CA Foundation Economics – Theory Of Production Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. ______________ shows the overall output generated at a given level of input
- Cost function
- Production function
- ISO cost
- Marginal rate of technical substitution,
Answer: 2. Production function
Production function states the relationship between inputs and outputs generated.
Question 2. If the LAC curve falls as output expands, this is due to
- Law of diminishing returns
- Economies of scale
- Law of variable proportion
- Dis-economics of scale
Answer: 2. Economies of scale
In the long run, when output expands total cost first increases, then becomes constant and finally decreases. When output expands, and the cost curve falls it is the first stage of returns to scale which occurs due to economies of scale.
Question 3. Isoquants are equal to:
- Product Lines
- Total utility lines
- Cost lines.
- Revenue lines
Answer: 1. Product Lines
An isoquant consists of alternative combinations of input to produce a given quantity of output and product lines are lines representing various combinations of factors of production to produce a given output.
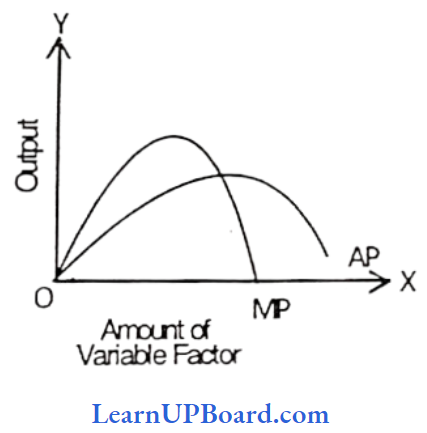
Question 4. The marginal product curve is above the average product curve when the average product is
- Increasing
- Decreasing
- Constant
- None
Answer: 1. Increasing
Marginal product and average product are so related. that when the average product increases, MP increases at a faster rate and cuts AP at its Maximum and when AP falls MP falls at a faster rate. So the marginal product curve is above the average product curve when AP is increasing,
Question 5. Increasing returns to scale can be explained in terms of:
- External and internal economies
- External and internal diseconomies
- External economics and internal diseconomies
- All of these
Answer: 1. External and internal economies
Increasing returns to scale i.e. When output increases more than the increase in input. It occurs due to external and internal economics.
Question 6. An isoquant is to an isocost line at the equilibrium point
- Convex
- Concave
- Tangent
- Perpendicular
Answer: 3. Tangent
An isoquant is tangent to an isocost line. This point of tangency defines the equilibrium position of a firm. A higher isoquant shows an unalterable point and a lower one shows underutilised resources. Hence an isoquant with an isocost line as tangent is the equilibrium position.
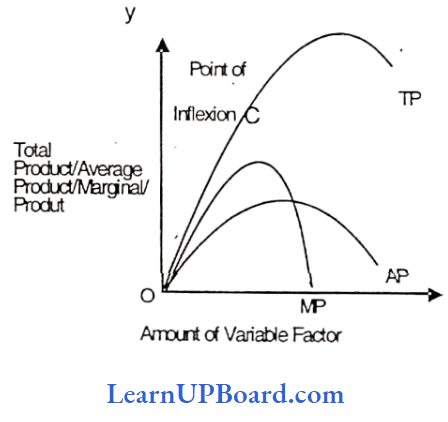
Question 7. At the point of inflexion, the marginal product is
- Increasing
- Decreasing
- Maximum
- Negative
Answer: 3. Maximum
A point of inflexion is a point in the first stage of the law of variable. proportion i.e. When MP becomes maximum. At this point, the slope of TP changes.
Question 8. Diminishing marginal returns implies
- Decreasing average variable costs
- Decreasing marginal costs
- Increasing marginal costs
- Decreasing average fixed costs
Answer: 3. Increasing marginal costs
Keeping other things constant when marginal cost increases with a considerable increase in variable factors, the marginal product declines. This is the second stage of law of variable proportion or the. stage of diminishing returns.
Question 9. If the marginal product of labour is below the average product of labour, it must be true that
- The marginal product of labour is negative.
- The marginal product of labour is zero
- The average product of labour is falling
- The average product of labour is negative
Answer: 3. Average product of labour is falling
Question 10. The law of variable proportion is valid when
- Only one input is fixed and all other inputs are kept variable
- All factors are kept constant.
- All inputs are varied in the same proportion,
- None of these
Answer: 1. Only one input is fixed and all other inputs are kept variable
The law of variable proportion occurs in the short- run. Short-run is a period when only one input is fixed and all other inputs are kept variable.
Question 11. Change in total revenue due to incremental change in quantity supplied is called
- Marginal Revenue
- Marginal Change
- Average Revenue
- Average Change. 1
Answer: 1. Marginal Revenue
Marginal revenue is defined as an addition made to the total revenue by selling one more unit of a commodity. It is the incremental change in total revenue.
‘ M.R.n = T.R.n-T.R.n-1
Question 12. An increase in all input leading to a less than proportional increase in output is called.
- Increasing returns to scale
- Decreasing returns to scale.
- Constant returns to scale
- Both increasing and decreasing returns to scale
Answer: 2. Decreasing returns to scale.
Decreasing returns to scale is the stage when the increase in the output is less than the increase in input, this occurs due to internal and external diseconomies.
