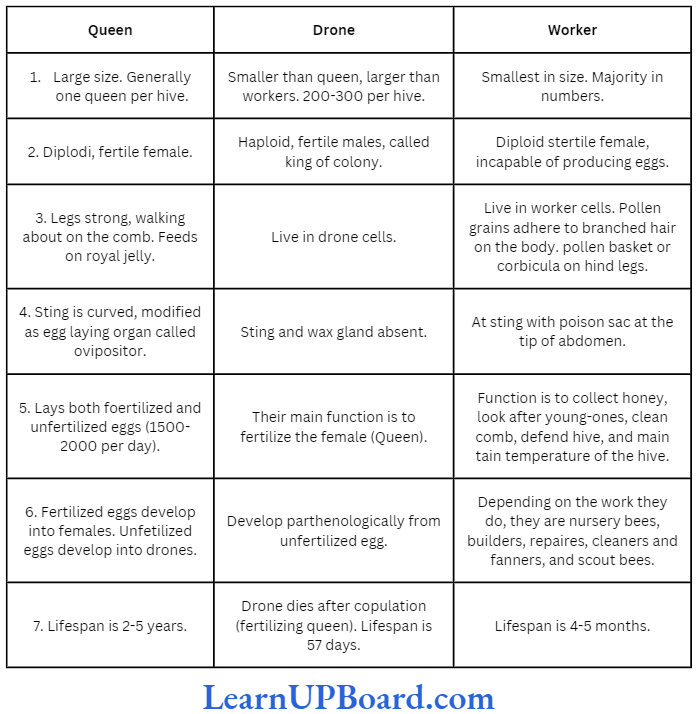
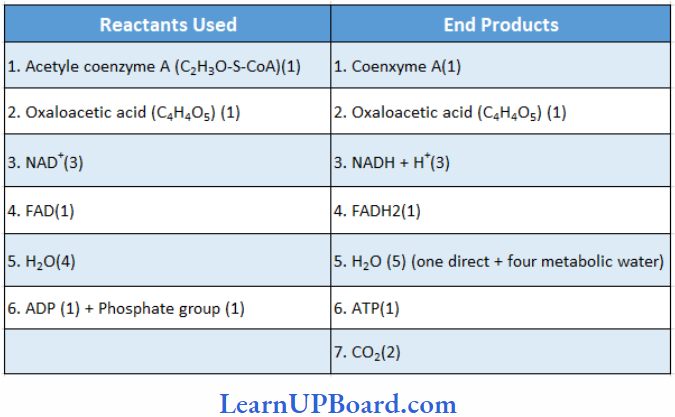
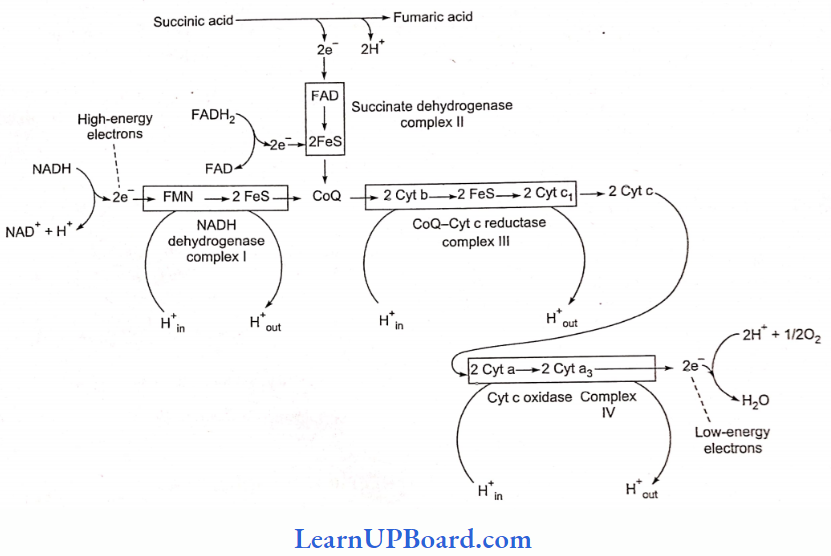
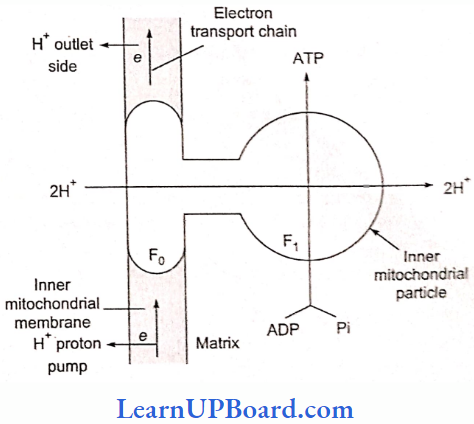
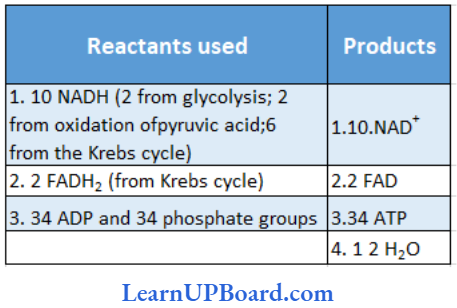
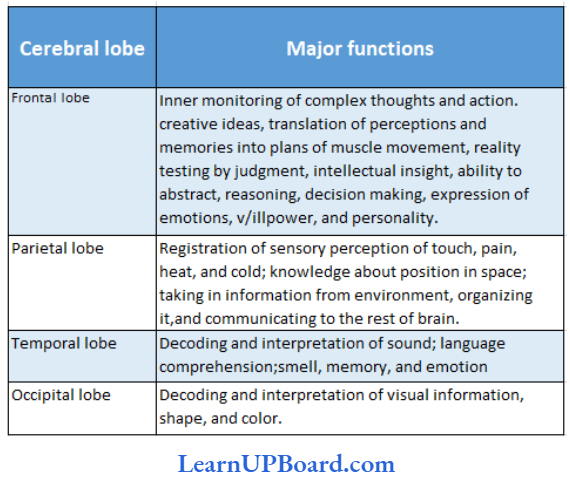
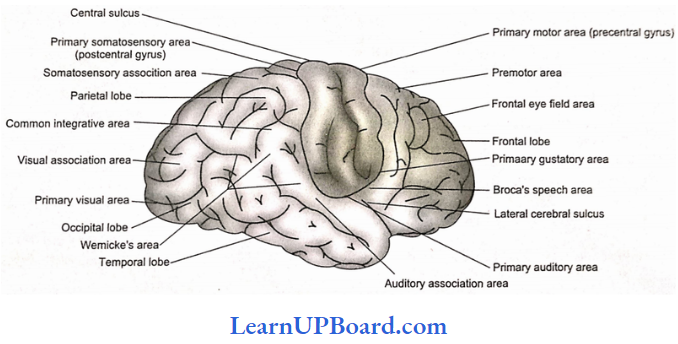
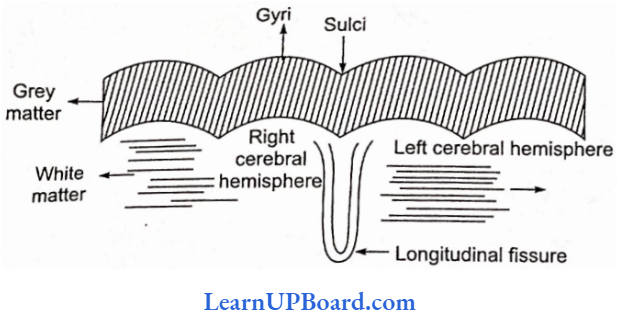
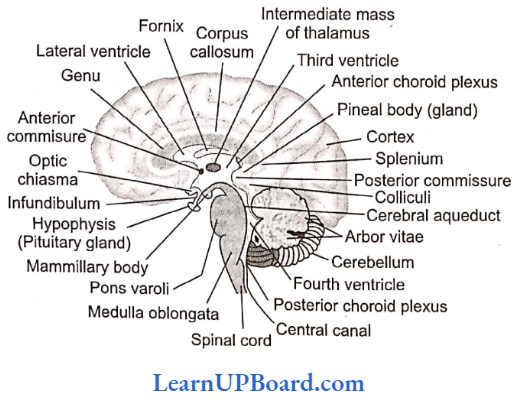
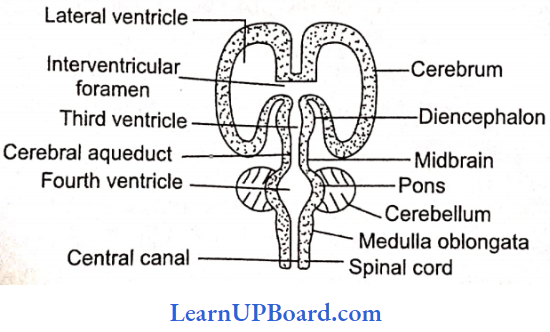
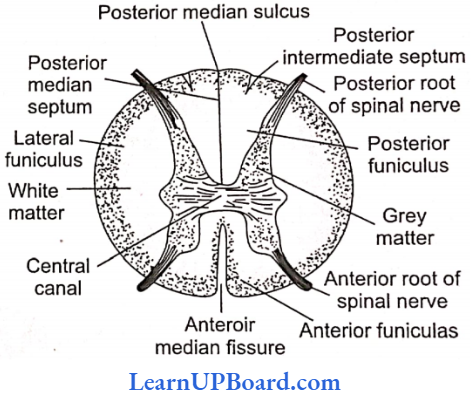
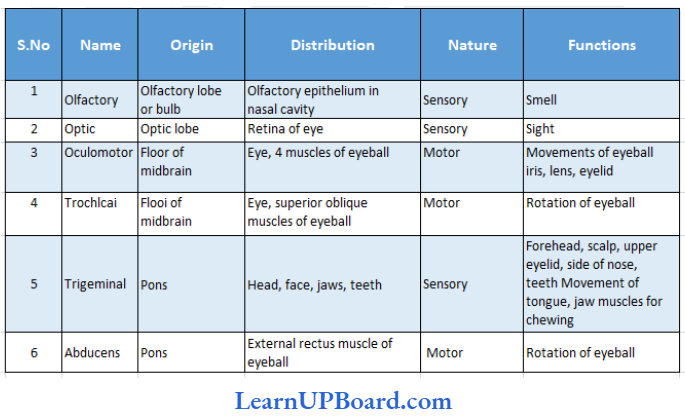
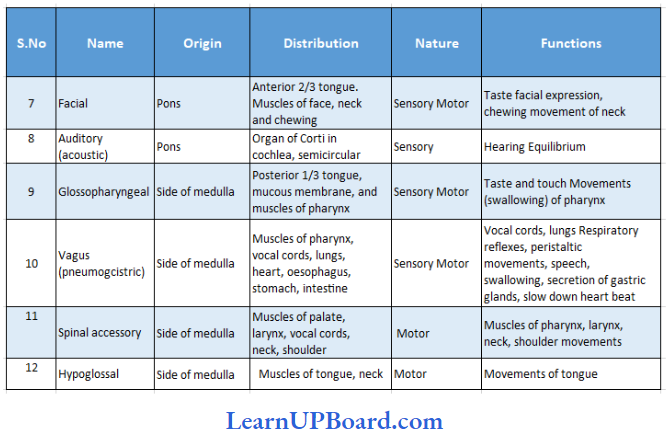
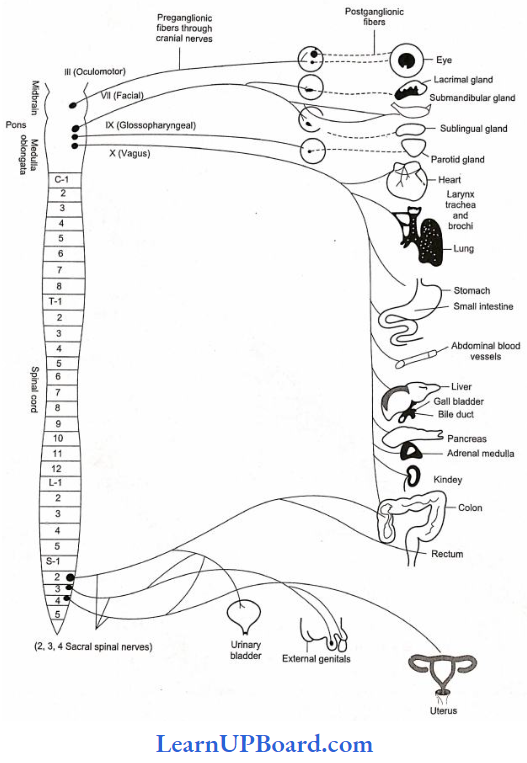
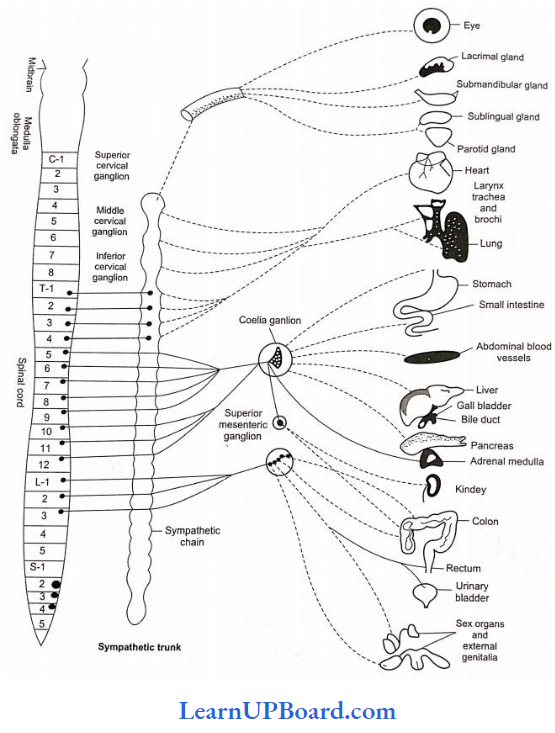
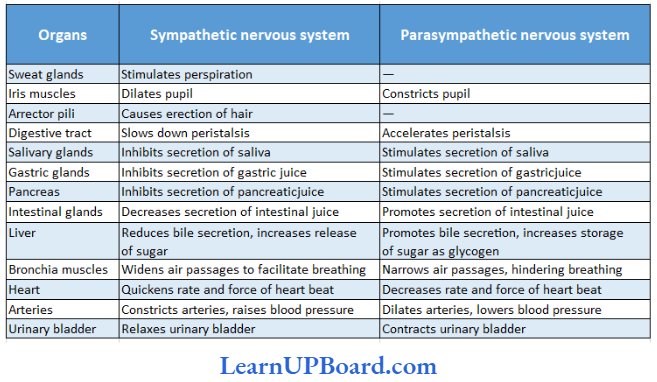
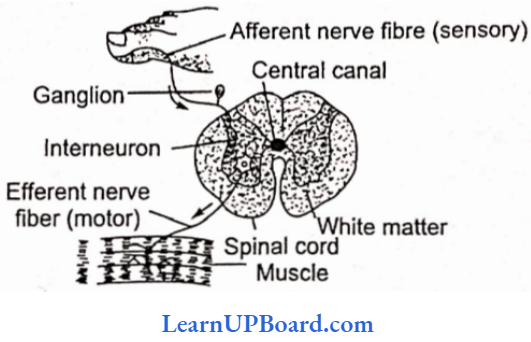
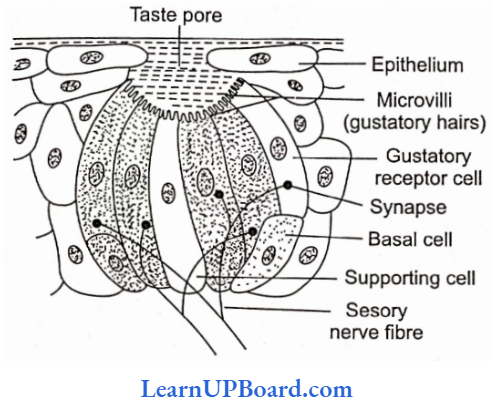
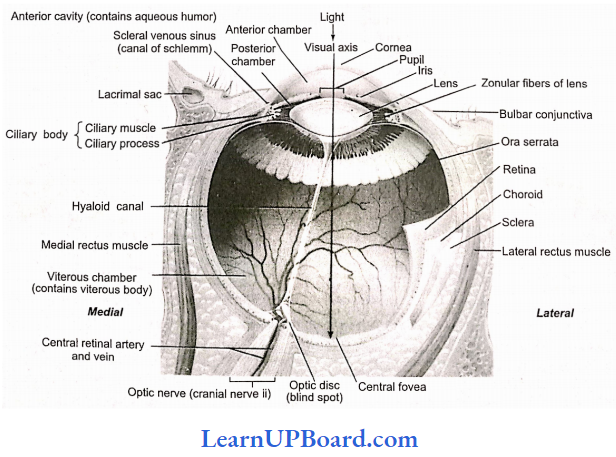
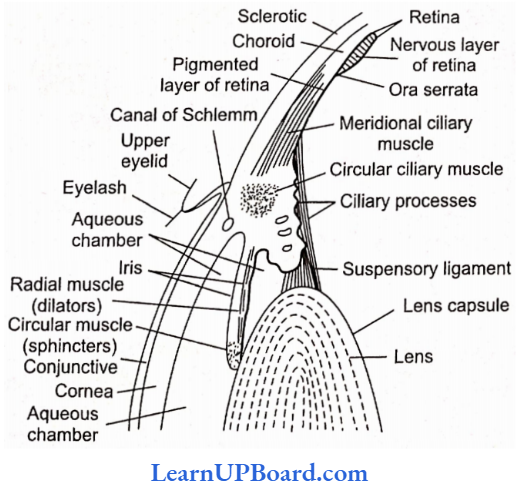
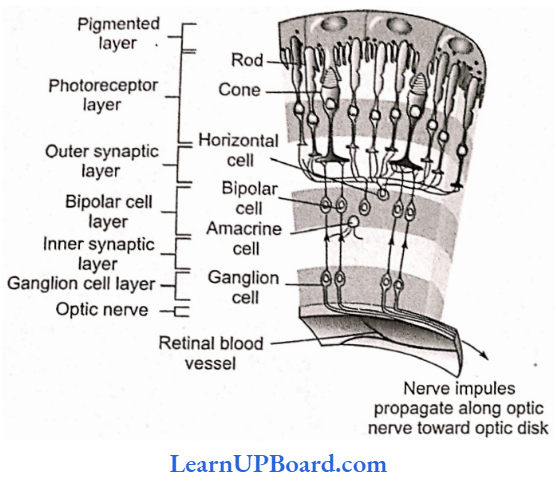
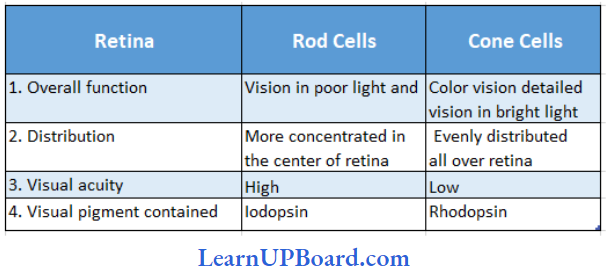
