NEET Biology MCQs
NEET Chemistry For Biomolecules Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Sucrose on hydrolysis gives
- β-D-glucose + α-D-fructose
- α-D-glucose + β-D-glucose
- α-D-glucose + β-D-fructose
- α-D-fructose + β-D-fructose.
Answer: 3. α-D-glucose + β-D-fructose
In sucrose, two monosaccharides are held together by a glycosidic linkage between C-1 of α-D-glucose and C-2 of β-D-fructose.
Sucrose \(\underrightarrow{\text { Hydrolysis }}\) \(\alpha \text { – } D \text {-glucose }+\beta \text { – } D \text {-fructose }\)
Question 2. The difference between amylose and amylopectin is
- Amylopectin have 1 → 4 α-linkage and 1 → 6 α-linkage
- Amylose has 1 → 4 α-linkage and 1 → 6 β-linkage
- Amylopectin have 1 →4 α-linkage and 1 → 6 β-linkage
- Amylose is made up of glucose and galactose.
Answer: 1. Amylopectin have 1 → 4 α-linkage and 1 → 6 α-linkage
Amylose is a linear polymer of α-D-glucose held by C1-C4 glycosidic linkage whereas amylopectin is a branched chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in which the chain is held by C1-C4 glycosidic linkage while branching occurs by C1-C6 glycosidic linkage.
Question 3. The correct corresponding order of names of four aldoses with the configuration given below respectively, is
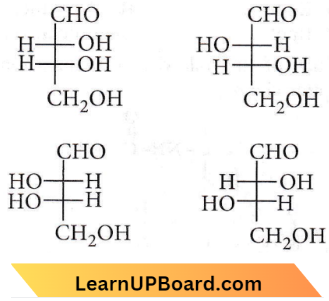
- L-erythrose, L-threose, L-erythrose, D-threose
- D-threose, D-erythrose, L-threose, L-erythrose
- L-erythrose, L-threose, D-erythrose, D-threose
- D-erythrose, D-threose, L-erythrose, L-threose.
Answer: 4. D-erythrose, D-threose, L-erythrose, L-threose.
Question 4. Which one given below is a non-reducing sugar?
- Glucose
- Sucrose
- Maltose
- Lactose
Answer: 2. Sucrose
All monosaccharides whether aldoses or ketoses are reducing sugars. Disaccharides such as sucrose, in which the two monosaccharide units are linked through their reducing centres, such as Le., aldehydic, or ketonic groups, are non-reducing.
Read and Learn More NEET MCQs with Answers
Question 5. D(+)-glucose reacts with hydroxyl amine and yields an oxime. The structure of the oxime would be
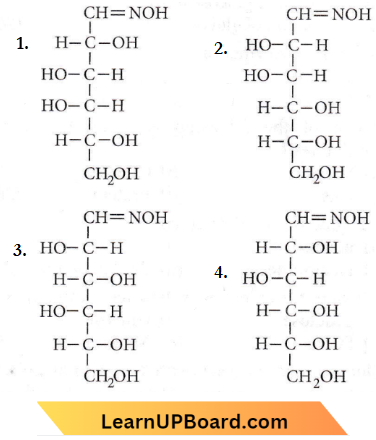
Answer: 4
Question 6. Which one of the following sets of monosaccharides forms sucrose?
- α-D-galactopyranose and α-D-glucopyranose
- α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-fructofuranose
- β-D-glucopyranose and α-D-fructofuranose
- α-D-glucopyranose and β-D- fructopyranose
Answer: 2. α-D-glucopyranose and β-D fructofuranose
Sucrose is formed by the condensation of α-D- glucopyranose and β-D-fructofuranose.
NEET biology MCQs
Question 7. Which one of the following statements is not true regarding (+)-lactose?
- On hydrolysis (+)-lactose gives equal amounts of D(+)-glucose and D(+)-galactose.
