NEET Questions On Alcohols Phenols Ethers
NEET Chemistry For Alcohols Phenols And Ethers Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. The general molecular formula, which represents the homologous series of alkanols is
- \(\mathrm{C}_n \mathrm{H}_{2 n+2} \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_n \mathrm{H}_{2 n} \mathrm{O}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_n \mathrm{H}_{2 n} \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_n \mathrm{H}_{2 n+1} \mathrm{O}\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{C}_n \mathrm{H}_{2 n+2} \mathrm{O}\)
All alcohols follow the general formula \(\mathrm{C}_n \mathrm{H}_{2 \pi+2} \mathrm{O}\).
⇒ \(\begin{gathered}
\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{OH}\left[\mathrm{CH}_{2+2} \mathrm{O}\right] ; \mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{OH}\left[\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_{(2 \times 2)+2} \mathrm{O}\right] \\
n=1, \quad n=2
\end{gathered}
\)
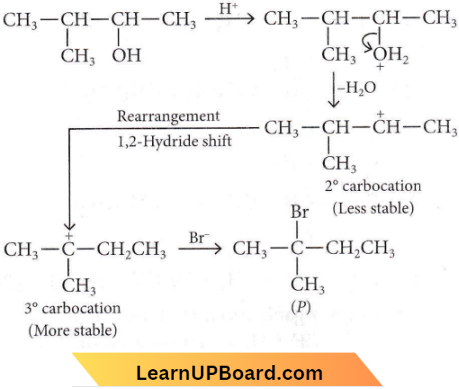
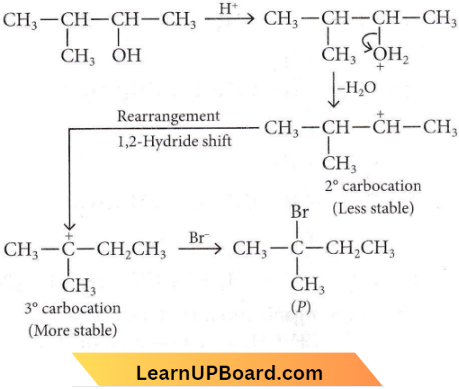
Question 2. Consider the following reaction and identify the product (P).
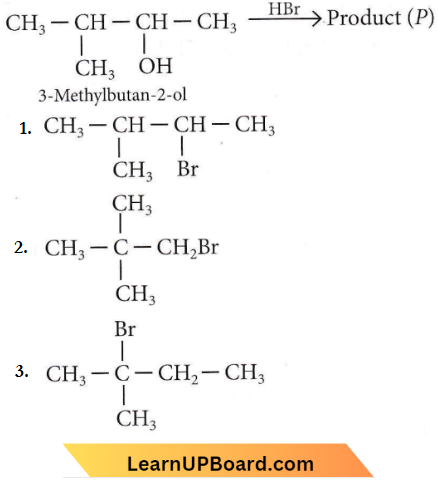
Answer: 3
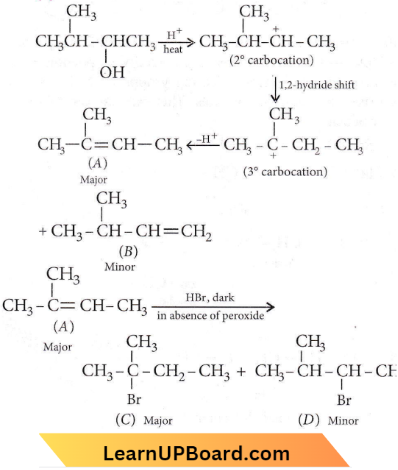
Question 3. Which of the following will be most readily dehydrated under acidic conditions?
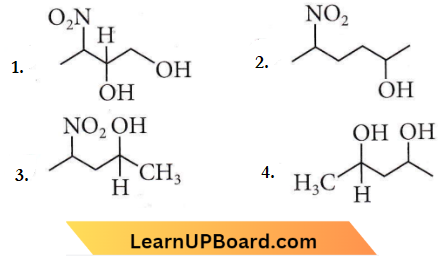
Answer: 4
NEET questions on Alcohols Phenols Ethers
Question 4. Given below are two statements:
Statement-1: The acidic strength of monosubstituted nitrophenol is higher than phenol because of the electron-withdrawing nitro group.
Statement 2: 0-nitrophenol, m-nitrophenol, and p-nitrophenol will have the same acidic strength as they have one nitro group attached to the phenolic ring. In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
- Both statement-1 and statement-2 are correct.
- Both statement-1 and statement-2 are incorrect.
- Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect.
- Statement 1 is incorrect but Statement 2 is
Answer: 3. Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect.
Read and Learn More NEET MCQs with Answers
Electron withdrawing groups (for example, -NO2) stabilize the phenoxide ion more by dispersing the negative charge relative to phenol (i.e. release of proton becomes easy) and thus, increase the acidic strength of phenols.
The particular effect is more when the substituent is present on o- and p-positions than in re-position to the phenolic group.
Thus, the acidic strength of nitrophenols decreases in the order: p-nitrophenol > o-nitrophenol > z-nitrophenol > phenol
Question 5. Given below are two statements:
Statement 1: In the Lucas test, primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols are distinguished on the basis of their reactivity with the cone. HCl + ZnCl2, known as Lucas Reagent.
Statement 2: Primary alcohols are most reactive and immediately produced turbidity at room temperature on reaction with Lucas Reagent.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
- Both statement 1 and statement 2 are correct.
- Both statement 1 and statement 2 are incorrect.
- Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect.
- Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct.
Answer: 3. Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect.
Tertiary alcohols are most reactive and immediately produce turbidity at room temperature while primary alcohols do not react with Lucas reagent at room temperature.
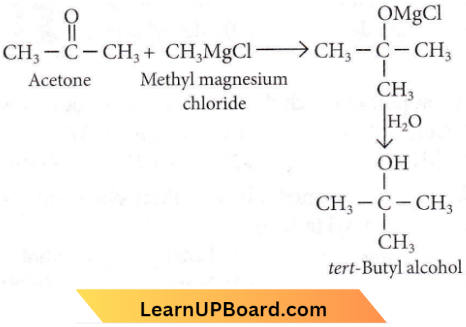
Question 6. The reaction between acetone and methyl magnesium chloride followed by hydrolysis will give
- isopropyl alcohol
- sec-butyl alcohol
- fert-butyl alcohol
- iso-butyl alcohol.
