Environmental Chemistry NEET MCQs
NEET Chemistry For Environmental Chemistry Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. The pollution due to oxides of sulphur gets enhanced due to the presence of
- Particulate matter
- Ozone
- Hydrocarbons
- Hydrogen peroxide
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
- (1), (4) only
- (1), (2), (4) only
- (2), (3), (4) only
- (1), (3), (4) only
Answer: 2. (1), (2), (4) only
The presence of particulate matter in polluted air catalyses the oxidation of sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide.
⇒ \(2 \mathrm{SO}_{2(g)}+\mathrm{O}_{2(g)} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{SO}_{3(g)}\)
The reaction can also be promoted by ozone and hydrogen peroxide.
⇒ \(\mathrm{SO}_{2(g)}+\mathrm{O}_{3(g)} \rightarrow \mathrm{SO}_{3(g)}+\mathrm{O}_{2(g)}\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{SO}_{2(g)}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_{2(l)} \rightarrow \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_{4(a q)}\)
Question 2. Match List-1 with List-2
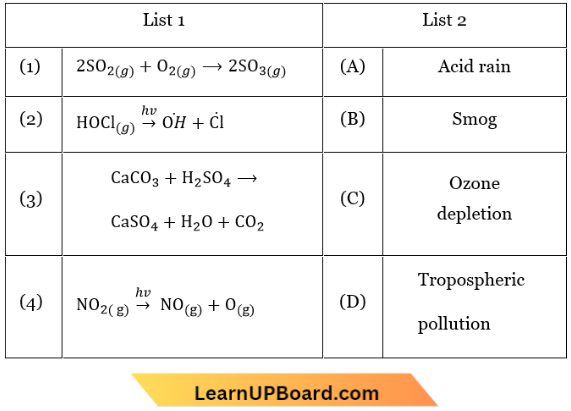
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
- (1) – (C), (2) – (B), (3) – (D), (4) – (A)
- (1) – (A), (2) – (B), (3) – (C), (4) – (D)
- (1) – (B), (2) – (C), (3) – (D), (4) – (A)
- (1) – (D), (2) – (C), (3) – (A), (4) – (B)
Answer: 4. (1) – (D), (2) – (C), (3) – (A), (4) – (B)
Photochemical smog: \(\mathrm{NO}_{2(g)}\) \(\longrightarrow{h v}\) \(\mathrm{NO}_{(g)}+\mathrm{O}_{(g)}\)
Ozone depletion: \(\mathrm{HOCl}_{(g)}\) \(\longrightarrow{h \mathrm{v}}\) \(\dot{\mathrm{O}} \mathrm{H}+\dot{\mathrm{Cl}}\)
Acid rain: \(\mathrm{CaCO}_3+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4 \longrightarrow \mathrm{CaSO}_4+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{CO}_2\)
Tropospheric pollution: \(2 \mathrm{SO}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}+\mathrm{O}_{2(\mathrm{~g})} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{SO}_{3(\mathrm{~g})}\)
Read and Learn More NEET MCQs with Answers
NEET questions on Environmental Chemistry
Question 3. Which of the following is not correct about carbon monoxide?
- It forms carboxyhaemoglobin.
- It reduces oxygen oxygen-carrying ability of blood.
- The carboxyhaemoglobin (haemoglobin bound to CO) is less stable than oxyhaemoglobin.
- It is produced due to incomplete combustion.
Answer: 3. It is produced due to incomplete combustion.
The carboxyhaemoglobin is about 300 times more stable than oxyhaemoglobin.
Question 4. Among the following, the one that is not a greenhouse gas is
- Sulphur dioxide
- Nitrous oxide
- Methane
- Ozone.
Answer: 1. Sulphur dioxide
Besides carbon dioxide, other greenhouse gases are methane, water vapours, nitrous oxide, CFCs and ozone.
Question 5. Which oxide of nitrogen is not a common pollutant introduced into the atmosphere both due to natural and human activity?
- N2O5
- NO2
- N2O
- NO
Answer: 1. N2O5
Environmental Chemistry multiple choice NEET
Question 6. Which of the following is a sink for CO?
- Microorganisms present in the soil
- Oceans
- Plants
- Haemoglobin
Answer: 1. Microorganisms present in the soil
Microorganisms present in the soil consume atmospheric CO
Question 7. Which one of the following is not a common component of photochemical smog?
