CA Foundation Economics – Theory Of Production And Cost Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Opportunity cost is
- Direct cost
- Total cost
- Cost of foregone oppurtunity
- Accounting cost
Answer: 4. Cost of foregone opportunity
Opportunity cost is the cost of the next best alternative forgone. It’s the cost of foregone opportunity.
Question 2. As output increases, the average fixed cost
- Remains constant
- Starts falling
- Start rising
- None
Answer: 2. Starts falling
The average fixed cost is expressed as
AFC = Fixed Cost/ Number of units produced
Fixed cost always remains fixed. It does not increase with an increase in output. So the average fixed cost falls as more and more units are produced as the fixed cost remains the same.
Question 3. Average fixed cost can be obtained through
- AFC = TFC/TS
- AFC = EC/TU
- AFC = TC/ PC
- AFC = TFC/TU
Answer: 4. AFC = TFC/TU
Average Fixed Cost = Total Fixed Cost / Number of units produced
In the given Question
AFC = Average fixed cost
TFC = Total Fixed cost
TU = Total no. of units produced.
Question 4. AFC curve Is
- Convex & downward sloping
- Conenvo & downward sloping
- Convox & upward sloping
- Conenvo & upward rising
Answer: 1. Convex & downward sloping
Average fixed cost always decreases with an Incroaso in output so the AFC curve Is convex and downward sloping.
Question 5. A firm’s average flood cost Is 20 at 6 units of output what will It be at 4 units of output?
- 60
- 30
- 40
- 20
Answer: 2. 60
A firm’s average flood cost Is 20 at 6 units of output
TFC/ Number of units
20 = TFC/6
So Total fixed cost = 20 × 6
= ₹ 120.
So Average Fixed Cost of 4 units of output
AFC = TFC / Number of units
AFC = \(\frac{120}{4}\).
= 30
Question 6. U-shaped average cost curve is based on:
- Law of Increasing Cost
- Law of decreasing cost
- Law of constant rot urns to scale
- Law of variable proportions
Answer: 4. Law of variable proportions
Avorago cost curve is U-shaped due to the law of variable proportion. In the the first stage, T.P increases so AC decreases, then T.P becomes constant and finally, T.P decreases and AC increases. Horico, it gives a U shape to the average cost curve
Question 7. When the shape of the average cost curve is upward, the marginal cost
- Must be decreasing
- Must be constant
- Must be rising
- Any of these
Answer: 3. Must be rising
Average cost and marginal cost are so related that when the average cost falls, MC falls at a faster rate, when AC rises, MC cuts AC at its minimum.
So when the AC curve is upward MC must be rising.
Question 8. If the total cost for 10 units is ₹ 600 and ₹ 640 for the 11th unit. The marginal cost of the 11th unit is
- ₹20
- ₹30
- ₹40
- ₹50
Answer: 3.
If the total cost for 10 units is ₹ 600 and ₹ 640 for the 11th unit.
Marginal Cost = TC – TC
= TC11– TC11-1
= 640 -600
= ₹ 40
Question 9. Economic cost excludes which of the following
- Accounting cost + explicit cost
- Accounting cost + implicit cost
- Explicit cost + Implicit cost
- Accounting cost + opportunity cost
Answer: 1. Accounting cost + explicit cost
Economics cost takes into account accounting (explicit) cost and in addition to this includes the amount of money the entrepreneur could have earned if he had invested his money and sold his se-does arc ether factors in the next best alternative use.
Economic Cost = Implicit cost e Explicit cost
OR = Accounting cost + Implicit cost
OR = Accounting cost e opportunity cost
Question 10. Which of the following cost curves is never ‘U’ shaped?
- Average total cost curve
- Marginal cost curve
- Total cost curve
- Total Fixed cost curve
Answer: 4. Total Fixed cost curve
Total fixed cost refers to the cost which remains the same even if the total increases. Rxed cost has no effect with an increase and decrease h production. Examples of such costs are rent factory charges, etc. Since fixed cost always remains constant so the fixed cost curve is not U shaped but it’s a straight
Question 11. Suppose, the total cost of production of commodity X is ₹ 1,25,000. Out of this cost, the implicit cost is ₹ 35,000 and the normal profit is ₹ 25,000. What will be the explicit cost of commodity X?
- 90,000
- 65,000
- 60,000
- 1,00,000
Answer: 2. 65,000
Suppose, the total cost of production of commodity X is ₹ 1,25,000. Out of this cost, the implicit cost is ₹ 35,000 and the normal profit is ₹ 25,000.
Total cost = ₹ 1,25,000
Implicit cost =₹ 35,000
Normal profit = ₹ 25,000 –
Explicit cost =?
Total cost = Explicit Cost + Implicit Cost + Normal Profit
1,25,000 = Explicit Cost + 35,000 + 25,000
Explicit Cost = ₹ 65,000
Question 12. What is the total cost of production of 20 units, if the fixed cost is X 5,000 and the variable cost is ₹ 2/-?
- 5,400
- 5,040
- 4,960
- 5,020
Answer: 2. 5,040
Total Cost = Fixed Cost + Variable Cost t
₹ 5,000 ÷ 20 × 2.
= ₹ 5040
Question 13. External economies accrue due to _________________
- Increasing returns to scale
- Increasing returns to factor
- Law of variable proportion
- Low cost
Answer: 1. Increasing returns to scale
External economies accrue to firms as a result of the expansion of the output of the whole industry. Increasing returns to scale occur due to external economies.
Question 14. At which point does the marginal cost curve intersect the average variable cost curve and short-run average total cost curve?
- At equilibrium points
- At their lowest points
- At their optimum points
- They don’t intersect at all
Answer: 2. At their lowest points
The marginal cost curve and average cost curve tend that when the AC curve falls, the MC curve falls faster when the AC curve rises MC curve rises at a faster rate and the MC curve cut the AC curve at its minimum .(lowest point).
Question 15. Implicit cost may be defined as the
- Costs which do not change over some time
- Costs which the firm incurs but doesn’t disclose
- Payment to the non-owners of the firm for the resources
- Money payment which the self-employed resources could have earned in their best alternative employment
Answer: 4. Implicit cost is the cost of self-employed resources.
It is the cost of inputs owned by the firms and used by the firm in its production process.
Implicit costs include:
- Return on money invested by the entrepreneur in .its own business
- Rent of self-owned building of the entrepreneur.
Question 16. A firm’s average fixed cost is ^ 40 at 12 units. What will be the average fixed cost at 8 units:
- ₹ 60
- ₹ 70
- ₹ 90
- ₹ 80
Answer: 1. ₹ 60
AFC = TFC/Number of units produced
40 = TFC/12
TFC = 40 × 12
= ₹ 480
Question 17. Returns to scale will said to be in operation when the quantity of
- All inputs are changed
- All inputs are changed in already established proportion
- all inputs are not changed
- One input is changed while the quantity of all other inputs remains the same
Answer: 2. All inputs are changed in already established proportion
Returns to scale come into operation when all inputs whether fixed or variable are changed in the same proportion i.e. the scale of production changes.
Question 18. Which of the following curves never touches any axis but is downward?
- Marginal cost curve
- Total cost curve
- Average fixed cost curve
- Average variable cost curve
Answer: 3. Average fixed cost curve
The average fixed cost curve never touches any axes but it slopes downward. Average fixed cost can never be zero even if there is no production so it can never touch any axes. AFC falls when output increases as fixed cost is always fixed. Hence, the curve is downward sloping.
Question 19. Which of the following is known as the Envelope curve?
- MC curve
- AFC curve
- LAC curve
- TFC curve
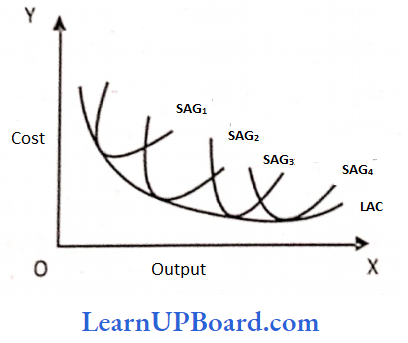
Answer: 3. LAC curve
The long-run average cost curve is called the enveloping curve os ft envelops all short-run average cost curves (SAC curves are tangent to the LAC curve)
Question 20. A firm producing 7 units of output has an average total cost of ₹ 150 and has to pay ₹ 350 to its fixed factors of production How much of the average lotal cost is made up of variable cost?
- 200
- 50
- 300
- 100
Answer: 4. 100
A firm producing 7 units of output has an average total cost of ₹ 150 and has to pay ₹ 350 to its fixed factors of production
ATC = TC / Number of units
150= T.C/7
Total cost of 7 units = 150 × 7 = 1050
Fixed Cost = 7 350
Total cost = Fixed Cost + Variable Cost
1050 = 350 + V.C.
So variable cost of 7 units = 1050 – 350 = ₹ 700
Average variable cost of 7 units = \(\frac{700}{7}\) = ₹ 100
Question 21. A firm’s average fixed cost is ₹ 20 at 6 units of output. What will it be at 3 units of output?
- ₹ 60
- ₹ 30
- ₹ 40
- ₹ 20
Answer: 3. ₹ 40
A firm’s average fixed cost is ₹ 20 at 6 units of output.
