Class 10 Biology Life Processes Nutrition Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Where do plants get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis?
Answer:
There are three raw materials besides sunlight. They are carbon dioxide, water and mineral salts.
- Carbon Dioxide. Atmosphere through stomata.
- Water. Soil through roots.
- Minerals. Soil with the help of roots.
Question 2. What is the role of acid in our stomach?
Answer:
Acid (HCl) is present in our gastric juice. It has several functions:
- Killing of germs entering along with food,
- Softening of food.
- Stoppage of action of salivary amylase.
- Conversion of proenzyme pepsinogen into enzyme pepsin,
- Acidify food for the action of the enzyme pepsin.
question on life processes class 10
Question 3. What is the function of digestive enzymes?
Answer:
Digestive enzymes are hydrolytic biocatalysts (hydrolases) which bring about the break up of complex substances of food into simpler, soluble and absorbable components.
Question 4. How is the small Intestine designed to absorb digested food?
Answer:
- The small intestine is the longest part of the alimentary canal.
- It is the area where all components of food are completely digested.
- The small intestine has a number of transverse folds or villi or increasing internal surface area.
- Villi are richly supplied with blood capillaries and a lymph vessel lacteal for quick removal of absorbed food.
- Enterocytes or surface cells of the small intestine have a brush border or microvilli. Microvilli increase the surface area of the cells several times for the absorption of food.
Class 10 Biology Life Processes Nutrition Multiple Choice Questions And Answers
Question 1. Most of the digestion and absorption of the food takes place in the
- Small intestine
- Liver
- Stomach
- Large intestine
Answer: 1. Small intestine
Question 2. Pseudopodia are
- Small hair-like structures present in unicellular organisms
- False feet developed in some unicellular organisms
- Long tube-like structures coming out of the mouth
- Suckers which are attached to the walls of the intestine.
Answer: 2. False feet developed in some unicellular organisms
Class 10 Biology Life Processes Nutrition Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Explain the significance of peristaltic movements that occur all along the gut during digestion.
Answer:
They are alternate contraction and expansion movements from the oesophagus to the large intestine. It moves the food forward automatically in a regulated manner depending upon the time required for the action of digestive enzymes and absorption of the digested materials.
Question 2. Leaves of a healthy potted plant were coated with Vaseline. Will the plant remain healthy for long? Give a reason for your answer.
Answer:
No. Due to the covering of the leaf with vaseline, the stomata become blocked. The plant can neither receive carbon dioxide for photosynthesis nor oxygen for respiration. There is no cooling by transpiration. The effect of sunburn can also occur. Later the plant with wither and die.
Question 3. Tooth enamel is the hardest substance in our body. Name the compound of which it is made up of At which pH of the mouth it gets eroded. State the role of bacteria present in the mouth. Suggest a method to prevent tooth decay.
Answer:
Enamel consists of calcium phosphate (95%) and proteins amelogenin and enamelin (5%). Enamel gets corroded in acidic conditions as created by plaque-forming bacteria Streptococcus mutans.
Brushing the teeth after each meal or at least twice a day will prevent plaque formation and tooth decay.
” life processes class 10 sample papers with solutions”
Question 4. Name the cells that control the opening and closing of the stomatal pore. How do they perform their function?
Answer:
Guard cells. Guard cells bring about the opening and closing of stomata by gain or loss of turgidity. When the stomata are open, guard cells withdraw K” ions from the surrounding epidermal cells. They also obtain water from the surrounding cells due to endosmosis.
Their elastic outer wall bends outwardly pulling the thickener wall also. This creates a pore in between the two guard cells. During closure movement, guard cells lose k ions and water to the surrounding epidermal cells. They become flaccid. The inner walls come closer and closer to the stomatal pore.
Question 5.
- Name two organisms that obtain food through parasitic mode.
- How do fungi obtain their food?
Answer:
- Parasitic Mode of Nutrition. Cuscuta (plant), Ascaris (animal).
- Fungi are generally saprophytes. They obtain nourishment from organic remains by first pouring digestive enzymes over them and then absorbing the dissolved materials.
Question 6. List two different functions performed by the pancreas in our body.
Answer:
The pancreas is a heterochrony gland
- Its exocrine part secretes digestive juice called pancreatic juice.
- Its endocrine region secretes hormones, insulin and glucagon.
Question 7. List in tabular form two differences between pepsin and trypsin.
Answer:
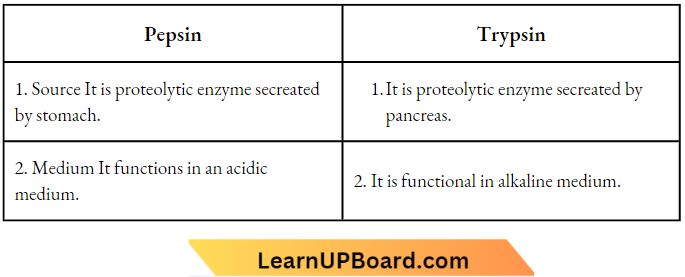
Question 8.