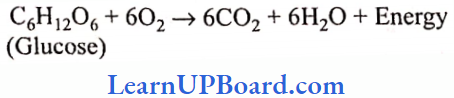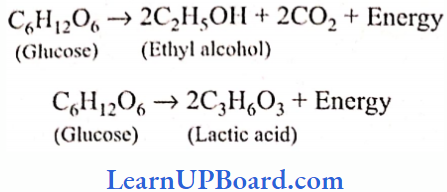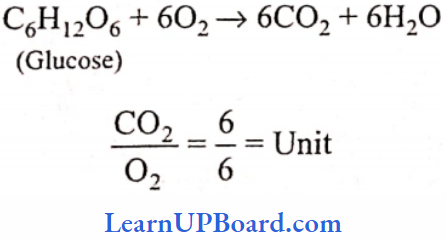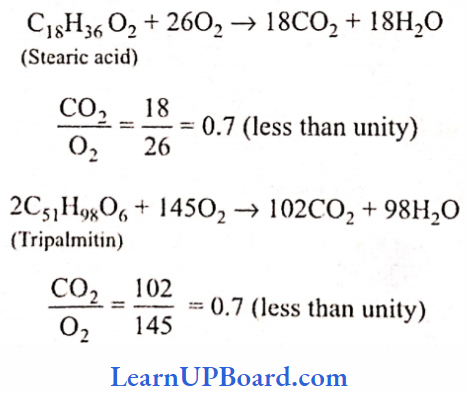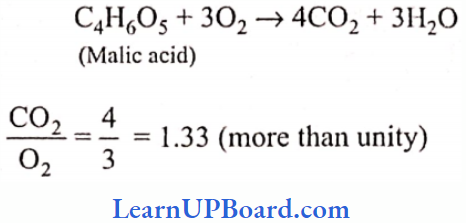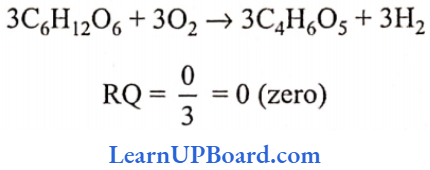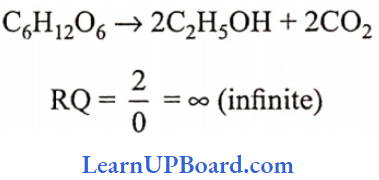Microbes In Human Welfare
Microbes In Household Products
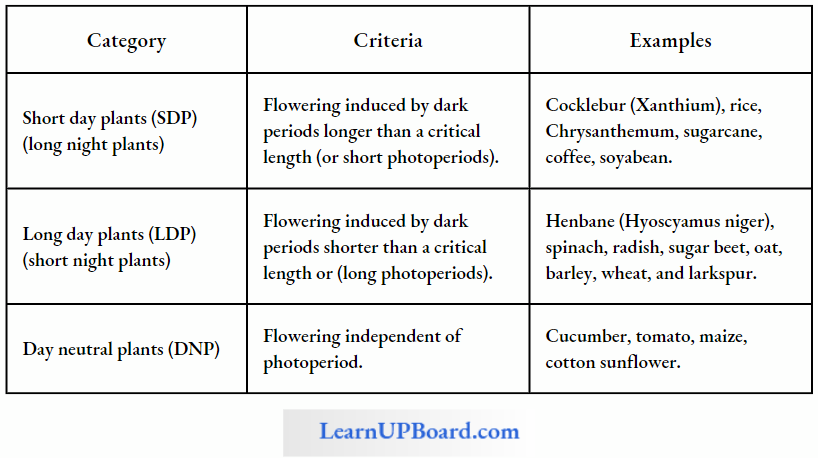
Dairy Products
- Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) such as Lactobacillus are added to milk. Lactobacillus converts the lactose sugar of milk into lactic acid.
- Milk can be changed into curd, yoghurt, and cheese. The starter used in the preparation of milk products actually contains millions of LAB.
- Curd: Indian curd is prepared by inoculating cream and skimmed milk with Lactobacillus acidophilus at a temperature of about 40°C or less. Curd is more nutritious than milk as it contains a number of vitamins, especially Vitamin B12 and organic acids.
- Yoghurt: It is produced by curdling milk with the help of Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus. It has the flavor of lactic acid and acetaldehyde.
