UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure
- Force
- Pressure
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure Objectives
- A push or pull applied on a body is called force.
- The strength of a force is expressed by its magnitude.
- Force is denoted by the letter ‘P and its unit is Newton (N).
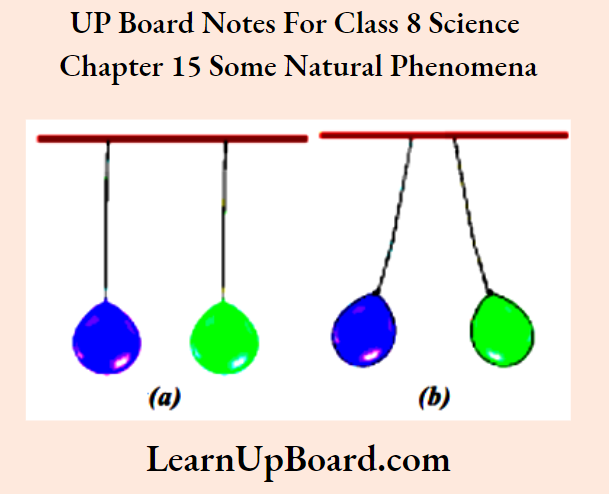
- When two forces act at the same point in opposing directions, the resultant force is equal to the difference between the applied forces and is in the direction of the greater force.
- When two forces act at the same point in the same direction, the resultant force is equal to the sum of the two applied forces.
- The effect of force changes when its direction and magnitude change.
- Force applied brings a change in the state of motion of an object.
- The speed of an object increases if the force applied to the object is in the direction of the motion of the object.
- The speed of an object decreases if the force applied to the object is in the direction opposite to that of the motion of the object
- Force can be of two types: contact force and non-contact force.
- Contact force acts when two or more objects are in direct physical contact with each other and bring about necessary changes.
- Muscular force, frictional force, mechanical force, etc., are examples of contact forces.
- The force exerted by the muscles of a body is called muscular force.
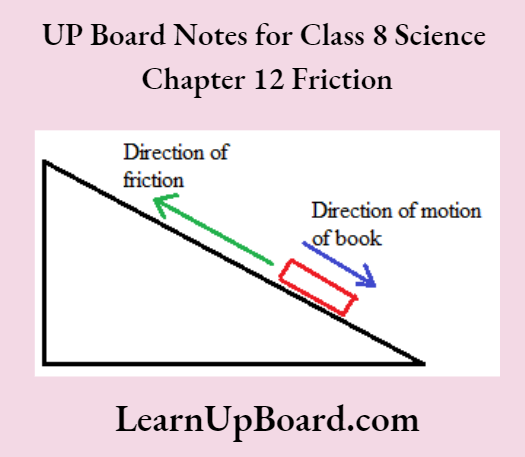
- A force that opposes the motion of an object and arises due to contact between two surfaces is called frictional force.
- The force applied by a machine is called mechanical force.
- Non-contact forces act from a distance without coming into direct contact with the body. Magnetic forces, electrostatic forces, gravitational forces, etc., are a few examples of non-contact forces.
- The force exerted by a magnet is called magnetic force.
- The force exerted by a charged body on another body is called electrostatic force.
- The force with which the Earth attracts all objects towards itself is called gravitational force.
- The amount of offeree acting per unit area is called pressure. The SI unit of pressure is Pascal (Pa). Pressure = Force/Area
- Pressure increases if the area over which the force is applied decreases and vice-versa.
- Liquids do not have a definite shape and hence, the pressure exerted by them depends upon the depth of the liquid column.
- Liquids exert pressure not only on the base of the container but also on its sides.
- The pressure exerted by the atmosphere on an object is called atmospheric pressure.
- Atmospheric pressure decreases with an increase in altitude.
Read and Learn More UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure Important Terms And Definitions
Pull: It is the force that is applied while picking up an object
Push: It is the force that is applied while kicking or hitting an object.
