Hydrocarbons NEET MCQs
NEET Chemistry For Hydrocarbons Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. The dihedral angle of the least stable conformer of ethane is
- 0°
- 120°
- 180°
- 60°
Answer: 1. 0°
The dihedral angle of the least stable conformer of ethane is 0°. The magnitude of torsional strain depends upon the angle of rotation about the C – C bond. This angle is also called dihedral angle or torsional angle. Of all the conformations of ethane, the staggered form has the least torsional strain, and the eclipsed form has the maximum torsional strain.
Question 2. 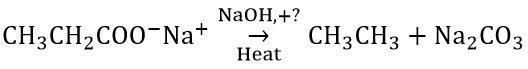
Consider the above reaction and identify the missing reagent/chemical.
- DIBAL-H
- B2H6
- Red Phosphorus
- CaO
Answer: 4. CaO
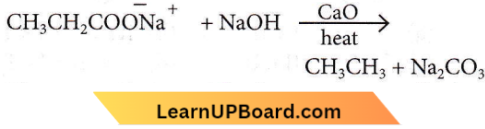
Question 3. Which of the following alkanes cannot be made in good yield by the Wurtz reaction?
- n-Hexane
- 2, 3-Dimethylbutane
- n-Heptane
- n-Butane
Answer: 3. n-Heptane
Wurtz reaction is used for the preparation of higher alkanes containing an even number of C-atoms. Thus this reaction cannot be used for the preparation of n-heptane.
Read and Learn More NEET MCQs with Answers
Question 4. The alkane that gives only one monochloride product on chlorination with Cl2 in the presence of diffused sunlight is
- 2,2-dimethylbutane
- Neopentane
- n-pentane
- Isopentane.
Answer: 2. Neopentane
In the chlorination of alkanes, hydrogen is replaced by chlorine. In neo-pentane, only one type of hydrogen is present, hence the replacement of any hydrogen atom will give the same product.
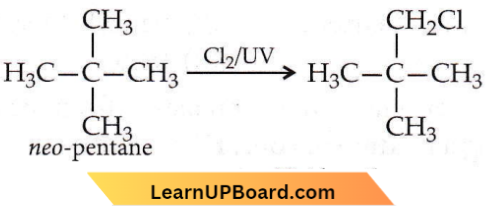
Question 5. Hydrocarbon (A) reacts with bromine by substitution to form an alkyl bromide which by Wurtz reaction is converted to gaseous hydrocarbon containing less than four carbon atoms. (A) is
- CH ≡ CH
- CH2 = CH2
- CH3 — CH3
- CH4
Answer: 4. CH4

Hydrocarbons NEET MCQs
Question 6. With respect to the conformers of ethane, which of the following statements is true?
- The bond angle changes but the bond length remains the same.
- Both bond angle and bond length change.
- Both bond angle and bond length remain the same.
- Bond angle remains the same but the bond length changes.
Answer: 3. Both bond angle and bond length remain the same.
Conformers of ethane have different dihedral angles but the same bond angle and bond lengths.
Question 7. The correct statement regarding the comparison of staggered and eclipsed conformations of ethane is
- The eclipsed conformation of ethane is more stable than staggered conformation even though the eclipsed conformation has torsional strain
- The staggered conformation of ethane is more stable than eclipsed conformation because staggered conformation has no torsional strain
- The staggered conformation of ethane is less stable than eclipsed conformation because staggered conformation has torsional strain
- The eclipsed conformation of ethane is more stable than staggered conformation because eclipsed conformation has no torsional strain.
Answer: 2. The staggered conformation of ethane is more stable than eclipsed conformation because staggered conformation has no torsional strain
Conformers of ethane have different dihedral angles but the same bond angle and bond lengths.
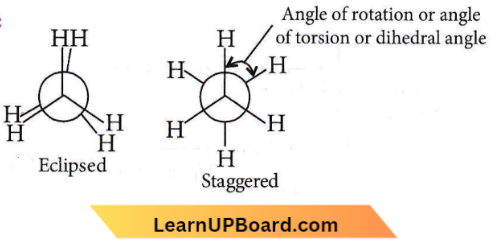
The magnitude of torsional strain depends upon the angle of rotation of the C-C bond. The staggered form has the least torsional strain and the eclipsed form has the maximum torsional strain. So, the staggered conformation of ethane is more stable than the eclipsed conformation.
Question 8. In the following the most stable conformation of n-butane is
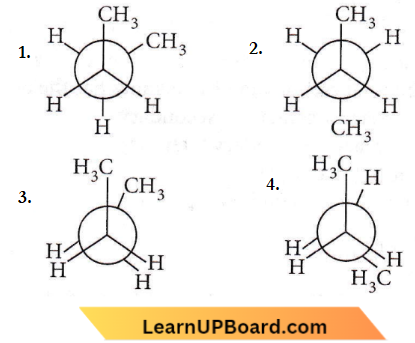
Answer: 2
The anti-conformation is the most stable conformation of n-butane as in this, the bulky methyl groups are as far apart as possible thereby keeping steric repulsion at a minimum
Question 9. Liquid hydrocarbons can be converted to a mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons by
- Oxidation
- Cracking
- Distillation under reduced pressure
- Hydrolysis.
Answer: 2. Cracking
The process of cracking converts higher alkanes into smaller alkanes and alkenes. This process can be used for the production of natural gas.
NEET questions on Hydrocarbons
Question 10. Which of the following conformers for ethylene glycol is most stable?
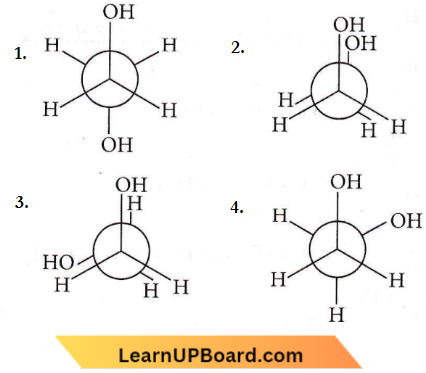
Answer: 4
The conformation (4) is most stable because of intermolecular H-bonding.
Question 11. The dihedral angle in the staggered form of ethane is
- 0°
- 120°
- 60°
- 180°
Answer: 3. 60°
The staggered form of ethane has the following structure and the dihedral angle is 60°, which means ‘H’ atoms are at an angle of 60° to each other.
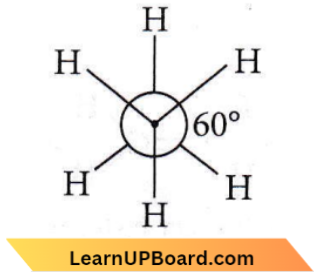
Question 12. Which of the following reactions is expected to readily give a hydrocarbon product in good yields?
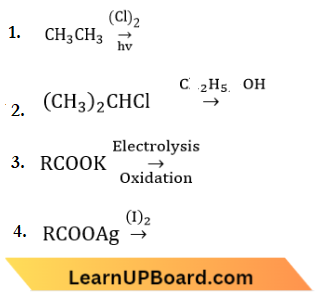
Answer: 3.
When an aqueous solution of sodium or potassium salt of a carboxylic acid is electrolyzed, hydrocarbon is evolved at the anode.
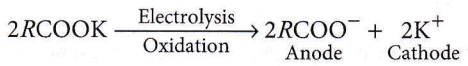
At anode: \(2 \mathrm{RCOO}^{-}-2 e^{-} \rightarrow \underset{ Alkane }{R-R}+2 \mathrm{CO}_2\)
Question 13. In commercial gasoline, the type of hydrocarbons that are more desirable is
- Linear unsaturated hydrocarbon
- Toluene
- Branched hydrocarbon
- Straight-chain hydrocarbon.
Answer: 3. Branched hydrocarbon
The branching of the chain increases the octane number of a fuel. A high octane number means better fuel
Question 14. The most stable conformation of n-butane is
- Gauche
- Staggered
- Skew boat
- Eclipsed.
Answer: 2. Staggered
Newman projections for n-butane are
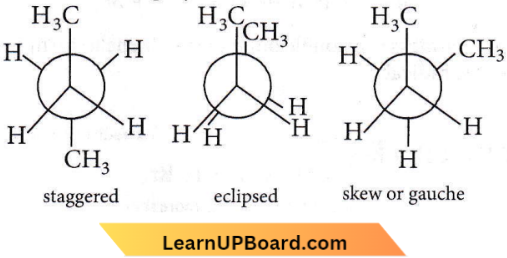
The staggered conformation has minimum repulsion between the hydrogen atoms attached tetrahedrally to the two carbon atoms. Thus, it is the most stable conformation.
Question 15. Which of the following is used as an antiknocking material?
- Glyoxal
- Freon
- T.E.L.
- Ethyl alcohol
Answer: 3. T.E.L.
Tetraethyllead(C2H5)4Pb, is used as an antiknocking agent in gasoline used for running automobiles.
