CA Foundation Economics Determination Of Prices Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. For maximum profit, the condition is
- AR =AC.
- MR – MC
- MR = AR
- MC = AR
Answer: 2. MR – MC
The profit maximization level of a firm is the level at which its marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost. The condition for maximum profit is MC = MR.
Question 2. Equilibrium price may be determined through
- Only demand
- Only supply
- Both demand & supply
- None
Answer: 3. Both demand & supply
The equilibrium price is the price of a product when its demand equals supply. The point of intersection of demand and supply curves is the equilibrium price.
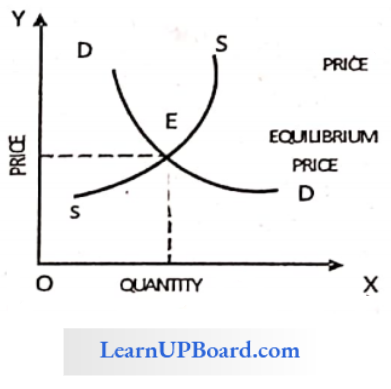
Question 3. If the price is forced to stay below the equilibrium price then consequently it can be said that
- Excess supply exists.
- Excess demand exists
- Either (1) or (2)
- Neither (1) nor (2)
Answer: 2. Excess demand exists
If the price is below the equilibrium price, supply remains the same, and the demand for the commodity increases.
The long run is the period when both, buyers and sellers get sufficient time to adjust their demand and supply. Hence, both demand and supply can change in the long run
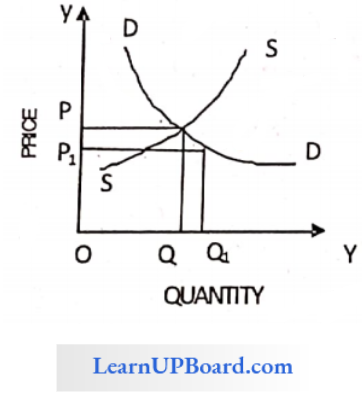
Question 4. An increase in supply with unchanged demand leads to
- Rise in price and fall in quantity
- Fall in both price and quantity
- Rise in both price and quantity
- Fall in price and rise in quantity
Answer: 4. Fall in price and rise in quantity
When there is an increase in supply, demand remains the same, the price of the good decreases, and the quantity demanded increases. It is evident from the following diagram:
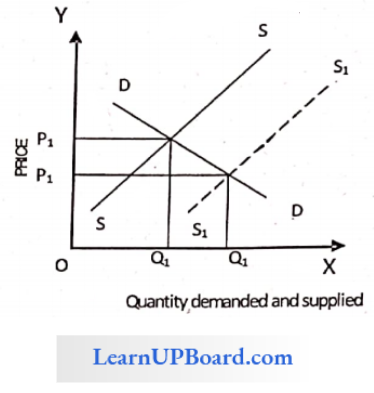
Question 5. In the long run
- Only demand can change
- Only supply can change.
- Both demand and supply can change
- None of these
Answer: 3. Both demand and supply can change
Question 6. The condition for producer equilibrium is
- TR = TVC
- MC = MR
- TC = TAC
- None of these
Answer: 2. MC = MR
Conditions for the producer’s equilibrium are :
- MC = MR.
- MC should cut MR from below.
Question 7. An increase in supply with demand remaining the same, brings about.
- An increase in equilibrium quantity and a decrease in equilibrium price.
- An increase in equilibrium price and a decrease in equilibrium quantity.
- Decrease in both equilibrium price and quantity.
- None of these.
Answer: 1. An increase in equilibrium quantity and a decrease in equilibrium price.
An increase in supply with demand remaining the same,
When there is an increase in supply, demand remains the same, the equilibrium price of goods decreases, and the equilibrium quantity increases. It is evident from the following diagram.
Question 8. When the price of a commodity is ₹ 20, the quantity demanded is 9 units and when its price is ₹ 19, the Quantity demanded is 10 units. Based on this information, what will be the marginal revenue resulting from an increase in output from 9 units to 10 units?