Question 13. Consider the following combinations of inputs and outputs
This production technology satisfies:
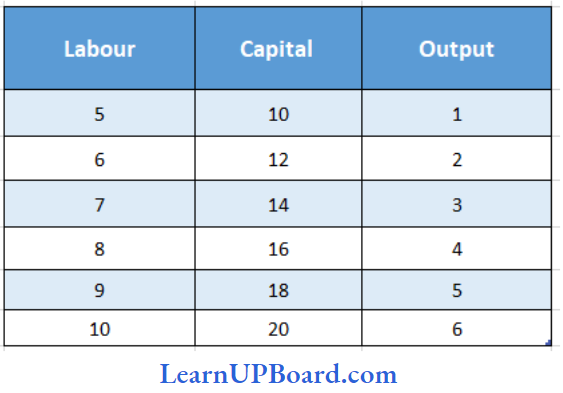
- Increasing returns to scale
- Diminishing returns to scale,
- Constant returns to scale
- Increasing returns initially, followed by decreasing returns to scale.
Answer: 3. Constant returns to scale
In the given production technology the increase in input is proportionate to the increase in output. With an increase of every 1 unit of labour and 2 units of capital the output increases by 1 unit. Hence, it is the case of constant returns to scale as both fixed and variable factors are changing (all factors are variable).
Question 14. During the stage of the law of diminishing returns
- MP and TP is the maximum
- MP and AP are decreasing
- AP is negative
- TP is negative
Answer: 2. MP and AP are decreasing
During the second stage of the Law of Diminishing Returns (i.e. Law of Variable Proportion) both MP and AP are decreasing because at this stage the optimum combination between fixed and variable factors has been attained and now if the input is increased, the output starts decreasing. At this stage, total product increases at a diminishing rate i.e. MP and AP decreases.
Question 15. Consider the following table:
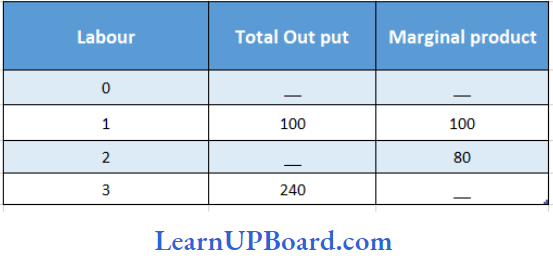
What is the total output, when 2 labourers are employed?
- 80
- 100
- 180
- 200
Answer: 3. 180
When 1 unit of labour is employed TP = 100, MP = 100 when the 2nd unit of labour is employed MP = 80 i.e. addition made to the total product is 80.
The total product when 2 labourers are employed is 100 + 80 = 180.
Or
MP2 =TP2 – T.P2-1
80 =TP2-100.
TP2 = 80+100
TP2 =180.
Question 16. Who has given the concept of Innovative Entrepreneurship?
- Robbins
- Adam Smith
- Schumpeter
- Sweezy
Answer: 3. Schumpeter
The concept of Innovative Entrepreneurship was given by Schumpeter.
Question 17. AT 10 units Total Cost → ₹ 200 , 20 units Total Cost → ₹ 600
Marginal Cost =?
- 50
- 40
- 30
- 400
Answer: 2. 40
Given Original total cost = ₹ 200
Original quantity produced = 10 units New total cost = ₹ 600
New quantity produced = 20 2units
Marginal coot h the addition made to the total cost by the production of an additional unit of output
Additional Coot = ₹ 600 – ₹ 200
= ₹ 400
Additional quantity produced = 20 units -10 units
= 10 units
∴ M. C = ½
= ₹ 40
Question 18. Average Fixed Cost – ₹ 20, Quantity Produced = 10 units. What will be the Average Fixed Cost of 20th units?
- ₹ 10
- ₹ 20
- ₹ 5
- None
Answer: 1. ₹ 10
Average Fixed Cost – ₹ 20, Quantity Produced = 10 units.
Average fixed cost (AFC) is the total fixed cost divided by the number of units produced i.e. AFC = TFC/Q
Whore Q is the number of units produced
TFC = ₹ 20 × 10 units
= ₹ 200
Q = 10 units
AFC = \(\frac{200}{20}\)
= ₹ 10
Since AFC steadily falls as output increases hence for the 20th unit AFC is ₹ 10
Question 19. What Is Production in Economics
- Croation / Addition of Utility
- Production of food grains
- Creation of services
- Manufacturing of goods
Answer: 1. Croation / Addition of Utility
In Economics, production is the process by which man utilizes or converts the resources of nature, v/orks upon them to make them satisfy human wants. The satisfying power of goods and services is called utility. Hence we can conclude that production can also be defined as the creation or addition of utility.
Question 20. External Economies of Scale are obtained by
- A firm
- A group of firm
- Small Production
- Society
Answer: 2. A group of firm
External Economies of scale accrue to firms as a result of expansion in the output of the whole industry and they are not dependant on the output level of individual firms. They are external in the sense that they accrue to firms not because of their internal situation but from outside i.e, expansion of the industry.
Question 21. If a firm’s output is zero, then
- AFC will be positive
- AVC will be zero
- Both of (1) and(2)
- None of (1) and (2)
Answer: 3. Both of (1) and(2)
Average fixed cost may be expressed as Fixed cost divided by the number of units. When the firm’s output is zero, the average fixed cost is positive as fixed cost is incurred even if no units are produced. Average variable cost may be expressed as variable cost per unit produced. When the firm’s output is zero, there will be no variable cost hence average variable cost will be zero.
