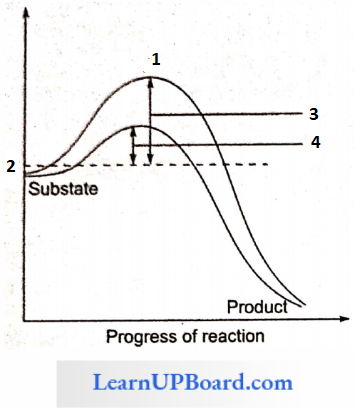
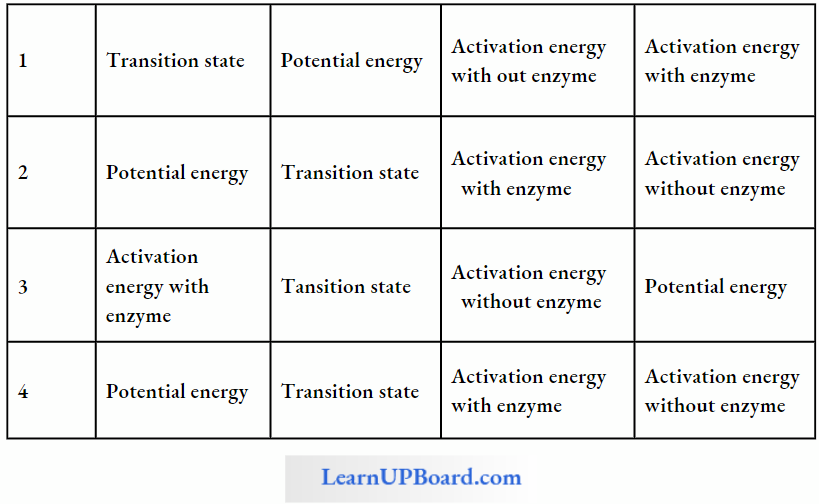
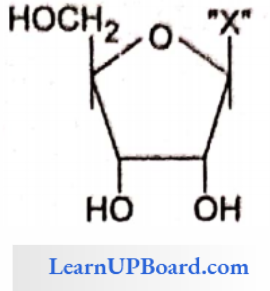
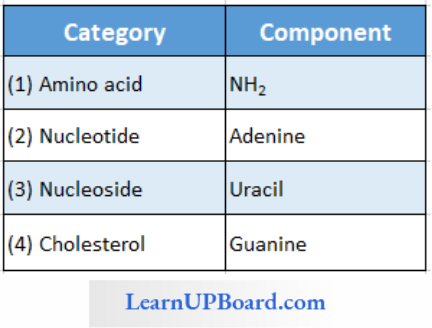
NEET Biology For Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. A stamen is regarded as a
- Microsporophyll
- Megasporophyll
- Microsporangium
- Megasporangium
Answer. 1. Microsporophyll
Question 2. A typical anther is generally
- Bisporangiate
- Tetrasporangiate
- Monosporangiate
- Multisporangiate
Answer. 2. Tetrasporangiate
Question 3. Development of anther in angiosperms is
- Leptosporangiate
- Eusporangiate
- Gradate
- Simple
Answer. 2. Eusporangiate
Question 4. The tapetal cells of anther show
- Haploidy
- Diploidy
- Triploidy
- Polyploidy
Answer. 4. Polyploidy
Question 5. Pro-Ubisch bodies are secreted by
- Endothecium
- Middle layers
- Tapetum
- Ubisch bodies
Answer. 3. Tapetum
Question 6. Fibrous bands present in endothecium of anther wall are made up of
- Sporopollenin
- α-cellulose
- Pectin
- Liguin
Answer. 2. α-cellulose
reproduction mcq
Question 7. Glandular type of tapetum secretes
- Sporopollenin
- Pollen kit
- Compatibility proteins
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 8. The exine of pollen grains (microspores) is composed of
- Pollen kit
- α-cellulose
- Sporopollenin
- Lignin
Answer. 3. Sporopollenin
Question 9. The number of germ pores in dicots and monocots pollen grains are, respectively,
- 1,3
- 2,3
- 3,1
- 3,2
Answer. 2. 3,1
Question 10. The two cells at which pollen grains are discharged are
- Larger generative cell and smaller vegetative cell
- Larger vegetative cell and smaller body cell
- Smaller vegetative cell and larger body cell
- Smaller generative cell and larger vegetative cell
Answer. 4. Smaller generative cell and larger vegetative cell
Question 11. Minerals required for the germination of pollen grains on stigma are
- Ca, B
- Mn, Ca
- N, S
- Fe, Ca
Answer. 1. Ca, B
Question 12. Pollen tube is produced by
- Exine
- Mn, Ca
- Both exine and intine
- Fe, Ca
Answer. 2. Mn, Ca
Question 13. Number of male gametes in one pollen tube is
- 1
- 2
- 4
- 6
Answer. 2. 2
Question 14. The chemical complex which controls the chemotrophic movement of pollen tube in style is
- K+, salts, amino acids
- Organic acids, K+
- Ca, B, inositol sugar complex
- Phenols and lignins
Answer. 3. Ca, B, inositol sugar complex
Question 15. The_____serves as a landing platform for pollen grains.