- (+)-Lactose is a β-glucoside formed by the union of a molecule of D(+)-glucose and a molecule of D(+)-galactose.
- (+)-Lactose is a reducing sugar and does not exhibit mutarotation.
- (+)-Lactose, C12H22O11 contains 8 -OH groups
Answer: 3. (+)-Lactose is a reducing sugar and does not exhibit mutarotation.
(+)-Lactose is a reducing sugar and all reducing sugars show mutarotation.
Question 8. Which one of the following does not exhibit the phenomenon of mutarotation?
- (+)-Sucrose
- (+)-Lactose
- (+)-Maltose
- (-)-Fructose
Answer: 1. (+)-Sucrose
Sucrose does not show mutarotation.
Mutarotation is the phenomenon of change in optical rotation shown by freshly prepared solutions of sugars. However, this property is not exhibited by all sugars.
Only those sugars which have a free aldehyde (-CHO) or ketone (C=O) group aldehyde are capable of ketone of the group showing and is therefore, incapable of showing mutarotation.
Question 9. Fructose reduces Tollens reagent due to
- Asymmetric carbons
- Primary alcoholic group
- Secondary alcoholic group
- Embolisation of fructose followed by conversion to aldehyde by base.
Answer: 4. Enolisation of fructose followed by conversion to aldehyde by base.
Under alkaline conditions of the reagent, fructose gets converted into a mixture of glucose and mannose (Lobry de Bruyn van Ekenstein rearrangement) both of which contain the -CHO group and hence, reduce Tollens’reagent to give silver mirror test
Question 10. The number of chiral carbons in β-D-(+) glucose is
- Five
- Six
- Three
- Four.
Answer: 4. Four.
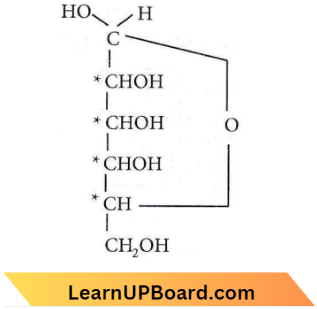
This structure of β-D-glucose has four asymmetric carbon atoms.
NEET biology practice questions
Question 11. Glycolysis is
- Oxidation of glucose to glutamate
- Conversion of pyruvate to citrate
- Oxidation of glucose to pyruvate
- Conversion of glucose to haem
Answer: 3. Oxidation of glucose to pyruvate
Glycolysis is the first stage in the oxidation of glucose. It is an anaerobic process and involves the degradation of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate with the generation of two molecules of ATP.
Question 12. Cellulose is a polymer of
- Glucose
- Fructose
- Ribose
- Sucrose.
Answer: 1. Glucose
Cellulose is a straight-chain polysaccharide composed of β-D-glucose units joined by β-glycosidic linkage between C1 of one glucose unit and C4 of the next glucose unit.
Question 13. Which of the following gives a positive Fehling solution test?
- Sucrose
- Glucose
- Fats
- Protein
Answer: 2. Glucose
Glucose reduces Fehling solution because glucose has a free -CHO group which is readily oxidised.
Question 14. α-D-glucose and β-D-glucose are
- Epimers
- Anomers
- Enantiomers
- Diastereomers.
Answer: 2. Anomers
Glucose forms a stable hemiacetal between the -CHO group and the -OH group on the 5th carbon. In this process, the 1st ‘C’ atom becomes asymmetric giving two isomers which differ in the configuration of the asymmetric carbon. These two isomers are called anomers.
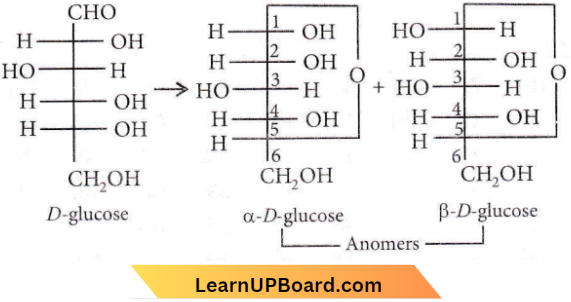
NEET biology practice questions
Question 15. Which of the following is the sweetest sugar?
