p-Block Elements NEET MCQs
NEET Chemistry For p Block Elements Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. In which of the following compounds, nitrogen exhibits the highest oxidation state?
- \(\mathrm{N}_2 \mathrm{H}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{NH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{N}_3 \mathrm{H}\)
- \(\mathrm{NH}_2 \mathrm{OH}\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{N}_3 \mathrm{H}\)
N2H2 ⇒ 2x + 4(+1) = 0
⇒ 2x +4=0 ⇒ x = -2
N3H ⇒ x + 3(+1) = 0 ⇒ x =-3
N3H ⇒ 3x + 1(+1) = 0
⇒ 3x + 1 = 0 ⇒ x = -1/3
NH2OH ⇒ x + 2 + 1(-2) + 1 = 0
⇒ x + 1 = 0 ⇒ x = -1
Thus, the highest oxidation state is -1/3
Question 2. Nitrogen forms N2, but phosphorus does not form P2, however, it converts P4, reason is
- Triple bond present between phosphorus atom
- pπ – pπ bonding is weak
- pπ – pπ bonding is strong
- Multiple bonds form easily.
Answer: 2. pπ – pπ bonding is weak
For strong n-bonding, pπ – pπ bonding should be strong. In the case of P, due to its larger size as compared to N-atom, pπ- Pπ bonding is not so strong.
Question 3. Which of the following oxides is most acidic?
- \(\mathrm{As}_2 \mathrm{O}_5\)
- \(\mathrm{P}_2 \mathrm{O}_5\)
- \(\mathrm{N}_2 \mathrm{O}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{Sb}_2 \mathrm{O}_5\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{N}_2 \mathrm{O}_3\)
Among N, P, As and Sb, the former has the highest electronegativity (EN) so its oxide is the most acidic.
As the electronegativity value of the element increases, the acidic character of the oxide also increases.
Read and Learn More NEET MCQs with Answers
Question 4. Which of the following has the highest dipole moment?
- \(\mathrm{SbH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{AsH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{NH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{PH}_3\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{NH}_3\)
Due to the greater electronegativity of nitrogen, the dipole moment for NH3 is greater.
p-Block Elements NEET MCQs
Question 5. The basic character of hydrides of the V group elements decreases in the order
- \(\mathrm{NH}_3>\mathrm{PH}_3>\mathrm{AsH}_3>\mathrm{SbH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{SbH}_3>\mathrm{AsH}_3>\mathrm{PH}_3>\mathrm{NH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{SbH}_3>\mathrm{PH}_3>\mathrm{AsH}_3>\mathrm{NH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{NH}_3>\mathrm{SbH}_3>\mathrm{PH}_3>\mathrm{AsH}_3\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{NH}_3>\mathrm{PH}_3>\mathrm{AsH}_3>\mathrm{SbH}_3\)
AI1 the hydrides of group V elements have one lone pair of electrons on their central atom. Therefore, they can act as Lewis bases. The basic character of these hydrides decreases down the group.
Question 6. Among the following oxides, the lowest acidic is
- \(\mathrm{As}_4 \mathrm{O}_6\)
- \(\mathrm{As}_4 \mathrm{O}_{10}\)
- \(\mathrm{P}_4 \mathrm{O}_6\)
- \(\mathrm{P}_4 \mathrm{O}_{10}\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{As}_4 \mathrm{O}_6\)
The acidic character of the oxides decreases with the decrease in the oxidation state and also decreases down the group
Question 7. Which of the following fluorides does not exist?
- NF5
- PF5
- ASF5
- SbF5
Answer: 1. NF5
Nitrogen cannot form pentahalides because it cannot expand its octet due to non-availability of d-orbitals.
Question 8. Which one has the lowest boiling point?
- \(\mathrm{NH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{PH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{AsH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{SbH}_3\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{PH}_3\)
The boiling point of hydrides increases with an increase in atomic number but ammonia has an exceptionally high boiling point due to hydrogen bonding. Thus, the correct order of boiling point is, BiH3 > SbH3 > NH3 > AsH3 > PH3
Question 9. The number of electrons shared in the formation of nitrogen molecules is
- 6
- 10
- 2
- 8
Answer: 1. 6
Nitrogen molecule is diatomic containing a triple bond between two N atoms, \(\ddot{\mathrm{N}} \equiv \ddot{\mathrm{N}}\) therefore, nitrogen molecule is formed by sharing six electrons
NEET questions on p-Block Elements
Question 10. Nitrogen is a relatively inactive element because
- Its atom has a stable electronic configuration
- It has a low atomic radius
- Its electronegativity is fairly high
- The dissociation energy of its molecule is fairly high.
Answer: 4. Dissociation energy of its molecule is fairly high.
N2 molecule contains a triple bond between N atoms having very high dissociation energy (946 kJ mol-1) due to which it is relatively inactive.
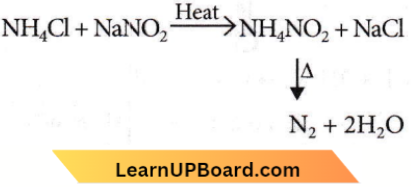
Question 11. Pure nitrogen is prepared in the laboratory by heating a mixture of
- \(\mathrm{NH}_4 \mathrm{OH}+\mathrm{NaCl}\)
- \(\mathrm{NH}_4 \mathrm{NO}_3+\mathrm{NaCl}\)
- \(\mathrm{NH}_4 \mathrm{Cl}+\mathrm{NaOH}\)
- \(\mathrm{NH}_4 \mathrm{Cl}+\mathrm{NaNO}_2\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{NH}_4 \mathrm{Cl}+\mathrm{NaNO}_2\)
Question 12. Which of the following statements is not correct for nitrogen?
- Its electronegativity is very high.
- d-orbitals are available for bonding.
- It is a typical non-metal.
- Its molecular size is small.
Answer: 2. d-orbitals are available for bonding.
In the case of nitrogen, d-orbitals are not available for bonding. N: 1s² 2s² 2p³
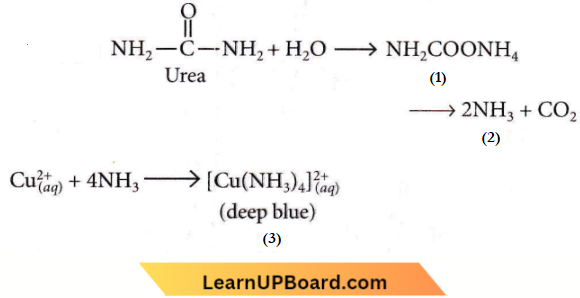
Question 13. Urea reacts with water to form A which will decompose to form B. B When passed through Cu(aq)2+, deep blue colour solution C is formed. What is the formula of C from the following?