- Stigma
- Style
- Ovary
- Pollen sac
Answer. 2. Style
Question 16. Chasmogamy is pollination in
- Bud condition
- Closed flowers
- Open flowers
- Unrelated flowers
Answer. 3. Open flowers
Question 17. Which of the following is/are ornithophilous?
- Erythrina
- Agave
- Grevillea
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 18. Maturation of gynoecium before anthers of the same flower is called
- Protogyny
- Protandry
- Heterogamy
- Dichogamy
Answer. 1. Protogyny
Question 19. When pollen grains of a flower fall on the stigma of an- other flower of the same plant, this condition is called
- Genetically self-pollination
- Genetically self-pollination and ecologically cross- pollination
- Ecologically cross-pollination
- Genetically cross-pollination and ecologically self-pollination
Answer. 2. Genetically self-pollination and ecologically cross- pollination
Question 20. In geitonogamy, pollen grains are transferred to
- Genetically different flower
- Genetically similar flower
- Stigma of another flower of a different plant
- Stigma of the same flower
Answer. 2. Genetically similar flower
” endosperm is present in mature seeds of”
Question 21. Which is not a contrivance for self-pollination?
- Homogamy
- Bud pollination
- Cleistogamy
- Dichogamy
Answer. 4. Dichogamy
Question 22. Which is generally not a characteristic of anemophilous flower?
- Unisexual nature
- Abundant pollen grains
- Bright color
- Reduction in number of sepals, petals, and ovules
Answer. 3. Bright color
Question 23. A characteristic of entomophilous pollen grains is the presence of
- Powdery nature
- Sticky pollen kit material
- Carotenoids
- Ubisch bodies
Answer. 2. Sticky pollen kit material
Question 24. Dioecious condition and epihydrophily is found in
- Vallisneria
- Salvia
- Zostera
- Coconut
Answer. 1. Vallisneria
Question 25. Bats are pollinator of
- Butea
- Adansonia
- Sunflower
- Callistemon
Answer. 2. Adansonia
Question 26. Pollen tube in Portulaca was first observed by
- P.Maheswari
- R.Cameraius
- G.B.Amici
- Nawaschin
Answer. 3. G.B.Amici
Question 27. When some natural barriers exist between the stamens and pistil to check self-pollination, it is known as
- Heterostyly
- Dichogamy
- Herkogamy
- Dicliny
Answer. 3. Herkogamy
Question 28. When the pollen tube enters the embryo sac, which one of the following is always destroyed?
- Antipodal
- Egg
- Synergid
- Polar nucleus
Answer. 3. Synergid
Question 29. Germination of pollen grain on the stigma is called
- Autogamy
- In situ germination
- In vivo germination
- In vitro germination
Answer. 4. In vitro germination
Question 30. In pea, the pollen tube comes out of the pollen grains present on slide having 10% sugar solution in about
- 5-10 min
- 15-30 min
- 5-7 days
- 1 month
Answer. 2. 15-30 min
Question 31. Types of ovules in angiosperms are
- 6
- 5
- 4
- 3
Answer. 1. 6
Question 32. The tetrad of megaspores produced from the megaspore mother cell is
- Isobilateral
- Linear
- Tetrahedral
- Decussate
Answer. 2. Linear
Question 33. When the body of the ovule, the embryo sac, and the micropyle lie at right angles to the funiculus, the ovule is called
- Amphitropous
- Anatropous
- Campylotropous
- Hemianatropous
Answer. 4. Hemianatropous
Question 34. When the hilum, chalaza, and micropyle of ovule lie in the same long axis, it is known as
- Amphitropous
- Anatropous
- Orthotropous
- Campylotropous
Answer. 3. Orthotropous
Question 35. How many megaspore mother cells are required to produce 100 eggs during meiosis?
- 1
- 100
- 50
- 25
Answer. 2. 100
Question 36. Ategmic ovule is found in
- Loranthus
- Tagetes
- Santalum
- Both (1) and (3)
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (3)
Question 37. Polygonum type of embryo sac is
- 7-celled, 8-nucleated structure
- 8-celled, 8-nucleated structure
- 6-celled, 8-nucleated structure
- 6-celled, 6-nucleated structure
Answer. 1. 7-celled, 8-nucleated structure
Question 38. The fusion of second male gamete with secondary nucleus is called
- Double fertilization
- Triple fusion
- Syngamy
- Triple fertilization
Answer. 2. Triple fusion
Question 39. Egg apparatus is situated at the composed of______end and is______cells.
- Micropylar, 2
- Chalazal, 3
- Micropylar, 3
- Chalazal, 2
Answer. 3. Micropylar, 3
Question 40. The phenomenon of double fertilization was discovered by
- Strasberger
- P. Maheshwari
- Amici
- Nawaschin
Answer. 4. Nawaschin
Question 41. In female gametophyte, which cell is the mother cell of endosperm?
