CA Foundation Economics Price Output Determination Under Different Market Forms Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. A competitive firm in the short run incurs losses. The firm continues production, if
- P > AVC
- P = AVC
- P < AVC
- P ≥ AVC
Answer: 4. P ≥AVC
In the short run, if the competitive firm is incurring losses then it will continue production only if its price is greater or equal to the average variable cost. If the price is less than the variable cost it means neither the fixed cost nor the variable cost can be covered. In such a situation, the producer shall stop production.
Question 2. Under market conditions, firms make normal profits in the long run
- Perfect competition.
- Monopoly
- Oligopoly
- None
Answer: 1. Perfect competition.
A perfectly competitive market is characterized by the free entry and exit of firms. In the long run, if the firm makes a profit, more sellers enter the industry and hence the profits are reduced to the equilibrium level. If there are losses, then more firms leave the industry resulting in an increase in profits to the equilibrium level. Hence competitive firms always incur normal profits.
Question 3. A monopolist can maximize his profits when
- His output is maximum
- He charges a high price
- His average cost is the minimum
- His marginal cost is equal to the marginal revenue
Answer: 4. His marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue
Profit maximization level is the level at which :
MC = MR
Question 4. Under which of the following market structures AR of the firm will be equal to MR?
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic Competition
- Oligopoly
- Perfect Competition
Answer: 4. Perfect Competition
In perfect competition firms are price takers. Hence they offer the same price i.e. the prices are the same throughout the market. Since the prices are the same or the AR and MR are also equal.
Question 5. Under Monopolistic competition, the cross elasticity of demand for the product of a single firm would be :
- Infinite
- Highly elastic
- Highly inelastic
- Zero
Answer: 2. Highly elastic
In the case of monopolistic competition, the products are less differentiated and all the brands are close substitutes of one another hence it has high elastic of cross elasticity.
Question 6. When AR = ₹ 10 and AC = ₹ 8 the firm makes
- Normal profit
- Net profit
- Gross profit
- Supernormal profit
Answer: 4. Supernormal profit
When AR = ₹ 10 and AC = ₹ 8
A firm makes a normal profit when AC = AR.
In the given question AR = 10 and AC = 8 i.e. average revenue is greater than average cost. So the firm makes a super normal profit. (Profit above normal profit is super normal profit).
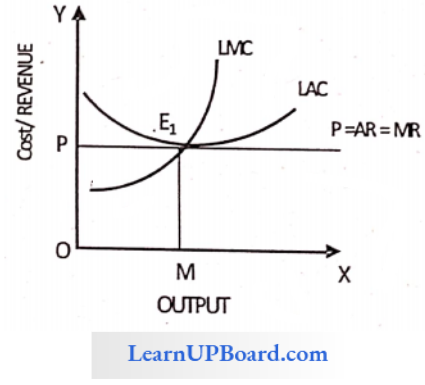
Question 7. What are the conditions for the long-run equilibrium of the competitive firm?
- LMC = LAC = P
- SMC = SAC = LMC
- P = MR
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
In the long run, competition will be at equilibrium at LMC = LAC = P ’ (When long-run marginal cost, long-run average cost, and price are equal) Also in the long run the firms operating under perfect competition is efficient at point E’
Where P = MR and SMC = SAC = LMC. –
Question 8. The kinked demand curve hypothesis is given by
- Alfred marshal
- A.C Pigou
- Sweezy
- Hicks & Allen
Answer: 3. Sweezy
The kinked Demand hypothesis was given by Sweezy, an American economist.
Question 9. Supernormal profits occur, when
- Total revenue is equal to total cost
- Total revenue is equal to variable cost
- The average revenue is more than the average cost
- Average revenue is equal to the average cost
Answer: 3. Average revenue is more than the average cost
Supernormal profits are the profits over and above the normal profit. Normal profit is included in the cost of the product (This profit is for recovering the fixed cost). If the product is sold above its cost supernormal profits occur. In other words, when AR > AC, supernormal profits occur.
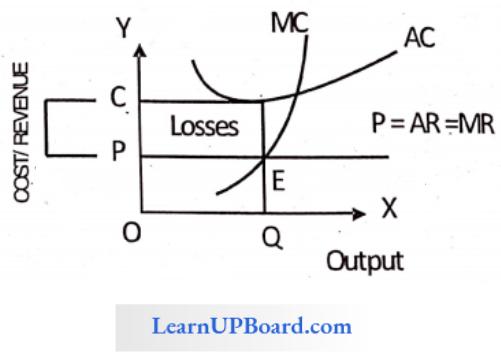
Question 10. If under perfect competition, the price line lies below the average cost curve, the firm would
- Make only Normal profits
- Incur losses
- Make abnormal profit
- Profit cannot be determined
Answer: 2. Incur losses
In perfect competition, if the price line (AR and MR curve) is below the AC curve the firm incurs losses i.e. AR or MR is less than AC.
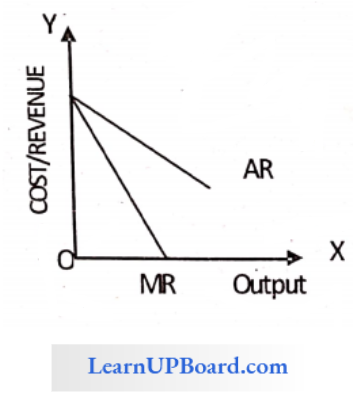
Question 11. The MR curve cuts the horizontal line between the Y-axis and the demand curve into
- Two unequal parts
- Two equal parts
- May be equal or unequal parts
- None of these
Answer: 2. Two equal parts
The slope of the average revenue curve is twice the slope of the marginal revenue curve hence MR curve units it into two equal parts.
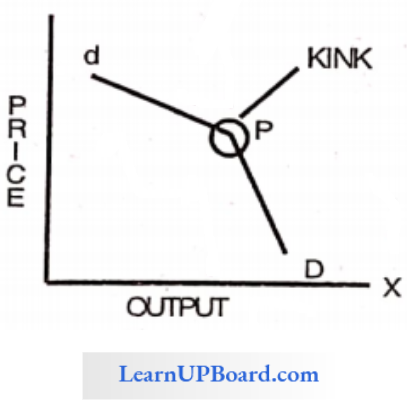
Question 12. The kinked demand curve is observed in _________________
- Duopoly market
- Monopoly market
- Competitive market
- Oligopoly market.
Answer: 4. Oligopoly market
In oligopolistic industries, prices remain sticky or inflexible for a long time. They tend to change infrequently even if in the face of declining cost. These inflexibilities lead to the kink shape of the demand curve. Therefore, oligopolistic markets have a kinked demand curve.
Question 13. Competitive firms in the long run earn
- Supernormal profit.
- Normal profit
- Losses
- None
Answer: 2. Normal profit
Question 14. For a monopolist, the necessary condition for equilibrium is
- P = MC
- P = MR = AR
- MR = MC
- None
Answer: 3. MR = MC
Question 15. A firm is in equilibrium when
- MC = MR
- Fixed costs exceed revenue
- Variable costs exceed revenues
- Total costs exceed revenues
Answer: 3. Variable costs exceed revenues
In the short run, the firms will be at a break-even point when variable cost = revenues. When variable cost is above revenues it means that the firm can neither recover its variable cost nor fi/ed cost. In this situation, the producer cannot survive for a long so he may shut down.
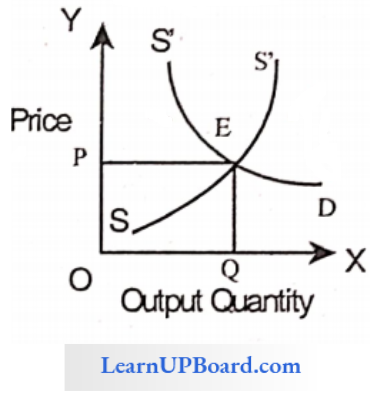
Question 16. __________________ Is the price at which demand for a commodity is equal to its supply
- Normal Price
- Equilibrium Price
- Short run Price
- Secular Price
Answer: 2. Equilibrium Price
The equilibrium price is the price at which the demand for a commodity is equal to its supply.
Question 17. OPEC is an example of
- Monopoly Competition
- Monopoly
- Oligopoly
- Duopoly
Answer: 3. Oligopoly
OPEC Question Organisation for Petroleum Exporting Countries. is an example of an oligopoly market because there are few sellers for petroleum in the world.
Question 18. ________________ Is an ideal Market.
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic
- Perfect Competition
- Oligopoly
Answer: 3. Perfect Competition
A perfectly Competitive Market is an ideal Market because it is characterized by many sellers selling identical products to many buyers and there is a freedom of entry and exit.
Question 19. Under this Market Situation demand curve is linear and parallel to the axis
- Perfect Competition
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic Competition
- Oligopoly
Answer: 1. Perfect Competition
Under Perfect competition demand curve is Linear and parallel to X axis because there are a huge number of buyers selling the same commodity at a particular price and as a result, each buyer and seller makes transactions in the market at a prevailing price.
Question 20. Which market has characteristics of product differentiation?
- Perfect Competition
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic Competition
- Oligopoly
Answer: 3. Monopolistic Competition
Monopolistic markets have a characteristic of product differentiation which is the most prominent feature of such a form of market where firms do not produce identical goods. They rather produce different varieties of commodities that are close substitutes for each other.
Question 21. Which of these are characteristics of Perfect Competition?
- Many Sellers & Buyers
- Homogeneous Product
- Free Entry and Exit
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Under perfect competition, there are a large number of buyers and sellers. A particular buyer has a negligible role in determining the price.
The product sold under this type of market structure is homogenous i.e. all units of a good are identical in color, shape, size, or packing of the product of each seller. Lastly; there is no legal or social restriction upon the entry of new firms into the industry. The choice of entering or leaving an industry lies on individual firms.
Question 22. The demand curve of oligopoly is
- Horizontal
- Vertical
- Kinked
- Rising left to right
Answer: 3. Kinked
In many oligopolistic industries, prices remain sticky or inflexible for a long time. This price rigidity has been clearly explained by the kinked demand curve hypothesis. The demand curve of an oligopoly market has a ‘Kink’ at the level of the prevailing prices.
The kink is formed at the prevailing price level. This is because the segment of the demand curve above the prevailing price level is highly elastic and the segment of the demand curve below the prevailing price level is inelastic.
Therefore, the demand curve formed under an oligopolistic market is kinked.
Question 23. MR Curve = AR = Demand Curve is a feature of which kind of Market?
- Perfect Competition
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic
- Oligopoly
Answer: 1. Perfect Competition
In perfect competition, all the goods are sold at a single price, by which average revenue (AR) equals marginal revenue (MR). This price is determined by the industry through the forces of demand and supply and this price is adopted by the firms.
