CA Foundation Economics – Price Determination Different Markets Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Which of the following is not an essential condition of pure competition?
- A large number of buyers and sellers
- Homogeneous product
- Freedom of entry
- Absence of transport cost
Answer: 4. Absence of transport cost
Pure competition is a part of perfect competition. The essential conditions of pure competition are:
- A large number of buyers and sellers
- Homogeneous products ‘
- Freedom of entry and exit of firms.
Question 2. Under which of the following forms of market structure does a firm have no control over the price of its product:
- Monopoly
- Oligopoly
- Monopolistic competition
- Perfect competition
Answer: 4. Perfect competition
Perfect competition is a price-taking firm. The prices in such a, market are determined by market forces of demand and supply. Neither the buyer nor the seller can influence the prices.
Question 3. Given the relation mR = P(1-1/e) if e>1 then
- MR > 0
- MR< 0
- MR = 0
- None
Answer: 1. MR > 0
Question 4. Profits of the firm will be more at
- MR = MC
- Additional revenue from extra units equals its additional cost
- Both of the above.
- None
Answer: 3. Both of the above.
Profits of the firm are maximum at profit maximization level i.e. MC=MR, Additional revenue from extra unit equals its additional cost.
Question 5. What should the firm do when Marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost?
- The firm should expand the output
- The effect should be made to make them equal
- Prices should be covered down
- All of these
Answer: 1. Prices should be covered down
When marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost, the producer shall expand output as it is profitable for the firm to expand output.
Question 6. Under a monopoly price discrimination depends upon
- The elasticity of demand for the commodity
- The elasticity of supply for a commodity
- Size of market
- All of above
Answer: 1. Elasticity of demand for commodity
Monopoly has a feature of price discrimination i.e. charging different prices from, different customers. It depends upon the elasticity of demand of various customers. Differences in elasticity forces the monopolist to charge different prices from different customers.
Question 7. Firms in a monopolistic market are price
- Takers
- Givers
- Makers
- Acceptors
Answer: 3. Makers
In a monopoly market, the prices are decided by the monopolist. He is the maker of the price. Buyers cannot influence the prices.
Question 8. The market which has two firms are known as :
- Oligopoly
- Duopoly
- Monopsony
- Oligopsony
Answer: 2. Duopoly
Duopoly is composed of two words – “Duo” and “Poly”. Duo means two and “poly” means seller. Hence, a duopoly is a market where there are two sellers.
Question 9. Monopolist can determine
- Price
- Output
- Either price or output
- None
Answer: 3. Either price or output
A monopolist firm is a price-maker firm. In this market, only the seller can influence the prices. He can determine either output or price.
Question 10. MR of the th unit is given by
- TRn/TRn-1
- TRn + TRn-1
- TRn-TRn-1
- All of these
Answer: 3. TRn-TRn-1
Marginal revenue is the addition made to the total revenue by producing one more unit of a commodity.
∴ It is expressed as: M.R.n =TRn-TRn-1
Question 11. The market structure in which the number of sellers is small and there is interdependence in decision-making by the firms is known as
- Perfect competition
- Oligopoly
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic competition
Answer: 2. Monopoly
Oligopoly is often described as “competition among the few”. It is characterized by a small number of sellers who are interdependent in decision-making.
Question 12. In perfect competition, since the firm is a price taker, the ____________________ curve is a straight line
- Marginal cost
- Total cost
- Total revenue
- Marginal revenue
Answer: 4. Marginal revenue
In a perfectly competitive market, the prices of all the firms are the same. Hence, there is no change in marginal revenue and the MR curve is a straight line.
Question 13. For a discriminating monopolist, the condition for equilibrium is
- MR > MC
- MR1 = MR2
- MRa = MRb = MC
- All of the above.
Answer: 3. MRa = MRb = Mc
One of the important conditions of price discrimination is that the seller should be able to divide his market into two or more submarkets. If marginal revenue in both markets is different then price discrimination is possible.
The seller will transfer his products more to that market which gives more marginal revenue. Suppose the MR of market A is more than market B.So the seller will transfer the products from market B to market. Due to this, the prices of market B will rise and A will fall.