- Butter milk: It is an acidulated product which is formed by inoculating skimmed milk with the starter culture of Streptococcus cremoris, S. lactis, Lactobacillus acidophilus, and Leuconostoc species at 22°C for 18 h.
- Sour cream: It is inoculated with Streptococcus lactis for producing lactic acid and with Leuconostoc cremoris for imparting the characteristic flavor.
- Cheese: It is a partially degraded concentrate of milk fat and casein manufactured by the activity of microorganisms. There are several hundred varieties of cheese which are prepared by selected types of microorganisms. The quality and characteristic taste of cheese are is determined by the biochemical activities of specific microorganisms. Cheese consists of milk curd that has separated from whey or liquid part. Cheese is of three types: (i) soft (50-80% water), (ii) semi-hard (about 45% water), and (iii) hard (less than 40% water). The method of preparing cheese with the help of microbes was known in Asia and Europe long before Christ. Large-holed Swiss cheese is ripened with the help of CO, producing bacterium called Propionibacterium sharmanii; Roquefort cheese or blue cheese uses Penicillium roquefortii: Camembert cheese employs Penicillium camembertii for ripening.
” microbes in human welfare”
Bread
- Selected strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (baker’s yeast) grown on molasses are used for this purpose.
- The kneaded flour is kept at a warm temperature for a few hours. It swells up. The phenomenon is called leavening.
- Leavening is caused by the secretion of three types of enzymes by yeast. They are amylase, maltase, and zymase.
- The leavened dough is baked. Both carbon dioxide and ethyl alcohol evaporate, making the bread porous and soft.
Dosa, Uppma, and Idli
Dosa, uppma, and idli are fermented preparations of rice and black gram. The two are allowed to ferment for 3-12 h with Leuconostoc and Streptococcus species of bacteria.