All the goods are sold at a prevailing price in the market by which AR equals MR at each level of quantity sold.
Question 24. In the long run, monopolists can
- Incur losses
- Must earn super-normal profits
- Wants to shut-down
- Earns only normal profits.
Answer: 2. Must earn super normal profits
The long run is a period long enough to allow the monopolist to adjust his plant size or use his existing plant at any level that maximizes his profit. In the absence of competition, the monopolist need not produce at the optimum level.
Therefore, the monopolist will not continue if he makes losses in the long run. He will continue to make super-normal profits even in the long run as the entry of outside firms is blocked.
Question 25. The demand curve of the firm and industry will be the same in which form of market.
- Monopolistic Competition
- Perfect Competition
- Monopoly
- Oligopoly.
Answer: 3. Monopoly
In the case of a monopoly market, the firm and the industry are the same as there is only one seller in the market. Hence the demand curve of the firm and industry are the same.
Question 26. An oligopoly having identical products is
- Pure oligopoly
- Imperfect oligopoly
- Price leadership
- Collusion.
Answer: 1. Pure oligopoly
An oligopoly is a market situation when there are few sellers in the market. When the sellers in the market sell homogeneous products, such an oligopoly is termed a pure oligopoly.
Question 27. The demand curve is equal to the M. R. curve in which market?
- Oligopoly
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic Competition
- Perfect Competition
Answer: 4. Perfect Competition
In a perfectly competitive market, all units are priced at the same level.
Therefore, P = MR = AR. Since every demand curve is the average revenue curve, so in a perfectly competitive market, the demand
the curve is a straight line parallel to the X-axis, i.e. demand is perfectly elastic. .
Question 28. The kinked demand hypothesis is designed to explain in the context of oligopoly.
- Price and output determination
- Price rigidity
- Collusion between firm
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Price rigidity
The kinked demand hypothesis is designed to explain the rigidity of price under an oligopolistic market. It helps to determine the price and output of the firm.
Question 29. Price discrimination can take place only in
- Monopolistic competition
- Oligopoly
- Perfect competition
- Monopoly
Answer: 4. Monopoly
Price discrimination refers to charging different prices to different customers. This is a feature of monopoly, as this situation is possible only in the case of monopoly as there is only one seller in the market and there is no competition.
Question 30. In oligopoly, the kink on the demand curve is more due to _________________
- Discontinuity in MR.
- Discontinuity in AR.
- Fulfillment of the assumption that a price cut is followed by others and a price increase by a firm is not followed by others.
- Price war amongst the firms.
Answer: 3. Fulfillment of the assumption that a price cut is followed by others and a price increase by a firm is not followed by others.
In the case of oligopoly, there is akink1 on the demand curve because ‘ the Segment of demand curve above prevailing price is highly elastic and segment of the demand curve below prevailing price level is inelastic.
The reason for the above is that the oligopolist believes if he lowers the price below the prevailing level its competitors will follow him but if he raises the price above the prevailing level, its competitors will not follow him.
Question 31. Price Discrimination is possible only when.
- The seller is alone.
- Goods are homogeneous.
- The market is controlled by the government.
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Seller is alone.
In the case of price discrimination, there is a condition that the seller should have some control over the supply of his product i.e. monopoly power in some form is necessary (not sufficient) to discriminate price.
So it can be said that to have monopoly power the seller should be alone to exercise price discrimination.
Question 32. Which of the following is not the feature of an imperfect competition?
- Product differentiation.
- Few sellers.
- Homogeneous products.
- Price wars.
Answer: 3. Homogeneous products.
Features of imperfect competition are:
- A large number of sellers.
- Product differentiation
- Freedom of Entry or Exit
- Non-price competition.
Question 33. Price taker firms.
- Do not advertise their product because it misleads the customers.
- Advertise their products to boost the level of demand.
- Do not advertise but give gifts along with the sold items to attract. customers.
- Do not advertise because they can sell as much as they wish at the prevailing price.
Answer: 4. Do not advertise because they can sell as much as they wish at the prevailing price.
In the case of perfect competition, firms are price takers who need not advertise their products because they can sell as much as they wish at the prevailing prices.
Question 34. Price rigidity is a situation found in which of the following market forms?
- Perfect competition,
- Monopoly.
- Monopolistic competition.
- Oligopoly.
Answer: 4. Oligopoly.
An oligopoly is a market structure having few sellers characterized by price rigidity which helps to determine the price and output of the firm.
Question 35. When the elasticity of demand is Equal to one in monopoly, marginal Revenue will be_________________
- Equal to one.
- Greater than one.
- Less than one.
- Zero.
Answer: 4. Zero.
MR = AR (e-1)/(e)
Where, e= 1
MR = AR (\(\frac{1-1}{1}\))
AR = \(\frac{0}{1}\)
MR = 0
Question 36. Which one of the following statements is Incorrect?
- Competitive firms are price takers and not price makers.
- Price discrimination is possible in monopoly only.
- Duopoly may lead to monopoly.
- The competitive firm always seeks to discriminate prices.
Answer: 4. The competitive firm always seeks to discriminate prices.
Monopoly control over the product gives rise to price- discrimination, hence it can take place only in monopolies and not in competitive firms.
Question 37. The toothpaste industry is an example of this.
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic competition
- Oligopoly
- Perfect competition.
Answer: 2. Monopolistic competition
Monopolistic competition is a market in which many sellers offer differentiated products to many buyers Example- Toothpaste industry where product differential is only slight, and the degree of control over price is only some.
Question 38. Monopolistic Competitive firms.
- Are small in size
- Have a small share in the total market
- Are very large
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
Monopolistic competitive firms are small in size compared to. monopolies and every monopolistic competitive firm has small share in the total market Example – Soap industry
Question 39. The price discrimination under monopoly will be possible under which of the following conditions?
- The seller has no control over the supply of his product.
- The market has the same condition all over
- The price elasticity of demand is different in different markets
- The price elasticity of demand is uniform.
Answer: 3. The price elasticity of demand is different in different markets
Conditions for price discrimination under monopoly are:
- The seller should have control over the supply of his product
- The seller should be able to divide his market into sub-markets
- The price elasticity of the product should be different in different markets.
- Not possible for buyers of low-priced markets to resell the product to buyers of high-priced markets.
Question 40. An oligopoly having identical products is known as
- Pure oligopoly
- Collusive oligopoly
- Independent oligopoly
- None of these.
Answer: 1. Pure oligopoly
An oligopoly having identical products is known as a pure oligopoly. For example industry.
Question 41. Which of these is the best example of oligopoly?
- OPEC
- SAARC
- WTO
- GATT.
Answer: 1. OPEC
Oligopoly is defined as competition among few. In other words, when there are few sellers in the market selling homogeneous or differentiated products, an oligopoly is said to exist.
OPEC (Oil and Petroleum Exporting Countries) is the best example of an oligopoly.
Question 42. Monopolists can fix him price of goods whose elasticity is .
- Less than 1
- More than 1
- Elastic
- Inelastic.
Answer: 1. Less than 1
Monopoly is a situation when there is a single seller in the market. Here the firm is the price maker. The price elasticity demand for a monopolist is less than one hence he can fix the price of the goods whose elasticity is less than one
Question 43. Perfectly competitive firm faces
- The perfectly elastic demand curve
- A perfectly inelastic demand curve
- Zero
- Negative.
Answer: 1. Perfectly elastic demand curve
Firms in a competitive market are price takers. This is because there are a large number of firms in the market who are producing identical or homogeneous products. As such these firms cannot influence the price of their products and hence they have a perfectly elastic demand curve.
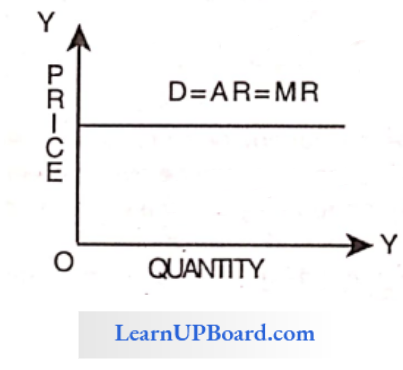
Question 44. In perfect Competition when the firm is a price taker, which curve among the following will be a straight line?
- Marginal Cost
- Average Cost
- Total Cost
- Marginal Revenue
Answer: 4. Marginal Revenue
In a perfect competitive market the firms are price – takers and the marginal revenue curve Is a straight line.
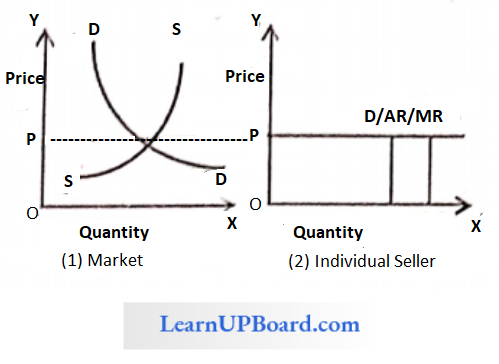
Firm’s Demand Curve Under Perfect Competition
Question 45. “Price Discrimination” can be best exercised by the Seller in.
- Oligopoly
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic competition
- Perfect competition
Answer: 2. Monopoly
Price discrimination cannot persist under perfect competition because the seller does not influence the market-determined rate. Price Discrimination requires an element of monopoly so that the seller can influence the price of his product.
Question 46. A firm encounters a “shut down” point when,
- Marginal cost equals the price of the profit-maximizing level of output
- Average fixed cost equals the price at the profit-maximizing level of output
- Average variable cost equals the price at the profit-maximizing level of output
- Average total cost equals the price at the profit-maximizing level of Output
Answer: 3. Average variable cost equals the price at the profit-maximizing level of output
A firm reaches a shutdown level when it is not being able to meet its variable cost. This means that the firm will not be able to make payments to labor, raw material suppliers, etc. In such a situation, the firm will not be able to recover its
variable cost even in the long run. Hence at this stage, the firm should stop production and shut down.
Question 47. Under which market Conditions do firms make only normal profits in the long run?
- Oligopoly
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic competition
- Duopoly
Answer: 3. Monopolistic competition
In the short-run, firms earn super-normal profits in the monopolistic competition thus giving incentives to new firms to enter the industry. As more firms enter, profits per firm will decrease as the total demand will be shared among a large number of firms. This will happen till all the profits are wiped away and all the firms earn only normal profits
Question 48. In monopolistic competition excess capacity in the firm ____________________
- Always exists
- Sometimes exists
- Never exists
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Always exists
An individual firm in the long run is in an equilibrium position at a position where it has excess capacity. Thus, the firms in monopolistic competition are not of optimum size and there exists excess capacity of production with each firm.