- ₹ 20
- ₹ 19
- ₹ 19
- ₹ 01
Answer: 3. ₹ 19
When the price of a commodity is ₹ 20, the quantity demanded is 9 units and when its price is ₹ 19, the Quantity demanded is 10 units. Based on this information,
The marginal revenue resulting from an increase in output from 9 units to 10 units is ₹10
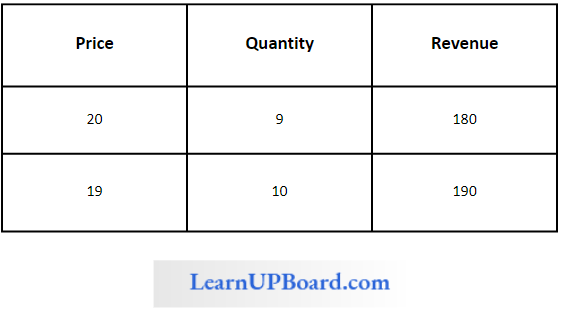
Marginal Revenue is (190-180) = ₹ 10
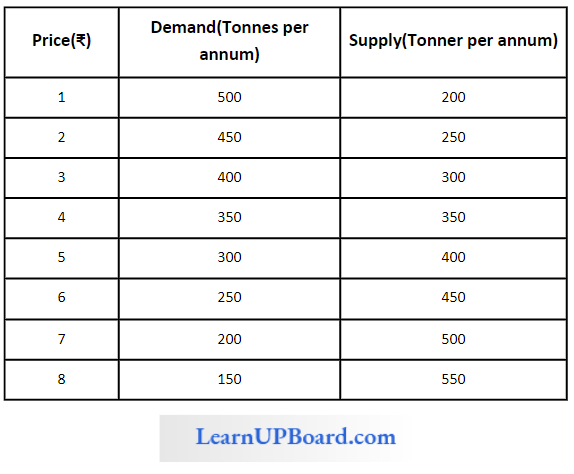
Question 9. From the following table, what will be the equilibrium market price
- ₹ 2
- ₹ 3
- ₹ 4
- ₹ 5
Answer: ₹ 3. 4
The equilibrium Market price is ₹ 4 because at this price demand and price are equal so the market price will tend to settle at this figure.
Question 10. If the price of a commodity is fixed, then with every increase in its sold quantity the total revenue will ___________________ and the marginal revenue will____________________
- Increase, also increase
- Increase, remain unchanged
- Increase, decline
- Remain fixed, increase.
Answer: 2. Increase, remain unchanged
If the price of a commodity is fixed, then with every increase in its sold quantity, the total revenue will increase, and the marginal revenue will remain unchanged. Marginal revenue is the change in total revenue. Resulting from the sale of an additional unit of the commodity.
Question 11. If supply decreases and demand remains constant, then equilibrium price will be?
- Increases
- Decreases
- No change
- Become Negative
Answer: 1. Increases
When supply falls and demand remains constant, then there will be excess demand in the economy, and to meet the
demand the price of the commodity will rise (Increase).
Question 12. According to Pigou, first-degree price discrimination charges prices to;
- Individual capacity
- Quantities sold
- Location
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Individual capacity
Under first-degree price discrimination, the monopolist separates the market into each consumer and charges them the price they are willing and able to pay thereby extracting the entire consumer surplus.
Question 13. What is the shape of the monopolist Average Revenue Curve?
- Falls from left to right
- Is parallel to X – axis
- Is parallel to Y – axis
- Rise from left to right
Answer: 1. Falls from left to right
The shape of the monopolist average revenue curve falls from left to right.
Question 14. What is the shape of a perfectly competitive Average Revenue Curve?
- Parallel to the X-axis
- Parallel to the Y-axis
- Fall from left to right
- Rise from left to right
Answer: 1. Parallel to the X axis
The curve of average revenue is parallel to X axis as per the perfect competition market.
Question 15. Monopsony means
- Where there are large firms
- There is a single buyer
- A small number of large buyers
- Single seller and single buyer
Answer: 2. There is a single buyer
A monopsony is a market condition in which there is only a single buyer – A single buyer dominates the market.
Question 16. When an increase in demand is equal to an increase in supply and the equilibrium price remains constant, then what about equilibrium quantity?
- Increases
- Decreases
- Remains Constant
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Increases
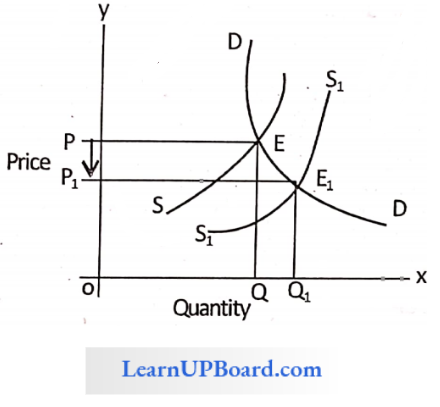
When an increase in demand is equal to an increase in supply and the equilibrium price remains constant
In case there is a simultaneous increase in demand as well as supply without a price change, the new equilibrium point will be. It can be observed that the quantity has moved from Q to Q1, changing the equilibrium point from E to E1 i.e. if the equilibrium price remains unchanged/constant, the equilibrium quantity will increase
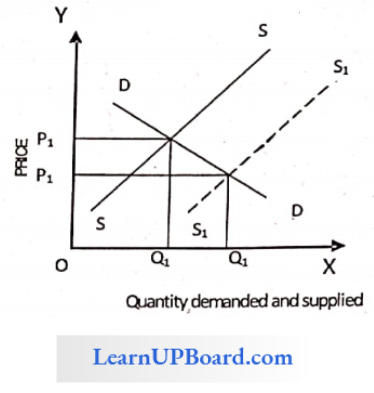
Question 17. An increase in supply with demand remaining the same brings about
- An increase in equilibrium quantity and a decrease in equilibrium price.