Weight: It is the force with which the Earth pulls a body towards itself.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And PressureForce
Applying force can move a stationary object or stop a moving object Force can also change the direction j of the motion of an object If the force applied is in the direction of the motion of the object, it increases the: speed of the object.
Any object thrown up in the air falls back to the Earth due to the Earth’s gravitational force. The gravitational force exerted by the Earth on an object is called its weight
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure Activity 1
Aim: To find the effect offeree on a stationary object
Procedure:
- Take a heavy box and try- to push it by yourself.
- Ask one of your friends to help you push the box in the same direction.
- Next, push the box and ask your friend to push it from the opposite direction.
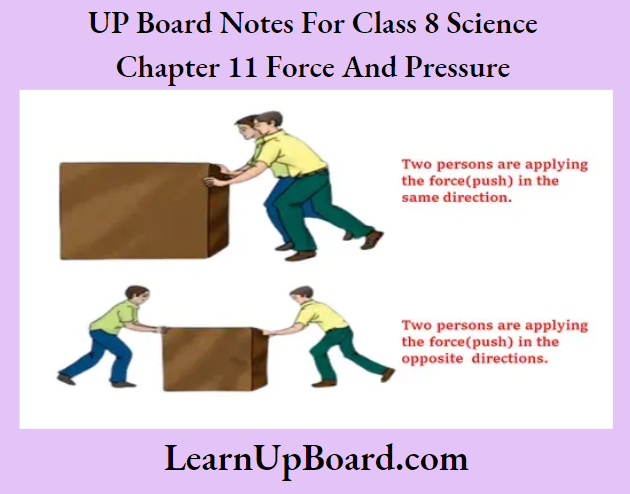
Observation: In the first case, it was difficult to push the box alone. However, with the help of a friend, it was easier to move the box in the same direction.
It was difficult to move the box when your friend applied force in the opposite direction.
Conclusion: In step 2, the forces were applied in the same direction and the resultant force was the sum of the two forces. Hence, the box moved easily. In step 3, the forces applied were in opposite directions and the resultant force was the difference of the two forces. The box moved in the direction of the greater force.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure Activity 2
Aim: To observe the effect of force on the motion of a moving object
Procedure:
- Take a rubber ball and place it on a table.
- Push the ball gently and observe if the ball begins to move.
- Push the moving ball again.
- Place your palm in front of the moving ball and remove it as soon as the ball touches your palm.

Observation: The Dali starts moving when it is pushed gently. When it is pushed again, the speed of the moving ball increases. When pain is placed in its path, the speed of the moving ball decreases.
Conclusion: Force can change the motion of an object and can even bring it to rest.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure Activity 3
Aim: To observe the effect of an applied force on the direction of motion of an object Procedure:
- Take a ball and push it gently.
- Place a ruler in front of the moving ball.
- Observe if the moving ball changes its direction on coming in contact with the ruler.
Observation: The direction of the moving ball changes on coming in contact with the ruler. Conclusion: Force can change the direction of motion of an object.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure Activity 4
Aim: To study the effect offeree on the shape of different objects
Observation table:
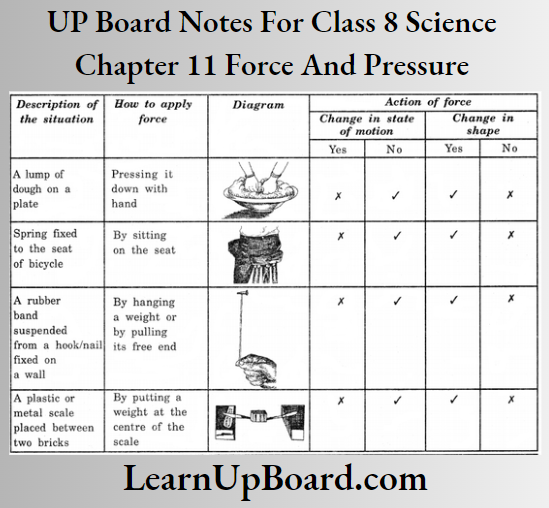
Conclusion: Force can change the shape of objects.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure Activity 5
Aim: To observe attraction and repulsion between two magnets Which are not in contact.
