Redox Reactions NEET MCQs
NEET Chemistry For Redox Reactions Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Which of the following is a redox reaction?
- Evaporation of H2O
- Both oxidation and reduction
- H2SO4 with NaOH
- In the atmosphere O3 from O2 by lightning
Answer: 2. Both oxidation and reduction
Redox reactions are those chemical reactions which involve both oxidation and reduction simultaneously.
Question 2. Without losing its concentration, ZnCl2 solution cannot be kept in contact with
- Pb
- Al
- Au
- Ag
Answer: 2. Al
Only ‘AI’ lies above ‘Zn’ in the electrochemical series, which can displace Zn from the ZnCl2 solution. Therefore, conc. of ZnCl2 will decrease when kept in an ‘Al’ container.
⇒ \(2 \mathrm{Al}+3 \mathrm{ZnCl}_2 \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{AlCl}_3+3 \mathrm{Zn}\)
Question 3. On balancing the given redox reaction, \(a \mathrm{Cr}_2 \mathrm{O}_7^{2-}+b \mathrm{SO}_{3(\mathrm{mq})}^{2-}+c \mathrm{H}_{(\mathrm{mq})}^{+} \rightarrow 2 a \mathrm{Cr}_{[(a q)}^{3+}+b \mathrm{SO}_{4(\mathrm{aq})}^{2-}+\frac{c}{2} \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_{(\mathrm{l})}\) the coefficient a, b and c are found to be respectively.
- 1,8,3
- 8,1,3
- 1,3,8
- 3,8, 1
Answer: 3. 1,3,8
⇒ \(\mathrm{Cr}_2 \mathrm{O}_{7(a q)}^{2-}+3 \mathrm{SO}_{3(a q)}^{2-}+8 \mathrm{H}_{(a q)}^{+} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{Cr}_{(a q)}^{3+}+3 \mathrm{SO}_{4(a q)}^{2-}+4 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_{(l)}\)
Question 4. Which of the following reactions is the metal displacement reaction? Choose the right option.
- \(2 \mathrm{~Pb}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_2 \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{PbO}+4 \mathrm{NO}_2+\mathrm{O}_2 \uparrow\)
- \(2 \mathrm{KClO}_3\)\(\longrightarrow{\Delta}\)\(2 \mathrm{KCl}+3 \mathrm{O}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{Cr}_2 \mathrm{O}_3+2 \mathrm{Al}\)\(\longrightarrow{\Delta}\)\(\mathrm{Al}_2 \mathrm{O}_3+2 \mathrm{Cr}\)
- \(\mathrm{Fe}+2 \mathrm{HCl} \longrightarrow \mathrm{FeCl}_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \uparrow\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{Cr}_2 \mathrm{O}_3+2 \mathrm{Al}\)\(\longrightarrow{\Delta}\)\(\mathrm{Al}_2 \mathrm{O}_3+2 \mathrm{Cr}\)
When a metal from the electrochemical series is mixed with the ions of a metal lower down in the electrochemical series, then more active metal displaces the less active one, this is known as metal displacement.
Hence, the correct reaction is \(\mathrm{Cr}_2 \mathrm{O}_3+2 \mathrm{Al}\)\(\longrightarrow{\Delta}\)\(\mathrm{Al}_2 \mathrm{O}_3+2 \mathrm{Cr}\)
Read and Learn More NEET MCQs with Answers
Question 5. What is the change in the oxidation number of carbon in the following reaction? \(\mathrm{CH}_{4(\mathrm{~g})}+4 \mathrm{Cl}_{2(\mathrm{~g})} \rightarrow \mathrm{CCl}_{4(l)}+4 \mathrm{HCl}_{(\mathrm{g})}\)
- +4 to+4
- 0 to+4
- -4 to+4
- 0 to-4
Answer: 3. -4 to+4
In CH4 the oxidation number of carbon is -4 while in CCl4, the oxidation number of carbon is +4. Thus, the change in oxidation number of carbon in the given reaction is from -4 to +4.
NEET Redox Reaction Questions
Question 6. The correct structure of tribromooctaoxide is Which of the following reactions are disproportionation reactions?
