Important Questions Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Principles Of Inheritance And Variation Very Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. The case of Down’s syndrome in humans is;
- Extra copy of an autosome
- Extra copy of a sex chromosome
- Absence of an autosome
- Absence of a sex chromosome
Answer: 1. Extra copy of an autosome
Question 2. Which of the following features shows the mechanism of sex determination in honeybees’
- An offspring formed from the union of a sperm and egg develops as a male
- Males have half the number of chromosomes than that of female
- The females are diploid having 32 chromosomes ”
- Males have fathers and can produce sons-.
questions on principles of inheritance and variation
Answer: 2. Males have half the number of chromosomes than females.
Question 3. Select the incorrect pair:
- Sickle-cell anaemia: Autosomes like recessive
- Haemophilia Autosome linked recessive trait,
- Colourblindness Sex sex-linked recessive trait
- Thalassemia: Autosome-linked recessive trait
Answer: 2. Haemophilia: Autosome-linked recessive trait
Read and Learn More Important Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter Wise
Question 4. An example of a human trait where a single gene can exhibit multiple phenotypic expression is
- Phenylketonuria
- Cystic fibrosis
- Thalassemia
- Haemophilia
Answer: 1. Phenylketonuria
Question 5. The life cycle of Drosophila melanogaster is completed in
- 7 days
- 14 days
- 21 days
- 28 days
Answer: 2. 14 days
Question 6. How many types of gametes would developed by an organism with genotype AaBBCcDD?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer: 4. 4
Question 7.Assertion (A): There is an expression of only one gene of the parental character in a Mendelian Monohybrid cross in Ft generation
Reason (R): In a dissimilar pair of factors one member of the pair dominates the other
- Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
- Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Answer: 1. Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
” class 12 biology chapter 5 questions and answers”
Question 8. In Pisum sativum, the flower colour may be Violet (V) or White (v). What proportion of the offspring in a cross of VV vv would be expected to be violet
- 25%
- 50%
- 75%
- 100%
Answer: 4. 100%
Question 9. Which one of the gene pairs is expected to give a ratio of 1 1: I I in the progeny of a Mendelian Dihybrid cross
- AaBb×AbBb
- A ABB × AaBb
- AaBb × aabb
- A ABB × aabb
Answer: 3. AaBh x aabb
Question 10. The progeny of a cross between two snap-dragon plants heterozygous for flower colour, bearing different coloured flowers would be:
- 25% red, 50%
- pink, 25% white
- 50% red, 50% white
- 75% red, 25% white
Answer: 2. 25% red. 50% pink, 25% white.
Question 11. Study the given pedigree of a family and select the trait that shows this pattern of inheritance
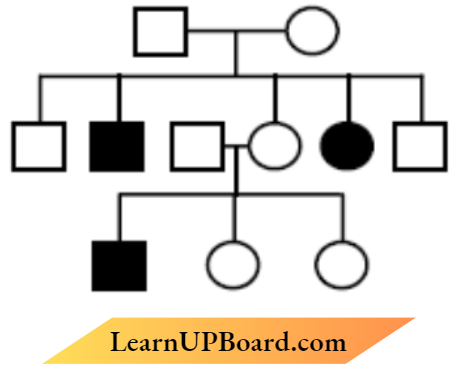
- Autosomal recessive, Phenylketonuria
- Sex-linked recessive. Colour-blindness
- Autosomal dominant. Myotonic dystrophy
- Sex-linked dominant. Vitamin I) resistant rickets
Answer: 1. Autosomal recessive. Phenylketonuria
Question 12. A child with blood group A has a father with blood group B and a mother with blood group AB What would be the possible genotypes of the parents and the child Choose the correct option:
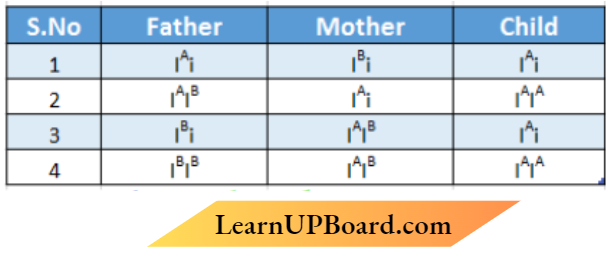
Answer: 3. Father – IBi, Mother – IAiB, Child – I A i
Question 13. In a hybrid Mendelian cross, garden pea plants heterozygous for violet flowers and round seeds are crossed with homozygous white flowers and wrinkled seeds. The genotypic and phenotypic ratio of F, progeny would be:
- 9:3:3: 1
- 1:2:2: 1
- 1:1.1.1
- 3: 1
Answer: 3. 1: 1: 1: 1
Question 14. Colour blindness is a sex-linked recessive trait in humans. A man with normal colour vision marries a woman who is colourblind. What would be the possible genotypes of the parents, the son and the daughter of this couple?