- Ozone
- Acrolein
- Peroxyacetyl nitrate
- Chlorofluorocarbons
Answer: 4. Chlorofluorocarbons
Question 8. Which one of the following statements regarding photochemical smog is not correct?
- Carbon monoxide does not play any role in photochemical smog formation.
- Photochemical smog is an oxidising agent in character.
- Photochemical smog is formed through a photochemical reaction involving solar energy.
- Photochemical smog does not cause
Answer: 4. Photochemical smog does not cause
Photochemical smog causes irritation in the eyes and throat.
NEET practice questions Environmental Chemistry
Question 9. Which one of the following is responsible for the depletion of the ozone layer in the upper strata of the atmosphere?
- Polyhalogens
- Ferrocene
- Fullerenes
- Freons
Answer: 4. Freons
Chlorofluorocarbons such as freon-11 (CFCI3) and freon-12 (CF2Cl2) emitted as propellants in aerosol spray cans, refrigerators, fire fighting reagents etc. are stable compounds and chemically inert.
They do not react with, any substance with which they come in contact and thus float through the atmosphere unchanged and eventually enter the stratosphere.
There they absorb UV radiation and break down liberating free atomic chlorine which causes the decomposition of ozone. This results in the depletion of the ozone layer.
⇒ \(\dot{\mathrm{Cl}}+\mathrm{O}_3 \rightarrow \mathrm{ClO}+\mathrm{O}_2 ; \mathrm{ClO}+\mathrm{O}_3 \rightarrow \dot{\mathrm{Cl}}+2 \mathrm{O}_2\)
Question 10. About 20 km above the earth, there is an ozone layer. Which one of the following statements about ozone and the ozone layer is true?
- It is beneficial to us as it stops UV radiation.
- Conversion of O3 to O2 is an endothermic reaction.
- Ozone is a triatomic linear molecule.
- It is harmful as it stops useful radiation. (1995)
Answer: 1. It is beneficial to us as it stops UV radiation.
About 20 km above the earth, there is an ozone layer.
The ozone layer is very beneficial to us because it stops harmful ultraviolet radiation from reaching the Earth.
Question 11. Given below are two statements.
Statement 1: The nutrient-deficient water bodies lead to eutrophication.
Statement 2: Eutrophication leads to a decrease in the level of oxygen in the water bodies.
Chemistry MCQs Environmental Chemistry NEET
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- Statement 1 is correct but Statement 2 is false.
- Statement 1 is incorrect but Statement 2 is true.
- Both Statement 1 and Statement 2 are true.
- Both Statement 1 and Statement 2 are false.
Answer: 2. Statement 1 is incorrect but Statement 2 is true.
The process in which nutrient-enriched water bodies support a dense plant population, which kills animal litter by depriving it of oxygen and results in subsequent loss of biodiversity is known as Eutrophication.
Question 12. Which one of the following statements is not true?
- Clean water would have a BOD value of 5 ppm.
- Fluoride deficiency in drinking water is harmful. Soluble fluoride is often used to bring its concentration up to 1 ppm.
- When the pH of rainwater is higher than 6.5, it is called acid rain.
- Dissolved Oxygen (DO) in cold water can reach a concentration of up to 10 ppm.
Answer: 3. When the pH of rainwater is higher than 6.5, it is called acid rain.
When the pH of rainwater drops below 5.6 it is called acid rain.
Environmental Chemistry quiz for NEET
Question 13. Which one of the following statements is not true?
- pH of drinking water should be between 5.5 and 9.5.
- The concentration of DO below 6 ppm is good for the growth of fish.
- Clean water would have a BOD value of less than 5 ppm.
- Oxides of sulphur, nitrogen and carbon, are the most widespread air pollutant.
Answer: 2. The concentration of DO below 6 ppm is good for the growth of fish.
Fish flies in water bodies polluted by sewage due to a decrease in dissolved oxygen (D.O.)
NEET MCQs on Environmental Chemistry
Question 14. Green chemistry means such reactions which
- Are related to the depletion of the ozone layer
- Study the reactions in plants
- Produce colour during reactions
- Reduce the use and production of hazardous chemicals.
Answer: 4. Reduce the use and production of hazardous chemicals.
Green chemistry is the design, development, and implementation of chemical products and processes to reduce or eliminate the use and generation of substances hazardous to human health and the environment.
Green chemistry also refers to the redesign of chemical products and processes with the goal of reducing or eliminating any negative environmental or health effects.