Question 49. Selling costs have to be incurred in case of
- Perfect Competition.
- Monopolistic Competition
- Monopoly
- None of these.
Answer: 2. Monopolistic Competition
Nonprice competition is an essential feature of monopolistic competition. Here the firms compete not based on price but on other factors such as aggressive marketing, product development, after-sale services, etc. Hence incurring of selling cost is an essential feature of monopolistic competition.
Question 50. In the market, the price and output equilibrium is determined based on:
- Total revenue and total cost
- Total cost and marginal cost
- Marginal revenue and marginal cost
- Only marginal cost.
Answer: 3. Marginal revenue and marginal cost
For the condition of equilibrium, two conditions are necessary
- Marginal revenue should be equal to marginal cost.
- The marginal cost curve should cut MR from below.
- Hence, equilibrium is determined based on marginal cost and marginal revenue.
Question 51. A perfect market is characterized by
- Existence of a large number of buyers and sellers
- Homogenous products
- Perfect knowledge of the market
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
A perfect market has the following characteristics :
- A large number of buyers and sellers
- Homogeneous products
- Free entry and exit
- Perfect knowledge of the market
- Movement of goods from one centre to another
- Uniform price.
Question 52. Which of the following is not a feature of the oligopoly market?
- Interdependence of the firms in decision-making
- Price rigidity
- Group behaviour
- Existence of a large number of firms.
Answer: 4. Existence of a large number of firms.
Oligopoly is described as ‘competition among the few’. It has the following characteristics:
- Interdependence of few firms in decision-making
- With the great importance of advertising and selling costs, firms compete on a non-price basis.
- Group behavior.
Question 53. A monopolist can fix
- Both price and output
- Either price or output
- Neither price nor output
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Both price and output
The term ‘monopoly’ means ‘alone to sell’. In a monopoly market, there is only one firm producing or supplying a product. Thus, the monopolist is free to determine both his price and output.
Question 54. In a perfectly competitive market, the demand curve of a firm is
- Elastic
- Perfectly elastic
- Inelastic
- Perfectly inelastic
Answer: 2. Perfectly elastic
Firms in a competitive market are price takers. This is because there are a large number of firms in the market who are producing identical or homogeneous products. As such these firms cannot influence the price of their products and hence, they have a perfectly elastic demand curve.
Question 55. In a competitive market, if the price exceeds the Average Variable Cost (AVC) but remains less than the Average Cost (AC) at the equilibrium, the firm is
- Making a profit
- Planning to quit
- Experiencing loss but should continue production
- Experiencing loss but should discontinue production.
Answer: 3. Experiencing loss but should continue production
In a competitive market, if the price exceeds the Average Variable Cost (AVC) but remains less than the Average Cost (AC) at the equilibrium,
The firm can be in an equilibrium position and still make losses. When the firm can meet its VC and a part of FC, it will try to continue production in the short run. If it recovers a part of FC, it will be beneficial for it to continue production because FC are already incurred and in such a case, it will be able to recover a part of them.
Thus, if the price exceeds the AVC but remains less than AC at equilibrium in a competitive market, the firm is experiencing a loss but should continue production.
Question 56. Price under perfect competition is determined by the.
- Firm
- Industry
- Government
- Society.
Answer: 2 . Industry
An industry consists of a large number of independent firms, having several factories, firms, or mines under its control. Each such unit in the industry produces a homogeneous product so that there is competition amongst goods produced by different units called firms.
When the total output of the industry is equal to the total demand, we say the industry is in equilibrium, and the price prevailing is the equilibrium price. Thus it can be said that price under perfect competition is determined by industry.
Question 57. Under monopoly, which of the following is correct
- AR and MR both are downward sloping
- MR lies halfway between AR and Y-axis
- MR can be zero or even negative,
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
The relationship between AR and MR of a monopoly firm can be stated as follows:
- AR and MR are both negative sloped (downward-sloping) curves.
- MR curve lies halfway between the AR curve and the Y axis, i.e. it cuts the horizontal line between the Y axis and AR into two equal parts.
- AR cannot be zero, but MR can be zero or even negative. Thus, all of the above statements are correct under monopoly.
Question 58. Non-price competition is very popular in
- Monopoly market
- Monopolistic competition
- Oligopolistic market
- Perfect competition.
Answer: 2. Monopolistic competition
In a mono-politically competitive market, sellers try to compete on a basis other than price, such as aggressive advertising, product development, better distribution arrangements, efficient after-sale service, and so on. A key base of non-price competition is a deliberate policy of product differentiation.
Question 59. In the kinked-demand curve model, the upper portion of the demand curve is
- Elastic
- Inelastic
- Perfectly Elastic
- Unitary Elastic.
Answer: 1. Elastic
The demand curve faced by an oligopolist according to the kinked demand curve hypothesis, has a kink at the level of the prevailing price. This is because the segment of the demand curve above the prevailing price level is highly elastic and the segment of the demand curve below the prevailing price level is inelastic.
Question 60. The equilibrium price for an industry in perfect competition is fixed.
- Input and Output
- Market demand and market supply
- Market demand and firms’ supply
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Market demand and market supply
Firms in a competitive market are price takers. This is because there are a large number of firms in the market who are producing identical or homogeneous products. As such these firms cannot influence the price in their capacities. They have to accept the price fixed (through the interaction of market demand and supply) by the industry as a whole.
Question 61. In a perfectly competitive market, if MR is greater than MC, then a firm should
- Increase its production
- Decrease its production
- Decrease its sales
- Increase its sales
Answer: 1. Increase its production
In a perfectly competitive market, if MR is greater than MC, there is always an incentive for the firm to expand its production further and gain by selling additional units.
Thus, the firm should increase its production if MR is greater than MC.
Question 62. The kinked demand curve is related to which market structure
- Oligopoly
- Monopoly
- Monopsony
- Monopolistic competition.
Answer: 1. Oligopoly
In oligopolistic industries, prices remain sticky or inflexible for a long time. They tend to change infrequently even if in the face of declining cost. These inflexibilities lead to the kink shape of the demand curve.
Therefore, oligopolistic markets have a kinked demand curve.
Question 63. In the long run, a monopolist always earns
- Normal profit
- Abnormal profit
- Zero profit
- Loss
Answer: 2. Abnormal profit
The long run is a period long enough to allow the monopolist to adjust his plant size or use his existing plant at any level that maximizes his profit. In the absence of competition, the monopolist need not produce at the optimum level.
Therefore, the monopolist will not continue if he makes losses in the long run. He will continue to make super normal profits even in the long run as entry of outside is blocked.
Question 64. Under which of the following forms of market structure does a firm have very considerable control over the price of its product?
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic Competition
- Oligopoly
- Perfect Competition
Answer: 1. Monopoly
In a monopoly, there is a single seller and there is only one firm producing and supplying a product. Each firm is a price maker and is in a position to determine the price of its product.
Question 65. One of the essential conditions of Perfect Competition is
- Product differentiation
- Many sellers and few buyers
- Only one price for identical goods at any one time
- The multiplicity of prices for identical products at any one time
Answer: 3. Only one price for identical goods at any one time
In case of perfect competition, the commodity or the goods are sold – at uniform prices throughout the market at any given point in time.
In other words, all firms individually are price takers; they have to accept the price determined by the market forces of demand and supply.
Question 66. The demand cun/e of an oligopolist is
- Determinate
- Indeterminate
- Circular
- Vertical
Answer: 2. Indeterminate
When an oligopolistic firm changes its price, its rival firms will retaliate or react and change their prices which in turn would affect the demand of the former firm. Therefore, an oligopolistic firm cannot have a sure and definite demand curve, since it keeps shifting as the rivals change their prices in reaction to the price changes made by it.
Question 67. Abnormal profits exist in the long run only under
- Perfect competition
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic competition
- Oligopoly
Answer: 2. Monopoly
Abnormal profits exist in the long run only under a monopoly. He will continue to make supernormal profits even in the long run as entry of outside firms is blocked.
Question 68. The distinction between a single firm and an Industry vanishes in which of the following market conditions?
- Perfect Competition
- Imperfect Competition
- Pure Competition
- Monopoly
Answer: 4. Monopoly
In a monopoly market, there is only one firm producing or supplying a product. This single firm constitutes the industry and as such there is no distinction between firm and industry in a monopolistic market or monopoly.
Question 69. Selling outlay is an essential part of which of the following market situations?
- Perfect Competition
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic Competition
- Pure Competition.
Answer: 3. Monopolistic Competition
In a mono-politically competitive market, sellers try to compete based on selling cost/outlay. Sellers attempt to promote their products not by cutting prices but by incurring high expenditure on publicity advertisement and sales promoting techniques. Thus, selling outlay is an essential part of a monopolistic competitive market.
Question 70. The Kinked demand curve model explains the market situation
- Pure Oligopoly
- Differentiated Oligopoly
- Collusive Oligopoly
- Price Rigidity
Answer: 4. Price Rigidity
In many oligopolistic industries, prices remain sticky or inflexible for a long time. They tend to change infrequently, even in the face of declining costs. The most popular explanation given for this price rigidity is the kinked demand curve hypothesis given by Paul A. Sweezy.
Question 71. For price discrimination to be successful, the elasticity of demand for the commodity in the two markets should be
- Same
- Different
- constant
- Zero
Answer: 2. Different
Conditions for price discrimination:
- The seller should have some control over the supply of his product.
- The seller should be able to divide his market into two or more sub-markets.
- The price elasticity of the product should be different in different sub-markets.
- It should not be possible for buyers of low-priced markets to resell the product to buyers of high-priced markets.
Question 72. The firm in a perfectly competitive market is a price taker. This designation as a price taker is based on the assumption that
- The firm has some but not complete control over its product price
- There are so many buyers and sellers in the market that anyone buyer or seller cannot affect the market
- Each firm produces a homogeneous product
- There is easy entry into or exit from the marketplace.
Answer: 2. Each firm produces a homogeneous product
The firm in a perfectly competitive market is a price taker. The designation as a price taker is based on the assumption that there are large numbers of buyers and sellers who compete among themselves and their number is so large that no buyer or seller is in a position to influence the demand or supply in the market.
Question 73. A market structure in which many firms sell products that are similar and identical is known as
- Monopolistic competition
- Monopoly
- Perfect competition
- Oligopoly
Answer: 3. Perfect competition
Perfect competition is a market where a firm sells homogenous products that are similar and identical.