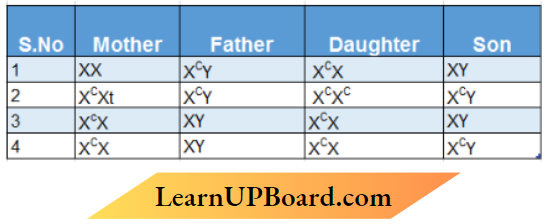
Answer: 1. Mother- XX, Father – XCY, Daughter- XCX, Son – XY
Question 15. Given below are the pairs of contrasting traits in Pisum sativum as studied by Mendel Select the incorrectly mentioned option from the table given below:
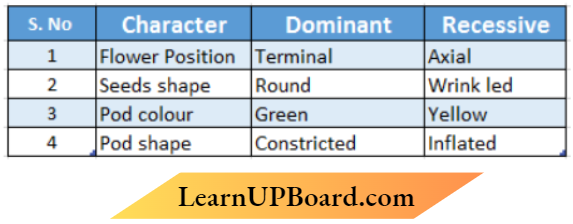
Answer: 1 Or 4
Question 16. How many types of gametes can be produced in a diploid organism which is heterozygous for 4 loci?
- 4
- 8
- 16
- 32
Answer: 3. 16
principles of inheritance and variation pyq neet
Question 17. Given below is a Karyotype obtained after analysis of foetal cells for a probable genetic disorder.
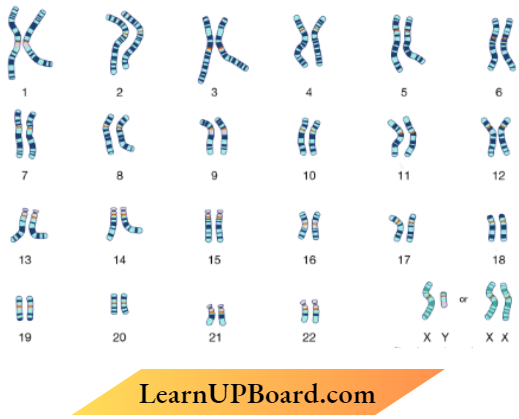
Based on the above Karyotype, the chromosomal disorder detected in the unborn foetus and the consequent symptoms the child may suffer from are
- Down’s syndrome: Gynecomastia, overall masculine development
- Down’s syndrome: Furrowed tongue, short stature
- Klinefelter’s syndrome Gynecomastia, Masculine development.
- Klinefelter’s syndrome: Rudimentary ovaries, short stature
Answer: 3. Klinefelter’s syndrome: Gynecomastia, Masculine development.
Question 18 The recombinant Frequency between the four linked genes is as follows:
- Between X and Y is 40%.
- Between Y and Z is 30%.
- Between Z and W is 10%.
- Between W and X. is 20%.