- Fructose
- Glucose
- Sucrose
- Maltose
Answer: 1. Fructose
Fructose is the sweetest among all the sugars and is highly soluble in water.
Question 16. Glucose molecule reacts with X number of molecules of phenylhydrazine to yield osazone. The value of X is (8)
- Two
- Three
- Four
- Five
Answer: 4. Five
Glucose first reacts with phenyl hydrazine giving phenylhydrazine. Then the adjacent -CHOH group is oxidized by a 2d phenyl hydrazine molecule and itself is reduced to aniline. The resulting carbonyl group reacts with 3’d phenyl hydrazine molecule giving osazone.
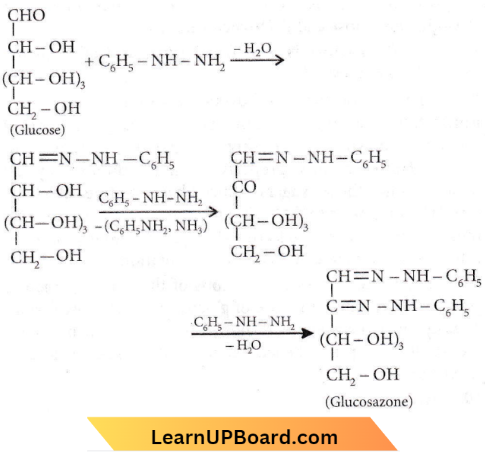
NEET biology practice questions
Question 17. The oxidation of glucose is one of the most important reactions in a living cell. What is the number of ATP molecules generated in cells from one molecule of glucose?
- 28
- 38
- 12
- 18
Answer: 2. 38
The oxidation of glucose is one of the most important reactions in a living cell.
⇒ \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_{12} \mathrm{O}_6+6 \mathrm{O}_2 \rightarrow 6 \mathrm{CO}_2+6 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}+38 \mathrm{ATP}\)
Question 18. The α-D-glucose and β-D-glucose differ from each other due to differences in carbon atoms with respect to its
- Number of OH groups
- Size of hemiacetal ring
- Conformation
- Configuration.
Answer: 4. Configuration.
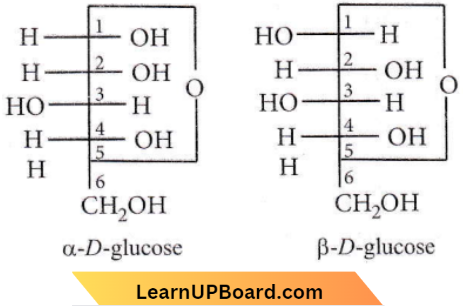
These isomers differ only in the orientation (or configuration) of the Cl atom.
Question 19. Chemically considering digestion is basically
- Anabolism
- Hydrogenation
- Hydrolysis
- Dehydrogenation.
Answer: 3. Hydrolysis
NEET biology chapter-wise questions
Question 20. On hydrolysis of starch, we finally get
- Glucose
- Fructose
- Both (1) and (2)
- Sucrose.
Answer: 1. Glucose
Glucose is produced commercially by the hydrolysis of starch by boiling it with dil. H2SO4 at 393 K under pressure of 2-3 bar.
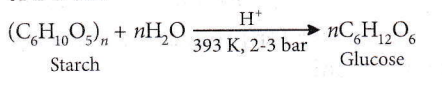
Question 21. Which of the following is a basic amino acid?
- Serine
- Alanine
- Tyrosine
- Lysine
Answer: 4. Lysine
Lysine is a basic amino acid
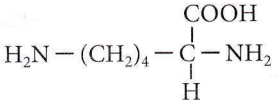
Question 22. The non-essential amino acids among the following is
- Lysine
- Valine
- Leucine
- Alanine.
