Hydrogen NEET MCQs
NEET Chemistry For Hydrogen Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. One would expect a proton to have a very large
- Charge
- Ionization potential
- Hydration energy
- Radius.
Answer: 3. Hydration energy
Proton (H+) ion being very small in size would have very large hydration energy
Question 2. The ionization of hydrogen atoms would give rise to
- Hydride ion
- Hydronium ion
- Proton
- Hydroxyl ion.
Answer: 3. Proton
It gives rise to Proton, \(\mathrm{H}_{(g)} \rightarrow \underset{\text { Tritium }}{\mathrm{H}_{(a q)}^{+}}+e^{-}\)
Question 3. Tritium a radioactive isotope of hydrogen, emits which of the following particles?
- Neutron(n)
- Beta(β–)
- Alpha (α)
- Gamma(γ)
Answer: 2. Beta(β–)
Tritium a radioactive isotope of hydrogen,
Tritium is a beta particle emitting radioactive isotope of hydrogen.
⇒ \(\underset{\text { Tritium }}{{ }_1^3 \mathrm{H}} \longrightarrow{ }_2^3 \mathrm{He}+\underset{\beta-\text {-particle }}{-1}{ }^0 e+0\)
Hydrogen NEET MCQs
Question 4. Which one of the following pairs of substances on reaction will not evolve H2 gas?
- Copper and HCl (aqueous)
- Iron and steam
- Iron and H2SO4 (aqueous)
- Sodium and ethyl alcohol
Answer: 1. Copper and HCl (aqueous)
Copper is a noble metal, as it lies below hydrogen in the electrochemical series. Therefore, it cannot displace hydrogen from dilute HCl. Iron and sodium lie above hydrogen in the electrochemical series, so they can liberate H2 either from steam or H2SO4 solution.
⇒ \(\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5-\mathrm{OH}+\mathrm{Na} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5-\mathrm{ONa}+1 / 2 \mathrm{H}_2\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{Fe}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4 \rightarrow \mathrm{FeSO}_4+\mathrm{H}_2\)
⇒ \(3 \mathrm{Fe}+4 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{Fe}_3 \mathrm{O}_4+4 \mathrm{H}_2\)
Read and Learn More NEET MCQs with Answers
Question 5. Water gas is produced by
- Passing steam through a red-hot coke
- Saturating hydrogen with moisture
- Mixing oxygen and hydrogen in a ratio of 1: 2
- Heating a mixture of CO2 and CH4 in petroleum refineries.
Answer: 1. Passing steam through a red-hot coke
⇒ \(\underset{\text { Steam }}{\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}}+\underset{\text { Red hot }}{\mathrm{C}} \longrightarrow \underbrace{\mathrm{H}_2+\mathrm{CO}}_{\text {Water gas }}\)
Question 6. Which of the following metals evolves hydrogen on reacting with cold dilute HNO3?
- Mg
- Al
- Fe
- Cu
Answer: 1. Mg
Mg reacts with nitric acid to give Mg(NO3)2 and evolves H2 gas \(\mathrm{Mg}+2 \mathrm{HNO}_3 \rightarrow \mathrm{Mg}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_2+\mathrm{H}_2\)
NEET questions on Hydrogen
Question 7. Which of the following statements about hydrogen is incorrect?
- Hydronium ion, H3O+ exists freely in solution.
- Dihydrogen does not act as a reducing agent.
- Hydrogen has three isotopes of which tritium is the most common.
- Hydrogen never acts as a cation in ionic salts.
Answer: 2. Dihydrogen does not act as a reducing agent. and 3. Hydrogen has three isotopes of which tritium is the most common.
⇒ \(\mathrm{CuO}+\mathrm{H}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{Cu}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{ZnO}+\mathrm{H}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{Zn}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{Fe}_3 \mathrm{O}_4+4 \mathrm{H}_2 \rightarrow 3 \mathrm{Fe}+4 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
Hydrogen has three isotopes of which protium is the most common and tritium is radioactive.
Question 8. Match List 1 with List 2.