NEET questions on Hydrocarbons
Question 16. The reactivity of hydrogen atoms attached to different carbon atoms in alkanes has the order
- Tertiary > primary > secondary
- Primary > secondary > tertiary
- Both (1) and (2)
- Tertiary > secondary > primary.
Answer: 4. Tertiary > secondary > primary.
The reactivity of the H-atom depends upon the stability of free radicals, therefore reactivity of the H-atom follows the order: 3°>2°>1°.
Question 17. Compound X on reaction with O3 followed by Zn/H2O gives formaldehyde and 2-methylpropanal as products. The compound X is
- 3-methyl but-l-ene
- 2-methyl but-l-ene
- 2-methyl but-2-ene
- pent-2-ene.
Answer: 1

So, X can be
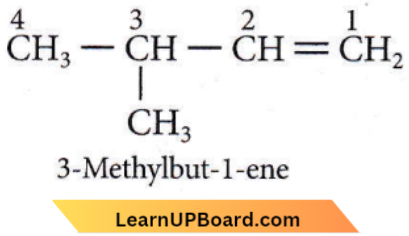
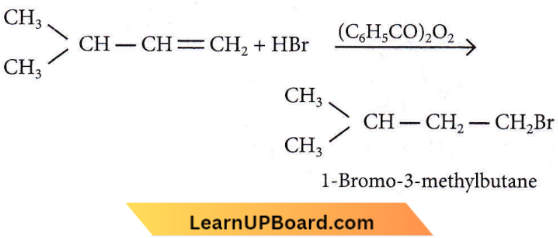
Question 18. The major product of the following chemical reaction is
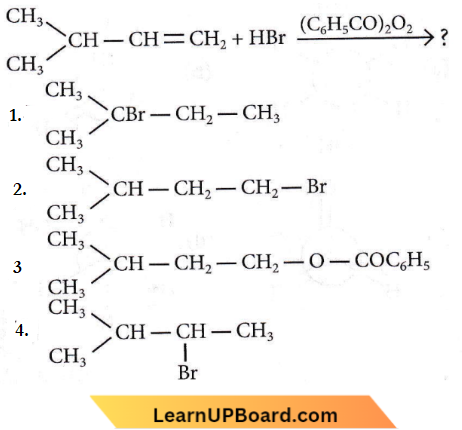
Answer: 2
In the presence of peroxide, an addition reaction takes place.
Question 19. An alkene on ozonolysis gives methanal as one of the products. Its structure is
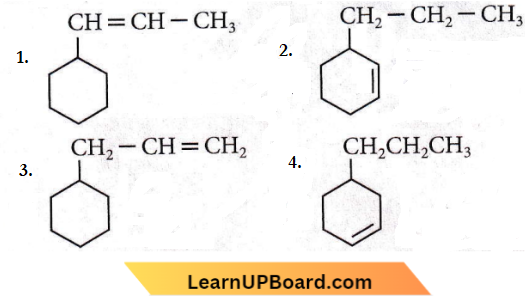
Answer: 3
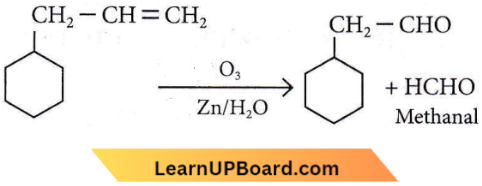
Hydrocarbons multiple choice NEET
Question 20. An alkene A on reaction with O3 and Zn—H2O gives propanone and ethanal in equimolar ratio. The addition of HCl to alkene A gives B as the major product. The structure of product B is
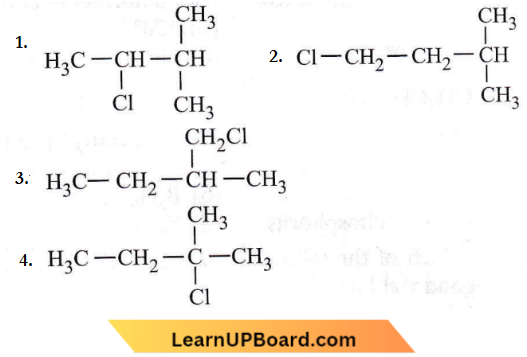
Answer: 4
An alkene A on reaction with O3 and Zn—H2O gives propanone and ethanal in equimolar ratio. The addition of HCl to alkene A gives B as the major product.
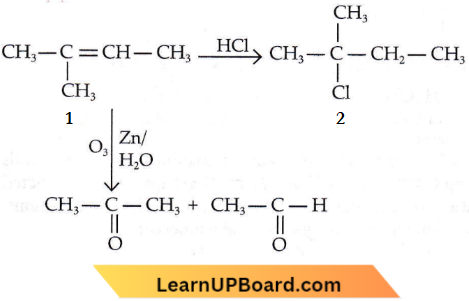
Addition of HCI to an alkene (1) will take place according to Markownikoff’s rule.
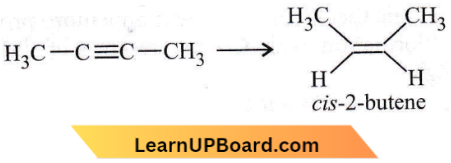
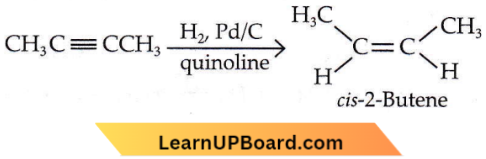
Question 21. The most suitable reagent for the following conversion is
- Hg2+/H+,H2O
- Na/liquid NH2
- H2, Pd/C, quinoline
- Zn/HCl
Answer: 3. H2, Pd/C, quinoline
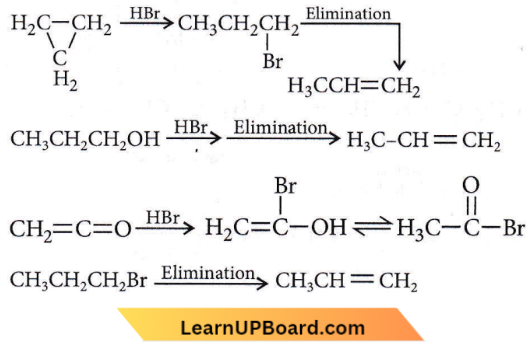
Question 22. Which of the following compounds shall not produce propene by reaction with HBr followed by elimination or direct only elimination reaction?
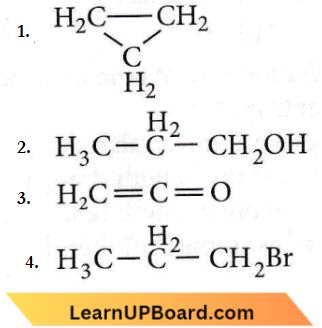
Answer: 3
Question 23. The compound that will react most readily with gaseous bromine has the formula
- C3H6
- C2H2
- C4H10
- C2H4
Amswer: 1. C3H6
The rate of free radical substitution with Br2(g) depends upon the stability of free radicals. Propenyl free radical is allylic free radical which is more stable.
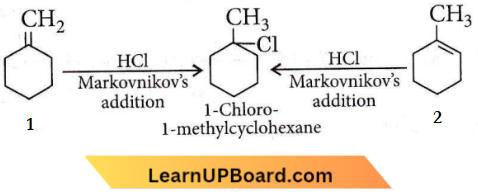
Question 24. In the reaction with HCl, an alkene reacts in accordance with the Markovnikovs rule to give a product 1-chloro-1-methyl-cyclohexane. The possible alkene is
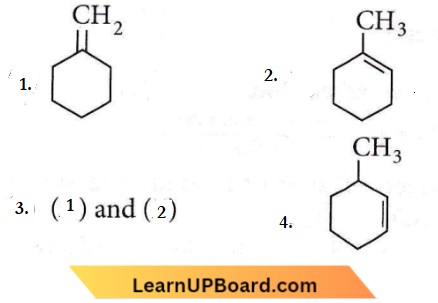
Answer: 3
Hydrocarbons multiple choice NEET
Question 25. Which of the following is not the product of dehydration of 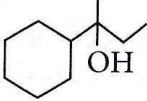 isomerism?
isomerism?