Procedure:
- Take a pair of bar magnets.
- Place one of the magnets over three round-shaped pencils or wooden rollers.
- Bring one end of the other magnet near the end of the magnet placed on the rollers. Ensure that the two magnets do not touch each other.
- Now, bring the other end of the magnet near the same end of the magnet placed on the rollers and note down the observation.

Observation: In the first case, the magnets repelled each other. In the second case, they attracted each other.
Conclusion: Two magnets can attract or repel each other without touching each other. Thus, a magnetic force is a non-contact force.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure Activity 6
Aim: To observe the properties of electrostatic force
Procedure:
- Take a plastic straw and cut it into two equal pieces.
- Suspend one of the pieces from the edge of a table with the help of a thread.
- Hold the other piece of the straw in your hand and rub its free end with a sheet of paper.
- Bring the rubbed end of the straw close to the suspended straw. Make sure that these two do not touch each other. Observe what happens and note it down.
- Now, rub the free end of the suspended piece of the straw’ with a sheet of paper.
- Bring the piece of the straw that was rubbed earlier near the free end of the suspended straw again.
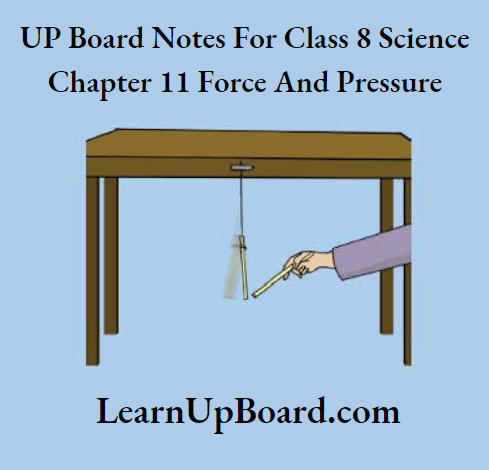
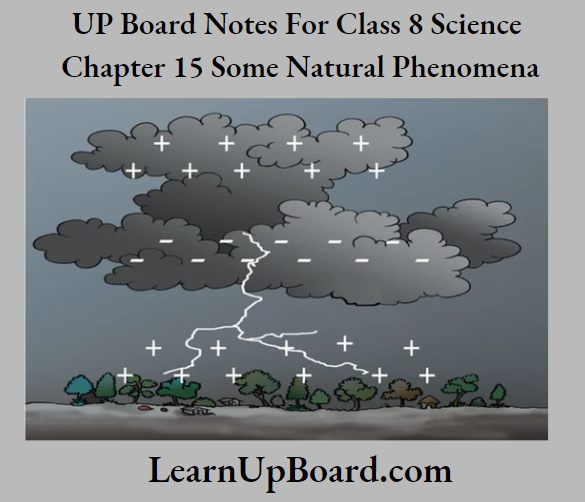
Observation: In the first case, both the straws attract each other due to unlike changes present on them. While in the second case, they repel each other due to the same type of change present in them.
Conclusion: Electrostatic force shows similar properties to a magnet. Like charges repel each other, while unlike charges attract each other. Thus, an electrostatic force is a non-contact force.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure Objective Type Questions
1. Multiple Choice Questions.
1. Which of the following is an example of contact force?
- Magnetic force
- Electrostatic force
- Gravitational force
- Frictional force
2. ‘What is the SI unit of force?
- meter/second
- Newton
- meter/hour
- Pascal
3. Which force is exerted by the Earth on all objects?
- Gravitational force
- Frictional force
- Electrostatic force
- Mechanical force
Answers:
- (4) Frictional force
- (2) Newton
- (1) Gravitational force
2. Fill in the blanks.
- The strength of a force is expressed by its______________.
- The force exerted by a charged body or another body)’ is__________.