Answer: 4. Alanine
NEET Biology chapter-wise questions
Question 23. Which structure(s) of proteins remains (s) intact during the denaturation process?
- Both secondary and tertiary structures
- Primary structure only
- Secondary structure only
- Tertiary structure only
Answer: 2. Primary structure only
During the denaturation of Proteins, 2° and 3° structures are destroyed but 1o structure remains intact.
Question 24. Which of the following compounds can form a zwitter ion?
- Aniline
- Acetanilide
- Benzoic acid
- Glycine
Answer: 4. Glycine
⇒ \(\mathrm{HOOC}-\underset{\text { Glycine }}{\mathrm{CH}_2-} \mathrm{NH}_2 \rightleftharpoons-\mathrm{OOC} \underset{\text { Zwitter ion }}{\mathrm{CH}_2}-\stackrel{+}{\mathrm{N}} \mathrm{H}_3\)
NEET Biology chapter-wise questions
Question 25. In a protein molecule, various amino acids are linked together by
- Peptide bond
- Dative bond
- α-glycosidic bond
- β-Glycosidic bond.
Answer: 1. Peptide bond
Question 26. Which of the statements about “Denaturation” given below are correct?
- Denaturation of proteins causes loss of secondary and tertiary structures of the protein.
- Denaturation leads to the conversion of a double strand of DNA into a single strand.
- Denaturation affects the primary structure which gets distorted.
- (2) and (3)
- (1) and (3)
- (1) and (2)
- (1), (2) and (3)
Anbswer: 3. (1) and (2)
Denaturation does not change the primary structure of the protein.
Question 27. Which functional group participates in disulphide bond formation in proteins?
- Thioester
- Thioether
- Thiol
- Thiolactone
Answer: 3. Thiol
Disulphide bond may be reduced to thiol by means of reagents i.e., NaBH4, which shows the presence of thiol group in disulphide bond formation.
NEET biology chapter-wise questions
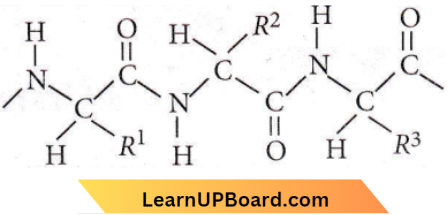
Question 28. Which of the following structures represents the peptide chain?
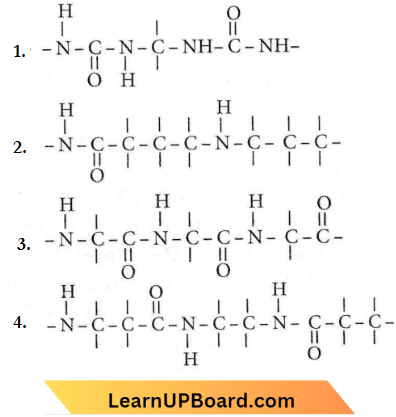
Answer: 3
In peptide linkage i.e., – CONH – group, the carboxyl group of one amino acid molecule forms an amide by combination with the amino group of the next amino acid molecule with the liberation of a water molecule.
Question 29. The correct statement in respect to protein haemoglobin is that it
- Functions as a catalyst for biological reactions
- Maintains blood sugar level
- Acts as an oxygen carrier in the blood
- Forms antibodies and offers resistance to diseases.
Answer: 3. Acts as an oxygen carrier in the blood
Four Fe2+ ions of each haemoglobin can bind with four molecules of O2 and it is carried as oxyhaemoglobin.
biomolecules objective questions NEET
Question 30. The helical structure of protein is stabilised by
- Dipeptide Bonds
- Hydrogen Bonds
- Ether Bonds
- Peptide Bonds.