- Other Foods Tempeh (Indonesia), tofu (Japanese), and sufu (Chinese) are fermented foods obtained from soya saucebrown flavored salty sauce fermented from soybean and wheat.
- Tender bamboo shoots can be used as vegetable directly as well as after fermentation. Several types of sausages are prepared by fermentation and curing of fish and meat.
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Notes
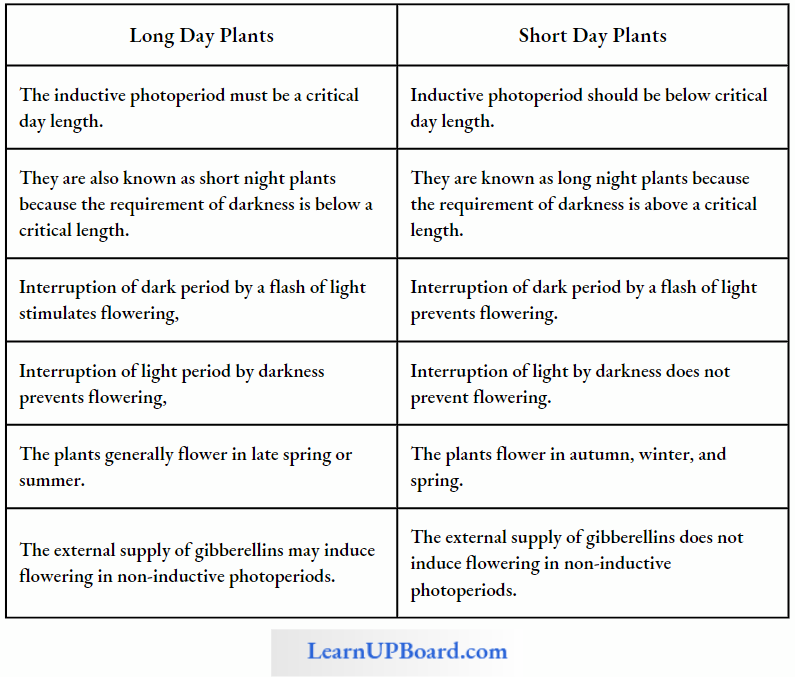
Toddy (Toddy palm or Caryota urens)
The unopened spadices of palm are tapped to obtain toddy. It is a refreshing drink which can be heated to produce jaggery or palm sugar. Toddy left for a few hours undergoes fermentation with the help of naturally occurring yeast to form beverage containing about 6% alcohol.
Microbes In Industrial Products
Fermentative activity of microbes is used industrially to obtain a number of products. Production on an industrial scale requires growing microbes in very large vessels called fermentors. The two common ones are alcoholic fermentation and antibiotics.
Fermented Beverages/Alcoholic Fermentation
- Yeast species used in alcoholic fermentation are Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer’s yeast), S. ellipsoidens (wine yeast), S. sake (sake yeast), and S. pireformis (ginger beer/ale yeast).
- The nutrient media are barley malt for beer, fermented rye malt for gin, fermented rice for sake, cashew-apple for fenny, potato for vodka, fermented cereals for whisky, fermented molasses for rum, and fermented juices for wines and brandy.
- Wine and beer are produced without distillation, whereas whisky (50% alcohol), brandy (65-70% alcohol), rum (40% alcohol), and gin (about 40% al- cohol) are produced by the distillation of fermented broth.
Antibiotics
- An antibiotic (Greek: against life) is a substance produced by a microorganism which in low concentration inhibits the growth and metabolic activity of pathogenic organisms without harming the host.
- This is among the most significant discoveries of the 20th century.
- The first antibiotic is generally associated with the name of Alexander Fleming (1928), when he discovered penicillin from Penicillium notatum.
- The antibiotic was, however, commercially extracted by the efforts of Ernst Chain and Howard Florey. The chemical was extensively used in treating wounded American soldiers in World War II. Fleming, Chain, and Florey were awarded Nobel Prize in 1945. A bulk of antibiotics is obtained from three groups of micro- organisms: Eubacteria, actinomycetes, and fungi.
- Antibiotics have greatly improved our capacity to treat deadly diseases such as plague, whooping cough, diphtheria, and leprosy. So, with reference to human beings, these are pro-life.
Chemicals, Enzymes, and Other Bioactive Molecules
Bioactive molecules are those molecules which are functional in living systems or can interact with their components. A number of them are obtained from microbes such as organic acids, enzymes, cyclosporin A, and statins.
Organic Acids
Certain microbes have the ability to convert carbohydrates into organic acids. This capability of microorganisms is applied in the industrial production of some commercially important organic acids. A few very-important organic acids are as follows:
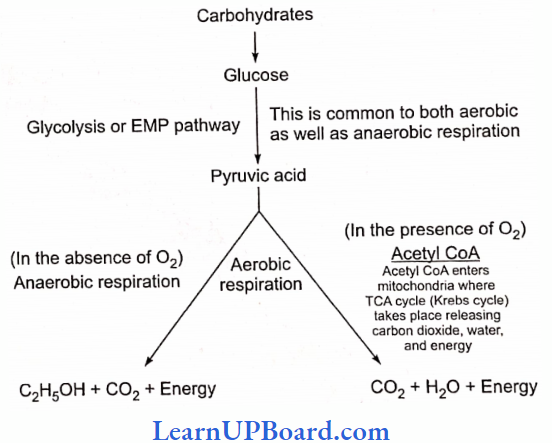
- Acetic acid: It is prepared from fermented alcohols with the help of acetic acid bacteria, Acetobacter aceti. Alcoholic fermentation by yeast is an anaerobic process, but the conversion of alcohol to acetic acid is aerobic one. It is used for the preparation of vinegar. It is also used in pharmaceuticals, coloring agents, insecticides, and plastic industries.
- Citric acid: It is obtained through fermentation carried out by fungi Aspergillus niger and Mucor species on sugary syrups. Yeast Candida lipolytica can also be employed, provided its nutrient medium is made deficient of iron and manganese. Citric acid is employed in dyeing, engraving, medicines, inks, flavoring, and preservation of food and candies.
- Gluconic acid: The acid is prepared by the activity of Aspergillus niger and Penicillium chtysogenum. Gluconate is used widely as a source of calcium for infants, cows, and lactating mothers.
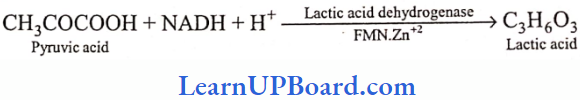
- Lactic acid: It was the first acid to be produced by industrial fermentation. It is commercially produced from fermentable carbohydrates such as corn and potato starch, molasses, and whey by using bacteria Lactobacillus bulgaricus and L. delbrueckii.
