hydrogen × 3) + (Atomic mass of oxygen × 1 ) + (Atomic mass of hydrogen × 1)
= (12 × 1) + (1 × 3) + (16 × 1) + (1 × 1)
= 12 + 3 + 16 + 1
= 32 u
Question 3. Write the formulae for the following and calculate the molecular mass for each one of them.
- Caustic potash
- Baking soda
- Caustic soda
- Common salt
Answer:
1. KOH
Molecular mass of KOH =39 +16 + 1= 36 u
2. NaHCO3
Molecular mass of NaHCO3 = 23+ 1+ 12+ 3 × 16
= 23 + 1 + 12+ 48
=84 u
3. CaCO3
The molecular mass of CaCO3
= 40 + 12 + 3 × 16=100 u
4. NaOH
Molecular mass of NaOH =23+16 + 1
=40u
5. C2H5OH
Molecular mass of C3H5OH or C2H6O =2 ×12 + 6 × 1 + 16
=24 + 6 + 16
=46 u
6. NaCl,
Molecular mass of NaCl = 23 + 35.5
= 58.5 u
Question 4. A metal weighing 6 g formed diatomic oxide upon heating in the presence of air. The oxide thus formed weighed 10 g. Write the chemical name of the compound.
Answer:
Given
A metal weighing 6 g formed diatomic oxide upon heating in the presence of air. The oxide thus formed weighed 10 g.
Suppose the metal is M. The oxide being diatomic, should have the formula as MO.
The amount of oxygen present in the oxide
= 10 -6 = 4g
∵ 32 g O2 =1 mol
∴ 4 g O2 =0.125 mol
The reaction for the formation of oxide can be written as
M + O2 → MO
Upon balancing we get,
M + O2 → 2MO
1 mole O2 reacts with 2 moles of metal
∴ 0.125 mole O2 reacts with 0.25 mole of metal
Hence, we get
0.25 mole of metal = 6 g
or1 mole of metal =24 g
Thus, the metal is magnesium and the oxide is
magnesium oxide (MgO).
Question 5. Find the number of atoms in 120 g of calcium and 120 g of iron. Which one has more atoms and how much is the difference?
[Atomic mass of Ca =40 u, Fe =56 u]
Answer:
Gram molecular mass of Ca = 40 g
∵ 40 g of Ca contains, several atoms
= 6.022 × 1023
120 g of Ca contains, several atoms
⇒ \(=\frac{6.022 \times 10^{23}}{40} \times 120\)
= 18.066 × 1023
= 1.8066 × 1024 atoms
Again, the gram molecular mass of Fe = 56 g
∵ 56 g of Fe contains several atoms
= 6.022 x 1023
∴ 120 g of Fe contains several atoms
⇒ \(=\frac{6.022 \times 10^{25}}{56} \times 120\)
= 12.904 x 1023 = 1.2904 x 1024 atoms
Therefore, 120g of calcium has more number of atoms.
Difference = (1.8066 -1.2904) x 1024
= 5.162 x 1023 atoms
Question 6. A sample of ethane (C2H6) gas has the same mass as 1.5 x 1020 molecules of methane (CH4 ). How many C2H6 molecules does the sample of gas contain?
Answer:
Given
A sample of ethane (C2H6) gas has the same mass as 1.5 x 1020 molecules of methane (CH4 ).
∵ 6.022 x 1023 molecules of methane have mass
= Gram molecular mass of methane (CH4)
=12+ 4 × 1 = 16 g
∴ 1.5 x 1020 molecules of methane have mass
⇒ \(=\frac{16 \times 1.5 \times 10^{20}}{6.022 \times 10^{23}}=3.98 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~g}\)
This is also the mass of ethane (C2H6).
Gram molecular mass of ethane (C2H6)
= 2 × 12+ 6 × 1 = 24 + 6
= 30 g As 30 g of ethane has several molecules
=6.022 × 1023
Question 7. If 3.42 g of sucrose is dissolved in 18 g of water in a beaker, then what will be the number of oxygen atoms in the solution?
Answer:
Step 1 Molar mass of sucrose,
C12H22O11 =12×12+ 1 × 22+ 16 ×11 = 342g/mol
∵ 342 g of sucrose = 1 mole sucrose
∴ 3.42 g ofsucrose \(=\frac{1 \times 3.42}{342}=0.01 \text { mole sucrose }\)
∵ 1 mole of sucrose (C12H22O11) contains O-atoms
= 11× 6.022 × 1023
∴ 0.01 mole of sucrose will contain O-atoms = 0.01× 11× 6.023×1023 = 6.6253 × 1022
Step 2 18 g water (H2O) = 1 mole O-atoms = 6.022 × 1023 O-atoms
Step 3 By adding the number of O-atoms present in 3.42 g sucrose and 18 g water, we get 6.022 × 1023 +6.6253 × 1022
= 1022(60.22+ 6.6253)
= 66.844 × 1022
= 6.68 × 1022 atoms
Question 8. When 3.0 g of carbon is burnt in 8.00 g of oxygen, 11.00 g of carbon dioxide is produced. What mass of carbon dioxide will be formed when 3.00 g of carbon is burnt in 50.0g of oxygen? Which law of chemical combination will govern your answer?
Answer:
Given
When 3.0 g of carbon is burnt in 8.00 g of oxygen, 11.00 g of carbon dioxide is produced.
First, we find the proportion of mass of carbon and oxygen in carbon dioxide.
