Important Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 – Biotechnology: Principles And Processes Very Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. After the separation of DNA fragments by gel electrophoresis and staining with ethidium bromide, a student placed the gel in the UV chamber under the I-V light. State a reason for doing so.
Answer:
Explanation: After Gel electrophoresis the separated DNA is visualized after staining in ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV light. The stained DN A fragments appear as orange-contoured bands.
Question 2.Assertion: When DN A from two different sources are cut fey the same restriction enzyme, the resultant DNA fragments have different kinds of sticky ends’.
Reason: These can be joined together end-to-end using DN A ligases.
- Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation. Assertion,
- Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
- The assertion is true, but Reason is false.
- Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer: 1. Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
Question 3. In biotechnology experiments, ‘molecular scissors’ used are
- Plasmid
- Restriction enzymes
- Vectors
- Sigma factor
Answer: 2. Restriction enzymes.
Question 4. Why do DNA fragments move towards the anode during gel electrophoresis?
Answer: DNA fragments are negatively charged.
Question 5. Write the function of a Bioreactor.
Answer: To produce the recombinant product in large quantities
Read and Learn More Important Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter Wise
Important Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 – Biotechnology: Principles And Processes Very Short Questions And Answers Short Question And Answers
Question 1. How is the use of “microinjection” different from using the ‘method of biolistics’ in biotechnology? Explain.
Answer:
Recombinant DNA is directly injected into the nucleus of an animal cell in a method called microinjection. In another method, cells are bombarded with high-velocity micro-particles of gold or tungsten coated with DNA in a method known as biolistics or gene gun.
Question 2. How are DN A fragments visualized during gel-elect phoresis? What is elution?
Answer: Separated DNA fragments stained with ethidium bromide, followed by exposure to UV radiations, removal of DNA bands from agarose gel, and its extraction from gel is elution.
Question 3. Explain the principle that helps in the separation of DMA fragments in Gel electrophoresis.
Answer:
Since DNA fragments are actively charged molecules they can be separated by forcing them to run e towards an anode-pole under an electric field through a medium (matrix), DNA fragments separate according to their through-seeing effect picked in agarose gel (matrix)
Question 4.
1. Given below is the stepwise schematic representation of the process of electrophoresis.
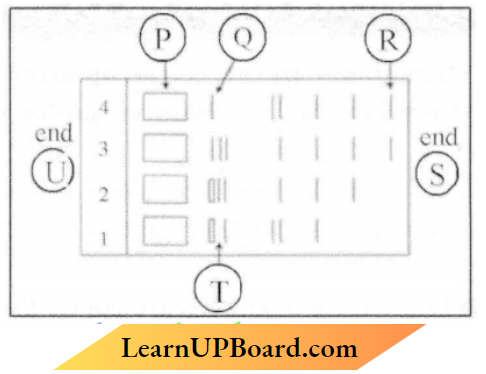
Identify the ‘alphabets’ representing
- Anode end
- The smallest or lightest DNA strand in the matrix
- Agarose gel
2. What is elution? State the importance of elution in this process.
Answer:
- Anode- S end
- R
- T
2. The separated bands of DN A are cut out from the agarose gel and extracted from the gel piece. This step is known as elution.
Importance:- The DNA fragments purified in this way are used in constructing recombinant DN A by joining them with cloning vectors.
Question 5.
1. Simple stirred-tank bioreactors are used to produce large quantities of recombinant proteins, stirring the contents and mixing them with oxygen. Write any four other advantages of using a stirred tank.
Answer:
- A stirred-tank reactor is usually cylindrical or with a curved base to facilitate the mixing of the reactor contents. The stirrer facilitates oxygen availability throughout the bioreactor that is tire bioreactor has an agitator system, an oxygen delivery system, a foam control system, and a temperature control system.
- pH control system, fermentation is contamination-free, and sampling ports so that small volumes of the culture can be withdrawn periodically.