Average fixed cost = TFC/ Number of units
20 = TFC/6
T.F.C. = 20 × 6 = ₹ 120.
Average fixed cost of 3 units of output = TFC/ Total units
⇒ \(\frac{120}{2}\)
= ₹ 40.
Question 22. Calculate the total cost of 4 units
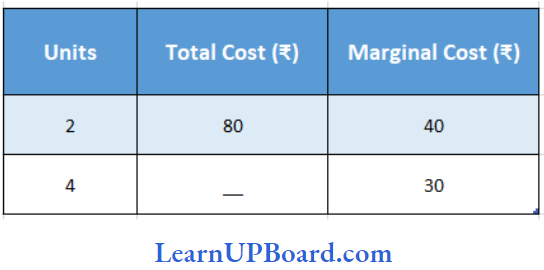
- 140
- 120
- 50
- 40
Answer: 1. 140
Let the total cost of producing 4 units be ₹ x
Marginal Cost = Change in Total/Cost Change in Total Quantity
= \(\frac{x-80}{4-2}\)
= 30
= \(\frac{x-80}{2}\)
= x- 80 = 60
= x = 60 + 80
=₹ 140
Question 23.
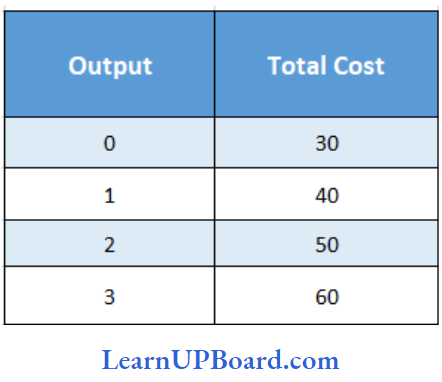
Find the average fixed cost of 3 units
- 10
- 0
- 65
- 60
Answer: 1. 10
= Average fixed cost /Quantity
= \(\frac{30}{3}\)
= 10
Question 24. Long run does not have
- Average Cost
- Total Cost
- Fixed Cost
- Variable Cost
Answer: 3. Fixed Cost
The long run is a period during which the firm can vary all its inputs, unlike the short run in which some inputs are fixed and others are variable. In other words, in the short run, the firm is tied with a given plant, in the long run, the firm moves from one plant to another, so the long run does not have any fixed cost.
Question 25. Which of the following cun/e is not U-shaped?
- AFC
- A VC
- MC
- TC.
Answer: 1. AFC
Fixed cost remains fixed irrespective of several units produced and therefore average fixed cost keeps on decreasing as more and more units are produced. Due to this, the average fixed cost curve always slopes downward throughout its length and it is not of U shape.
Question 26. From the following details, find out the average variable cost of 10 units
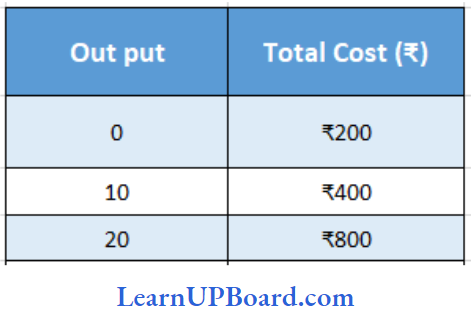
- ₹ 40
- ₹ 20
- ₹ 200
- ₹ 400
Answer: 2. 20
Variable cost per unit = Difference in cost/ Difference in units produced
⇒ \(\frac{400-200}{10}\)₹
= ₹ 20 per unit
Variable cost of 10 units = ₹ 20× 10
= ₹ 200
Therefore, average variable cost = \(\frac{200}{10}\)₹
= ₹ 20
Question 27. The total cost incurred for 10 units is T 400 and 20 units is ^ 800. Find the marginal cost.
- ₹ 400
- ₹ 40
- ₹ 200
- ₹ 20
Answer: 2. ₹ 40
The total cost incurred for 10 units is T 400 and 20 units is ^ 800.
Variable/Marginal cost may be expressed as:
Difference in cost/difference in units
In the given case
Marginal Cost = \(\frac{800-400}{20-10}\)₹
= \(\frac{400}{10}\)₹
= ₹ 40 per unit.
Question 28. Which one of the following is correct?
- AFC = AVC + ATC
- ATC = AFC-AVC
- AVC = AFC + ATC
- AFC = ATC – AVC.
Answer: 4. AFC = ATC – AVC.
The total cost of a business is the sum of the total variable cost and total fixed cost. Symbolically, TC = TFC + TVC. Similarly, average total cost is a sum of average variable cost and average fixed cost i.e. ATC = AFC + AVC. This formula can also be expressed as:
AFC = ATC – AVC
Question 29. Calculate AFC of 3 units from the following data:
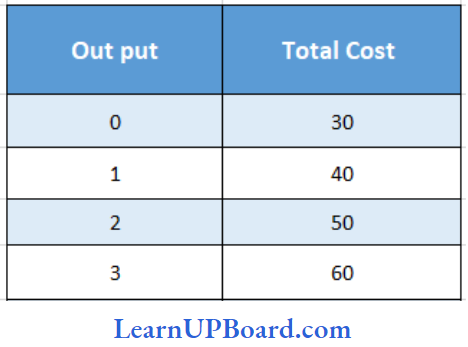
- ₹ 30
- ₹ 15
- ₹ 10
- ₹ 5
Answer: 3. ₹ 10
Fixed cost is the cost incurred even when no production is done, whereas the cost incurred on the production of units is called variable cost. Total cost is the summation of fixed cost and variable cost.
In the given case, at 0 units of output, the total cost is ₹ 30. This total cost comprises of only fixed costs and not variable costs as no units are produced.
Fixed cost always remains the same, irrespective of the number of units.
Therefore, the average fixed cost of 3 units will be:
AFC = TFC/ Number of units
AFC of 3 units = \(\frac{30}{3}\)₹
= ₹ 10
Question 30. Find AFC of 3 units
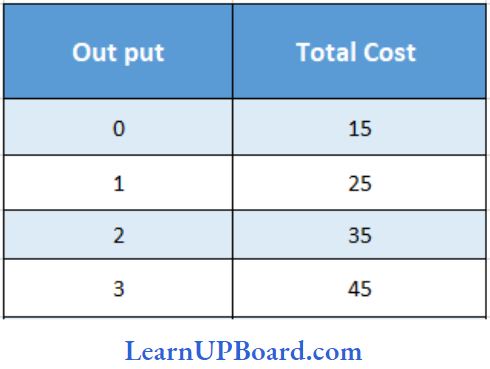
- 5
- 10
- 15
- 25
Answer: 1. 5
Fixed cost remains the same, irrespective of the level of output.
In the given case, fixed cost = ₹ 15
Average fixed cost of.3 units = Total fixed cost / Number of units
= ₹ \(\frac{15}{3}\)
AFC of 3 units = ₹ 5
Question 31. What will be the TVC if we produce 2 units?
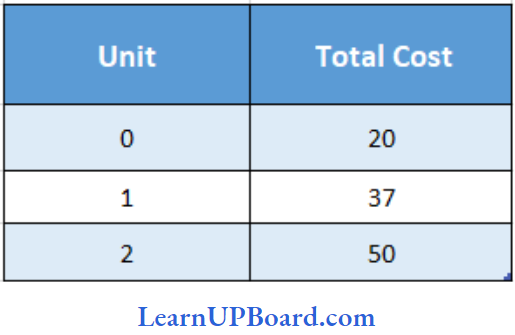
- 15
- 05
- 17
- 30
Answer: 4. 30
At zero units of output TC = FC (since TC= FC+VC) So FC = 20,
At 2 units of output: TC = 50 and FC = 20 so variable cost = Total cost – Fixed cost
⇒ 50 – 20 = 30
Question 32. The total cost of production of 10 units is ^ 200. When production is increased to 20 units its total cost becomes ? 600. What will be its marginal cost?
- 400
- 40
- 4
- 30
Answer: 2.
Marginal Cost is expressed as:
The total cost of production of 10 units is ^ 200. When production is increased to 20 units its total cost becomes ₹ 600
Difference in total cost/ Difference in total units
= \(\frac{600-200}{20-10}\)₹
= \(\frac{400}{10}\)₹
= ₹ 40 per unit.
Question 33.
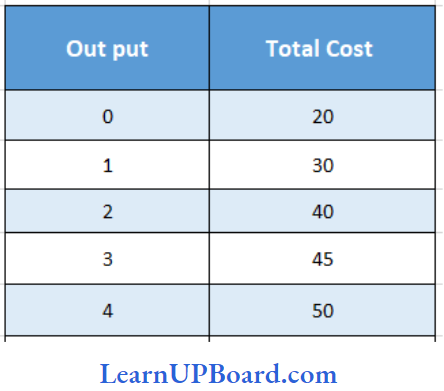
What will be the AFC at 4 units of output?
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Answer: 4. 5
Average fixed cost is expressed as:
= Total fixed cost / Quantity = \(\frac{20₹ }{4 units}\)
= ₹ 5 units per unit
Question 34. Payments made to outsiders for their goods and services are called
- Opportunity cost
- Real cost
- Explicit cost
- Implicit cost
Answer: 3. Explicit cost
Explicit cost (or Accounting cost) takes care of all the payments and charges made by the entrepreneur to the suppliers of various productive factors example, wages to workers employed, prices for the raw materials, fuel and power used, rent for the hired building, interest on money borrowed for doing business etc. These costs are included in the cost of production.