Answer: 2. Hydrogen Bonds
α-Hellt structure is formed when the chain of α-amino acids coil as a right-handed screw because of the formation of hydrogen bonds between amide groups of the same peptide chain, i.e., NH group in one unit is linked to carbonyl oxygen of the fourth unit by hydrogen bonding. This H-trending is responsible for holding the helix in a stable position.
Question 31. Which is not a true statement?
- α-Carbon of α-amino acid is asymmetric.
- All proteins are found in the L-form.
- The human body can synthesise all the proteins it needs.
- At pH = 7, both ammo and carboxylic small groups exist in ionised form.
Answer: 2. All proteins are found in L-form
Some proteins are also found in the D-form.
Quetsion 32. 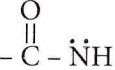 (peptide bond)
(peptide bond)
biomolecules objective questions NEET
Which statement is incorrect about peptide bonds?
- The C – N bond length in proteins is longer than the usual bond length of the N – C bond.
- Spectroscopic analysis shows the planar structure of the
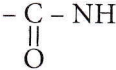 group.
group. - The C – N bond length in proteins is smaller than the usual bond length of the C – N bond.
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. The C – N bond length in proteins is longer than the usual bond length of the N – C bond.
A Peptide bond is formed by the reaction of the -COOH group of one amino acid with the -NH3 group of another amino acid and is represented as
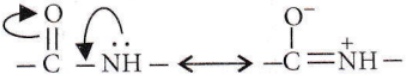
As some double bond character is found between C-N bonds, the bond length of C-N in protein should be smaller than the usual C-N bond.
Question 33. Which is the correct statement?
- Starch is a polymer of α-glucose.
- Amylose is a component of cellulose.
- Proteins are composed of only one type of amino acid.
- In the cyclic structure of fructose, there are four carbons and one oxygen atom.
Answer: 1. Starch is a polymer of α-glucose.
Starch is also known as amylum which occurs in all green plants. A molecule of starch (C6H10O5)n is built of a large number of α-glucose rings joined through oxygen atoms.
biomolecules objective questions NEET
Question 34. Haemoglobin is
- A Vitamin
- A Carbohydrate
- An Enzyme
- A Globular Protein.
Answer: 4. A Globular Protein.
Haemoglobin is a globular protein of four subunits, each subunit having a heme moiety and a polypeptide chain (Two α and two β chains).
Question 35. The secondary structure of a protein refers to
- Regular folding patterns of continuous portions of the polypeptide chain
- Three-dimensional structure, especially the bond between amino acid residues that are distant from each other in the polypeptide chain
- Mainly denatured proteins and structures of prosthetic groups
- Linear sequence of amino acid residues in the polypeptide chain.
Answer: 1. Regular folding patterns of continuous portions of the polypeptide chain
Question 36. During the process of digestion, the proteins present in food materials are hydrolysed to amino acids. The two enzymes involved in the process proteins \(\underrightarrow{\text { enzyme }(A)}\) polypeptides \(underrightarrow{\text { enzyme }(B)}\) amino acids, are respectively.
- Invertase and zymase
- Amylase and maltase
- Diastase and lipase
- Pepsin and trypsin
Answer: 4. Pepsin and trypsin
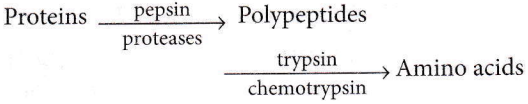
Question 37. Enzymes are made up of
- Edible proteins
- Proteins with specific structure
- Nitrogen-containing carbohydrates
- Carbohydrates.
Answer: 2. Proteins with specific structure
Biomolecules MCQs with answers NEET
Question 38. Which of the following is correct?
- Cycloheptane is an aromatic compound.
- Diastase is an enzyme.
- Acetophenone is an ether.
- All of these.
Answer: 2. Diastase is an enzyme.