Question 74. A firm having a kinked demand curve indicates that
- If the firm reduces the price, competitive firms also reduce the price
- If the firm increases the price, competitive firms also increase the price
- If the firm reduces the price, competitive firms do not reduce the price
- If the firm increases the price, competitive firms do not increase the price
Answer: 2. Both (1) and (4) above
In a firm having a kinked demand curve indicates that the firm has reduced, the price, and the competitive firm also reduces the price but if the firm increases the price, competitive firms do not increase the price.
Question 75. Price discrimination will not be profitable if the elasticity of demand is ______________ In different markets
- Uniform
- Different
- Less
- Zero
Answer: 1. Uniform
Price discrimination is a method of pricing adopted by the monopolist to earn abnormal profits. It refers to the practices of charging different prices for different units of the same commodity. Thus, it will not be profitable, if the elasticity of demand is uniform in different markets.
Question 76. In the long run, which of the following statements is true for a firm in a perfectly competitive industry?
- It operates at its minimum average cost
- The price is more than the average fixed cost
- The marginal cost is greater than the marginal revenue
- The fixed cost is lower than the total variable cost
Answer: 1. It operates at its minimum average cost
In the long run, plants are used at full capacity, so that there is no wastage of resources i.e. MC = AC. The firm adjusts its plant size to produce that level of output at which the LAC is the minimum.
Thus, we can say that a firm in a perfectly competitive industry operates at its minimum average cost.
Question 77. The firm will attain equilibrium at a point where MC curve cuts from below.
- AR curve
- MR curve
- AC curve
- AVC curve.
Answer: 2. MR curve
The MC curve cuts the MR curve from below. In other words, MC should have a positive slope.
Question 78. In a monopoly market, a producer has control only over
- Price of the commodity
- Demand for the commodity
- Both (1) and (2)
- Utility of the product.
Answer: 1. Price of the commodity
The monopolist or the producers in a monopoly market may use their monopolistic power to realize maximum revenue and may also adopt price discrimination. Therefore they have control only over the price of the commodity.
Question 79. One of the following is not correct about perfect competition
- Purchase and Sale of homogeneous goods
- Existence of marketing costs
- Absence of transportation costs
- Perfect mobility of factors of production.
Answer: 2. Existence of marketing costs
Perfect competition has the following features:
- A large number of buyers and sellers of a commodity
- Homogeneous Product
- Perfect Knowledge
- Freedom of Entry and Exit
- No Extra Transport Cost
- Independent Decision Making
- Perfect Mobility
Question 80. The kinked demand curve under oligopoly is designed to show
- Price and output determination
- Price rigidity
- Price leadership
- Collusion among rivals.
Answer: 2. Price rigidity
The kinked demand curve hypothesis has a kink’ at the level of the prevailing price. This kink is formed to show price rigidity.
Question 81. “I am making a loss, but with the rent, l have to pay, I can’t afford to shut down at this point.” If this entrepreneur is attempting to maximize profits or minimize losses.
- Rational, if the firm is covering its variable cost
- Rational, if the firm is covering its fixed cost
- Irrational, since plant closing is necessary to eliminate losses
- Irrational, since fixed costs are eliminated if a firm shuts down.
Answer: 1. Rational, if the firm is covering its variable cost
A point of operation where a firm is indifferent between continuing operation and shutting down temporarily. The shutdown point is the combination of output and price where a firm earns just enough revenue to cover its total variable costs.
Question 82. The kinked demand curve is the demand curve of
- Perfect Competition
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic Competition
- None of the above.
Answer: 4. None of the above.
The kinked demand curve is the demand curve of an oligopoly.
Question 83. Price discrimination will be profitable only if the elasticity of demand in different markets is
- Uniform
- Different
- Less
- Zero
Answer: 2. Different
Price discrimination will be profitable only if the elasticity of demand in different markets is different because
Monopolist fixes a high price for their product for those buyers whose price Elasticity of demand for a product is less than one. This implies that when the monopolist charges a higher price from them, they do not significantly reduce their purchases in response to the high price.
Question 84. Under which of the following forms of market structure does a firm have no control over the price of its production?
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic Competition
- Oligopoly
- Perfect Competition.
Answer: 4. Perfect Competition.
In perfect competition, a firm has no control over the price of its product because there are large numbers of sellers and each seller produces such a small share of the total output that any change in his output will not have a significant effect
on the market price and there is a large number of buyers so that no buyer can change its output by its action. The firms are said to be ‘price takers’.
Question 85. __________________ Is that situation in which a firm bases its market policy, in part on the expected behavior of a few close rivals.
- Oligopoly
- Monopolistic Competition
- Monopoly
- Perfect Competition.
Answer: 1. Oligopoly
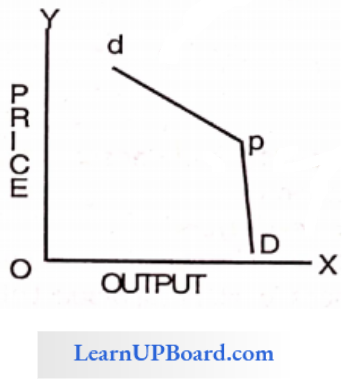
Solve questions No. 86, 87, and 88 based on the following figure
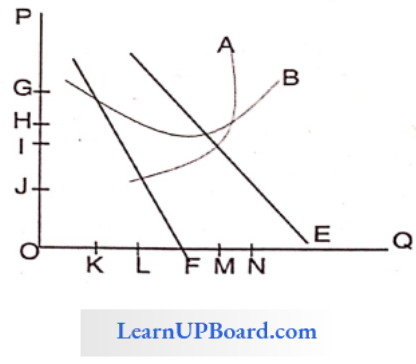
An oligopoly is a market structure in which there is interdependence of firms in decision-making. This is because when the number of competitors are few any change in price, output, or product by a firm will have a direct effect on the fortunes of the rivals, who will then retaliate by changing their price.
Question 86. In the above figure, curve E is the firm’s
- Marginal Cost Curve
- Average Cost Curve
- Demand Curve
- Marginal revenue Curve.
Answer: 3. Demand Curve
Curve-E is the Average Revenue curve which is also known as the Demand Curve.
Question 87. The above figure represents a
- Monopolist
- Perfectly competition industry
- Perfectly competitive firm
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Monopolist
- The given curve is a Monopolist curve because:
- AR and MR are both negatively sloped
- MR curve lies half-way between the AR curve and the Y-axis,
- i. e. it cuts the Horizontal line between the Y-axis and AR into two equal parts.
- AR cannot be zero, but MR can be zero or negative.
Question 88. In the above figure, the firm’s marginal revenue curve is a curve
- E
- A
- F
- B
Answer: 3. F
The marginal revenue curve is curve F because it lies halfway between the AR curve and the Y-axis.
Question 89. The price elasticity of demand for a product is infinite under
- Perfect competition
- Monopolistic competition
- Monopoly
- Oligopoly.
Answer: 1. Perfect competition
The price elasticity of demand for a product is infinite under perfect competition as there are large numbers of buyers and sellers who compete among themselves and their number is so large that no buyer or seller is in a position to influence the demand or supply in the market.
Question 90. Comparing a Monopoly and a Competitive firm the Monopolist will
- Produce less and sell at a lower price
- Produce more and sell at a lower price
- Produce less and sell at a higher price
- Produce zero and sell at a lower price
Answer: 3. Produce less and sell at a higher price
Monopoly is an extreme form of imperfect competition with a single seller of a product that has no close substitute as compared with a perfectly competitive market. In perfect competition, average and marginal revenue are identical but this is not the case in monopoly as a monopolist knows that if he wishes to increase his sales he will have to reduce the price of a
product. Thus, produce less at a higher price at times.
Question 91. The reason for the kinked demand curve is that
- The oligopolists believe that competitors will follow output increases but not output reductions.
- The oligopolists believe that competitors will follow price increases but not output reductions.
- The oligopolists believe that competitors will follow price cuts but not price rises.
- The oligopolists believe that competitors will follow price increases but not output increases
Answer: 3. The oligopolists believe that competitors will follow price cuts but not price rises.
The reason for the Kinked Demand curve is that the oligopolists believe that competitors will follow price cuts but not price rises. This kink is formed at a prevailing price level. This is because the segment of the demand curve above the prevailing price level is highly elastic and the segment of the demand curve below the prevailing price level is inelastic.
Question 92. A discriminating monopolist will charge a higher price in the market in ______________
- Which the demand for its product is.
- Highly elastic relatively elastic
- Relatively inelastic
- Perfectly elastic.
Answer: 3. Relatively inelastic
A discriminating monopolist charges a higher price in a market that has a relatively in elastic demand. The market which is highly responsive to price changes is charged less. On the whole, the monopolist benefits from such discrimination.
Question 93. If a firm under monopoly wants to sell more, its average revenue
- The curve will be aligned.
- Horizontal Vertical
- Downward sloping
- Upward sloping
Answer: 3. Downward-sloping
If a firm under monopoly wants to sell more, its average revenue curve will be a downward sloping line because the seller charges a single price for all units he sells, average revenue per unit is identical to the price, and thus the market demand curve is the average revenue curve for the monopolist. *
Question 94. Who sets the price of the product under perfect competition?
- Government
- Consumers
- Sellers
- Both buyers and sellers
Answer: 4. Both buyers and sellers
The price of the product under perfect competition is set by both buyers and sellers.
Question 95. Which is the first-order condition for the firm to maximize profit.
- AC = MR
- AC = AR
- MC = MR
- MR = AR
Answer: 3. MC = MR
The first order condition for the firm to maximize the profits is when marginal cost is equal to the marginal revenue.
Question 96. Which market has the concept of ’group 1 equilibrium in the long run?
- Oligopoly
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic competition
- Perfect competition.
Answer: 3. Monopolistic competition
In the long run, monopolistic competition has the concept of group equilibrium. Group equilibrium represents the price and the output of organizations having close substitutes.
Question 97. Which of the following is incorrect?
- Even monopolistic can earn losses.
- Firms in the perfectly competitive market is price takers.
- It is always beneficial for a firm in a perfectly competitive market to discriminative prices.
- The kinked demand curve is related to an oligopolistic market.
Answer: 3. It is always beneficial for a firm in a perfectly competitive market to have discriminative prices.
It is always beneficial for a firm in a perfectly competitive market to discriminate prices. This statement is incorrect.
Question 98. The average revenue curve is also known as
- Profit Curve
- Demand Curve
- Average Cost Curve
- Indifference Curve
Answer: 2. Demand Curve
Average Revenue curve is also known as Demand Curve
Question 99. Which is not characteristic of monopoly?
- The firm is price taker
- There is a single firm
- The firm produces a unique product
- The existence of some advertising.
Answer: 1. The firm is a taker
A monopoly is not a price taker but a price maker.