Enzymes
Hardly 1.0-1.5% of the total known enzymes are employed in industry and medicine.
- Pectinases: These enzymes are obtained from fungi grown on pectin-containing medium. Examples are Aspergillus niget and Byssochlamys fulvo. These enzymes are used in enhancing juice extraction and clearing of juices.
- Proteases: Proteases are obtained from Mortierella renispora, Aspergillus, and Bacillus species. These enzymes are used in detergents to remove proteinaceous spots. Bottled juices are also clarified using protease and pectinase.
- Amylases: Amylases degrade starch. These enzymes are obtained from Aspergillus, Rhizopus, and Bacillus species. Amylases, glucoamylases, and glucoisomerases are employed in the conversion of corn starch into fructose-rich corn syrup.
- Streptokinase (tissue plasminogen activator or TPA): It is an enzyme obtained from the cultures of some hemolytic streptococci. It has fibrinolytic effect; it is used to dissolve blood clots in heart patients.
Cyclosporin A
- It is an 11-membered cyclic oligopeptide obtained through the fermentative activity of fungus Trichoderma polysporum.
- It has antifungal and anti-inflammatory properties. It is used as an immunosuppressive agent in organ transplant patients.
Statins
- Statins are the products of fermentation activity of yeast Monascus purpureus which resembles melonate and is the competitive inhibitor of B-hydroxy-ẞ-meth-ylglutaryl-CoA reductase (or HMG-CoA reductase).
- This competitively inhibits cholesterol synthesis. It is used as cholesterol lowering agent.
Microbes In Sewage Treatment
- Sewage is a collective noun used to represent municipal waste (both liquid and solid waste) generated in cities and towns which is carried off in sewerage.
- It contains large amount of domestic water and waste including human and animal excreta, microbes, and everything that enters sewerage system.
- Sewage or municipal waste should not be passed into rivers, streams, and other water bodies, because it not only contains human excreta and other organic wastes but a number of pathogenic microbes.
- It is made less polluted by passing it through STPs.
- The treatment of waste water is done by the hetero- trophic microbes naturally present in the sewage.
- The various steps in sewage treatment are as follows:
- Primary treatment
- It is the physical process of removal of large and small particles from sewage through sequential filtration and sedimentation.
- Initially, floating debris is removed by sequential filtration. Then the grit (soil and small pebbles) is removed by sedimentation.
- The sewage is first shredded and churned. It is then passed through many screens or skimmers to remove large pieces of organic matter. Now it is passed into a large primary settling tank having a gentle slope.
- Grit, sand, and other heavy particles settle down.
- All solids that undergo sedimentation of screened organic matter collectively consti- tute primary sludge.
- Primary sludge can be used for preparing compost or manure directly. It can also be burnt.
- The waste water (primary effluent) after removing the primary sludge contains fine organic matter. It is passed for secondary treatment.
- Secondary treatment or biological treatment
- It involves biological process of microbial degradation of organic matter.
- There are three main methods: use of oxidation tanks, trickling filter method, and activated sludge method.
- In activated sludge method, the effluent from primary settling tank is passed into an aeration tank. It is agitated mechanically.
- Primary treatment
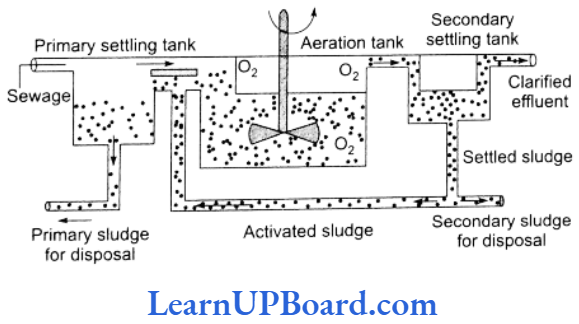
- Air is pumped into the effluent. It contains a large population of aerobic heterotrophic microbes, including bacteria and fungi.
- The microbes form flocs (masses of bacteria associated with fungal filaments).
- The BOD (biological oxygen demand) of the effluent rises initially and the treatment continues till the BOD decreases to a certain level.
- It is taken to secondary settling tank where the flocs undergo sedimentation.
- The sediment is called activated sludge. (This can be the inoculant for the next sec- ondary treatment.)
- The supernatant is allowed to pass into rivers and streams.
- The activated sludge is taken to anaerobic sludge digesters along with the primary sludge.
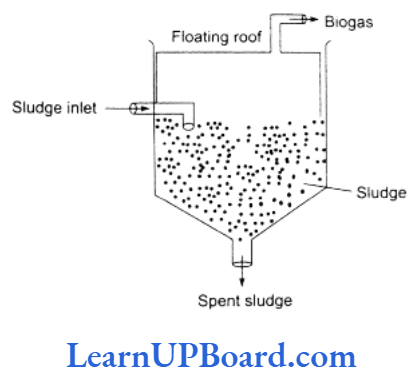
- Here, anaerobic microbes act upon organic matter to first produce monomers and then organic acids.
- This converts the latter into a mixture of gases such as methane, hydrogen sulfide, and carbon dioxide.
- The gaseous mixture is called biogas. It is inflammable and can be used as a source of energy.
- The spent sludge is used as manure and land fill or can be burnt. Pathogens present in the original sewage get killed during anaerobic digestion.
- Tertiary treatment
It is a physiochemical process in which chlorine gas, zirconium, ozone gas, perchlorate salts, UV rays, and reverse osmosis are used to remove DDT, pesticides, pathogens, and turbidity from waste water. It is preferred when water is to be used for domestic use.
” microbes in household products class 12″
River Action Plans
- Prior to 1985, very few cities and towns had STPs.
- Municipal waste water was discharged directly into rivers resulting in their pollution and high incidence of water borne diseases.
- In order to protect the major rivers of India from sewage pollution, the Ministry of Environment and Forests has initiated the development of STPs under the National River Conservation Authority. Examples are Ganga Action Plan (GAP), Yamuna Action Plan, etc.
Microbes In Production Of Biogas
- Biogas is a mixture of gases produced from degradable organic matter by the activity of various anaerobic bacteria.
- The microorganisms involved in biogas production are mainly facultative and strict anaerobic bacteria.
- The most important among them are methanogenic archaebacteria, represented by Methanobacterium.
