Important Questions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Biotechnology And its Applications Very Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. Nematode Specific Genes were introduced into the tobacco host plant using a vector
- pBR322
- Plasmid
- Bacteriophage
- Agrobacterium
Answer: 4. Agrobacterium
Question 2. ‘Cry genes’ that code for insecticidal toxins are present in
- Cotton bollworms
- Nematodes
- Corn borer
- Bacillus
Answer: 4. Bacillus thuringiensis
biology most important questions
Question 3. Mention the chemical change that pro-insulin undergoes, to be able to act as mature insulin.
Answer: Removal of C – peptide (from pro-insulin)
Question 4. What are Cry genes? In which organism are they present H
Answer: The genes that code for lit toxin Cry proteins or toxic proteins are present in Bacillus thingies
Read and Learn More Important Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter Wise
Important Questions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Biotechnology And its Applications
Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Name the Indian crop variety for which in 1997 an American company got a patent right through the IS Patent and Trademark Office. Why did the company claim it to be an invention or a novelty?
Answer:
- An American company got patent rights on Basmati rice through the US Patent and Trademark Office.
- This allowed the company to sell a ‘new’ variety of Basmati in the US and abroad
- This ‘new’ variety of Basmati had been derived from Indian farmer’s varieties. Indian Basmati was crossed with semi-dwarf varieties and claimed as an invention or a novelty.
Question 2. Name one toxin gene isolated from B.thuringiensis and its target pest.
Answer: Toxin gene crvlAc cell Ab targets pest-cotton Bol 1 worm crylAb, controls corn borer
OR
Why does the toxin produced by B.thuringiemis not kill the Bacillus?
Answer: Bt Toxin protein exists as inactive protoxins, the inactive toxin is converted into an active form of toxin only in the presence of the alkaline pH which is not available in the Bacillus.
Question 3. What are cry proteins? With the help of a suitable example, explain how it acts as a biological pesticide.
Answer:
- Cry Protein The insecticidal protein which is produced by the soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis is called cry protein
- For example, proteins encoded by the genes cryl.Ac and cryllAb control the cotton bollworms. The club controls corn borer.
reproduction in flowering plants questions and answers pdf class 12
Question 4.
1. One of the potential uses of genetic engineering is in the correction of a gene defect that has been diagnosed in a child or embryo, Explain how gene therapy is of help in ADA deficiency.
Answer:
- Gene therapy is a collection of methods that allows the correction of a gene defect that has been diagnosed in a child or embryo. Here genes are inserted into a person’s cells and tissues to treat a disease. Correction of a genetic defect involves the delivery of a normal gene into the individual or embryo to take over the function of and compensate for the non-functional gene.
- The disorder is caused due to the deletion of the gene for adenosine deaminase. In some children ADA deficiency can be cured by bone marrow transplantation: in others, it can be treated by enzyme replacement therapy, in which functional ADA is given to tire patients by injection. However, the problem with both of these approaches is that they are not completely curative.
- As a first step towards gene therapy, lymphocytes from the blood of the patient are grown in a culture outside the body A functional ADA cDNA (using a retroviral vector) is then introduced into these lymphocytes, which are subsequently returned to the patient, as these cells are not immortal, the patient requires a periodic infusion of such genetically engineered lymphocytes, if the gene isolated from marrow cells producing ADA is introduced into cells at early embryonic stages, it could be a permanent cure
2. A schematic diagram of matured human insulin is given below :
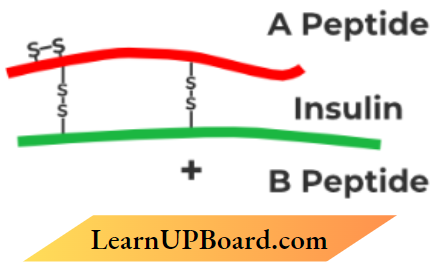
How is the process of its formation naturally in the human body different from that of its formation by rDNA technology? Explain,
- Insulin consists of two short polypeptide chains: chain A and chain B, that are linked together by disulfide bridges In mammals, including humans, insulin is synthesized as a pro-hormone which contains an extra stretch called the C peptide.
- This peptide is not present in the mature insulin and is removed during maturation into insulin. The main challenge for the production of insulin using rDNA techniques was getting insulin assembled into a mature form.
- Eli Lilly an American company prepared two DNA sequences corresponding to A and B, chains of human insulin, and introduced them in plasmids to produce insulin chains.
- Chains A and B were produced separately, extracted, and combined by creating disulfide bonds to form human insu1in
Question 5. What are transgenic animals? How are they being used for vaccine safety and chemical safety testing? Explain.
Answer:
Transgenic animals: Animals that have had their DNA manipulated to possess and express an extra or foreign or transgene.
- Transgenic mice are being developed for use in testing the safety of the vaccine before they are used in humans or transgenic mice are being used to test the safety of the polio vaccine, if successful and found reliable they could replace the use of monkeys to test the safety of batches of the vaccine.
