CA Foundation Solutions For Business Laws The Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008 Self-Study Questions And Answers
Question1. What do you understand by a limited liability partnership?
Answer:
Limited liability partnership
- Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) Act was passed by parliament on 12th December 2008 and assent by the President was given on 7th January 2009.
- It has 81 Sections and 4 Schedules
- Schedule 1 – Mutual rights and duties of partners and partnership in the absence of agreement.
- Schedule 2 – Conversion of Firm to LLP.
- Schedule 3 – Conversion of Private Ltd. to LLP.
- Schedule 4 – Conversion of Public Ltd. to LLP.
- Partnership Act does not apply to LLP forms of business.
Limited Liability Partnership – Meaning and Concept:
Meaning:
- Is a new form of business with limited liability.
- It is a mid-way between a partnership firm and a Private Limited Company.
- It contains elements of ‘body corporate’ and ‘partnership’ forms of business.
Question 2. What are the Characteristics of Salient Features of a Limited Liability Partnership?
Answer:
The Characteristics of Salient Features of a Limited Liability Partnership
- It is a body corporate.
- It has perpetual succession.
- Separate Legal Entity.
- Mutual Agency between partner and LLP only.
- Rights and duties as per agreement.
- Artificial legal person.
- Common seal.
- Limited liability of partners.
- The designated Partner is responsible for legal compliance.
- Must have a minimum of 2 individual partners and a maximum no limit.
- LLP cannot be formed for charitable and non-economic purposes.
- Can be investigated by the Central Government through the appointment of competence authority.
- Compromise, arrangements will be as per LLP Act, 2008.
- Forms are to be e-filed on the portal of www.mca.gov.in using a digital signature.
- LLP formed, incorporated, or registered outside India having a place of business in India is called a Foreign LLP. It can become a partner in an Indian LLP.
Question 3. How many Advantages of a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) are there?
Answer:
Advantages of a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP
- Easy formation or dissolution.
- Limited Liability of Partners.
- Less legal formalities.
- Flexible capital structure.
- Low-cost compliance.
Question 4. What are the steps followed for the Incorporation of a Limited Liability Partnership?
Answer:
Essential Elements for Incorporation:
- At least two designated partners.
- Registered office in India along with utility bill as proof.
- Designated Partners must be individuals.
- One of them must be resident in India.
- Designated Partner must have DPIN i.e. Designated Partner Identification Number which is allotted by MCA.
- LLP Agreement consisting of all rights and duties of partners.
- In the absence of LLP Agreement provisions of Schedule First of LLP Act, 2008.
- Name of LLP form of business.
Incorporation of Limited Liability Partnership Process:
Step 1: Elect members and design among them at least two designated partners.
Step 2: Obtain the DPIN of Designated Partners and a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) to sign the e-form.
Step 3: Fill e-form Limited Liability Partnership-1 for the reservation of the name (Up to 6 choices can be indicated).
Step 4: Once LLP-1 is approved, fill LLP-2 giving details of all partners along with Designated Partners who have consented to be partners.
Step 5: Draft the LLP Agreement and file it with a registrar in E-form LLP-3 within 30 days of incorporation of LLP.
Question 5. The distinction between a Limited Liability Partnership and a Partnership Firm.
Answer:
The difference between a Limited Liability Partnership and a Partnership Firm
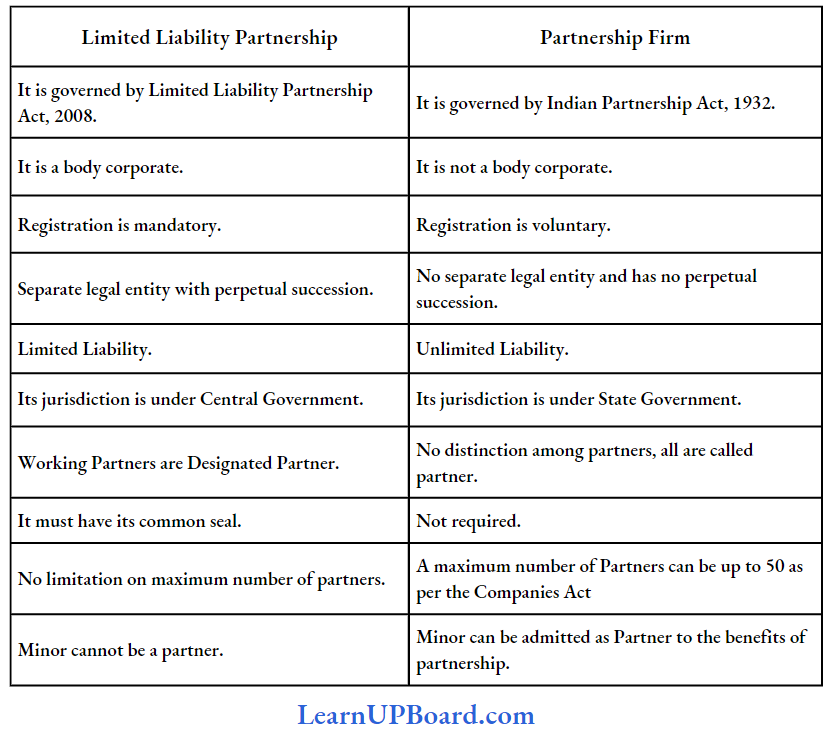
Question 6 Distinguish between a Limited Liability Partnership and a Limited Liability Company (LLC).