Gradually the MR of B will start increasing. He will continue to transfer units from B to A till the marginal revenue from both markets becomes equal. After this point, it will be no longer profitable to transfer units and hence the position of equilibrium will be when
MRa = MRb = Mc
Question 14. The average revenue curve is also known as
- Profit curve
- Demand curve
- Supply curve
- Average cost curve.
Answer: 2. Demand curve
In a perfect competition market, the same price prevails throughout the market. Since the price is constant hence the demand of the commodity determines the total revenue and average revenue. Due to this reason, the A.R. curve can also be called the demand curve.
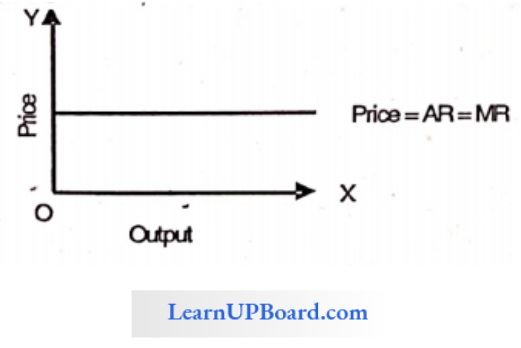
Question 15. Given, AR = 5 and Elasticity of demand = 2 Find MR.
- +2.5
- -2.5
- +1.5
- + 2.0
Answer: 1. +2.5
Given, AR = 5 and Elasticity of demand = 2
MR = AR × (e-1)/ e
= 5× \(\frac{2-1}{2}\)
= 5 × \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= + 2.5
Question 16. If a seller obtains ₹ 3,000 after selling 50 units and ₹ 3,100 after selling 52 units, then marginal revenue will be
- ₹ 59.62
- ₹ 50.00
- ₹ 60.00
- ₹ 59.80
Answer: 2. ₹ 50.00
A seller obtains ₹ 3,000 after selling 50 units and ₹ 3,100 after selling 52 units
S.P of 50 units = ₹ 3,000
S.P of 52 units = ₹ 3, 100
∴ S.P of additional 2 units = ₹ 100 & marginal revenue of 1 unit
= \(\frac{100}{2}\)
= ₹ 50
Question 17. A firm will close down in the short period if its AR is less than :
- AC
- AVC
- MC
- None of the above
Answer: 2. AVC
In the short run, if the firm can meet its VC and a part of the fixed cost it will try to continue production. If it recovers a part of FC, it will be beneficial to continue production. However, if a firm is unable to meet its AVC, it will be better for it to shut down.
Question 18. Which one of the following expressions is correct for Marginal Revenue?
MR = AR (1-e)/e
MR = TR1 – TRn-1
MR – ΔTR / Δ Q
MR = TR/Q
Answer: 3. MR – ΔTR / Δ Q
Marginal revenue is the rate of change in total revenue resulting from the sale of an additional unit.
- Where MR is the marginal revenue
- TR is the total revenue
- Q is the number of commodities sold
- Stands for small change.
Question 19. The market for the ultimate consumer is known as
- Wholesale market
- Regulated market
- Unregulated market
- Retail market
Answer: 4. Retail market
The market for the ultimate consumer is known as the retail market.
Question 20. For a firm to become profitable it should expand output whenever
- Marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost
- Marginal revenue is less than marginal cost
- Marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost
- Average revenue is greater than average cost.
Answer: 3. Marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost
It will be profitable for the firm to expand output whenever marginal revenue is greater than the marginal cost, and to keep on expanding
output until marginal revenue equals marginal cost. Not only marginal cost should be equal to marginal revenue, but its curve should cut the marginal revenue curve from below.
Question 21. Based on the nature of transactions, a market may be classified into
- Spot market and future market
- Regulated market and unregulated market
- Wholesale market and retail market
- Local market and national market.
Answer: 1. Spot market and future market
Based on the nature of transactions market may be classified into:
- Spot Market: It refers to those markets where goods are physically transacted on the spot.
- Future Market: It is related to a transaction that involves contracts of a future date.
Question 22. In a very short period of the market:
- Supply changes but demand remains the same
- Supply changes but the price remains the same
- Supply remains fixed
- Supply and demand both changes
Answer: 3. Supply remains fixed
In a very short period market, it is not possible and easy to increase the supply as it is very difficult to install new machinery or increase more labor so, in this market supply is fixed.