Diastase is an enzyme that hydrolyses starch into maltose
Question 39. The function of enzymes in the living system is to
- Catalyse biochemical reactions
- Provide energy
- Transport oxygen
- Provide immunity.
Answer: 1. Catalyse biochemical reactions
Question 40. Which of the following statements about enzymes is true?
- Enzymes catalyse chemical reactions by increasing the activation energy.
- Enzymes are highly specific both in binding chiral substrates and in catalysing their reactions.
- Enzymes lack in nucleophilic groups.
- Pepsin is a proteolytic enzyme.
Answer: 4. Pepsin is a proteolytic enzyme.
Biomolecules MCQs with answers NEET
Question 41. Enzymes take part in a reaction and
- Decrease the rate of a chemical reaction
- Increase the rate of a chemical reaction
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these.
Answer; 2. Increase the rate of a chemical reaction
Enzyrnes being a biocatalyst increases the rate of a chemical reaction by providing alternative lower activation energy pathways.
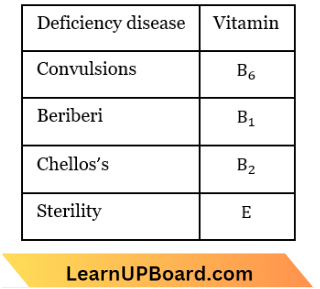
Question 42. RBC deficiency is a deficiency disease of
- Vitamin B2
- Vitamin B12
- Vitamin B6
- Vitamin B1
Answer: 2. Vitamin B12
Anaemia is a disease in which the body does not have enough red blood cells (RBC) due to a lack of vitamin B-12. This vitamin is needed to make red blood cells.
Question 43. A deficiency of vitamin B1 causes the disease
- Convulsions
- Beriberi
- Cheilosis
- Sterility.
Answer: 2. Beri-beri
Question 44. Which of the following is not a fat-soluble vitamin?
- Vitamin B complex
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin A
Answer: 1. Vitamin B complex
Vitamin B complex is not a fat-soluble vitamin. It is a water-soluble vitamin.
NEET biomolecules practice questions
Question 45. Which of the following vitamins is water soluble?
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin K
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin B
Answer: 4. Vitamin B
Vitamins B and C are water soluble whereas vitamins A, D, E and K are fat soluble
Question 46. The human body does not produce
- Enzymes
- DNA
- Vitamins
- Hormones.
Answer: 3. Vitamins
Certain organic substances required for regulating some of the body processes and preventing certain diseases are called vitamins, which cannot be synthesised by the human body.
Question 47. Vitamin B12 contains
- Fe (2)
- Co (3)
- Zn (2)
- Ca (2)
Answer: 2. Co (3)
Vitamin B12 is chemically named a cyanocobalamin having molecular formula C63H88O14N14PCo.
NEET biomolecules practice questions
Question 48. Given below are two statements.
- Statement 1: A unit formed by the attachment of a base to 1′-position of sugar is known as a nucleoside.
- Statement 2: When nucleoside is linked to phosphorous acid at the 5′-position of the sugar moiety, we get nucleotide.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
- Statement 1 is true but Statement 2 is false.
- Statement 1 is false but Statement 2 is true.
- Both Statement 1 and Statement 2 are true.
- Both Statement 1 and Statement 2 are false.
Answer: 1. Statement 1 is true but Statement 2 is false.
When nucleoside is linked to phosphoric acid (not phosphorous acid) at the 5′-position of the sugar moiety, we get nucleotide.
Question 49. The central dogma of molecular genetics states that genetic information flows from
- Amino acids → Proteins → DNA
- DNA → Carbohydrates → Proteins
- DNA → RNA → Proteins
- DNA → RNA → Carbohydrates
Answer: 3. DNA → RNA → Proteins
Genetic information flows from
DNA \(\underrightarrow{\text { Transcription }}\) RNA \(\underrightarrow{\text { Translation }}\) Proteins
NEET biomolecules practice questions
Quetsion 50. The correct statement regarding RNA and DNA, respectively is
- The sugar component in RNA is arabinose and the sugar component in DNA is ribose
- The sugar component in RNA is 2′-deoxyribose and the sugar component in DNA is arabinose
- The sugar component in RNA is arabinose and the sugar component in DNA is 2′-deoxyribose
- The sugar component in RNA is ribose and the sugar component in DNA is 2′-deoxyribose.