In CO2, C: O =12: 32 or 3: 8
In other words, we can say that
12.00 g carbon reacts with oxygen =32.00 g
∴ 3.00 g carbon will react with oxygen = 8 g
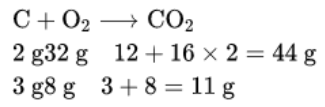
Therefore, 3.00 g of carbon will always react with 8.0g of oxygen to form 11 g of carbon dioxide, even if a large amount (50.00 g) of oxygen is present. This means when 3.00 g of carbon is burnt in 50.00 g of oxygen, only 8.00 g of oxygen will be used to produce.
11.00 g of carbon dioxide. The remaining 42.00 g of oxygen will remain as it is. This reaction will be governed by the law of constant proportions.
Question 9. Which has more number of atoms? 100 g of N2 or 100 g of NH3
Answer:
The molar mass of 1 mole of N2 = 2 × 14= 28 g
∵ 28 g of N2 has several molecules
=6.022 x 1023
∴ 100 g of N2 has several molecules
⇒ \(=\frac{6.022 \times 10^{23} \times 100}{28}=2.1 \times 10^{24}\)
Atoms in 100 g of N2 = 2.1 x 1024 × 2
= 4.2 × 1024 atoms.
Similarly, the molar mass of 1 mole of
NH3= 14 + 3X1 =17 g
∵ 17g NH3 has number of molecules =6.022 × 1023
∴ 100 g NH3 has several molecules
⇒ \(=\frac{6.022 \times 10^{24} \times 100}{17}=3.54 \times 10^{24}\)
Atoms in 100 g of
NH3 =3.54 × 1024 × 4 = 1.416 x1024
Thus, 100 g of NH3 has more number of atoms.
Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms And Molecules Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
- State the law of constant proportion.
- In a compound carbon and oxygen react in a ratio of 3:8 by mass to form carbon dioxide. What mass of oxygen is required to react completely with 9 g carbon?
Answer:
- The law of constant proportion states that “a pure chemical compound always consists of the same elements that are combined in a fixed (or definite) proportion by mass”.
- Carbon: oxygen (by mass) =3: 8 i.e. 3 g of carbon requires 8 g of oxygen to form carbon dioxide.
∴ 9 g of carbon requires (3 × 8) 24 g of oxygen to form carbon dioxide.
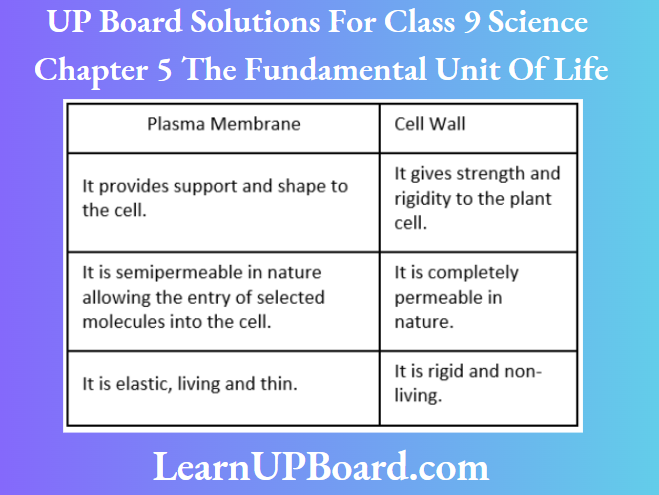
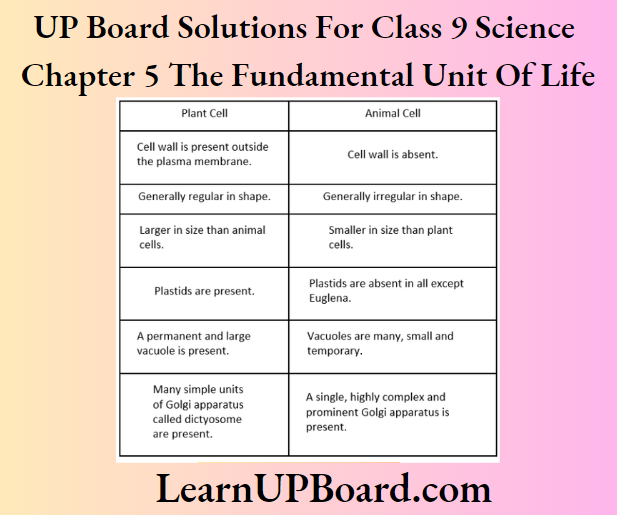
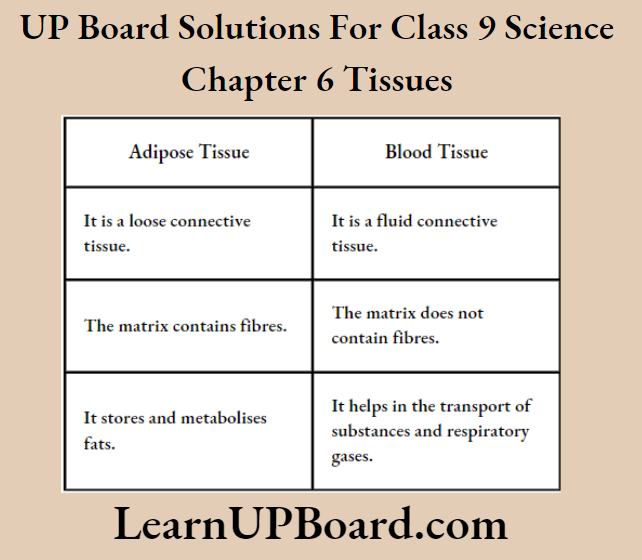
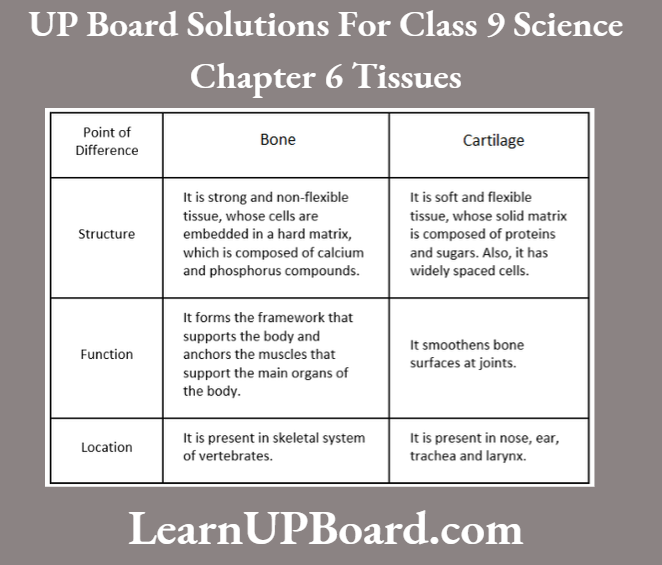
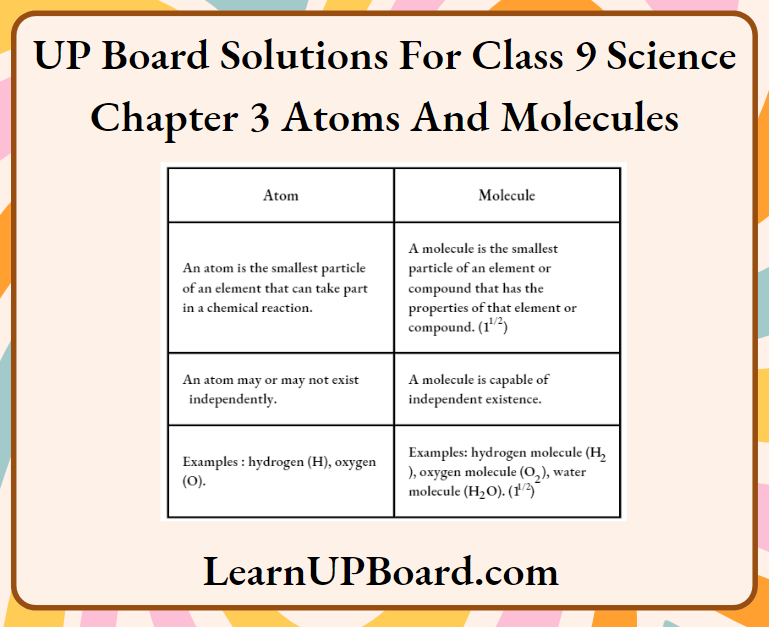
Question 2. State three points of differences between an atom and a molecule.
Answer:
Question 3. Calcium carbonate decomposes on heating to form calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. When 10 g of calcium carbonate is decomposed completely then 5.6 g of calcium oxide is formed. Calculate the mass of carbon dioxide formed. Which law of chemical combination will you use in solving this problem? State the law.
Answer:
Given
Calcium carbonate decomposes on heating to form calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. When 10 g of calcium carbonate is decomposed completely then 5.6 g of calcium oxide is formed.
The reaction occurs as follows:
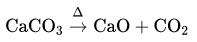
According to the law of conservation of mass, Total mass of reactant(s) = Total mass of products(s)
⇒ 10 g = 5.6 g + Mass of CO2
⇒ Mass of CO2 =10 —5.6 =4.4g
This problem is solved using the law of conservation of mass according to which mass can neither be created nor be destroyed during a chemical reaction.
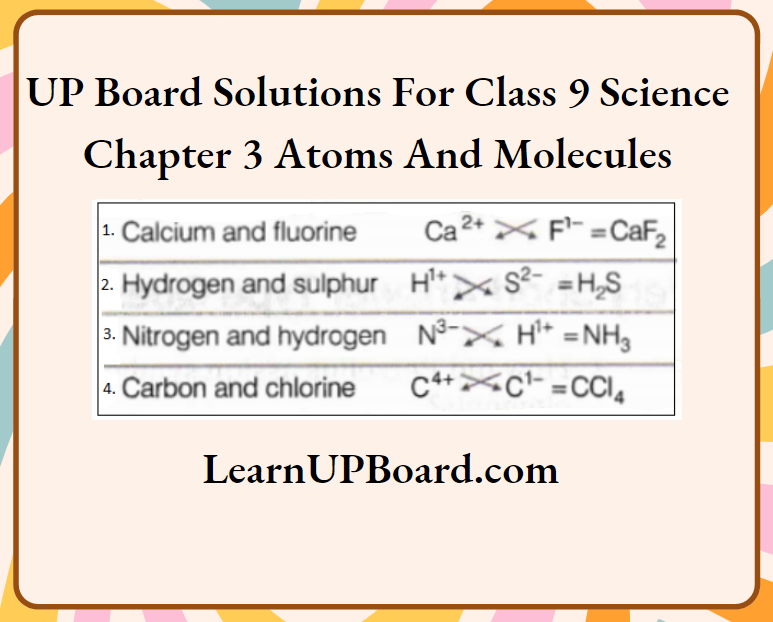
Question 4. Give the formulae of the compounds formed from the following sets of elements.