Question 35. Direct Cost is also known as
- Indirect Cost
- Traceable Cost
- Opportunity Cost
- AccountingCost.
Answer: 2. Traceable Cost
Indirect cost is also known as non-traceable cost. Traceable cost is also known as direct cost. Accounting cost is also known as explicit cost.
Question 36. A firm’s AFC is ₹ 200 at 10 units of output what will be it at 20 units of output?
- 500
- 100
- 150
- 200
Answer: 2. 100
AFC = TFC/ Output
Now, TFC for 10 units of output = 200 × 10 = 2000
AFC for 20 units = \(\frac{2000}{20}\)
= 100
Question 37. Long run price is also called by the name of ________________
- Market price
- Normal price
- Administered price
- Wholesale price.
Answer: 2. Normal price
Long Run price is also known as Normal price
Question 38. What will be the AFC of 2 units according to the table given below
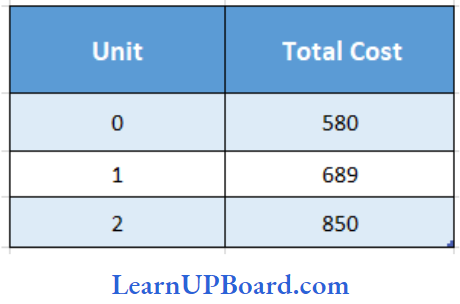
- 105
- 135
- 235
- 290
Answer: 4. 290
TC at 0 Units of output = ₹ 580
TFC = ₹ 580.
AFC = TFC/Output
= \(\frac{580}{2}\)
= 290
Question 39. Fixed cost is known as _______________
- Prime
- Supplementary
- Overhead
- Direct
Answer: 3. Overhead
Fixed cost is also known as overhead cost since it continues to exist even if the operations are suspended. For example rent of factory.
Question 40. Average Revenue Curve is also known as.
- Profit curve
- Demand curve
- Supply curve
- Average cost curve
Answer: 2. Demand curve
The average Revenue Curve is also known as the Demand Curve.
Question 41. The supply curve remains unchanged, an increase in demand will lead to.
- A fall in price
- A rise in price
- No change in price.
- An increase in supply.
Answer: 2. A rise in price
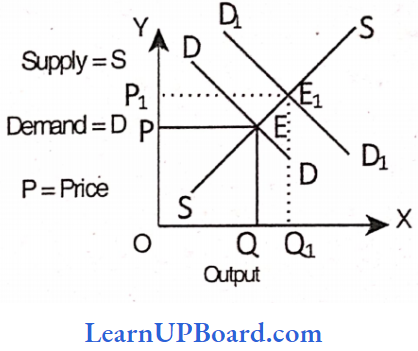
An increase in demand without a change in supply to leads in price and quantity
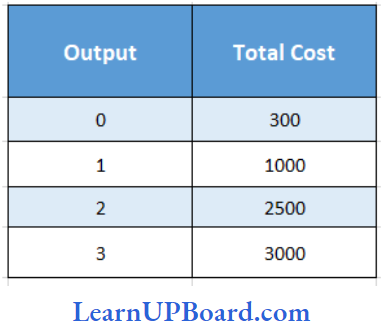
Question 42. Find out AFC of 3 units:
- 100
- 200
- 300
- 400
Answer: 1. 100
Average fixed cost (AFC) = total fixed cost/ Number of units
In The given case,
Total fixed cost = ₹ 300
AFC for 3 units = \(\frac{300}{3}\)₹
= ₹ 100
Hence, AFC for 3 units is ₹ 100
Question 43.
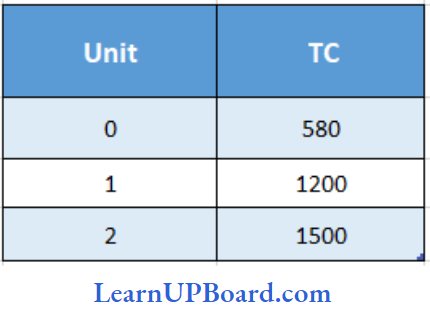
Calculate AFC at 2nd unit of output
- ₹ 235
- ₹ 290
- ₹ 310
- ₹ 920
Answer: 2. ₹ 290
Average fixed cost (AFC) = total fixed cost/ Number of units
In The given case,
Total fixed cost = ₹ 580
AFC for 3 units = \(\frac{580}{2}\)₹
= ₹ 290
Question 44. In the long run, all factors are
- Fixed
- Variable
- All factors remain unchanged
- None.
Answer: 2. Variable
The long run is the period during which the firm can vary all of its inputs. In other words, in the long run, all factors are variable and no factor is fixed.
Question 45. What will be the AFC of 3 units of Output as per the table given below?
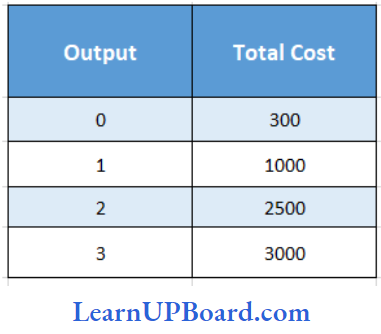
- 100
- 1,000
- 200
- 400
Answer: 1. 100
Total Fixed Cost =₹ 300
Total output = 3 units
∴ AFC = TFC/ Q
= \(\frac{300}{3}\)
= ₹ 100
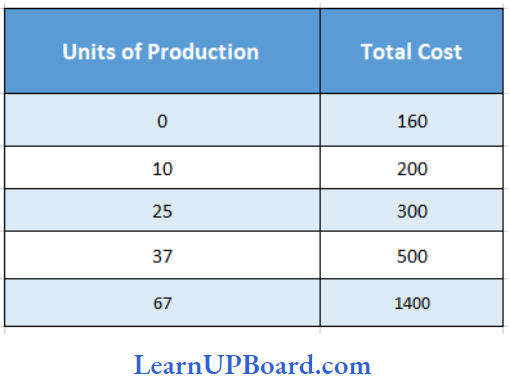
Question 46. What will be the marginal cost of 67 units of production according to the table given below
- 10
- 20
- 30
- 50
Answer: 3. 30
Change in total cost = 1400 – 500 = ₹ 900
Change in units of production = 67 – 37 = 30 units
MC per unit = Change in Total Cost/Change in units
= \(\frac{900}{30}\) ₹
= ₹ 30
Question 47. Which of the following is known as the Envelope Curve?
- Average variable cost curve
- Average total cost curve
- Long run average cost curve.
- Short-run average cost curve
Answer: 3. Long run average cost curve.
If a firm has a choice that a plant can be varied by infinitely small gradations so that there are an infinite number of plants corresponding. to which there are numerous average cost curves. In this case, the long-run average cost Curve will be a smooth curve enveloping all these short-run average cost curves. Thus, the long-run average cost curve is also known as the envelope curve.
Question 48. The average fixed cost for producing an output of 6 units of.a product a firm is ₹ 30. The same cost for producing an output of 4 units will be ₹ ____________________
- 50
- 45
- 25
- 20
Answer: 2. 45
The average fixed cost for producing an output of 6 units of.a product a firm is ₹ 30
Total Fixed Cost (TFC)= 30 × 6 = ₹ 180
AFC for 4 units of output = TFC/Quantity
\(\frac{180}{Q}\) = ₹ 45
Question 49 .
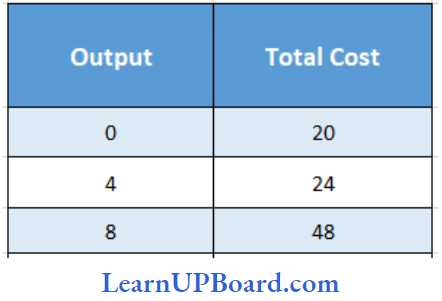
What will be the AFC of 4 units of Output
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Answer: 4. 5
Total Fixed Cost (TFC) = ₹ 20
Total units of output (Q) = 4 units
AFC = TFC/Q
= \(\frac{20}{4}\)
= ₹ 5
Question 50. Suppose the total cost of production of commodity ‘X’ is? 1,25,000 Out of other cost implicit is? 35,000 and the normal profit is T 25,000 what will be the explicit cost of commodity ‘X’?
- ₹ 60,000
- ₹ 65,000
- ₹ 90,000
- ₹ 80,000
Answer: 2. ₹ 65,000
Suppose the total cost of production of commodity ‘X’ is ₹1,25,000 Out of other cost implicit is ₹35,000 and the normal profit is T 25,000
Explicit Cost = Total Cost – Implicit Cost – Normal Profit
= 1, 25 000 – 35, 000- 25,000
=₹ 65, 000
Question 51. What will be the total fixed cost for the production of three units as per the details given below
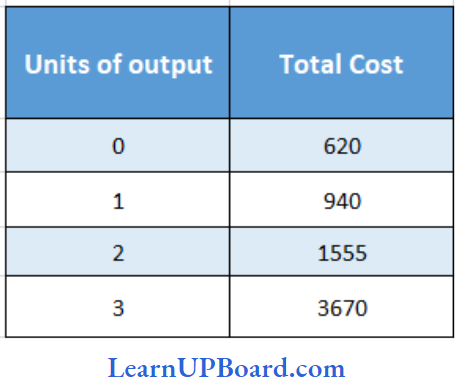
- 620
- 640
- 1115
- 2650
Answer: 1. 620
Fixed cost is the cost which remains fixed even if the total output is zero. Also,
Total Cost = Fixed Cost + Variable Cost
At zero units of output, the variable cost will be zero.