- Transgenic animals are made that carry genes that make them more sensitive to toxic substances than non-transgenic animals, they are exposed to the toxic substances, and the effects are studied (which allows to obtain results in less time)
class 12 biology chapter 2 important questions and answers
Question 6. A child is born with ADA-deficiency
- Suggest an ex-phi in a procedure for a possible life-long (permanent) cure.
- Name any other possible treatment for this disease.
Answer:
- In gene therapy, lymphocytes from the blood of a patient are grown in a culture outside the body, functional ADA cDNA is introduced into these lymphocytes, and these cells are returned to the patient’s body at an early embryonic stage.
- Bone marrow transplantation, enzyme replacement therapy
Question 7. How has the use of agrobacterium as vectors helped in controlling Meloidegyne incognita infestation in tobacco plants? Explain in the correct sequence.
Answer:
- Using the Agrohucteriwti vector nematode specific genes are introduced into the host plant.
- Sense and antisense strands of mRNA are produced.
- ds RNA is formed.
- ds RNA initiates RNAi
- Prevents translation of mRNA or silencing of mRNA of parasite or nematode.
- The parasite will not survive.
Question 8.
- What are transgenic animals?
- Name the transgenic animal having the largest number amongst all the existing transgenic animals.
- Mention any three purposes for which these animals are produced.
Answer:
- Animals that have had their DNA manipulated to possess and express an extra/foreign gene
- Mice
- Normal physiology and development
- Study of disease.
- Biological products
- Vaccine safety
- Chemical safety testing
Question 9. Explain the various steps involved in the production of artificial insulin.
Answer: Two DNA sequences corresponding to A and B polypeptide chains of human insulin were prepared, and these were introduced into Kco/I to produce A and B chains separately, these chains were extracted and combined by creating disulfide bonds.
previous year board questions chapter wise class 12 pdf
Question 10. What was the challenge for the production of insulin using rDNA techniques? How did Eli Lilly produce insulin using rDNA technology?
OR
Explain how Eli Lilly, an American company produced insulin by recombinant DNA technology.
Answer:
- In mammals, including humans, insulin is synthesized as a pro-hormone which contains an extra stretch called the C peptide. This C peptide is not present in the mature insulin and is removed during maturation into insulin.
- The main challenge for the production of insulin using rDNA techniques was getting insulin assembled into a mature form. In 1983, Eli Lilly an American company prepared two DN A sequences corresponding to A and B, chains of human insulin, and introduced them in plasmids of Jf.coli to produce insulin chains.
- Chains A and B were produced separately, extracted, and combined by creating disulfide bonds to form human insulin.
Question 11. Name the organism from which the ‘cry’ genes are isolated. Mention with the help of suitable examples why and how bio-technologists have made use of ‘cry’ genes.
Answer:
- Bt toxin genes were isolated from Bacillus t and incorporated into several crop plants such as cotton. The choice of genes depends upon the crop and the targeted pest, as most – Bt toxins are insect-group sped tic.
- The toxin is coded by a gene crylAc named cry. There are a number of them, for example, the proteins encoded by the genes crylAc and cryllAb control the cotton bollworms, and that of crylAb controls corn borer.
- B. thingie misforms protein cn stats during a particular phase of their growth. These crystals contain a toxic insecticidal protein. The Bt toxin protein exists as inactive protoxins but once an insect ingests the inactive toxin, it is converted into an active form of toxin due to the alkaline pH of the gut which solubilises the crystals.
The activated toxin binds to the surface of midgut epithelial cells and creates pores. that cause cell swelling and lysis and eventually cause the death of the insect.
Important Questions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Biotechnology And its Applications Long Question And Answers
Question 1. Read the following paragraph and answer the questions that follow :
Biotechnology revolves around the “gene of interest”, to open various avenues for human welfare in health, medicine pharma, agriculture etc, using different techniques, tools, and processes. One of the breakthroughs of biotechnology in medicine is the gene therapy.
- Name the human disease for which gene therapy was used for the first time.
- Explain the steps of gene therapy carried out to cure (the disease using the lymphocytes of (lie patient. Why is (his therapy not a permanent cure for the disease?
- Write the possible permanent cure of the disease by the gene therapy that is in progress.
Answer:
- ADA deficiency
- As a first step towards gene therapy. lymphocytes from the blood of the patient are grown in a culture outside the body. A functional ADA cDNA (using a “retroviral vector) is then introduced into these lymphocytes, which are subsequently returned to the patient. However, as these cells are not immortal, the patient requires periodic infusion of such genetically engineered lymphocytes.
- If the gene isolated from marrow cells producing ADA is introduced into cells at early embryonic stages, it could be a permanent cure.
Question 2.RINA interference (RNAi) holds great potential as a therapeutic agent for the treatment of human diseases and as a biocontrol agent for controlling pests in the field of agriculture.
Answer:
- The graph given below illustrates the use of RNAi for the potential treatment of disorders of cholesterol metabolism. Some people possess genetic mutations with elevated levels of the ‘ApoB’ gene which predisposes them to coronary artery diseases Lowering the amount of’ApoB’ can reduce the number of lipoproteins and lower the blood cholesterol.