Answer:
Difference between a Limited Liability Partnership and a Limited Liability Company (LLC)
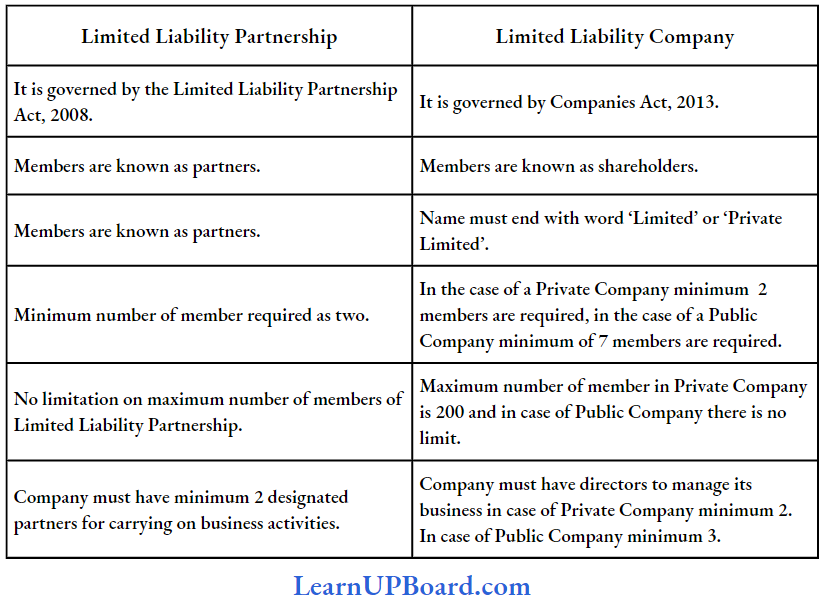
Question 7. What is the difference between partnership and co-ownership as per The Indian Partnership Act, of 1932?
Answer:
Difference between Partnership and Co-ownership:
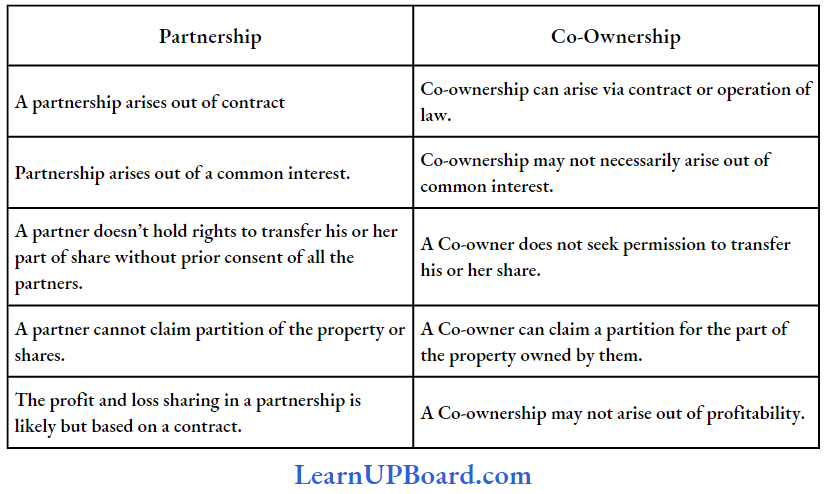
CA Foundation Solutions For Business Laws The Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008 Descriptive Questions
Question 1. What are the essential elements to form a LLP in India as per the LLP Act, 2008?
Answer:
The essential elements to form a LLP in India as per the LLP Act, 2008
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) is an alternative corporate business form that gives the benefits of limited liability of a company and the flexibility of a partnership. Thus, it is a hybrid between a company and a partnership.