Answer: 3. fert-butyl alcohol
Question 7. The structure of intermediate A in the following reaction is
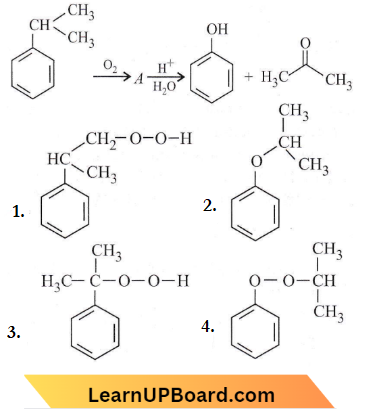
Answer: 3
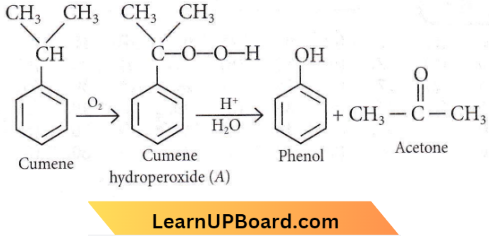
Alcohols Phenols And Ethers NEET MCQs
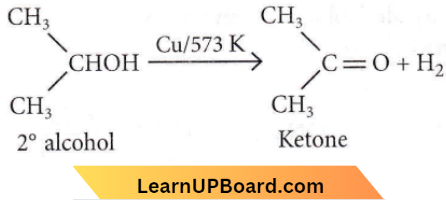
Question 8. When vapors of a secondary alcohol is passed over heated copper at 573 K, the product formed is
- A carboxylic acid
- An aldehyde
- A ketone
- An alkene.
Answer: 3. A ketone
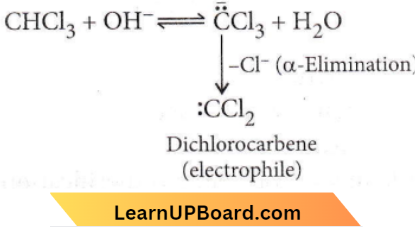
Question 9. In the reaction,
the electrophile involved is
- Dichloromethyl cation \(\left({ }_{\mathrm{C}}^{+} \mathrm{HCl}_2\right)\)
- Formyl cation \((\stackrel{\rightharpoonup}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{HO})\)
- Dichloromethyl anion \(\left(\overline{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{HCl}_2\right)\)
- Dichlorocarbene \((:\left.\mathrm{CCl}_2\right)\)
Answer: 4. Dichlorocarbene \((:\left.\mathrm{CCl}_2\right)\)
It is Reimer-Tiemann reaction. The electrophile formed is dichlorocarbene (CCl) which is formed according to the following mechanism
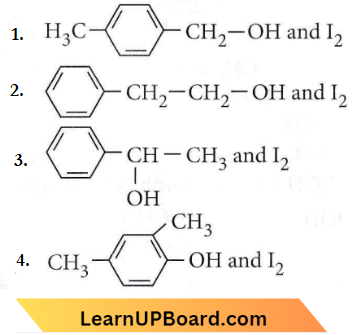
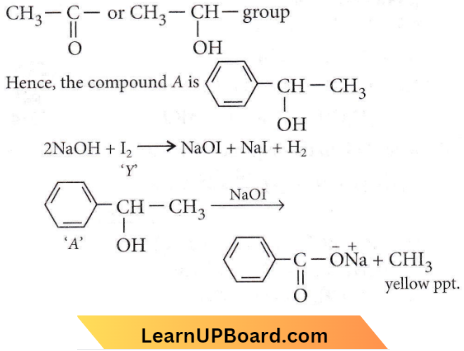
Question 10. Compound A, C8H10O, is found to react with NaOI (produced by reacting Y with NaOH) and yields a yellow precipitate with a characteristic smell. A and Y are respectively
Answer: 3
Alcohols Phenols And Ethers NEET MCQs
As the compound is giving yellow precipitate with NaOI that shows it is undergoing a haloform reaction. Haloform reaction is shown by the compounds having
Question 11. Identify the major products P, Q, and R in the following sequence of reactions
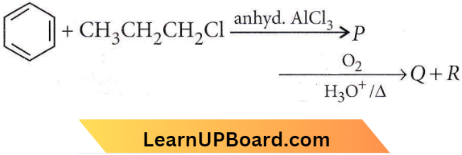
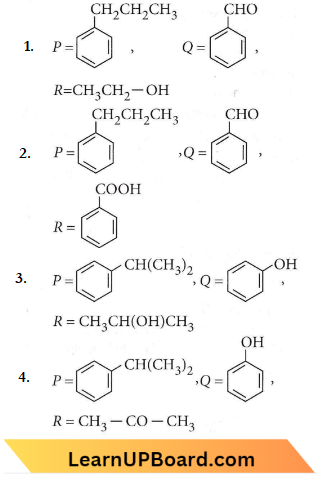
Answer: 4
Question 12. Which one is the most acidic compound?
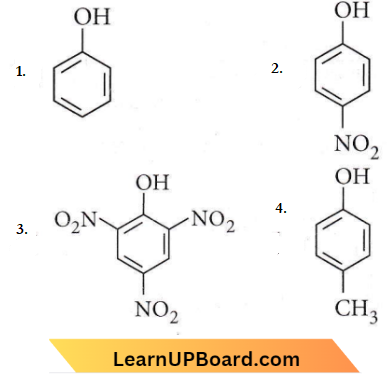
Answer: 3
Electron withdrawing groups increase the acidity while electron donating groups decrease the acidity of phenol.
Alcohols Phenols Ethers Multiple Choice NEET
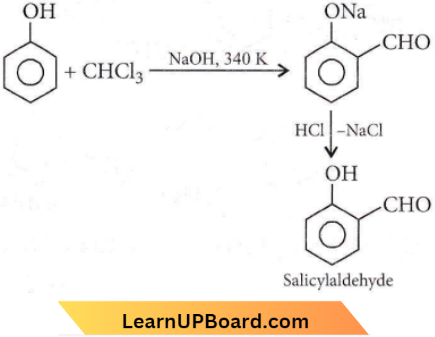
Question 13. The reaction of phenol with chloroform in the presence of dilute sodium hydroxide finally introduces which one of the following functional groups?