620 = Fixed Cost + 0
So total fixed cost = ₹ 620.
Fixed cost remains constant irrespective of units of output.
Hence at 3 units of output also total fixed cost will be ₹620.
Question 52. Cost in terms of pain, discomfort, and disability involved in supplying the various factors of production by their owners are termed as
- Social cost
- Explicit cost
- Real cost
- Implicit cost
Answer: 3. Real cost
Real cost refers to all those payments which are made to the factors of production to compensate for the efforts, pains, exertions or sacrifices suffered by them.
Real cost = efforts, pains, exertions and sacrifices of labour and capital + wait and abstinence of entrepreneur.
Real cost is the cost in terms of pain and sacrifice made to produce goods and services. It includes the cost of producing goods and services as well as the cost of all resources used and the cost of not employing those resources in alternative uses.
Question 53. Which of the following is known as the Envelope Curve?
- Average variable cost curve
- Average total cost curve
- The long-run average cost curve
- Short run average cost curve.
Answer: 3. Long run average cost curve
Long Run Average Cost Curve (LAC) is a U-shaped curve. When the LAC curve is declining it is tangent to the failing portions of the short-run cost curves and when the LAC is rising it is tangent to the rising portions of the short-run cost curves. In simple words, the long-run average cost curve envelops all the short run cost curves and – hence is known as the envelope curve.
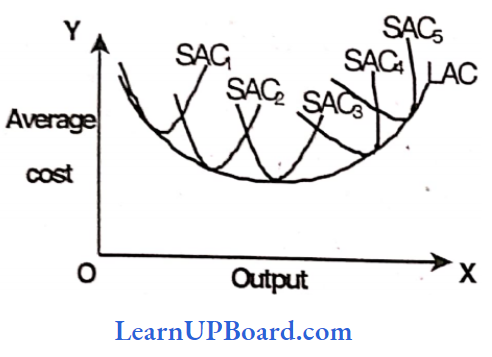
Question 54. The cost of resources owned and employed by the entrepreneur himself in his business is termed as _________________ cost.
- Explicit
- Implicit
- Fixed
- Variable.
Answer: 2. Implicit
Implicit costs are the costs for which payment in money terms is not made. These are the cost of factors owned by the entrepreneur himself and employed in his own business. For example, An entrepreneur uses his land for production. If he had rented that land he would have earned rent.
So the cost of using his land in the business is known as the implicit cost.
Question 55. A firm will close down in the short period if its average revenue is less than its:
- Average cost
- Average variable cost
- Marginal cost
- Average fixed cost ’
Answer: 2. Average variable cost
A firm should close down in the short run if it is not able to recover its variable cost. A firm shall continue to run if it is not able to meet its fixed cost because it may recover it in future. But variable cost. is incurred to meet the payment of raw material, labour etc. which should be met otherwise the firm should close down.
Question 56. A firm’s total cost is ? 200 at 5 units of output and X 220 at 6 units of output. The marginal cost of producing 6th unit of output will be ________________
- 20
- 120
- 220
- 320.
Answer: 1. 20
Marginal Costn = TCn-TCn-1
= TC6-TC6-1
= TC6-TC5
= 220 – 200
= ₹ 20 per unit
Question 57. Consider the following data Units of
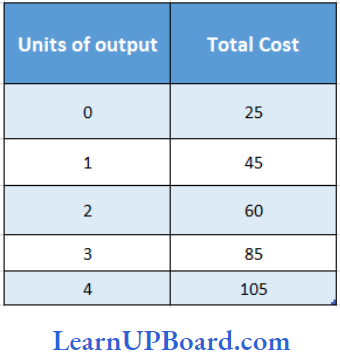
The Average Variable Cost (AVC) for an output of 4 units will be
- ₹ 20
- ₹ 30
- ₹ 25
- ₹ 26
Answer: 1.₹ 20
VCP.U. Difference in Total Cost/ Difference in units produced
= \(\frac{105 -25}{4-0}\)
= \(\frac{80}{4}\)
= ₹ 20 p.u
VC of 4 units = 20 × 4
= ₹ 80
AVC = \(\frac{80}{4}\)
= ₹ 20
Question 58. The change in total cost due to one unit change in the output is called _______________ cost.
- Marginal
- Average
- Average variable
- Average fixed
Answer: 1. Marginal
Marginal cost is the addition made to the total cost by production of an additional unit of output.
Question 59. When the AC curve is rising, the MC curve must be ______________ to it.
- Equal
- Above
- Below
- Parallel.
Answer: 2. Above
When the AC curve rises as a result of an increase in output, MC is more than AC i.e. MC curve is above the AC curve.
Question 60. The Average fixed cost for producing an output of 6 units of a product by a firm is ₹ 30. The same cost for producing an output of 4 units will be ₹ _______________
- 50
- 45
- 25
- 20
Answer: 2. 45
AfC = TfC/ Number of units
30 = TFC/6
∴ TFC = 30 × 6 = ₹ 180
So, AVC for 4 units of output = \(\frac{180}{4}\)
= ₹ 45
Question 61. Which of the following cost curves will slope downward and does not touch the x-axis?
- Average cost curve
- Marginal cost curve
- Average variable cost curve
- Average fixed cost curve.
Answer: 4. Average fixed cost curve.
The total fixed cost is a constant amount, i.e. it is fixed in nature. The average fixed cost will steadily fall as output increases. Therefore, if we draw the average fixed cost curve it will slope downwards throughout its length but will not touch to x-axis as AFC cannot be zero.
Question 62. Suppose the total cost production of a commodity ‘x’ is ₹ 1,25,000 out of which Implicit cost is ₹ 35,000 and normal profit is ₹ 25,000. What would be the explicit cost of commodity x?
- 90,000
- 65,000
- 1,00,000
- 60,000
Answer: 2. 65,000
Total cost = ₹ 1,25,000
Implicit cost = ₹ 35,000
Normal profit = ₹ 2,50,000
Explicit cost =?
Total cost = Explicit cost + Implicit cost + Normal profit
1,25,000 = Explicit cost + 35,000 + 25,000 = 1,25,000 -435,000 – 25,000
= 65, 000
Question 63. In which of the following cases opportunity cost concept apply?
- Resources have alternative uses
- Resources have limited uses
- Resources have no use
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Resources have alternative uses
Opportunity cost refers to the cost of opportunity forgone involving a comparison between the alternative chosen and the alternative forgone. It relates to the sacrificed alternatives
Thus, the opportunity cost concept applies where the resources have alternative uses.
Question 64. Direct costs are also known as _____________________
- Traceable costs
- Indirect costs
- Opportunity costs
- Real costs.
Answer: 1. Traceable costs
Direct costs are costs that are readily identified and are traceable to a particular product operation or plant. It is also known as Traceable Cost.
Question 65. Which statement below is correct in reference in Average Fixed Cost
- Never becomes zero
- The curve never touches the X-axis
- The curve never touches the y-axis
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Average fixed cost never touches any axis but it slopes downward, Average fixed cost can never be zero even if there is no production so it can never touch any axis. AFC falls when output increases as ffxed cost is always fixed.
Question 66. Marginal cost changes due to changes in ________________ cost.
- Total
- Fixed
- Average
- Variable
Answer: 4. Variable
Marginal copy is the addition made to the total cost by the production of an additional unit of output. It is independent of fixed cost, It is only the variable costs which change with a change in the level of output in the short run.
Question 67. A firm produces 10 units of a commodity at an average total cost of ? 200 and with a fixed cost of? 500. Find out the component of average variable cost in the total cost
- ₹ 300
- ₹ 200
- ₹ 150
- ₹ 100
Answer: 3. ₹ 150
A firm produces 10 units of a commodity at an average total cost of ? 200 and with a fixed cost of? 500.
The average total cost of 1 unit = ₹ 200
Total cost of 10 units = 200 × 10 = ₹ 2,000
Total fixed cost = ₹ 500
Total variable cost = total cost – total fixed cost = 2,000 – 500 = ₹ 1,500
Variable cost of 1 unit = 1500/10 = ₹ 150
Hence, a component of average variable cost in the total cost is = ₹ 150.
Question 68. The average total cost to a firm is ₹ 600 when it produces 10 units of output and ₹ 640 when the output is 11 units. The MC of the 11th unit is
- ₹ 40
- ₹ 540
- ₹ 840
- ₹ 1,040
Answer: 4. 1,040
The average total cost to a firm is ₹ 600 when it produces 10 units of output and ₹ 640 when the output is 11 units.
The average total cost of 10 units of output ₹ 600 Average total cost of 11 units of output = is ₹ 640
The marginal cost of 111h unit=Total cost of 11 units -Total cost of 10 units
= (640 × 11) – (600 × 10) ₹
= ₹ 1,040
Question 69. The average cost of producing 50 units of any commodity is ₹ 250 and the fixed cost is ₹ 1,000. What will be the average fixed cost of producing 100 units of the commodity?