- Muscular force is also known as__________ force.
Answers:
- Magnitude
- Electrostatic force
- Contact
3. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Two objects must interact with each other for any force to act upon them.
- A charged body attracts another charged body due to gravitational force.
- A push or pull on a body is called force.
Answers:
- False
- False
- True
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Why force of gravity is termed a non-contact force? Explain.
Answer
The force of gravity can act on distant objects that are not in direct contact with the Earth, for example, falling leaves. Hence, it is termed a non-contact force.
Question 2. Why does an object moving on a smooth surface stop by itself?
Answer
An object moving on a smooth surface stops by itself due to the frictional force, which acts between it and the surface on which it is moving. Friction acts in a direction opposite to that of the motion of the object. The surface that looks smooth has many irregularities on it These irregularities lock with the irregularities on the surface of the moving object and stops it.
Question 3. How does the force apply to change the speed of an object?
Answer
If the force is applied in the direction of motion of the object, the speed of the object increases. However, if the force is applied in the direction opposite to that of the motion of the object, the speed of the object decreases.
Question 4. When is the net force applied equally to zero? Give an example.
Answer
When two forces are applied from opposite directions and are equal in magnitude then the net force applied is equal to zero. A game of tug of war is an example of this.
I 1.2 Pressure
- Force per unit area is called pressure. Just like solids, liquids and gases also exert pressure. The air; around us exerts pressure on us. It is called atmospheric pressure. Astronauts wear a special ‘space suit’! to maintain normal atmospheric pressure for their bodies as there is no atmosphere in space.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure Force And Pressure Activity 7
Aim: To determine if the pressure exerted by a liquid at the bottom of the container in which it is kept depends on the amount of liquid present in the container
Procedure:
- Take a transparent glass tube or a Plastic pipe of about 15 cm in length and 5-5.75 cm in diameter.
- Take a piece of a thin sheet of a good-quality rubber balloon.
- Stretch and fasten the rubber sheet tightly over one end of the pipe.
- Hold the pipe in the middle, keeping it in a vertical position, and pour some amount of water into the pipe through its open end.
- Note down your observation.
- Pour some more amount of water into the pipe and note down your observation again.

Observation: When some amount of water is poured in the pipe, the rubber balloon bulges out The bulging increases upon pouring more water in the pipe.
Conclusion: The pressure exerted by a liquid at the bottom of the container in which it is kept depends on the amount of liquid present in the container.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure Activity 8
Aim: To determine that liquid exerts pressure on the walls of the container in which they are kept
Procedure:
- Take a discarded plastic bottle.
- Fix a cylindrical glass tube, a few centimeters long near the bottom of the bottle by using molten wax.
- Cover the mouth of the glass tube with a thin rubber sheet and fill the bottle half with water.
- Note down your observation.
- Pour some more water into the bottle and observe the rubber sheet.

Observation: The rubber sheet bulges out. On adding more water in the bottle, the bulging of the rubber sheet increases.
Conclusion: The bulging of the rubber sheet shows that liquids exert pressure on the walls of the container in which they are kept.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure Activity 9
Aim: To find if liquids exert equal pressure at the same depth
Procedure:
- Take an empty plastic bottle.
- Drill four holes close to the base of the bottle. Make sure that the holes are at the same height as the tie base.
- Fill the bottle with water and observe.

Observation: Four different streams of water coming out of the holes fall at the same distance from the bottle.
Conclusion: Water falling at the same distances proves that liquids exert equal pressure at the same depth.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure Activity 10
Aim: To determine the effect of atmospheric pressure on an object
Procedure:
- Take a good-quality rubber sucker and press it hard on a smooth plane surface.
- Now, try to pull the rubber sucker off the surface.

Observation: The rubber sucker sticks to the plane surface when pressed hard. It is very difficult to pull the rubber sucker from the plane surface.