- Calcium and fluorine
- Hydrogen and sulphur
- Nitrogen and hydrogen
- Carbon and chlorine
Answer:
Question 5. A vessel containing 28 g of carbon monoxide gas to which 16 g of oxygen gas is added and the mixture is left for a few hours. When checked there was only one kind of gas (carbon dioxide) in the vessel. What change would you observe in the overall mass of the content? Give a reason for your answer.
Answer:
Given
A vessel containing 28 g of carbon monoxide gas to which 16 g of oxygen gas is added and the mixture is left for a few hours. When checked there was only one kind of gas (carbon dioxide) in the vessel.
Carbon monoxide (CO) reacts with oxygen (O2) to form carbon dioxide (CO2). There will not be any change in the overall mass of the content of the vessel as the mass of the product formed is equal to the mass of reactants.
i.e. Mass of CO2 =Mass of CO + mass of O2
= 28+16 = 44 g
The above observation is based on the law of conservation of mass.
Question 6. Write the Latin names of sodium and iron.
Answer:
Latin names of sodium and iron
Latin name of sodium (Na) = Natrium
Latin name of iron (Fe) =Ferrum.
Question 7. Which of the following symbols of elements are incorrect? Give their correct symbols.
- Cobalt (CO)
- Carbon (c)
- Aluminium (AL)
- Helium (He)
Answer:
- CO is an incorrect symbol of cobalt. Its correct symbol is Co.
- c is the incorrect symbol of carbon. Its correct symbol is C.
- AL is an incorrect symbol of aluminium. Its correct symbol is Al.
- For helium, He is the correct symbol.
Question 8.
- What is the relative atomic mass of an element?
- What is the average atomic mass of hydrogen?
Answer:
- Relative atomic mass is defined as the number of times a given atom is heavier than 1 /12th of the mass of 1 atom of C-12.
- The atomic mass of hydrogen is taken as lu whereas actually, it is 1.008 u.
Question 9. Define atomic mass unit. State how atoms exist.
Answer:
Atomic mass unit
- The atomic mass unit (amu) is defined as the mass unit equal to exactly 1/12th of the mass of one atom of the C-12 isotope.
- Atoms may exist independently in a free state (For example., He, Ne and Ar) or in a combined state.
- The combined form of atoms may have similar kinds of atoms (H2, N2, O2 etc.) or different kinds of atoms (H2O, CO2, H2S etc).
Question 10. Classify each of the following based on their atomicity.
- F2
- NO2
- N2O
- C2H6
- P4
- H2O2
- P4O10
- HCl
- He
- O3
- CH4
- Ag
Answer:
- Monoatomic: Ag, He
- Diatomic: HCl, F2
- Triatomic : NO2, N2O, O3
- Tetraatomic : P4, H2O2
- Polyatomic : C2H6, P4O10, CH4
Question 11. How do molecules react?
Answer:
Molecules exist in the following two forms
- Molecules of elements These are formed by the combination of two or more atoms of the same element, for example., O2, H2, P4 etc.
- Molecules of compounds These are formed by the combination of atoms of different elements. For example., NH3, CO2 etc.
Question 12. State the number of atoms present in each of the following chemical species.
- CO2-3
- PO3-4
- P2O5
- CO
Answer:
1. Number of atoms in CO2-3
= Number of C-atoms + Number of O-atoms
= 1 + 3 = 4
2. Number of atoms in PO3-4
= Number of P-atoms + Number of O-atoms
=1+4=5
3. Number of atoms in P2O5
= Number of P-atoms + Number of O-atoms
=2+5=7
4. Number of atoms in CO
= Number of C-atoms + Number of O-atoms =1+1=2
Question 13. Write the cations and anions present (if any) in the following compounds.
- CH3COONa
- NaCl
- H2
- NH4NO3
Answer:
Question 14. Give the names of any two elements present in the following compounds: Baking powder, common salt, sulphuric acid
Answer:
- Baking powder (NaHCO3) Sodium, hydrogen, carbon and oxygen.
- Common salt (NaCl) Sodium and chlorine.
- Sulphuric acid (H2SO4) Sulphur, hydrogen and oxygen.
Question 15.
- Give one word for the following:
- Positively charged ion
- A group of atoms carrying a charge
- Mention any two important rules for writing a chemical formula.
Answer:
- Cation
- Polyatomic ion
- Two rules for writing a chemical formula are:
- When a compound consists of a metal and a non-metal, the symbol of the metal is written first and on the left whereas of non-metal on its right.
- The valencies or charges on the ions must be balanced in the chemical formula.
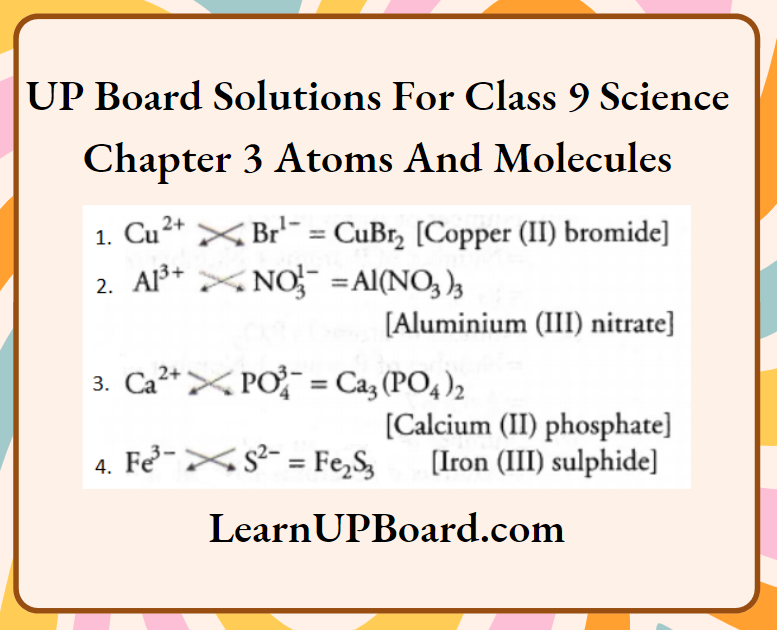
Question 16. Write the molecular formulae for the following compounds.