- Synergid
- Antipodal
- Central cell
- Egg
Answer. 3. Synergid
Question 42. Ploidy level of endosperm in angiosperm is generally
- n
- 2n
- 3n
- 6n
Answer. 3. 3n
Question 43. Most common type of endosperm is
- Nuclear
- Cellular
- Helobial
- Any of these
Answer. 1. Nuclear
Question 44. Coconut milk is a
- Solid endosperm
- Liquid endosperm
- Helobial type of endosperm
- Degenerated product of cellular endosperm
Answer. 2. Liquid endosperm
Question 45. Ruminate endosperm is commonly found in the seeds of
- Euphorbiaceae
- Cruciferae
- Annonaceae (areca nut)
- Compositae
Answer. 3. Annonaceae (areca nut)
Question 46. Perisperm is
- Degenerate secondary nucleus
- Remnant of nucellus
- Peripheral part of endosperm
- Degenerate synergids
Answer. 2. Remnant of nucellus
Question 47. Suspensor in a dicot embryogeny is
- 6-10 celled
- I-celled
- 10-20 celled
- Absent
Answer. 1. 6-10 celled
Question 48. Epiblast is
- Reduced cotyledon in grass embryo
- Embryo of grass
- Covering of radical
- Covering of plumule
Answer. 1. Covering of plumule
pollen tetrad
Question 49. Which is not true regarding gametophytic self-incompatibility?
- It is controlled by multiple alleles.
- It is due to genotype of pollen.
- Germination of pollen grain is prevented.
- Sporopollenin is involved.
Answer. 4. Sporopollenin is involved.
Question 50. The production of apomitic embryo from the cells of nucellus or integument is called
- Parthenocarpy
- Sporophytic budding
- Adventive polyembryony
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer. 2. Sporophytic building
Question 51. What will be the ploidy of endosperm and zygote if the cross is made between 6n plant and 4n plant?
- 5n, 8n
- 8n, 5n
- 10n, 7n
- 6n, 4n
Answer. 3. 10n, 7n
Question 52. Development of sporophyte without gametic fusion is known as
- Apomixis
- Apospory
- Apogamy
- Agamospermy
Answer. 4. Agamospermy
Question 53. Agamospermy is
- Adventive embryony
- Diplospory
- Apospory
- All of these
Answer. 3. Apospory
Question 54. The terms “sporoderm” and “spermoderm” are used to represent, respectively,
- Spore wall and sperm wall
- Anther wall and seed coat
- Spore wall and seed coat
- Integument of ovule and sperm wall
Answer. 4. Integument of ovule and sperm wall
Question 55. In some angiosperms and gymnosperms, multiple embryos are produced in which of the following way/ways?
- By fertilization of synergids or antipodal cells by sperms.
- By cleavage of single zygote.
- One or more cells of the nucellus or integument develop into embryo.
- All of these.
Answer. 3. One or more cells of the nucellus or integument develop into embryo.
Question 56. There exists a close association between the alga and the fungus within lichen. The fungus
- Fixes atmospheric nitrogen for the alga
- Provides protection, anchorage, and absorption for the alga
- Provides food for the alga
- Releases oxygen for the alga
Answer. 2. Provides protection, anchorage, and absorption for the alga
Question 57. Fungal flagellum originates from
- Dictyosomes
- Kinetosomes
- Glyxisomes
- Oxysomes
Answer. 2. Kinetosomes
Question 58. The famous Irish famine is related to a disease of potato known as
- Late blight
- Early blight
- Dry rot of potato
- None of the above
Answer. 1. Late blight
Question 59. ________ constitutes an edible fungus.
- Agaricus
- Morchella
- Lycoperodon
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 60. Dolipore septum is only characteristic of
- Phycomycetes
- Zygomycetes
- Ascomycetes
- Basidiomycetes
Answer. 4. Basidiomycetes
Question 61. Vitamin B12 is released by [Maharashtra CET 2005]
- Penicillium
- Ustilago
- Puccinia
- Smut
Answer. 1. Penicillium
Question 62. Litmus is obtained from
- Lecanora
- Cetreria
- Cladonia
- None of the above
Answer. 1. Lecanora
Question 63. Zygospore formation occurs in
- Mucor
- Plasmodium
- Lentinus
- Peciza
Answer. 1. Mucor
Question 64. Fungi causing white rust belong to which order?
- Ustilaginales
- Chytridiates
- Uredineles
- Perenosporales
Answer. 2. Chytridiates
Question 65. Zygospore is formed from
- Gametangial copulation
- Gametic union
- Zygote
- Oogamy
Answer. 3. Zygote
Question 66. Fungi differ from algae in having
- Chitinous cell wall and chlorophyll absent
- Chitinous cell wall and chlorophyll present
- Cellulosic cell wall and chlorophyll absent
- Cellulosic cell wall and chlorophyll present
Answer. 1. Chitinous cell wall and chlorophyll absent
Question 67. In the following question, an Assertion (A) is followed by a corresponding Reason (R). Consider them and answer accordingly.
Assertion: Fungi are widespread in distribution and they even live on or inside other plants and animals.
Reason: Fungi are able to grow anywhere on land, water, or on other organisms because they have a variety of pig- ments, including chlorophyll, carotenoids, fucoxanthin, and phycoerythrin.
- If A is correct and R is its explanation.
- If A is correct and R is not its explanation.