Conclusion: The rubber sucker sticks to the plane surface because atmospheric pressure acts on it The rubber sucker can be pulled off from the surface only when the applied force is more than the atmospheric pressure.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure Objective Type Questions
A. Multiple Choice Questions.
1. ‘Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) atmospheric pressure increases as height increases
(b) Atmospheric pressure remains the same at all heights
(c) Atmospheric pressure decreases as height increases
(d) atmospheric pressure decreases as height decreases
2. How does pressure exerted by a liquid change with depth?
(a) It decreases with depth
(b) It increases with depth
(c) It does not change with depth
(d) It cannot be determined
3. What is pressure?
(a) Volume/Area
(b) Force/Area
(c) Mass/Area
(d) Density/Area
Answers:
- (c) Atmospheric pressure decreases as height increases
- (b) ll increases will deeply
- (b) Force/Area
B. Fill in the blanks.
- The SI unit of pressure is_____.
- The envelope of air all around us is known as__________.
Answers:
- Pascal (Pa)
- Atmosphere
C. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Pressure depends on the area of contact between two surfaces.
- ‘When a liquid is put in a vessel, it exerts pressure at its bottom only.
Answers:
- True
- False
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Why are nail tips made pointed?
Answer
Pressure is force per unit area. The lesser the area the more is pressure. The tips of the nails are made pointed so that maximum pressure can Degenerate per unit force applied and hence, the nails can penetrate in an object easily.
Question 2. Why do divers wear special suits?
Answer
The pressure deep in the sea is very high and can cause damage to the human body. That is why divers wear specially designed suits to protect themselves from high pressu^.
Question 3. Why do cutting instruments have a sharper edge?
Answer
As pressure is force per unit area, all instruments used for cutting, like knives, blades, etc., have a sharp cutting edge. This decreases the area of contact between the surface of the instrument and the object and the pressure exerted by a given force increases.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure Textbook Exercises
Question 1. Give two examples of each of the situations in which you push or pull to change the state of motion of objects.
Answer
- A batsman hitting a ball (Push)
- Drawing water from a well (Pull)
Question 2. Give two examples of situations in which applied force causes a change in the shape of an object.
Answer
- Pressing a lump of dough on a plate.
- A spring fixed in the seat of a bicycle pressed down due to the weight of the rider.
Question 3. Fill in the blanks in the following statements.
- To draw water from a well we have to___________ the rope.
- A charged body__________ an uncharged body towards it
- To move a loaded trolley we have to___________ it.
- The north pole of a magnet____________the north pole of another magnet.
Answer:
- Pull
- Attracts
- Push or pull
- Repels
Question 4. An archer stretches her bow while aiming at the target. She then releases the arrow, which begins to move toward the target. Based on this information, fill up the blanks in the following statements.
- To stretch the bow, the archer applies a force that causes a change in its.__________
- The force applied by the archer to stretch the bow is an example of___________ force.
- The type of force responsible for a change in the state of motion of the arrow is an example of a__________ force.
- While the arrow-‘ moves toward the target, the forces acting on it are due to
that due to__________ of air.
Answer:
- Shape
- Muscular
- Contact
- Gravity, friction
Question 5. In the following situations, identify the agent exerting the force and the object on which it acts. State the effect of the force in each case.
Answer:
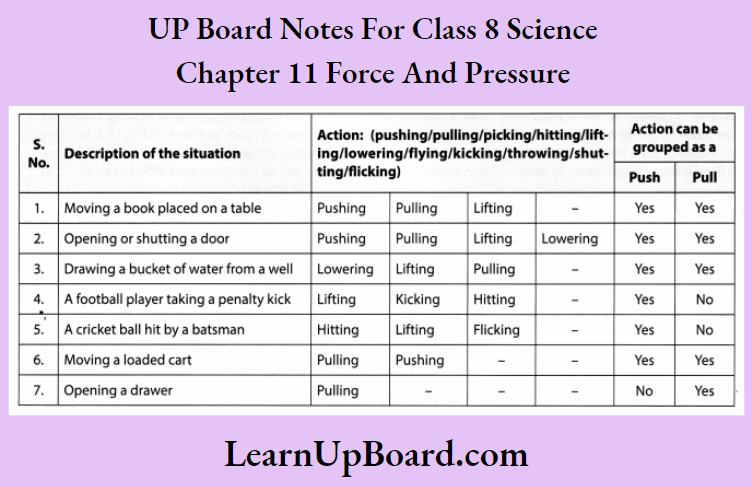
Question 6. A blacksmith hammers a hot piece of iron while making a tool. How does the force due to hammering affect the piece of iron?