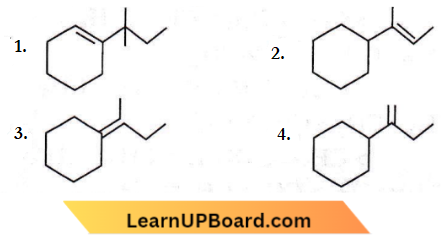
Answer: 1
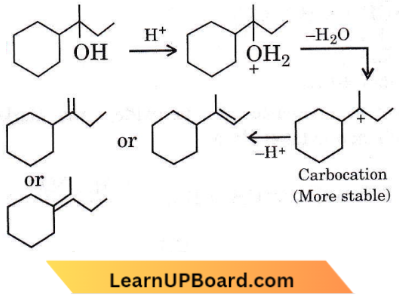
Question 26. In the following reaction

Answer: 1
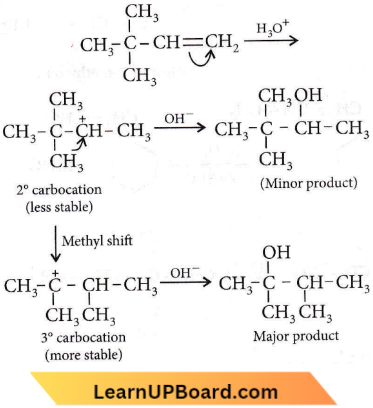
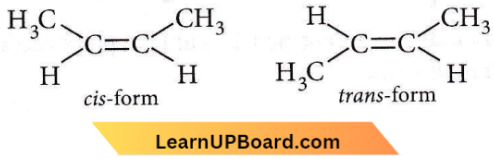
Question 27. Which of the following compounds will exhibit cis-trans (geometrical) isomerism?
- Butanol
- 2-Butyne
- 2-Butenol
- 2-Butene
Answer: 4. 2-Butene
Cis-trans isomerism is exhibited by compounds having C – C, C – N, and N – N groups, due to restricted rotation around the double bond. Among the given options, only 2-butene exhibits geometrical isomerism.
Question 28.
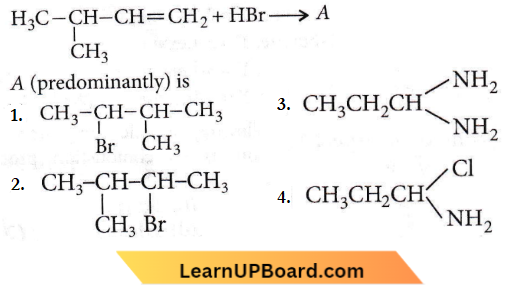
Answer: 4
Question 29. Which of the compounds with molecular formula C5H10 yields acetone on ozonolysis?
- 3-Methyl-1-butene
- Cyclopentane
- 2-Methyl-1-butene
- 2-Methyl-2-butene
Answer: 4. 2-Methyl-2-butene
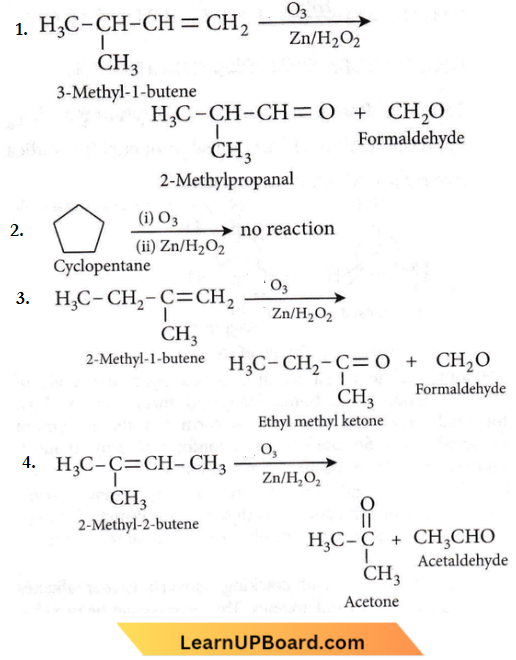
NEET practice questions Hydrocarbons
Question 30. Which one of the following alkenes will react faster with H2 under catalytic hydrogenation conditions?
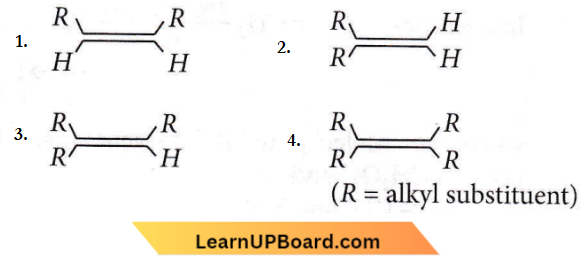
Answer: 1
The relative rates of hydrogenation decrease with the increase of steric hindrance. Most stable alkene, slowly it undergoes hydrogenation to give the product. The least substituted alkene is less stable and more reactive.
Order of stability is:
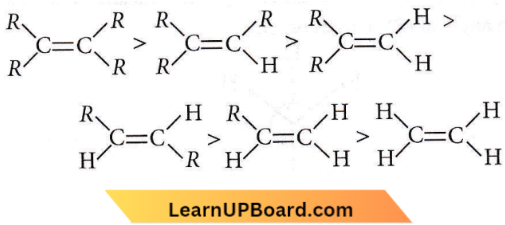
Hence, alkene which will react faster with H, is that which is most unstable
Question 31. The reaction of HBr with propene in the presence of peroxide gives
- Isopropyl bromide
- 3-bromopropane
- Allyl bromide
- n-propyl bromide.
Answer: 4. n-propyl bromide.
The formation of n-propyl bromide in the presence of peroxide can be explained as follows:
Step 1: Peroxide undergoes fission to give free radicals \(\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{O}-\mathrm{O}-\mathrm{R} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{R}-\dot{\mathrm{O}}\)
Step 2: HBr combines with free radicals to form bromine free radicals. \(R-\dot{\mathrm{O}}+\mathrm{HBr} \longrightarrow \mathrm{R}-\mathrm{OH}+\dot{\mathrm{Br}}\)
Step 3: Br attacks the double bond of the alkene to form a more stable free radical
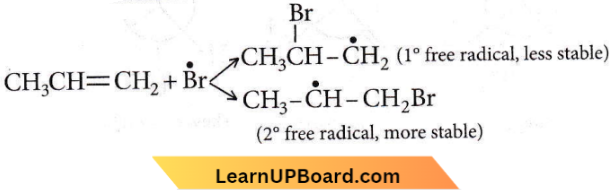
Step 4: More stable free radical attacks on HBr. \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \dot{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{HCH}_2 \mathrm{Br}+\mathrm{HBr} \longrightarrow \underset{n-\text { Propyl bromide }}{\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{Br}+\dot{\mathrm{Br}}}\)
Step 5: \(\dot{\mathrm{Br}}+\dot{\mathrm{Br}} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Br}_2\)
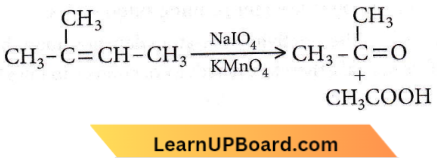
Question 32. The compound, 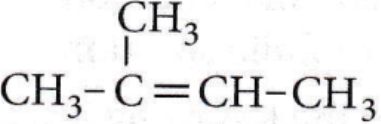 on reaction with NaIO4 in the presence of KMnO2 gives
on reaction with NaIO4 in the presence of KMnO2 gives
- CH3COCH3
- CH3COCH3 + CH3COOH
- CH3COCH3 + CH3CHO
- CH3CHO + CO3
Answer: 2. CH3COCH3 + CH3COOH
Question 33. Geometrical isomers differ in
- Position of functional group
- Position of atoms
- Spatial arrangement of atoms
- Length of the carbon chain.
Answer: 3. Spatial arrangement of atoms
Geometrical isomers are those isomers that possess the same molecular and structural formula but differ in the arrangement of atoms or groups in space due to hindered rotation around the double-bonded atoms.
Chemistry MCQs Hydrocarbons NEET
Question 34. In preparation of alkene from alcohol using Al2O3 which is the effective factor?
- Porosity of Al2O3
- Temperature
- Concentration
- Surface area of Al2O3
Answer: 2. Temperature
Temperature is an effective factor because at different temperatures it forms different products
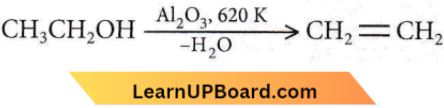
This is intramolecular dehydration. At lower temperatures, intermolecular dehydration takes place between two molecules of alcohol and ether will be formed.
Question 35. Which reagent converts propane to 1-propanol?
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}, \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{B}_2 \mathrm{H}_6, \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2, \mathrm{OH}^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{Hg}(\mathrm{OAc})_2, \mathrm{NaBH}_4 / \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- Aq. KOH
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{B}_2 \mathrm{H}_6, \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2, \mathrm{OH}^{-}\)
Propene adds to diborane (B2H6) giving an additional product. The addition compound on oxidation gives l-propanol. Here the addition of water takes place according to anti-Markownikoff ‘s rule
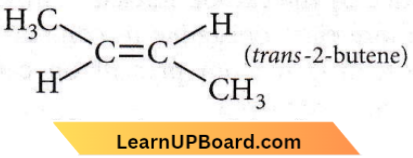
Question 36. Which is maximum stable?
- 1-Butene
- cis-2-Butene
- trans-2-Butene
- All have the same stability.
Answer: 3. trans-2-Butene
This is the most stable as the repulsion between two methyl groups is the least.