Answer: 4. The sugar component in RNA is ribose and the sugar component in DNA is 2′-deoxyribose.
Question 51. In DNA, the linkages between different nitrogenous bases are
- Phosphate linkage
- H-bonding
- Glycosidic linkage
- Peptide linkage.
Answer: 2. H-bonding
Nitrogenous bases are linked together by hydrogen bonds.
Question 52. The segment of DNA which acts as the instrumental manual for the synthesis of the protein is
- Ribose
- Gene
- Nucleoside
- Nucleotide.
Answer: 2. Gene
Genes are responsible for protein synthesis.
Question 53. In DNA, the complementary bases are
- Adenine and guanine; thymine and cytosine
- Uracil and adenine; cytosine and guanine
- Adenine and thymine; guanine and cytosine
- Adenine and thymine; guanine and uracil
Answer: 3. Adenine and thymine; guanine and cytosine
DNA contains two types of nitrogenous bases
Purine → Adenine (A) and guanine (G)
Pyrimidine → Cytosine (C) and thymine (T)
The purine and pyrimidine bases pair only in certain combinations. Adenine pairs with thymine (A:T) by two hydrogen bonds and guanine with cytosine (G: C) by three hydrogen bonds.
Biomolecules multiple choice questions
Question 54. RNA and DNA are chiral molecules, their chirality is due to
- Chiral bases
- Chiral phosphate ester units
- D-sugar component
- L-sugar component.
Answer: 3. D-sugar component
The constituents of nucleic acids are nitrogenous bases, sugar and phosphoric acid. The sugar present in DNA is D(-)-2-deoxyribose and the sugar present in RNA is D(-)- ribose. Due to these D(-)-sugar components, DNA and RNA molecules are chiral molecules.
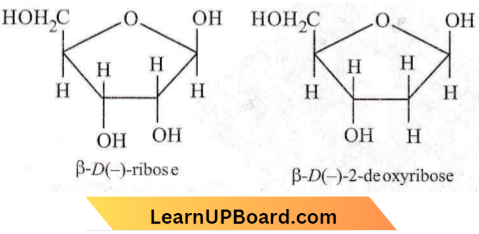
Question 55. A sequence of how many nucleotides in messenger RNA makes a codon for an amino acid?
- Three
- Four
- One
- Two
Answer: 1. Three
The four bases in mRNA: adenine, cytosine, guanine and uracil have been shown to act in the form of triplets; each triplet behaving as a code for the synthesis of a particular amino acid
Question 56. Chargaff’s rule states that in an organism
- The amount of adenine (A) is equal to that of thymine (T) and the amount of guanine (G) is equal to that of cytosine (C)
- The amount of adenine (A) is equal to that of guanine (G) and the amount of thymine (T) is equal to that of cytosine (C)
- The amount of adenine (A) is equal to that of cytosine (C) and the amount of thymine(T) is equal to that of guanine (G)
- Amounts of all bases are equal.
Answer: 1. Amount of adenine (A) is equal to that of thymine (T) and the amount of guanine (G) is equal to that of cytosine (C)
Amount of A = T and that of G = C
Question 57. Which of the following is correct about H-bonding in nucleotide?
- A – T, G – C
- A – G, T – C
- G – T, A – C
- A – A, T – T
Answer: 1. A – T, G – C
Biomolecules multiple choice questions
Question 58. An example of a biopolymer is
- Teflon
- Neoprene
- Nylon-6,6
- DNA.