Question 22. The functions of the entrepreneur are
- Risk bearing
- Initiating a business enterprise and resource co-ordinating
- Introducing innovations
- All of the above
Answer: 4. Initiating a business enterprise and resource co-ordinating
The entrepreneur has also been called the organiser, the manager or risk- the taker. The task of an entrepreneur Is to initiate production work and to bear the risks Involved.
An entrepreneur performs the following functions:
- Initiating a business enterprise and resource coordination
- Risk-bearing or uncertainty-bearing
- Innovation
Question 23. The law of diminishing returns is applicable in
- Manufacturing industry
- Agriculture
- Neither (1) nor (2)
- Any economic activity at a point in time
Answer: 4. Any economic activity at a point in time
The law of diminishing returns states that as more and more factors of production are employed, the total production first increases, and then eventually declines. This law applies to all economic activities at some point or the other.
Question 24. The labour force wants more.
- Facility
- Leisure
- Benefit all of the above
Answer: 2. Leisure
Labour is one of the factors of production. A labourer has to choose between hours of labour and hours of leisure. The labour force prefers to have more of rest and leisure than earning money.
Question 25. Production activity in the short run is analysed by
- Returns to scale
- Economies of scale
- Law of variable proportion
- None of these
Answer: 3. Law of variable proportion
Short-run is a period when only one factor is fixed and the rest are variable. The law of variable proportion operates in the short run. Therefore, in the short- run production activity is analysed by this law.
Question 26. Increasing returns to scale occur due to
- Economies of scale
- Specialization
- Indivisibility of factors
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Increasing returns to scale occurs when the output increases more than the increase in input. This occurs due to economies of scale it occurs due to the indivisibility of factors and returns to scale may also increase because of greater possibilities of specialization of land and machinery.
Question 27. The law of diminishing returns is applicable in______________________
- Only manufacturing industries
- Only agriculture
- Neither in agriculture nor in industries
- In all economic activities after a limit
Answer: 4. In all economic activities after a limit
The law of diminishing returns states that as more and more factors of production are employed, the total product first increases and then eventually declines. This law applies to all economic activities after a limit.
Question 28. The law of increasing returns is applicable because of ___________________
- Indivisibility of factors
- Specialization
- Economies of scale
- Both (1) & (2) above
Answer:
- The two causes of the Law of Increasing Returns are:
- Indivisibility of Factors.
- Division of Labour and specialization.
- Hence both options A and B are correct.
Question 29. When output decreases by 20% due to an increase in inputs,
- This stage is called the law of
- Increasing returns to scale decreasing returns to scale
- Constant returns to scale
- None of the above
Answer: 4. None of the above
The law of constant returns states that with an increase in input, the output also increases in the same proportion. However, in the given question, the output is decreasing by 20% due to an increase in input. This is not the case with constant returns to scale. This is neither the case of increasing returns to scale nor decreasing returns to scale, hence, the answer would be none of the above.
Question 30. In the first stage of the law of variable proportions, the total product increases at the _____________________________
- Decreasing rate
- Increasing rate
- Constant rate
- Both 1 and 2.
Answer: 2. Increasing rate
The law of variable proportion states that as we increase the quantity of one input which is combined with other fixed inputs, the MP of variable input eventually declines.
It is divided into three stages (laws):
- Law of increasing returns
- Law of decreasing returns
- Law of negative returns
Question 31. What will be the total product when two labourers are hired according to the table given below?
No. of labourers Total product Marginal product
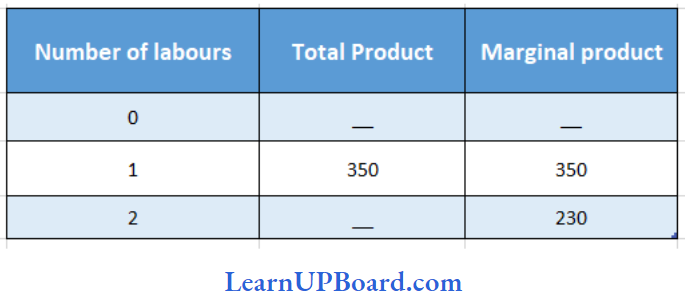
- 680
- 580
- 350
- 230
Answer: 2. 580
TPn = TPn-1 + MPn
= 350 + 230
= 580
Question 32. Which function shows the relationship between input and output?
- Consumption function
- Investment function
- Production function
- Cost function
Answer: 3. Production function
Production function states the relationship between inputs and output i.e. the maximum amount of output that can be produced with given quantities of inputs under a given state of technical knowledge.
Question 33. External economies are enjoyed:
- Large producers only
- As the firm expands
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
External economies are those economies which accrue to firms as . a result of expansion in the output of the whole industry and they are not dependent on the output level of individual firms. Externa! economies are enjoyed by large producers.
Question 34. The Law of Diminishing Returns is applicable in
- Only in manufacturing industries
- Only in agriculture
- Neither in agriculture nor in industries
- All economic activities after a point.
Answer: 4. All economic activities after a point.
The law of diminishing returns occurs in the short run and states that as more and more units of variable factors are employed to a fixed factor total product first Increases and then eventually declines.
This law occurs in all economic activities after a point of time because after reaching an optimum combination the factors become over-utilized and lead to lesser production.
Question 35. The concept of Returns to Scale is related to
- Very short period
- Short period
- Long period
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Long period
Long-run. refers to the period when all the factors change and no factor is fixed. When all inputs are changed in the same proportion, it leads to a change in scale. Therefore, returns to scale occur in the long run.