Answer
The force applied by the hammer flattens the piece of iron, i.e., it changes its shape and size.
Question 7. An inflated balloon was pressed against a wall after it had been rubbed with a piece of synthetic cloth. It was found that the balloon sticks to the wall. What force might be responsible for the attraction between the sticking balloon and the wall?
Answer
The electrostatic force is responsible for the attraction between the balloon and the wall.
Question 8. Name the forces acting on a plastic bucket containing water held above ground level in your hand. Discuss why the forces acting on the bucket do not bring a change in its state of motion.
Answer
Forces acting on the plastic bucket are:
(i) Force of gravity acting downwards
(ii) The muscular force of arms acting upwards
The two forces do not bring any change in the state of motion of the bucket because both these forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Thus, they cancel each other and the net force on the bucket is zero.
Question 9. A rocket has been fired upwards to launch a satellite in its orbit. Name the two forces acting on the rocket immediately after leaving the launching pad.
Answer
When the rocket leaves the launching pad, the ‘following forces act on it:
(i) Gravitational force of the Earth which pulls rocket towards the ground.
(ii) Frictional force due to the Earth’s atmosphere which opposes its mot on.
Question 10. When we press the bulb of a dropper with its nozzle in water, the air in the dropper is seen to escape in the form of bubbles. Once we release the pressure on the bulb, water gets filled in the dropper. The rise of water in the dropper is due to:
a) Pressure of water
b) Gravity of the Earth
c) Shape of a rubber bulb
d) Atmospheric pressure
Answer:
(d) Atmospheric pressure
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure Hots Corner
A. Why do your ears ‘pop’ as you go higher up on mountains?
As we go higher up on mountains, our ears ‘pop’ because the air pressure around the ears decreases, causing an imbalance between the pressure inside and outside the ears.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure Practice Exercise Objective Type Questions
1. Give one word for each of the following.
- Pressure exerted by the air around us
- Force acting on a surface per unit area
- A substance used for reducing friction
- The force applied by the muscles of a human being or animal
- A push or pull acting on a body, which changes its state o* rest or motion
- The force exerted by a charged body on another charged or uncharged body
Answers:
- Atmospheric pressure
- Pressure
- Lubricants
- Muscular force
- Force
- Electrostatic force
2. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- If two forces act on an object from opposite directions, the resultant force is the sum of both forces.
- Pressure exerted by a liquid at the base of the tie container in which it is kept depends on the depth of the liquid column.
- The lesser the area of contact, the lesser is the effect of the force acting on an object
- Mountaineers often suffer from nose bleeds at high altitudes.
Answers:
- False
- True
- False
- True
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force And Pressure Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Why school bags are provided with broad straps?
Answer
We know that the higher is the area of contact, the lesser is the pressure applied on an object School bags with broad straps occupy larger area and do not exert too much pressure on the shoulders. Hence, children do not feel strain on their shoulders.
Question 2. State where pressure is the greatest and the least inside a bottle filled with water.
Answer
In a bottle filled with water, pressure is the greatest at the bottom of the bottle and it is the least at the top. This is because the pressure exerted by liquids depends upon the depth o{the liquid column.
Question 3. If atmospheric pressure is so high, why are we not crushed by it?
Answer
The body of living organisms is made up of cells, which have fluids that exert pressure from within. The pressure exerted from inside the cell is equal to the atmospheric pressure. Thus, we are prevented from being crushed.