- ₹ 10
- ₹ 30
- ₹ 20
- ₹ 05
Answer: 1. ₹ 10
The average cost of producing 50 units of any commodity is ₹ 250 and the fixed cost is ₹ 1,000.
The fixed cost of producing 50 units is 1,000 and the fixed cost of producing 100 units will also be the same i.e. ₹ 1,000.
The Average Fixed Cost of 100 units Fixed Cost 1,000
AFC= Fixed cost/ Quantity
= \(\frac{1000}{100}\) ₹
= ₹ 10
Question 70. A company produces 10 units of output and incurs ₹ 30 per unit as variable cost and ₹ 5 per unit of fixed cost. What will be the total cost of producing 10 units?
- ₹ 300
- ₹ 35
- ₹ 305
- ₹ 350
Answer: 4. ₹ 350
A company produces 10 units of output and incurs ₹ 30 per unit as variable cost and ₹ 5 per unit of fixed cost.
The total cost of producing 10 units is:
Total Cost → Total Fixed Cost + Total Var. Cost
⇒ 10 × 5 + 10 × 30
⇒ 50 + 300
= ₹ 350
Question 71. Based on the following data, what will be the marginal cost of the 6th unit of output?
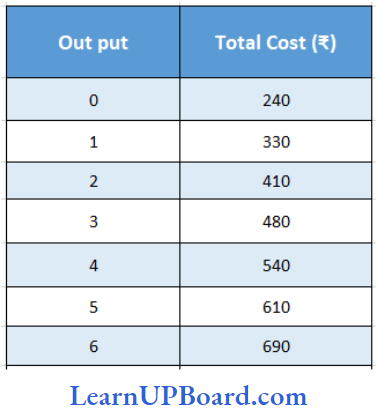
- ₹ 133
- ₹ 75
- ₹ 80
- ₹ 450
Answer: 3. ₹ 80
Question 72. The positively sloped (rising) part of the long-run average cost curve indicates the working of the_________________.
- Diseconomies of scale
- Increasing returns to scale
- Constant returns to scale
- Economies of scale
Answer: 1. Diseconomies of scale
The positively sloped (rising) part of the long-run average cost curve indicates the working of the diseconomies of scale. Because rising LFAC and diminishing returns to scale result from internal and external diseconomies of scale.
Question 73. The average fixed cost curve is always
- Declining when output increases
- U-shaped, if there are increasing returns to scale
- U-shaped, if there are decreasing returns to scale
- Intersected by marginal cost at its minimum point
Answer: 1. Declining when output increases
Average fixed cost will steadily decline as output increases. If we draw an AFC it will slope downwards throughout its length but will not touch the x-axis as AFC can’t be zero.
Question 74. The planning curve is related to which of the following?
- Short-run average cost curve
- The long-run average cost curve
- Average variable cost
- Average total cost.
Answer: 2. Long run average cost curve
Answer: 4. Average total cost.
A long-range average cost curve is often called a planning curve because a firm plans to produce any output in long run by choosing a particular plant in the long run and the average cost curve corresponding to the given output.
Question 75. Using the following data find out the marginal cost (MC) of the sixth unit Solve the question
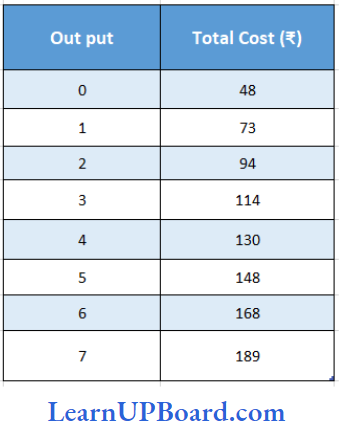
- 24
- 16
- 20
- 21
Answer: 3. 20
M C = ΔTC/ ΔQ
= MCn = TCn – TCn-1
= MC6 = TC6 – TC5
MC = 168 – 148
= 20
Question 76. What will be the marginal cost, when output is 5 units?
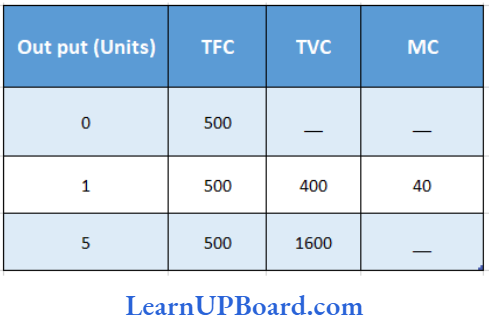
- 300
- 400
- 500
- 600
Answer: 1. 300
M.C = Δ T.C / ΔQ = Change in Total Cost/ Change in Quantity
T.F.C = 500
T.V.C for 5 units =1,600
T.C. for 5 units
= T.F.C + T.V.C
= 500 + 1,600
= 2,100
T.F.C = 500
T.V.C for 1 unit = 400
T.C. for 1 unit
= 500 + 400 = 900
= \(\frac{1200}{4}\) = 300
Question 77. Diminishing marginal returns implies
- Decreasing average variable costs
- Decreasing marginal costs
- Increasing marginal costs
- Decreasing fixed costs.
Answer: 3. Increasing marginal costs
It states that as one input variable is increased there is a point at which the marginal increase in output increases and then begins to decrease, leading to an increase in the marginal cost with every additional unit.
Question 78. When the output of a firm increases in the short run, its average fixed cost
- Increases
- Decreases
- Remains constant
- First declines and then rises.
Answer: 2. Decreases
Since TFC is a constant amount, AFC will steadily fall as output increases.
Question 79. Which of the following cost curves is never ‘U’ shaped?
- Average cost curve
- Marginal cost curve
- Average variable cost curve
- Average fixed cost curve.
Answer: 4. Average fixed cost curve.
The average fixed cost curve is never “U” shaped because it slopes Downward through its length and never touches X1 axis.
Question 80. Fixed cost curve normally
- Starts from the origin
- Is U shaped
- Is vertical line
- Is a horizontal line.
Answer: 4. Is a horizontal line.
Fixed costs are those costs which are independent of output i.e. they do not change with changes in output. Thus, the fixed cost curve normally is a horizontal line.
Question 81. A rational producer will produce in the stage in which the marginal product is positive and
- MP > AP
- MP = AP
- MP < AP
- MP is zero.
Answer: 3. MP < AP
A rational producer will produce in the stage in which the marginal product is positive and MP<AP. As in this case, a producer could increase the average product of labour by decreasing the quantity of labour slightly.
Question 82. The vertical difference between TVC and TC curves is equal to
- MC
- A VC
- TFC
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. TFC
The total cost of a business is the sum of total variable cost and total fixed cost or symbolically TC = TFC + TVC. upward showing thereby that as output increases, total variable cost increases. This curve starts from the origin which shows when output is zero, variable costs are also nil. The total cost curve thus has been obtained by adding vertically the total fixed cost curve and the total variable cost curve.
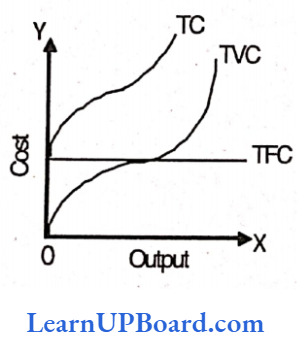
Question 83. What happens to marginal cost when average cost increases?
- Marginal cost is below average cost
- Marginal cost is above average cost
- Marginal cost is equal to average variable cost
- Marginal cost is equal to average cost.
Answer: 2. Marginal cost is above average cost
The relationship between marginal cost and the average cost is the same as that between any other marginal average quantity when the average cost rises as a result of an increase in output marginal cost is more than the average cost.
Question 84. If the market price of good is more than the opportunity cost of producing it, then
- The market price of the product will increase in the long run
- Producers will increase supply in the long run
- Marginal cost is above average cost
- The situation will remain unchanged as long as supply and demand remain in balance. ‘
Answer: 2. Marginal cost is above average cost
If the market price of a good is more than the opportunity cost of producing it then the producer will increase supply in the long run that is the amount of a good or service that producers are willing and able to offer to the market at various prices during the time.
Question 85. A firm has variable costs of ₹ 1,000 at 5 units of output. If fixed costs are X 400. what will be the average total cost at 5 units of output?
- 360
- 600
- 260
- 400
Answer: 3. 260
A firm has variable costs of ₹ 1,000 at 5 units of output. If fixed costs are X 400.
Variable Cost = ₹ 1,000 at 5 unit Fixed Cost = ₹ 400
Total cost = Variable cost + Fixed cost v =1000 + 400
= 1400 at 5 units.
Average total cost = \(\frac{1400}{5}\)
= ₹ 280
Question 86. The average total cost of producing 50 units is ₹ 250 and the total fixed cost is ₹ 1,000. What is the average fixed cost of producing 100 units?
- 5
- 30
- 20
- 10
Answer: 4. 10
The average total cost of producing 50 units is ₹ 250 and the total fixed cost is ₹ 1,000.
ATC of 50 units = ₹ 250
TFC = ₹1,000
AFC of 100 units = \(\frac{1000}{100}\)
= ₹ 10
Question 87. When the average fixed cost is ₹ 20 at 6 units of output, what will it be at 4 units of output?