- Copper (2) bromide
- Aluminium (3) nitrate
- Calcium (2) phosphate
- Iron (3) sulphide
Answer:
Question 17.
- An element X has a valency of 2. Write the chemical formula for
- Bromide of the element
- Oxide of the element.
- Define the formula unit mass of a substance.
Answer:
1. Valency of X = 2
Valency of bromine =1
∴ The formula of compound
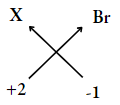
= XBr2
2. Valency of X =2
Valency of oxygen = 2
∴ The formula of compound
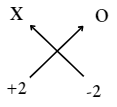
= X2O2 or XO
Formula unit mass is the sum of atomic masses of all atoms present in a formula unit of a compound. It is calculated by adding the atomic masses of all the atoms present in one formula unit.
Question 18. Write the chemical formulae of the following compound, using the criss-cross method.
- Magnesium bicarbonate
- Barium nitrate
- Answer:
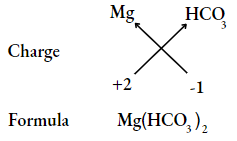
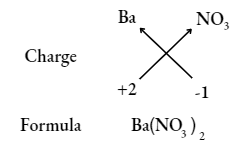
Question 19. Find the ratio by mass of the combining elements in the following compounds.
- CaCO3
- MgCl2
- H2SO4
- C2H5OH
Answer:
CaCO3 → Ca : C : O = 40 : 12 : 48
= 10: 3:12
MgCl2 → Mg : Cl = 24 : 2 × 35.3 = 24 : 71
H2SO4 H : S : O = 2 × 1 : 32 : 4 × 16
= 2:32:64 = 1:16:32
C2H5OH → C : H : O = 2x 12 : 6x 1 : 16
= 24:6:16 =12:3:8
Question 20. Nitrogen and hydrogen atoms combine in a ratio of 14 : 3 by mass to form an ammonia molecule. Find the formula of the ammonia molecule by calculating the molar ratio. [Given atomic mass of N = 14 u and H = 1 u]
Answer:
Given
Nitrogen and hydrogen atoms combine in a ratio of 14 : 3 by mass to form an ammonia molecule.
Number of nitrogen atoms present in the molecule
⇒ \(=\frac{\text { Proportion by mass }}{\text { Atomic mass }}=\frac{14}{14}=1\)
Number of hydrogen atoms present in the molecule _ Proportion by mass Atomic mass
⇒ \(=\frac{\text { Proportion by mass }}{\text { Atomic mass }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{3}{1}=3\)
This means many nitrogen and hydrogen atoms combined in ratio =1:3
Thus, the formula of a molecule of ammonia is NH3.
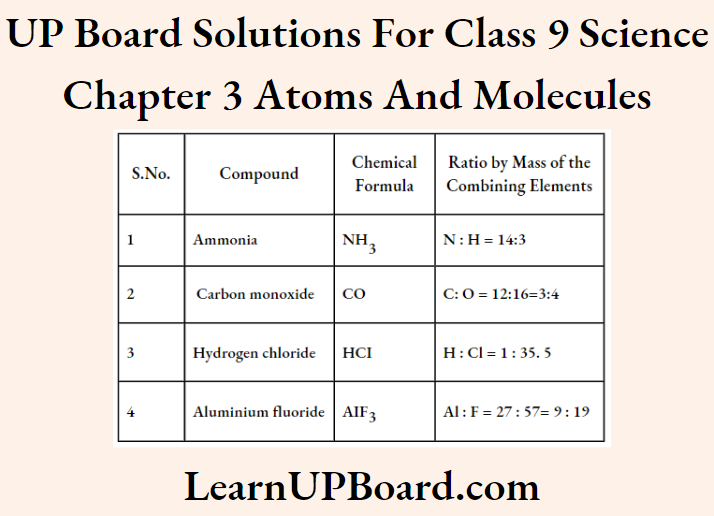
Question 21. Give the chemical formulae for the following compounds and compute the ratio by mass of the combining elements in each one of them.
- Ammonia
- Carbon monoxide
- Hydrogen chloride
- Aluminium fluoride
Answer:
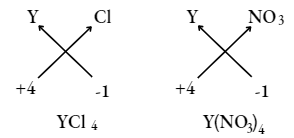
Question 22. An element Y has a valency of 4, write the formula for its
- Chloride Sol.
- Nitrate
- Chloride
- Nitrate
Answer:
Question 23. Out of the following which has more atoms?