This leads to only profitable commodities like vegetables flowers, fish, eggs, fruit, milk, etc. which are perishable and are examples of a very short period market.
Question 23. Which of the following is correct?
- MR = AR (e – 1)/e
- MR = AR (e +1)/e
- MR = AR (1- e)/e
- None of the above
Answer: 1. MR = AR (e – 1)/e
MR. AR and price elasticity of demand are uniquely related to one another through the formula, MR = AR × (e-1) / e, therefore, is the
Question 24. According to Behavioural Principles.
- A firm should not produce at all if its total variable costs are not met.
- A firm will be making maximum profits by expanding output to the’ level where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
According to Behavioural Principles:
- Principle 1: A firm should not produce at all if its total variable costs are not met is better to shut down in such a case.
- Principle 2: The firm will be making maximum profits by expanding output to the level where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost as additional units add more to revenue than to cost.
Question 25. Market consists of
- Buyer and Seller
- One price for one product at a given time
- Both (1) and (2)
- None
Answer: 3. None
A market is a collection of buyers and sellers with the potential to trade.
The elements of a market are:
- Buyers and sellers
- A product or service.
- Bargaining for a price
- Knowledge about market conditions and
- One price for a product or service at a given time.
Question 26. Demand for a product is unitary elastic then
- MR = 0
- MR > 0
- MR<0
- None of the above
Answer: 1. MR = 0
Marginal revenue, average revenue, and price elasticity are related through the following formula
MR = AR × (e-1)/e, e = Price elasticity of demand
If elasticity = 1, MR = AR × (1-1)/1
MR = AR × (0)/1
= 0
Question 27. Which of the following is true, when the firm is at equilibrium?
- MC < MR
- MC curve cuts the MR curve from below
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of the above
Answer: 2. The MC curve cuts the MR curve from below
At the point of equilibrium, MC = MR and
MC curves cut the MR curve from below. At this point, a firm will earn maximum profits,
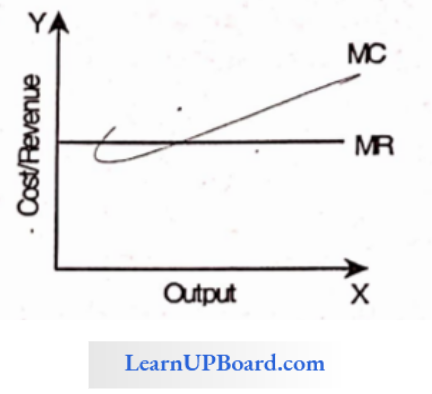
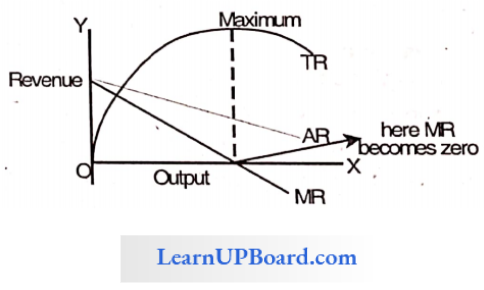
Question 28. When TR is at its peak then MR is equal to
- Zero
- Positive
- Negative
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Zero
The relationship between TR and MR is that initially.
- Total Revenue curve increases at a diminishing rate due to diminishing marginal revenue.
- When marginal revenue becomes zero, total revenue is maximum. t
- Total revenue starts falling again when marginal revenue is negative.
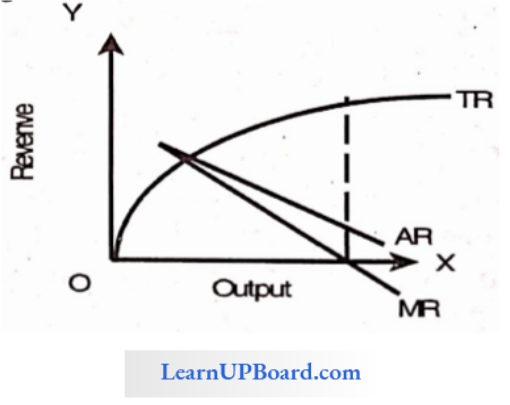
Question 29. When the price is ₹ 20, the Quantity demanded is 10 units, and the price is decreased by 5% then the quantity demand is increased by 10% then the Marginal revenue is
- 10
- 11
- 9
- 20
Answer: 3. 9
When the price is ₹ 20, the Quantity demanded is 10 units, and the price is decreased by 5% then the quantity demand is increased by 10%
MR = TR/Q ; TR = P x Q
TR (existing)= 20 × 10 = 200
TR (new) = ((20 – (5% of 20)) × ( 10 + (10% of 10)).