- ₹ 60
- ₹ 30
- ₹ 40
- 20
Answer: 2. ₹ 30
AFC = 20 at 6 units of output
TFC = 20 × 6
= 120
AFC at 4 units of output
= \(\frac{120}{4}\)
= ₹ 30
Question 88. Modern industrial units face ____________________ technology of production.
- U shaped
- L shaped
- Dish shaped
- J shaped
Answer: 2. L shaped
L-shaped cost curve.
U U-shaped cost curve could exist only when the state of technology remains constant but, the empirical evidence shows that the state of technology changes in the long run.
Therefore, modern industrial units face an ‘L’ shaped cost curve rather than ‘U’ shaped cost curve.
Question 89. What will be AVC in the production of 3 units according to the following cost data?
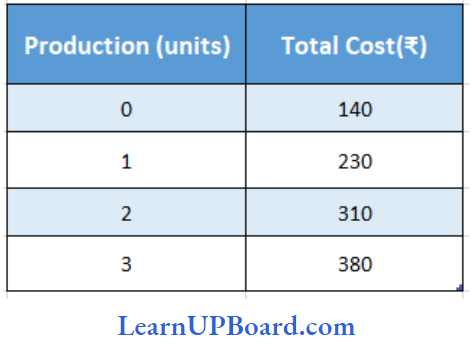
- 80
- 100
- 110
- 240
Answer: 2. 100
AVC = TVC/Q
= TC- TFC/ Q
= \(\frac{380-140}{3}\)
= \(\frac{240}{3}\)
= 80.
Question 90. The costs which remain fixed over a certain range of output but suddenly jump to a new higher level when production goes beyond a given limit are called:
- Variable cost
- Semi-variable cost
- Stair-step variable cost
- Jumping cost.
Answer: 3. Stair- step variable cost
Stair-Step Variable Costs are the costs which increase in a stair-step fashion i.e. they remain fixed over a certain range of output, but suddenly jump to a new higher level when output goes beyond a given limit. example. The fixed salary of the foreman will have a sudden jump if another foreman is appointed when the output crosses a particular limit.
Question 91. A firm producing 9 units of output has an average total cost of ? 200 and has to pay ₹ 630 to its fixed cost of production. How much of the average total cost is made up of variable costs?
- ₹ 150
- ₹ 130
- ₹ 70
- ₹ 300
Answer: 2.₹ 130
A firm producing 9 units of output has an average total cost of ? 200 and has to pay ₹ 630 to its fixed cost of production.
Variable Cost = Total Cost – Fixed Cost = (200 × 9) – 630
= 1,170
AVC = TVC/Q
⇒ \(\frac{1170}{9}\)
= ₹ 130
Question 92. The cost of one thing in terms of alternative given up is known as
- Opportunity Cost
- Real Cost
- Production Cost
- Physical Cost.
Answer: 1. Opportunity Cost
Opportunity cost is concerned with the cost of forgone opportunity; it involves a comparison between the policy that was chosen and the policy that was rejected.
For example, the opportunity cost of using capital is the interest that it can earn in the next best use with equal risk.
Question 93. In the short run, when the output of a firm increases, its average fixed cost
- Remains constant
- Decreases
- Increases
- First decreases and then rises
Answer: 2. Decreases
Yes in the short run, when the output of a firm increases its average fixed cost decreases. When the output is 100 units the AFC will be ₹ 20. And now if the output increases to 200 units, AFC will be ₹ 10. Hence, cost decreases.
Question 94. What will be the average variable cost of producing 5 units of blankets as per the details given in the following table?
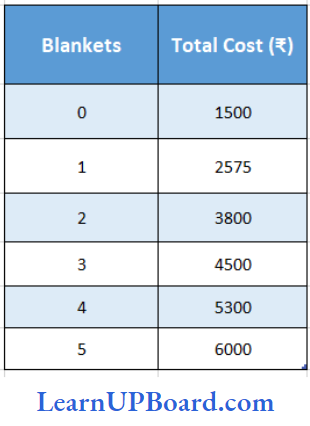
- ₹ 500
- ₹ 750
- 900
- 1,000
Answer: 3. ₹ 900
Average variable Difference in Total Cost/Difference in units
⇒ \(\frac{6000-1500}{5-0}\)
= \(\frac{4500}{5}\)
= ₹ 900 per unit
Question 95. Which of the following is/are example(s) of an economic cost?
- Wage paid to labourers
- Raw materials purchase, cost
- Interest paid on short-term loan
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Economic cost = explicit cost + implicit cost.
Explicit cost refers to those costs only which involve cash payments of the entrepreneur of the firm.
Implicit cost refers to the amount of money the entrepreneur could have earned if he had invested his money and sold his services and other factors in the next best alternatives.
Question 96. Opportunity Cost is:
- Marginal cost
- Variable cost
- Total fixed cost
- None of these.
Answer: 4. None of these.
Opportunity Cost of a given activity is defined as the value of the next best activity and it is not related to any cost. It means sacrificing of one good for another good to give satisfaction to self.
Question 97. The “law of diminishing returns ” applies to
- The short run, but not the long run
- The long run, but not the short run
- Both the short run and the long run
- Neither the short run nor the long run
- Answer: 1. The short run, but not the long run
The law of diminishing return’ applies to the short run but not in the long run as in the short run a fixed cost does not change while a variable cost changes but in the long run both change. Supply Production cannot increase in the short run whether there is a loss or profit.
Question 98. Linear homogenous production function is based on
- Increasing returns to scale
- Decreasing returns to scale
- Constant returns to scale
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Constant returns to scale
Linear Homogenous production is based on constant return to scale because output increases in the same way as an increase in input or we can say that an increase in output is equal to an increase in input. Sole proprietorship production is based on a constant return to scale for a lifetime.
Question 99. Which of the following cun/e is not U-shaped?
- AFC
- MC
- AVC
- TC
Answer: 1. AFC
AFC is the cost obtained by dividing the total fixed cost by the number of units of output.
AFC = TFC/Q
= (Total Fixed Cost)/ (No. of units of output)
TFC can never be U-shaped as it will fall as total output increases and will not touch the X-axis. It can also never be zero.
Question 100. Which of the following curves never touches any axis but is downward
- Marginal cost curve
- Total cost curve
- Average fixed cost curve
- Average variable cost curve
Answer: 3. Average fixed cost curve
Average fixed cost is a curve that cannot touch any axis so, it can never be zero. When total production increases then average fixed cost steadily falls but never touches the axis.
Question 101. External economies accrue due to __________________
- Increasing returns to scale
- Increasing returns to factor
- Law of variable proportions
- LOW cost
Answer: 1. Increasing returns to scale
Increasing return to scale means when there is an increase in output is more than an increase in input or in other words increases in, output an increase in input and there are some factors or external economies which tend to increase return to scale.
Question 102. A firm’s average fixed cost is ? 20 at 6 units of output what will be at 3 units of output?
- ₹ 60
- ₹ 30
- ₹ 40
- ₹ 20
Answer: 3. ₹ 40
The average fixed cost is 20 at 6 units and what will be at 3 units
AFC at 6 units = 20
AFC at 3 units = \(\frac{20}{3}\) × 6
= ₹ 40
As we AFC is decreasing steadily by increasing total production. So, AFC at 3 units is 40, and at 6 is 20.
Question 103. Which of the following is correct?
- AFC = AVC + ATC
- ATC = AFC-AVC
- AVC = AFC + ATC
- AFC = ATC-AVC
Answer: 4. AFC = ATC-AVC
Average fixed can be obtained in two ways:
AFC = TFC/ Q= Total Fixed Cost / Number of units of output
AFC = ATC-AVC
Where, ATC = Average total cost and AVC = Average variable cost. .
Question 104. The vertical difference between TVC and TC curves is equal to
- MC
- AVC
- TFC
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. TFC
Total Variable Cost (TVC) and Total Cost (TC) is differences of TFC (Total Fixed Cost) Formula Derived is:
TC = TVC + TFC
TC – TVC = TFC
This is the vertical difference between Total Variable Cost and Total Cost.
Question 105. The cost of one thing in terms of alternative given up
- Real cost
- Production cost
- Opportunity cost
- Physical cost (1 mark)
Answer: 3. Opportunity cost
Opportunity cost is the cost that means the next best activity or sacrificing of one good thing for another.
Question 106. The cost which remains fixed over a certain range of output but suddenly jumps to a new higher level when production goes beyond a given limit are called
- Variable cost
- Semi-variable cost
- Stair-step variable cost
- Jumping cost
Answer: 3. Stair-step variable cost
2 Stair-step Variable cost which means the cost which remains fixed for a long time but suddenly jumps to a new higher level when production goes beyond a given limit.
Question 107. The shape of the Average Fixed cost curve is?
- Falls from left to right
- Rises from left to right
- Parallel to x-axis
- Parallel to y-axis
Answer: 1. Falls from left to right
The shape of Average Fixed Cost is hyperbola in shape it falls from left to right but does not touch the x-axis.
Question 108. The price of a commodity is best expressed as
- Exchange value
- Cost of goods sold
- Production cost
- Nominal value
Answer: 1. Exchange value
The price of a commodity is expressed as its exchange value as it is the price at which jt will be sold or purchased.
