UP Board Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Population Problems And Control Learning objectives
After completing this chapter, you will be able to:
- Define the terms-population density, demography, birth rate, death rate, growth rate, etc.;
- Trace the trends for rise in Indian population over the decades;
- List the factors responsible for rapid rise of population in India and the world;
- Describe the disadvantages of enormously increasing population;
- Explain the need for controlling population growth;
- List and describe various methods ntraception for population control.
India is the second-most populous country in the world, next to China. India comprises more than 15% of the world’s total population. The ever-increasing human population is putting an ever-increasing load on resources. It is therefore the prime responsibility of each one of us to help educate people and take necessary steps to check our fast-growing population.
| Class 10 Science | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Transformation of Sentences |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Science |
Few terms to remember
- Population: The number of people living in a particular area or a country at a particular time is called the population of that area or country.
- Demography: The statistical study of human population of a region is called demography. It deals with population growth, ratio of age and sex and population density in a particular region.
- Population density: The number of persons per unit area at any given time.
- Birth rate or natality: The number of live births per 1000 persons in a year.

- Death rate or mortality: The number of deaths per 1000 persons in a year.
- Growth rate of population: The difference between the birth rate and the death rate. If the birth rate is more than death rate, the population grows. If the birth rate is lesser than death rate, the population declines. The population growth rate in 2016 was 1.19%.
- Census: It is an official enumeration of the population done periodically. The census is the most comprehensive source of demographic, social and economic data.
UP Board Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Population Problems And Control Population
Population growth in India
The human population is growing. The population of India was about 24 crores in the year 1901. Except for a slight fall in 1911-21, the population of India has been steadily increasing for the last 100 years (Table 14.1). The total population of India has multiplied by about 4 times within last one hundred years (1911-2011). As per the census of 2011, as on March 2011, the population of India was 1,210,193,422,
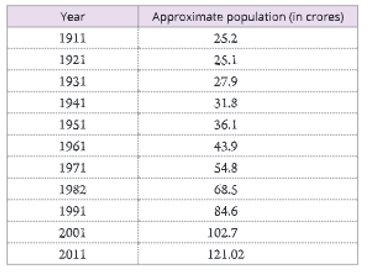
i.e. about 121.02 crores. This alarming rate of rise in human population is a cause of concern.
Factors responsible for population explosion in India
- Advancement in agriculture: This has helped in the availability of more food, and hence, less starvation and malnutrition.
- Advancement in medicine: This has helped in controlling epidemic diseases, leading to increasing life span. Thus, more and more people are living longer, reaching reproductive age and producing more children.
- Religious and social customs: Because of the prevailing social customs and religious beliefs, many people do not adopt family planning measures, leading to the rise in population.
- Industrialization: This has helped in better production, storage and distribution of food, more employment opportunities and more prosperity.
- Illiteracy: Even though a sizeable number of our population is educated, a large proportion is still illiterate, ignorant and superstitious. They are not aware of the benefits of family planning. This results in overpopulation.
- Economic reasons: Children are considered to be helping hands to increase the income of the family.
- Desire of a male child: In most societies, the male child is considered to be essential for keeping up the name of the family from one generation to another. Due to this, the parents want to have at least one son and in this process they give birth to many children.
- Lack of recreation: Because of poverty and poor standard of living, there are not many recreation facilities available and sex provides recreation to such people.
Factors responsible for increase in human population in the world
- Better health care is available for all. There are more facilities, doctors and medicines for health care.
- Better food supplies are available. The food shortage has been minimized due to agricultural revolution. As a result more and better quality of food is produced and made available to all.
- Fewer deaths as compared to ancient times. This s due to the discoveries of medicines and vaccines which have controlled and even wiped out many diseases. More patients get cured and live longer.
- Large-scale immunization against epidemic diseases.
- Better nutrition facilities are available, specially for growing children. As a result, more and more children are healthy and are reaching the reproductive age.
UP Board Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Population Problems And Control Growth Curves
What are population growth curves?
Population growth curves
Curves obtained by plotting the number of individuals in a population against time are called population growth curves. The factors that influence population growth curves are mainly environmental factors. There are two types of population growth curves,
- J-shaped growth curve, and
- S-shaped (sigmoid) growth curve.
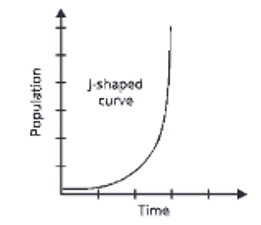
J-shaped population growth curve
increasing exponentially and becomes double in size during a constant period of time. The growth is exponential and the curve is known as J-shaped curve as given in.
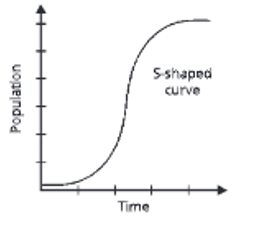
S-shaped (sigmoid) population growth curve
In this population growth curve, the population first increases slowly and then more rapidly. Finally it slows down and fluctuates within a narrow range due to limitation by environmental factors. Thus, an S-shaped (sigmoid) curve is obtained showing the maximum population size an environment can sustain.