= 19 × 11 = 209
ΔTR = 209 – 200 = 9
ΔQ = 20-19 = 1
MR = \(\frac{9}{1}\)
= 9
Question 30. Which of the following represents the supply curve in a perfect competitive market?
- MC curve
- AC curve
- AR curve
- MR curve
Answer: 1. MC curve
A perfectly competitive firm’s supply curve is that portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above the minimum of the average variable cost curve.
In other words, the firm produces by moving up and down along its marginal cost curve. The marginal cost curve is thus the perfectly competitive firm’s supply curve.
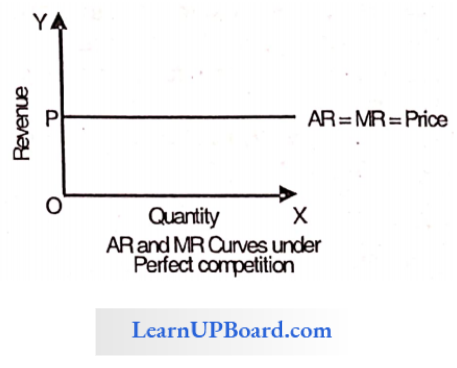
Question 31. When TR is max, then MR is
- Zero
- One
- Both (1) & (2)
- None
Answer: 1. Zero
When Total Revenue is max, then Marginal Revenue is zero.
Question 32. ___________ is also called a free market as there are no stipulations on the transactions
- Unregulated
- Regulated
- Retail
- Spot
Answer: 1. Unregulated
- Unregulated Market: It is also called a free market as there are no stipulations on the transactions.
- Regulated Market: In this market, transactions are statutorily regulated to put an end to unfair practices. Such markets may be established for specific products or a group of products.
- Example: Stock exchange.
Question 33. In this market, transactions involve contracts with a promise to pay and deliver goods at some future date
- Spot market
- Future market
- Unregulated market
- Retail market
Answer: 2. Future market
Based on the Nature of Transactions
- Spot or cash Market: Spot transactions or spot markets refer to those markets where goods are exchanged for money payable either immediately or within a short period.
- Forward or Future Market: In this market, transactions involve contracts with a promise to pay and deliver goods at some future date.
Question 34. A firm reaches its shutdown point
- When the price is less than AVC in the long run.
- When the price is less than AVC in the short run.
- When the price is more than AC in the long run.
- When the price is more than AC in the short run.
Answer: 2. When the price is less than AVC in the short run.
A firm reaches its shutdown point when the price is less than AVC in the short run
i.e. AR < AVC
AVC = Average Variable Cost AR = Average Revenue
It is a matter of common sense that a firm should produce only if it will do better by producing than by not producing. The firm always has the option of not producing at all.
If a firm’s total revenues are not enough to make good even the total variable cost, the firm should shut down.
In other words, a competitive firm should shut down if the price is below AVC.
Shutting down is temporary and does not necessarily mean going out of business.
Question 35. The demand for goods increases from 15 units to 16 units if the price decreases from ₹ 40 to ₹ 38. What will be the MR of the 16th unit?
- 8
- 16
- 38
- 15
Answer: 1. 8
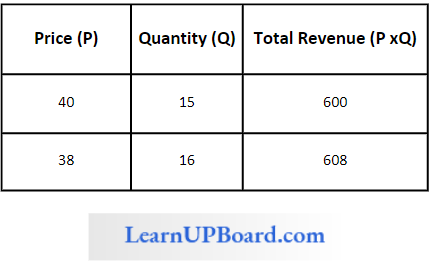
The demand for goods increases from 15 units to 16 units if the price decreases from ₹ 40 to ₹ 38.