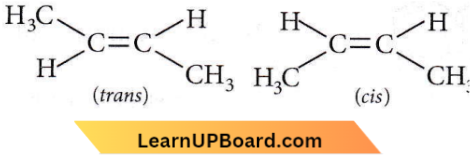
Question 37. 2-Butene shows geometrical isomerism due to
- Restricted rotation about the double bond
- Free rotation about the double bond
- Free rotation about single bond
- Chiral carbon.
Answer: 1. Restricted rotation about the double bond
Due to restricted rotation about double bonds, 2-butene shows geometrical isomerism.
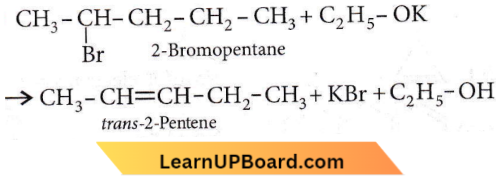
Question 38. 2-Bromopentane is heated with potassium ethoxide in ethanol. The major product obtained is
- trans-2-pentene
- 1-pentene
- 2-ethoxy pentane
- 2-ds-pentene.
Answer: 1. trans-2-pentene
Question 39. In a reaction, 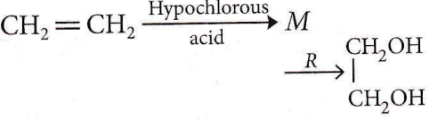 where, M = Molecule and R = Reagent. M and R are
where, M = Molecule and R = Reagent. M and R are
- CH3CH2OH and HCl
- CH2 = CH2 and heat
- CH3CH2Cl and NaOH
- CH2Cl – CH2OH and aq. NaHCO3
Answer: 4. CH2Cl – CH2OH and aq. NaHCO3
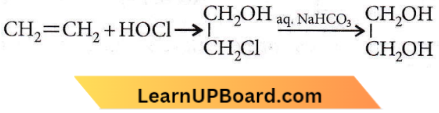
Therefore, M = CH2CI-CH2OH and
R = ag.NaHCO3
Chemistry MCQs Hydrocarbons NEET
Question 40. The reaction, CH2 = CH – CH2 + HBr → CH2CHBr – CH3 is
- Electrophilic substitution
- Free radical addition
- Nucleophilic addition
- Electrophilic addition.
Answer: 4. Electrophilic addition.
In this reaction, HBr undergoes heterolytic fission as HBr → H+ + Br–
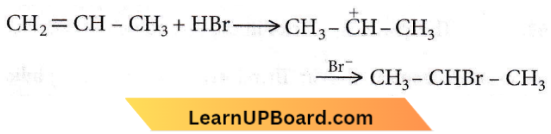
This is an example of an electrophilic addition reaction
Question 41. Which of the following has zero dipole moment?
- 1-Butene
- 2-Methyl-1-propene
- cis-2-Butene
- trans-2-Butene
Answer: 4. trans-2-Butene
Question 42. One of the following which does not observe the anti-Markownikoff addition of HBr, is
- Pent-2-ene
- Propene
- But-2-ene
- But-1-ene.
Answer: 3. But-2-ene
In the case of but-2-ene (CH3– CH-CH- CH2)both double-bonded carbons are identical. Therefore, it does not observe the anti-Markownikoff addition of HBr
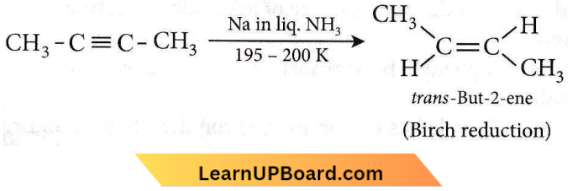
Question 43. Reduction of 2-butyne with sodium in liquid ammonia gives predominantly
- cis-2-butene
- No reaction
- Trans-2-butene
- n-butane.
Answer: 3. Trans-2-butene
Reduction of non-terminal alkynes with Na in Liq. NH3 at 195 – 200 K gives trans-alkene.
Question 44. The restricted rotation about the carbon double bond in 2-butene is due to
- Overlap of one s and sp²-hybridized orbitals
- Overlap of two sp²-hybridized orbitals
- Overlap of one p and one sp²-hybridized orbitals
- Sideways overlap of two p-orbitals.
Answer: 4. Sideways overlap of two p-orbitals.
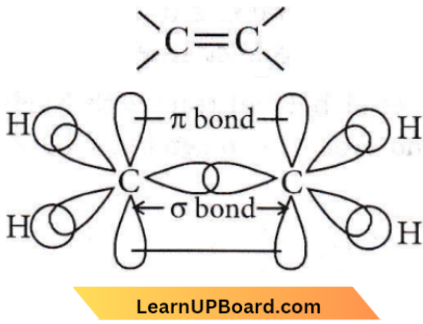
Restricted rotation is due to sideways overlap of two p-orbitals.
Question 45. Which one of the following can exhibit cis-trans isomerism?
- CH3 – CHCl – COOH
- H – C ≡ C – Cl
- ClCH =CHCl
- ClCH2 – CH2Cl
Answer: 3. ClCH =CHCl
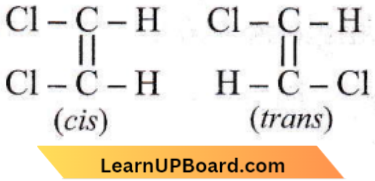
1, 2-Dichloroethene exhibits cis-trans (geometrical) isomerism
Question 46. In the following reaction, 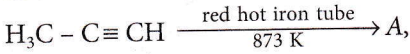 the number of sigma(σ) bonds present in the product A, is
the number of sigma(σ) bonds present in the product A, is
- 21
- 9
- 24
- 18
Answer: 1. 21
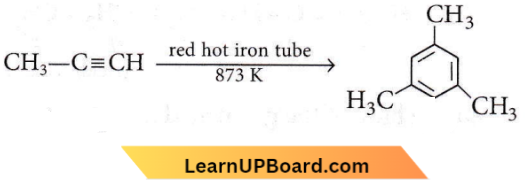
There are 21 σ bonds.
Question 47. Which one is the correct order of acidity?
- \(\mathrm{CH} \equiv \mathrm{CH}>\mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{C} \equiv \mathrm{CH}\) \(>\mathrm{CH}_2=\mathrm{CH}_2>\mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{CH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{CH} \equiv \mathrm{CH}>\mathrm{CH}_2=\mathrm{CH}_2\) \(>\mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{C} \equiv \mathrm{CH}>\mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{CH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{CH}_3>\mathrm{CH}_2=\mathrm{CH}_2\) \(>\mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{C} \equiv \mathrm{CH}>\mathrm{CH} \equiv \mathrm{CH}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_2=\mathrm{CH}_2>\mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{CH}=\mathrm{CH}_2\) \(>\mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{C} \equiv \mathrm{CH}>\mathrm{CH} \equiv \mathrm{CH}\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{CH} \equiv \mathrm{CH}>\mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{C} \equiv \mathrm{CH}\) \(>\mathrm{CH}_2=\mathrm{CH}_2>\mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{CH}_3\)
Alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes follow the following trend in their acidic behavior:
⇒ \(\stackrel{s p}{\mathrm{HC}} \equiv \stackrel{s p}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}>\stackrel{s p^2}{\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{C}}=\stackrel{s p^2}{\mathrm{CH}_2}>\stackrel{s p^3}{\mathrm{CH}_3}-\stackrel{s p^3}{\mathrm{CH}_3}\)
This is because sp-hybridised carbon is more electronegative than sp²-hybridized carbon which is further more electronegative than sp³-hybridised carbon.
Hence, in ethyne proton can be released more easily than ethene and ethane.
Among alkynes, the order of acidity is HC ≡ CH > CH3 -C ≡ CH > CH3 -C ≡ C- CH3 This is due to the +1 effect of – CH3 group.
Chemistry MCQs Hydrocarbons NEET
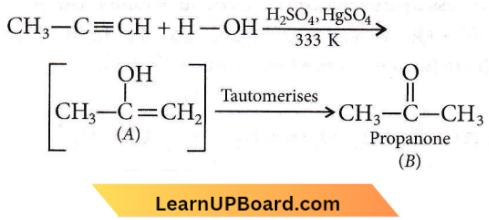
Question 48. Predict the correct intermediate and product in the following reaction:
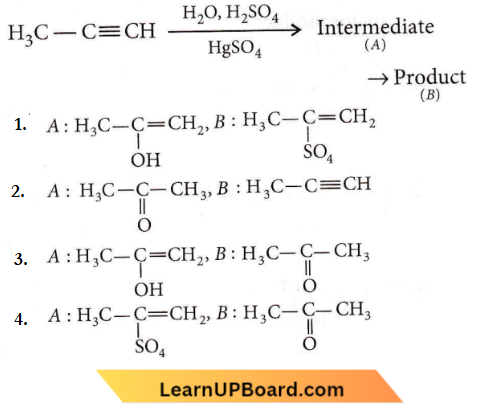
Answer: 3
In the case of unsymmetrical alkynes addition of H2O occurs in accordance with Markownikoff’s rule.