- 50 g of Cu,
- 50 g of Fe
[Atomic mass of Cu = 63.5 u, Fe =56 u]
Answer:
Number of atoms in 63.5 g Cu = 6.022 × 1023
Number of atoms in 1 g \(\mathrm{Cu}=\frac{6.022 \times 10^{23}}{63.5}\)
Number of atoms in 50g Cu
⇒ \(=\frac{6.022 \times 10^{23}}{63.5} \times 50\)
⇒ \(4.74 \times 10^{23} \text { atoms }\)
Number of atoms in 56 g Fe = 6.022 x 1023
Number of atoms in 1 g Fe \(=\frac{6.022 \times 10^{23}}{56}\)
Number of atoms in 50 g Fe \(=\frac{6.022 \times 10^{23}}{56} \times 50\)
⇒ \(=5.37 \times 10^{23} \text { atoms }\)
∴ 50 g of Fe has more number of atoms.
Question 24. A compound XH is formed by the combination of an element X with hydrogen. Find the valency of the element. State the formula of the compound formed by the combination of X with nitrogen and X with oxygen.
Answer:
Given
A compound XH is formed by the combination of an element X with hydrogen.
In the compound XH, the valency of elements X is 1.
1. The valency of nitrogen is 3.
The valency of element X is 1.
∴ The formula of the compound = NX3
2. The valency of oxygen is 2.
The valency of element X is 1.
∴ The formula of the compound = OX2.
Question 25. During photosynthesis, a six-carbon atom molecule, glucose (C6H12O6), is formed. Calculate its molecular mass.
[Atomic mass C = 12.0uH = 1.0u and O = 16.Ou]
Answer:
Given
During photosynthesis, a six-carbon atom molecule, glucose (C6H12O6), is formed. C
The molecular mass of glucose
= 6 × atomic mass of C+ 12 × atomic mass of H + 6 atomic mass of O
= 6 × 12 +12 × 1+6 × 16
= 72 + 12 + 96
=180 u
The molecular mass of glucose =180 u
Question 26. 6 g of coke consisting of 100% carbon, is burnt in the air. Find the number of oxygen atoms consisting of the carbon dioxide gas thus formed.
Answer:
Given
6 g of coke consisting of 100% carbon, is burnt in the air.
Each carbon atom combines with two oxygen atoms on combustion as follows:
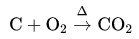
6 g of coke consist \(\frac{6}{12} \times N_A\)
Hence, the number of oxygen atoms
⇒ \(=2 \times \frac{6}{12} \times N_A=N_A\)
⇒ \(\left(N_A=6.022 \times 10^{23} \text { atoms }\right)\)
Question 27. The mass of a single atom of M is 3.05x 10-22g. What is its atomic mass? What would this element be? Check the periodic table for possible answers.
Answer:
Given
The mass of a single atom of M is 3.05x 10-22g.
1 mole = atomic mass of an element
= 6.022 x 1023 atoms
∵ Mass of 1 atom = 3.05 x 10-22 g
∴ Mass of 6.022 x 1023 atoms
= 3.05 x 1(T22 x 6.022 x 1023 =183.671g
This is nearly the atomic mass of tungsten (W183.8).
Question 28. What are polyatomic ions? Give examples.
Answer:
Polyatomic ions
A group of atoms carrying a charge and behaving like one entity is known as a polyatomic ion. For example., an oxygen atom and hydrogen atom combine to form a hydroxide ion (OH–) and one C-atom and three O-atoms combine to form a carbonate ion (CO2-3).
Question 29. Give the names of the elements present in the following compounds.
- Quicklime
- Hydrogen bromide
- Baking powder
- Potassium sulphate
Answer:
- Quicklime Calcium oxide — CaO Elements Calcium and oxygen
- Hydrogen bromide — HBr Elements Hydrogen and bromine
- Baking powder Sodium hydrogen carbonate — NaHCO3 Elements Sodium, hydrogen, carbon and oxygen
- Potassium sulphate — K2SO4 Elements Potassium, sulphur and oxygen.
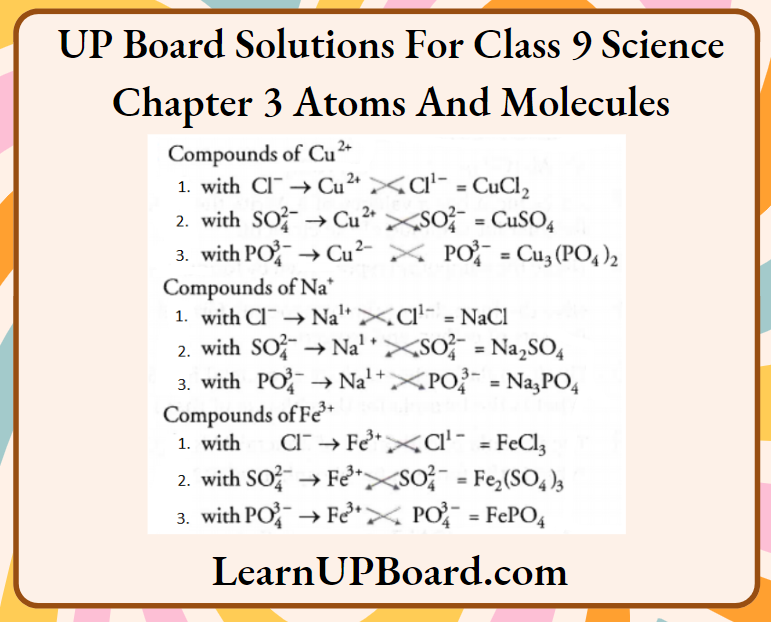
Question 30. Write the molecular formulae of all the compounds that can be formed by the combination of the following ions.