- \(\mathrm{CuSO}_4\)
- \(\left[\mathrm{Cu}\left(\mathrm{NH}_3\right)_4\right]^{2+}\)
- \(\mathrm{Cu}(\mathrm{OH})_2\)
- \(\mathrm{CuCO}_3 \cdot \mathrm{Cu}(\mathrm{OH})_2\)
Answer: 2. \(\left[\mathrm{Cu}\left(\mathrm{NH}_3\right)_4\right]^{2+}\)
Urea reacts with water to form A which will decompose to form B. B When passed through Cu(aq)2+, deep blue colour solution C is formed.
Question 14. Aqueous solution of ammonia consists of
- \(\mathrm{H}^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{OH}^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{NH}_4^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{NH}_4^{+}\) and \(\mathrm{OH}^{-}\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{NH}_4^{+}\) and \(\mathrm{OH}^{-}\)
Aqueous solution of ammonia contains \(\mathrm{NH}_4^{+}\) and OH- ions.
NEET questions on p-Block Elements
Question 15. Which of the following oxides of nitrogen is paramagnetic?
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{N}_2 \mathrm{O}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{N}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{N}_2 \mathrm{O}_5\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{NO}_2\)
NO2 is paramagnetic due to the presence of one unpaired electron.
Question 16. Which of the following is a nitric acid anhydride?
- \(\mathrm{NO}\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{N}_2 \mathrm{O}_5\)
- \(\mathrm{N}_2 \mathrm{O}_3\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{N}_2 \mathrm{O}_5\)
When two molecules of nitric acid undergo heating, lose a water molecule to form an anhydride.
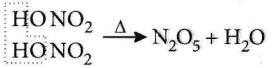
Thus, N2O5 is nitric acid anhydride.
Question 17. When copper is heated with a cone. HNO3 it produces
- \(\mathrm{Cu}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_2,\mathrm{NO}\) and \(\mathrm{NO}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{Cu}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_2\) and \(\mathrm{N}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{Cu}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_2\) and \(\mathrm{NO}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{Cu}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_2\) and \(\mathrm{NO}\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{Cu}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_2\) and \(\mathrm{NO}_2\)
Question 18. Zn gives H2 gas with H2SO4 and HCl but not with HNO3 because
- Zn acts as an oxidising agent when reacting with HNO3
- HNO3 is a weaker acid than H2SO4 and HCl
- In the electrochemical series, Zn is above the hydrogen
- NO3 is reduced in preference to hydronium ion.
Answer: 4. NO3 is reduced in preference to hydronium ion.
Zinc is in the top position of hydrogen in the electrochemical series. So, Zn displaces H2 from dilute H2SO4 and HCI with liberation of H2.
⇒ \(\mathrm{Zn}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4 \longrightarrow \mathrm{ZnSO}_4+\mathrm{H}_2\)
On the other hand, HNO2 is one oxidising agent. Hydrogen obtained in the reaction is converted into H2O.
⇒ \(\mathrm{Zn}+2 \mathrm{HNO}_3 \rightarrow \mathrm{Zn}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_2+2 \mathrm{H}\)
⇒ \(2 \mathrm{HNO}_3 \rightarrow \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}+2 \mathrm{NO}_2+\mathrm{O}\)
⇒ \(2 \mathrm{H}+\mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
Question 19. Sugarcane in reaction with nitric acid gives
- CO2 and SO2
- (COOH)2
- 2HCOOH(two moles)
- No reaction.
Answer: 2. (COOH)2
⇒ \(\underset{\text { Cane sugar }}{\mathrm{C}_{12} \mathrm{H}_{22} \mathrm{O}_{11}}+\underset{\text { From } \mathrm{HNO}_3}{18[\mathrm{O}]} \longrightarrow \underset{\text { Oxalic acid }}{6(\mathrm{COOH})_2}+5 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
NEET questions on p-Block Elements
Question 20. Which of the following phosphorus is the most reactive?
- Scarlet phosphorus
- White phosphorus
- Red phosphorus
- Violet phosphorus
Answer: 2. White phosphorus
White phosphorus has low ignition temperature so it is the most reactive among all the allotropes.
Question 21. Each of the following is true for white and red phosphorus except that they
- Are both soluble in CS2
- Can be oxidised by heating in air
- Consist of the same kind of atoms
- Can be converted into one another.
Answer: 1. Are both soluble in CS2
Red phosphorus is insoluble in CS2 and only white P is soluble in C2.
Question 22. A compound X upon reaction with H2O produces a colourless gas ‘Y with rotten fish smell. Gas Y is absorbed in a solution of CuSO4 to give Cu3P2 as one of the products. Predict the compound ‘X.
- \(\mathrm{Ca}_3 \mathrm{P}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{NH}_4 \mathrm{Cl}\)
- \(\mathrm{As}_2 \mathrm{O}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{Ca}_3\left(\mathrm{PO}_4\right)_2\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{Ca}_3 \mathrm{P}_2\)
A compound X upon reaction with H2O produces a colourless gas ‘Y with rotten fish smell. Gas Y is absorbed in a solution of CuSO4 to give Cu3P2 as one of the products.
⇒ \(\underset{\mathrm{Y}}{\mathrm{Ca}_3 \mathrm{P}_2}+6 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow 3 \mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_2+ \underset{\mathrm{Y}}{2 \mathrm{PH}_{3(g)}}\)
⇒ \(3 \mathrm{CuSO}_4+ \underset{\mathrm {Y}}{2 \mathrm{PH}_3} \rightarrow \underset{\text {Copper phosphide}}{\mathrm{Cu}_3 \mathrm{P}_2}+3 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4\)
Question 23. PH4I + NaOH forms
- \(\mathrm{PH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{NH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{P}_4 \mathrm{O}_6\)
- \(\mathrm{P}_4 \mathrm{O}_{10}\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{PH}_3\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{PH}_4 \mathrm{I}+\mathrm{NaOH} \rightarrow \mathrm{NaI}+\mathrm{PH}_3+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
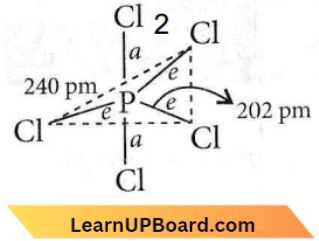
Question 24. Identify the incorrect statement related to PCl5 from the following:
- PCl5 molecule is non-reactive.