- If A is correct but R is wrong.
- If both A and R are wrong.
Answer. 3. If A is correct but R is wrong.
Question 68. Which of the following fungus can cause diseases in humans?
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Rhizopus stolonifer
- Ashbya gossypii
- Propionibacterium
Answer. 1. Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Question 69. Red rot of sugarcane and white rust of radish are, respectively, caused by
- Albugo candida and Cercospora
- Colletotrichum and Fusarium
- Pythium and Phytophthora
- Albugo candida and Puccinia graminis
- Colletotrichum and Albugo candida
Answer. 5. Colletotrichum and Albugo candida
Question 70. Terrestrial fungus is
- Utricularia
- Sargassum
- Agaricus
- Albugo
Answer. 3. Agaricus
Question 71. The fungus in which sexual reproduction is absent or is under abnormal conditions is
- Phycomycetes
- Ascomycetes
- Basidiomycetes
- Deuteromycetes
Answer. 4. Deuteromycetes
Question 72. The edible part of mushroom is
- Basidiocarp
- Primary mycelium
- Secondary mycelium
- Tertiary mycelium
Answer. 1. Basidiocarp
Question 73. VAM stands for
- Vesicular Arbuscular Mycorrhizae
- Vesicle Arbuscular Mycorrhizae
- Veremicular Arbuscular Mycorrhizae
- Vacuolar Arbuscular Mycorrhizae
Answer. 1. Vesicular Arbuscular Mycorrhizae
Question 74. Ascomycetes are
- Club fungi
- Algal fungi
- Pin molds
- sac fungi
Answer. 4. sac fungi
Question 75. Genus Aspergillus and Claviceps belong to
- Phycomycetes
- Asomycetes
- Basidiomycetes
- Deuteromycetes
Answer. 2. Asomycetes
Question 76. Among rust, smut, and mushroom, all three
- Are pathogens
- Are saprobes
- Bear ascocarbs
- Bear basidiocarps
Answer. 4. Bear basidiocarps
Question 77. In the following table, identify the correct matching of the crop, its disease, and the corresponding pathogen:
Crop-Disease Pathogen
1. Citrus-Canker A. Pseudomonas rubrilineans
2. Potato-Late blight B. Fusarium udum
3. Root-Root-knot C. Meloidogyne injection
4. Pigeonpea-See gall D. Phytophthora infestans
A B C D
(1) 1 2 3 4
(2) 1 4 3 2
(3) 4 3 2 1
(4) 3 4 1 2
Answer. 2. 1 4 3 2
Question 78. The cell walls of fungi consist of
- Cellulose
- Hemicellulose
- Chitin
- Both (1) and (3)
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (3)
Question 79. Aspergillus niger is used for the manufacture of
- Citric acid and gluconic acid
- HCl and HNO3
- Fumaric and malic acids
- Succinic and fumaric acids
Answer. 1. Succinic and fumaric acids
Question 80. Beedle and Tatum gave “one gene and one enzyme” hypothesis while working on
- Salmonelly typhimurium
- Neurospora crassa
- Escherichia coli
- Diplococcus pneumoniae
Answer. 2. Neurospora crassa
Question 81. An organism with eukaryotic multicellular nature obtains its nutrition through its cell wall. It should be placed under
- Mycota
- Plantae
- Animalia
- Monera
Answer. 1. Mycota
Question 82. Which of the following pair belongs to basidiomycetes?
- Puffballs and Claviceps
- Morchella and mushrooms
- Peziza and stink horns
- Bird’s nest fungi and puffballs
Answer. 4. Bird’s nest fungi and puffballs
what is monosporic development
Question 83. Toxins released by plants to save themselves from fungal attack are
- Phytotoxins
- Phytoalexins
- Calmodulins
- Aquaporins
Answer. 2. Phytoalexins
Question 84. LSD is extracted from
- Claviceps
- Cannabis
- Agaricus
- Amanita
Answer. 1. Claviceps
Question 85. The pathogen for leaf spot disease in Arachis hypogea is
- Fusarium
- Cercosporia
- Alternaria
- Hemianatropous
Answer. 2. Cercosporia
Question 86. Tundu disease of wheat is due to infection caused by
- Nematode and fungi
- Fungi and bacteria
- Nematode and bacteria
- Algae and fungi
Answer. 3. Nematode and bacteria
Question 87. “Ergot of rye” is caused by
- Claviceps purpurea
- Sclerospora graminicola
- Cannabis sativa
- Algae and fungi
Answer. 1. Claviceps purpurea
Question 88. Which of these is foliose lichen?
- Cladonia
- Graphis
- Parmeia
- Lecanora
Answer. 3. parmeia
Question 89. Saccharomyces is commercially used in industry.