- Name the process by which autotrophs prepare their own food.
- List three events which occur during this process.
- State two sources from which plants obtain nitrogen for the synthesis of proteins and other compounds.
Answer:
- Photosynthesis.
- Events In Photosynthesis:
- Photolysis of water.
- Absorption of solar energy and production of assimilatory power (ATP + NADPH).
- Reduction of carbon dioxide.
- Nitrate and Ammonium from soil.
class 10 science chapter 6 life processes question answer
Question 9. What are the Final products formed after the digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats?
Answer:
- Carbohydrates – Glucose.
- Proteins – Amino acids.
- Fats – Fatty acids and Glycerol.
Question 10. Mention the role of the following in digestion
- Pepsin
- Saliva
- Villi
- Bile juice.
Answer:
- Pepsin. Breaks down protein into peptones and proteoses in an acidic medium.
- Saliva.
- Moistening the food
- Sterilising the food by lysozyme
- Partial digestion of starch into maltose.
- Villi. Absorption of digested food by increasing surface area and having microvilli over their cells.
- Bile Juice.
- Neutralizing the acidity and making the chyme coming from the stomach alkaline.
- Emulsification of fat.
Question 11. List the role of each of the following in the digestive system:
- Muscles of stomach
- Hydrochloric acid
- Mucus.
Answer:
- Muscles of Stomach.
- Mixing of gastric juice with food,
- Breaking food into smaller pieces by churning movement.
- Hydrochloric Acid. It sterilizes, softens and acidifies the food in the stomach for the action of enzyme peps
- Mucus.
- It lubricates the food for easy passage of food in the alimentary canal.
- The mucus protects the wall of the alimentary canal from its own digestive enzymes.
Question 12.
- Why does a piece of bread taste sweet when chewed for some time?
- “Cellulose acts as a roughage in man but serves as a source of nutrients in cow”. Justify the statement.
Answer:
- In the mouth, food mixes with saliva. Saliva contains the enzyme ptyalin or salivary amylase that hydrolyses star to sweet sugar maltose.
- In human beings, cellulose cannot be digested as they do not have any enzyme or bacteria to metabolize Cellulose functions as roughage in the human digestive system. In cows, the stomach contains cellulose ferment bacteria that convert cellulose to glucose state.
previous year questions of life processes class 10
Question 13. What is photosynthesis?
Answer:
Photosynthesis is the process of the formation of organic food from inorganic raw materials (CO2, H2O) with the he! of sunlight inside chlorophyll-containing cells.
Question 14. Complete the following flow chart as given instructions
Answer:
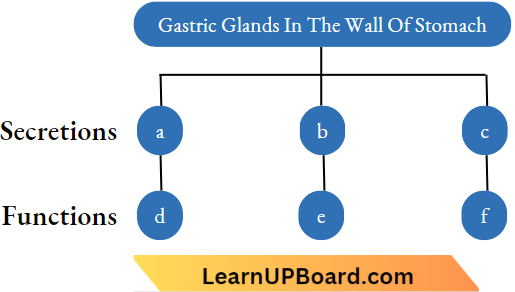
- Mucus— (d) Moistening of food, protection of the inner lining of the stomach from HCl.
- HCI—(e) Killing of germs, softening of food and providing acidic medium.
- Pepsin—(f) Digests proteins in an acidic medium.
Question 15. State the role played by the following in the process of digestion
- Explain
- Enzyme trypsin
- Enzyme lipase
- List two functions of finger-like projections present in the small intestine.
Answer:
- That is
- Trypsin. Digestion of proteins.
- Lipase. Digestion of emulsified fat.
- Villi.
- Brings intestinal wall in contact with food
- Increasing surface area for digestion and absorption of food.
Class 10 Biology Life Processes Nutrition Long Answer Type Questions And Answers
Question 1. List two differences between holozoic nutrition and saprophytic nutrition. Give two examples of each of them.
Answer:
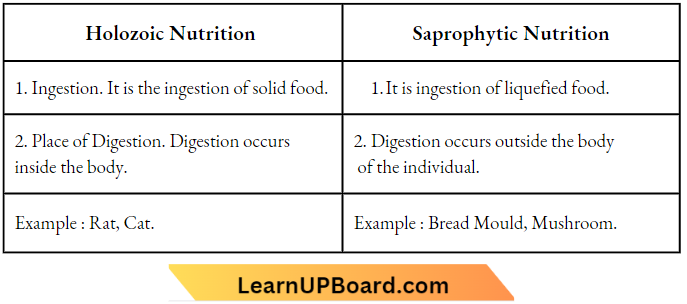
State the roles of the liver and pancreas.