- Three equatorial P – Cl bonds make an angle of 120° with each other.
- Two axial P – Cl bonds make an angle of 180° with each other.
- Axial P – Cl bonds are longer than equatorial P – Cl bonds.
Answer: 1. PCl2 molecule is non-reactive.
It is a reactive gas as it easily provides Cl2 gas.
p-Block Elements multiple choice NEET
Question 25. PCl3 reacts with water to form
- \(\mathrm{PH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{PO}_3, \mathrm{HCl}\)
- \(\mathrm{POCl}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{PO}_4\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{PO}_3, \mathrm{HCl}\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{PCl}_3+3 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{PO}_3+3 \mathrm{HCl}\)
Question 26. Which of the following oxoacids of phosphorus has the strongest reducing property?
- \(\mathrm{H}_4 \mathrm{P}_2 \mathrm{O}_7\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{PO}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{PO}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{PO}_4\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{PO}_2\)
Acids which contain P – H bonds have strong reducing properties. Among the given compounds, H3PO2 is the strongest reducing agent as it contains two P – H bonds.
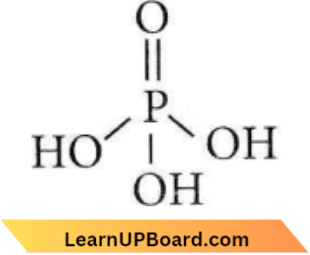
Question 27. Which is the correct statement for the given acids?
- Phosphinic acid is a monoprotic acid while phosphonic acid is a diprotic acid.
- Phosphinic acid is a diprotic acid while phosphonic acid is a monoprotic acid.
- Both are diprotic acids.
- Both are triprotic acids.
Answer: 1. Phosphinic acid is a monoprotic acid while phosphonic acid is a diprotic acid.
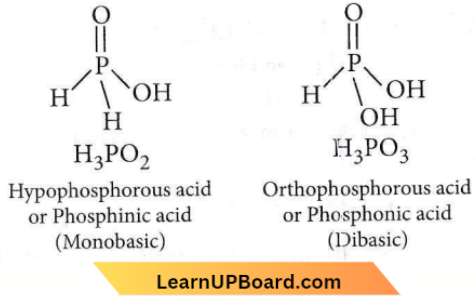
Question 28. Strong reducing behaviour of H3PO2 is due to
- High electron gain enthalpy of phosphorus
- High oxidation state of phosphorus
- Presence of two —OH groups and one P—H bond
- Presence of one —OH group and two P—H bonds.
Answer: 4. Presence of one —OH group and two P—H bonds.
All oxyacids of phosphorus which have P-H bonds act as strong reducing agents. H3PO2 has two P-H bonds hence, it acts as a strong reducing agent.
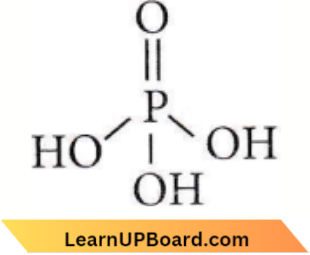
Question 29. Which of the following statements is not valid for oxoacids of phosphorus?
- Orthophosphoric acid is used in the manufacture of triple superphosphate.
- Hypophosphorous acid is a diprotic acid.
- All oxoacids contain tetrahedral four-coordinated phosphorus.
- All oxoacids contain at least one P = O unit and one P—OH group.
Answer: 2. Hypophosphorous acid is a diprotic acid.
Hypophosphorous acid is a monoprotic acid
p-Block Elements multiple choice NEET
Question 30. Oxidation states of P in \(\mathrm{H}_4 \mathrm{P}_2 \mathrm{O}_5, \mathrm{H}_4 \mathrm{P}_2 \mathrm{O}_6, \mathrm{H}_4 \mathrm{P}_2 \mathrm{O}_7\) are respectively
- +3, +5, +4
- +5, +3, +4
- +5, +4, +3
- +3, +4, +5
Answer: 4. +3, +4, +5
The oxidation state can be calculated as:
H4P2O5 : +4 + 2x+ 5(- 2) = 0 = 2x – 6 = 0 = x = +3
H4P2O6 : +4 + 2x + 6(- 2) = 0 = 2x – 8 = 0 t x= +4
H4P2O7 : +4 + 2x + 7(- 2) = 0 + 2x – 10 = 0 = x = +5
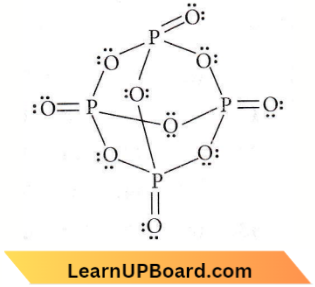
Question 31. How many bridging oxygen atoms are present in P4O10?
- 6
- 4
- 2
- 5
Answer: 1. 6
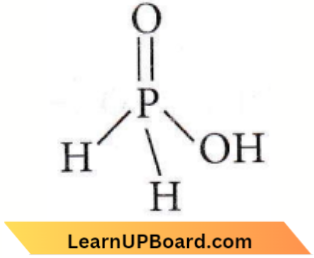
Question 32. The structural formula of hypophosphorous acid is
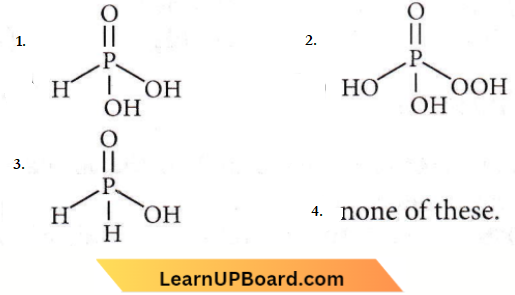
Answer: 3
The formula of hypophosphorous acid is H3PO2 as shown in (3). It is a monobasic acid
Question 33. H3PO2 is the molecular formula of an acid of phosphorus. Its name and basicity respectively are
- Phosphorous acid and two
- Hypophosphorous acid and two
- Hypophosphorous acid and one
- Hypophosphoric acid and two.
Answer: 3. Hypophosphorous acid and one
H3PO2 is named as hypophosphorous acid. As it contains only one P-OH group, its basicity is one.