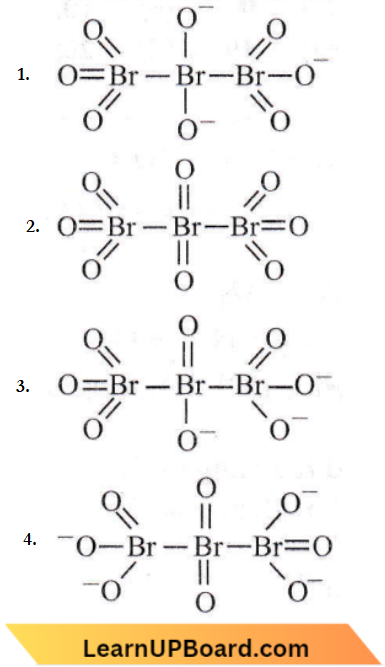
Answer: 2
Question 7. Which of the following reactions are disproportionation reactions?
- \(2 \mathrm{Cu}^{+} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Cu}^{2+}+\mathrm{Cu}^0\)
- \(3 \mathrm{MnO}_4^{2-}+4 \mathrm{H}^{+} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{MnO}_4^{-}+\mathrm{MnO}_2+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(2 \mathrm{KMnO}_4\) \(\longrightarrow{\Delta}\)\(\mathrm{K}_2 \mathrm{MnO}_4+\mathrm{MnO}_2+\mathrm{O}_2\)
- \(2 \mathrm{MnO}_4^{-}+3 \mathrm{Mn}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \longrightarrow 5 \mathrm{MnO}_2+4 \mathrm{H}^{+}\)
Select the correct option from the following.
- (1) and (4) only
- (1) and (2) only
- (1), (2) and (3)
- (1), (3) and (4)
Answer: 2. (1) and (2) only
Disproportionation reactions are those in which the same element/compound gets oxidised and reduced simultaneously.
⇒ \(2 \mathrm{Cu}^{+}\)\(\longrightarrow\)\(\mathrm{Cu}^{2+}+\mathrm{Cu}^0\)
⇒ \(3 \mathrm{MnO}_4^{2-}+4 \mathrm{H}^{+} \longrightarrow \stackrel{+7}{\mathrm{MnO}_4^{-}}+\stackrel{+4}{\mathrm{MnO}_2}+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
Question 8. The oxidation state of Cr in CrO5 is
- -6
- +12
- +6
- +4
Answer: 3. +6
CrO5 has a butterfly structure having two peroxo bonds.
Peroxo oxygen has -1 oxidation state.
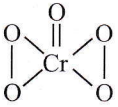
Let the oxidation state of Cr be ‘x’
CrO5: x+4(-1)+1(-2) =0 + x=+6
Question 9. The correct order of N-compounds in its decreasing order of oxidation states is
- \(\mathrm{HNO}_3, \mathrm{NO}, \mathrm{N}_2, \mathrm{NH}_4 \mathrm{Cl}\)
- \(\mathrm{HNO}_3, \mathrm{NO}, \mathrm{NH}_4 \mathrm{Cl}, \mathrm{N}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{HNO}_3, \mathrm{NH}_4 \mathrm{Cl}, \mathrm{NO}, \mathrm{N}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{NH}_4 \mathrm{Cl}, \mathrm{N}_2, \mathrm{NO}, \mathrm{HNO}_3\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{HNO}_3, \mathrm{NO}, \mathrm{N}_2, \mathrm{NH}_4 \mathrm{Cl}\)
⇒ \(\stackrel{+5}{\mathrm{HNO}_3,} \stackrel{+2}{\mathrm{NO}}, \stackrel{0}{\mathrm{~N}}, \stackrel{-3}{\mathrm{NH}_4 \mathrm{Cl}}\)
Redox Reactions Multiple Choice NEET
Question 10. For the redox reaction, \(\mathrm{MnO}_4^{-}+\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{O}_4^{2-}+\mathrm{H}^{+} \rightarrow \mathrm{Mn}^{2+}+\mathrm{CO}_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\). The correct coefficients of the reactants for the balanced equation are
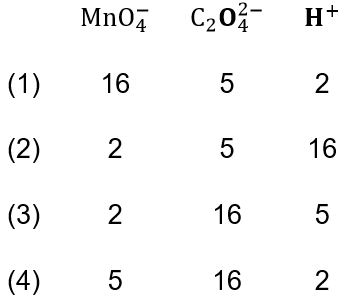
Answer: 2
For the redox reaction, \(\mathrm{MnO}_4^{-}+\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{O}_4^{2-}+\mathrm{H}^{+} \rightarrow \mathrm{Mn}^{2+}+\mathrm{CO}_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\).
The correct balanced equation is \(2 \mathrm{MnO}_4^{-}+5 \mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{O}_4^{2-}+16 \mathrm{H}^{+} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{Mn}^{2+}+10 \mathrm{CO}_2+8 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
Question 11. Hot concentrated sulphuric acid is a moderately strong oxidizing agent. Which of the following reactions does not show oxidizing behaviour?