Essential Elements to in Corporate LLP:
Under the LLP Act, 2008, the following elements are very essential to form an LLP in India:
- To complete and submit incorporation documents with the Registrar electronically.
- To have atleast two partners for incorporation (whether individual or body corporate).
- To have a registered office in India to which all communication will be made.
- To appoint a minimum of two individuals as designated partners who will be responsible for some duties. Atleast one of them should be resident in India.
- Designated partner (s) should hold a Designated Partner Identification Number (DPIN) allotted by MCA.
- To execute a partnership deed or agreement between and partner intense or between the LLP and its partner.
- Decide upon LLP name. LLPs are body corporate and hence must be registered with the Registrar of LLP.
Question 2. Explain the essential elements to incorporate a Limited Liability Partnership and the steps involved therein under the LLP Act, 2008.
Answer:
The essential elements to incorporate LLP are:
- To complete and submit incorporation document in the form prescribed by the registrar electronically;
- To have at least two partners for incorporation of LLP (individual or body corporate);
- To have a registered office in India to which all communications will be made and received;
- To appoint a minimum of two individuals as designated partners who will be responsible for some duties including doing all acts, matters, and things as are required to be done by the LLP. At least one of them should be resident in India.
- A person or nominee of a body corporate intending to be appointed as a designated partner of LLP should hold a Designated Partner Identification Number (DPIN) allotted by MCA.
- To execute a partnership agreement interse or between the LLP and its partners. In the absence of any agreement the provisions as set out in the first schedule of the LLP Act, 2008 will be applied.
- LLP Name – Limited liability Partnerships are bodies corporate and must be registered with the Registrar of LLP after following the provisions specified in the LLP Act.
Question 3. “LLP is an alternative corporate business form that gives the benefits of limited liability of a company and the flexibility of a partnership”. Explain.
Answer:
“LLP is an alternative corporate business form that gives the benefits of limited liability of a company and the flexibility of a partnership”.
A LLP is a new form of legal business entity with limited liability. It is an alternative corporate business vehicle that not only gives the benefits of limited liability at low compliance cost but allows its partners the flexibility of organizing their internal structure as a traditional partnership.
- The LLP is a separate legal entity and, while the LLP itself will be liable for the full extent of its assets, the liability of the partners will be limited.
- LLP provides the benefits of limited liability but allows its members the flexibility of organizing their internal structure as a partnership based on a mutually arrived agreement.
- Owing to its flexibility in its structure and operation, the LLP is a suitable vehicle for small enterprises and investment by venture capital.
LLP is a hybrid between a company and a partnership:
Some features or advantages of LLP are:
- It is organized and operates based on agreement.
- It provides flexibility without imposing detailed legal and procedural requirements.
- Easy to form.
- All partners enjoy limited liability.
- It has a flexible capital structure.
- It is easy to dissolve.
Question 4. Discuss the conditions under which LLP will be liable and not liable for the acts of the partner.
Answer:
The conditions under which LLP will be liable and not liable for the acts of the partner
A Limited Liability Partnership, popularly known as LLP combines the advantage of both the company and Partnership into a single form of organization.
- In an LLP one partner is not responsible or liable for another partner’s misconduct or negligence.
- Every partner of an LLP would be, for the business of the LLP, an agent of the LLP but not of the other partners. Liability of partners shall be limited except in case of unauthorized acts, fraud, and negligence.
- But a partner shall not be personally liable for the wrongful acts or omission of any other partner.
- An obligation of the limited liability partnership whether in a contract or otherwise, is solely the obligation of the LLP. The liabilities of the LLP shall be met out of the property of the LLP.
Liability of LLP and its fraudulent partner shall be unlimited if an act carried out by a limited liability partnership, or any of its partners,
- With Intent to defraud creditors or any other person, or
- For any fraudulent purpose.
The liability of the LLP and partners who acted with intent to defraud creditors or for any fraudulent purpose shall be unlimited for all or any of the debts or other liabilities of the LLP.
Question 5. State the circumstances under which LLP may be wound. up by the Tribunal under the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008.
Answer:
The circumstances under which LLP may be wound. up by the Tribunal under the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008
The winding up of an LLP may either be voluntary or by the Tribunal and LLP such winding up may be dissolved. (Section 63)
LLP may be wounded up by the Tribunal (Section 64) in the following circumstances:
- If the LLP decides that LLP be wound up by the Tribunal.
- For more than six months, the number of partners in LLP has been reduced to below two.
- If the LLP is unable to pay its debts
- If the LLP has acted against the interests of the sovereignty and integrity of India.