MRn= TRn– Trn-1
MR16 = TR16– TR16-1
MR16 = TR16– TR15
MR16 = 608 – 600
MR16 = 8
Question 36. If a seller obtains ₹ 6,000 after selling 50 units and ₹ 6,204 after selling 53 units, then marginal revenue will be
- 204
- 68
- 118
- 120
Answer: 2. 68
If a seller obtains ₹ 6,000 after selling 50 units and ₹ 6,204 after selling 53 units
MR = TR/ Quantity
TR = P × Quantity
6000 = P × 50
⇒ \(\frac{6000}{50}\) = P × 50
120 = P
MR = \(\frac{6204-6000}{53-50}\)
= \(\frac{204}{3}\)
= 68
Question 37. Based on the nature of the transaction, a market may be classified into
- Regulated and Unregulated Market –
- Wholesale and Retail Market
- Cash and Forward Market
- National and International Market
Answer: 3. Cash and Forward Market
Cash and forward market: In this market, transactions involve contracts v/fth a promise to pay and deliver goods at some future date.
Question 38. When a firm produces 7 units of production and the TR is ₹ 42 after raising the production to 8 units TR reaches ₹46 marginal revenue will be
- 6
- 4
- 5
- 8
Answer: 2. 4
Question 39. A market where goods are exchanged for money payable either immediately or within a short space of time.
- Forward market
- Regulated market
- Spot market
- Wholesale market
Answer: 3. Spot market
Spot or cash market: Spot transactions or spot markets refer to those markets, where goods are exchanged for money payable, either immediately or within a short spot time.
Question 40. What is the average revenue when ABC Ltd. sells 121 units and TR is ₹ 6,050?
- 6,000
- 6,050
- 50
- 100
Answer: 3. 50
Average Revenue = Total revenue/ Number of units
= \(\frac{6050₹}{121units}\)
= ₹ 50 per unit
Question 41. When ABC Ltd. sells 130 units at ₹ 50 p.u. then total revenue will be
- 18,550
- 12,050
- 6,000
- 6,500
Answer: 4. 6,500
Total Revenue = Number of units × Revenue per unit
= 130 × ₹ 50
= ₹ 6500/-
Question 42. Answer the following questions
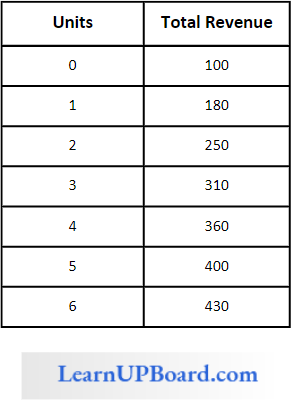
Find the marginal revenue at 5 th unit is:
- 60
- 55
- 45
- 40
Answer: 4. 40
Marginal revenue at 5th unit = TUn – TUn-1
= 400 – 360
= 40/-
Question 43. Which one is not a part of the elements of a market?
- Buyers and sellers
- A product or service
- Bargaining for a price
- Volume of business
Answer: 4. Volume of business
The element that is not a part of the market is the volume of business.
Question 44. In the market structure, the demand curve is also known as
- Marginal cost curve
- Average revenue curve
- Total production curve
- Marginal utility curve
Answer: 2. Average revenue curve
In the market structure demand curve is also known as the Average revenue curve
Question 45. The secular period is also known as
- Very short period
- Very long period.
- Short period
- Long period
Answer: 2. Very long period
The secular period is also known as the very long period.
Question 46. The total revenue curve initially increases at a diminishing rate due to
- Diminishing average revenue curve.
- Diminishing marginal revenue curve.
- Diminishing average fixed revenue curve.
- Diminishing cost curve.
Answer: 2. Diminishing marginal revenue curve.
TR Curve, i.e. Total revenue curve initially increases at a diminishing rate due to the diminishing marginal revenue at stage 1 of the law of variable proportion.
Question 47. The total revenue curve is
- Positively Sloped
- Negatively Sloped
- Downward Sloped
- Vertical to X axis
Answer: 1. Positively Sloped
Total revenue i.e., (TR) curve is positively sloped in the case of a perfect competitive market.