Question 109. Accounting cost is Economic cost
- Equal to
- Less than
- More than
- Not Included
Answer: 2. Less than
Accounting cost is explicit cost and economic cost is Explicit + Cost + National cost therefore, accounting cost is less than economic cost.
Question 110. When AC Curve is at minimum then MC Curve is?
- Minimum then AC Curve
- Equals to AC Curve
- ‘ Above AC Curve
- Less than AC Cun/e
Answer: 2. Equals to AC Curve
When the average cost is minimum, MC is equal to the Ac. In other words, the MC curve cuts the AC curve at its minimum point.
Question 111. Which of the following equations represents the profit maximisation condition?
- MC = MR
- MC > MR
- – MC < MR
- None.
Answer: 1. MC = MR
Profit will be at the maximum level when marginal Revenue is equal to marginal cost therefore, it can cover its cost and survive in the economy.
Question 112. MC curve of a firm in a perfectly competitive industry depicts?
- Demand curve
- Supply curve
- Average cost curve
- Total cost curve
Answer: 2. Supply curve
MC curve is rising upward in a competitive market therefore, it depicts the supply curve.
Question 113. Issues requiring decision-making in the context of business are:
- How much should be the optimum output at what price should the firm sell?
- How will the product be placed in the market?
- How to combat the risks and uncertainties involved?
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
All the given options are required for making business decisions in the context of business therefore, the answer will be (4) all of the above.
Question 114. The law of production does not include?
- Returns to scale
- Law of variable proportion
- Law of diminishing returns to a factor
- Least cost combination factors
Answer: 4. Least cost combination factors
The least cost combination factor is not included in the law of production function.
Question 115. A firm producing 15 units of output has an average cost of ₹ 250 and ₹ 125 as per unit cost for fixed factors of production.
The average variable cost will be
- 180
- 150
- 125
- None of the above
Answer: 3. 125
Average total cost (ATC) = AFC + AVC
ATC = 250; AFC = 125
AVC = ATC- AFC
= 250-125
= ₹ 125
Question 116. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
- AC is sloping downwards, MC is below AC
- AC is sloping downwards, MC must fall
- AC is sloping upwards, MC is above AC
- MC cuts AC at its lowest point.
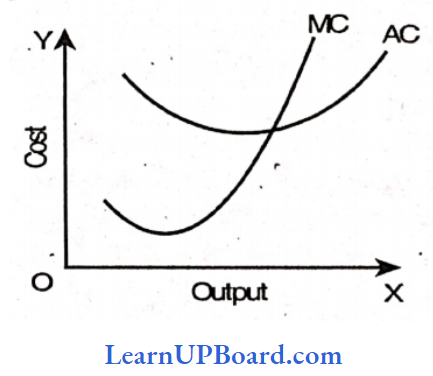
Answer: 2. AC is sloping downwards, MC must fall
The relationship between Average cost and Marginal cost is as follows:
- When average cost falls as a result of an increase in output, marginal cost is less than average cost.
- When the average cost rises as a result of an increase in output, the marginal cost is more than the average cost.
- When the average cost is minimum, the marginal cost is equal to the average cost.
Question 117. Diminishing marginal returns implies.
- Decreasing average fixed cost *
- Decreasing average variable cost
- Decreasing marginal cost
- Increasing marginal cost
Answer: 4. Increasing marginal cost
Diminishing marginal Returns implies an increase in marginal cost.
Marginal cost is the increase in the total cost of production if one additional unit of output is produced.
Question 118. Opportunity Cost is
- Recorded in the book of accounts
- Sacrificed alternative
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of the above
Answer: 4. None of the above
Opportunity cost is the cost of the next best alternative foregone. It is generally not recorded in the books of accounts. Thus, it can be said that opportunity cost is the sacrificed alternative whose cost is not recorded in books of accounts.
Question 119. Which of the following is true?
- TC = TFC + TVC
- TC + TVC + TFC
- 2TC – TVC = TFC
- None
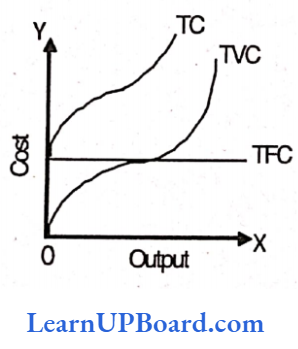
Answer: 1. TC = TFC + TVC
Total Cost = Total Fixed Cost + Total Variable Cost i.e. TC = TFC + TVC
Question 120. Total Economic Cost = Explicit Cost + Implicit Cost
- Normal Profit
- Super Normal Profit
- Loss
- None
Answer: 1. Normal Profit
Total Economic Cost = Explicit Cost + Implicit Cost + Normal Profit
As economic cost includes :
- Normal return a money capital invested by the entrepreneur himself in his cum business.
- The wages or salary not paid to the entrepreneur, but could have been earned if the services had been sold somewhere else.
- It also takes into account, accounting costs. And also the normal profit earned.
Question 121. The economic cost of production differs from the accounting cost of production
- Partially True
- True
- False
- None
Answer: 2. True
- The economic cost of production differs from the accounting cost. production is TRUE as
- Economic cost includes both explicit cost and implicit cost.
- Whereas Accounting cost only includes the amount spent i.e. Explicit Cost
Question 122. Which curve is never U- U-shaped
- AFC
- AVC
- AC
- None
Answer: 1. AFC
The average fixed cost curve is never U-shaped. The average Fixed Cost diminishes as the production increases (though the fixed cost remains constant) .
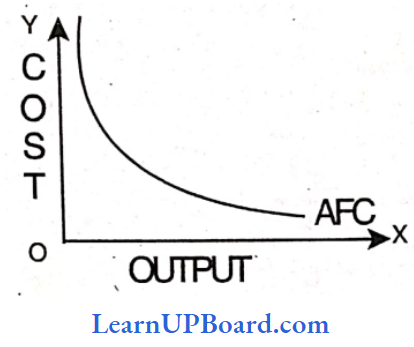
AFC = TF/ Q
It will slope downwards throughout its length but will not touch the X-axis as AFC cannot be zero.
And AVC and AC curves are U-shaped i.e.
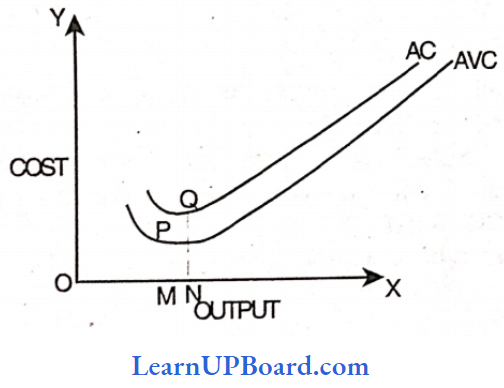
Question 123. Use the table and answer the following questions
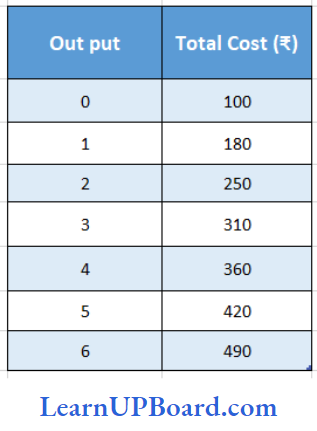
The average fixed cost of 4 units of output is:
- 80
- 90
- 25
- 350
Answer: 3. 25
In the given table, we see that o level of output TC = 100 which is also equal to TFC.
TC = TFC= 100
Thus TFC of 4 units = 100
AFC = TFC/Q
= \(\frac{100}{4}\)
= 25
Question 124. The average variable cost of 5 units of output
- 84
- 64
- 420
- 104
Answer: 2. 64
AVC at 5 units
AFC = TVC/Q
TVC = TC-TFC
= 420- 100
= 320
= \(\frac{320}{5}\)
= 64
Question 125. The marginal cost of 5th unit of output is
- 60
- 70
- 540
- 90
Answer: 1. 60
MC = at 5 units MC = TC5-TC5-1
= TC5 – TC4
= 420 – 360
= 60
Question 126. The total cost is ₹ 4,200 and the fixed cost is ₹ 1,200 then find the variable cost
- ₹ 5,450
- ₹ 1,200
- ₹ 4,200
- ₹ 3,000
Answer: 4. ₹ 3000
TC = 4200
TFC = 1200
Variable cost = ₹ 4200 – v 1200,
= ₹ 3000
Question 127. A Firm producing 7 units of output has an average total cost of ₹ 150 and has to pay₹ 350 to its fixed factors of production whether it produces or not? How much of the average total cost is made up of variable costs?
- 200
- 50
- 300
- 100
Answer: 4. 100
A Firm producing 7 units of output has an average total cost of ₹ 150 and has to pay₹ 350 to its fixed factors of production whether it produces or not?
Units = 7, ATC= 150, PC = 350
150 × 7 = TC
TC = 1050
TC = FC + VC
1050 = 350 + 700
ATC = AFC + AVC
TC/Q = FC/Q+ VC/Q
= \(\frac{1050}{7}\) = \(\frac{350}{7}\)+ \(\frac{700}{7}\)
= 150 = 50 + 100
Thus Average variable cost is ₹ 100.