- -COOH
- -CHCl2
- -CHO
- -CH2Cl
Answer: 3. -CHO
This is Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
Question 14. Which of the following reaction(s) can be used for the preparation of alkyl halides?
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{OH}+\mathrm{HCl}\) \(\underrightarrow{\mathrm{Anh} . \mathrm{ZnCl} l_2}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{OH}+\mathrm{HCl} \longrightarrow\)
- \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \mathrm{COH}+\mathrm{HCl} \longrightarrow\)
- \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_2 \mathrm{CHOH}+\mathrm{HCl}\) \(\underrightarrow{\text { Anh. } \mathrm{ZnCl}_2}\)
- 1 and 2 only
- 4 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
Answer: 4. 1, 3 and 4 only
1° and 2° alcohols react with HCI in the presence of an anhydrous ZICI2 as a catalyst while in the case of 3° alcohols, ZnCI2 is not required.
Quetsion 15. Which of the following will not be soluble in sodium hydrogen carbonate?
- 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol
- Benzoic acid
- o-Nitropbenol
- Benzene sulphonic acid
Answer: 3. o-Nitropbenol
The reaction is as follows: Acid + \(\mathrm{NaHCO}_3 \rightarrow\) Sodium salt of acid+ \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{CO}_3\)
Among all the given compounds, o-nitrophenol is a weaker acid than \(\mathrm{HCO}_3^{-}\). Hence, it does not react with \(\mathrm{NaHCO}_3\).
Question 16. The number of isomeric alcohols of molecular formula C6H14O which give positive iodoform test is
- Three
- Four
- Five
- Two.
Answer: 2. Four
The iodoform test is positive for alcohols with the formula R – CHOH – CH3.
Among C6H14O isomers, the ones with positive iodoform tests are:
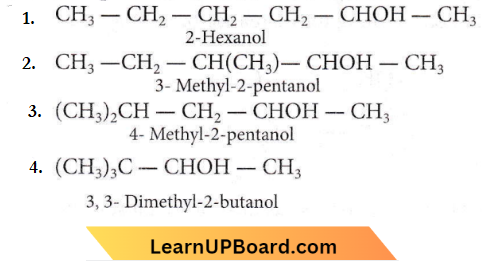
Alcohols Phenols Ethers Multiple Choice NEET
Question 17. In the following sequence of reactions, the end product (C) is
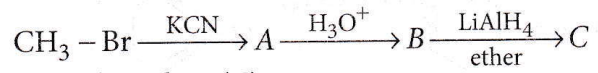
- Acetone
- Methane
- Acetaldehyde
- Ethyl alcohol.
Answer: 4. Ethyl alcohol.
Quetsion 18. In the following reactions, the major products (A) and (C) are respectively
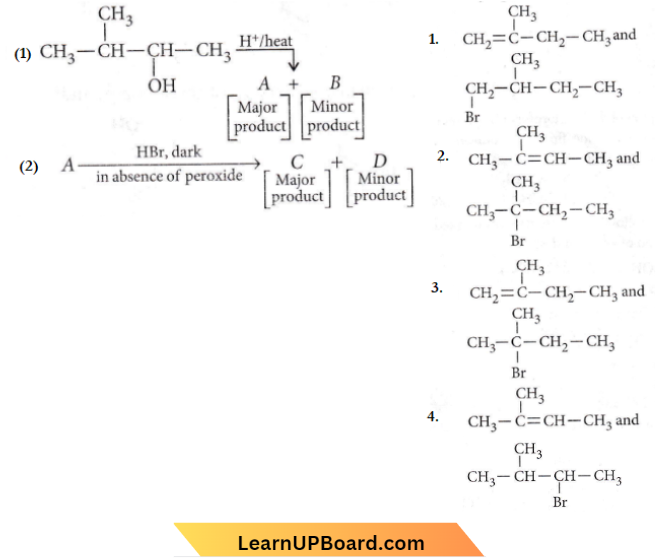
Answer: 2
Question 19. Given are cyclohexanol(1), acetic acid(2), 2,4,6-trinitrophenol (3), and phenol (4). In these, the order of decreasing acidic character will be
- 3>2>4>1
- 2>3>1>4
- 2>3>4>1
- 3>4>2>1
Answer: 1. 3>2>4>1
Since phenols and carboxylic acids are more acidic than aliphatic alcohols, we find that cyclohexanol (1) is the least acidic. Out of the two given phenols, 3 is more acidic than 4.
This is because of the presence of three highly electron-withdrawing -NO2 groups on the benzene ring which makes the O-H bond extremely polarized. This facilitates the release of H as H+.
Thus, 3 and 4.
ln acetic acid, the electron-withdrawing 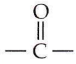 in the -COOH group polarises the O-H bond and increases the acidic strength. Acetic acid is therefore more acidic than phenol or cyclohexanol.
in the -COOH group polarises the O-H bond and increases the acidic strength. Acetic acid is therefore more acidic than phenol or cyclohexanol.
∴ The order of acidic character is 3 > 2 > 4 > 1
NEET Practice Questions Alcohols Phenols Ethers
Question 20. Which of the following compounds has the most acidic nature?
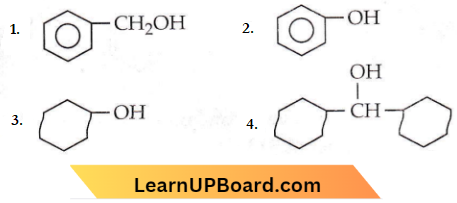
Answer: 2
Phenol is the most acidic of all the given compounds. In phenol, the electron-withdrawing phenyl ring polarizes the O-H bond, thereby facilitating the release of H as H+ and hence, phenol is most acidic.
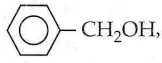
The electron-withdrawing effect of the phenyl ring is somewhat diminished by the – CH2 group and it is therefore, less acidic than phenol. In (3) and (4), -OH group is attached to alkyl groups which, due to their +1 effect reduces the polarity of -OH bond and so, the acidic strength is low.
Question 21. Among the following four compounds
- Phenol
- Methyl phenol
- Mefa-nitrophenol
- Para-nitrophenol
The acidity order is
- 4>3>1>2
- 3>4>1>2
- 1>4>3>2
- 2>1>3>4
Answer: 1. 4>3>1>2
In phenols, the presence of electron-releasing groups decreases the acidity, whereas the presence of electron-withdrawing groups increases the acidity, compared to phenol.