Select the option that shows the correct order of the position of W, X. Y and Z genes on the chromosome:
- Y – X -Z -W
- Y – W – Z – X
- X- Y -Z -W
- Z – X – Y – W
Answer: 2. Y – W – Z – X
Question 19. Write the possible genotypes of a person with blood group ‘B
Answer:
The genotype for blood group B is H1 in homozygous condition and H is in heterozygous condition
Question 20. Write the dominant traits in pea plants observed by Mendel concerning:
- colour of a pea pod.
- flower position.
Answer:
- Green pod colour was the dominant
- The terminal flower position was recessive to the axial position
Question 21. Write the symbolic representation used in a pedigree chart showing
- a carrier mother and
- a sufferer son, concerning haemophilia.
Answer:
A carrier mother→![]()
A sufferer’s son → ![]()
Question 22. Assert ion: The progenies of a test cross can be easily analysed to predict the genotype of the test organism.
Reason: In a typical test cross, an organism showing a recessive phenotype is crossed with a recessive parent instead of self-crossing
- Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion
- Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion
- The assertion is true, but Reason is false
- Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer: 3. Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
Question 23.
1. Name a human genetic disorder due to the following :
- An additional X-chromosome in a male
- Deletion of one X-chromosome in a female
Answer:
- Klinefelter’s Syndrome
- Turner’s Syndrome
2. State what does aneuploidy lead to.
Answer:
Abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell. Down’s Syndrome or Turner’s Syndrome or Klinefelter’s Syndrome
Question 24. State Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment.
Answer:
When two pairs of traits (characters) are combined in a hybrid segregation of one pair of characters is independent of the other pair of characters.
Question 25. Write one example of each of the organisms exhibiting
- Male heterogamety, and
- Female heterogamety.
Answer:
- Human or Drosophila or Grasshopper
- Birds Chicken
Question 26. Write the sex of a human having XXY chromosomes with 22 pairs of autosomes. Name the disorder this human suffers from.
Answer:
Mate, Klinefelter’s syndrome
Question 27. Name the type of cross that would help to find the genotype of a pea plant bearing violet flowers.
Answer:
Test cross
Question 28. A colour-blind bos is born to a couple with normal colour vision. Write the genotype of the parents.
Answer:
Mother-Xc
X Father-XY
Important Questions Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Principles Of Inheritance And Variation Short Question And Answers
Question 1.
1. Write two closely linked genes that control a-Thalassemia.
Answer:
Thalassemia is controlled by two closely linked genes HBA1 and HBA2 on chromosome 16 of each parent and it is observed due to mutation or deletion of one or more of the four genes
2. Differentiate between Thalassemia and Sickle cell anaemia based on their effect on the globin molecule of haemoglobin.
Answer:
Thalassemia differs from sickle-cell anaemia in. that the former is a quantitative problem of synthesising too few globin molecules while the latter is a qualitative problem of synthesising an incorrectly functioning globin
Question 2.
1. Mendel did not explain the expression of incomplete dominance in plants, (give an example of a flower exhibiting incomplete dominance. Name and state the Law of Mendel that the genes which exhibit incomplete dominance follow.
Answer:
- Antirrhinum Snapdragon or Dog flower or Four o’clock plant or A Law of segregation.
- Allele or factors of a pair segregate from each other such that a gamete receives only one of the two factors.
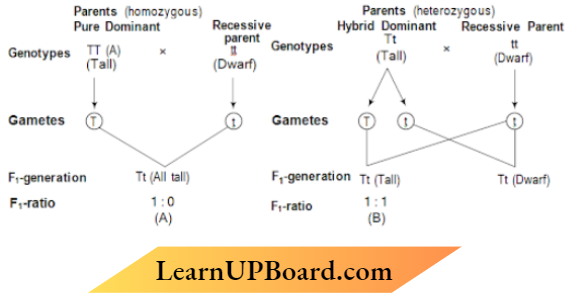
2. Your teacher gave you a tall pea plant and asked you to find out whether the plant is homozygous or heterozygous. Mow will you proceed to find the genotype of the given plant?
Answer:
The Genotype was found by test cross. The Crossing of Unknown plant with recessive parent.