Question 49. The pair of electrons in the given carbanion, CH3C≡ C–, is present in which of the following orbitals?
- sp²
- sp
- 2p
- sp³
Answer: 2. sp²
⇒ \(\mathrm{CH}_3-\stackrel{s p}{\mathrm{C}} \equiv \stackrel{s p}{\mathrm{C}}\)
Thus, a pair of electrons is present in the sp-hybridized orbital
Question 50. In the reaction H-C ≡ CH 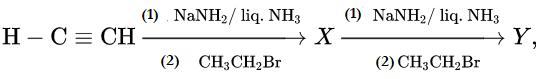 X and Y are
X and Y are
- X = 2-butyne, Y = 2-hexyne
- X = 1-butyne, Y = 2-hexyne
- X = 1-butyne, Y = 3-hexyne
- X = 2-butyne, Y = 3-hexyne.
Answer: 3. X = 1-butyne, Y = 3-hexyne
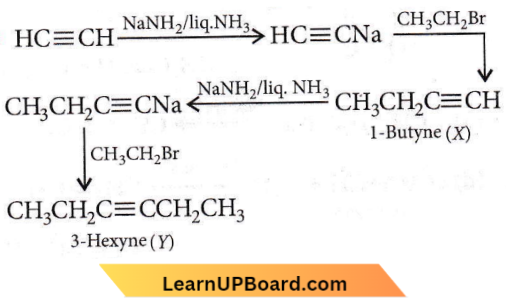
Hydrocarbons quiz for NEET
Question 51. Which of the following organic compounds has the same hybridization as its combustion product (CO2)?
- Ethane
- Ethyne
- Ethene
- Ethanol
Answer: 2. Ethyne
⇒ \(\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_2+\frac{5}{2} \mathrm{O}_2 \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{CO}_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
Both ethyne and CO2 have sp-hybridization.
⇒ \(\mathrm{O}=\stackrel{s p}{\mathrm{C}}=\mathrm{O} \quad \stackrel{s p}{\mathrm{HC}} \equiv \stackrel{s p}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}\)
Question 52. In the following reaction: 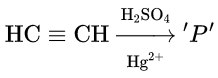 Product ‘P’ will not give
Product ‘P’ will not give
- Tollens’ reagent test
- Bradys reagent test
- Victor Meyer test
- Iodoform test.
Answer: 3. Victor Meyer test
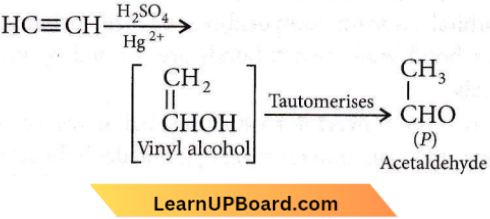
Acetaldehyde does not give Victor Meyer a test.
Question 53. Which of the following reagents will be able to distinguish between 1-butyne and 2-butyne?
- NaNH2
- HCl
- O2
- Br2
Answer: 1. NaNH2
Terminal alkynes (l-butyne) react with NaNH2 to form sodium acetylide and evolve hydrogen but 2-butyne does not.
Question 54. Considering the state of hybridization of carbon atoms, find out the molecule among the following which is linear.
- CH3 — CH = CH — CH3
- CH3 — C ≡ C — CH3
- CH3=CH —CH3 —C ≡ CH
- CH3 — CH2 — CH3
Answer: 2. CH3 — C ≡ C — CH3
CH3 – C ≡ C-CH3
In the case of sp³ hybridized carbon, the bond angle is 109°28′; sp² hybridized carbon, the bond angle is 120° and sp hybridized carbon, the bond angle is 180°.
So, only 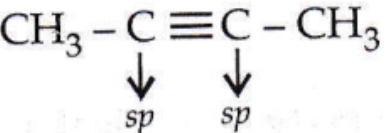 is linear.
is linear.
Question 55. Base strength of
- \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{C} \stackrel{-}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2\),
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{C}=\stackrel{-}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}\)
- and \(\mathrm{H}-\mathrm{C} \equiv \overline{\mathrm{C}}\)
is in the order of
- (A) > (C) > (B)
- (A) > (B) > (C)
- (B) > (A) > (C)
- (C) > (B) > (A)
Answer: 2. (A) > (B) > (C)
⇒ \(\mathrm{H}-\underset{s p}{\mathrm{C}} \equiv \underset{s p}{\mathrm{C}}-\mathrm{H}>\underset{s p^2}{\mathrm{CH}_2}=\underset{s p^2}{\mathrm{CH}_2}>\underset{s p^3}{\mathrm{CH}_3} \mathrm{CH}_3\)
Conjugate base of the given acid: \(\stackrel{-}{\mathrm{C}} \equiv \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H}<\stackrel{-}{\mathrm{C H}} =\mathrm{CH}_2<\stackrel{-}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{CH}_3\)
The conjugate base of stronger acid is weaker and vice-versa.
Hydrocarbons quiz for NEET
Question 56. Predict the product C obtained in the following reaction of 1-butyne.
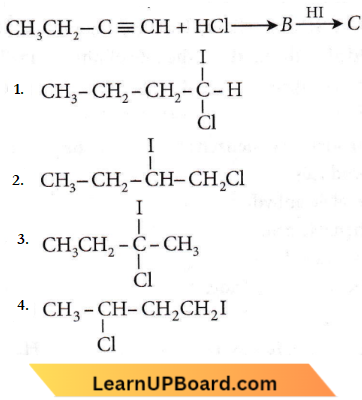
Answer: 3
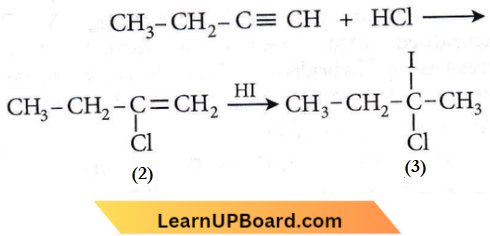
According to Markownikoff’s rule, during hydrohalogenation to an unsymmetrical alkene, the negative part of the addendum adds to a less hydrogenated (i.e. more substituted) carbon atom.
Question 57. Products of the following reaction: ![]() are
are
- CH3COOH + CO2
- CH3COOH + HOOCCH2CH3
- CH3CHO + CH3CH2CHO
- CH3COOH + CH3COCH3
Answer: 2. CH3COOH + HOOCCH2CH3
On ozonolysis, higher alkynes form diketones which are further oxidized to dicarboxylic acid.
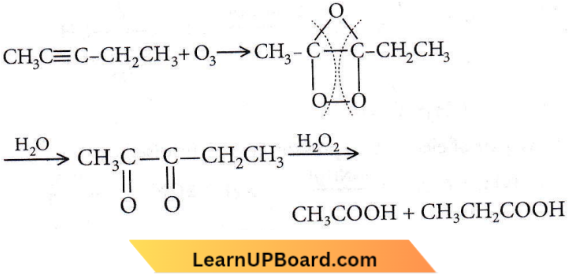
Hydrocarbons quiz for NEET
Question 58. When CH3CH2CHCl2 is treated with NaNH2, the product formed is
Answer: 2
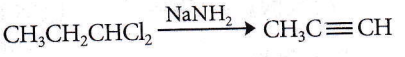
Question 59. When acetylene is passed through dil. H2SO4 in the presence of HgSO4, the compound formed is
- Acetic acid
- Ketone
- Ether
- Acetaldehyde.
Answer: 4. Acetaldehyde.
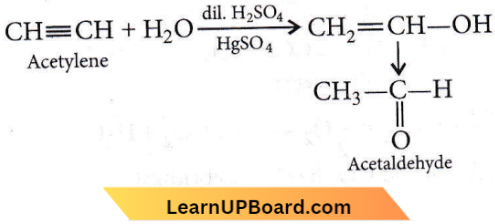
Question 60. The cylindrical shape of an alkyne is due to
- Two sigma C – C and one π C – C bonds
- One sigma C – C and two π C-C bonds
- Three sigma C – C bonds
- Three π C – C bonds.
Answer: 2. One sigma C – C and two π C-C bonds
In alkyne, two carbon atoms constituting the triple bond are sp-hybridised’Carbon undergoes sp-hybridization to form two sp-hybrid orbitals. The two 2p-orbitals remain unhybridized. Hybrid orbitals form one sigma bond while two π-bonds are formed by unhybridised orbitals.
Question 61. ![]() The reagent is
The reagent is
- Na
- HCl in H2O
- KOH in C2H5OH
- Zn in alcohol.
Answer: 3. KOH in C2H5OH
A powerful base is needed to carry out a second dehydrohalogenation reaction, for example, a hot alcoholic KOH solution or alkoxide ion.