Cu2+, Na+, Fe3+, Cl–, SO2-4 , PO3-4
Answer:
Question 31. In a reaction, 5.3 g of sodium carbonate reacted with 6 g of ethanoic acid. The products were 2.2 g of carbon dioxide, 0.9 g of water and 8.2 g of sodium ethanoate. Show that these observations are in agreement with the law of conservation of mass.
Sodium carbonate + Ethanoic acid → Sodium ethanoate + Carbon dioxide + Water
Answer:
Total mass of reactants = Mass of sodium carbonate + Mass of ethanoic acid = 5.3 + 6.0 = 11.3 g
Total mass of products =Mass of sodium ethanoate + Mass of carbon dioxide + Mass of water = 8.2 + 2.2 + 0.9 = 11.3 g
Since the sum of masses of reactants is equal to the sum of masses of products, therefore, the observation made is in agreement with the law of conservation of mass.
Question 32. Hydrogen and oxygen combine in a ratio of 1:8 by mass to form water. What mass of oxygen gas would be required to react completely with 3 g of hydrogen gas?
Answer:
Given
Hydrogen and oxygen combine in a ratio of 1:8 by mass to form water.
Since H and O combine in the ratio of 1: 8 by mass.
Therefore, \(\frac{\text { Mass of } \mathrm{H}}{\text { Mass of } \mathrm{O}}=\frac{1}{8}\)
Let the mass of oxygen required to react completely with 3 g of hydrogen gas be x.
⇒ \(\frac{3}{x}=\frac{1}{8}\)
or x = 24 g
Therefore, 24 g of oxygen is required to react with 3 g of hydrogen to form water.
Question 33. Why is it not possible to see an atom with the naked eye?
Answer:
- Atoms are very small, they are smaller than anything we can imagine. More than millions of atoms when stacked would make a layer barely as thick as a sheet of paper.
- These are very small in radii and measured in terms of nanometers (1nm =10-9m). Hence, it is not possible to see an atom with the naked eye.
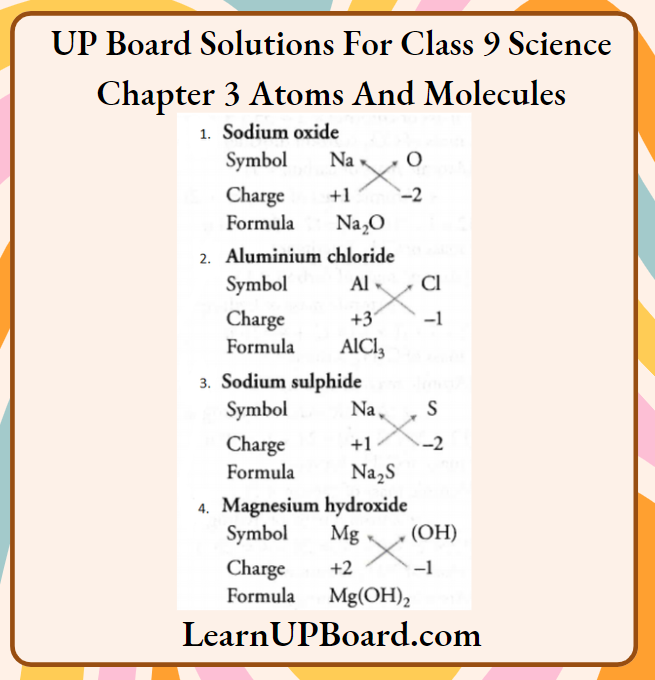
Question 34. Write down the formulae of
- Sodium oxide
- Aluminium chloride
- Sodium sulphide
- Magnesium hydroxide
Answer:
Sodium oxide
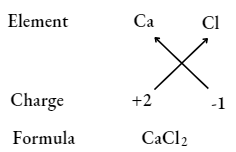
Question 35. What is meant by the term chemical formula?
Answer:
Chemical formula
It is the shortest way to represent a compound with the help of symbols and valency (charge) of elements, for example., Element
Question 36. How many atoms are present in a
- H2S molecule and
- PO3-4 ion?
Answer:
- In H2S molecule, three atoms
- [i.e. 2 atoms of H + 1 atom of S] are present.
- InPO3-4 ion, five atoms
- [i.e. 1 atom of P + 4 atoms of O] are present.
Question 37. Calculate the formula unit masses of ZnO, Na2O, K2CO3. [Given, atomic mass of Zn = 65 u, Na = 23u, K = 39u, C = 12u andO = 16u]
Answer:
Formula unit mass of ZnO (zinc oxide)
= 65 +16 =81 u
Formula unit mass of Na2O(sodium oxide)
= (23 x 2) + (16 x 1) = 46 + 16 = 62 u
Formula unit mass of K2CO3 (potassium carbonate) = (39 x 2) + (12 x 1) + (16 x 3)
= 78+12 + 48 =138 u
Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms And Molecules Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. How did Berzelius assign symbols to the elements?
Answer:
Berzelius assigned symbols to the elements by taking the first one or two letters of the element’s name in English and in some cases the symbols have been taken from the names of elements in different languages such as Latin, German, Greek etc.
Question 2. Give an example of a triatomic molecule of an element.
Answer: Ozone (O2)
Question 3. Which is octatonic, carbon or sulphur?
Answer: Sulphur (S8)
Question 4. Write one example of each.
- Tetra-atomic molecule
- Diatomic molecule
Answer: Phosphorus (P4)
Question 5. Is argon monoatomic or diatomic?
Answer: Argon is monoatomic because its atom can exist independently.