Answer: 4. DNA.
DNA is an example of a biopolymer
Question 59. The couplings between base units of DNA is through
- Hydrogen bonding
- Electrostatic bonding
- Covalent bonding
- Van der Waal’s forces
Answer: 1. Hydrogen bonding
Question 60. Which of the following statements is not correct?
- Ovalbumin is a simple food reserve in egg whites.
- Blood proteins thrombin and fibrinogen are involved in blood clotting.
- Denaturation makes the proteins more active.
- Insulin maintains sugar levels in the blood of the human body.
Answer: 3. Denaturation makes the proteins more active.
Question 61. Which of the following hormones is produced under the conditions of stress which stimulate glycogenolysis in the liver of human beings?
- Thyroxin
- Insulin
- Adrenaline
- Estradiol
Answer: 3. Adrenaline
Adrenaline hormone helps to release fatty acids from fat and glucose from liver glycogen under the condition of stress. Hence, it is also called flight or fight hormone.
Question 62. Which of the following hormones contains iodine?
- Testosterone
- Adrenaline
- Thyroxine
- Insulin
Answer: 3. Thyroxine
Biomolecules multiple choice questions
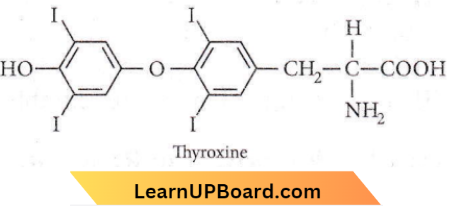
Question 63. Which of the following is an amine hormone?
- Insulin
- Progesterone
- Thyroxine
- Oxypurin
Answer: 3. Thyroxine
Thyroxine is an amine hormone and water-soluble hormone containing an amino group.
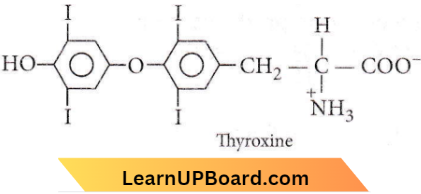
Question 64. Which one of the following is a peptide hormone?
- Adrenaline
- Glucagon
- Testosterone
- Thyroxine
Answer: 2. Glucagon
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, synthesised by the a-cells of the pancreas.
Question 65. The hormone that helps in the conversion of glucose to glycogen is
- Cortisone
- Bile acids
- Adrenaline
- Insulin.
Answer: 4. Insulin
Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas that lowers blood glucose levels by promoting the uptake of glucose by cells and the conversion of glucose to glycogen by the liver and skeletal muscle
Biomolecules multiple choice questions
Question 66. Which one is responsible for the production of energy in biochemical reactions?
- Thyroxine
- Adrenaline
- Oestrogen
- Progesterone
Answer: 1. Thyroxine
It is a hormone secreted from the thyroid gland. It controls various biochemical reactions involving the burning of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats to release energy.
Question 67. The cell membranes are mainly composed of
- Fats
- Proteins
- Phospholipids
- Carbohydrates.
Answer: 3. Phospholipids
Cell membranes are mainly composed of phospholipids.
Question 68. Phospholipids are esters of glycerol with
- Three carboxylic acid residues
- Two carboxylic acid residues and one phosphate group
- One carboxylic acid residue and two phosphate groups
- Three phosphate groups
Answer: 2. Two carboxylic acid residues and one phosphate group
Phospholipids may be regarded as derivatives of glycerol in which two of the hydroxy groups are esterified with fatty acids while the third is esterified with some derivatives of phosphoric acid.
Biomolecules MCQs with answers NEET
Question 69. The number of molecules of ATP produced in the lipid metabolism of a molecule of palmitic acid is
- 56
- 36
- 130
- 86
Answer: 3. 130
In lipid metabolism, a molecule of palmitic acid (C15H31 – COOH) produces 130 adenosine triphosphate molecules (ATP).