- Tracy Zimmerman and her colleagues used RNAi in 2006 to reduce the level of of’ApoB’ in non-human primates Cynomofgus monkeys One group of monkeys was given RNAi treatment (Small interfering RNAs. siRNAs) (doses mg/kg siRNAs), a second group of monkeys were given RNAi treatment (doses 2.5 mg/kg siRNAs) and a third group of monkeys were injected with saline as control
The results of the experiments are illustrated in the graph given below :
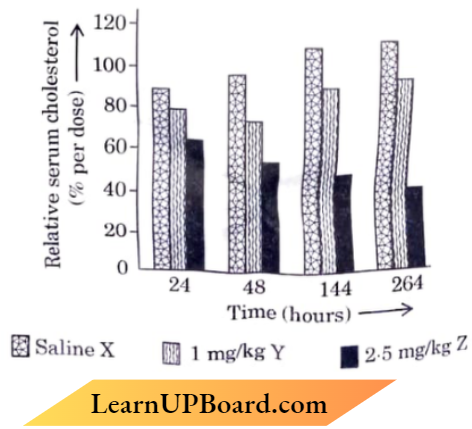
human reproduction class 12 important questions pdf
1. Write your interpretation from the bars X and Z obtained after 264 hours of treatment of monkeys with saline and 2.5 night siRNAs treatment respectively, in comparison to the bars obtained after 24 hours of treatment with saline and 2.5 mg/kg siRNAs.
Answer:
- Lowering the amount of’ApoB’ can reduce the number of lipoproteins and lower the blood cholesterol. According to the graph, we can infer that administering RNAi to the monkeys did indeed reduce the level of the ‘ApoB’ gene which in turn led to lower levels of Relative serum cholesterol
- Also, the reduction in Relative serum cholesterol level was found to be directly proportional to the amount of Si RNA administered, that is, the group of monkeys that were given RNAi treatment (Small interfering RNAs, siRNAs) (doses 1 mg/kg siRNAs) had less Relative serum cholesterol than the group of monkeys were injected saline as control and more Relative serum cholesterol than the group of monkeys was given RNAi treatment (doses 2 5 mg/kg siRNAs).
2. A tobacco plant made transgenic using RNA interference is protected from the parasite Meloidogym incognitia. How is the transgenic tobacco plant able to prevent itself from infestation by the nematode? Explain briefly,
Answer:
- A nematode Mdoidegyne incognitia infects the roots of tobacco plants and causes a great reduction in yield. A novel strategy was adopted to prevent this infestation which was based on the process of RNA interference (RNAi) RNAi takes place in all eukaryotic organisms as a method of cellular defense.
- This method involves the silencing of a specific mRN A due to a complementary dsRNA molecule that binds to and prevents translation of the mRN A (silencing).
The source of this complementary RNA could be infection by viruses having RNA genomes or mobile genetic elements (transposons) that replicate via an RNA intermediate. I sing Agrobacterium vectors, nematode-specific genes were introduced into the host plant. The introduction of DNA was such that it produced both sense and anti-sense RNA in the host cells. - These two RNAs being complementary to each other formed a double-stranded (dsRNA) that initiated RNAi and thus, silenced the specific mRNA A of the nematode. The consequence was that the parasite could not survive in a transgenic host expressing specific interfering RNA. The transgenic plant therefore got itself protected from the parasite.
Question 3. Explain the three different approaches used in the treatment of a person suffering from Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) Deficiency.
Answer:
- In some children ADA deficiency can be cured by bone marrow transplantation; in others
- It can be treated by enzyme replacement therapy, in which functional ADA is given to the patient by injection.
- However, the problem with both of these approaches is that they are not completely curative. As a first step towards gene therapy, lymphocytes from the patient’s blood are grown in a culture outside the body. A functional ADA cDNA (using a retroviral vector) is then introduced into these lymphocytes, which are returned to the patient.
- However, as these cells are not immortal, the patient requires periodic infusion of such genetically engineered lymphocytes. However, if the gene isolated from marrow cells producing ADA is introduced into cells at early embryonic stages, it could be a permanent cure.
Question 4. Insulin in the human body is secreted by the pancreas as prohormone or proinsulin. The schematic poly pet ide structure of proinsulin is given below. This proinsulin needs to undergo processing before it becomes functional in the body. Answer the questions that follow
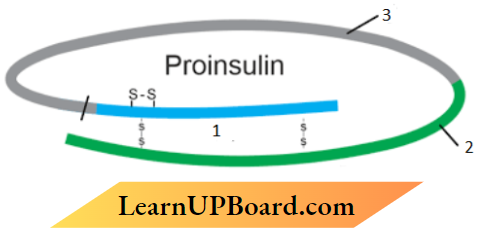
- State the change the proinsulin undergoes at the time of its processing to become functional.
- Name the technique the American company Eli Lilly used to commercialize human insulin.
How are the two polypeptides of a functional I insulin chemically held together?
Answer:
- a ‘C’ Peptide is removed
- rDNA technology or Recombinant DNA Technology.
- Disulfide bonds.
