Important Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 – Microbes In Human Welfare Question And Answers
Question 1. What for are Cyclosporin A anil Streptokinase bioactive molecules prescribed by a doctor
Answer:
- Cyclosporin A – It is used as an immunosuppressive agent.
- Streptokinase – It is used as a clot bluster for removing clots from blood vessels.
Question 2. Assertion: Large holes in ‘Swiss cheese’ are due to the production of a large amount of carbon dioxide by a specific microbe
Reason: The specificity of the characteristic texture, flavour and taste of Swiss cheese is due to the use of the bacterium Propionibacterium Sherman.
- Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
- Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
- The assertion is true, but Reason is false
- Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer: 1. Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion
microbes in human welfare
Question 3. Some cyanobacteria in aquatic and terrestrial environments that enrich the soil by fixing atmospheric nitrogen are
- Rhizobium and Azotobacter
- Azospirillum and Glomus
- Anabaena and Nostoc
- Azospirillumand Azotobacter
Answer: 3. Anabaena and Nostoc
Read and Learn More Important Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter Wise
Question 4. The microbes commonly used in kitchens are
- Lactobacillus and Yeast
- PeniciiHum and Yeast
- Microspora and E.coli
- Rhizopus and
Answer: 1. Lactobacillus and
Important Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 – Microbes In Human Welfare Short Question And Answers:
Question 1. Fanners are often suggested to use the following organisms in their cropland to improve soil fertility. Explain.
- Rhizobium
- Anabaena
Answer:
- Rhizobium is a bacterium found in soil that helps in fixing nitrogen in leguminous plants
- It attaches to the roots of the leguminous plant and produces nodules. These nodules fix atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into ammonia that can be used by the plant for its growth and development.
- Anabaena plays a significant role in farming where it is used as a biofertilizer and soil stabilizer.
Question 2. Organic farmers use Trichoderma and liacuas as biological control agents. Explain.
Answer:
- Trichoderma – species are free-living fungi that are very common in the root ecosystems. They are effective biocontrol agents of several plant pathogens Baculoviruses are pathogens that attack Insects and other arthropods.
- Baculovirus – The majority of baculovirus ruses used as biological control agents are in the genus Nucleopolyhedrovtrus. These viruses are excellent candidates for species-specific, narrow-spectrum insecticidal applications. They have been shown to have no negative impacts on plants, mammals, birds, fish or even on non-target insects.
“human health and welfare “
Question 3. A particular cyanobacterium is spread by (lie farmers in their fields while growing paddy). Name the cyanobacteria used and give two advantages of it.
Answer:
Cyanobacteria like Anaebena. Nosiocetc can fix atmospheric No, decompose organic wastes and residues, detoxify heavy metals, pesticides, and other xenobiotics, catalyze nutrient cycling, suppress the growth of pathogenic microorganisms in soil and water, and produce some bioactive compounds that contribute to plant growth.
Question 4. Study the given diagrams of Sewage Treatment Plants (STP) and answer the questions that follow:
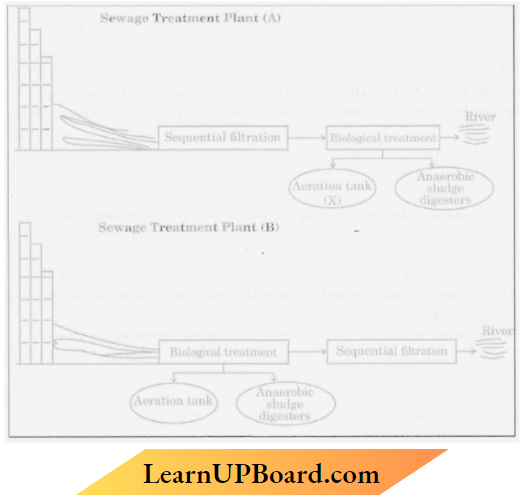
- Which of the two Sewage Treatment Plants? (A) or (B), will be more effective in treating human excreta in municipal waste?
- How is the primary effluent treated in the aeration tanks till there is a significant reduction in the BOD of (the effluent?