- If the LLP made a default in filing with the Registrar the Statement of Account and Solvency for five consecutive financial years.
- If the tribunal thinks that it is just and equitable LLP may be wound up.
Question 6. State the circumstances under which a LLP and its partners may face unlimited liability under the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008.
Answer:
Unlimited liability in case of fraud (Section 30 of LLP Act, 2008):
- In case of fraud:
- In the event of an act carried out by an LLP, or any of its partners
- With intent to defraud creditors of the LLP or any other person, or for any fraudulent purpose
- The liability of the LLP and partners who acted with intent to defraud creditors or for any fraudulent purpose.
- shall be unlimited for all or any of the debts or other liabilities of the LLP.
- However, in case any such act is carried out by a partner, the LLP is liable to the same extent as the partner unless it is established by the LLP that such act was without the knowledge or the authority of the LLP.
- Where any business is carried on with such intent or for such purpose as mentioned in sub-section (1), every person who was knowingly a party to the carrying on of the business in the manner aforesaid shall be punishable with:
- Imprisonment for a term which may extend to 2 years and
- With a fine which shall not be less than ₹ 50.000 but which may extend to ₹ 5 Lakhs.
- Where a LLP or any partner or designated partner or employee of such LLP has conducted the affairs of the LLP fraudulently, then without prejudice to any criminal proceedings which may arise under any law for the time being in force.
- The LLP and any such partner or designated partner or employee shall be liable to pay compensation to any person who has suffered any loss or damage because of such conduct.
However, such LLP shall not be liable if any such partner or designated partner or employee has acted fraudulently without knowledge of the LLP.
Question 7. Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) gives the benefits of limited liability of a company on one hand and the flexibility of a partnership on the other. Discuss.
Answer:
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) gives the benefits of limited liability of a company on one hand and the flexibility of a partnership on the other.
- Limited Liability Partnership means a partnership formed and registered under the LLP Act.
- It is a hybrid form of business organization structure which combines the advantages of both
- The corporate form of organization
- The partnership firm.
- It is viewed as an alternative corporate business vehicle that provides its partners the benefits of limited liability at low-cost compliance and at the same time flexibility of running the business as per traditional partnership structure.
- LLP since is a separate legal entity will be fully liable for all its liabilities to the extent that all its assets but the liability of the partner will be limited up to their agreed contribution only i.e. limited liability.
- Due to the greater flexibility in its structure and operation LLP is a suitable and most viable business form for small enterprises and investment by venture capitalists and other risk investors.
Question 8. State the rules regarding the registered office of a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) and change therein as per provisions of the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008.
Answer:
Rules regarding the registered office of LLP and change therein (section 13):
- Every LLP shall have a registered office to which all communications and notices may be addressed and where they shall be received.
- A document may be served on an LLP or a partner or designated partner thereof by sending it by post under a certificate of posting by registered post or by any other manner, as may be prescribed.
- At the registered office and any other address specifically declared by the LLP for the purpose in such form and manner as may be prescribed.
- An LLP may change the place of its registered office and file the notice of such change with the registrar in such form and manner and subject to such conditions as may be prescribed and any such change shall take effect only upon such filing.
- If the LLP contravenes any provisions of this section, the LLP and its partners shall be punishable with a fine which shall not be less than ₹ 2,000 but which may extend to ₹ 25,000.
Question 9. Explain the incorporation by registration of a Limited Liability Partnership and its essential elements under the LLP Act, 2008.
Answer:
Incorporation by Registration
- After filing of incorporation document and the declaration form issued by a professional engaged in the incorporation of LLP, the Registrar shall retain the incorporation document within 14 days:
- Register the incorporation document, and
- Issue a certificate of incorporation of LLP
- The certificate shall be signed by the Registrar and authenticated by his official seal.
- The certificate shall be conclusive evidence that LLP is incorporated by the name specified therein.
Following are the essential elements to Incorporate A LLP
Under the LLP Act, 2008, the following elements are very essential to form an LLP in India:
- To submit complete documents to the Registrar electronically.
- To have atleast two partners for incorporation of LLP (ie. individual or body corporate).
- To have a registered office in India to which all communications will be made and received.
- To appoint a minimum of two individuals as designated partners who will be responsible for the number of duties and carrying out day-to-day duties or works. Atleast one of them should be resident in India.
- A person or nominee of a body corporate intending to be appointed as a designated partner of LLP should hold a Designated Partner Identification Number (DPIN) allotted by MCA.