Question 3. Why is the frequency of red-green colour blindness more in human males than in females? Explain.
Answer:
The gene for colour blindness is located on the X chromosome in humans, it is a recessive gene, since human males have a single X chromosome the recessive gene always expresses when present, whereas in human females as they have two X chromosomes (the trait is expressed only if both the sex chromosomes have this reason e gene
Question 4. A lipophilic father can never pass the gene for haemophilia to his son. Explain.
Answer:
It is a sex-linked recessive disorder in which the X chromosome has the haemophilic gene, the Son inherits an ‘S’ chromosome from the father and the gene for haemophilia is not present on the S chromosome
Question 5.
1. What happens when chromatids fail to segregate during cell division cycle? Explain your answer with an example.
Answer:
Failure of segregation of chromatids during the cell division cycle results in the gain or loss of a chromosome (s), called aneuploidy. For example, Down’s syndrome results in the gain of an extra copy of chromosome 21
2. ABO blood groups are a good example of co-dominance. Justify.
Answer:
In blood groups I ‘ and I1’ are present together they both express their types of sugars this is because of co-dominance, lienee red blood cells have both A and B types of sugar polymers
Question 6.
1. Generally it is observed that human males suffer more than human females, who rarely suffer from it. Explain giving reasons.
Answer:
This is a sex-linked X chromosomes recessive disease, the heterozygous female carrier for haemophilia may transmit the disease to sons (mate progeny), and the possibility of a female becoming a haemophimophilia is extremely rare haemophilia because the mother of such a female has to be at least carrier and the father should be haemophilic.
2. F1 progeny of pea plant bearing violet flowers and snapdragon plant bearing red flowers were soiled to produce their respective F2 progeny. Compare the phenotypes, the genotypes and the pattern of inheritance of their respective F1 progeny.
Answer:
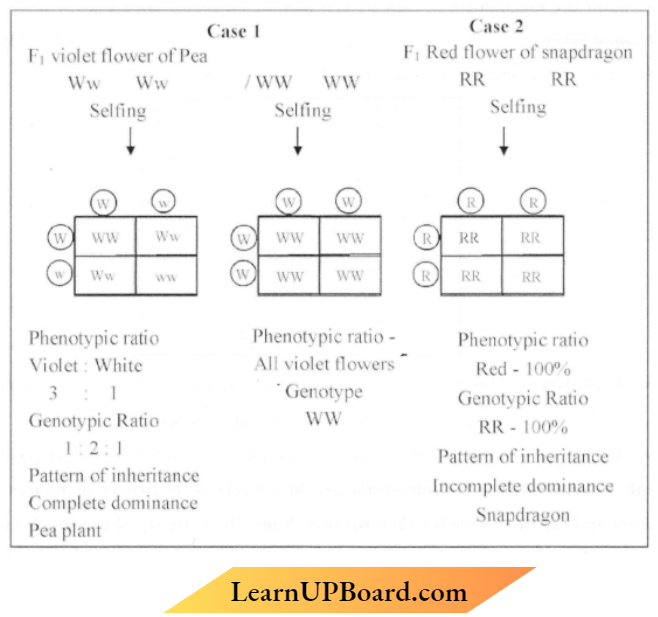
Question 7.
1. Differentiate between pleiotropy and polygenic inheritance by taking one example of each.
2. How is polygenic inheritance different from pleiotropic? Give one example of each.
Answer:
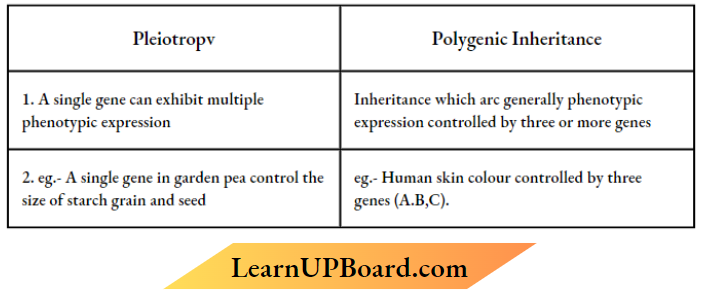
Question 8.