UP Board Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Population Problems And Control Problems Posed By Increasing Population
The problems posed by increasing population are of two types:
1. Problems posed to large families
2. Problems posed to the country
Problems posed to large families
- Poor health of the mother: Because of frequent pregnancies, the mother may suffer from ill-health.
- Poor housing: More family members means more space. The family may not afford a good, clean and spacious house.
- Economic pressure: The large family will need more resources. This will lead to immense economic pressure on the parents affecting the quality of life.
- Malnutrition: The family members may not get enough food. This will lead to malnutrition and deficiency diseases.
- Poor medical care: The family members will require constant medical support. However, because of medical facilities being expensive, it may not be possible to provide everyone with adequate medical support.
- Improper education: Proper educational facilities may not be provided to the children.
Problems posed to the country
A high population growth in India has drastic environmental implications like overcrowding, decrease in per capita income, and depletion of food, land, fuel and consumer resources. Like atomic explosion, population explosion is also equally harmful for our existence.
- Urbanization and environmental degradation: Due to increasing population, farmlands in the rural areas can no longer support the living expenses of additional people. This has resulted in a continuous migration of a large number of people to urban areas with the hope of finding jobs and a better life. This has led to an increase in the urban population. The growth in urban population puts pressure on the urban environment by increasing the number of squatter settlements, and slum dwellers in slums with no proper sanitation facilities, causing pollution of air, water and soil.
- Increasing population and transportation: Increase in population results in a corresponding
- increase in the means of transport in rural areas in general and in urban areas in particular. The total number of vehicles has increased tremendously. Increase in the number of automobiles has increased the pollution load (air pollution, water pollution and solid waste pollution).
- Increasing population and education: We all know that education is one of the most important aspect for economic and social upliftment. Although the literacy rate is growing, but we still have the largest illiterate population in the world. The increasing population further adds up to the problems of providing education to all.
- Increasing population, agricultural development and environmental degradation: In order to meet the food requirement of the ever-increasing population, new agricultural techniques have been adopted. The application of modern scientific techniques, agrochemicals (fertilizers and pesticides), expansion in irrigation facilities and the development of high-yielding varieties of seeds have created hazardous environmental problems.
- Increasing population and deforestation: Due to substantial increase in the agricultural land, lots of forests have been cut down. Due to deforestation, excessive irrigation and natural hazards, such as floods, etc., land is being degraded and wasteland is increasing. The increased use of fertilizers and pesticides to boost agricultural productivity has immense adverse effects on land and water resources of our country. Agricultural land has been extensively polluted due to pollution from fertilizers and pesticides.

- Population, industrial development and environmental pollution: Growth in human population has resulted in increased requirements of food, shelter and day-to-day products. To meet these requirements, industry has expanded and industrial growth has made many Indian cities centres of health hazards, due to environmental pollution.
- Increasing population and water: The availability of water is limited. Increasing population will need more water. Thus, availability of water will be scarce with the increase in population.
- Increasing population and depleting energy sources: Energy is needed for almost all our day-to-day activities whether for cooking, transportation, factories or at home. Presently we are largely dependent on fossil fuels such as coal and petroleum for energy. At the current rate of consumption, our fossil fuel reserves will be exhausted within a few hundred years. Increasing population will need even more and more energy. This will further complicate the situation.
- Increasing population and depletion of mineral reserves: Our mineral reserves are limited, once finished they cannot be replenished (i.e. they are non-renewable). More population means more requirements of minerals, leading to fast depletion of mineral resources.

UP Board Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Population Problems And Control Population control and Family Planning
It is very necessary to control the overgrowing population and to educate people to accept small family norm and create awareness about population explosion and its impact on the family, society and the nation. The government has taken many measures for providing family planning guidance and support, and family welfare measures.
There are various ways to prevent fertilization and hence to check the increasing population. Some of these are discussed here.
Education
The most effective method is to impart education to the people about various ways of fertility control. Education helps to make people aware of the advantages of a small family and the disadvantages of a large family.
Preventive Methods
These methods prevent pregnancy and obstruct the fusion of the egg and the sperm. Some of the important preventive methods are discussed below.
Surgical Methods
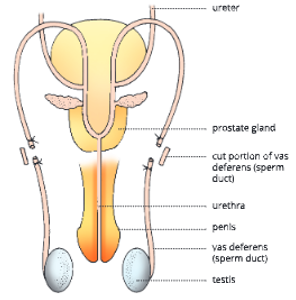
1. Vasectomy (for males): This is a method of sterilization in males. In this method, each sperm duct or vas deferens is cut and tied (ligated) at both ends by a thread. The small piece between the two ligatures is then removed.
By doing so the sperms cannot reach the ejaculatory duct and hence cannot be deposited in the female reproductive tract during intercourse. This procedure is easy and quick and has no harmful effect on manliness of any kind and does not reduce libido.