NEET MCQs on Hydrocarbons
Question 62. A compound is treated with NaNH2 to give sodium salt. Identify the compound.
- C2H2
- C6H6
- C2H6
- C2H4
Answer: 1. C2H2
A compound is treated with NaNH2 to give sodium salt.
Alkynes react with strong bases like NaNH2 to form sodium acetylide derivatives known as acrylics.
⇒ \(\mathrm{H}-\mathrm{C} \equiv \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H}+\mathrm{NaNH}_2 \longrightarrow \mathrm{H}-\mathrm{C} \equiv \overline{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{Na}^{+}+1 / 2 \mathrm{H}_2\)
Question 63. The shortest C-C bond distance is found in
- Diamond
- Ethane
- Benzene
- Acetylene.
Answer: 4. Acetylene
The shortest C- C distance (1.20 Å) is in acetylene.
Question 64. Acetylenic hydrogens are acidic because
- Sigma electron density of the C – H bond in acetylene is nearer to carbon, which has 50% s-character
- Acetylene has only open hydrogen in each carbon
- Acetylene contains the least number of hydrogens among the possible hydrocarbons having two carbons
- Acetylene belongs to the class of alkynes with the molecular formula, CnH2n-2.
Answer: 1. Sigma electron density of the C – H bond in acetylene is nearer to carbon, which has 50% s-character
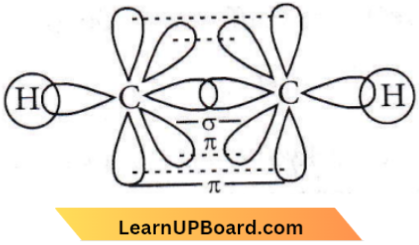
The formation of a C-H bond in acetylene involves a sp-hybridised carbon atom. Since s-electrons are closer to the nucleus than p-electrons, the electrons present in a bond having more s-characters will be closer to the nucleus. In alkynes, the character is 50%, and the electrons constituting this bond are more strongly bonded by the carbon nucleus.
Thus acetylenic C-atom becomes more electronegative in comparison to sp², sp³ and hence the hydrogen atom Present on the carbon atom (≡C-H) can be easily removed
Question 65. Which is the most suitable reagent among the following to distinguish compound (3) from the rest of the compounds?
- CH3-C ≡ C-CH3
- CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH3
- CH3-CH2C ≡ CH
- CH3-CH ≡ CH2
- Bromine in carbon tetrachloride
- Bromine in acetic acid
- Aik. KMnO4
- Ammoniacal silver nitrate
Answer: 4. Ammoniacal silver nitrate
Compound 3 possessing the terminal alkyne only reacts with ammoniacal AgNO3 and thus can be distinguished from 1, 2, and 4 compounds.
NEET MCQs on Hydrocarbons
Question 66. Consider the following compound/species:
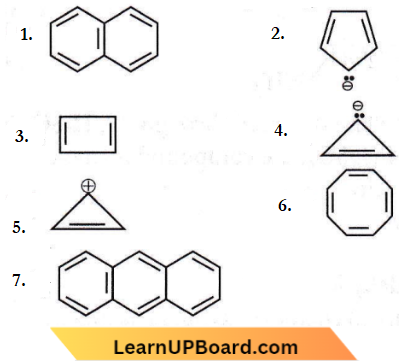
The number of compounds/species which obey Huckel’s rule is __________
- 2
- 5
- 4
- 6
Answer: 3. 4
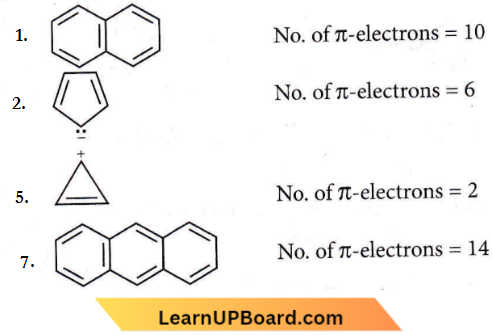
These compounds obey Huckel’s rule as these contain (4n + 2)π electrons.
Question 67. Which compound amongst the following is not an aromatic compound?
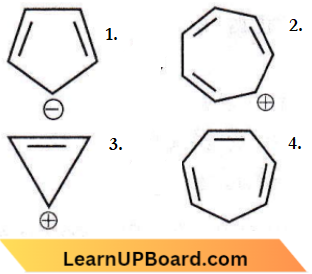
Answer: 4
Compound (4) is not an aromatic compound as reflected by the non-planarity of the methylene bridge (-CH2-) with respect to other atoms. However, the tropylium cation is aromatic due to planarity.
NEET MCQs on Hydrocarbons
Question 68. Among the following the reaction that proceeds through an electrophilic substitution is
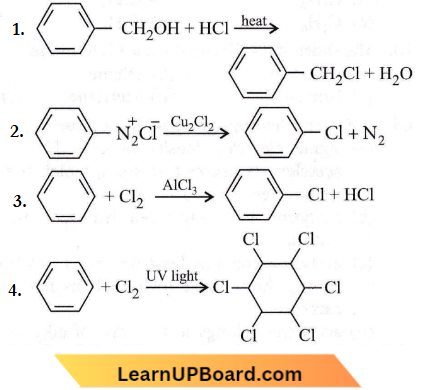
Answer: 3
The attacking species in the reaction given in option (3) is an electrophile i.e., \(\begin{aligned}
& \delta+ \\
& \mathrm{Cl}
\end{aligned}\)
Therefore, it is an electrophilic substitution reaction.
Question 69. Which of the following can be used as the halide component for the Friedel-Crafts reaction?
- Chlorobenzene
- Bromobenzene
- Chloroethene
- Isopropyl chloride
Answer: 4. Isopropyl chloride
Friedel Crafts Reaction:
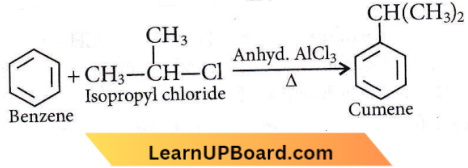
Chlorobenzene, bromobenzene, and chloroethene are not suitable halide components as the C-X bond acquires some double bond character due to the resonance of a lone pair of electrons with π-bond
Question 70. In which of the following molecules, all atoms are coplanar?
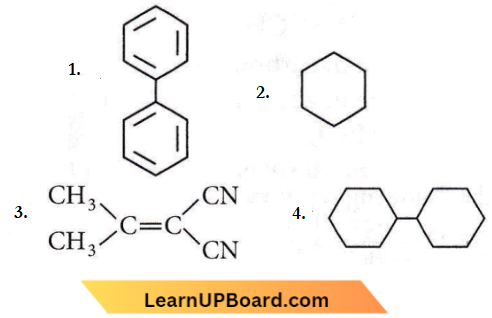
Answer: 1
Biphenyl is coplanar as all C-atoms are sp² hybridized.
NEET MCQs on Hydrocarbons
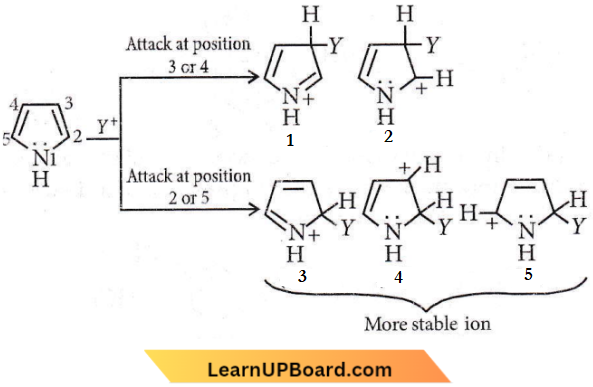
Question 71. In pyrrole, the electron density is maximum on
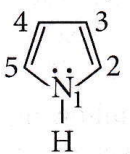
- 2 and 3
- 3 and 4
- 2 and 4
- 2 and 5
Answer: 4. 2 and 5
Pyrrole has maximum electron density on 2 and 5. It generally interacts with electrophiles at the C-2 or C-5 due to the highest degree of stability of the protonated intermediate.
Attack at position 3 or 4 yields a carbonation that is a hybrid of structures (1) and (2). Attack at position 2 or 5 yields a carbonation that is a hybrid not only of structures (3) and (4) (analogous to 1 and 2) but also of structure (5).
The extra stabilization conferred by (5) makes this ion the more stable one. Also, attack at position 2 or 5 is laster because the developing positive charge is accommodated by three atoms of the ring instead of only two.
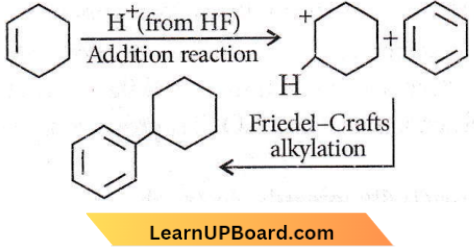
Question 72. In the given reaction, the product P is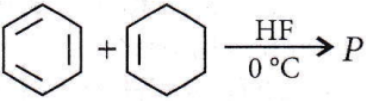 the product P is?
the product P is?