Answer:
- Sewage Treatment Plants (A) will be more effective in treating human excreta in municipal waste.
- The primary effluent is taken to aeration tanks, where it is constantly agitated mechanically. Air is pumped into it. periodically A large number of aerobic heterotrophic microbes grow in the aeration tank to form floes.
- Due to microbial activity, the organic matter gets digested The microbes convert it into microbial biomass and release the minerals Due to the breakdown of organic matter, the BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) of the wastewater reduces to about 10 to 15% of raw sewage.
“human welfare society plan pdf “
Question 5. Write the different components of activated sludge. Explain the different ways it can be used further in the sewage treatment process.
Answer:
- Dining secondary treatment BOD- of sewage or wastewater is reduced significantly the effluent is then passed into a settling tank where the bacterial “floes are allowed to sediment called activated sludge.
- The floes are masses of bacteria associated with fungal filaments to form mesh-like structures.
Question 6.
1. Name the genus of baculovirus that acts as a biological control agent despite being a pathogen. Justify by giving three reasons that make it an excellent candidate for the job,
Answer:
Genus – Nucleopolyhedrovirus, species-specific, Narrow spectrum. No negative impact on (plants or mammals or birds or fish) non-target organisms.
2. ‘’Micro-organisms play an important role in the biological treatment of sewage.” Justify
Answer:
Primary effluent is passed into aeration tanks, constantly agitated and the air is pumped in. This allows the growth of useful aerobic microbes into flow or masses of bacteria and fungal filaments), these microbes consume organic matter and reduce the Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) of effluent.
Question 7.
- Mention the difference in the level of BOD before and after the secondary treatment of sewage water.
- Write the importance of floes during the secondary treatment of sewage.
Answer:
1. Before – High. After- Low
2. Reduces BOP Biochemical Oxygen Demand
Question 8. Expand ‘LAB’. How are LABs beneficial to humans? (Write any two benefits).
Answer:
Lactic Acid Bacteria,
- They produce acid which partially digests the milk protein or sets milk into curd.
- They improve nutrition and quality by producing Vitamin B.
- Check disease-causing microbes in our stomach
Question 9. Your advice is sought to improve the nitrogen content of the soil to be used for the cultivation of a noil-leguminous terrestrial crop.
- Recommend two microbes that can enrich the soil with nitrogen.
- Why do leguminous crops not require such enrichment of the soil?
Answer:
- Azospiri/fum Azotobacter Anabaena Nosioc Oscillaloriu rankia
- They can fix atmospheric nitrogen, due to the presence of Rhizobium which is a V-fixing bacteria in their root nodules.
microbes in human welfare notes pdf download
Question 10. Why are microbes like Spirulina being produced on a commercial scale? Mention its two advantages.
Answer:
- As a source of food protein.
- Reduces environmental pollution or solves the problem of hunger and malnutrition or a rich source of protein or low-cost production.
Question 11.Name (the microbes that help the production of the following products commercially:
- Statin
- Citric acid
- Penicillin
- Butyric acid
Answer:
- Monascus purpureas
- Aspergillus
- PenicilHum notatum
- Clostridium butylicum
Question 12. Name the first antibiotic discovered and by whom.
Answer: Penicillin by A. Fleming.
Question 13. What is the pathogenic property of baculovirus, used as a biological agent? Name the genus of these organisms.
Answer:
- Baculoviruses are pathogens that attack insects and other arthropods.
- The majority of baculoviruses used as biological control agents are in the genus
Question 14. Explain the changes that mills undergo when a suitable starter or inoculum is added to it. flow does the end product formed prove to be beneficial for human health?
Answer:
Lactobacillus lactic acid bacteria (LAB) present in inoculum, grows in milk at a suitable optimum temperature, multiplies converting milk to curd,-and produces acids that coagulate and partially digest the milk proteins. This improves its nutritional quality by increasing Vitamin B12, and LAB checks diseases causing.
Question 15. Why does an organic farmer intentionally not use toxic chemicals to kill the pests which damage the last crops? Explain giving three reasons.