Question 36. The function of an entrepreneur is:
- Initiating an enterprise and resource coordination
- Risk bearing
- Introducing innovations
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
An entrepreneur is a person who combines all factors of production, bears risk and initiates the process of production.
An entrepreneur performs the following functions:
- Initiating a business and resource coordination:
- Risk-bearing and uncertainty-bearing
- Taking innovations
Question 37. Which of the following is not a characteristic of land?
- It is a gift of nature
- It is a mobile factor of production
- It is limited in quantity
- Its productive power is indestructible.
Answer: 2. It is a mobile factor of production
A factor of production should have the following characteristics to be called land :
- It is a gift of nature
- It is strictly limited in quantity
- It is indestructible
- It cannot be shifted from one place to another.
- It is a specific factor of production
Question 38. A production function is defined as the relationship between
- The quantity of physical inputs and physical output of a firm
- Stock of inputs and stock of output
- Prices of inputs and output
- Price and supply of a firm.
Answer: 1. The quantity of physical inputs and physical output of a firm
Production function states the relationship between inputs and output i.e. the maximum amount of output that can be produced with given quantities of inputs under a given state of technical knowledge.
Question 39. Production activity in the short period is analysed with the help of
- Law of variable proportion
- Laws of returns to scale
- Both (1) & (2)
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Law of variable proportion Laws of returns to scale
Production function states the relationship between inputs and outputs. The production activity can be in the short run or long-run. A short period is a period which is too short for a firm to install new capital equipment to increase production. This is done when the law of variable proportion is analysed
Question 40. Which of the following is the reason for the working of the law of increasing returns?
- Fuller utilisation of fixed
- FactorsIndivisibility of the factors
- Greater specialization of labour
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
The causes of the law of increasing returns are:
- Indivisibility of factors.
- Division of labour and specialisation.
- When a variable factor is increased, fuller utilisation of the fixed factor becomes possible and it results in increasing returns.
- Hence, all of the above are the reasons for working on the law of increasing returns.
Question 41. External economies can be achieved through
- Foreign trade only
- Superior managerial skill
- Extension of transport and credit facilities
- External assistance.
Answer: 3. Extension of transport and credit facilities
External economies of scale are those which accrue to firms as a result of expansion in the output of the whole industry.
These are available to one or more of the firms in the form of:
- Cheaper raw materials and capital equipment
- Technological external economies
- Development of skilled labour
- Growth of ancillary industries
Better transportation and marketing facilities. Thus, external economies can be achieved through the extension of transport and credit facilities
Question 42. External economies arise due to
- Growth of ancillary industries
- High cost of technologies
- Increase in the price of factors of production
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Growth of ancillary industries
External economies arise due to the following reasons:
- Cheaper raw materials and capital equipment
- Technological external economies
- Development of skilled labour
- Growth of ancillary industries
- Better transportation and marketing facilities
Question 43. Innovation theory of entrepreneurship is propounded by
- Knight
- Schumpeter
- Max Weber
- Peter Drucker
Answer: 2. Schumpeter
The concept of innovative entrepreneurship was propounded by Schumpeter.
Question 44. Production function is
- Purely technical relationship between input & output
- Purely an economic relationship between input & output
- Both the technical & economic relationship between input & output
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Purely a technical relationship between input & output
Production function:
Production function states the relationship between inputs and the output i.e. the maximum amount of the output that can be produced with the given quantities of inputs under a given state of technical knowledge. ,
Thus, the production function is purely a technical relationship between input & output.
Question 45. The concept of returns to scale is related with
- Very short period
- Short period
- Long period
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Long period
Long-run refers to the period when all the factors change and. no factor is fixed, when all inputs are changed in the same proportion, it leads to a change in scale. Therefore, returns to scale occur in the long run.
Question 46. In the Cobb-Douglas production function, two inputs are
- Land and Labour
- Labour and Capital
- Capital and Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur and land
Answer: 2. Labour and Capital
Cobb-Douglas Production function applies not to an individual firm but to the whole of manufacturing. In this case, output is manufacturing production and inputs used are labour and capital.
Question 47. Which one of the following is not a characteristic of land?
- A gift of nature
- Its supply is fixed
- An active factor of production
- It has different uses.
Answer: 3. An active factor of production
As a theoretical concept, land has the following characteristics:
- Land is Nature’s gift.
- The supply of land is fixed.
- It has indestructible powers.
- It is a passive factor.
- It has different uses.
Hence, land is not an active factor of production, the option is the correct answer
Question 48. An Entrepreneur undertakes which one of the following functions?
- Initiating a business and resource coordination
- Risk or uncertainty-bearing
- Innovations
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
An entrepreneur performs the following functions in general:
- Initiating a business enterprise & resource coordination.
- Risk bearing/uncertainty bearing.
- Innovations. .
‘ Hence, option i.e. all of the above is the correct answer.
Question 49. To increase its production, Hariharan a manufacturer of shoes, increases. all the factors of production in his unit by 100%. But at the end of the year, he finds that instead of an increase of 100%, his production has increased by only 80%. Which law of returns to scale is operating in this case?
- Increasing returns to scale
- Decreasing returns to scale
- Constant returns to scale
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Decreasing returns to scale
To increase its production, Hariharan a manufacturer of shoes, increases. all the factors of production in his unit by 100%. But at the end of the year, he finds that instead of an increase of 100%, his production has increased by only 80%.