Among the meta and para-nitrophenols, the latter is more acidic as the presence of – NO2 in the group at the para position stabilizes the phenoxide ion to a greater extent than when it is present at the meta position.
Thus, correct order of acidity is: para -nitrophenol(4) > meta-nitrophenol(3) > phenol(1) > methyl phenol(2)
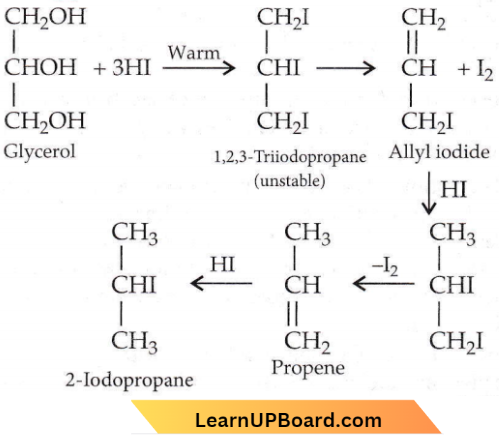
Question 22. When glycerol is treated with excess of HI, it produces
- 2-Iodopropane
- Allyl Iodide
- Propene
- Glycerol Triiodide.
Answer: 1. 2-Iodopropane
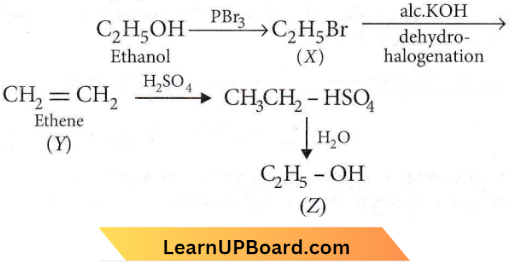
Question 23. Consider the following reaction:
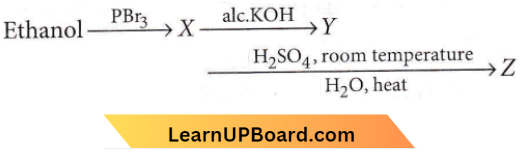
the product Z is
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{O}-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{CH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{O}-\mathrm{SO}_3 \mathrm{H}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{OH}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_2=\mathrm{CH}_2\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{OH}\)
NEET Practice Questions Alcohols Phenols Ethers
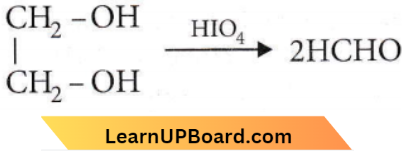
Question 24. HOCH2CH2OH on heating with periodic acid gives
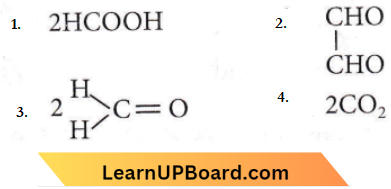
Answer: 3
When 1,2-diol-like ethylene glycol is treated with HIO2 each alcoholic group is oxidized to a carbonyl group by HIO2. Since in glycol, both the -OH groups are terminal, so oxidation would yield two formaldehyde molecules.
Question 25. Consider the following reaction product Z is
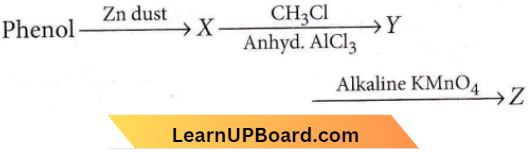
- Benzaldehyde
- Benzoic acid
- Benzene
- Toluene.
Answer: 2. Benzoic acid
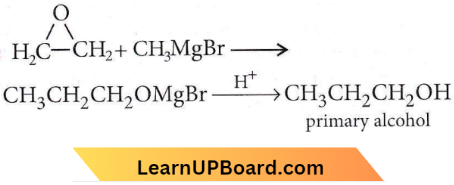
Question 26. Ethylene oxide when treated with Grignard reagent yields
- Primary alcohol
- Secondary alcohol
- Tertiary alcohol
- Cyclopropyl alcohol.
Answer: 1. Primary alcohol
Question 27. Which one of the following compounds is most acidic?
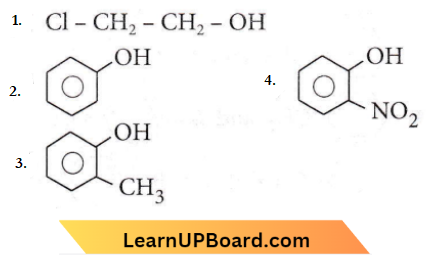
Answer: 3
Phenols are much more acidic than alcohols, due to the stabilization of phenoxide ion by resonance.
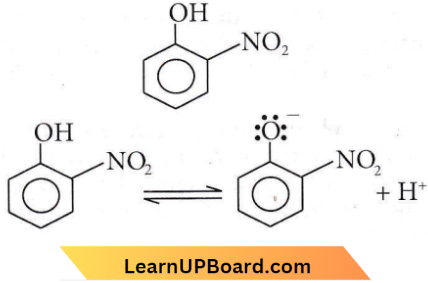
-NO2 is the electron-withdrawing group and helps in stabilizing the negative charge on the oxygen hence equilibrium shifts in the forward direction, and more H+ are removed easily Hence, it is the most acidic.
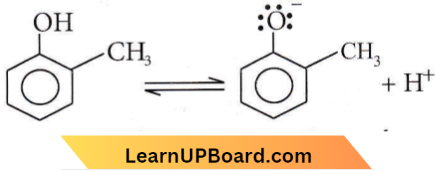
CH3 is the electron-donating group. Hence, electron density increases on the oxygen and destabilizes the product. Thus, equilibrium shifts in the backward direction.
Chemistry MCQs Alcohols Phenols Ethers NEET
Question 28. Which one of the following will not form a yellow precipitate on heating with an alkaline solution of iodine?
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}(\mathrm{OH}) \mathrm{CH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}(\mathrm{OH}) \mathrm{CH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{OH}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{OH}\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{OH}\)
The formation of a yellow precipitate on heating a compound with an alkaline solution of iodine is known as an iodoform reaction. Methyl alcohol does not respond to this test. Iodoform test is exhibited by ethyl alcohol, acetaldehyde, acetone, methyl ketones, and those alcohols that possess the CH3CH(OH)- group.