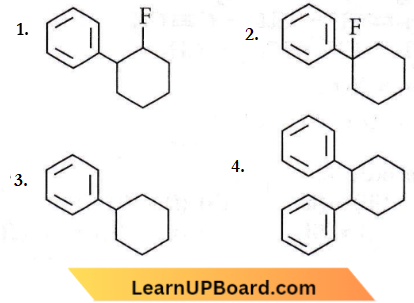
Answer: 3
Question 73. Consider the nitration of benzene using a mixed cone. H2SO4 and HNO3. If a large amount of KHSO4 is added to the mixture, the rate of nitration will be
- Unchanged
- Doubled
- Faster
- Slower.
Answer: 4. Slower.
Consider the nitration of benzene using a mixed cone. H2SO4 and HNO3. If a large amount of KHSO4 is added to the mixture,
Mechanism of nitration is: \(\mathrm{HNO}_3+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4 \rightarrow \mathrm{NO}_2^{+}+2 \mathrm{HSO}_4^{-}+\mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{O}^{+}\)
If a large amount of KHSO4 is added then conc. of HSO–4 ions increase and the reaction will be shifted in a backward direction hence, the rate of nilration will be slower.
Hydrocarbons NEET question bank
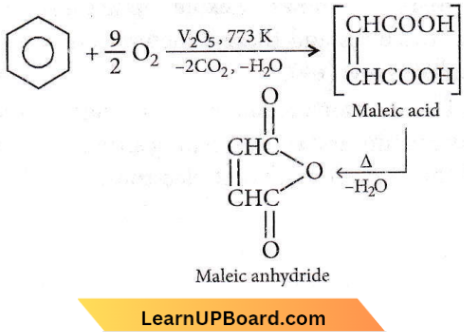
Question 74. The oxidation of benzene by V2Os in the presence of air produces
- Maleic anhydride
- Benzoic acid
- Benzaldehyde
- Benzoic anhydride.
Answer: 1. Maleic anhydride
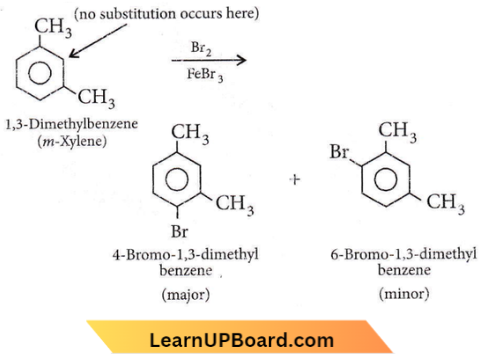
Question 75. What products are formed when the following compound is treated with Br2 in the presence of FeBr3?
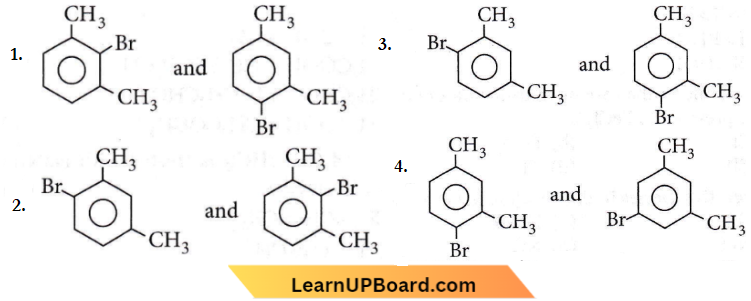
Answer: 3
– CH3 group is o,p-directing. Because of crowding, no substitution occurs at the carbon atom between the two – CH3 groups in m-xylene, even though two – CH3 groups activate that position.
Question 76. Some meta-directing substituents in aromatic substitution are given, Which one is most deactivating?
- — COOH
- — NO2
- — C ≡ N
- — SO3H
Answer: 2. — NO2
-NO2 is most deactivating due to – I and – M effect
Question 77. Which of the following compounds will not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction easily?
- Nitrobenzene
- Toluene
- Cumene
- Xylene
Answer: 1. Nitrobenzene
Nitrobenzene is strongly deactivated, hence will not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction.
Question 78. Which of the following chemical systems is nonaromatic?
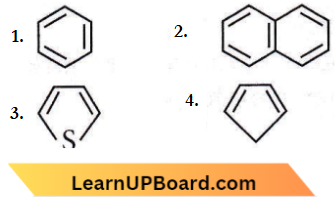
Answer: 4
The molecules that do not satisfy the Huckel rule or (4n + 2)π-electron rule are said to be non-aromatic. The compound (4) has a total of 4πe–. It does not follow (4n + 2)π tule. So, it is a non-aromatic compound.
Hydrocarbons NEET question bank
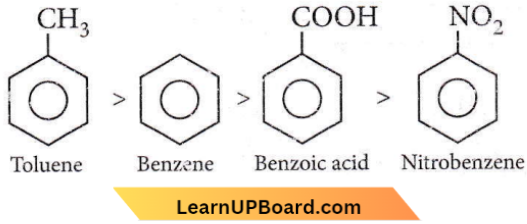
Question 79. Among the following compounds, the one that is most reactive toward electrophilic nitration is
- Benzoic acid
- Nitrobenzene
- Toluene
- Benzene.
Answer: 3. Toluene
As the +I effect increases reactivity towards electrophilic reactions decreases and as -I or -M elect increases, reactivity toward electrophilic reactions decreases thus, the order is
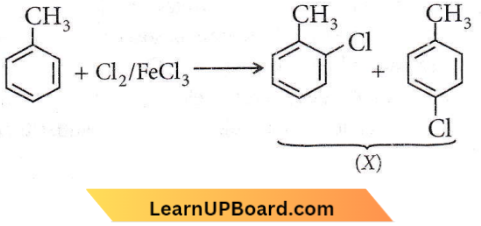
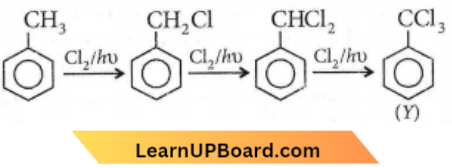
Question 80. The reaction of toluene with Cl2 in the presence of FeCl3 gives X and the reaction in the presence of light gives Y. Thus, X and Y are
- X = benzal chloride, Y = o-chlorotoluene
- X = m-chlorotoluene, Y = p-chlorotoluene
- X = o- and p-chlorotoluene, Y = trichloromethyl benzene
- X = benzyl chloride, Y= m-chlorotoluene.
Answer: 3. X = o- and p-chlorotoluene, Y = trichloromethyl benzene
The reaction of Cl2 in the presence of FeCl3, with toluene yields a ring substitution product.
In presence of sunlight, free radical reaction takes place.
Question 81. Benzene reacts with CH3Cl in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 to form
- Chlorobenzene
- Benzyl chloride
- Xylene
- Toluene.
Answer: 4. Toluene.
This is Friedel-Crafts alkylation.
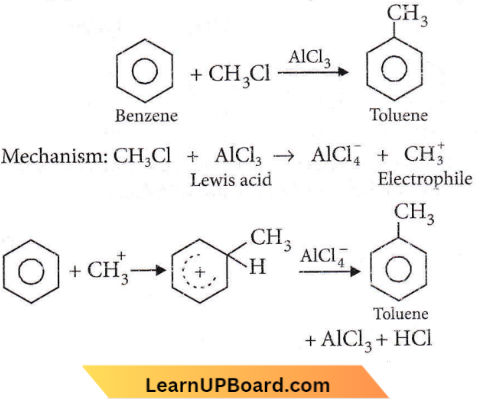
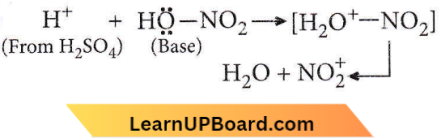
Question 82. Nitrobenzene can be prepared from benzene by using a mixture of cones. HNO3 and cone. H2SO4. In the mixture, nitric acid acts as an
- Acid
- Base
- Catalyst
- Reducing agent.
Answer: 2. Base
Nitrobenzene can be prepared from benzene by using a mixture of cones. HNO3 and cone. H2SO4. In the mixture
Hydrocarbons NEET question bank
Question 83. Which one of the following is most reactive towards electrophilic attack?
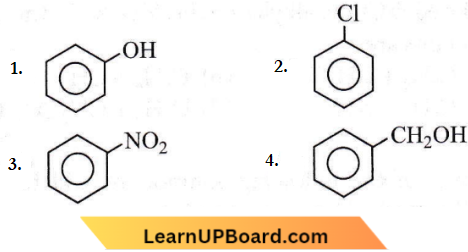
Answer: 1
Groups like, -CI and -NO, show -I effet -I group attached to the benzene ring decrease the electron density and hence less; prone to electrophilic attack. -OH not only shows the -I effect but also the +M effect which predominates the -I character and electron density is increased in the benzene ring which facilitates electrophilic attack.