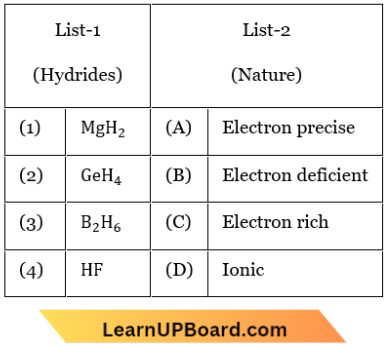
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) -(D), (2) – (A), (3) – (B), (4) – (C)
- (1) -(C), (2) – (A), (3) – (B), (4) – (D)
- (1) -(A), (2) – (B), (3) – (D), (4) – (C)
- (1) -(B), (2) – (C), (3) – (D), (4) – (A)
Answer: 1. (1) -(D), (2) – (A), (3) – (B), (4) – (C)
MgH2 – Ionic hydride
GeH4 – Electron Precise hydride
B2H6 – Electron-deficient hydride
HF – Eiectron rich hydride
Question 9. Which of the following is electron-deficient?
- (BH3)2
- PH3
- (CH3)2
- (SiH3)2
Answer: 1. (BH3)2
Boron hydrides are electron-def,cient compounds.
Hydrogen multiple choice questions NEET
Question 10. The method used to remove the temporary hardness of water is
- Synthetic resins method
- Calgon’s method
- Clark’s method
- Ion-exchange method.
Answer: 3. Clark’s method
Clarks process is used to remove the temporary hardness of the water. In this method, quick lime is added. The bicarbonates present in temporary hard water react with lime water to form insoluble calcium and magnesium carbonates which can be easily filtered off.
⇒ \(\underset{\text{Quick lime}}{\mathrm{CaO}}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \longrightarrow \underset{\text{Lime water}}{{\mathrm{Ca}{\mathrm{OH}}_2}}\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{Ca}\left(\mathrm{HCO}_3\right)_2+\mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_2 \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{CaCO}_3 \downarrow+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{Mg}\left(\mathrm{HCO}_3\right)_2+2 \mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_2 \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{CaCO}_3 \downarrow+\mathrm{Mg}(\mathrm{OH})_2 \downarrow+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
Question 11. The number of hydrogen-bonded water molecule(s) associated with CuSO4. 5H2O is
- 3
- 1
- 2
- 5
Answer: 2. 1
The ionic formulation of CuSO4 · 5H2O is [Cu(H2O)4]H2O · SO4, in which four H2O molecules are coordinated to a central Cu2+ ion while the fifth H2O molecule is hydrogen bonded to the sulfate group.
NEET practice questions on Hydrogen
Question 12. Which of the following groups of ions makes the water hard?
- Sodium and bicarbonate
- Magnesium and chloride
- Potassium and sulphate
- Ammonium and chloride
Answer: 2. Magnesium and chloride
The hardness of water is due to the presence of bicarbonates, chlorides, and sulfates of Ca and Mg. Hence, hard water will consist of Mg2+ and Cl– ions.
Question 13. At its melting point, ice is lighter than water because
- H2O molecules are more closely packed in a solid state
- Ice crystals have a hollow hexagonal arrangement of H2O molecules
- On melting of ice, the H2O molecules shrink in size
- Ice forms mostly heavy water on first melting.
Answer: 2. Ice crystals have a hollow hexagonal arrangement of H2O molecules
In ice crystals, water molecules are linked through H-bonds in a hollow hexagonal arrangement so, the volume is large and the density is less. In a liquid state, this hollow arrangement breaks into closer arrangements of molecules. Consequently, the density is increased in a liquid state.
Chemistry MCQs on Hydrogen for NEET
Question 14. Match the following and identify the correct option.
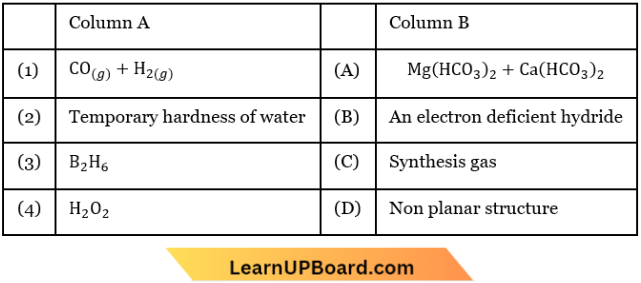
- 1-C; 2-A; 3-B; 4-A
- 1-C; 2-B; 3-A; 4-D
- 1-C; 2-D; 3-B; 4-A
- 1-A; 2-C; 3-B; 4-D
Answer: 1. 1-C; 2-A; 3-B; 4-A
Question 15. The structure of H2O2 is
- Spherical
- Non-planar
- Planar
- Linear.