2. After downstream processing, the product of the biosynthetic stage cannot be marketed directly. Why? Give two reasons.
Answer:
- After completion of the biosynthetic stage, the product has to be subjected to a series of processes before it is ready for marketing as a finished product The processes include separation and pu rill a ton. which are collectively referred to as downstream processing
- The product has to be formulated with suitable preservatives Such formulation has to undergo thorough clinical trials as in the case of drugs Strict quality control testing for each product is also required.
- The downstream processing and quality control testing vary from product to product.
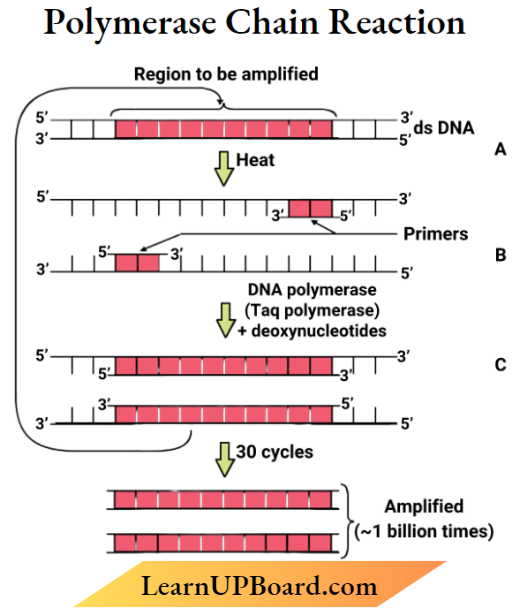
Question 6. Explain only with the help of a self-explanatory diagram, the three basic steps of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR),
OR
Explain three steps involved in polymerase chain reaction.
OR
Describe the technique that is very effectively used to get a large amount of desired DNA for research and detailed investigation.
Answer:
- By using PCR (polymerase chain reaction) denatured desired DNA,
- Separate into 2 strands white each acting as a template
- For each strand, a separate set of pr mortised (two times).
- With the help of dextrin) nucleotides and I as polymerase DNA polvoiearase isolated from Thermus aquaticus)
- Results in extension of DNA primer
The process of PCR takes place in three steps
- Desaturation Two strands of DNA are separated by heating Each strand acts as a template.
- Annealing Two sets of primers are attached and annealed to the separated DNA strands
- Extension Taq polymerase catalyzes the extension of primers using genomic DNA as a template and nucleotides provided in the reaction.
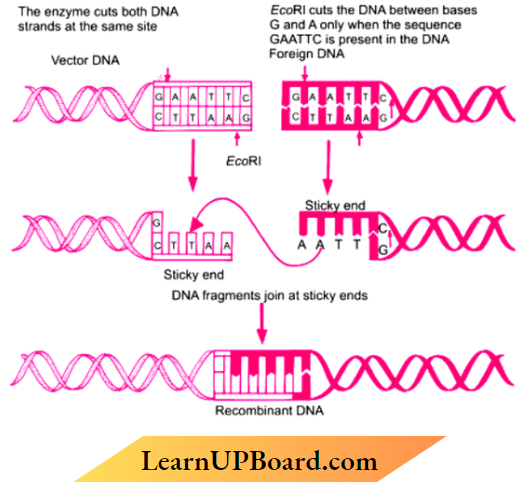
Question 7. Explain the three steps carried out in the formation of recombinant DNA using the enzyme EcoRI.
OR
Explain the action of EcoRI on DNA technology experiments.
Answer:
EcoRI cuts vector DNA. foreign DNA gene of interest. at palindromic site 3’CTTAAG 5’, 5’ GAATTC 3′ (between bases G and A only), sticky end (overhanging stretch of bases) formed at each strand Joining of sticky ends from DNA fragments by the enzyme DNA Ligase, Recombinant DNA(rDNA) is formed.