1. How does mutation occur?
Answer:
Eosstdeletion or gain (insertion duplication or addition) or change in position of DNA segments/chromosome
2. Differentiate between point mutation and frameshift mutation.
Answer:
Mutation due to a change in a single base pair of DNA is point mutation. Insertion or deletion of one or two bases changes the reading frame from the point, of insertion or deletion.
Question 9. Explain the mechanism of ‘sex determination’ in birds. How does it differ from that of human beings?
Answer:
In birds, sex determination takes place by the ZW -method;
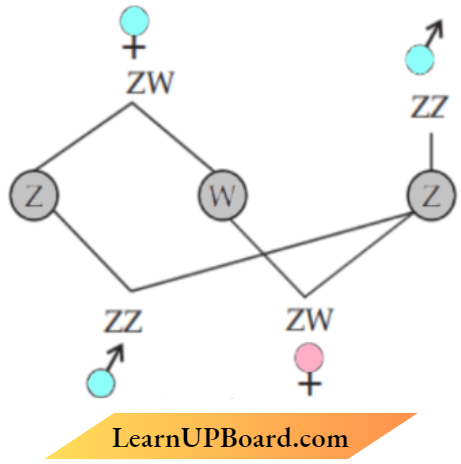
- In Birds, female heterogamety female produces (Z) type and (W) type of gametes in the case of bird males in hornogamety (ZZ) and female is heterogamety.
- In 11 humans being male heterogamety male produces (X) type and (Y) type of gametes.
Question 10. Both Haemophilia and Thalassemia are blood-related disorders in humans. Write their causes and the difference between the two. Name the category of genetic disorder they both come under.
Answer:
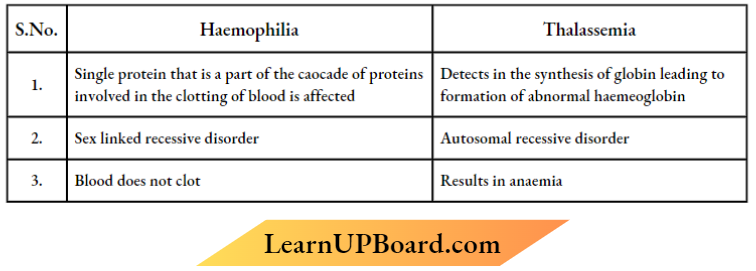
Mendelian disorder
Important Questions Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Principles Of Inheritance And Variation Long Question And Answer
Question 1. The cytological observations made in several insects led to the development of the concept of the genetic or chromosomal basis of the sex-determination mechanism. The honey bee is an interesting example to study the mechanism of sex determination. Study the schematic cross between the male and the female honey bees given below and answer the questions that follow :
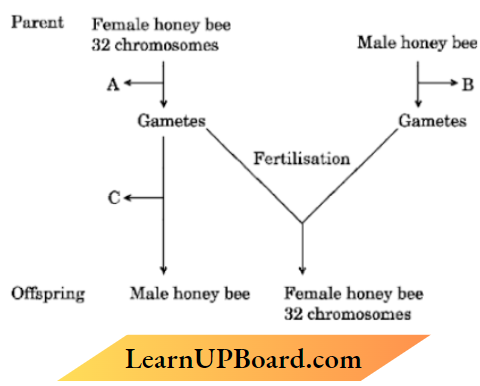
1. Identify the cell divisions V and ‘IT’ that lead to gamete formation in female and male honey bees respectively.
Answer:
- ‘A’-Meiosis
- ‘B’-Mitosis
2. Name the process ( that leads to the development of the male honey bee (drone).
Answer:
‘C’-Parthenogenesis
Question 2. T.H. Morgan carried out a cross on Drosophila involving genes for body colour (y+/Y) and genes for eye colour (w +/w). Study the schematic representation of the cross-opto I I generation and answer the questions that follow :
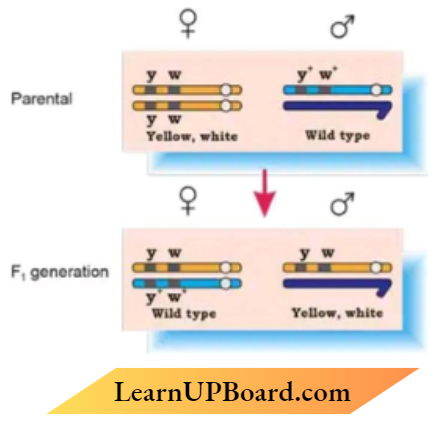
- Name the kind of cross it represents.
- Identify and write the dominant phenotype concerning eye colour.
- What are these genes located on the chromosome shown referred to as?
Answer:
- Dihybrid cross
- The red-eye phenotype of w
- Linked genes or sex-linked genes
Question 3. Mendel crossed a homozygous pea plant having yellow and round seeds with another pea plant hearing green and wrinkled seeds, lie found that in some of the IS populations new combination of parental characters was observed. How will you explain the appearance of a new combination of parental characters in IS offspring? Support your answer with the help of Punned Square.
Answer: When two pairs of traits are combined in a hybrid segregation of one pair of characters is independent of the other pair of characters.
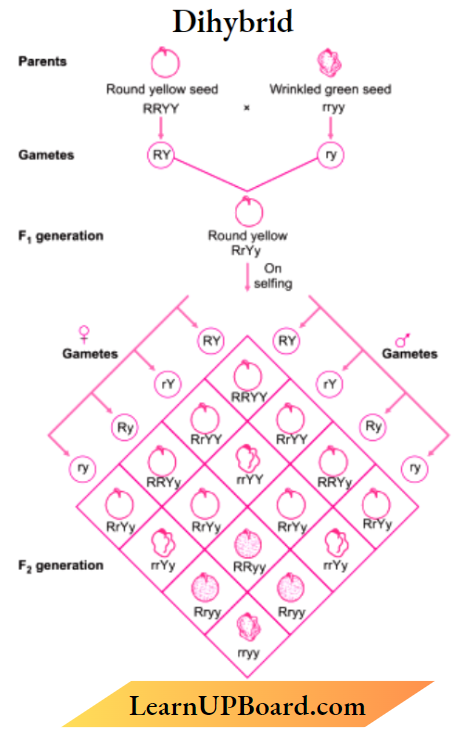
Phenotypic ratio
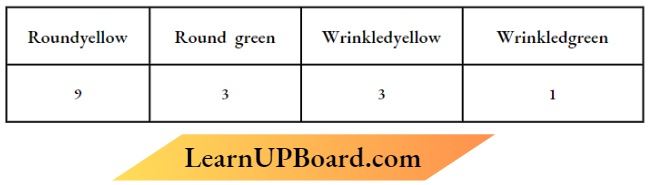
Genotypic ratio
Question 4.
1. Write the scientific name of the organism Thomas Hunt Morgan and his colleagues worked with for their experiments. Explain the correlation between linkage and recombination concerning genes as studied by them.
Answer:
Trosophikttnehmogasier
They observed that two genes (located closely on a chromosome) did not segregate independently of each other (Fe ratio deviated very significantly from 9:3:3: 1) lightly linked genes tend to show very fewer (lesser) recombinant frequency of parental traits/show higher (more) frequency of parental type loosely linked genes show higher percentage (more) of recombinant frequency of parental traits Or lower frequency percentage of parental type genes present on the same chromosome are said to be linked and the recombinant frequency depends on their relative distance on the chromosome.
2. How did Sturtevant explain gene mapping while working with Morgan?
Answer:
He used the frequency of recombination between gene pairs on the same chromosome, as a measure of the distance between genes and ‘mapped’ their position on the chromosome.