Question 84. The order of decreasing reactivity towards an electrophilic reagent, for the following, would be
- Benzene
- Toluene
- Chlorobenzene
- Phenol
- (B) > (D) > (A) > (C)
- (D) > (C) > (B) > (A)
- (D) > (B) > (A) > (C)
- (A) > (B) > (C) > (D)
Answer: 3. (D) > (B) > (A) > (C)
Benzene having any activaling group i.e., – OH, – R undergoes electrophilic substitution easily as compared to benzene itself. Thus, toluene and phenol undergo electrophilic substitution easily. Chlorine due to -I-reflect deactivates the ring. So, it is difficult to Larry about the electrophilic substitution in chlorobenzene.
Hence, the order is C6H5OH > C6H5CH3 > C6H6 > C6H5Cl.
Question 85. Using anhydrous AlCl3 as a catalyst, which one of the following reactions produces ethylbenzene (PhEt)?
- H3C – CH2OH + C6H6
- CH3 – CH = CH2 + C6H6
- H2C = CH2 + C6H6
- H3C – CH3 + C6H6
Answer: 3. H2C = CH2 + C6H6
Question 86. Which one of the following is a free-radical substitution reaction?
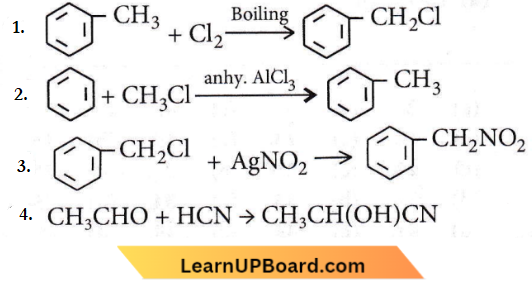
Answer: 1
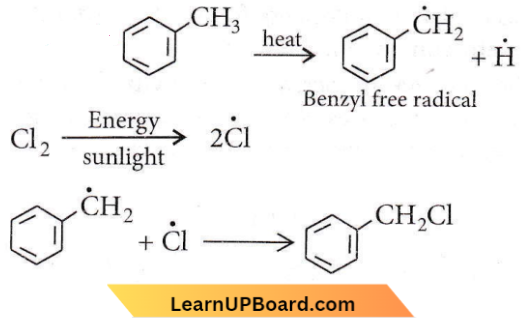
Question 87. The correct order of reactivity towards the electrophilic substitution of the compounds aniline (1), benzene (2), and nitrobenzene (3) is
- 3 > 2 > 1
- 2 > 3 > 1
- 1 < 2 > 3
- 1 > 2 > 3
Answer: 4. 1 > 2 > 3
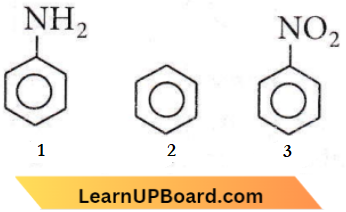
– NH2 group is electron donating hence increasing electron density on ring. Benzene is also electron-rich due to the delocalization of electrons. -NO2 the group is electron withdrawing hence, decreases electron density on the ring. Thus, the correct order for electrophilic substitution is 1>2>3.
Hydrocarbons NEET question bank
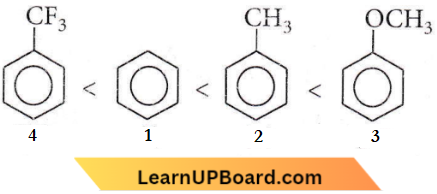
Question 88. Increasing the order of electrophilic substitution for the following compounds
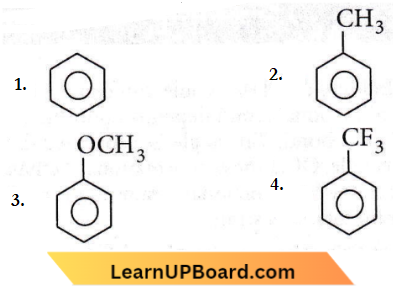
- 4 < 1 < 2 < 3
- 3 < 2 < 1 < 4
- 1 < 4 < 3 < 2
- 2 < 3 < 1 < 4
Answer: 1. 4 < 1 < 2 < 3
Due to -I effect of F atom, -CF3 on the benzene ring, deactivates the ring and does not favor electrophilic substitution. While – CH3 and – OCH3 are an electron-donating group that favors electrophilic substitution in the benzene ring at the ‘ortho’ and ‘para’ positions. The +I effect of -OCH3 is more than – CH3, therefore the correct order for electrophilic substitution is
Question 89. In Friedel-Crafts reaction, toluene can be prepared by
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_6+\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{Cl}\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{Cl}+\mathrm{CH}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_6+\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{Cl}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_6+\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COCl}\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_6+\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{Cl}\)
In the Friedel-Crafts reaction, toluene is obtained by the action of CH3Cl on benzene in the presence of AlCl3
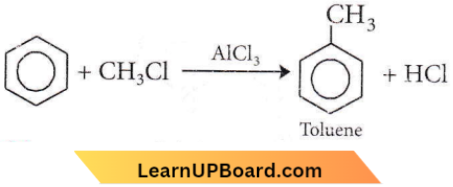
Question 90. In Friedel-Crafts alkylation, besides AlCl3 the other reactants are
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_6+\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{Cl}\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_6+\mathrm{CH}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_6+\mathrm{NH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_6+\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COCl}\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_6+\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{Cl}\)
In Friedel-Crafts reaction, Toluene an alkyl group is introduced into the benzene ring in the presence of a Lewis is acid (AlCl3) catalyst. The reaction is
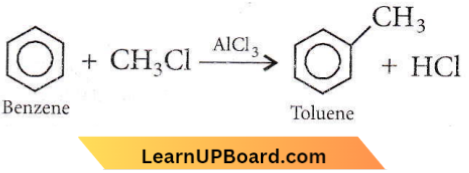
Question 91. Which of the following compounds will be most easily attacked by an electrophile?

Answer: 1
-OH, -Cl, and -CH3 groups in benzene are ortho, para directing, groups. But among these – OH group is strongly activating while – CH3 is weakly activating and – Cl is deactivating. Thus, phenol will be most easily attacked by an electrophile.
Hydrocarbons NEET question bank
Question 92. Which one of these is not compatible with arenes?
- Electrophilic additions
- Delocalisation of π-electrons
- Greater stability
- Resonance
Answer: 1. Electrophilic additions
Arenes undergo electrophilic substitution reactions and are resistant to addition reactions, due to delocalization of m-electrons. These are also stabilized by resonance.
Question 93. Among the following compounds (1-3) the correct order of reaction with electrophiles is
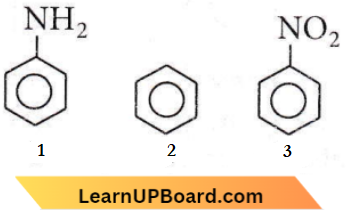
- 1>2>3
- 1=2>3
- 2>3>1
- 3<1<2
Answer: 1. 1>2>3
In structure 3, the withdrawal of electrons by -NO2 causes a decrease in reaction rate while in structure I, there is an electron-releasing effect by the – OCH3 group which accelerates the reaction.
The order of reactivity towards electrophile is 1>2>3
Question 94. Electrophile in the case of chlorination of benzene in the presence of FeCl3 is
- Cl
- FeCl3
- Cl+
- Cl–
Answer: 3. Cl+
⇒ \(\mathrm{Cl}_2+\mathrm{FeCl}_3 \longrightarrow \mathrm{FeCl}_4^{-}+\mathrm{Cl}^{+}\)
Question 95. The reactive species in the nitration of benzene is
- \(\mathrm{NO}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{HNO}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}\)
Nitronium ion (NO+2) is an electrophile that actually attacks the benzene ring.
Question 96. Which is the correct symbol relating to the two Kekule structures of benzene?
- \(\rightleftharpoons\)
- \(\longrightarrow\)
- \(\equiv\)
- \(\longleftrightarrow\)
Answer: 4. \(\longleftrightarrow\)
Benzene shows Kekule structures which are resonating structures and these structures are separated by a double-headed arrow (\(\leftrightarrow\)).
Hydrocarbons NEET question bank
Question 97. Select the true statement about benzene amongst the following
- Because of unsaturation benzene easily undergoes addition
- There are two types of C – C bonds in the benzene molecule
- There is cyclic delocalization of π-electrons in benzene
- Monosubstitution of benzene gives three isomeric products.
Answer: 3. There is cyclic delocalization of π-electrons in benzene
Due to resonance all the C – C bonds in the benzene possess the same nature and the resonating structures are obtained because of the delocalization of π-electrons.