Question 4. Mountaineers always carry oxygen cylinders while climbing a mountain. What will happen if they do not carry it and why?
Answer
Mountaineers carry oxygen cylinders while climbing high mountains to avoid suffocation. As we go to a higher altitude, the layer of air that surrounds us becomes thinner. Due to lesser air, there is a decrease in the number of oxygen molecules per breath and this makes a person suffocate at high altitudes.
Also Read
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe.
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 8 Cell: Structure and Functions
- Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Chapter 12 Friction
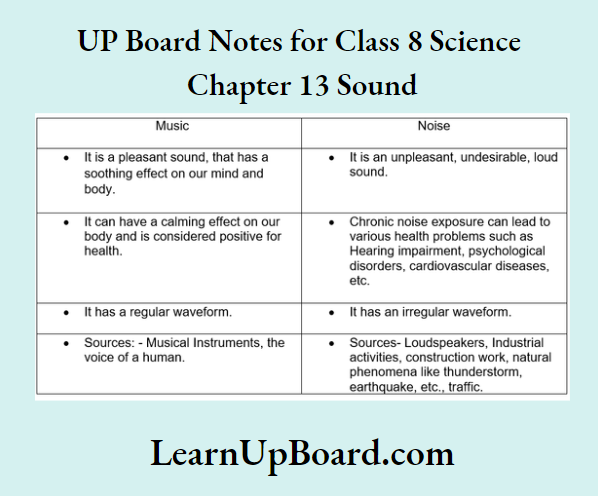
- Chapter 13 Sound
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
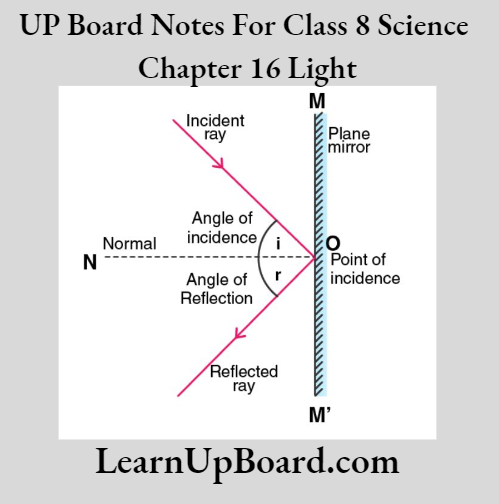
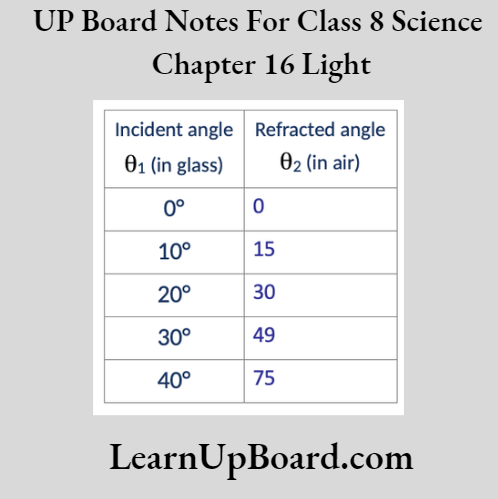
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
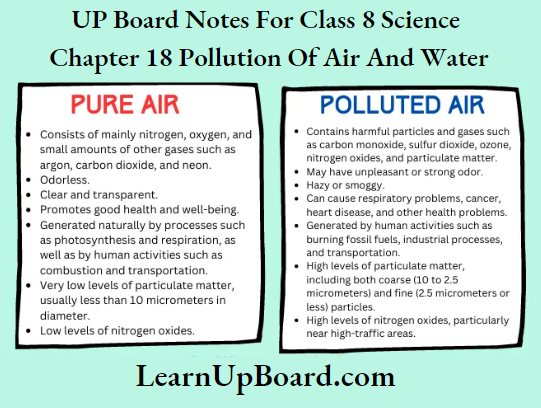
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water