When output increases in a smaller proportion with an increase in all inputs, decreasing returns to scale are said to prevail. In this case, inputs are increased by 100% in comparison to outputs which are increased by 80%.
Question 50. The linear homogeneous production function is based on
- Increasing returns to scale
- Decreasing returns to scale
- Constant returns to scale
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Constant returns to scale
Question 51. Which of the following statements is true about an ISO-Quant Curve?
- It represents those combinations of two factors of production that will give the same level of output
- It represents those combinations of all the factors that will give the same level of output
- It slopes upward to the right
- It can touch either axis.
Answer: 1. It represents those combinations of two factors of production that will give the same level of output
An ISO-quant represents all those combinations of two factors of production which are capable of producing the same level of output.
Question 52. Production is defined as:
- Creation of matter
- Creation of utility in matter
- Creation of infrastructural facilities
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Creation of utility in matter
By production we mean the process by which man utilises or converts the resources of nature, working upon them to make them satisfy human
wants.
Question 53. The long-period production function is related to
- Laws of variable proportions
- Laws of returns to scale
- Laws of diminishing returns
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Laws of returns to scale
Long period production function is related to the law of returns to scale which relates to the long-period production function by changing one or more of its factors. The long-period production function is related to laws of returns to scale v/hich relates to the long-period production function by changing one or more of its factors.
Question 54. The conclusion drawn from the Cobb-Douglas production function is that labour contributed about and capital about of the increase in the manufacturing production.
- (¾) th ,(¼)th
- ½, ½
- (¼)th, (¾) th
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. (¾) th ,(¼)th
Cobb-Douglas production function states that labour contributed about and capital about (¾) th th of the increase in the (¼)th manufacturing production Q = KLaC (1-a)
Where ‘Q’ is output, ‘L’ is the quantity of labour, ‘C’ is the quantity of capital, ‘K’ and ‘a’ are positive constants.
Question 55. ISO quants are also known as
- Production possibility curves
- Indifference curves
- Production indifference curves
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Indifference curves
ISO quants are also known as production indifference curves. They show all those combinations of different factors of production which give the same output to the producer. ISO quants are similar to indifference curves of the theory of consumer behaviour.
Question 56. Human capital refers to
- Savings by individuals
- Mobilisation of savings
- Human skills and abilities
- Productive investment.
Answer: 3. Mobilisation of savings
Human capital refers to human skill and ability. This is called human capital because a good deal of investment has gone into the creation of these human abilities.
Question 57. The Law of Variable Proportions is associated with
- Short period
- Long period
- Both short and long periods
- Neither short nor long period.
Answer: 1. Short period
The law of variable proportions examines the production function with one-factor variable, keeping quantities of other factors fixed. This law operates in the short run when all the factors of production cannot be increased or decreased simultaneously. In other words, it refers to the input-output relationship.
Question 58. Which one of the following statements is not correct?
- The land has indestructible powers
- Labour is mobile
- Capital is nature’s gift
- Land is a passive factor.
Answer: 3. Capital is nature’s gift
Capital has been rightly defined as ‘produced means of production’. If has been produced by man by working with nature. Therefore, capital may well be defined as man-made instruments. of
Question 59. Which of the following is not a characteristic of labour?
- It is perishable
- It has weak bargaining power
- Labour and Labour power cannot be separated
- Labour is not mobile
Answer: 4. Labour and Labour power cannot be separated
Labour is not mobile. This is not a characteristic of labour. Labour is mobile.
Question 60. Which among the following is not a characteristic of Land?
- It is an active factor
- It has a variety of uses
- Its production powers are indestructible
- Its supply is limited
Answer: 1. It is an active factor
Land is a passive factor of production. It is not an active factor.
Question 61. When the average product rises as a result of an increase in the quantity of variable factor, the marginal product is
- Equal to the average product
- More than average product
- Less than average product
- Becomes negative
Answer: 2. More than average product
When the average product rises as a result of an increase in the quantity of variable factors, marginal product is more than the average product.
Question 62. Suppose the first four units of a variable input generate a corresponding total output of 150,200, 350, 550. What will be the marginal product of the third unit of input?
- 50
- 100
- 150
- 200
Answer: 3. 150
Suppose the first four units of a variable input generate a corresponding total output of 150,200, 350, 550.
The marginal product of the third unit of input = TP3-TP2
= 350 – 250
= 150
The marginal product of the third unit of input is 150
Question 63. The famous Cobb-Douglas production function is based on studies of _____________ industries in the United States of America.
- Manufacturing
- Construction
- Consumer
- Aviation
Answer: 1. Manufacturing
A famous statistical production function is the Cobb-Douglas production function. Paul H. Douglas and C.W. Cobb of the U.S.A. Studied the production function of the American manufacturing industries. In its original form, this production function applies not to an individual firm but to the whole of manufacturing in the United States.
Question 64. In Economics, the entire process of __________________________ utilities in the form of goods and services.
- Consumption
- Production
- Exchange
- Distribution
Answer: 2. Production
Production is nothing but the creation of utilities in the form of goods and services. For example, in the production of a woollen suit, utility is created in some form or the other. Firstly wool is changed into woolen cloth at the spinning and weaving mill (utility created by changing the form) then it is taken to a place where it is to be sold (utility added by transporting it).
Since woollen clothes are used only in winter, it will be retained until such time when then they are required by purchasers(time utility). In the whole process, services of various groups of people are utilized (as that of mil
Question 65. Cobb Douglas function is given by Q = KLa Ca
- If α + β > 1, increasing returns
- If α + β > 1, increasing returns to scale
- If α + β < 1, diminishing returns
- If α + β = 1, decreasing returns to scale.