Question 8. Name any two natural cloning vectors. Give reasons that make them act as cloning vectors. Write the two characteristics the engineered vectors are made to possess
Answer:
Plasmids, bacteriophages, ability to replicate within bacterial cells. high copy number within the bacterial cells Characteristics of engineered Vectors: easy linking of foreign DNA, Selection of recombinants from non-recombinants or selectable markers.
Question 9. Name the most commonly used bioreactor in biotechnology labs. Mention the most essential components this bioreactor must have to provide the optimum conditions to the culture medium, resulting in the production of a large volume of the desired product.
Answer:
The most commonly used bioreactor is the stirring type.
It has the following components.
- Stirring type agitator system,
- O2 Delivery System
- Foam control system
- Temperature control system
- pH control system
Question 10.
- How has the development of bioreactors helped in biotechnology?
- Name the most commonly used bioreactor and describe its working.
Answer:
- Larger biomass large volume of culture can be processed leading to higher yields of desired specific products (protein or enzymes), under controlled condition
- Stirring type
- Mixing of reactor contents evenly (with an agitator system or a stirrer)
- Facilitates oxygen availability
- Temperature, PH1 foam control under optimum conditions
Question 11. Explain the roles of the following with the help of an example each in recombinant)NA technology:
- Restriction Enzymes –
- Plasmids
Answer:
- It recognizes a specific sequence of base pairs or palindromes. and cuts the D’NA strand at a specific site example EcoRI Hind 11
- Act as vectors cloning of desired alien gene or foreign gene eg pBR322 or plasmid of Salmonella or plasmid of Agrohacterimive Plasmid or Tumour including Plasmid
Question 12.
1. Explain the significance of ‘palindromic nucleotide sequence’ in the formation of recombinant DNA
Answer:
Palindromic nucleotide sequence The significance of the Palindromic nucleotide sequence is that the sequences read the same in both directions. This is important during the process of replication, transcription, and directional repair mechanisms.
2. Write the use of restriction endonuclease in the above process.
Answer:
- The same restriction endonuclease binds to both the vector and the foreign DNA, cutting each of the two strands of the double helix at specific points in their sugar-phosphate backbone of recognition sequence for restriction endonucleases ‘ palindromic sequence of vector and foreign DNA.
- Cut strands a little away from the center of the palindrome sites creates overhanging stretches or ticky ends
Question 13. Describe the roles of heat, primers, and the bacterium Thermus aquatic us in the process of PC R.
Answer:
- Heat – Denaturation or separation of DN A into two strands
- Primer– Enzyme DNA Polymerase extends the primers using the nucleotides provided in the reaction and the genomic DNA as a template.
- Thermus aqimfiats – Source of thermostable DNA polymerase: Taq polymerase
Question 14.Mention the role of (1) selectable marker, (2) Ori, and (3) drop-in Ecoli cloning vector pBR322.
Answer:
Selectable marker in addition to the vector requires a selectable marker, which helps in identifying and eliminating non-transformants and selectively permitting the growth of the transformants.
Origin of replication (ori): This is a sequence from where replication starts and any piece of DNA when linked to this sequence can be made to replicate within the host cells. This sequence is also responsible for controlling the copy number of the linked DNA. So, if one wants to recover mam copies of the target DNA it should be cloned in a vector whose origin supports high
copy number
Repressor of primer (Rop): It is a small dimeric protein that participates in the mechanism that controls the copy number of the plasmid It codes for the proteins involved in the replication of the plasmid
Important Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 – Biotechnology: Principles And Processes Long Question And Answers
Question 1. Read the paragraph given below and answer the questions that follow:
Enzyme Taq polymerase is extracted from a eubacteria microorganism Thermits aquaticus from Yellowstone National Park in Montana. ISA and isolated by Chien et al. (1976). Taq polymerase successfully replaced the DNA polymerase from E.coli that was being used in PCR earlier and this shift revolutionized the PCR technique,
- Taq polymerase after its discovery replaced E.coli DNA polymerase in the PCR technique. Explain giving reasons why the need felt for the change.