Question 34. Which one of the following substances is used in the laboratory for fast drying of neutral gases?
- Phosphorus pentoxide
- Active charcoal
- Anhydrous calcium chloride
- Na3PO4
Answer: 1. Phosphorus pentoxide
P2O5 absorbs moisture much more readily than anhydrous CaCl2
NEET practice questions p-Block Elements
Question 35. P2O5 is heated with water to give
- Hypophosphorous acid
- Phosphorous acid
- Hypophosphoric acid
- Orthophosphoric acid.
Answer: 4. Orthophosphoric acid.
⇒ \(\mathrm{P}_2 \mathrm{O}_5+3 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\) \(\underrightarrow{^{\Delta}}\) \(2 \mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{PO}_4\)
Question 36. The basicity of orthophosphoric acid is
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Answer: 2. 3
Orthophosphoric acid, H3PO4 contains three P-OH groups and is, therefore, tribasic
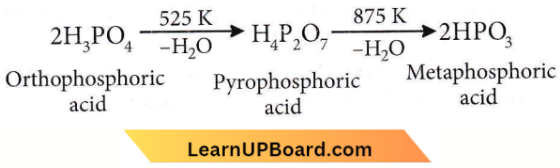
Question 37. When orthophosphoric acid is heated to 600°C, the product formed is
- \(\mathrm{PH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{P}_2 \mathrm{O}_5\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{PO}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{HPO}_3\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{HPO}_3\)
On heating, it gives pyrophosphoric acid at 525 K and metaphosphoric acid at 875 K
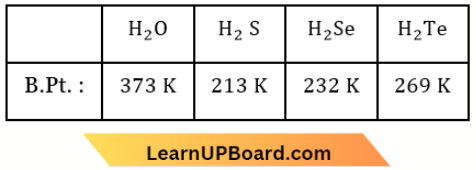
Question 38. Given below are two statements:
Statement-1: The boiling points of the following hydrides of group 16 elements increase in the order: H2O < H2S < H2Se < H2Te.
Statement 2: The boiling points of these hydrides increase with the increase in molecular mass.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
- Both statement-1 and statement-2 are correct.
- Both statement-1 and statement-2 are incorrect.
- Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect.
- Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct.
Answer: 2. Both statement-1 and statement-2 are incorrect.
Question 39. Which is the correct thermal stability order for H2E (E = O, S, Se, Te and Po)?
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Se}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Te}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Po}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Se}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Te}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Po}\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Se}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Te}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Po}\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Po}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Te}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Se}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Po}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Te}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Se}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
The thermal stability of hydrides decreases from H2O to H2Po. This is because as the size of atom E it H2E increases, the bond H-E becomes weaker and thus, breaks on heating. Therefore, the correct order of thermal stability is H2Po < H2Te < H2Se < H2S < H2O.
NEET practice questions p-Block Elements
Question 40. The acidity of diprotic acids in aqueous solutions increases in the order
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Se}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Te}\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Se}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Te}\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Te}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Se}\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Se}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Te}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Se}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Te}\)
As the atomic size increases down the group, the bond length increases the bond strength decreases and the cleavage of the E-H bond becomes easier thus, more will be acidity. Thus, the correct order is: H2S < H2Se < H2Te.
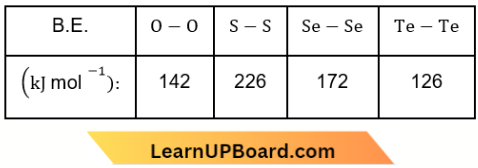
Question 41. Which of the following bonds has the highest energy?
- S-S
- O-O
- Se-Se
- Te-Te
Answer: 1. S-S
The bond energy of S – S is exceptionally high due to its catenation tendency.
Question 42. Which of the following does not give oxygen on heating?
- \(\mathrm{K}_2 \mathrm{Cr}_2 \mathrm{O}_7\)
- \(\left(\mathrm{NH}_4\right)_2 \mathrm{Cr}_2 \mathrm{O}_7\)
- \(\mathrm{KClO}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{Zn}\left(\mathrm{ClO}_3\right)_2\)
Answer:
⇒ \(\left(\mathrm{NH}_4\right)_2 \mathrm{Cr}_2 \mathrm{O}_7\) \(\underrightarrow{^{\Delta}}\) \(\mathrm{N}_2+\mathrm{Cr}_2 \mathrm{O}_3+4 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{Zn}\left(\mathrm{ClO}_3\right)_2\) \(\underrightarrow{^{\Delta}}\) \(\mathrm{ZnCl}_2+3 \mathrm{O}_2\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{KClO}_3\) \(\underrightarrow{^{\Delta}}\) \(\mathrm{KCl}+3 / 2 \mathrm{O}_2\)
⇒ \(2 \mathrm{~K}_2 \mathrm{Cr}_2 \mathrm{O}_7\) \(\underrightarrow{^{\Delta}}\) \(2 \mathrm{~K}_2 \mathrm{CrO}_4+\mathrm{Cr}_2 \mathrm{O}_3+3 / 2 \mathrm{O}_2\)
Question 43. Which would quickly absorb oxygen?
- Alkaline solution of pyrogallol
- Cone. H2SO4
- Lime water
- Alkaline solution of CuSO4
Answer: 1. Alkaline solution of pyrogallol
The alkaline solution of pyrogallol absorbs oxygen quickly.
Question 44. Oxygen will directly react with each of the following elements except
- P
- Cl
- Na
- S
Answer: 2. Cl
Chlorine does not react directly with oxygen.
NEET practice questions p-Block Elements
Question 45. It is possible to obtain oxygen from air by fractional distillation because
- Oxygen is in a different group of the periodic table from nitrogen
- Oxygen is more reactive than nitrogen
- Oxygen has higher b.pt. Than nitrogen
- Oxygen has a lower density than nitrogen.
Answer: 3. Oxygen has higher b.pt. Than nitrogen
Air is liquefied by making use of the |oule Thomson effect (cooling by expansion of the gas). Water vapour and CO2 are removed by solidification.