- To execute a partnership agreement between the partners, inter se or between the LLP and its partner. In the absence of any agreement the provisions as set out in the first schedule of the LLP Act, 2008 will be applied.
- LLP should have a name.
Question 10. “An LLP (Limited Liability Partnership) is a type of partnership in which participants’ liability is fixed to the amount of money they invest whereas an LLC (Limited Liability Private/Public Company) is a tightly held business entity that incorporates the qualities of a corporation and a partnership”. In line with the above statement elaborate on the difference between LLP and LLC.
Answer:
The distinction between LLP and LLC:
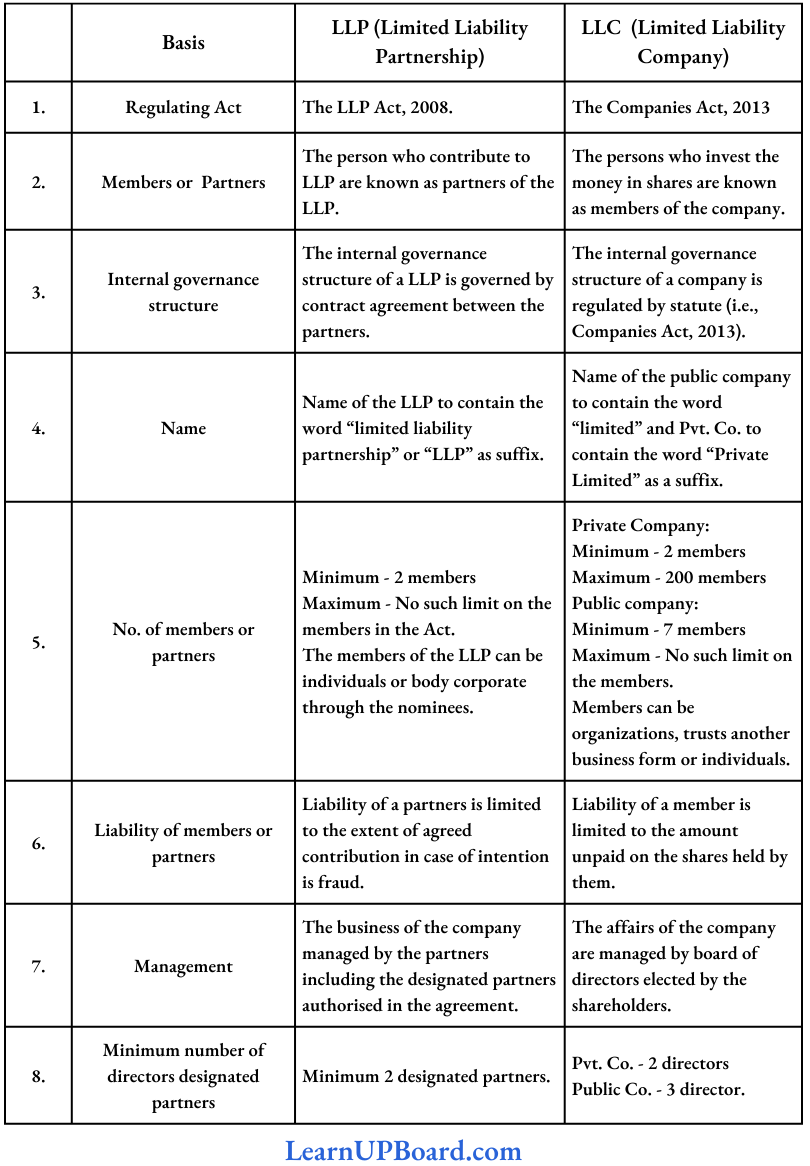
Question 11. Discuss the liabilities of a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) and its partners in case of fraud as per the provisions of the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008.
Answer:
The liabilities of a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) and its partners in case of fraud as per the provisions of the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008
As per section 30 of the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008, in the event of any act carried out by an LLP, or any of its partners, with intent to defraud creditors of the LLP or any other person.
- For any fraudulent purpose, the liability of the LLP and partners who acted fraudulently shall be unlimited for all or any of the debts or other liabilities of the LLP.
- Every person who was knowingly a party to the carrying on of the business in the manner aforesaid shall be punishable with imprisonment for a term which may extend to 2 years and with a fine which shall not be less than ₹ 50,000.
- But which may extend to ₹ 5 lakhs and shall also be liable to pay compensation to any person who has suffered any loss or damage because of such conduct.However, in case any such act is carried out by a partner, the LLP is liable to the same extent as the partner unless it is established by the that such act was without the knowledge or the authority of the LLP.