Answer: 2. If α + β > 1, increasing returns to scale
The cobb-Douglas function is given by Paul H. Douglas and C.W. Cobb of the U.S.A. studied the production of American Manufacturing industries. They describe that output is manufacturing and input is labour and capital. It is given by Q = K La C(1-a) if, a + b > 1, increasing the return to scale.
Question 66. Production is defined as
- Creation of matter
- Creation of utility in matter
- Creation of infrastructural facilities
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Creation of utility in matter
Man cannot create matter. Man can create only utility in matter. Production should not be taken as the creation of matter but it is taken as the creation of utility in matter.
For Example: When a man produces a table, he does not create the matter of which the wood is composed of. He only transforms wood into chairs and utility to wood which did not have utility before workers, shopkeepers, agents etc.) to contribute to the enhancement of utility. Thus, the entire process of production is nothing but creation of form utility, place utility, time utility and/or personal utility
Question 67. The conclusion drawn from Cobb Douglas’s production function is that labour contributed about and capital to the increase in manufacturing production.
- (¾)th, (¼)th
- (½)th, (½)th’
- (¼)th, (¾)th,’
- None of the above
Answer: 1. (¾)th, (¼)th
As Cobb-Douglas function is below:
Q = K La C(1-a)
This shows that labour produces ¾ th and capital produces ¼ of the increase in manufacturing production
Question 68. At the point of inflexion, the marginal product is
- Increasing
- Decreasing
- Maximum
- Negative
Answer: 3. Maximum
A point of inflexion is a point where the marginal product is at maximum. First marginal product utility increase then reaches at maximum points which is the point of inflexion and then decreases. Marginal product can be negative.
Question 69. Isoquants are equal to
- Product lines
- Total utility lines
- Cost lines
- Revenue lines
Answer: 1. Product lines
Isoquants are similar to indifference curves of the theory of consumer behaviour. An isoquant represents all those combinations which are capable of producing the same level of output. The production indifference curve is another. Name of isoquants as it represents product lines.
Question 70. Increasing returns to scale can be explained in terms of
- External and internal economics
- External and internal diseconomies
- External economies and internal diseconomies
- All of these
Answer: 1. External and internal economics
An increasing return to scale means an increase in output is greater than the increase in input and an increasing return to scale caused due to external and internal economies while a decreasing return to scale is caused due to external and internal diseconomies.
According to Cobb- the production function is stated as Q = KLa C(1-a)
When ‘Q’ is output, ‘L’ is the quantity of labour and ‘C’ is the quantity of capital. ‘K’ and ‘a’ are positive constants.
Question 71. Which of the following statements about factors of production is not true
- Land is a passive factor
- The land is a gift of nature
- Land is immobile
- Land is perishable
Answer: 4. Land is immobile
Characteristics of land are:
- The land is a gift of nature
- The supply of land is fixed
- The land is permanent and has indestructible power
- Passive factor
- Land in Immobile.
Therefore, land is not perishable and option will be the answer.
Question 72. Which of the following is considered as production in economics?
- Helping a blind person crossing the road
- Group dance performance in a college’s annual function
- Holding a child who is falling from a wall
- Performing art in a theatre
Answer: 4. Performing an art in a theatre
Production consists of various processes to add utility to natural resources for gain greater satisfaction from them by making use of personal skills in the form of services.
Example: Performing an art in a theatre.
Question 73. The marginal, average and total product of a firm in the short run will not comprise with
- When marginal product is at a maximum, average product is equal to marginal product, and total product is rising
- When an average product is maximum, the average product is equal to the marginal product, and the total product is rising
- When the marginal product is negative, total product and average product falling
- When total product is increasing, average product and marginal product may be either rising or falling
Answer: 1. When marginal product is at a maximum, average product is equal to marginal product, and total product is rising
The relationship between the average product and the marginal product is as follows:
- When the average product rises, the marginal product is more than the average product
- When an average product is maximum, MP = AP
- When the average product falls, the marginal product is less than the average product.
- Hence, option (1) is not the relation between MP and AP.
Question 74. Supply of land ___________ in case of economy?
- Elastic
- Inelastic
- Perfectly elastic
- Perfectly inelastic
Answer: 4. Perfectly inelastic
The supply of land is perfectly inelastic in the case of the economy. Land is v strictly limited in quantity. It is different from other factors of production in that no change in demand can affect the amount of land in existence. However, it is relatively elastic from the point of view of a firm.
Question 75. MP is the slope of
- TP
- AP
- Both
- None
Answer: 1. TP
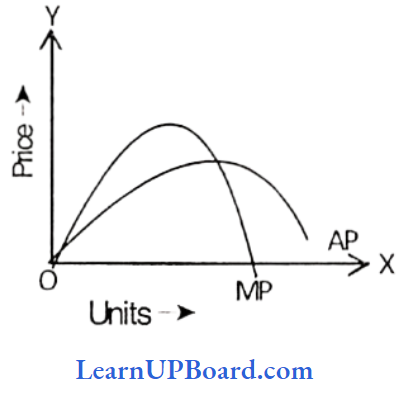
Marginal Product is the slope of Total Product as the total product is the total output resulting from the efforts of all factors of production combined together at any time. Marginal product is the change in total product per unit change in the quantity of variable factor, i.e. it is the addition made in additional unit of output.