The remaining constituents of liquid air i.e., liquid oxygen and liquid nitrogen are separated by means of fractional distillation as fractional distillation is a process of separation of mixture based on the difference in their boiling points. (b.pt. of O2 = – 183°C : b.pt. of N2 = -195.8°C)
Question 46. Match the following:
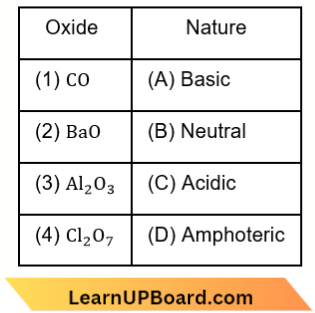
Which of the following is the correct option?
- 1-A, 2-B, 3-C, 4-D
- 1-B, 2-A, 3-D, 4-C
- 1-C, 2-D, 3-A, 4-B
- 1-D, 2-C, 3-B, 4-A
Answer: 2. 1-B, 2-A, 3-D, 4-C
CO – neutral, BaO – basic,
Al2O3 – amphoteric and Cl2O7 – acidic.
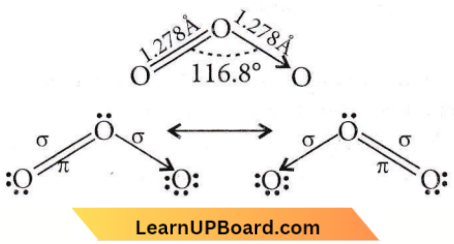
Question 47. The angular shape of the ozone molecule (O3) consists of
- 1σ and 1π bond
- 2σ and 1π bond
- 1σ and 2π bonds
- 2σ and 2π bonds
Answer: 2. 2σ and 1π bond
The angular shape of the ozone molecule (O3)
Question 48. The gases respectively absorbed by alkaline pyrogallol and oil of cinnamon are
- \(\mathrm{O}_3, \mathrm{CH}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2, \mathrm{O}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{SO}_2, \mathrm{CH}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{N}_2 \mathrm{O}, \mathrm{O}_3\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{O}_2, \mathrm{O}_3\)
Alkaline pyrogallol absorbs O2 and oil of cinnamon absorbs O3
Question 49. Nitrogen dioxide and sulphur dioxide have some properties in common. Which property is shown by one of these compounds, but not by the other?
- Is soluble in water.
- Is used as a food preservative.
- Forms acid-rain.
- Is a reducing agent.
Answer: 2. Is used as a food preservative.
NO2 is not used as a food preservative.
Chemistry MCQs p-Block Elements NEET
Question 50. Sulphur trioxide can be obtained by which of the following reactions?
- \(\mathrm{CaSO}_4+\mathrm{C}\) \(\underrightarrow{^{\Delta}}\)
- \(\mathrm{Fe}_2\left(\mathrm{SO}_4\right)_3 \underrightarrow{^{\Delta}}\)
- \(\mathrm{S}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4 \underrightarrow{^{\Delta}}\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4+\mathrm{PCl}_5 \underrightarrow{^{\Delta}}\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{Fe}_2\left(\mathrm{SO}_4\right)_3 \underrightarrow{^{\Delta}}\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{Fe}_2\left(\mathrm{SO}_4\right)_3\) \(\underrightarrow{^{\Delta}}\) \(\mathrm{Fe}_2 \mathrm{O}_3+3 \mathrm{SO}_3\)
Question 51. Match List 1 with List 2
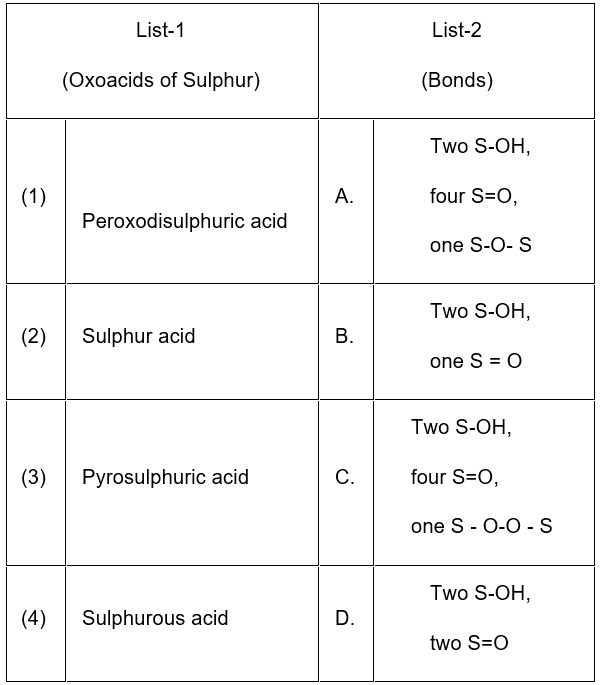
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- 1-A, 2-C, 3- D, 4-B
- 1-C, 2-D, 3-B, 4-A
- 1-A, 2-C, 3-B, 4-D
- 1-C, 2-D, 3-A, 4-B
Answer: 4. 1-C, 2-D, 3-A, 4-B
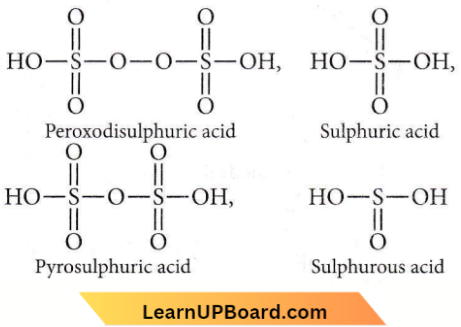
Question 52. Which of the following oxoacids of sulphur has — O — O — linkage
- H2SO3, sulphurous acid
- H2SO4, sulphuric acid
- H2S2O8, peroxodisulphuric acid
- H2S2O7, pyrosulphuric acid
Answer: 3. H2S2O2, peroxodisulphuric acid
Peroxodisulphuric acid, H2S2O8 has – O – O linkage.
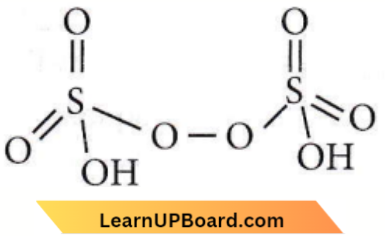
Question 53. Identify the correct following:
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}_2 \mathrm{O}_7\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}_2 \mathrm{O}_8\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}_2 \mathrm{O}_7\)
Chemistry MCQs p-Block Elements NEET
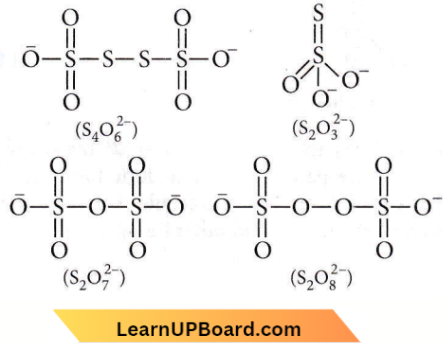
Question 54. In which pair of ions do both species contain an S — S bond?