- What is a primer and its importance in PCR?
- What is the importance of PC R as a diagnostic tool?
Answer:
- The Lincoln DNA polymerase cannot cany out PCR at high temperatures (as it becomes inactive) whereas thermostable DNA polymerase (is isolated from a bacterium.
- Thermits that remain active during the high temperature-induced denaturation of double-stranded DNA.
- A primer is a small segment of DNA that binds to a complementary strand of DNA.
- Primers are necessary to start the functioning of DNA polymerase enzyme and therefore are necessary in polymerase chain reaction.
- PCR is important because it can generate several copies of a DNA sequence in a very short period.
- It is also important in forensic science as a tool for genetic engineering. Early detection of diseases like cancer AJDS genetic disorders.
Question 2. Restriction endonucleases are a class of bacterial enzymes that recognize a specific short sequence of nucleotides within a double-stranded DNA molecule The natural purpose of these enzymes is to protect bacteria from pathogens, notably bacteriophages. There are different classes of restriction enzymes, but type-11 restriction enzymes are widely used in manipulating DNA as they recognize short sequence nucleotides that are typically palindromes.
- Name a specific restriction endonuclease and write the palindromic nucleotide sequence in the DNA recognized by this enzyme. Also, indicate the site at which it cuts.
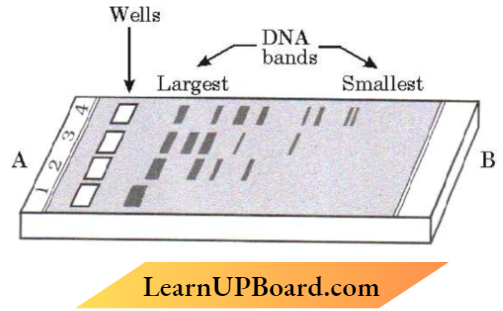
- A piece of DNA is cut by a restriction enzyme. The fragments are then separated by gel electrophoresis and stained by ethidium bromide. Write the principle on which gel electrophoresis works.
Answer:
1. EcoRl comes from Escherichia Coli RY 13 Recognition Sequence 5-GAATTC 3′
3’-CTTAAG-5’
The site at which it Cut 5’— G AATTC—3′
3’—CTTAA G—5′
2. The cutting of DNA by restriction endonucleases results in the fragments of DNA These fragments can be separated by a technique known as gel electrophoresis. Since DNA fragments are negatively charged molecules they can be. separated by forcing them to move towards the anode under an electric field through a medium/matrix. Nowadays the most commonly used matrix is agarose which is a natural polymer extracted from seaweeds. The DNA fragments separate (resolve) according to their size through the sieving effect provided by the agarose gel.
- Hence, the smaller the fragment size, the farther it moves. The separated DNA fragments can be visualized only after staining the DNA with a compound known as ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV You can see bright orange colored bands of DNA in an ethidium bromide-stained gel exposed to UV light. The separated bands of DN A are cut out from the agarose gel and extracted from the gel piece
This step is known as elution. The DNA fragments purified in this way are used in constructing recombinant DNA by joining them with cloning vectors.
Question 3. Explain how an antibiotic resistance gene in a cloning vector (plasmid pBR322) helps in selecting the recombinants front the non-recombinants.
Answer:
- In the closing vector pBR322 the genes encoding for resistance to antibiotics such as ampicillin. tetracycline is considered as a selectable marker:
- These markers are used to identify and eliminate non-transformants and permit the growth of trial formats in media containing antibiotics.
For example, you can ligate a foreign DNA at the BartiH I site of the tetracycline resistance gene in the vector pBR322. The recombinant plasmids will lose tetracycline resistance due to the insertion of foreign DNA but can still be selected from non-recombinant ones by plating the transformants on a tetracycline-containing medium.
- The transformants growing on an ampicillin-containing medium are then transferred to a medium containing tetracycline.