- Baking
- Wine
- Butter
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 90. Black rust of wheat is a fungal disease caused by
- Puccinia tritici
- Claviceps purpurea
- Melampsora lini
- Sclerospora graminicola
Answer. 1. Puccinia tritici
Question 91. Taxonomy of fungi is based on
- Sexual reproduction
- Nutrition
- Shape of sporocarp
- Cell wall
Answer. 1. Sexual reproduction
Question 92. Cellulose is a major component of cell walls of
- Pythium
- Xanthomonas
- Pseudomonas
- Saccharomyces
Answer. 1. Pythium
Question 93. Trichoderma harzianum has proved a useful microorganism for
- Bioremediation of contaminated soils
- Reclamation of wastelands
- Gene transfer in higher plants
- Biological control of soil-borne plant pathogens
Answer. 4. Biological control of soil-borne plant pathogens
Question 94. The athlete’s foot disease in humans is caused due to
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- Virus
- None of the above
Answer. 2. Fungi
Question 95. Which one is the wrong pairing for the disease and its causal organism?
- Loose smut of wheat-Ustilago nuda
- Root knot of vegetables-Meloidogyne sp.
- Late blight of potato-Alternaria solani
- Black rust of wheat-Puccinia graminis
Answer. 3. Late blight of potato-Alternaria solani
Question 96. Which one of the following has haplontic life cycle?
- Ustilago
- Wheat
- Funaria
- Polytrichum
Answer. 1. Ustilago
Question 97. Sexual reproduction in fungi may occur by means of
- Sporangiospore, oospore, and ascospore
- Zoospore, oospore, and ascospore
- Sporangiospore, ascospore, and basidiospore
- Oospore, ascospore, and basidiospore
Answer. 4. Oospore, ascospore, and basidiospore
Question 98. Lichens growing on tree bark are called
- Lignicolous
- Terricolous
- Corticolous
- Saxicolous
Answer. 3. Corticolous
Question 99. Common mycobionts and phycobionts of lichen body are, respectively,
- Ascomycetes, Chlorophyceae
- Ascomycetes, Cyanophyceae
- Basidiomycetes, Chlorophyceae
- Basidiomycetes, Cyanophyceae
Answer. 1. Ascomycetes, Chlorophyceae
Question 100. Foliose lichens are attached to the substratum at one or few places with the help of
- Branched, multicellular rhizoids
- Holdfast
- Rhizines
- Rhizomorph
Answer. 3. Rhizines
Question 101. Specialized structure in the thallus of lichen for nitrogen fixation and retaining moisture is
- Cyphellae
- Isidia
- Cephalodia
- Soredia
Answer. 3. Cephalodia
Question 102. Select the correct statement with respect to mycorrhizal roots:
- These do not differ in shape from normal roots.
- These often show a wooly covering.
- These possess root cap but lack root hairs.
- Fungal partner is commonly a member of ascomycetes.
Answer. 2. These often show a wooly covering.
Question 103. Which of the following feature is not related with virus?
- Infectivity and host specificity.
- Presence of genetic material.
- Occurrence of certain enzymes.
- Presence of respiration.
Answer. 4. Presence of respiration.
Question 104. Most of the viruses are/have
- Enveloped nucleo-protein structure
- Non-enveloped nucleo-protein structure
- Infectious protein particles
- Double-stranded DNA as well as dsRNA
Answer. 2. Non-enveloped nucleo-protein structure
Question 105. Infectious RNA particles without protein coat
- Have high molecular weight
- Were discovered by Alper
- Are known to cause disease in plants only
- More than one option is correct
Answer. 3. Are known to cause disease in plants only
Question 106. Yeast is used in the production of
- Lipase and pectinase
- Bread and beer
- Cheese and butter
- Citric acid and lactic acid
Answer. 2. Bread and beer
Question 107. Which one of the following microbes forms symbiotic association with plants and helps them in their nutrition?
- Aspergillus
- Glomus
- Trichoderma
- Azotobacter
Answer. 2. Glomus
Question 108. Which statement is wrong for viruses?
- All of them have helical symmetry.
- They have the ability to synthesize nucleic acids and proteins.
- Antibiotics have no effect on them.
- All are parasites.
Answer. 1. All of them have helical symmetry.