Question 128. A Firm has a variable cost of X 2,000 at 5 units of output. If fixed costs are? 800, what will be the average total cost at 5 units of output?
- 560
- 120
- 240
- 2,800
Answer: 1. 560
A Firm has a variable cost of X 2,000 at 5 units of output. If fixed costs are? 800,
Units = 5
VC= 2000
Fc= 800
TC = FC + VC
= 2000 + 800
= 2800
ATC = TC/ Q
= \(\frac{2800}{5}\)
= 560
Question 129. Which of the following Statements is false?
- Economic costs include the opportunity costs of the resources owned by the firm.
- Accounting costs include only explicit costs.
- Economic profit will always be less than accounting profit if resources owned and used by the firm have any opportunity costs.
- Accounting profit is equal to total revenue less implicit costs.
Answer: 4. Accounting profit is equal to total revenue less implicit costs.
Accounting profit is equal to total revenue less implicit cost Accounting profit = TR – Implicit Cost
Question 130. The average cost curve is
- ‘U’ Shaped
- Positively sloped
- Negatively sloped
- Rectangular hyperbola
Answer: 1. ‘U’ shaped. –
The average cost curve is ‘U’ shaped due to the law of variable proportion.
Question 131. Isoquants are equal to
- Product lines
- Total utility lines
- Cost lines
- Revenue lines
Answer: 1. Product lines
An Isoquant consists of alternative combinations of input to produce a given quantity of output and product lines are lines representing various combinations of factors of production to produce a given output.
Question 132. Average fixed cost can be obtained through.
- AFC = TFC/TS
- AFC= EC/TU
- AFC= TC/PC
- AFC = TFC/TU
Answer: 4. AFC = TFC/TU
Use the table below to answer Questions 133 to 135.
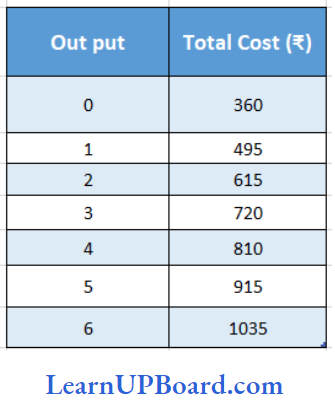
Question 133. The average fixed cost of 3 units of output is ______________
- 180
- 225
- 120
- 134
Answer: 3. ₹ 120
AFc = IFC/Q
AFC = \(\frac{360}{3}\)
= ₹120
AFC = ₹ 120
Question 134. The marginal cost of the fifth unit of output is _______________
- ₹ 174
- ₹ 225
- ₹ 675
- ₹ 105
Answer: 4. ₹ 105
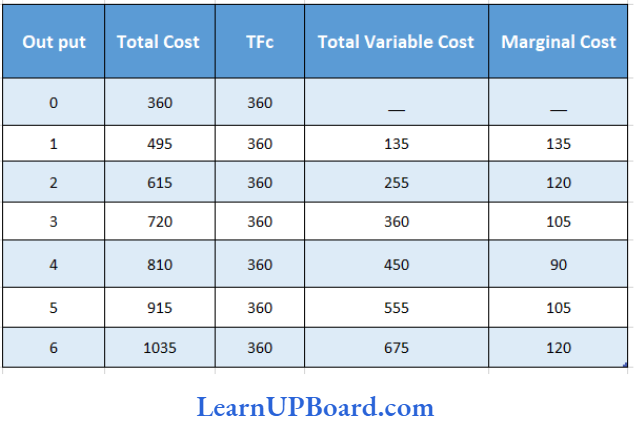
Marginal Cost of the Fifth unit = 105
Question 135. Diminishing marginal returns starts to occur between __________________units
- 4 and 5
- 3 and 2
- 5 and 6
- 1 and 2
Answer: 1. 4 and 5
According to the above table, Diminishing marginal return starts to occur between 4 and 5 units.
Question 136. The difference between TFC and TC is equal to
- Zero
- TVC
- MC
- AFC
Answer: 2. TVC
The difference between TFC and TC is equal to TVC
TC = TFC +TVC
TVC = TC – TFC
Question 137. The Marginal Revenue curve moves________________ and the Marginal cost curve moves ______________
- Downward, Downward,
- Downward, Upward upward,
- Upward, Downward,
- Downward, Remains same.
Answer: 2. Downward, Upward upward,
The marginal revenue curve is downward sloping and below the demand curve and the additional gain from increasing the quantity sold is lower than the chosen market price. Both these curves are intersected at their minimum points by Marginal Cost (MC), which slopes upward.
If the price of the variable input increases all three cost curves move upwards as shown alongside. They retain their shape and characteristics as described above.
Question 138. The average revenue curve is also known as
- Firm’s Demand Curve
- Marginal Revenue Curve
- Total Revenue Curve
- Marginal Cost Curve
Answer: 1. Firm’s Demand Curve
The average revenue curve is also known as a demand card in the business market. Average revenue is the division of total revenue (TR) by quantity (Q) which also means Average revenue is equal to the price of each product.
Question 139. If quantity demanded for a commodity increases from 15 units to 20 units there is a 25 percent decrease in price. If the initial price was ₹ 20, then what is the marginal revenue?
- 15
- 20
- 0
- 10
Answer: 3. 0
If quantity demanded for a commodity increases from 15 units to 20 units there is a 25% decrease in price. The initial price is ₹ 20;
⇒ 20-25 % of 20
= 20-5
= ₹15
Then marginal revenue will be zero.
Question 140. The marginal, average and total product curves encountered by the firm producing in the short-run exhibit all of the following relationships except ______________
- When TP is rising, Average and Marginal products may be either rising or falling.
- When the marginal product is negative, the total product and Average Product is falling
- When the Average product is maximum, marginal product equals Average Product and the total product is rising
- When Marginal Product is at maximum, Average Product equals Marginal Product and the total product is rising
Answer: 4. When Marginal Product is at maximum, Average Product equals Marginal Product and total product is rising
The marginal, average and total product curves encountered by the firm producing in the short run exhibit all of the following relationships except when marginal product is at maximum, average product equals marginal product and total product is rising.
Question 141. Marginal cost can be directly derived from
- Total variable cost
- Total fixed cost.
- Average cost
- Average fixed cost
Answer: 2. Total fixed cost.
It is derived from the variable cost of production, given that fixed costs do not change as output changes, hence, no additional fixed cost is incurred in producing another unit of a good or service once production has already started.
Question 142. Total economic cost = implicit cost + explicit cost +
- Normal Profit
- Abnormal Profit
- Economic Profit
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Normal Profit
Total economic cost
- Implicit Cost +
- Explicit Cost +
- Normal Cost.
Question 143. The marginal product of a variable input is described as?
- The additional output resulting from one unit increase in both the variable and fixed inputs
- The additional output resulting from one unit increase in fixed input
- The additional output resulting from one unit increase in the variable inputs
- The additional output resulting from all unit increases in variable inputs
Answer: 3. The additional output resulting from one unit increase in the variable inputs
The marginal cost is the cost of producing one extra unit of output, in the short run, the fixed cost does not change by producing one ‘ extra unit, thus the marginal cost is entirely comprised of the variable cost.
Question 144. Total profits are maximized when?
- TR equal TC
- The TR curve and the TC curve are parallel
- TC exceeds TR
- TR exceeds TC
Answer: 4. TR exceeds TC
The profits are maximized where the gap between the total revenue and the total cost curves is the maximum. This happens only when both the curves are parallel to each other. The profits will be positive only when the total revenues exceed the total cost.
Question 145. A firm producing 7 units of output has an average total cost of 7 150 and has to pay 7 350 to its fixed factors of production whether it produces or not. How much of the average total cost is made up of variable costs?
- ₹ 100
- ₹ 200
- ₹ 50
- ₹ 300
Answer: 1. 100
Number of units = 7
ATC = ₹150
TFC = ₹ 350
AVC = ATC- AFC
= 150-50
= ₹ 100
Question 146. Economic costs include
- Implicit costs
- Explicit costs
- Implicit and explicit costs
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Implicit and explicit costs
Economic costs include both Explicit and implicit costs. Therefore, economic costs are useful for businessmen while making decisions.
Question 147. At the shut-down point, the price is
- Below ATC
- Below AVC
- Equal to ATC
- Above AVC
Answer: 2. Below AVC
The firm always has the option of not producing at all. If a firm’s total revenues are not enough to make goods even the total variable cost. The firm should shut down. In other words, a competitive firm should shut down if the price is below AVC
Question 148. Economic cost includes which of the following?
- Accounting cost
- Implicit cost
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of the above
Answer: 3. None of the above
Both (1) and (2)
Economic cost includes both accounting cost (actual payment) and implicit cost (notional expense).
Question 149. External economies are due to
- Development of skilled labor
- Technologies
- Cheaper raw material
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
External Economies are due to the development of skilled labour, technology, cheaper raw materials, etc.
Question 150. The planning curve is related to
- Long-run average cost curves
- Short-run average cost curves
- Average revenue curve
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Long-run average cost curves
Long Run Average Cost Curve:
Long Run Average Cost Curve is after called a planning curve because a firm plans to produce any output in the long run by choosing a plant on the long-run average cost curve.