- \(\mathrm{S}_4 \mathrm{O}_6^{2-}, \mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_3^{2-}\)
- \(\mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_7^{2-}, \mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_8^{2-}\)
- \(\mathrm{S}_4 \mathrm{O}_6^{2-}, \mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_7^{2-}\)
- \(\mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_7^{2-}, \mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_3^{2-}\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{S}_4 \mathrm{O}_6^{2-}, \mathrm{S}_2 \mathrm{O}_3^{2-}\)
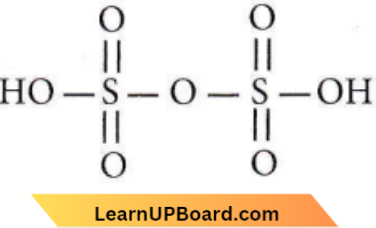
Question 55. Oleum is
- Castor oil
- Oil of vitriol
- Fuming H2SO4
- None of these.
Answer: 3. Fuming H2SO4
Pyrosulphuric acid or oleum (+6) is H2S2O7 which is obtained by dissolving SO3 and is called fuming sulphuric acid.
Question 56. Match List 1 (substances) with List 2 (processes) employed in the manufacture of the substances and select the correct option.
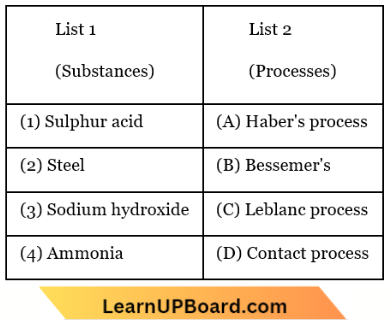
- 1-A, 2-D, 3-B, 4-C
- 1-A, 2-B, 3-C, 4-D
- 1-D, 2-C, 3-B, 4-A
- 1-D, 2-B, 3-C, 4-A
Answer: 4. 1-D, 2-B, 3-C, 4-A
Question 57. Statement 1: Acid strength increases in the order given as HF « HCl« HBr « HI.
Statement 2: As the size of the elements F, Cl, Br, and I increases down the group, the bond strength of HF, HC1, HBr, and HI decreases and so the acid strength increases.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
- Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is true.
- Both statement 1 and statement 2 are true.
- Both statement 1 and statement 2 are false.
- Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is false.
Answer: 2. Both statement 1 and statement 2 are true.
Question 58. In which one of the following arrangements the given sequence is not strictly according to the properties indicated against it?
- \(\mathrm{CO}_2<\mathrm{SiO}_2 <\mathrm{SnO}_2<\mathrm{PbO}_2\): Increasing oxidizing power
- \(\mathrm{HF}<\mathrm{HCl}<\mathrm{HBr}<\mathrm{HI}\) : Increasing acidic strength
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S} <\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Se}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Te}\) : Increasing pK values
- \(\mathrm{NH}_3<\mathrm{PH}_3<\mathrm{AsH}_3<\mathrm{SbH}_3\) : Increasing acidic character
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S} <\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Se}<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Te}\) : Increasing pK values
pKa
H2O: 14
H2S: 7
H2Se: 3.872
H2Te: 2.6
Question 59. Which of the following statements is not true for halogens?
- All form monobasic oxyacids.
- All are oxidizing agents.
- All but fluorine show positive oxidation states.
- Chlorine has the highest electron-gain enthalpy.
Answer: 3. All but fluorine show positive oxidation states.
All halogens show both positive and negative oxidation states while fluorine shows only negative oxidation states except +1 in HOF.
p-Block Elements quiz for NEET
Question 60. Which one of the following orders is correct for the bond dissociation enthalpy of halogen molecules?
- \(\mathrm{Br}_2>\mathrm{I}_2>\mathrm{F}_2>\mathrm{Cl}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{F}_2>\mathrm{Cl}_2>\mathrm{Br}_2>\mathrm{I}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{I}_2>\mathrm{Br}_2>\mathrm{Cl}_2>\mathrm{F}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{Cl}_2>\mathrm{Br}_2>\mathrm{F}_2>\mathrm{I}_2\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{Cl}_2>\mathrm{Br}_2>\mathrm{F}_2>\mathrm{I}_2\)
The order of bond dissociation enthalpy is
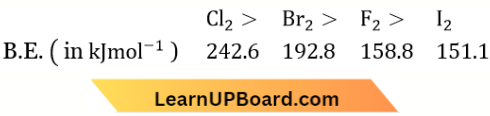
A reason for this anomaly is the relatively large electron-electron repulsion among the lone pairs in F2 a molecule where they are much closer to each other than in the case of Cl2
Question 61. The variation of the boiling points of the hydrogen halides is in the order HF > HI > HBr > HCl. What explains the higher boiling point of hydrogen fluoride?
- There is strong hydrogen bonding between HF molecules.
- The bond energy of HF molecules is greater than in other hydrogen halides.
- The effect of nuclear shielding is much reduced in fluorine which polarises the HF molecule.
- The electronegativity of fluorine is much higher than for other elements in the group.
Answer: 1. There is strong hydrogen bonding between HF molecules.
The variation of the boiling points of the hydrogen halides is in the order HF > HI > HBr > HCl.
HF forms strong intermolecular H-bonding due to the high electronegativity of F. Hence, the boiling point of HF is abnormally high. Boiling points of other hydrogen halides gradually increase from HCl to HI due to an increase in the size of halogen atoms from Cl to I which further increases the magnitude of van der Waals forces.
Question 62. Among the following which is the strongest oxidising agent?
- Br2
- I2
- Cl2
- F2
Answer: 4. F2
Standard reduction potentials of halogens are positive and decrease from fluorine to iodine. So, F2 is the strongest oxidising agent.
Question 63. Which one of the following arrangements does not give the correct picture of the trends indicated against it?
- F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2: Bond dissociation energy
- F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2: Electronegativity
- F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2: Oxidizing power
- F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2: Electron gain enthalpy
Answer: 1. F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2: Bond dissociation energy and 4. F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2: Electron gain enthalpy
In the case of diatomic molecules (X2) of halogens, the bond dissociation energy decreases in the order: Cl2 > Br2 > F2> I2.