2. Tubectomy (for females): This is a method of sterilization in females (Fig. 14.7). It involves cutting of the Fallopian tubes or oviducts and tying the ends to prevent passage of ova down the
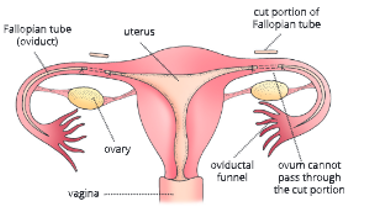
- Fallopian tubes. In this method, the eggs continue to be released but do not pass through the oviducts and hence, no fertilization takes place. Further when sperms are deposited during intercourse they cannot travel to the oviduct and hence no fertilization can occur. In a new method, tubectomy is performed with the help of a laparoscope. With the help of a laparoscope the abdominal organs can be viewed by a flexible optical fibre lens and a cold light source. This surgery is performed by making a small (1 cm) hole in the abdomen.
Contraception methods
- These methods involve prevention of fertilization and conception. Contraception results in birth control and is the basis of family planning. Contraception may be natural or mechanical. The main methods of contraception are summarized in Table.
1. Natural methods of contraception: If copulation is avoided for a few days, i.e. at +3 days of the first day of ovulation which is likely to be the time
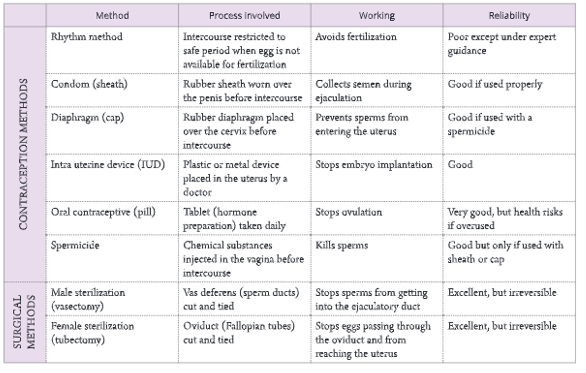
- period when the ovum is available in the oviduct, fertilization can be avoided. This is called rhythm method of contraception.
- Another natural method of contraception is coitus interruptus. In this method, the penis is withdrawn from the vagina prior to ejaculation. All these methods require extreme self-discipline and self-control.
2. Mechanical (Barrier) methods of contraception: Mechanical barriers are used to prevent the passage of semen to the Fallopian tube or to prevent implantation.
- Condoms or nirodh: It is a thin rubber tube worn over the penis before sexual intercourse. The ejaculate gets collected in this tube and is not discharged into the vagina.
- Diaphragm or cervical cap: It is a large thin rubber cap fixed on a flexible metal ring. It is fitted over the cervix of uterus in a woman’s body to prevent the passage of sperms into the cervical canal.

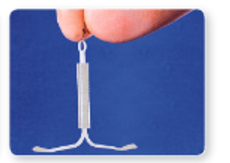
3. Intrauterine device (IUD) or loop: It is a very effective method to avoid conception. IUD or loop is made of plastic or stainless steel. It is inserted in the uterus. Its insertion causes certain secretions which prevent the implantation of embryo in the uterine wall.
4. Chemical methods of contraception
- Spermicides: In this method, strong spermicidal (sperm-killing) chemical creams, jellies, etc., are applied in the vagina before copulation, which kill the sperms and prevent fertilization.5. Hormonal methods of contraception
- Oral contraceptives or pills: Oral contraceptives prevent ovulation in females. These pills should be taken daily. Birth control pills contain synthetic hormones resembling oestrogen and progesterone which prevent ovulation but allow monthly shedding of the uterine lining through menstrual bleeding.
Corrective methods
- Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP): If conception has taken place, the birth of a child can be avoided by corrective methods. Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) can be done
- by induced abortion or aspiration by a trained doctor. Abortion is a method by which pregnancy can be terminated by either mechanical method or by using hormones. Aspiration involves a virtual vacuuming of the uterine contents by a suction device.
- MTP should be considered as a last step that can be taken. It should be taken only in case of an emergency or if there is an evidence of a genetic disease in the foetus and removal of foetus is necessary for the life of the mother. Abortion. can be legally permitted only within 5 months of pregnancy by a trained doctor on the request of the would be mother. Even husband’s consent is necessary for this.
UP Board Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Population Problems And Control Summary
- India is the second most populous country in the world only next to China. As per the 2011 census, population of India was 121.02 crore.
- The statistical study of human population is called demography.
- Population density means number of individuals per square kilometre at any given time.
- Advancement in agriculture, medicine, industrialization, religious and social customs, illiteracy, economic reasons and desire of a male child are some factors responsible for the growth of population explosion in India.
- Increasing population poses problems to the family as well as the nation.
- The enormous increase of the population can be controlled by education, preventive methods, contraception and corrective methods of population control.
- Preventive surgical methods include, vasectomy (in males) and tubectomy (in females).
- Rhythm method and coitus interruptus are the natural methods of contraception.
- Condoms, diaphragm and intra uterine device are the mechanical contraceptives.
- Spermicides are the chemical contraceptives and oral contraceptive pills are the hormonal contraceptives.
- If conception has taken place, the birth of the foetus can be avoided by corrective methods. MTP can be done using aspiration method or induced abortion.