Question 29. n-Propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol can be chemically distinguished by which reagent?
- PCl5
- Reduction
- Oxidation with potassium dichromate
- Ozonolysis
Answer: 3. Oxidation with potassium dichromate
n-Propyl alcohol on oxidation with potassium dichromate gives an aldehyde which on further oxidation gives an acid. Both aldehydes and acids contain the same number of C atoms as the original alcohol.
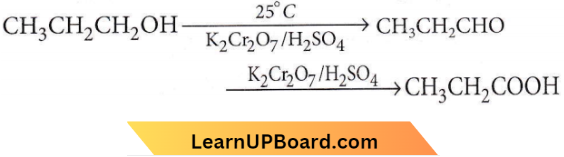
Isopropyl alcohol on oxidation gives a ketone with the same number of C atoms as the original alcohol.
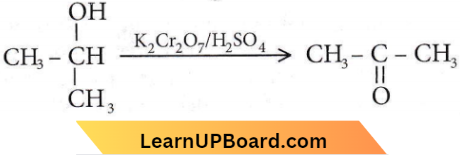
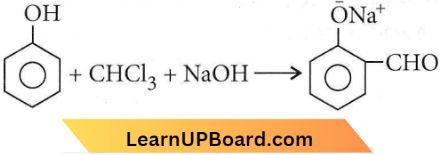
Question 30. When phenol is treated with CHCl3 and NaOH, the product formed is
- Benzaldehyde
- Salicylaldehyde
- Salicylic acid
- Benzoic acid.
Answer: 2. Salicylaldehyde
This reaction is called the Reimer-Tiemann reaction
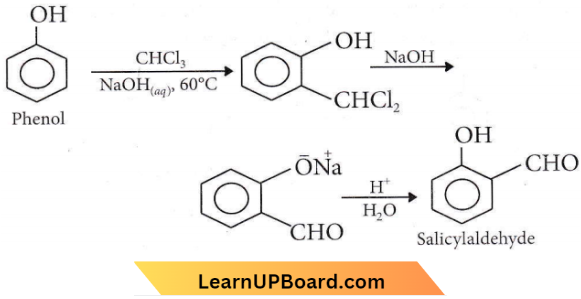
Question 31. Which of the following is correct?
- On reduction, any aldehyde gives secondary alcohol.
- The reaction of vegetable oil with H2SO4 gives glycerine.
- Alcoholic iodine with NaOH gives iodoform.
- Sucrose in reaction with NaCl gives inverted sugar.
Answer: 3. Alcoholic iodine with NaOH gives iodoform.
⇒ \(\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{OH}+4 \mathrm{I}_2+\mathrm{NaOH} \longrightarrow \mathrm{CHI}_3+\mathrm{NaI}\)
+ \(\mathrm{HCOONa}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
Iodoform is a pale yellow solid which crystallizes in hexagonal plates.
Chemistry MCQs Alcohols Phenols Ethers NEET
Question 32. The correct acidic order of the following is
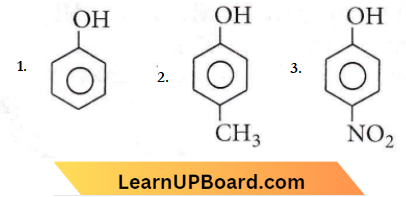
- 1>2>3
- 3>1>2
- 2>3>1
- 1>3>2
Answer: 2. 3>1>2
Phenol exists as a resonance hybrid of the following structures.
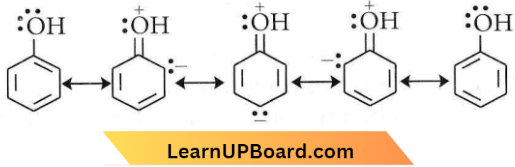
Thus, due to resonance, the oxygen atom of the – OH group acquires a positive charge and hence attracts the electron pair of the O-H bond leading to the release of a hydrogen atom as a proton.
Once the phenoxide ion is formed it stabilises itself by resonance which is more stable than the parent phenol as there is no charge separation.
Effect of substituent: The presence of electron withdrawing groups (-NO2, -X, -CN) increases the acidity of phenols while the presence of electron releasing groups (-NH2 -CH3) decreases the acidity of phenols.
This explains the following order of acidity: p-nitrophenol > phenol >p-cresol.
Question 33. The reaction of 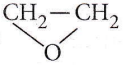 with RMgX leads to the formation of
with RMgX leads to the formation of

Answer: 1
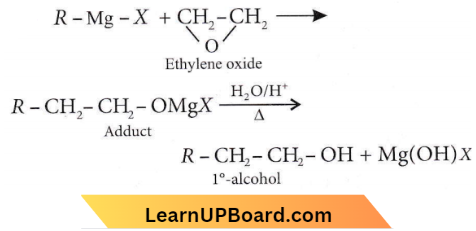
Question 34. When 3,3-dimethyl-2-butanol is heated with H2SO4, the major product obtained is
- 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene
- cis and trans isomers of 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene
- 2,3-dimethyl-1-butene
- 3,3-dimethyl 1-butene
Answer: 1. 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene
Alcohols Phenols Ethers quiz for NEET
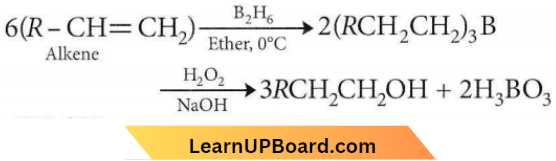
Question 35. The alkene R – CH = CH2 reacts readily with B2H6 and the product on oxidation with alkaline hydrogen peroxides produces
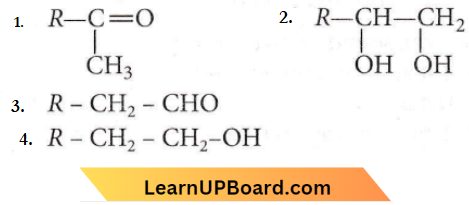
Answer: 4
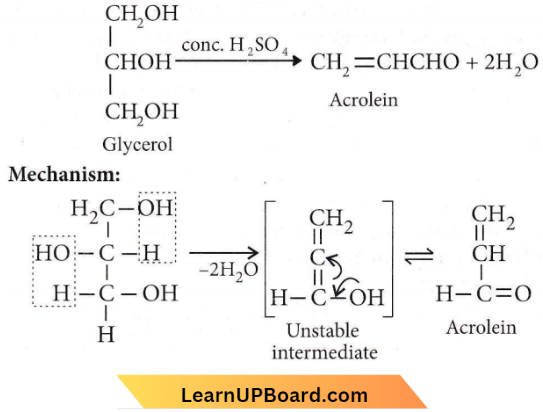
Question 36. On heating glycerol with cone. H2SO4, a compound is obtained which has a bad odor. The compound is
- Acrolein
- Formic acid
- Allyl alcohol
- Glycerol sulfate.