Question 109. Bacteria can be considered to be a plant because
- Some bacteria are photosynthetic
- Some bacteria have chlorophyll
- Some bacteria can make their own food
- Bacteria have cell wall
Answer. 4. Bacteria have cell wall
Question 110. The major component of bacterial cell wall is a polymer called
- Chitin
- Xytan
- Cellulose
- Peptidoglycan
Answer. 4. Peptidoglycan
Question 111. Oxytetracycline is produced by
- Mycoplasma
- Actinomycetes
- Cyanobacteria
- Eubacteria
Answer. 2. Actinomycetes
Question 112. Cyanobacteria existed
- 2.9 billion
- 3.4 billion
- 1 million
- Peptidoglycan
Answer. 2. 3.4 billion
Question 113. Which of the following is nonsymbiotic, anaerobic, non- photosynthetic nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
- Clostridium
- Nostoc
- Anabaena
- Azotobacter
Answer. 1. Clostridium
Question 114. Bacterial cell includes all except
- Nuclear material without membrane
- Cell wall of murein
- DNA compound with histones
- Ribosomes
Answer. 3. DNA compound with histones
Question 115. Pigments phycocyanin and phycoerythrin are present in
- Bacillariophyceae
- Archeabacteria
- Eubacteria
- Cyanobacteria
Answer. 4. Cyanobacteria
Question 116. Barophilic prokaryotes
- Grow slowly in highly alkaline frozen lakes at high altitudes
- Occur in water containing high concentration of barium hydroxide
- Grow and multiply in very deep marine sediments
- Readily grow and divide in sea water enriched in any soluble salt of barium
Answer. 3. Grow and multiply in very deep marine sediments
Question 117. Teichoic acid is present in
- Gram +ve bacteria
- Gram-ve bacteria
- Spirochaete
- Actinomycetes
Answer. 2. Gram-ve bacteria
Question 118. For retting of jute, the fermenting microbe used is
- Helicobacter pylori
- Mesophilic bacteria
- Streptococcus lactis
- Butyric acid bacteria
Answer. 4. Butyric acid bacteria
Question 119. Free-living aerobic nitrogen-fixing bacterium is
- Azotobacter
- Rhizobium
- Clostridium
- Anabaena
Answer. 1. Azotobacter
Question 120. Cyanobacteria is
- Nitrogen-fixing free-living photosynthetic organism
- Symbiotic mycorrhizae
- Photosynthetic algae
- Saprophytic fungus
Answer. 1. Nitrogen-fixing free-living photosynthetic organism
Question 121. Genetic elements which may be present inside as well as in extrachromosomal entities are
- Episomes
- Mesosomes
- Oxysomes
- Autosomes
Answer. 1. Episomes
Question 122. The bacterial cell wall is made up of
- Cellulose
- Hemicellulose
- Both (1) and (2)
- Peptidoglycan
- Glycogen
Answer. 4. Peptidoglycan
Question 123. The most widely used bioweapon is
- Bacillus subtilis
- Pseudomonas putida
- Bacillus anthracis
- None of the above
Answer. 3. Bacillus anthracis
Question 124. A bacterial cell divides once every minute and it takes 1 h to fill a cup. How much time will it take to fill half the cup?
- 30 min
- 60 min
- 29 min
- 59 min
Answer. 4. 59 min
Question 125. Bacteria is pathogenic due to
- Mitochondria
- Cell membrane
- Cell wall
- Nuclic acid
Answer. 4. Nuclic acid
Question 126. Which of the following is non-pathogenic bacteria of colon?
- Escherichia coli
- Balantidium coli
- Entamoeba coli
- Enterobius vermicularis
Answer. 2. Balantidium coli
Question 127. Treponema pallidum is
- Causative agent of syphilis
- The example of spirochaete bacterium
- The causative agent of sexually transmitted disease
- All are correct
Answer. 4. All are correct
Question 128. Which of the following is correct?
- Bacteria are only autotrophic.
- Bacteria are only heterotrophic.
- Most are heterotrophic but a few are autotrophic.
- Most bacteria are autotrophic but a few are heterotrophic.
Answer. 3. Most are heterotrophic but a few are autotrophic.
Question 129. The Widal test is performed as diagnostic value in
- Tuberculosis
- Typhoid
- Cholera
- Tetanus
Answer. 2. Typhoid
Question 130. The two bacteria found to be very useful in genetic engineering experiments are
- Nitrosomonas and Klebsiella
- Escherichia and Agrobacterium
- Nitrobacter and Azotobacter
- Rhizobium and Diplococcus
Answer. 2. Escherichia and Agrobacterium
Question 131. Pili of bacteria are useful for
- Locomotion
- Sexual contacts
- Asexual reproduction
- Transformation
- Feeding
Answer. 2. Sexual contacts
Question 132. The bacterium (Clostridium botulinum) that causes botulism is
- An obligate acrobe
- A facultative anaerobe
- An obligate anaerobe
- A facultative acrobe
Answer. 3. An obligate anerobe
Question 133. In prokaryotes, what helps in anaerobic respiration?
- Mitochondria
- Folds of plasma membrane
- Ribosomes
- Cell wall
Answer. 2. Folds of plasma membrane
Question 134. Blue green algae as Nostoc and Anabaena can photosynthesize due to the presence of
- Heterocysts
- Akinetes
- Chromatophores
- Leghemoglobin
Answer. 3. Chromatophores
Question 135. The exceptional feature of blue green algae which is the basis of their study is
- Aplanospores
- Sclerodia
- Heterocysts
- Haplospores
Answer. 3. Heterocysts
Question 136. Crown galls are caused in plants due to the infection of
- Insects
- Virus
- Bacteria
- Fungi
Answer. 3. Bacteria
Question 137. Curing of tea leaves is brought about by the activity of
- Fungi
- Bacteria
- Micorrhizae
- Viruses
Answer. 2. Bacteria
Question 138. In prokaryotes, chromatophores are
- Specialized granules responsible for coloration of cells
- Structures responsible for organizing the shape of the organism
- Inclusion bodies lying free inside the cells for carry- ing out various metabolic activities
- Internal membrane systems that may become exten- sive and complex in photosynthesis bacteria
Answer. 4. Internal membrane systems that may become exten- sive and complex in photosynthesis bacteria
Question 139. Which one of the following pathogens causes canker discase?