- An increase in equilibrium price and a decrease in equilibrium quantity.
- Decrease in both equilibrium price and quantity.
- None of these
Answer: 1. An increase in equilibrium quantity and a decrease in equilibrium price.
An increase in supply with demand remaining the same brings about.
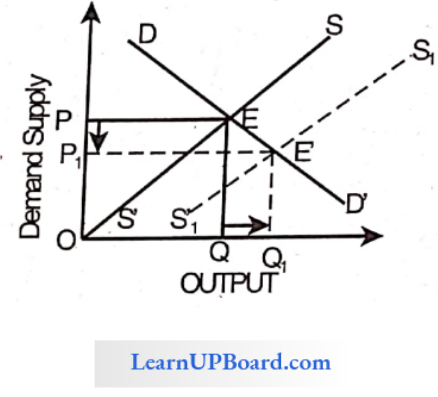
In the above diagram, we can see that when there is an increase in. Supply curve i.e. from SS’ to S1S1′ where the demand curve remains the same i.e. DD’ with price ‘P’ and quantity ‘Q’.
Then as a result there is an increase in equilibrium quantity i.e., from Q for and price decreases i.e., from P to P1, And the equilibrium point shifted downwards, i.e. from E to E’.
Question 18. The equilibrium quantity increases, but the charges in the equilibrium price are uncertain when.
- Both demand and supply decrease
- Demand increases and supply decreases
- Both demand and supply increase
- Demand decreases and supply increases
Answer: 3. Both demand and supply increase
Two possible outcomes when the supply and demand curve shift in the same direction:
- When both demand and supply increase, the equilibrium quantity increases, but the change in equilibrium price is uncertain.
- When both demand & supply decrease, the equilibrium quantity decreases, but the change in equilibrium price is uncertain.
Question 19. When both demand and supply increase, how does it affect the equilibrium quantity and equilibrium price?
- The equilibrium quantity increases, but the change in equilibrium price is uncertain.
- The equilibrium quantity decreases, but the change in equilibrium price is uncertain.
- Equilibrium price increases but the change in equilibrium quantity f is uncertain
- Equilibrium price decreases but the change in equilibrium quantity is uncertain.
Answer: 1. When both demand and supply increase. The equilibrium quantity increases, but the change in equilibrium price is uncertain increases but the change in equilibrium price is uncertain.
Question 20. When there is a change in demand and a change in supply, what will be the net influence on price if the change in supply is greater than the change in demand?
- Increase
- Decrease
- No effect
- uncertain change
Answer: 1. Increase
When the supply increases, it results in an excess supply at the earlier equilibrium price. So there will be competition among sellers, which reduces the price. A price fall leads to a rise in demand and a fall in supply.
Question 21. Under which of the following market conditions? both average and marginal revenue are the same?
- Perfect competition
- Monopolistic competition
- Monopoly
- Oligopoly
Answer: 1. Perfect competition
Average Revenue = Marginal Revenue = Perfect competition only.
Question 22. ‘Average revenue curve’ is also known as
- Production possibility curve
- Supply curve
- Demand curve
- Indifference curve
Answer: 3. Demand curve
Another name for the Average Revenue Curve is the Demand Curve.
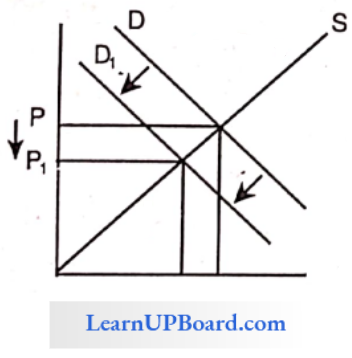
Question 23. When demand for a commodity is decreasing as a result of fall in income and its supply remains constant, what will be impact on its price?
- Price increases
- Price decreases
- No change
- Uncertain change
Answer: 2. Price decreases
If supply is constant and demand decreases, the equilibrium price decreases.
Question 24. In which of the following, prices are determined by market forces of demand and supply?
- Duopoly Competition
- Perfect Competition
- Monopolistic Competition
- Natural Market
Answer: 2. Perfect Competition
Under Perfect Competition, market forces of demand and supply determine the prices and all sellers and buyers individually are price takers.
Question 25. Suppose a seller realizes ₹100 by selling the 10th unit of commodity and. ₹ 120 by selling the 11th unit. What is the MR of, the 11th unit? 1
- 100
- 120
- 20
- 10
Answer: 3. 20
Suppose a seller realizes ₹100 by selling the 10th unit of commodity and. ₹ 120 by selling the 11th unit.
MRn = TR11-TR10 .
MR11 = TRn-TRn-1 .
120- 100
= 20
MR of, the 11th unit = 20