Answer: 1. Acrolein
Question 37. Ethanol and dimethyl ether form a pair of functional isomers. The boiling point of ethanol is higher than that of dimethyl ether, due to the presence of
- H-bonding in ethanol
- H-bonding in dimethyl ether
- CH3 group in ethanol
- CH3 group in dimethyl ether.
Answer:1. H-bonding in ethanol
Ethanol and dimethyl ether form a pair of functional isomers. The boiling point of ethanol is higher than that of dimethyl ether
H-bonding in ethanol
Alcohols Phenols Ethers quiz for NEET
Question 38. Increasing order of acid strength among p-methoxyphenyl,p-methyl phenol and p-nitrophenol is
- p-nitrophenol, p-methoxyphenyl, p-methyl phenol
- p-methyl phenol, p-methoxyphenyl, p-nitrophenol
- p-nitrophenol, p-methyl phenol, p -methoxyphenyl
- p-methoxyphenyl, p-methylphenol, p-nitrophenol.
Answer: 4. p-methoxyphenyl, p-methylphenol, p-nitrophenol.
– OCH3, – CH3 are electron donating groups and decrease the acidic character of phenols. -NO2, is an electron-withdrawing group and tends to increase the acidic character. The electron-donating effect of -OCH3 group (+R effect) is more than that of – CH3 group (+1 effect). Thus, the order is p-methoxyphenol < p-methylphenol < p-nitrophenol.
Question 39. Which one of the following on oxidation gives a ketone?
- Primary alcohol
- Secondary alcohol
- Tertiary alcohol
- All of these
Answer: 2. Secondary alcohol
2° alcohols on oxidation give ketones, 1° alcohols form aldehydes.
Question 40. What is formed when a primary alcohol undergoes catalytic dehydrogenation?
- Aldehyde
- Ketone
- Alkene
- Acid
Answer: 1. Aldehyde
Primary alcohol undergoes catall.tic dehydrogenation to give aldehyde.
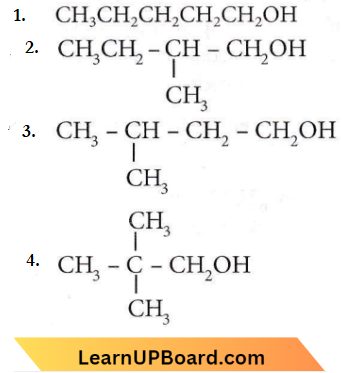
Question 41. How many isomers of C5H11OH will be primary alcohols?
- 5
- 4
- 2
- 3
Answer: 2. 4
4-isomers are possible for C5H11OH.
Question 42. HBr reacts fastest with
- 2-methyl propan-1-ol
- methyl propan-2-ol
- propan-2-ol
- propan-l-ol.
Answer: 2. methylpropan-2-ol
Generates 3° carbocation which is a very stable intermediate, thus it will react more rapidly with HBr.
NEET MCQs on Alcohols Phenols and Ethers
Question 43. When phenol is treated with excess bromine water. It gives
- m-bromophenol
- o- and p-bromophenols
- 2,4-bromophenol
- 2,4,6-tribromophenol.
Answer: 4. 2,4,6-tribromophenol.
Phenol in reaction with excess bromine water gives 2,4,6 – tribromophenol.
Question 44. The compound which reacts fastest with Lucas reagent at room temperature is
- Butan-1-ol
- Butan-2-ol
- 2-Methylpropan-1-ol
- 2-Methylpropan-2-ol.
Asnwer: 4. 2-Methylpropan-2-ol.
2-Methylpropan-2-ol reacts rapidly with Lucas reagent at room temperature.
Question 45. Which one of the following compounds will be most readily attacked by an electrophile?
- Chlorobenzene
- Benzene
- Phenol
- Toluene
Answer: 3. Phenol
-OH group being an electron donor increases the electron density in phenol. Thus, the electron density in phenol is higher than that of toluene, benzene, and chlorobenzene.
Question 46. Propene, CH3CH=CH2 can be converted into 1-propanol by oxidation. Indicate which set of reagents amongst the following is ideal for the above conversion.
- KMnO4 (alkaline)
- Osmium tetroxide (OSO4/CH2Cl2)
- B2H6 and alk.H2O2
- O3/Zn
Answer: 3. B2H6 and alk.H2O2
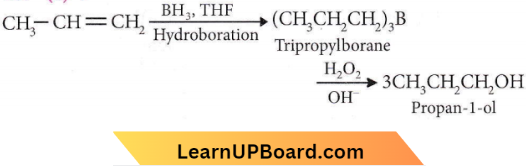
Question 47. Phenol is heated with CHCl3 and aqueous KOH when salicylaldehyde is produced. This reaction is known as
- Rosenmund’s reaction
- Reimer-Tiemann reaction
- Friedel-Crafts reaction
- Sommelet reaction.
Answer: 2. Reimer-Tiemann reaction
Treatment of phenol with CHCI3 and aqueous hydroxide introduces the – CHO group, onto the aromatic ring generally ortho to the – OH group. This reaction is known as Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
Question 48. Lucas’s reagent is
- cone. HCl and anhydrous ZnCl2
- cone. HNO3 and hydrous ZnCl2
- cone. HCl and hydrous ZnCl2
- cone. HNO3 and anhydrous ZnCl2
Answer: 1. cone. HCl and anhydrous ZnCl2
Question 49. Methanol is industrially prepared by
- Oxidation of CH4 by steam at 900°C
- Reduction of HCHO using LiAIH4
- The reaction of HCHO with a solution of NaOH
- Reduction of CO using H2 and ZnO-Cr2O3.
Answer: 4. Reduction of CO using H2 and ZnO-Cr2O3.