MPn= TPn -Tn-1
Or ΔTP/ΔQ = ΔTP
ΔQ = Change in Quality
For Questions (76 to 78) use the data table given below:
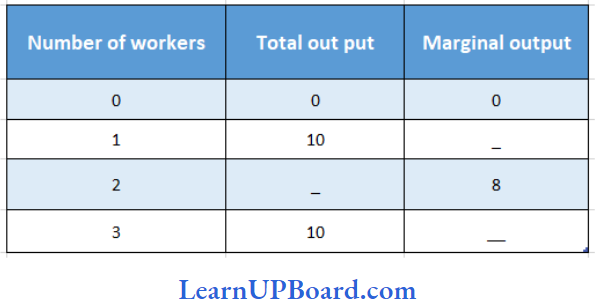
Question 76. What will be the total output for 2 workers?
- 6
- 18
- 12
- 17
Answer: 2. 18
Question 77. What will be the marginal output for 3 workers?
- 6
- 12
- 7
- 8
Answer: 1. 6
Question 78. Average Product for three labour
- 12
- 11
- 8
- None
Answer: 3.8
For Answers (76 to 78) use the data table given below:
At the first unit of output. Total output and Marginal output are equal i.e.
TP = MP = 10 units (given as TP = 10)
TP = ∑MP
∴ TP = 10 + 8 = 18 units of output
As Mpn = TPn = TPn-1
i.e. TPn = TP3 i.e.
∴ Total product at 3 units of labour (worker)
TPn-1 = TP3-1 = TPn-2
∴ Total product at 2 units of labour (worker)
MPn = MP3 = i.e. marginal product at 3 units of labour (worker)
24 units- 18 units = 6 units.
And marginal product is Maximum at 8 units of labour.
Question 79. The concept of innovative entrepreneurship was given by
- Marshall
- Schumpeter
- J. K. Mehta
- Adam Smith
Answer: 2. Schumpeter
The concept of innovative entrepreneurship was propounded by Schumpeter.
Question 80. Which activity is the best of nil tho production activities
- Production
- Exchange
- Investment
- Consumption
Answer: 3. Investment
Investment is the base for all production.
Question 81. When output increases more than the increase in input it occurs due to
- External and internal diseconomies
- External and internal economies
- External diseconomies and internal diseconomies
- External economies and internal economies
Answer: 2. External and internal economies
Internal economies of scale are firm-specific, while external economies of scale occur based on larger changes and costs down while increasing the volume of output.
Question 82. A functional relationship between inputs and output is called
- Cost function
- Revenue function
- Consumption
- Production function
Answer: 4. Production function
The production function is a technical relationship between the amount of inputs that a firm uses and the maximum level of output that can be obtained.
Question 83. Among the following statements which is incorrect about isoquants
- Isoquants are negatively sloped
- Isoquants are convex to the origin
- Isoquants are not intersecting
- Isoquants are concave to origin
Answer: 2. Isoquants are convex to the origin
Isoquants are convex to the origin:
Like indifference curves, isoquants are convex to the origin. To understand this fact, we have to understand the concept of diminishing marginal rate of technical substitution (MRTS), because the convexity of on isoquant implies that the MRTS diminishes along the isoquants.
Question 84. External economies can be achieved through
- Technological external economies
- External assistance
- Development of unskilled labour
- Superior managerial efficiency
Answer: 1. Technological external economies
External Economies can be achieved through all external sources like technology etc. Un-skilled labour development and superior managerial efficiency are internal economies.
Question 85. Marginal product will be at the point of inflexion is
- Maximum
- Minimum
- Negative
- Zero
Answer: 1. Maximum
At the point of inflexion, the marginal product is maximum up to the point of inflexion. TP has been increasing at an increasing rate resulting in increasing MP
Question 86. Production may be defined as an act of
- Creating utility
- Destroying utility
- Earning profit in the best way
- Providing services professionally
Answer: 1. Creating utility
Production may be defined as the act of creating utility. Production may be defined as an act of making goods and thus adding utility to the object.
Question 87. Which of the following is correct about Marginal Product?
- What are produced units when all factors of production are employed at optimum efficiency?
- The extra output obtained from employing an additional unit of a factor
- The left revenue to the entrepreneur after he has incurred all expenses
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. The left revenue to the entrepreneur after he has incurred all expenses
The extra output obtained from employing an additional utility of a factor
Marginal product refers to the addition to the total product When an additional unit of a commodity is employed and thus produced.
MP =TPA-Tpn-1
Question 88. According to Cobb-Douglas production function, labour contribution in increasing manufacturing production is
- 2/3
- 3/4
- 1/4
- 1/2
Answer: 2. 3/4
Cobb – Douglas production function, labour contribution is increasing manufacturing production is 3/4
Question 89. When the Average Product falls, the marginal product is the Average product.
- Less than
- More than
- Equal to
- Maximum
Answer: 1. Less than
When Average Product falls marginal product is less than the average product.
Question 90. How many kinds are Economics of scale
- 5
- 3
- 2
- 1
Answer: 3. 2
There are two types of Economies of scale
Question 91. In the short run, the Law of variable proportions is also known as
- Law of increasing returns
- Law of diminishing returns
- Law of decreasing returns
- Law of constant returns
Answer: 2. Law of diminishing returns
In the short run, the law of variable proportion is known as the law of diminishing returns.
Question 92. The Law of returns to scale is.