- \(\mathrm{Cu}+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4 \rightarrow \mathrm{CuSO}_4+\mathrm{SO}_2+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{S}+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4 \rightarrow 3 \mathrm{SO}_2+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{C}+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4 \rightarrow \mathrm{CO}_2+2 \mathrm{SO}_2+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{CaF}_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4 \rightarrow \mathrm{CaSO}_4+2 \mathrm{HF}(\mathrm{NE}\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{CaF}_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4 \rightarrow \mathrm{CaSO}_4+2 \mathrm{HF}(\mathrm{NE}\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{CaF}_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4 \rightarrow \mathrm{CaSO}_4+2 \mathrm{HF}\)
Here, the oxidation state of every atom remains the same so, it is not a redox reaction.
Question 12.
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2+\mathrm{O}_3 \longrightarrow \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}+2 \mathrm{O}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2+\mathrm{Ag}_2 \mathrm{O} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{Ag}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{O}_2\)
The role of hydrogen peroxide in the above reactions is respectively
- Oxidizing in (1) and reducing in (2)
- Reducing in (1) and oxidizing in (2)
- Reducing in (1) and (2)
- Oxidizing in (1) and (2)
Answer: 3. Reducing in (1) and (2)
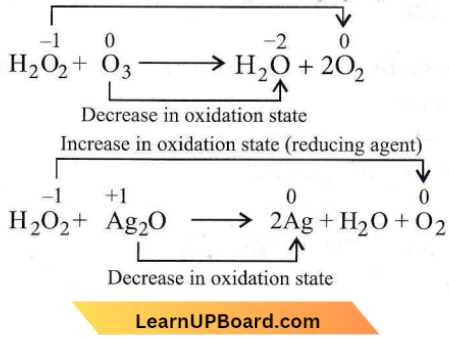
H2O2 acts as a reducing agent in both the reactions in which O2 is evolved
Question 13. The pair of compounds that can exist together is
- \(\mathrm{FeCl}_3, \mathrm{SnCl}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{HgCl}_2, \mathrm{SnCl}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{FeCl}_2, \mathrm{SnCl}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{FeCl}_3, \mathrm{KI}\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{FeCl}_2, \mathrm{SnCl}_2\)
Both FeCI2 and SnCl2 are reducing agents with low oxidation numbers.
Question 14. A mixture of potassium chlorate, oxalic acid and sulphuric acid is heated. During the reaction which element undergoes maximum change in the oxidation number?
- S
- H
- Cl
- C
Answer: 3. Cl
A mixture of potassium chlorate, oxalic acid and sulphuric acid is heated.
⇒ \(\stackrel{+1+5-2}{\mathrm{KClO}_3}+(\mathrm{COOH})_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \stackrel{+6}{\mathrm{~S}} \mathrm{O}_4 \longrightarrow\)\(\mathrm{K}_2^{+6} \mathrm{SO}_4+\mathrm{KCl}+\mathrm{CO}_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\).
Redox Reaction Practice Questions NEET
Question 15. Oxidation numbers of P in PO43-, of S in SO42- and of Cr in Cr2O7 are respectively
- +3, +6 and +5
- +5, +3 and +6
- -3, +6 and +6
- +5, +6 and +6
Answer: 4. +5, +6 and +6
Let the oxidation number of P in \(\mathrm{PO}_4^{3-}\) be r.
∴ x+4(-2)=-3 = x=+5
Let the oxidation number of S in \(\mathrm{SO}_4^{2-}\) be y.
∴ y+4(-2)=-2 + y=+6
Let oxidation number of Cr in \(\mathrm{Cr}_2 \mathrm{O}_7^{2-}\) be z.
∴ 2z+7(-2)=-2 + z=*6
Question 16. The number of moles of MnO4 required to oxidize one mole of ferrous oxalate completely in an acidic medium will be
- 7.5 moles
- 0.2 moles
- 0.6 moles
- 0.4 moles.
Answer: 4. 0.4 moles.