- The recombinants will grow in an ampicillin-containing medium but not on that containing tetracycline. But. recombinants will grow on the medium containing both antibiotics.
Question 4.
- Write the mechanism that enables Agrobacterium impatiens to develop tumors in their host dicot plant.
- State how Agrobacterium tumefadmsand some retroviruses have been modified as useful cloning vectors.
Answer:
- file bacterium Agrobacterium tumefacient delivers a piece of DN A known as T-DNA present in its plasmid to transform the host plant cell into a tumor (and direct tumor cells to produce the chemical required by the pathogen).
- The Ti plasmid of A.tumifaciens has been disarmed 1 modified so that it is no longer pathogenic to the host plant but is still able to use the mechanism to deliver genes of interest into plants. Retroviruses have also been disarmed or modified now and are used as cloning sectors to transfer desirable genes into animal cells
Question 5.
- Name the most commonly used bioreactor. Why are these bioreactors used?
- How is the operation in a bioreactor carried out to achieve the desired end
Answer:
- Stirred tank bioreactor, to obtain large quantities of desired products from the culture medium containing cloned organisms with genes of interest
- By providing optimum growth conditions for the living materials such as temperatures of F1 substrate salts or vitamins oxygen(and four conditions)
(OR) Explain the process of amplification of genes of interest using PCR technique.
Answer: PCR – Technique
- Denaturation – The two strands of the gene of interest are separated as DNA templates under high-temperature
- Annealing – The two DNA primers attached to the two separated DNA template strands
- Extension – Taq polymerase extends the primers (in 5′ → 3′ using deoxynucleotides provided in the medium)
The Cycle is repeated to gel the multiple copies of the gene of interest
Important Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 – Biotechnology: Principles And Processes Case Study-Based Questions
Read The Following Passage And Answer Any Four Questions From 1 To 5 :
- Experiments involving cloning genes and expressing proteins require the use of host cells to receive the foreign cloned gene In some experiments, prokaryotes such as l’.. coli and Bacillus subtil is, and eukaryotes such as the budding yeast (Saccharomyces are used as host cells for DNA cloning.
- These host cells are relatively easy to grow in the laboratory and have been studied extensively for decades. Their genetics have been well-understood and therefore can be manipulated to make them appropriate hosts. Many types of cells can be converted into biochemical factories using rDNA technology to produce various kinds of biomolecules. coli and B. subtil are both commonly used as host cells for DNA cloning Fortunately, humans have become very experienced at cultivating microbes cheaply and efficiently on large and small production scales.
- Over the centuries, brewers and bakers have learned to employ yeast cells to manufacture beer, bread, and related food products. In terms of impact on human health, probably the most important product made by bacteria is antibiotics.
Question 1. The most commonly used eukaryotic microorganism used in biotechnology is :
- E.coli
- Bacillus
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Drosophila
Answer: 1. E.coli
Question 2. Over the centuries, brewers and bakers have learned to employ yeast cells to manufacture man’s household products. Select the option with all the correct answers from the given list:
- Bread. Idli, Roquefort cheese
- Bread, Toddy, Swiss cheese
- Dosa, Idli, Bread
- Lipases, Pectinases, Zymase
Answer: 3. Dosa, Idli, Bread
Question 3. The most common products made by certain bacteria that have a great impact on human health are:
- Antibiotics.
- Bioactive molecules
- Enzymes
- Fermented drinks
Answer: 1. Antibiotics.
Question 4. The best-known host cells for DNA cloning and producing various kinds of biomolecules are:
- Agrobacteriumtumefaciens
- Escherichia
- Bacteriophage lambda
- Bacteriophage X174
Answer: 2. Escherichia
Question 5. The enzyme that is not required to manipulate the genetics of the microorganism to convert them into biochemical factories is :
- Restriction endonuclease
- DNA polymerase
- Lactase
- Ligase
Answer: 3. Lactase