Question 100. Price discrimination is profitable only when
- Different markets are kept separate
- Distance between the consumer and the market is more
- The elasticity of demand in different markets is different
- The consumers are segregated based on their purpose of use of the commodity.
Answer: 3. Elasticity of demand in different markets is different
Price discrimination is profitable only when the elasticity of demand in different markets is different.
Question 101. When the industry is dominated by one large firm which is considered the leader of the group, the market is described as
- Open oligopoly
- Perfect oligopoly
- Partial oligopoly
- Organized oligopoly.
Answer: 3. Partial oligopoly
An oligopoly is partial when the industry is dominated by one large firm which is considered or looked upon as the leader of the group. The dominating firm will be the price leader. In partial oligopoly. The market will be conspicuous by the absence of price leadership.
Question 102. Which of the following is not an objective of price discrimination?
- To hold the extra stocks
- To earn maximum profits
- To enjoy economies of scale
- To secure equity through pricing.
Answer: 1. To hold the extra stocks
The objectives of price discrimination are here:
- To earn maximum profit
- To dispose of surplus stock
- To enjoy economies of scale
- To capture the foreign market
- To secure equity through pricing
Question 103. Which of the following statement is not correct? .
- Under a monopoly, there is no difference between a firm and an industry.
- A monopolist may restrict the output and raise the price.
- Commodities offered for sale under perfect competition will be heterogeneous.
- Product differentiation is peculiar to monopolistic competition.
Answer: 3. Commodities offered for sale under perfect competition will be heterogeneous.
Commodities offered for sale under perfect competition will be homogenous. There are large numbers of buyers and sellers who compete among themselves and their number is so large that no buyer or seller is in a position to influence the demand and supply in the market being the commodity dealt in it is homogeneous, in the sense that the goods produced by different firms are identical.
Question 104. Under perfect competition, a firm is described as
- Price taker and not a price maker
- Price maker and not a price taker
- Neither the price maker nor the price taker
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Price taker and not price maker
Under perfect competition firms is described as price takers and
not price makers. This is because there are a large number of firms in the market that are producing identical or homogenous » products. As such these firms cannot influence the price in their capacities. They have to accept the price fixed (through the interaction of total demand and total supply) by the industry as a whole.
Question 105. Under which of the following forms of market structure does a firm l have no control over the price of its product?
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic Competition
- Oligopoly
- PerfectCompetition.
Answer: 4. Perfect Competition.
Under perfect competition, a firm has no control over the price of its product. Firms have to accept the price as given and as such they are price takers rather than price makers.
They cannot increase the price individually because of the fear of losing the customer to other firms.
Question 106. Condition for the equilibrium of the firm.
- MR = MC
- AR = AC
- MC curve cuts MR curve from below
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
Conditions for Equilibrium of the firm are
Marginal revenue should be equal to marginal cost i.e. MR = MC
MC curve should cut MR curve from below i.e. MC should have a positive slope. Hence both conditions
Question 107. What is/are the features of oligopoly
- Kinked Demand curve
- Cartel
- Downward sloping demand curve
- Both (1) and (2) are correct
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2) are correct
An oligopoly is a type of market in which there are only a few buyers and sellers (generally 2 to 10) and it was
So many features also and these are as follows:
- Cartel
- Kinked Demand Curve
- Interdependence
- Group Behaviour
- Importance of advertising and selling costs
Question 108. Monopoly is undesirable due to
- It has prices higher than competitive firms
- It produces less output than competitive firms
- It discriminates on prices.
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. It discriminates on prices
Monopoly means where only one seller exists and takes all the profits. It has some features from his point of view and undesirable also from
The public point of view these are:
- Price Discrimination
- Produced less output than competitive firms
- Prices are higher than competitive firm
Question 109. In long-run equilibrium, undue perfect competition is/are satisfied by which condition
- MC = MR
- AC = AR
- CMC = LAC = P
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above.
The equilibrium point is judged in the long run when there is/are
- Marginal Cost = Marginal Revenue or MC = MR
- Average Cost = Average Revenue or AC = AR
- Long run Marginal Cost = Long Run Average Cost = Price or LMC
= LAC = P
Question 110. In the long run monopolists
- Incur losses
- Must earn super-normal profits
- Wants to shut down
- Earns only normal profits.
Answer: 2. Must earn super-normal profits
Monopoly means one seller and many buyers. A monopoly is a kind of market in which a seller is known as a monopolist and as his business has grown for a long time then he not only earns normal profits but also abnormal profits which is known as super profits. So, they must earn super-normal profits in the long run.
Question 111. The demand curve of the firm and industry will be the same in which form of the market
- Monopolistic competition
- Perfect competition
- Monopoly
- Oligopoly
Answer: 3. Monopoly
The demand curve of the firm and industry will same in the monopoly market as the price is set by the industry and the firm has to choose the level of output that yields maximum profits.
Question 112. The equilibrium price for an industry in perfect competition
is fixed through
- Input and output
- Market demand and market supply
- Market demand and firms’ supply
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Market demand and market supply
Equilibrium is that price at which both demand and supply are equal and therefore, no buyer who wanted to buy at that price becomes dissatisfied and none of the sellers is dissatisfied that they could not sell his goods at that price. The equilibrium price in perfect competition is fixed through Market Supply and Market Demand.
Question 113. Market form in which there is only one buyer and one seller is
- Oligopoly
- Duopoly
- Bilateral Monopoly
- Monopsony
Answer: 3. Bilateral Monopoly
A bilateral Monopoly is a type of market in which there are only one seller and one buyer.
Question 114. The structure of the Toothpaste Industry in India is best described as
- Perfectly competitive
- Monopolistic
- Monopolistically competitive
- Oligopolistic
Answer: 2. Monopolistic
The monopolistic market has differentiated products with close substitutes just like Toothpaste Industries.
Question 115. Product differentiation is the main feature of which market?
- Oligopoly
- Monopolistic
- Discriminating Monopoly
- Perfect competition.
Answer: 2. Monopolistic
In a monopolistic competitive market, there are large numbers of buyers and sellers each selling a differentiated product.
Question 116. Which market has a single seller and single Buyer?
- Duopoly
- Monopsony
- Bilateral Monopoly
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Bilateral Monopoly
Bilateral Monopoly is a market structure in which there is only a single buyer and a single seller i.e. it is a combination of a monopoly market and a monopsony market.
Question 117. In the Long run perfect competitive market incurs
- Normal profit
- Supernormal profit
- Losses
- Constant Returns
Answer: 1. Normal profit
In the long run, firms will ‘just be earning normal profit because if in the short run, they earning supernormal profit new firms will be attracted and supply will rise which lead to a fall in prices and vice versa.
Question 118. Which one of the following is not the feature of Oligopoly?
- Interdependency
- Selling cost
- Free Entry
- None of the above group behavior
Answer: 3. Free Entry
Features of oligopoly are:
- Strategic Interdependence
- Importance of advertising and selling cost
- Group behavior.
- Therefore, free entry is not a feature of an oligopoly market.
Question 119. Price leadership is the characteristic of
- Oligopoly
- Monopoly
- Perfect competition
- Discriminating Monopoly
Answer: 1. Oligopoly
Price leadership can be by a dominant firm, a low-cost firm or it can be barometric price leadership.
Question 120. MR Curve in perfect competition is
- Parallel to X- axis
- Parallel to Y- axis
- Fall from left to right
- Rise from left to right
Answer: 1. Parallel to X- axis
MR curve in perfect competition is parallel to the x-axis. Because a perfectly competitive firm is a price taker and faces a horizontal demand curve, its MC curve is also horizontal and coincides with its AC curve.
Question 121. Which of the following is not the characteristic of MR?
- When TR is maximum, then MR is zero
- MR cannot be negative
- MR slopes downward from left to right
- MR Curve is below AR Curve
Answer: 2. MR cannot be negative
Properties of MR are:
- When TR is maximum, then MR is zero
- MR can be negative
- MR slopes downward
- MR curve is below the AR curve
- Because MR can be negative.
Question 122. Which out of these is not a feature “of perfect competition?
- Homogeneous
- A large number of buyers and sellers.
- Free entry and exit
- Selling cost.
Answer: 4. Selling cost.
Feature of a perfectly competitive market
- A large number of buyers and sellers
- Products are homogenous
- Firms are free to center and exit
- Consumers have perfect knowledge.
- Therefore selling cost is not included in a perfectly competitive market ‘ .
Question 123. What is the characteristic feature of monopoly?
- Homogeneous goods
- Strong barriers to entry
- Perfect competition
- The perfectly elastic demand curve
Answer: 2. Strong barriers to entry
Monopoly is a market situation in which there is a single seller and a large number of buyers.
Its features are:
- Single seller of the product
- Barriers to entry
- No close-substitute of product
- Market power.
Question 124. A discriminating monopolist to reach an equilibrium position, his decision on total output depends upon
- How much total output should be produced?
- How the total output should be distributed between the two sub-markets?
- Both (1) and (2)
- None
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
To attain an equilibrium position, a discriminating monopolist has to make three main decisions regarding his output.
- How much total output should be produced?
- How the total output should be distributed between the two
sub-markets? and. - What price he should change in the two sub-markets?
Question 125. Price discrimination is possible only in
- Monopoly
- Perfect Competition
- Oligopoly
- Monopolistic Competition
Answer: 1. Monopoly
Price discrimination is a method of pricing that is adopted by a monopolist to earn abnormal profits. It is a method in which different prices are charged for different units of the same commodity. Thus, this method is only possible in a monopoly market situation.
Question 126. The kinked demand curve is
- Highly elastic at above the prevailing price
- Inelastic at below the prevailing price
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
In an oligopoly market, the demand curve is kinked-shaped at the level of the prevailing price. The reason behind this is that the demand curve above the prevailing price level is highly elastic and the segment below the prevailing price level is inelastic.
In other words, a high prices, the firm faces relatively elastic demand, and at low prices, relatively inelastic demand.
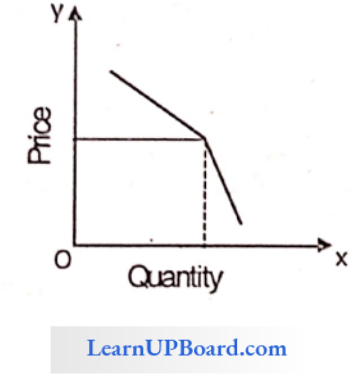
Question 127. The demand curve is horizontal in the case of _________________________
- Monopoly
- Perfect Competition
- Imperfect Competition
- Monopolistic Competition
Answer: 2. Perfect Competition
In a perfectly competitive market, firms are price taker i.e. they cannot influence the price in their individual capacity. Price is determined by the industry. Thus, the demand curve of this market is horizontal i.e. parallel to the x-axis.