Answer:
- Toxic chemicals can have adverse side effects cause biomagnification,
- it kills both useful and harmful life forms indiscriminately,
- It eradicates pests not control pests,
- Beneficiary predatory and parasitic insects which depend upon them as food or hosts would not be able to survive,
- It disturbs the food chain food webs or vibrant ecosystems.
Question 16.
1. Organic farmers prefer biological control of diseases and pests to the use of chemicals for the same purpose. Justify.
Answer:
- Reduces dependence on toxic chemicals.
- Protects our ecosystem or environment.
- Protects and conserves non-target organisms they are species-specific.
- These chemicals being non-biodegradable may pollute the Permanently.
- These chemicals being non-biodegradable may cause biomagnification.
2. Give an example of a bacterium, a fungus and an insect that are used as biocontrol agents.
Answer:
- Bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis Fungus Trichodcnva.
- Insect Lady bird or Dragonfly or Moth.
Question 17. The three microbes are listed below. Name the product produced by each one of them and mention their use.
- spergillusniger
- Trichodermtt polysporum
- Monascus purpure
Answer:
- Aspergillus niger – Citric Acid, natural preservative or flavouring agent.
- Trichodennapolysporum – Cyclosporin A, immunosuppressive agent.
- Monascus purpureas – Statin, blood cholesterol-lowering agent.
Question 18. Baculoviruses are good examples of biocontrol agents. Justify by giving three reasons.
Answer:
- Species-specific narrow-spectrum insecticidal application
- They have no negative impact on plants mammals or birds or fish or non-target insects
- They are beneficial for 1 PM (Integrated Pest Management) or the Pest Management Programme.
microbes in human welfare class 12 ncert
Question 19. Secondary treatment of the sewage is also called Biological treatment. Justify this statement and explain the process.
Answer:
Involves biological organisms such as aerobic and anaerobic microbes or bacteria and fungi to digest or Consume organic waste Primary effluent is passed into an aeration tank where vigorous growth of aerobic microbes (floes) takes place. BOD is reduced (microbes consume a major part of organic matter), effluent is passed to a settling tank where floe sediment produces activated sludge, and sludge is pumped to an anaerobic sludge digester to digest bacteria and fungi.
Question 20. Identify A, B, C, D, and E and find the following table :
Answer:
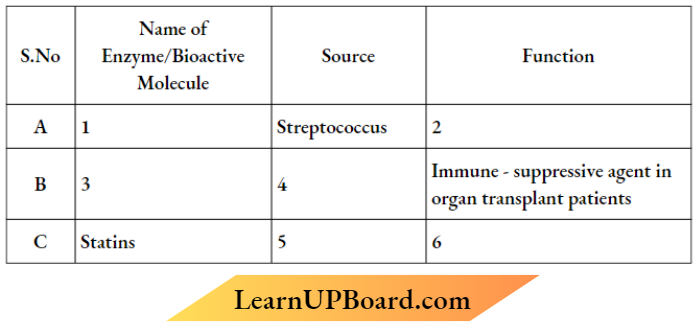
- Streptokinase
- ‘clot buster’
- cyclosporin A
- Trichoderma polysporrum.
- Monascus purpureus
- Blood-cholesterol-lowering agents.
Important Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 – Microbes In Human Welfare Long Question And Answers
Question 1. Describe the process of secondary treatment given to municipal wastewater (sewage) before it can be released into fresh waterbodies. Mention another benefit provided by this process.
Answer:
Process of secondary treatment Passing of primary effluent into a large aeration tank which is constantly agitated mechanically and air is pumped into it allowing vigorous growth of useful aerobic microbes into floes
↓
Microbes consume a major part of organic matter in effluent which significantly reduces BOD
↓
Now effluent is passed into a settling tank where floes are allowed to settle or sediment called activated sludge
↓
Digestion of activated sludge by anaerobic microbes and effluents from secondary treatment can be released into river or stream
↓
This resulted in the production of Biogas (CH4, IBS and CO2) which can be used as a source of energy.