- The other bacteria involved are Bacillus, Cellulomonas, Clostridium, and Ruminococcus.
- These bacteria are commonly found in anaerobic sludge formed during sewage treatment. Methanogens occur in the rumen of cattle where they act upon cellulose.
Composition of Biogas
- The major component of biogas is methane (about 50-70%), which is highly inflammable. The second major component is carbon dioxide (30-40%). The mixture of other gases (viz., H2, H2S, etc.) constitutes 10%.
- The calorific value of biogas is 4429 kcal/m3 at 50% methane content.

Commercial Production of Biogas
- The technology for biogas production was developed in India by IARI (Indian Agriculture Research Institute) and KVIC (Khadi and Village Industries Commission).
- A biogas plant has a large (10-15 ft. deep) concrete-or brick-lined air-tight cylindrical tank called digester.
- It has a charge pit for the passage of slurry into the digester, a floating gas holder of metal with an outlet for gas, and a pit for the removal of sludge or manure. The raw materials used in biogas plants are cattle dung, night soil, farm refuse, water weeds (e.g., Eichhornia), and other organic wastes.
- It is converted into slurry with 90% water content and fed into the digester.
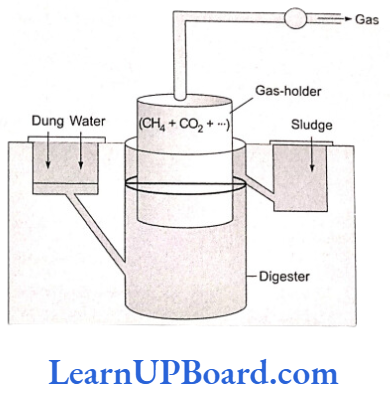
- Cattle dung contains Methanobacterium and other methanogens which are normally present in the rumen of cattle for aiding the digestion of cellulose.
- An inoculum can also be provided when a gobar gas plant is to be initiated.
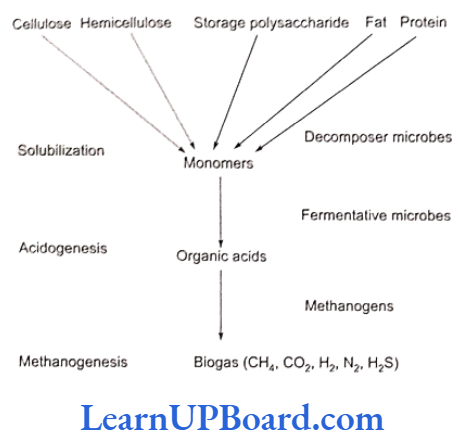
- The formation of biogas is a three-step anaerobic process:
- Solubilization (decomposition)
- Organic wastes are composed of lipids, proteins, cellulose, hemicelluloses, and lignin. In the first stage of biogas generation, facultative anaerobic decomposers are active.
- They secrete hydrolytic enzymes, e.g., lipases, cellulases, proteases, and peptidases.
- The enzymes break down the complex organic components into simpler and soluble substances. The latter are commonly called monomers.
- Acidogenesis
- Monomers are changed into organic acids with the help of fermentating microbes. The most common organic acid produced during acidogenesis is acetic acid.
- Hydrogen and carbon dioxide are produced as by-products.
- Methanogenesis
- Methanogens or methane-producing bacteria become active.
- They act on various components of microbial digestion and fermentation. Some important basic reactions are as follows:
- Solubilization (decomposition)
“chapter 10 biology class 12 notes “
Microbes As Biocontrol Agents
Biological Pest Control or Biopesticide
- Biopesticides are the organisms which are applied to destroy pests. These are used to destroy the weeds as well as the insect pests. Two basic types of biopesticides are bioherbicides and bioinsecticides.
- Transgenic plants are genetically engineered plants to develop resistance against pests. Examples are transgenic tobacco and transgenic cotton.
- Smoother crops are those crops which do not allow the weeds to grow nearby, e.g., barley, rye, Sorghum, millet, sunflower, alfalfa, soybean, marigold, etc. Smoother crops eliminate weeds through chemicals. Crop rotation with these crops will naturally reduce the incidence of weeds.
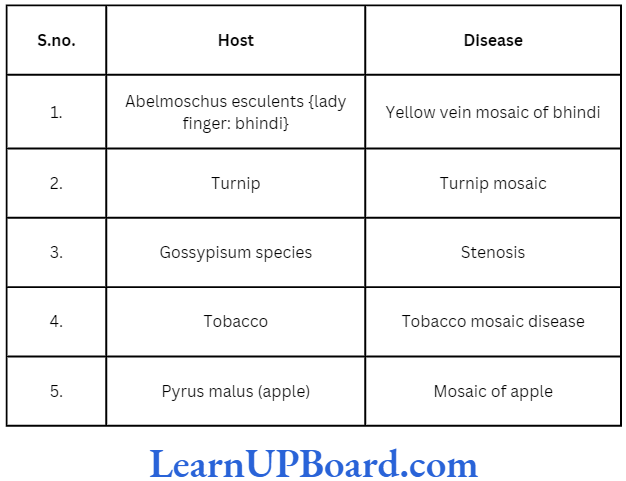
- Catch/trap crops: Around the major crop in the field, some early growing crop is sown in strips which is termed as catch or trap crop. The pests get attracted towards the early grown trap crop and then can be easily killed by cutting and destroying the trap crop. A good example of trap crop is bhindi (okra) which is sown around the cotton field to attract the jassid and spotted bollworm. Sesame is also a good trap crop to attract the red hairy caterpillar from the cotton field. Bioherbicides: These involve the biological control of weeds by some living organisms. For example, the use of insects feeding on a specific weed or the use of microorganisms which will cause diseases in weeds. Some common examples are as follows:
- In India and Australia, the overgrowth of Opuntia (prickly pear cactus) was checked by the introduction of cochineal insect (Cactoblastis cactorum).
- The first bioherbicide was a mycoherbicide called Devine. It was derived from a fungus Phytophthora palmivora which controls the growth of milk weed vines in Citrus orchards.
- Another mycoherbicide called Collego has been derived from the conidia of fungus Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. It controls the growth of northern jointvetch (Aeschynomene virginica; family: Leguminosae) growing in rice fields.
- The extensive growth of Hypericum perforatum or kalmath weed was checked in the USA by the introduction of Chrysolina beetles.
- Water hyacinth has been successfully controlled in Florida using the indigenous fungus Cercospora rodmanii.
