Class 12th Biology Important Questions Chapter 6 Evolution Very Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Mention one example each from plants and animals exhibiting divergent evolution.
Answer:
Thorn of Bougaimilira and tendrils of Cucurbita, forelimbs of whales bats, cheetahs,s and humans (all mammals or vertebrate hearts or vertebrate drains
Question 2. Write the names of the following:
- A 15 ape-like mya primate
- A 2 mya primate that In ed in East African grasslands
Answer:
- Dryopithecus
- Australopithecines or Australopithecus or Homo habilis
Question 3. State two postulates of Oparin and Haldane concerning the origin of life.
Answer:
- The first form of life could have come from existing non-living organic molecules RNA And Protein
- Formation of life was preceded by chemical evolution or formation of diverse organic, molecules from inorganic coast entrants
“molecular basis of inheritance class 12 notes bank of biology “
Class 12th Biology Important Questions Chapter 6 Evolution Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Wings of birds and wings of butterflies contribute to locomotion, and the evolution of such organs is a result.
Answer:
They are not anatomically similar in structure but perform the same function, hence these are analogous structures type of evolution is convergent evolution similar habitats of birds and butterflies have resulted in. the selection of similar adaptive features (wings.) in different groups of organisms, but towards the same function convergent evolution.
Read and Learn More Important Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter Wise
Question 2. According to the Darwinian theory of natural selection, the rate of appearance of new forms is linked to the life cycle or the life span of an organism. Explain with the help of an example.
Answer:
A colony of bacteria (say A) growing in a given medium has built-in variation in terms of the ability to utilize a feed component, a change in the medium composition would bring out only that part of the population B) that can survive under the new conditions In due course of time this variant population outgrows the others and appears as new species thus organisms with shorter life-cycle or life-span will undergo evolution faster or for the same thing to happen in fish or fowl would take millions of years as life spans of these animals are in years.
Question 3. Explain the Ilardy-Weinberg principle with the help of an algebraic equation.
Or
With the help of an algebraic equation, how did Ilardy-Weinberg explain that in a given population the frequency of occurrence of alleles of a gene is supposed to remain the same through generations?
Answer:
The Principle says that allele frequency in a population is stable and is constant from generation to generation, the gene pool remains constant and expressed as p2 +2pq+ q2/ ( p+q)2
- Where p2 = frequency of individuals with A A genotype
- Where q2= frequency of individuals with a genotype
- Where 2pq = frequency of individuals with Aa genotype
“biology class 12 ch 6 “
Question 4. What is adaptive radiation? How did Darwin explain it?
Answer:
The process of the evolution of different species in a given geographical area starting from a point and radiating to other areas of geography (habitats) is called adaptive radiation He observed that there were many different varieties of finches (Darwin’s finches) in the same island, and all those varieties evolved ou the island itself, from the original seed-eating features many other forms with altered beaks arose to become insectivorous or vegetarian finches.
Question 5.
1. Differentiate between analogous and homologous structures.
Answer:
- Aitalogous-Anatomically embryonic development, origin, and structure are not similar though perform similar functions and are a result of convergent evolution.
- Honiologus – Anatomically embryonic development, origin, and structure are similar (but perform different functions) and are a result of divergent evolution.
2. Select and write analogous structures from the list given below :
- Wings of butterflies and birds
- Vertebrate hearts
- Tendrils of bougainvillea and cucurbita
- Tubers of sweet potato and potato
Answer: 1 Or 4
Question 6. How can the Hardy- Weinberg Equilibrium be affected? Explain giving three reasons.
Answer:
- Gene Migration Or Gene Flow: When the migration of a section of the population occurs to another place and gene frequencies change in the original as well as in the new population.
- Genetic drift: If the same change occurs by chance or new genes or alleles are added to the new population and these are lost from the old population.
- Mutation: Pro existing advantageous mutations when selected will result in new phenotypes.
- Genetic recombination: Variation in characteristics will be there because of genetic recombination, during meiosis and also due to random fusion of gametes.
- Natural selection: Heritable variations enabling better survival enabled organisms to reproduce and leave a greater number of progeny.
Question 7. Write the characteristics of Raniapithecus, Drvopitheeiis, and Neanderthal man.
Answer:
- Raniapithecus: I fairy Or walked like gorillas and chimpanzees, more man-like.
- Drvopitheeiis: Hairy or walked like gorillas and chimpanzees, more aped ike.
- Neanderthal man: brain size is 1400cc, used hides to protect their body or buried their dead,
Question 8. Excessive and continuous use of pesticides has resulted in the evolution of some new species of pests. Explain what must have led to this. What is this type of evolution called?