⇒ \(\mathrm{CO}+2 \mathrm{H}_2\) \(\underrightarrow{\mathrm{ZnO}-\mathrm{Cr}_2}\) \({\mathrm{O}_3} \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{OH}\)
NEET MCQs on Alcohols Phenols and Ethers
Question 50. Consider the following reaction
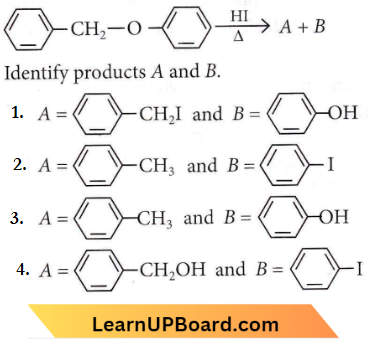
Answer: 1
Alkyl aryl ethers are cleaved at the alkyl-oxygen bond due to a more stable aryl-oxygen bond. The reaction yields phenol and alkyl halide.
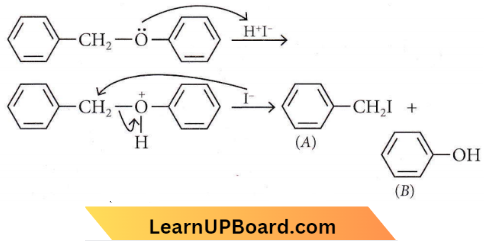
Question 51. Anisole on cleavage with HI gives
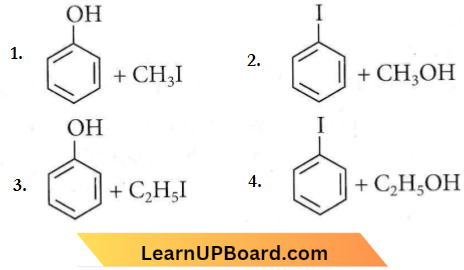
Answer: 1
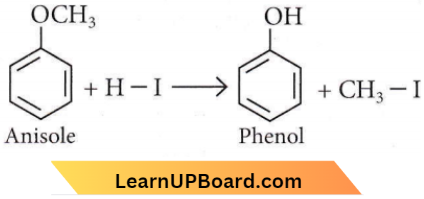
Alcohols Phenols Ethers NEET question bank
Question 52. The compound that is most difficult to protonate is
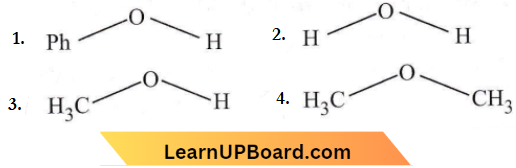
Answer: 1
The lone pair of oxygen is in conjugation with the phenyl group so, it is the least basic among the given compounds and is most difficult to protonate.
Question 53. The major products C and D formed in the following reactions respectively are \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{O}-\mathrm{C}\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3\) \(\underrightarrow{\text { excess } \mathrm{HI}}\) C+D
- \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{I}\) and \(\mathrm{I}-\mathrm{C}\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{OH}\) and \(\mathrm{I}-\mathrm{C}\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{I}\) and \(\mathrm{HO}-\mathrm{C}\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{OH}\) and \(\mathrm{HO}-\mathrm{C}\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{I}\) and \(\mathrm{I}-\mathrm{C}\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3\)
Ethers are readily attacked by HI to give an alkyl halide and alcohol. But when heated with excess of HI, the product alcohol first formed reacts further with HI to form the corresponding alkyl iodide.
⇒ \(\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{O}-\mathrm{R}^{\prime}+\underset{\text { (excess) }}{2 \mathrm{HI}}\) \(\underrightarrow{\text { (Heat) }}\) \(\mathrm{RI}+\mathrm{R}^{\prime} \mathrm{I}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
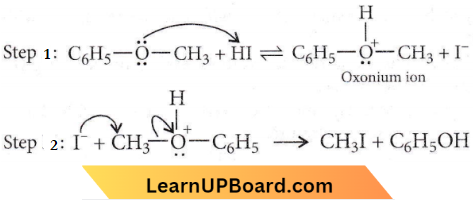
Question 54. The heating of phenyl methyl ether with HI produces
- Iodobenzene
- Phenol
- Benzene
- Ethyl chloride.
Answer: 2. Phenol
In case of phenyl methyl ether, methyl phenyl oxonium ion 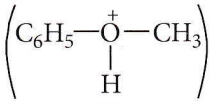 is formed by protonation of ether. The O-CH3 bond is weaker than O-C6H5 bond as O-C6H5 has a partial double bond character. Therefore, the attack by I– ion breaks O-CH3 bond to form CH3l.
is formed by protonation of ether. The O-CH3 bond is weaker than O-C6H5 bond as O-C6H5 has a partial double bond character. Therefore, the attack by I– ion breaks O-CH3 bond to form CH3l.
Question 55. The reaction can be classified as
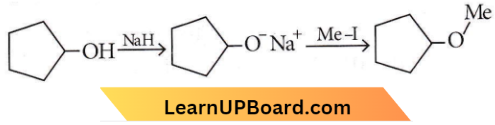
- Dehydration reaction
- Williamson alcohol synthesis reaction
- Williamson ether synthesis reaction
- Alcohol formation reaction.
Answer: 3. Williamson ether synthesis reaction
Williamson ether synthesis reaction involves the treatment of sodium alkoxide with a suitable alkyl halide to form an ether.
Alcohols Phenols Ethers NEET question bank
Question 56. The reaction is called
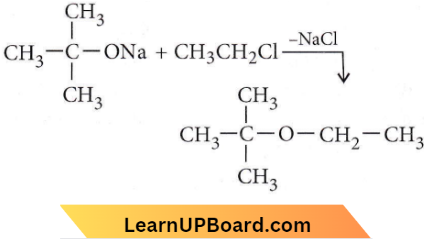
- Etard reaction
- Gattermann-Koch reaction
- Williamson synthesis
- Williamson continuous etherification process.
Answer: 3. Williamson synthesis
Williamson synthesis is the best method for the preparation of ether.
Question 57. Among the following sets of reactants which one produces anisole?