- Bioinsecticides: These are non-persistent, non-toxic, and biodegradable. These include the following:
- Pathogens, parasites, and predators:
- A well known example of biological control of an insect pest is the destruction of large populations of aphids (a pest on crucifers) by an insect called lady bug or praying mantis which feeds on aphids.
- Hoverfly larvae (syrphid larvae) are very effective in keeping the aphids (plant bugs) under check as they feed on aphids only. Dragon flies are useful to get rid of aphids and mosquitoes.
- Mosquito larvae are easily controlled by rearing the larvicidal fish Gambusia (mosquito fish).
- Sugarcane scale insects are controlled by the coccinellid predators (Cailochorus negriti and Pharoscymnus homi); the fluted scale insect (Leerya purchasi), a common pest on Citrus trees, by the lady bird beetles (Rodolia cardinalis); and Nephantis serinopa, a dangerous pest on coconut palms, by Perisicrola nephanticdis and Trichospilus pupivora.
- Baculoviruses are pathogens that attack insects and other arthopods. NPV (Nuclearpolyhedrovirus) based insecticide has been found to eliminate bollworms which cause extensive damage to cotton. It is species specific and has narrow spectrum.
- Trichoderma species are effective biocontrol agents of several plant pathogens. Trichoderma species are free-living fungi that are very common in root ecosystems.
- Sterilization strategy
Screw worm (Cochliomyia hominivorax) was eradicated by releasing sterile males. - Insect hormone or pheromones
- Pheromones are those chemical messengers which help in communication, sending alarm signals, marking trails, or attracting males.
- These are secreted by females. Traps containing pheromones are placed in infected fields. Males attracted by the trap become unavailable for reproduction.
- In confusion technique, the pheromone-containing papers are spread all over the field; so, males can no longer locate the females.
- Introduction of molting hormone ecdysone or juvenile hormones at inappropriate times results in the early death of insect pests.
- Natural insecticides
- These are obtained from living organisms (plants). Examples are rotenones obtained from the roots of Derris elliptica; nicotine obtained from tobacco; pyrethrum and cinerin (pyrethroids) obtained from Chrysanthemum cinerarifolium); azadirachtin obtained from margosa (Azadirachta indica) leaves; and thurioside obtained from mutant strains of a bacterium called Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt).
- Thurioside is a proteinaceous toxin and is ef fective against several insects such as moths, flies, mosquitoes, and beetles which accumulate as crystals inside the bacteria during sporulation.
- Pathogens, parasites, and predators:
ch 10 biology class 12 notes
Integrated Pest Management
- Sustainable pest management is otherwise known as integrated pest management (IPM), i.e., the integration of tactics for the control of a single pest on one or more crops.
- The overall objective of IPM is to create and maintain situations in which insects are prevented from causing significant damage to crops.
Microbes As Biofertilizers
- Organic farming is the raising of unpolluted crops through the use of biofertilizers that provide optimum nutrients to crop plants.
- Organisms that can be used to improve the nutrient quality of soil through biological activity are known as biofertilizers.
- The main sources are bacteria, cyanobacteria, and fungi. In paddy fields, cyanobacteria serve as an important biofertilizer.
- Symbiotic N2 fixing bacteria such as Rhizobium leguminosarum fix atmospheric N2 in the root nodules of legumes.
- Frankia (actinomycetes) fixes N2 in the root nodules of non-legume plants (e.g., Casuarina and Alnus).
- Symbiotic cyanobacteria (blue green algae) such as Anabaena azollae fix atmospheric N2 in the leaves of Azolla (water fern). Azolla pinnata (a pteridophyte) is used as an excellent fertilizer in rice field.
- Anabaena cycadae lives in the coralloid root of Cycas (a gymnosperm).
- Aulosira is the most active, non-symbiotic nitrogen fixer in rice fields in India.
- Free living nitrogen fixers such as Azospirillum and Azotobacter enrich the nitrogen content in soil.
- Mycorrhiza: It is symbiotic association between the fungus and roots of higher plants (seed plants). Many members of genus Glomus form mycorrhiza. The fungal partner absorbs phosphorus from the soil and passes it to the plant. Plants having mycorrhizal associations show resistance to root-borne pathogens, tolerance to salinity and drought, and an overall increase in growth and development. It is of two types:
- Ectomycorrhizae (ectotrophic or ectophytic): Hyphae of fungus only form mantle on the outer surface of the root, increasing the absorption of water and minerals, e.g., Pinus, oak, etc. Mycorrhiza absorbs and stores nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and calcium.
- Endomycorrhizae (endotrophic or endophytic): Fungal hyphae penetrate into cortex and cells of root, e.g., orchids, coffee, and woody plants. These are also called vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizae or VAM, because cortical cells swell and form vesicles or arbuscles. They play a significant role in providing phosphorus nutrition in plants.
Assertion-Reasoning Questions
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R).
- If both Assertion and Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion, then mark (1).
- If both Assertion and Reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion, then mark (2).
- If Assertion is true but Reason is false, then mark (3).
- If both Assertion and Reason are false, then mark (4).
Question 1. Assertion: Curd is more nutritious than milk.
Reason: LAB present in curd checks the growth of disease-causing microbes.
Answer. 2. If both Assertion and Reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion, then mark (2).
Question 2. Assertion: After 24 h, toddy becomes unpalatable.
Reason: Toddy left for a few hours undergoes fermentation.
Answer. 1. If both Assertion and Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion, then mark (1).
Question 3. Assertion: Newer antibiotics are required to be produced regularly.
Reason: Pathogens often develop resistance to existing antibiotics.
Answer. 1. If both Assertion and Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion, then mark (1).
Question 4. Assertion: Cyclosporin A is antifungal and immunosuppressive medicine.
Reason: It stimulates the activation of T-cells and prevents rejections.
Answer. 3. If Assertion is true but Reason is false, then mark (3).
Question 5. Assertion: Barley, sorghum, and millet are smoother crops.
Reason: They favor the growth of some common weeds.
Answer. 3. If Assertion is true but Reason is false, then mark (3).
Question 6. Assertion: Agricultural output increased several times after the introduction of DDT.
Reason: DDT was the first insecticide used on a wide scale.
Answer. 1. If both Assertion and Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion, then mark (1).
Question 7. Assertion: The disadvantages of chemical pesticides can be overcome by the use of biopesticides.
Reason: Biopesticides are the harmless pesticides of biological origin which are used to control weeds and pests without causing any significant damage.
Answer. 1. If both Assertion and Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion, then mark (1).