Answer:
- Excess use of herbicides, pesticides, etc. only resulted in the selection of resistant varieties in a much lesser time scale.
- Hence, resistant organisms seel Is appear in a time scale of months or years and not centuries.
- These are examples of evolution by anthropogenic action.
- This also tells us that evolution is not a directed process in die sense of determinism.
- It is a stochastic process based on chance events in nature and chance mutation in the organisms.
“class 12th biology molecular basis of inheritance “
Question 9. What type of organs eye of an Octopus and that of a human called? Give another example from the animal group and one from the plants of such organs. Name and explain the evolutionary process they exhibit.
Answer:
- The eyes of the octopus and mammals are an example of analogous organs. Sweet potato (root modification) and potato.
- Wings of butterflies and birds.
- The similar habitat has resulted in the selection of similar adaptive features in different groups of organisms but toward the same function, analogous structures are a result of convergent evolution – different structures evolving for the same function and hence having similarity.
Class 12th Biology Important Questions Chapter 6 Evolution Long Question And Answers
Question 1.
1. Describe the observations made on the collection of white-winged moths and dark-winged moths in England between the years 1850 and 1920. What did these observations lead to?
Answer:
Before industrialization tree bark was covered with light-colored lichens, In this background white-winged moth survived but dark colored moth was picked out. by predators, post-industrialization tree trunks became- dark due to industrial smoke and soot, under this condition, and the white-winged moth did not survive due to predators, while the dark-winged/melanized moth survived, this showed that organism that is better adapted to survive are selected by Nature/Natural selection.
2. How is the use of herbicides, pesticides, and antibiotics by humans for various purposes, comparable with the observations made on moths in the above question? What is this type of phenomenon called?
Answer:
Excessive use of these chemicals has resulted in the selection of resistant varieties, in u much lesser time (scale).
These are examples Of evolution by anthropogenic action.
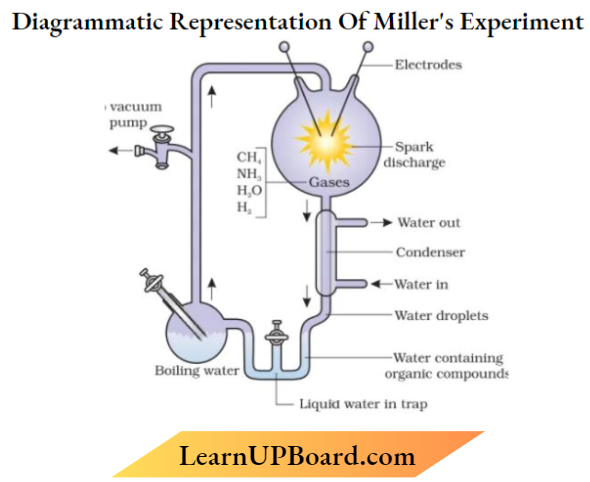
Question 2. Describe S.E. Miller’s experiment. Comment on the observations he made and his contribution towards the origin of life on Earth.
Answer:
High temperature (800″C), high energy radiation, reducing atmosphere created, by electric discharge in a closed flask, containing CH4, IE. NIC. and water vapors in the experimental setup.
bank of biology class 12 molecular basis of inheritance
Observation and Contribution
- Formation of amino acids
- The first form of life arose slowly through evolutionary forces in front of living molecules or abiogenesis.
Question 3. Taking an example of white-winged moths and dark-winged moths of England in pre and post-industrialised eras, explain evolution by natural selection.
Answer:
An interesting observation supporting evolution by natural selection comes from England In a collection of moths made in the 1850s, therefore before industrialization set in, it was observed that there were more white-winged moths on trees than dark-winged or melanic moths.
- However, in the collection carried out from the same area, but after industrialization, in 1920, there were more dark-winged moths in the same area, therefore the proportion was reversed.
- The explanation put forth for this observation was that ‘predators will spot a moth against a contrasting background’.
- During the post-industrialization period, the tree trunks became dark due to industrial smoke and soot. Under this condition, the white-winged moth did not survive due to predators, dark winged or melanised moth survived.
- Before industrialization set in, thick growth of almost white-colored lichen covered the trees – in that background, the white-winged moth survived but the Clark color. red moth was picked out by predators.
- Lichen will not grow in areas that are polluted. Hence, moths that were able to camouflage themselves, therefore, hide in the background, survived.
- This understanding is supported by the fact that in areas where industrialization did not occur example in rural areas, the count of matric moths was low.
- This showed that in a mixed population, those that can better adapt, survive and increase in population size. Remember that no variant is completely wiped out.