- Meloidogyne ineognita
- Anguina tritici
- Xanthomonas citri
- Pseudomonas rubilineans
- Phytophthora infestans
Answer. 3. Xanthomonas citri
Question 140. Find out the pairs which are correctly matched:
(a) Cyanobacteria (1) Biopesticides
(b) Mycorrhiza (2) Solubilization of phosphate
(c) Bacillus (3) Cry protein thuringiensis
(d) Single-cell protein (4) Rhizobia
- (a) and (2)
- (b) and (3)
- (c) and (3)
- (a) and (3)
- (b) and (4)
Answer. 2. (b) and (3)
Question 141. Which one of the following statements about mycoplasma is wrong?
- They are pleomorphic.
- They are sensitive to penicillin.
- They cause diseases in plants.
- They are called PPLO (pleuropneumonia-like organisms).
Answer. 2. They are sensitive of penicillin.
Question 142. The presence of a cluster of polar flagella is termed as
- Monotrichous
- Amphitrichous
- Lophotrichous
- Peritrichous
Answer. 3. Lophotrichous
Question 143. Some bacteria can live also in the absence of oxygen. These are
- Obligate aerobes
- Facultative aerobes
- Obligate anaerobes
- Facultative anaerobes
Answer. 2. Facultative aerobes
Question 144. What are the infoldings of plasma membrane called in prokaryotes which store respiratory pigments?
- Glyoxysomes
- Oxysomes
- Mesosomes
- Cristae
Answer. 3. Mesosomes
Question 145. Plasmid is
- Small extrachromosomal circular self-replicating DNA that can carry genes into the host organism
- Bacteriophage
- DNA found in mitochondria
- DNA incorporated in bacteria
Answer. 1. Small extrachromosomal circular self-replicating DNA that can carry genes into the host organism
Question 146. Difference between Gram -ve and Gram +ve bacteria is in their
- Cell membrane
- Cell wall
- Ribosome
- Mitochondria
Answer. 2. Hemicellulose
Question 147. The cell wall of bacterium is made up of
- Cellulose
- Hemicellulose
- Lignin
- Peptidoglycan
- Glycogen
Answer. 4. Peptidoglycan
Question 148. Which of the following monerans lack cell wall?
- Actinomycetes
- Photosynthetic bacteria
- Eubacteria
- None of the above
Answer. 4. None of the above
Question 149. Bacteria can live under sub-zero temperature for
- More than 1000 years
- 100-1000 years
- Few years
- Few days
Answer. 1. More than 1000 years
Question 150. Set of bacterial diseases is
- Diphtheria, leprosy, and plague
- Malaria, mumps, and polio
- Cholera, typhoid, and mumps
- Tetanus, TB, and malaria
Answer. 1. Diphtheria, leprosy, and plague
Question 151. In prokaryotes, genetic recombination can occur during
- Transduction
- Transformation
- Conjugation
- All of these
Answer. 1. Transduction
Question 152. Thermococcus, Methanococcus, and Methanobacterium exemplify
- Archaebacteria that contain protein homologous to eukaryotic core histones
- Archaebacteria that lack any histones resembling those found in eukaryotes but whose DNA is negatively supercoiled
- Bacteria whose DNA is relaxed or positively su- percoiled but which have a cytoskeleton as well as mitochondria
- Bacteria that contain a cytoskeleton and ribosomes
Answer. 1. Archaebacteria that contain protein homologous to eukaryotic core histones
Question 153. Which one of the following is not a characteristic of Gram-positive bacteria?
- Cell wall is smooth.
- Mesosomes are distinctively prominent.
- Basal body of flagellum contains two rings.
- Outer membrane is present.
- Murein content of cell wall is 70-80%.
Answer. 1. Cell wall is smooth.
Question 154. Pathogenicity of bacteria causing tuberculosis and leprosy is due to
- Cholesterol
- Ergosterol
- Prostaglandins
- Glycerol
- Wax-D
Answer. 5. Wax-D
Question 155. Bacterial leaf blight of rice is caused by a species of
- Xanthomonas
- Pseudomonas
- Alternaria
- Erwinia
Answer. 4. Erwina
Question 156. Streptomyces griseus gives which of these antibiotics?
- Chloramphenicol
- Sterptomycin
- Tetracycline
- Penicillin
Answer. 1. Chloramphenicol
Question 157. Indirect transfer of genetic material from one bacterium to another through bacteriophase is
- Transduction
- Transcription
- Conjugation
- Translation
- Transformation
Answer. 2. Transcription
Question 158. Bacterial brown rot of potato is caused by
- Xanthomonas citri
- Escherichia coli
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- Pseudomonas solanacearum
- Salmonella typhosa
Answer. 1. Xanthomonas citri
Question 159. Which of the following is a bacterial disease?