Question 6. Give the difference between a cation and an anion.
Answer:
The difference between a cation and an anion
Cation It is a positively charged ion.
For example., Na+, K+,Ca2+,Mg2+ etc.
Anion is a negatively charged ion.
For example., Cr–, Br–, F–,O2-, N3- etc.
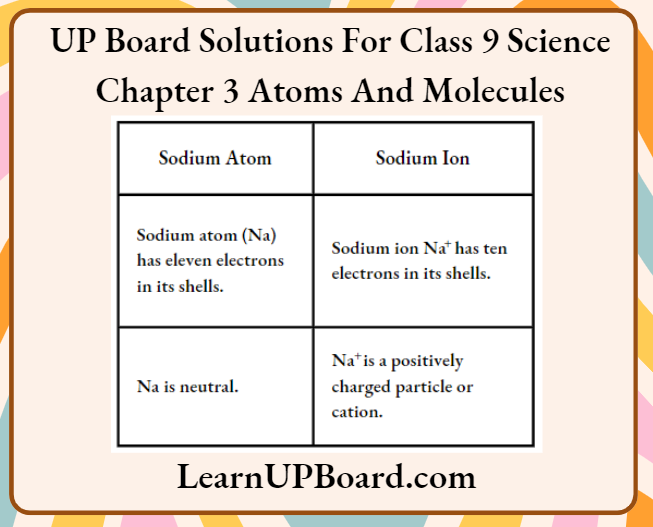
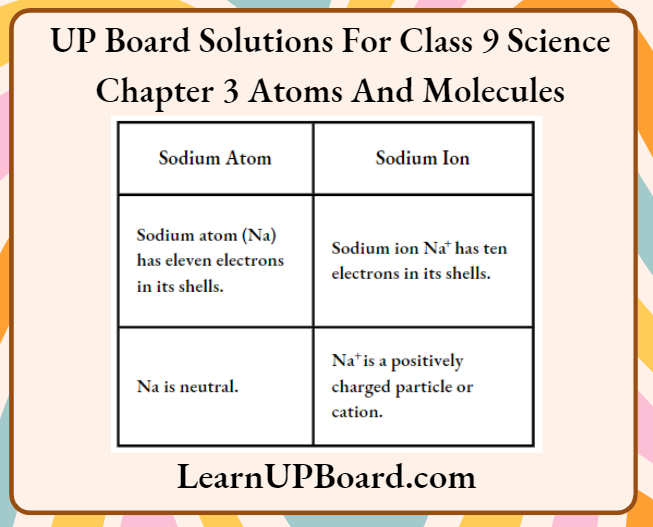
Question 7. What is the difference between a sodium atom and a sodium ion?
Answer:
The difference between a sodium atom and a sodium ion
Question 8. Define a polyatomic ion. Give one example of it.
Answer:
Polyatomic ion
A group of atoms carrying charge in a single entity is called a polyatomic ion. For example., sulphate ion (SO2-4) has five atoms.
Question 9. Choose an ionic compound among S8 , Cu(NO3)2 , P4 , H2 and O2?
Answer: Cu(NO3 )2 is an ionic compound because it has Cu2+ and NO–3 ions.
Question 10. What is the molecular formula of aluminium hydroxide?
Answer:
The molecular formula of aluminium hydroxide
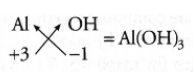
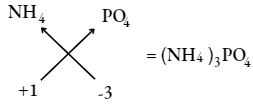
Question 11. What is the chemical formula of ammonium phosphate?
Answer:
Chemical formula of ammonium phosphate
Question 12. Choose the correct formulae of sodium sulphide and sodium sulphite: NaS, Na2SO4, Na2S or Na2SO3.
Answer: Sodium sulphide = Na2S Sodium sulphite = Na2SO3
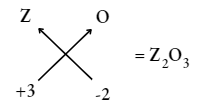
Question 13. An element Z has a valency of 3. What is the formula of the oxide of Z?
Answer:
Question 14. If an element X has its valency equal to 3, what will be its formula with carbonate ion?
Answer:
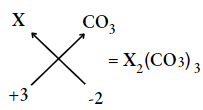
Question 15. Calculate the formula unit mass of Na2CO3. [Atomic mass of Na = 23 u, C = 12 u, 0= 16 u]
Answer: Na2CO3 =2 × 23+ 12 + 3 × 16=106 u
Question 16. Calculate the formula unit mass of NaHCO3. [Atomic mass of Na =23 u, H =1 u, C =12 u, O = 16 u]
Answer:
NaHCO3 – (Atomic mass of Na) + (Atomic mass of H) + (Atomic mass of C) + (3 × Atomic mass of O)
= (23 + 1 + 12 + 3 × 16)
= 84 u
Question 17. What is the mass of sodium in 58.5 g of NaCl?
Answer:
Mass of sodium in 58.5 g of NaCl
23g [∵ Mass of sodium = 58.5— mass of Cl =58.5-35.5 = 23]
Question 18. Which postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory can explain the law of definite proportions?
Answer:
‘The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound This postulate explains the law of definite proportions.
Question 19. Which postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory is the result of the law of conservation of mass?
Answer:
The postulate which is the result of the law of conservation of mass is “atoms are indivisible particles, which can neither be created nor be destroyed in a chemical reaction”.
Question 20. Define atomic mass unit.
Answer:
Atomic mass unit
One atomic mass unit (u) is the mass unit equal to exactly 1/12th of the mass of one atom of the C-12 isotope.