- Short run
- Long run
- Short and Long run
- Medium run
Answer: 2. Long run
The laws of return to scale is applicable in the long run only.
Question 93. Which of the following is not a passive factor of production?
- Land
- Building
- Labour
- Machine
Answer: 3. Labour
Labour is not a passive factor of production i.e. Labour is an active factor, without the active participation of labour, land and capital may not produce anything.
Question 94. Which one of the following is not a necessary function of an entrepreneur?
- Risk and uncertainty-bearing
- Initiating a business enterprise
- Innovations
- Suspension of day-to-day production activities.
Answer: 4. Suspension of day-to-day production activities.
- The functions of an entrepreneur are:
- Initiating business enterprise
- Risk-bearing and uncertainty-bearing
Question 95. The land is heterogeneous because of
- Lands are alike
- Lands are not alike
- Lands are fixed
- Lands are mobile
Answer: 2. Lands are not alike
The land is heterogeneous because no two lands are alike they differ in size, fertility and situation.
Land is a gift of nature, fixed in supply, passive, and immobile.
Question 96. When TP is decreasing, MP becomes?
- Positive
- Zero
- Undefined
- Negative.
Answer: 4. Negative
When TP is increasing, MP is increasing, MP is zero, TP is maximum, when MP is negative and average revenue is diminishing, TP is decreasing/diminishing.
Question 97. Profit is an income from
- Land
- Investment
- Business
- Labour
Answer: 3. Business
Profit is an income from business.
Profit is the revenue that remains after expenses in a business. The main aim of business is the acquisition of profits.
Question 98. If the output has to max then
- MR < MC
- MR = MC
- MR > MC
- None of the above
Answer: 2. MR = MC
If the output is to be maximum level then the Marginal Revenue should be equal Marginal Cost.
When MR, MC, a firm has maximum output produced with additional products/outputs for maximum revenue.
Question 99. Marginal Cost changes due to changes in cost
- Total
- Fixed
- Average
- Variable
Answer: 4. Variable
Marginal cost is the addition made to the total cost by the production of an additional unit of output. It is independent of fixed cost. It is only the variable cost which changes with a change in the level of output in the short run.
Question 100. Which cost increases continuously with the increase in production?
- Fixed cost
- Variable cost
- Total cost
- Average cost
Answer: 2. Variable cost
Variable cost increases as production increases as every additional unit of output increases the variable cost. Find cost remains the same.
Question 101. The market where small quantities of goods are sold-
- Wholesale
- Retail
- Manufacturers
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Retail
The market where small quantities of goods sold are Retail
Question 102. The Law of variable proportion Is associated with.
- Short period
- Long period
- Both short & long periods
- Neither short nor long-period
Answer: 1. Short period
The law of variable proportion Applies to short-run periods. The law of variable proportion exhibits the relationship between the change of output In respect do tho change in only one variable factor, only In the short-run economy.
Question 103. Producer’s surplus arises when
- The price of the commodity is more than tho minimum price at which the producer is willing to supply.
- The price of the commodity is less than the minimum price at which the producer is willing to supply.
- The price of the commodity is equal to the minimum price the, producer is willing to supply at.
- The price of the commodity is zero to the maximum price the producer is willing to supply at.
Answer: 1. The price of the commodity is more than the minimum price at which the producer is willing to supply.
A producer surplus is generated by market prices more than the lowest price producers would otherwise be willing to accept for their goods.
Question 104. The scale of production can be changed in
- Short period
- Very short period
- Long period
- Both short and very short period
Answer: 3. Long period
Since all the factors are only variable in the long run, the scale of production is only changed in the long run, thus, the law of returns to scale will only apply in the long run.
Question 105. Which of the following is not a quality of the factor of land
- Passive factor
- Active factor
- Heterogeneous
- Trimobile
Answer: 2. Active factor
The land is not an active factor unless human effort is exercised on land, it does not produce anything on its own.
Question 106. The concept of “Innovative Entrepreneurship” was propounded by
- Joel Dean
- Schumpeter
- Marshall
- Karl Marx
Answer: 2. Schumpeter
According to Schumpeter, the true function of an entrepreneur is to introduce innovations.
Question 107. Returns to scale occur in
- Small run
- Long run
- Very-small run
- Undetermined
Answer: 2. Long run
Returns to scale (i.e. all factors are variable) occur due to long-run
Question 108. Which one of the following is not a characteristic of land?
- Land is immobile
- Land is an active factor
- The land has multiple uses.
- Land is heterogeneous
Answer: 2. Land is an Active factor
Land is a passive factor of production not an active factor of production. like labour. Unless human efforts are involved land cannot produce anything on its own.
Question 109. When TP is decreasing, MP becomes
- Zero
- Negative
- Positive
- Infinite
Answer: 2. Negative
At the stage of Negative Returns, the total product declines, MP becomes negative and the average product starts diminishing.
Question 110. Technical relationship between inputs and output:
- Production function
- Supply function
- Marketing function
- Social function
Answer: 1. Production function
Production function states the technological relationship between inputs and outputs that results from the use of a firm’s scarce resources.
Question 111. The stage of “Decreasing Returns to Scale” will occur, when
- A decrease in output is greater than the increase in input
- A decrease in output is greater than the increase in input
- An increase in output is greater than the increase in input
- An increase in output is less than the increase in input
Answer: 4. Increase in output is less than the increase in input
If the increase in output is less than an increase in input it is called decreasing returns to scale.