Answer: 2. Non-planar
Hydrogen peroxide has a non-planar structure
Hydrogen quiz for NEET
Question 16. The volume strength of 1.5 N H2O2 solution is
- 8.8
- 8.4
- 4.8
- 5.2
Answer: 2. 8.4
Normality (N) = 1.5
We know that the equivalent weight of H2O2 is 17 and the strength of H2O2= Normality x Equivalent weight
= 1.5 x 17 = 25.5
⇒ \(\underset{(2 \times 34=68 \mathrm{~g})}{2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}+\underset{(22.4 \mathrm{~L})}{\mathrm{O}_2}\)
Since 68 grams of H2O2, produces 22.4 litres of oxygen at NTP therefore, 25.5 grams of H2O2, will produce = 22.4/68 x 25.5 = 8.4 litre of hydrogen
Thus, the volume strength of the given H2O2, solution is 8.4
Question 17. The O – O – H bond angle in H2O2 is
- 106°
- 109°28′
- 120°
- 97°
Answer: 4. 97°
The bond angle of O – O – H in H2O2, is 97°
NEET MCQs on Hydrogen
Question 18. Hydrogen peroxide molecules are
- Monoatomic and form X2-2 ions
- Diatomic and form X– ions
- Diatomic and form X2– ions
- Monoatomic and form X– ions
Answer: 2. Diatomic and form X– ions
H2O2 is diatomic and forms H+ + HO2– (X–) (hydroperoxide ion).
Question 19. Which of the following is the true structure of H2O2?
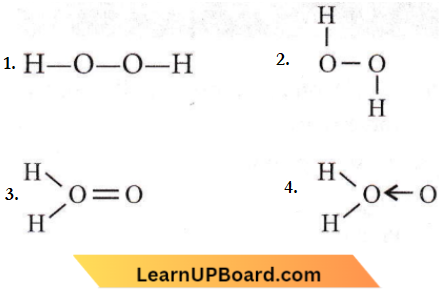
Answer: 2
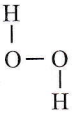 is the true structure of H2O2
is the true structure of H2O2
NEET MCQs on Hydrogen
Question 20. The reaction of H2O2 with H2S is an example of a reaction.
- Addition
- Oxidation
- Reduction
- Acidic
Answer: 2. Oxidation
It is an example of an oxidation reaction.
⇒ \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2 \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{S}\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2\) oxidises \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}\) into \(\mathrm{S}\).
Question 21. Which of the following statements is not correct?
- Hydrogen is used to reduce heavy metal oxides to metals.
- Heavy water is used to study the reaction mechanism.
- Hydrogen is used to make saturated fats from oils.
- The H-H bond dissociation enthalpy is lowest as compared to a single bond between two atoms of any element.
- Hydrogen reduces oxides of metals that are more active than iron.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
- 4, 5 only
- 1, 2, 3 only
- 2, 3, 4, 5 only
- 2, 4 only
Answer: 1. 4, 5 only
Statements 4 and 5 are incorrect.
The H-H bond dissociation enthalpy is the highest for a single bond between two atoms of any element. Hydrogen reduces oxides of metals that are less reactive than iron.
Hydrogen NEET question bank
Question 22. Some statements about heavy water are given below,
- Heavy water is used as a moderator in nuclear reactors.
- Heavy water is more associated than ordinary water.
- Heavy water is a more effective solvent than ordinary water.
Which of the above statements is correct?
- (1) and (2)
- (1), (2), and (3)
- (2) and (3)
- (1) and (3)
Answer: 1. (1) and (2)
Heavy water is used for slowing down the speed of neutrons in nuclear reactors, hence used as a moderator. The boiling point of heavy water is greater (37 4.42 K) than that of ordinary water (373 K), hence heat water is more associated. The Dielectric constant of ordinary water is greater than that of heavy water, hence ordinary water is a better solvent.