Question 128. What is the characteristic of monopolistic competition?
- Price elasticity is low for the product concerned
- A large number of sellers
- No degree of control over the price
- One buyer
Answer: 2. A large number of sellers
Monopolistic competition is an imperfect market where many producers sell differentiated products.
Its characteristics are:
- A large number of sellers.
- Product differentiation
- Freedom of entry and exit
- Non-price competition
Question 129. If a perfectly competitive firm earns super-normal profits then
- AR > MR
- AR < MR
- AR = MR
- None of the above
Answer: 3. AR = MR
In the case of perfect competition, super normal profit arises when its average revenue is more than its average total cost. There is no change in the Demand curve, i.e.
AR = MR = Demand.
Question 130. Live and let live are characteristics of which of the following markets?
- Perfect Competition
- Monopoly Competition
- Imperfect Competition
- Oligopoly Competition
Answer: 4. Oligopoly Competition
An oligopoly market forms cartols because thoro are a few firms, all of which are similar in size. Orio’s strategy is to adopt a ‘live and lot live philosophy’. Specifically, the dominant firm accepts the personnel of fringe firms and sets the price to maximize its profit, taking into account the fringe firms’ behavior. This is called price leadership by the dominant firm.
Question 131. In which of the following markets there are there only two sellers?
- Duopoly Competition
- Perfect Competition
- Monopoly Competition
- Perfect Competition and Duopoly
Answer: 1. Duopoly Competition
Duopoly Is a subset of an oligopoly, a market situation in which there are only two firms In the market.
Where In an oligopoly market thorn are few firms and a large number of buyers with some degree of control our their prices.
Question 132. The degree of elasticity in a perfect competition market
- Perfectly elastic
- Inelastic
- Perfectly Inelastic
- Plastic
Answer: 1. Perfectly elastic
The degree of elasticity in a perfect competition market is perfectly elastic because the firm is a price taker, the demand curve ’I)’ facing an Individual competitive line is given by a horizontal line ul Ilia level of market pi ice set by Ilia industry. In oilier words, the demand caused by each Him is medically (or infinitely) elastic
When a firm earns supernormal profits Its average revenues are more than its average total cost. Thus, in addition to the normal rate of profit, the firm earns some additional profits.
Question 133. A perfectly competitive firm earns supernormal profits when
In the short run, a competitive firm earns super-normal profits, But in the long run, It earns normal profits only.
- ATC < MC
- ATC > MC
- MR < AR
- MR > AR
Answer: 1. ATC < MC
Whon a firm oarns supornormal profits Its avorago rovonuos aro more than its avorago total cost. Thus, in addition to the normal rate of profit, the firm earns some additional profits. The short-run perfect competitive firm earns super normal profits, But in the long run, It earns normal profits only
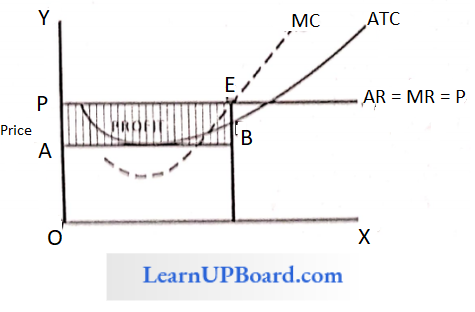
Question 134. A firm is said to earn a normal profit when
- AC = AR
- MC = MR
- AR = NR
- MC > MR
Answer: 1. AC = AR
When the average revenue of a firm is just equal to its average cost, a firm earns normal profits or zero economic profits, i.e.
AC = AR
It is to be noted that here a normal profit percentage for an entrepreneur for his managerial services is already included in the cost of production.
Question 135. Two firms are selling cold- drinks and competing with some identical characteristics, This is an example of
- Duopoly
- Monopoly
- Oligopoly
- Monopolistic
Answer: 1. Duopoly
A duopoly market is the subset of an oligopoly market where two and only two firms are there in the market.
Therefore, when there are two firms of cold- drink that are selling cold- drinks and competing with some identical characteristics. This is an example of a Duopoly market.
Question 136. Group Behaviour is a characteristic of
- Oligopoly
- Monopoly
- Perfect Competition
- Monopolistic Competition.
Answer: 1. Oligopoly
Group behavior is a characteristic of an oligopoly market. The theory of oligopoly is a theory of group behavior, not mass or individual behavior and to assume profit-maximizing behavior on the oligopolists’ part may not be very valid. The firms may agree to pull together as a group in the promotion of their common interest.
Each oligopolist closely watches the business behavior of the other oligopolists in the industry and designs his moves based on some assumptions of how they are likely to behave.
Question 137. Myth in the Real world
- Oligopoly
- Duopoly
- Perfect Competition
- Monopoly
Answer: 3. Perfect Competition
Myth in the Real world is a perfect competition market as in this market there are large numbers of buyers and sellers but they sell all homogenous goods which is not possible in real situation. And here all firms are price-takers.
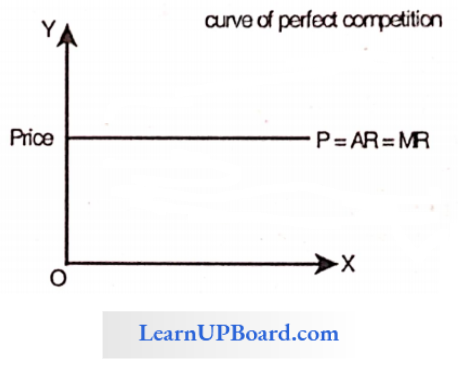
Question 138. _____________ Oligopoly refers to that situation where the firms sell their products through a centralized body.
- Syndicate oligopoly
- Organized oligopoly
- Collusive oligopoly
- Partial oligopoly
Answer: 1. Syndicate oligopoly
Syndicated oligopoly refers to a situation where the firms sell their products through a centralized body.
Organized oligopoly refers to a situation where the firms organize themselves into a central association for fixing prices, output, quotas, etc.
Question 139. The similarity between monopolistic and perfect competition is
- In the short run, both earn super-normal profit
- In the long term, both earn a normal profit
- In the short run, their prices remain, constant
- None
Answer: 2. In the long term both earn normal profit
The similarity between monopolistic and perfect competition is in the long run both earn normal profits. As long run is a period long enough to allow a monopolist to adjust his plant size or use his existing plant at any level that maximizes his profit.
In the absence of competition, the monopolist need not produce at an optimum level. Therefore, the monopolistic will not continue if he makes losses in the long, run. He will continue to make normal profits even in the long run.
Question 140. Which Market has a downward demand curve?
- Monopolistic competition
- Monopoly
- Perfect competition
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
Monopolistic Competition and Perfect Monopoly competition markets both have downward downward-sloping demand curves.
In all forms of imperfect competition, the average revenue curve of an individual firm slopes downwards as in these market forms when a firm increases the price of its product, its quantity demanded decreases and vice versa.
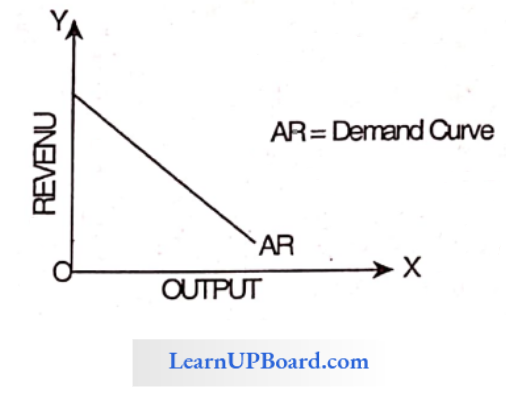
Question 141. The kinked demand hypothesis is designed to explain the Oligopolistic market.
- Collusion between firms
- Price and output determination
- Rigidity of price
- Price leadership
Answer: 3. Rigidity of price
In the context of oligopoly, the kinked demand curve hypothesis is designed to explain price rigidity. The curve is more elastic above the kink and less elastic below it. This means that the response to a price increase is less than the response to a price decrease.
Question 142. The Aluminum Industry is an example o( which type of oligopoly.
- Opon oligopoly
- Full oligopoly
- Pure oligopoly
- Syndicated oligopoly
Answer: 3. Pure oligopoly
In the case of puro oligopoly, the product of different firms In the industry is Identical or homogenous like in the aluminum Industry.
Question 143. In which market price is determined by the market forces of demand and supply?
- Pure competition
- Perfect competition
- Monopolistic competition
- Oligopoly
Answer: 1. Pure competition
Perfect competition is a form of the market In which there are a large number of buyers and sellers competing with, each other in the purchase and sale of goods, respectively and no Individual buyer or seller has any influence over the price. Thus, perfect competition is an ideal form of market structure in which there is the greatest degree of competition.
Question 144. Railways charge comparatively cheaper fees to senior citizens. These an examples of
- Price discrimination
- Market analysis
- Profit discrimination
- Demand forecasting
Answer: 1. Price discrimination
Railway charges comparatively cheaper foros from senior citizens because It has monopoly power and can practice price discrimination i.o. charging different prices from different customers.
Question 145. Smart Phones market Is an example of
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic Composition
- Oligopoly
- Perfect Competition
Answer: 3. Oligopoly
The cell phone industry is an oligopoly because four large firms are competing to produce 70 to 80% of the output.
Question 146. Collusion is impossible if an industry has
- A large number of firms
- Only flow number of firms
- Only two firms
- A limited number of firms
Answer: 1. A large number of firms
Collusion is a non-competitive, secret, and sometimes illegal agreement between rivals that attempts to disrupt the market’s equilibrium. The act of collusion involves people or companies which would typically compete against one another, but who conspire to work together to gain an unfair market advantage. Collusion is generally seen in an Oligopoly market hence is not possible in the case of a large number of firms.
Question 147. When the industry is dominated by one large firm it is called
- Partial oligopoly
- Full oligopoly
- Organized oligopoly
- Closed oligopoly
Answer: 1. Partial oligopoly
Partial oligopoly refers to a market situation where the industry is dominated by one large firm and other firms of the industry follow the price policy determined by their leader.
Question 148. Choose the incorrect statement regarding the barometric price leadership.
- Live and let live philosophy is followed
- An old and experienced firm acts as a loader
- Price decided by assessing market conditions
- The price decided by the leader is generally accepted by the rest of all
Answer: 1. Live and let live philosophy is followed
Barometric price leadership refers to situations in which a’ price leader acts as a barometer of prevailing market conditions for other firms in the industry.