⇒ \(\left[5 e^{-}+\mathrm{MnO}_4^{-}+8 \mathrm{H}^* \rightarrow \mathrm{Mn}^{2+}+4 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \ldots\right.(1)] \times 2\)
⇒ \(\left[\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{O}_4^{2-} \rightarrow 2 e^{-}+2 \mathrm{CO}_2 \ldots \text { (2) }\right] \times 5\)
Question 17. Which is the best description of the behaviour of bromine in the reaction given below? \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{Br}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{HOBr}+\mathrm{HBr}\)
- Proton acceptor only
- Both oxidised and reduced
- Oxidised only
- Reduced only
Answer: 2. Both oxidised and reduced
Question 18. The oxidation states of sulphur in the anions \(\mathrm{SO}_3^2-\), \(\mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_4^{2-}\) and \(\mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_6^{2-}\) follow the order
- \(\mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_4^{2-}<\mathrm{SO}_3^{2-}<\mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_6^{2-}\)
- \(\mathrm{SO}_3^{2-}<\mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_4^{2-}<\mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_6^{2-}\)
- \(\mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_4^{2-}<\mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_6^{2-}<\mathrm{SO}_3^{2-}\)
- \(\mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_6^{2-}<\mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_4^{2-}<\mathrm{SO}_3^{2-}\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_4^{2-}<\mathrm{SO}_3^{2-}<\mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_6^{2-}\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{SO}_3^{2-}: x+(-2) 3=-2\) or \(x-6=-2\) or \(x=+4\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_4^{2-}: 2 x+(-2) 4=-2\)
or \(2 x-8=-2\) or \(2 x=+6\)
∴ x = +3
⇒ \(\mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_6^{2-}: 2 x+(-2) 6=-2\)
or \(2 x-12=-2\) or \(2 x=+10\)
∴ x = +5
Oxidation states follow the order : \(\mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_4^{2-}<\mathrm{SO}_3^{2-}<\mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_6^{2-}\)
NEET Chemistry Redox Reactions
Question 19. The oxidation state of Fe in Fe2O3 is
- 5/4
- 4/5
- 3/2
- 8/3
Answer: 4. 8/3
⇒ \(\mathrm{Fe}_3 \mathrm{O}_4: 3 x+4(-2)=0 \Rightarrow x=+\frac{8}{3}\)
Question 20. Reaction of sodium thiosulphate with iodine gives
- Tetrathionate ion
- Sulphide ion
- Sulphate ion
- Sulphite ion.
Answer: 1. Tetrathionate ion
⇒ \(2 \mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{~S}_2 \mathrm{O}_3+\mathrm{I}_2 \rightarrow \underset{\mathrm{Sodium tetrathionate}}{\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{~S}_4 \mathrm{O}_6}+2 \mathrm{NaI}\)
Question 21. The oxide, which cannot act as a reducing agent is
- CO2
- ClO2
- NO2
- SO2
Answer: 1. CO2
Since carbon is in its maximum oxidation state of +4, therefore, carbon dioxide (CO2) cannot act as a reducing agent.
Question 22. Which substance is serving as a reducing agent in the following reaction? \(14 \mathrm{H}^{+}+\mathrm{Cr}_2 \mathrm{O}_7^{2-}+3 \mathrm{Ni} \rightarrow 7 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}+2 \mathrm{Cr}^{3+}+3 \mathrm{Ni}^{2+}\)
- H+
- Cr2O2-7
- H2O
- Ni
Answer: 4. Ni
Since the oxidation number of Ni increases from 0 to 2, therefore it acts as a reducing agent.
Question 23. The oxidation state of I in H4IO6– is
- +1
- – 1
- + 7
- + 5
Answer: 3. + 7
Let r = Oxidation state of l. Since oxidation state of H = +1 and oxidation state of O = – 2, therefore for H4IO6–, we get (4 x 1) + x + (6x – 2) = -1 or x = +7
Redox Reactions Quiz For NEET
Question 24. Consider the change in the oxidation state of bromine corresponding to different emf values as shown in the given diagram:
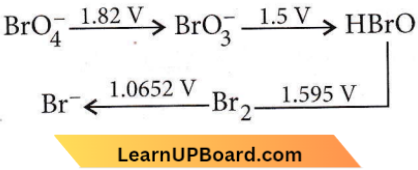
Then the species undergoing disproportionation is
- BrO–3
- BrO–4
- Br2
- HBrO
Answer: 4. HBrO
For a reaction to be spontaneous, E°cell, should be positive as ΔG° = -nFE°cell
HBrO → Br2; E° = 1.595 V, SRP (cathode)
HBrO → BrO–3; E° = -1.5 V, SOP (anode)
2HBrO → Br2 + BrO–3
E°cell = SRP (cathode) – SRP (anode)
= 1.595 – 1.5 = 0.095 V
E°cell> 0 ⇒ ΔG° < 0 (spontaneous)