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CHO} ; \mathrm{RMgX}\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{OH} ; \mathrm{NaOH} ; \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{I}\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{OH}\); neutral \(\mathrm{FeCl}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{CH}_3 ; \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COCl} ; \mathrm{AlCl}_3\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{OH} ; \mathrm{NaOH} ; \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{I}\)
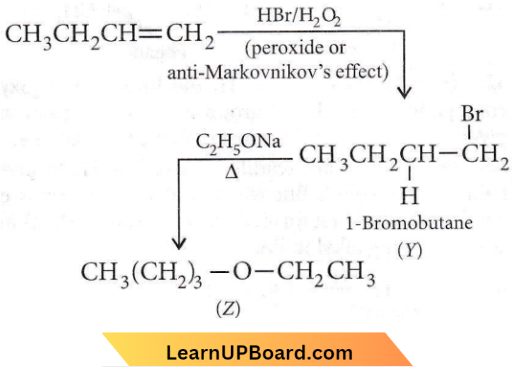
Question 58. Identify Z in the sequence of reactions: \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}=\mathrm{CH}_2\) \(\underrightarrow{\mathrm{HBr} / \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2}\) Y \(\underrightarrow{\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{ONa}} \) Z
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3-\left(\mathrm{CH}_2\right)_3-\mathrm{O}-\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_3\)
- \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_2 \mathrm{CH}-\mathrm{O}-\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3\left(\mathrm{CH}_2\right)_4-\mathrm{O}-\mathrm{CH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{CH}\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)-\mathrm{O}-\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_3\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{CH}_3-\left(\mathrm{CH}_2\right)_3-\mathrm{O}-\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_3\)
Alcohols Phenols Ethers NEET question bank
Question 59. Among the following ethers, which one will produce methyl alcohol on treatment with hot concentrated HI?
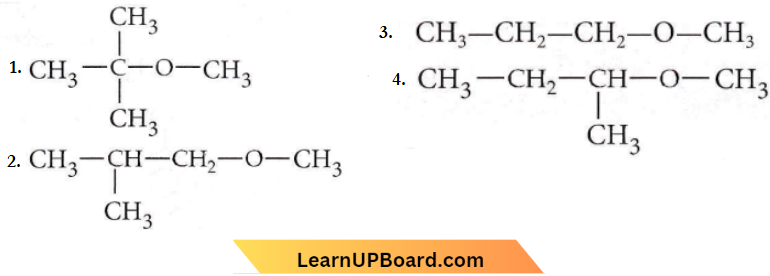
Answer: 1
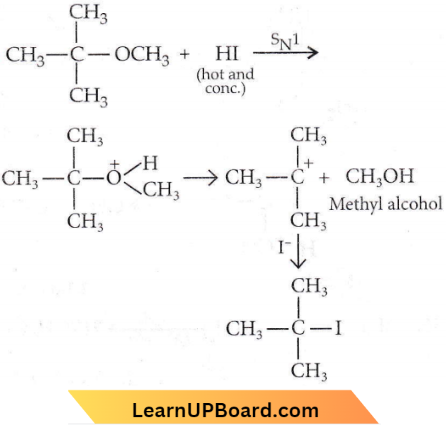
Question 60. In the reaction, which of the following compounds will be formed?
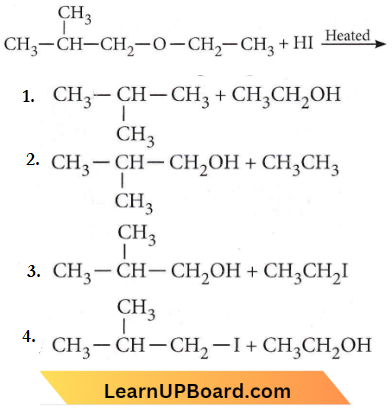
Answer: 3
The alkyl iodide produced depends on the nature of the alkyl groups. If one group is Me and the other a primary or secondary alkyl group, it is methyl iodide that is produced. This can be explained by the assumption that the mechanism is SN2, and because of the steric effect of the larger group, I– attack the smaller methyl group.
When the substrate is a methyl t-alkyl ether, the products are t-RI and MeOH. This can be explained by SN1 mechanism, the carbonium ion produced being the t-alkyl since a tertiary carbonium ion is more stable than a primary or secondary carbonium ion.
Question 61. The major organic product in the reaction is \(\mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{O}-\mathrm{CH}\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_2+\mathrm{HI} \longrightarrow\) products
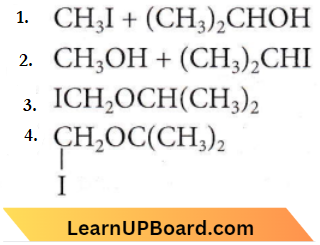
Answer: 1
With cold HI, a mixture of alkyl iodide and alcohol is formed. In the case of mixed ethers, the halogen atom attaches to a smaller and less complex alkyl group.
CH3OCH(CH3)2 + HI → CH3I + (CH3)2CHOH
Alcohols Phenols Ethers NEET question bank
Question 62. Ethyl chloride is converted into diethyl ether by
- Perkins reaction
- Grignard reaction
- Wurtz synthesis
- Williamson synthesis.
Answer: 4. Williamson synthesis.
⇒ \(\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5-\mathrm{Cl}+\mathrm{Na}-\mathrm{O}-\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5 \longrightarrow \mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5-\mathrm{O}-\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5+\mathrm{NaCl}\)
Question 63. Which one of the following compounds is resistant to nucleophilic attack by hydroxyl ions?
- Diethyl ether
- Acetonitrile
- Acetamide
- Methyl acetate
Answer: 1. Diethyl ether
Diethyl ether is a saturated compound, so it is resistant to nucleophilic attack by a hydroxyl ion (OH–). Other compounds have unsaturation and the unsaturated ‘C’ atom bears partial +ve charge, therefore they undergo easy nucleophilic attack by OH– ion.
Question 64. The compound which does not react with sodium is
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CHOHCH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{OH}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{OCH}_3\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{OCH}_3\)
Ethers are very inert. The chemical inertness of others is due to the absence of an active group in their molecules’ Since CH3 – O – CH3 is inert and does not contain an active group, therefore it does not react with sodium
Alcohols Phenols Ethers NEET question bank
Question 65. Which one is formed when sodium phenoxide is heated with ethyl iodide?
- Phenetole
- Ethyl phenyl alcohol
- Phenol
- None of these
Answer: 1. Phenetole
Phenetole is formed when sodium phenoxide is heated with ethyl iodide.
⇒ \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{ONa}+\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{I}\) \(\underrightarrow{\Delta}\) \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{OC}_2 \mathrm{H}_5\)