Answer:
- Role Of Liver. Storage of glycogen, formation of urea, formation of prothrombin, fibrinogen and heparin, secretion of bile, detoxification, and elimination of pathogens.
- Role Of Pancreas. Secretion of hormones insulin and glucagon, secretion of pancreatic juice for digestion-pancreatic amylase, pancreatic lipase and trypsin.
Name the organ which performs the following functions in humans:
- Absorption of digested food
- Absorption of water.
Answer:
- Absorption Of Digested Food Mostly in the ileum part of the small intestine.
- Absorption Of Water. Partly in the ileum and partly in the large intestine.
Explain the statement, “Bile does not contain any enzyme but it is essential for digestion”.
Answer:
Role Of Bile In Digestion.
- Neutralization and alkalisation of chyme coming from the stomach.
- Emulsification of fat.
ch 6 science class 10 important questions
Question 2. Name the glands, associated with the digestion of starch in the human digestive tract and mention their role.
Answer:
- Salivary Glands. Their secretion called saliva contains the enzyme ptyalin or salivary amylase which converts part of starch into maltose and dextrins.
- Pancreas. Pancreatic amylase changes starch and dextrins into maltose.
- Intestinal Glands. They secrete disaccharidases which hydrolyse disaccharides into monosaccharides:
- Sucrose-Glucose + Fructose.
- Lactose-Glucose + Galactose.
- Maltose-Glucose + Glucose.
How is the required pH maintained in the stomach and small intestine?
Answer:
- In the stomach, acidic pH is maintained by HCl.
- In the intestine, alkaline pH is maintained by bile and pancreatic juice.
Question 3. Mention the location of four major glands associated with the digestive system of humans and explain the functions of each.
Answer:
Four Major Glands. Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gastric glands.
- Salivary Glands. Three pairs— parotid below the ear, submaxillary at an angle of the lower jaw and sublingual below the tongue.
- Salivary glands secrete saliva. Saliva moistens the food, disinfects it with lysozyme and partly digests starch/glycogen into maltose.
- Liver It occurs on the right upper side of the abdomen below the diaphragm. The liver secretes bile for neutralization an alkalisation of chyme, emulsification of fat, storage of glycogen and many nondigestive functions.
- Pancreas. It lies behind the stomach with its head connected to the duodenum by the pancreatic duct. Digestive secretion of the pancreas, called pancreatic juice contains lipolytic, amylolytic and proteolytic enzymes for the digestion of all major components of food.
- Gastric Glands. They occur inside the stomach. The secretion called gastric juice contains HCl and the proteolytic enzyme pepsin which breaks down protein in an acidic medium to form peptones and proteoses.
Question 4. What function is served by:
- Pyloric sphincter
- Anal sphincter.
Answer:
Pyloric Sphincter — Release of chyme into duodenum.
Anal Sphincter — Release of faeces through the anus.
Question 5. What is the nutrition in
- Fungi
- Amarbel?
Answer:
- Nutrition In Fungi. It is commonly saprotrophic, for example, Rhizopus and mushroom. A few fungi are parasitic.
- Amarbel (Cuscuta). Heterotrophic, holoparasite.
Name the part of the alimentary canal where:
- Food is completely digested
- Secrete juice that has trypsin
- Secrete bile
- Absorb water from unabsorbed food.
Answer:
Mention the names of any two secretions by the gastric glands and state one role played by each in our body.
Answer:
- Gastric Glands. HCl and Pepsin.
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl).
- Pepsin.
Question 6. Write the function of the following in the human alimentary canal:
- Saliva
- HCl in stomach
- Bile juice
- Villi.
Answer:
- Function of Saliva,
- Moistening the food
- Conversion of starch into maltose by salivary amylase.
- Function of HCl.
- Disinfection of food
- Acidification of food for the action of pepsin.
- The function of Bile Juice:
- Deacidification of food and making it alkaline
- Emulsification of fat.
- The function of Villi. Increase the surface area of the small intestine for absorption.
Write one function of the following enzymes:
- Pepsin
- Lipase.
Answer:
- Function of Pepsin. Digestion of proteins to form peptones and proteoses.
- Function of Lipase. Digestion of fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
Question 7. A gas is released during photosynthesis. Name the gas and also state the way by which the gas is evolved.
Answer:
Oxygen. It is formed during photosynthetic splitting or photolysis of water.
Question 8. Why is nutrition necessary for the human body?
Answer:
Nutrition Is Required For
- Obtaining energy
- Materials for the formation of new cells
- Repair of damaged cells and tissues
- Development of immunity.