Question 149. Competition among a few is described in
- Monopoly
- Oligopoly
- Duopoly
- Monopsony
Answer: 2. Oligopoly
There is no certainty in how firms will compete in oligopoly, it depends upon the objectives of the firm and the nature of the product.
Question 150. Which of the following is not a coalition of perfect competition?
- A large number of firms
- Perfect mobility of factors
- Informative advertising to ensure that consumers have good information
- Freedom of entry and exit into and out of the market
Answer: 3. Informative advertising to ensure that consumers have good information
The conditions of a perfect competitive market are as follows:
- Large no of buyers and sellers
- Free entry & exist
- Perfect Substitutes etc.
Question 151. Oligopoly industries are characterized by
- A few dominant firms and substantial barriers to entry
- A few large firms and no entry barriers
- A large number of small firms and no entry barriers
- One dominant firm and low entry barriers
Answer: 1. A few dominant firms and substantial barriers to entry
A few dominant firms and substantial barriers to entry Oligopoly industries are characterized by a few dominant firms and substantial barriers to entry.
Question 152. The long-run equilibrium outcomes in monopolistic competition and perfect competition are similar, because in both market structures:
- The efficient output level will be produced in the long run
- Firms will be producing at a minimum average cost
- Firms realize all economies of scale
- Firms will only earn normal profit
Answer: 4. Firms will only earn a normal profit
The long-run equilibrium outcomes in monopolistic competition and perfect competition are similar because in both market structures firms will only have normal profits. ‘
Question 153. Pure oligopoly is based on the _________________________ production
- Homogeneous
- Differential
- Unrelated
- Related
Answer: 1. Homogeneous
Pure oligopoly is based on Homogeneous production.
Question 154. In The competition of oligopoly, the kinked demand curve hypothesis is designed to explain.
- Price rigidity
- Price and output determination.
- Price leadership
- Collusion
Answer: 1. Price Rigidity
In the oligopoly market, the linked demand curve hypothesis is designed to explain price rigidity.
Question 155. Given AR = 5 and elasticity of demand = 2 find MR.
- +2.5
- -2.5
- + 1.5
- + 2.0
Answer: 1. +2.5
Given AR = 5 and elasticity of demand = 2
MR = AR × (e-1)/(e)
= 5 × \(\frac{2-1}{2}\)
= +2.5
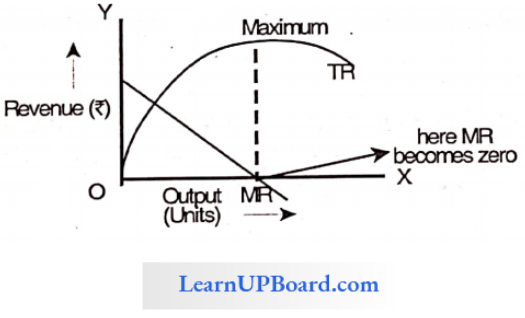
Question 156. When TR is max, then MR is
- Zero
- One
- Both (1) and (2)
- None
Answer: 1. Zero
When Total Revenue is max then marginal revenue is Zero.
Question 157. A firm to attain the equilibrium position under perfect competition has ‘ to satisfy which of the following conditions?
- MR > MC
- MR = MC
- MR curve should cut MC curve from below
- MC curve should cut MR curve from below
Answer: 4. The MC curve should cut the MR curve from below
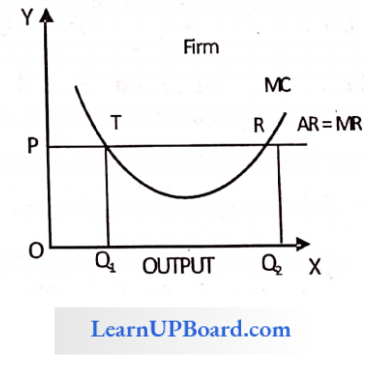
At R, the MC curve is cutting the MR curve from below. Hence, R is the point of equilibrium T, MC curve is cutting the MR curve from above. Hence, T is not the point of equilibrium.
Question 158. Electricity companies sell electricity at a cheaper rate for power consumption in rural areas than for industrial consumption. This is an example of
- Product discrimination
- Perfect competition
- Price discrimination
- Price taker
Answer: 3. Price discrimination
Electricity companies sell electricity at a cheaper rate for power consumption in rural areas than for industrial consumption.
Price discrimination is a method of pricing that is adopted by a Monopolist to earn abnormal profit. It is a method in which different prices are charged for different units of the same commodity.
Question 159. Which of the following is an example of monopolistic competition?
- De Beers and Diamonds
- Hotel and Pubs
- Microsoft and window
- Dell and Lenovo
Answer: 2. Hotel and Pubs
In Monopolistic competition, large number of buyers and a large number of firms in the industry. Differentiated products that are close substitutes but not perfect substitutes Example: Hotels and Pubs.
Question 160. Who propounded the price rigidity under kinked demand curve model of oligopoly?
- Adam Smith
- Karl Marx
- Keynes
- Paul A. Sweezy
Answer: 4. Paul A. Sweezy
American economist Paul A. Sweezy propounded the price rigidity under the kinked demand curve model of oligopoly.
Question 161. The demand for generic goods like soap is ________________ the demand for Lux soap is ________________
- Inelastic, elastic
- Elastic, inelastic
- Inelastic, inelastic
- Elastic, elastic
Answer: 4. Elastic, elastic
The demand for generic goods like soap is elastic the demand for LUX soap is elastic.
Question 162. Zero economic profit emerges due to which of the following conditions?
- The average revenue is more than the average total cost.
- Marginal revenue is just equal to marginal cost.
- Marginal revenue is just not equal to marginal cost.
- Average revenue is just equal to the average total cost.
Answer: 4. Average revenue is just equal to the average total cost.
Zero economic profit emerges because to average revenue is just equal to the average total cost.
Question 163. Non-price competition is observed in which type of the following market?
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic competition
- Duopoly
- Oligopoly
Answer: 2. Monopolistic competition
Non-price competition is observed in the monopolistic competition market.
Features of monopolistic competition are:
- Product differentiation
- Freedom of entry and exit
- Large numbers of buyers and sellers
- Non-price competition
Question 164. A group of firms that explicitly agree (collude) to coordinate their activities is called a/an.
- Oligopoly
- Duopoly
- Monopoly
- Cartel
Answer: 4. Cartel
Cartels are often formed in industries where there are few firms all of which are similar in size. A group of firms that explicitly agree to coordinate their activities is known as a cartel.
Question 165. Which one of the following is not a characteristic of oligopoly?
- Strategic interdependence
- A large number of firms selling close substitutes.
- Importance of selling cost
- Group behaviour
Answer: 2. Large number of firms selling close substitutes.
Large numbers of firms selling close substitutes is not a feature of oligopoly.
Features of oligopoly are:
- Few firms or sellers
- Example: Cold drinks
Question 166. Which of the following is not a feature of the monopoly market?
- Large seller of the product
- No close – substitutes
- Market, power
- Single seller of the product
Answer: 1. Large seller of the product
Features of the monopoly market are:
- Single seller of the product
- Barriers to Entry
- No close substitutes
- Market power
Question 167. Price discrimination refers to charging ____________________ prices for units of _________________ commodity.
- Different, different, same
- Different, same, same
- Same, different, same
- Same, same, different
Answer: 1. Different, different, same
Price discrimination is a method of pricing adopted by a monopolist to earn abnormal profits. It refers to the practices of charging different prices for different units of the same commodity.
Price discrimination is a selling strategy that charges customers different prices for the same product or service based on what the seller thinks they can get the customer to agree to. In pure price discrimination, the seller charges each customer the maximum price they will pay.
Question 168. There are 4 firms in the market
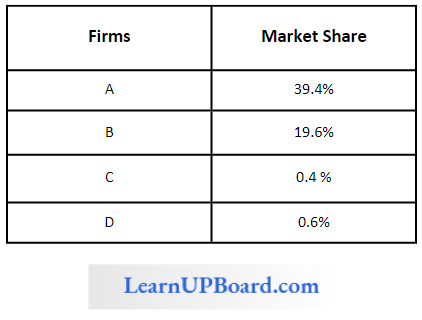
Which type of market structure can be most suitable here?
- Oligopoly
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic
- Perfect Competition
Answer: 1. Oligopoly
Oligopoly is often described as ‘competition among the few’. Prof. Stigler defines oligopoly as a “situation in which a firm bases its market policy, in part, on the expected behavior of a few close rivals”. In other words, when there are few (two to ten) sellers in a market selling homogeneous or differentiated products, an oligopoly is said to exist.
Oligopolies mostly arise due to those factors which are responsible for the emergence of monopolies. Unlike a monopoly where a single firm enjoys absolute market power, under an oligopoly a few firms exercise their power to keep possible competitors out.
Question 169. A market condition in which there is only a single seller and a single buyer.
- Monopsony
- Bilateral Monopoly
- Monopolistic Competition
- Oligopoly.
Answer: 2. Bilateral Monopoly
A bilateral monopoly exists when a market has only one supplier • and one buyer. The one supplier will tend to act as a monopoly power and look to charge high prices to the one buyer.’ The lone buyer will look towards paying a price that is as low as possible.
Question 170. Charging lower prices from senior citizens for railway tickets is an example of
- Subsidized pricing
- Concessional pricing
- Price discrimination
- Product pricing
Answer: 3. Price discrimination
Under third-degree price discrimination, price varies by attributes such as location or by customer segment. Here the monopolist will divide the consumers into separate sub-markets and charge different prices in different sub-markets.
Examples: Dumping, charging different prices for domestic and commercial uses, lower prices in railways for senior citizens, etc.
Question 171. Which of the following is not a characteristic of perfect competition
- A large no. of sellers and buyers
- Freedom of entry and exit
- Inefficient allocation of resources
- Homogeneous Product.
Answer: 3. Inefficient allocation of resources
Inefficient allocation of resources is not a characteristic of perfect competition. A market is said to be perfectly competitive if it has large number of buyers and sellers, homogeneous product, free entry and exit, perfect mobility of factors of production, perfect
knowledge about the market conditions, insignificant transaction costs, no government interference, and absence of collusion.
Question 172. When the industry is dominated by one large firm, then it is .
- Full oligopoly
- Syndicated oligopoly
- Organized oligopoly
- Partial oligopoly
Answer: 4. Partial oligopoly
When the industry is dominated by one large firm, then it is a partial oligopoly. Oligopoly is a form of imperfect competition and is usually described as competition among a few. Hence, Oligopoly exists when there are two to ten sellers in a market selling homogeneous or differentiated products. These firms sell homogeneous as well as differentiated products in the market.