This is due to the relatively large electron-electron repulsion among the lone pairs is F, then in the case of Cl2.
The oxidising power, electronegativity and reactivity decrease in the order: F2 > C2 > Br2 > I2
Electron gain enthalpy of halogens follows the given order: Cl2>F2>Br2>I2
The low value of electron gain enthalpy of fluorine is probably due to the small size of the fluorine atom.
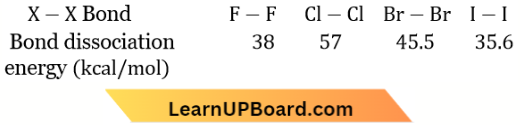
Question 64. Which one of the following orders is not in accordance with the property stated against it?
- F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2: Bond dissociation energy
- F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2: Oxidising power
- HI > HBr > HCl > HF: Acidic property in water
- F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2: Electronegativity
Answer: 1. F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2: Bond dissociation energy
The lower value of bond dissociation energy of fluorine is due to the high inter-electronic repulsions between non-bonding electrons in the 2p-orbitals of fluorine. As a result, the F – F bond is weaker in comparison to the CI – Cl and Br – Br bonds.
p-Block Elements quiz for NEET
Question 65. Which statement is wrong?
- Bond energy of F2 > Cl2
- Electronegativity of F > Cl
- F is more oxidising than Cl
- Electron affinity of Cl > F
Answer: 1. Bond energy of F2 > Cl2
Due to more repulsion in between non-bonding electron pairs (2p) of two fluorines (due to the small size of F-atom) in comparison to non-bonding electron pairs (3p) in chlorine, the bond energy of F, is less than Cl2.
B.E(F2) = 158.8 kJ/mole and
B.E. (Cl2) =242.6 kJ/ mole
Question 66. Which of the following has the greatest electron affinity?
- I
- Br
- F
- Cl
Answer: 4. Cl
In general, the electron affinity decreases from top to bottom in a group. But in group 17, fluorine has lower electron affinity as compared to chlorine due to the very small size of the fluorine atom. As a result, there are strong interelectronic repulsions in the relatively small 2s orbitals of fluorine and thus, the incoming electron does not experience much attraction
Question 67. Which of the following displaces Br2 from an aqueous solution containing bromide ions?
- \(\mathrm{I}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{I}_3^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{Cl}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{Cl}^{-}\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{Cl}_2\)
Since chlorine is a stronger oxidising agent than bromine, therefore it will displace bromine from an aqueous solution containing bromide ions. \(\mathrm{Cl}_2+2 \mathrm{Br}^{-} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{Cl}^{-}+\mathrm{Br}_2\)
Question 68. Which of the following species has four lone pairs of electrons?
- I
- O
- Cl–
- He
Answer: 3. Cl–
Outer electronic configuration of \(\mathrm{Cl}=3 s^2 3 p_x^2 3 p_y^2 3 p_z^1\)
Outer electronic configuration of \(\mathrm{Cl}^{-}=3 s^2 3 p_x^2 3 p_y^2 3 p_z^2\),
i.e., 4 lone pair of electrons
Question 69. Match the following:
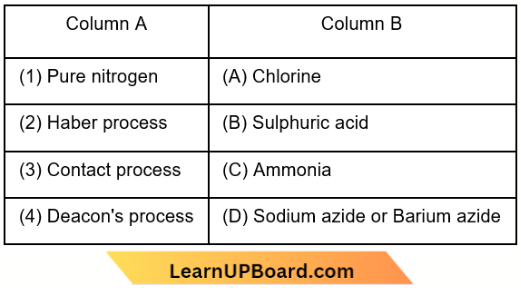
Which of the following is the correct option?
- 1-D, 2-C, 3-B, 4-A
- 1-A, 2-B, 3-C, 4-D
- 1-B, 2-D, 3-A, 4-C
- 1-C, 2-D, 3-B, 4-A
Answer: 1. 1-D, 2-C, 3-B, 4-A
NEET MCQs on p-Block Elements
Question 70. When Cl2 gas reacts with hot and concentrated sodium hydroxide solution, the oxidation number of chlorine changes from
- Zero to +1 and zero to -5
- Zero to -1 and zero to +5
- Zero to -1 and zero to +3
- Zero to +1 and zero to -3
Answer: 2. Zero to -1 and zero to +5
⇒ \(\stackrel{0}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{l}_2+\underset{\text{(hot and conc.)}}{6 \mathrm{NaOH}} \rightarrow 5 \stackrel{-1}{\mathrm{NaCl}}+\mathrm{NaClO}_3+3 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
This is an example of a disproportionation reaction and oxidation state of chlorine changes from 0 to -1 and +5
Question 71. Which of the following is used in the preparation of chlorine?
- Both MnO2 and KMnO4
- Only KMnO4
- Only MnO2
- Either MnO2 or KMnO4
Answer: 1. Both MnO2 and KMnO4
⇒ \(\mathrm{MnO}_2+4 \mathrm{HCl} \rightarrow \mathrm{MnCl}_2+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{Cl}_2 \uparrow\) \(2 \mathrm{KMnO}_4+16 \mathrm{HCl} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{KCl}+2 \mathrm{MnCl}_2+8 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}+5 \mathrm{Cl}_2 \uparrow\)
Question 72. Which of the following elements is extracted commercially by the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of its compound?
- Cl
- Br
- Al
- Na
Answer: 1. Cl
Chlorine is obtained by the electrolysis of brine (concentrated NaCl solution). Chlorine is liberated at the anode.
Question 73. When chlorine is passed over dry slaked lime at room temperature, the main reaction product is
- Ca(ClO2)2
- CaCl2
- CaOCl2
- Ca(OCl)2
Answer: 3. CaOCl2
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
Question 74. In the manufacture of bromine from seawater, the mother liquor containing bromides is treated with
- Carbon dioxide
- Chlorine
- Iodine
- Sulphur dioxide.
Answer: 2. Chlorine
Bromide in the mother liquor (containing MgBr2) is oxidised to Br2 by passing CI2 which is a stronger oxidising agent.
⇒ \(2 \mathrm{Br}^{-}+\mathrm{Cl}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{Br}_2+2 \mathrm{Cl}^{-}\)
NEET MCQs on p-Block Elements
Question 75. The bleaching action of chlorine is due to
- Reduction
- Hydrogenation
- Chlorination
- Oxidation.