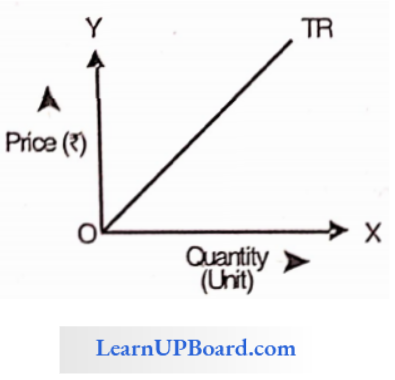
Question 48. Marginal revenue will be positive where the price elasticity of demand is
- Zero
- More than one
- Less than one
- Equal to one
Answer: 2. More than one
Marginal revenue, average revenue, and price elasticity are related through the following formula.
MR = AR × (e-1) / e, e = Price elasticity of demand,
If the elasticity of more than one e > 1 MR will be positive
MR = AR × \(\frac{2-1}{2}\)
MR = 2 × \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= 1
Question 49. Does a seller realize ₹ 25,000/- after selling 15 units and he realizes ₹35,000/- after selling 25 units, what is the marginal revenue here?
- 2,500/-
- 100/-
- 1,000/-
- 3,500/-
Answer: 3. 1,000/-
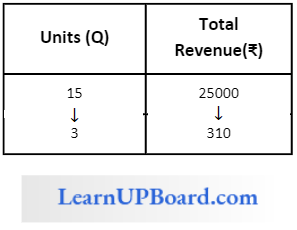
MR = TR/Q
MR = \(\frac{10000}{10}\)
= 1000
Question 50. Which of the following is the price at which the quantity demanded of a commodity is equal to the quantity supplied of the commodity and there is no unsold stock or no unsupplied demand?
- Selling Price
- Market Clearing Price
- Asking Price
- Future Price
Answer: 2. Market Clearing Price
Market clearing price is the price at which the quantity demanded of a commodity is equal to the quantity supplied of the commodity and there is no unsold stock or no unsupplied demand.
Question 51. Which of the following is not an element of a market?
- Knowledge about market conditions.
- No bargaining for a price
- A product or service
- Buyer and Seller
Answer: 2. No bargaining for a price
The elements of a market are:
- Buyers and sellers
- A product or Services
- Bargaining for a price
- Knowledge about market conditions
- One price for a product or service at a given time
Question 52. The________________ is the market where the commodities are bought and sold in bulk or large quantities transactions generally take place between trades.
- Wholesale market
- Regulated market
- Local market
- Retail market
Answer: 1. Wholesale market
Wholesale market is the market where the commodities are bought and sold in bulk or large quantities, transacties is generally take place between trades.
Question 53. Based on the nature of transactions market can be classified as
- Wholesale market and retail market.
- Future market and spot market.
- Regulated market and unregulated market.
- Money market and future market.
Answer: 2. Future market and spot market.
Based on the Nature of Transactions:
- Spot or cash market
- Forward or future market
Question 54. Demand Curve is also known as
- MR Curve
- AR Curve
- MC Curve
- MR Reserve
Answer: 1. MR Curve
The demand curve is also known as the Marginal revenue curve in a market.
Question 55. Prices in monopoly are higher than prices under
- Oligopoly
- Duopoly
- Monopoly
- Perfect Competition
Answer: 4. Perfect Competition
Prices in a monopoly are high as compared to prices in perfect competition. Monopolies are price makers and charge prices to increase their revenues more as compared to other market forms.
Question 56. In an Oligopoly upper part shows which elasticity
- Less than
- Greater than
- Zero
- Negative
Answer: 2. Greater than
In oligopoly, the kinked demand curve has two parts the upper part being relatively more elastic and the lower part being less elastic than the upper part.
Question 57. Which of the following is closely related to perfect competition?
- Mobiles
- Cars
- Utensils
- Agricultural Products
Answer: 4. Agricultural Products
Agricultural products are not highly competitive markets but are closely related to a perfect competitive market.