Question 173. In an oligopoly, sellers try to act as
- Price taker
- Price maker
- Price indicators
- Price barriers
Answer: 1. Price taker
Oligopolies are price setters (makers) rather than price takers. Barriers to entry are high. The most important barriers are government licenses, economies of scale, patents, access to expensive and complex technology, and strategic actions by incumbent firms designed to discourage or destroy nascent firms.
Question 174. The kinked demand curve is designed to explain
- Price and output determination
- Price rigidity
- Price leadership
- Collusion among rivals
Answer: 2. Price rigidity
In the context of oligopoly, the kinked demand curve hypothesis is designed to explain Price rigidity. The curve is more elastic above the kink and less elastic below it. This means that the response to a price increase is less than the response to a price decrease
Question 175. In the case of monopoly, the price elasticity of demand is
- Elastic
- More elastic
- Negative
- Infinite
Answer: 3. More elastic
Monopoly power, also called market power, is the ability to set price. Firms with market power face a downward-sloping demand curve. Hence, negative.
Question 176. The kinked demand curve model of oligopoly assumes that
- The response (of consumers) to a price increase is less than the response to a price decrease
- The response (of consumers) to a price increase is more than the response to a price decrease
- The elasticity of Demand is constant
- Demand is perfectly elastic.
Answer: 1. The response (of consumers) to a price increase is less than the response to a price decrease
The kinked demand curve model of oligopoly assumes that the response to a price increase is less than the response to a price decrease, the response to a price increase is more than the response to a price decrease. The elasticity of demand is constant regardless of whether the price increases or decreases.
Question 177. In which form of the market structure is the degree of control over the price of its product by a firm is very large?
- Monopoly
- Imperfect competition
- Oligopoly
- Perfect competition
Answer: 1. Monopoly
In a monopolistic market structure, the degree of control over the price of its product by a firm is very large.
Question 178. Under perfect competition in the long run there will be
- Normal profit
- Supernormal profit
- Production
- Cost
Answer: 1. Normal profit
In perfect competition, in the long run, there will be Normal profits. Perfect Competition Long Run equilibrium results in ail
firms receiving normal profits or zero economic profits.
Question 179. The degree of control over price is very considerable in
- Monopoly
- Perfect competition
- Oligopoly
- Monopolistic competition
Answer: 1. Monopoly
In a Monopoly market structure, the degree of control over the price of its product by a firm is very large. In a monopoly type of market structure, there is only one seller, so a single firm will control the entire market. It can set any price it wishes since it has all the market powers. Consumers do not have any alternative and must pay the price set by the seller.
Question 180. In which of the market firms does price discrimination not persist?
- Monopoly
- Oligopoly
- Monopolistic Competition
- Perfect Competition.
Answer: 4. Perfect Competition
In a monopoly, the seller adopts this method of pricing to earn abnormal profits. It is important to remember that price discrimination cannot persist under perfect competition since the seller has no control over the market price of the product/service.
Question 181. Nuclear Power represents which type of market structure
- Government Monopoly
- Perfect Competition
- Monopolistic Competition
- Oligopoly
Answer: 1. Government Monopoly
Nuclear power represents a government monopoly type of market. structure.
Question 182. The monopoly market and Monopsony market combination is called
- Duopoly Market
- Oligopoly Market
- Bilateral Monopoly Market
- Monopolistic Market
Answer: 3. Bilateral Monopoly Market
A monopoly market and monopsony market combination is called as bilateral monopoly market.
Question 183. The marginal revenue curve listens to the demand curve in monopolistic competition due to
- Below; product differentiation
- Above; Barriers to entry
- Above; Product-differentiation
- None of these
Answer: 1. Below; product differentiation
The marginal revenue curve lies below its demand curve in monopolistic competition due to product differentiation.
Question 184. In monopoly MR is AR.
- Less than
- Greater than
- Equal
- Any of the above
Answer: 1. Less than
In monopoly, MR is always less than AR, as AR i.e prices are always greater than marginal revenue to earn economic profit.
Question 185. Non- Price competition typically occurs within
- Monopoly
- Perfect Competition
- Monopolistic
- Oligopoly
Answer: 3. Monopolistic
A monopolistic competition has non-price competition. In nonprice competition all firms are safe and they don’t need to reduce their profit margins.
Sellers attempt to provide and promote their products not by cutting prices but by incurring expenditure on publicity and
advertisement.
Question 186. On the upper side of the kinked demand curve, what is the elasticity of
- Less elastic
- Inelastic
- Relatively elastic
- Infinite
Answer: 3. Relatively elastic
On the upper side of the kinked demand curve elasticity of demand is relatively more elastic than the elasticity on the lower side of the demand curve.
Question 187. Price rigidity is a concept of
- Perfect competition
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic
- Oligopoly
Answer: 4. Oligopoly
Price rigidity is a feature of oligopoly as price does not change easily in response to changes in demand. If a firm raises the price others keep constant. Hence, it is not rational to keep prices increasing, so prices are rigid.
Question 188. A firm should produce fill MC _____________ MR
- Greater
- Less
- Equal
- All of the above
Answer: 3. Equal
According to economic theory, a firm expands production until the point marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue
Question 189. Which of the following statements is correct?
- Price rigidity is an important feature of monopoly
- Selling Costs are possible under perfect conditions. ,
- Under perfect competition factor of production do not move freely as there are legal restrictions
- An industry consists of many firms
Answer: 4. An industry consists of many firms
Price rigidity is an important feature of an oligopoly and not a monopoly. Selling costs are not possible under perfect competition as well as a monopoly market. Under perfect competition, there is freedom of entry and exit.An industry consists of various firms. Hence, option (d) is correct.
Question 190. In this type of market, there are large numbers of buyers and sellers with identical products
- Imperfect competition.
- Oligopoly
- Perfect competition
- Monopolistic competition
Answer: 3. Perfect competition
Features of perfect competition:
- A large number of buyers and sellers.
- Homogenous/identical products.
- Free entry and exit.
- Perfect knowledge of the market conditions on the part of buyers and sellers.
- Negligible transaction costs.
- All firms are individual price takers.
Question 191. The kinked demand curve is also known as
- Sweezy’s model
- Adam’s model
- Revisionary model
- Economic trade model
Answer: 1. Sweezy’s model
The kinked demand curve hypothesis was given by an American economist Paul A Sweezy. Hence, this is called Sweezy’s model.
Question 192. On the upper part of the kinked demand curve, the demand is
- Elastic
- Inelastic
- Neutral
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Elastic
The upper segment of the kinked demand curve is relatively elastic and the lower segment is relatively inelastic. The difference in elasticities is due to the particular competitive reaction pattern assumed by the kinked demand curve hypothesis.
Question 193. The long-run equilibrium of a competitive firm is achieved at
- LAR = LMR = P = LMC = LAC
- LMR = LAR = LMC +1 = LAC
- LAR = LMR +1 = P+1 = LAC
- P = LMC = LAC – LMR + LAR
Answer: 1. LAR = LMR = P = LMC = LAC
In the long run, under perfect competition, the market mechanism leads to optimal allocation of resources. The optimality is shown by
The following outcomes are associated with the long-run equilibrium of the industry:
- The output is produced at the minimum feasible cost
- Consumers pay the minimum possible price which just covers the marginal cost i.e.
- MC = AR. (P = MC)
- Plants are used to fully capacity in the long run, so that there is no wastage of resources i.e. (MC = AC)
- The firm earns only normal profits i.e. AC = MR
- Firms maximize profits (i.e, MC = MR), but the level of profits will be just normal
- There is an optimum number of firms in the industry.
- LAR = LMR = P = LMC = LAC
Question 194. The producer is an oligopolistic market that fixes its price at
- A price less than the price charged by a monopoly as well as a perfectly competitive market.
- A price more than the price charged by a perfectly competitive market as well as a monopoly
- A price higher than the one charged by a monopoly and less than that of a perfectly competitive market.
- A price higher than that charged by a perfectly competitive market and less than that of a monopoly.
Answer: 4. A price higher than that charged by a perfectly competitive market and less than that of a monopoly
The producer in an oligopolistic market fixes its price at a price higher than that charged by a perfectly competitive market and less than that of a monopoly.
Question 195. Which of the following is a behavior of oligopoly?
- Group behaviour
- Individual behavior
- Relative behaviour
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Group behavior
The theory of oligopoly is a theory of group behavior, not of mass or individual behavior, and assumes profit-maximizing behavior.
Question 196. Where there are a large number of letters in a market and there is a very high degree of competition between them, the elasticity of supply is
- Infinite
- Zero
- More than one
- Less than one
Answer: 2. Zero
Where there are a large number of sellers in a market, and there is a very high degree of competition between them, the elasticity of supply is zero.
Question 197. Which of the following markets may earn supernormal profit in the long run
- Perfect competition
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic
- None of these
Answer: 2. Monopoly
Monopoly being only a single seller in the market can earn supernormal profits in the long run.
Question 198. “Product differentiation” is characteristic of
- Perfect competition
- Monopolistic competition.
- Oligopoly competition
- Duopoly competition
Answer: 2. Oligopoly competition
Product Differentiation is an essential feature of Monopolistic competition.
Question 199. The “Kinked demand curve” hypothesis explains which of the following concepts?
- Price leadership
- Price rigidity
- Group behaviour
- Independent pricing
Answer: 2. Price rigidity
The “Kinked Demand Curve” in Oligopoly explains the concept of Price rigidity.
Question 200. In which type of Market, the product is homogeneous?
- Pure Oligopoly.
- Pure Monopoly
- Pure Duopoly
- Pure Competition
Answer: 4. Pure Competition
Pure Competition is a market where there are a large number of buyers and sellers dealing with the same homogeneous goods and there is free to entry and free exit.
Question 201. When a new firm enters the market and competes with the existing firm is a situation called?
- Open Oligopoly
- Open Oligopoly
- Collusive Oligopoly
- Competitive Oligopoly
Answer: 1. Open Oligopoly
Based on entry and exit, an oligopoly is classified as an open oligopoly or closed oligopoly. Here, new firms are entering and competing with existing firms. It is an open oligopoly.
Question 202. Which of the following is characteristic of Monopoly?
- The industry is dominated by a larger no. of firms
- Freedom to entry and exit.
- No close substitutes
- Only two firms in the market
Answer: 3. No close substitutes
Monopoly is characterized by No close substitutes and a Single
Question 203. Not an objective of Price Discrimination?
- To enjoy Economics of scale
- To dispose of surplus stock
- To escape the foreign market
- To secure equity through pricing
Answer: 3. To escape foreign market
To Escape Foreign Market
To escape a foreign market is not an objective of price discrimination. Monopoly is characterized by No close substitutes and Single sellers.