- Red rust of tea
- Citrus canker
- Red rot of sugarcane
- Late blight of potato
Answer. 4. Late blight of potato
Question 160. Shorter generation time of E. coli compared to eukaryotes may be explained on the basis of
- Shape
- Large surface: volume ratio
- Presence of cell wall
- Absence of organelles
Answer. 2. Large surface: volume ratio
Question 161. Division in a bacteria cell is carried out through
- Multiple fission
- Binary fission
- Budding
- Plasmotomy
Answer. 2. Binary fission
Question 162. Antibiotic resistance genes are present on
- Plastid
- DNA
- Plasmid
- RNA
Answer. 2. DNA
Question 163. Cyanobacteria is the member of
- Fungi
- Protozoa
- Monera
- Pteridophytes
Answer. 3. Monera
Question 164. The Gram-negative bacteria detect and respond to the chemicals in their surroundings by
- Muramic acid
- Lipopolysaccharide
- Volutin granules
- Porins
Answer. 3. Volutin granules
Question 165. Which of the following is not a bacterium?
- Methanogens
- Diatoms
- Archaebacteria
- Blue green algae
Answer. 2. Diatoms
Question 166. A bacterium is capable of withstanding extreme heat, dryness, and toxic chemicals. This indicates that it is probably able to form
- A thick peptidoglycan wall
- Endospores
- Endotoxins
- Endogenous buds
Answer. 2. Endospores
Question 167. The vector for plague is
- Anopheles
- Aedes
- Xenopsylla
- Culex
Answer. 2.
Question 168. Lung tuberculosis is caused by
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Escherichia coli
Answer. 3. Streptococcus pneumoniae
Question 169. An example of symbiotic bacteria is
- Erwinia amylovora
- Rhizobium leguminosarum
- Xanthomonas campestris
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Answer. 2.
Question 170. Nonpathogenic bacteria found in our vermiform appendix is
- Entamoeba histolytica
- Shigella
- Escherichia coli
- Ascaris
Answer. 2. Shigella
Question 171. Which one of the following organisms possesses characteristics of both plant and animal?
- Euglena
- Bacteria
- Mycoplasma
- Paramecium
Answer. 3. Mycoplasma
Question 172. The scientist who coined the term “protista” to include both plant- and animal-like unicellular organisms was
- Robert Koch
- (2) E.F. Haeckel
- L. Pasteur
- Joseph Lister
Answer. 1. Robert Koch
Question 173. Protista includes
- Protozoa, algae, and fungi
- Algae, bryophyta, bacteria, and fungi
- Fungi, slime molds, and vascular plants
- Protozoa, bacteria, algae, and bryophyta
Answer. 2. Algae, bryophyta, bacteria, and fungi
Question 174. Slime molds belong to kingdom
- Monera
- Protista
- Plantae
- Animalia
Answer. 1. Monera
Question 175. Which protist reproduces both by binary fission and conjugation?
- Amoeba
- Paramecium
- Euglena
- Monocystis
Answer. 2. Paramecium
Question 176. Total parasites belongs to protozoan group
- Sporozoa
- Ciliata
- Sarcodina
- Zooflagellata
Answer. 2. Ciliata
Question 177. Protozoan protists respire through
- Pseudopodia
- Contractile vacuole
- Mitochondria
- General surface
Answer. 1. Pseudopodia
Question 178. Which one is not a protozoan protist?
- Plasmodium vivax
- Paramecium caudatum
- Enterobius vermiclaris
- Trypanosoma gambiense
Answer. 2. Paramecium caudatum
Question 179. Protozoan protists are differentiated on the basis of
- Nuclei
- Size
- Shape
- Locomotory structures
Answer. 3. Shape
Question 180. Endoparasitic protistan protozoans belong to
- Sporozoa
- Ciliata
- Sarcodina
- Mastigophora
Answer. 4. Mastigophora
Question 181. Protozoan found commonly in human colon is
- Entamoeba coli
- Plasmodium. vivax
- Aedes. aegypti
- All of these
Answer. 1. Entamoeba coli
Question 182. Primary grouping of protozoan protists is based on
- Locomotor organelles
- Size and shape
- Mode of feeding
- Mode of reproduction
Answer. 1. Locomotor organelles
Question 183. Protozoans are able to live efficiently due to their
- Motility
- Rapid reproduction
- Ability to manufacture food
- Specialized organelles
Answer. 1. Motility
Question 184. Protista contains
- Euglena, dinoflagellates, and yeast
- Amoeba, Paramecium, and Hydra
- Euglena, Paramecium, and mushroom
- Amoeba, Paramecium, and dinoflagellates
Answer. 4. Amoeba, Paramecium, and dinoflagellates
Question 185. Cyanobacteria are also referred to as
- Golden algae
- Slime molds
- Blue green algae
- Protists
Answer. 3. Blue green algae
Question 186. Which one of the following does not differ in E.coli and Chlamydomonas?
- Chromosomal organization
- Cell wall
- Cell membrane
- Ribosomes
Answer. 3. Cell membrane
Question 187. Nuclear membrane is absent in
- Agaricus
- Volvox
- Nostoc
- Penicillium
Answer. 3. Nostoc
Question 188. Maximum nutritional diversity is found in the group
- Antimalia
- Monera
- Plantae
- Fungi
Answer. 2. Monera
Question 189. The most abundant prokaryotes helpful to humans in making curd from milk and in the production of antibiotics are the ones categorized as
- Archaebacteria
- Chemosynthetic autotrophs
- Heterotrophic bacteria
- Cyanobacteria
Answer. 3. Heterotrophic bacteria