Class 10 Biology Chapter 4.1 Accumulation Of Variation During Reproduction Heredity
Individuals of a species appear similar because they have a common body design. Careful observation shows that they have subtle differences. These differences or variations are quite small and fewer in the case of asexually reproducing organisms. They are quite abundant in sexually reproducing organisms. In sugarcane fields multiplied by vegetative propagation, all the plants look similar except for minor differences. This is because in asexual reproduction variations develop only due to errors in DNA replication.
In sexually reproducing organisms, variations are so abundant that we can easily recognize one individual from another.
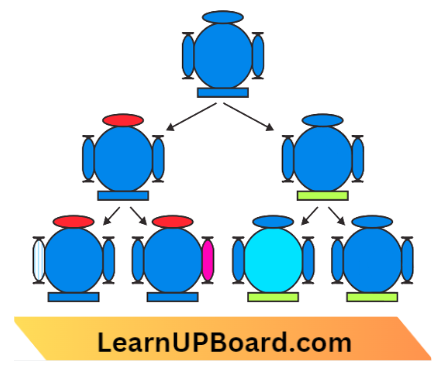
- There is a regular reshuffling of variations as well as the addition of new variations due to
- Separation of homologous chromosomes during gametogenesis.
- Chance coming together of individual chromosomes in gametes.
- I am crossing over during meiosis.
- Chance coming together of homologous chromosomes during fertilization.
- Change in genetic material due to error of DNA copying and faulty distribution of chromosomes.
variation definition class 10
Class 10 Biology Chapter 4.1 Accumulation Of Variation During Reproduction
Why with each generation, does inheritance provide a common basic body design, along with differences from the previous generation?
Variations appear during reproduction, whether it is asexual or sexual. Each new generation inherits two things from the parent generation.
- A common body design and subtle changes are present in that generation. The new generation develops its variations in addition to variations received from the parents.
- The process of accumulation of variations goes on. Of course, there are fewer in asexually reproducing organisms like bacteria and numerous in sexually reproducing organisms.
- However, all the variations do not survive. Harmful variations are eliminated with the death of the individuals. Useful variations survive as they increase the adaptability and competence of the individuals.
- Neutral variations may persist or get eliminated. Some of them can help the individuals in pre-adaptation like surviving during heat waves in temperate areas or resisting a new insecticide and antibiotic.
Therefore, environmental factors determine the usefulness and accumulation of variations. The variants form the basis for the evolution of new types.
Class 10 Biology Chapter 4.1 Accumulation Of Variation During Reproduction Short Question And Answers
Question 1. If trait A exists in 10% of a population of an asexually reproducing species and trait B exists in 60% of the same species, which trait is likely to have arisen earlier?
Answer:
A trait that is present in a larger number of individuals must have developed earlier than the one that is present in a smaller number of individuals. Therefore, trait B present in 60% population must have developed earlier than trait A found in 10% population.
Question 2. How does the creation of variations in a species promote survival?
Answer:
All types of variations do not promote survival.
Two types of variations promote survival.
- Useful variations that help the individuals to better adapt to the environment and enhance competitiveness in the struggle for existence.
- Preadaptation or those neutral variations become useful in the changing environment.
For example, bacteria can tolerate higher temperatures if a heat wave sweeps a temperate region.
What is the importance of variation
Question 3. State the two advantages of variations.
Answer:
They help in the struggle for existence and natural selection.
Some variations function as preadaptation to changing environments and adverse conditions.
Question 4. Variations that confer an advantage to an individual organism only will survive in a population. Justify.
Answer:
Survival of an individual depends upon its ability to tolerate stressful conditions of the environment, compete with other individuals, and obtain proper food, shelter, and mate.
- It results in differential reproduction and transfer of useful variations to the next generation.
- Under stressful conditions, variations that function as pre-adaptations will be useful and help some individuals to survive while others remain weak and die.
Question 5. Explain how organisms create an exact copy of themselves.
Answer:
Organisms create exact copies of themselves through reproduction. In reproduction, whether asexual or sexual, the genetic traits of the parents are transferred to the individuals of the new generation. Hence, the exact copy. Of course, some small variations do occur due to errors in DNA copying and shuffling of chromosomes.
the importance of variation class 10th
Question 6. Define the term variation. Why is variation beneficial to a species? List two reasons for the appearance of variations among the progeny formed by sexual reproduction
Answer:
Variation: It is the difference in structure, physiology, or behavior among individuals of the same species. Advantages. See SAQ 1.
Reasons: Separation of two chromosomes of each type during meiosis
- Crossing over
- Chance coming together of chromosomes during fertilization
- Errors in DNA copying and mutations.