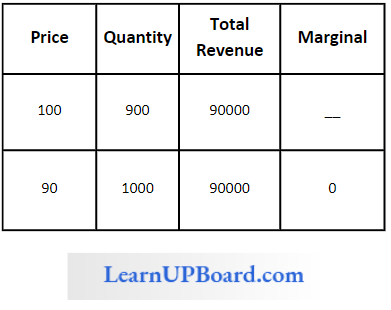
Question 58. If the price of good is X 100 per unit & quantity demanded is 900 units. If the price decreases to X 90 per unit then the demand increases to 100 units calculate marginal revenue
- 0
- 10
- 90
- 100
Answer: 1. 0
If the price of good is X 100 per unit & quantity demanded is 900 units. If the price decreases to X 90 per unit then the demand increases to 100 units
Question 59. No substitutions are found in which form of Market
- Perfect competition
- Oligopoly
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic Competition
Answer: 3. Monopoly
No substitutes are found in the monopoly form of the market. An oligopoly has fewer substitutes as compared to a monopoly, but in perfect competition, every product is a substitute of each other.
Question 60. The market is the direct relationship between
- Buyer and seller.
- Whole seller and retailer
- Consumer and manufactures
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Buyer and seller.
The market is the direct relationship between a buyer and seller. Where the buyer and seller are the essential elements of the market and they influence the price.
Question 61. Which commodity is best for the short-term period market?
- Fruits and Vegetables
- Automobiles
- Electronic goods
- All of the above.
Answer: 1. Fruits and Vegetables
For a short-term period market is best for perishable goods like fruits and vegetables that are needed in day-to-day life.
Question 62. Demand for a firm’s product when expressed as in percentage of an industry demand it signifies the firm.
- Product share
- Market share
- Demand
- Supply
Answer: 2. Market share
Demand for a firm’s product when expressed as in percentage of an industry demand it signifies the market share of the firm.
Question 63. Which of the following is true?
- Perfect competition sells a heterogenous product
- Oligopolistic incurs a good amount of selling cost.
- Monopolist always earns super-normal profits.
- Oligopolistic economies do not get a hike in their normal profit.
Answer: 2. Oligopolistic incurs a good amount of selling cost.
In an oligopolistic market, advertising & selling and have great importance. Therefore, oligopolistic incurs a good amount of selling cost.
Question 64. Which of the following is correct?
- Total revenue is equal to price × Quantity
- The sum of Average Revenue
- The sum of Quantity sold X marginal revenue
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Total revenue is equal to price x Quantity
The formula for the total revenue (TR) is
TR = P × Q, where P is price and Q is quantity sold.
Question 65. Who introduced the ‘time element’ in economics?
- Adam Smith
- Alfred Marshall
- Robert Malthus
- J. M. Keynes
Answer: Alfred Marshall
Alfred Marshall introduced the time element in economics. In the parts of very short period, short period, long period & very long period.
Question 66. Which of the following is not a characteristic of the market?
- Advertisement and awareness
- Buyer and seller
- Bargaining power
- Product or service
Answer: 1. Advertisement and awareness
The main characteristic of a market is the buyer and seller, they have bargaining power and they have products or services.
Question 67. In the initial stage, total revenue is increasing at a decreasing rate due to
- Diminishing marginal revenue
- Negative marginal revenue
- Multi-level marginal revenue
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Diminishing marginal revenue
TR increases as long as MR is positive and declines (has a negative slope) when MR is negative. TR curve initially increases at a diminishing rate due to diminishing MR and reaches a maximum and then it falls when MR becomes zero, the TR is maximum and the slope of TR is zero.
Question 68. When MR = MC the firm will incur
- Maximum profits
- Minimum profits
- Maximum losses
- Minimum losses
Answer: 1. Maximum profits
Profits are maximum when MR = MC and the MC curve cuts the MR curve from below.
Question 69. The price of goods expresses value.
- Exchange
- Cost
- Demand
- Fair
Answer: 1. Exchange
The price of Goods expresses its exchange value in the market.
Question 70. Which one of the following is not an element of the market?
- Buyer
- Service
- Firm
- Bargaining for Price
Answer: 3. Firm
The elements of the market are buyers and sellers, goods or services, bargaining for price, knowledge about the market conditions, and a price for goods or services at a given time.
Question 71. Based on the nature of the transaction, a market can be classified into which of the following?
- Cash and Forward Market
- National and International Market
- Organized and Unorganized Market
- Retail and Wholesale Market.
Answer: 1. Cash and Forward Market
Based on the nature of transactions, the market has been classified into cash and forward market.