Answer: 4. Oxidation.
The bleaching action of chlorine is due to oxidation in the presence of moisture. The bleaching effect is permanent.
⇒ \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{Cl}_2 \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{HCl}+[\mathrm{O}]\)
Colouring matter + [O] → Colourtress matter
Question 76. Bleaching powder reacts with a few drops of cone. HCl to give
- Chlorine
- Hypochlorous Acid
- Calcium Oxide
- Oxygen.
Answer: 1. Chlorine
⇒ \(\mathrm{CaOCl}_2+2 \mathrm{HCl} \rightarrow \mathrm{CaCl}_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{Cl}_2\)
Question 77. Among the following, the correct order of acidity is
- \(\mathrm{HClO}_2<\mathrm{HClO}<\mathrm{HClO}_3<\mathrm{HClO}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{HClO}_4<\mathrm{HClO}_2<\mathrm{HClO}<\mathrm{HClO}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{HClO}_3<\mathrm{HClO}_4<\mathrm{HClO}_2<\mathrm{HClO}\)
- \(\mathrm{HClO}<\mathrm{HClO}_2<\mathrm{HClO}_3<\mathrm{HClO}_4\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{HClO}<\mathrm{HClO}_2<\mathrm{HClO}_3<\mathrm{HClO}_4\)
The acidic character of the oxoacids increases with an increase in the oxidation number of the halogen atom i.e., \(\mathrm{HClO}<\mathrm{HClO}_2<\mathrm{HClO}_3<\mathrm{HClO}_4\).
This can be explained on the basis of the relative stability of the anions Ieft after the removal of a proton. Since the stability of the anion decreases in the order : \(\mathrm{ClO}_4^{-}>\mathrm{ClO}_3^{-}>\mathrm{ClO}_2^{-}>\mathrm{ClO}^{-}\) acid strength also decreases in the same order.
Question 78. Which of the statements given below is incorrect?
- O3 molecule is bent.
- ONF is isoelectronic with O2N–.
- OF2 is an oxide of fluorine.
- Cl2O7 is an anhydride of perchloric acid.
Answer: 3. OF2 is an oxide of fluorine.
OF2 (oxygen difluoride) is a fluoride of oxygen because fluorine is more electronegative than oxygen.
Question 79. The correct order of increasing bond angles in the following species is
- \(\mathrm{Cl}_2 \mathrm{O}<\mathrm{ClO}_2<\mathrm{ClO}_2^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{ClO}_2<\mathrm{Cl}_2 \mathrm{O}<\mathrm{ClO}_2^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{Cl}_2 \mathrm{O}<\mathrm{ClO}_2^{-}<\mathrm{ClO}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{ClO}_2^{-}<\mathrm{Cl}_2 \mathrm{O}<\mathrm{ClO}_2\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{ClO}_2^{-}<\mathrm{Cl}_2 \mathrm{O}<\mathrm{ClO}_2\)
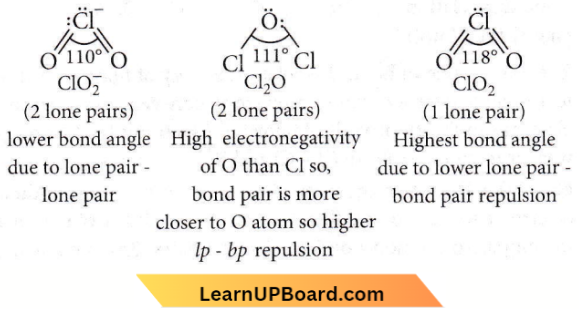
NEET MCQs on p-Block Elements
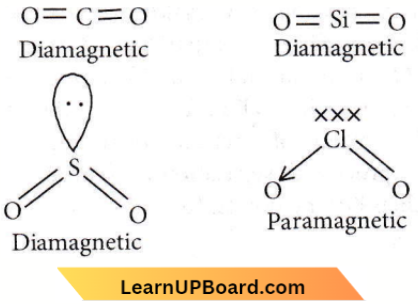
Question 80. Which one of the following oxides is expected to exhibit paramagnetic behaviour?
- CO2
- SiO2
- SO2
- ClO2
Answer: 4. ClO2
Question 81. Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): ICi is more reactive than I2.
Reason (R): The I — Cl bond is weaker than the I — I bond. In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
- Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- (A) is correct but (R) is not correct.
- (A) is not correct but (R) is correct.
Answer: 1. Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
In general, interhalogen compounds are more reactive than halogens (except fluorine). This is because the X-X’ (ICl) bond in interhalogens is weaker than the X-X (I-I) bond in halogens except for the F-F bond.
Question 82. Match the interhalogen compounds of column A with the geometry in column B and assign the correct code.
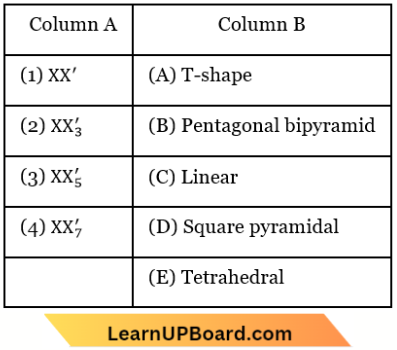
- 1-C, 2-A, 3-D, 4-B
- 1-E, 2-D, 3-C, 4-B
- 1-D, 2-C, 3-B, 4-A
- 1-C, 2-D, 3-A, 4-B
Answer: 1. 1-C, 2-A, 3-D, 4-B
Question 83. Given below are two statements: One is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R:
Assertion A: Helium is used to dilute oxygen in the diving apparatus.
Reason R: Helium has a high solubility in O2.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
- A is true but R is false.
- A is false but R is true.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer: 1. A is true but R is false.
Helium is used as a diluent for oxygen in modern diving apparatus because of its very low solubility in blood.
Question 84. Noble gases are named because of their inertness towards reactivity. Identify an incorrect statement about them.
- Noble gases have large positive values of electron gain enthalpy.
- Noble gases are sparingly soluble in water.
- Noble gases have very high melting m and boiling points.
- Noble gases have weak dispersion forces.
Answer: 3. Noble gases have very high melting m and boiling points.
Noble gases have very low melting and boiling points because the only type of interatomic interaction in these elements is weak dispersion forces.
Question 85. Match the Xenon compounds in Column A with their structure in Column B and assign the correct code.
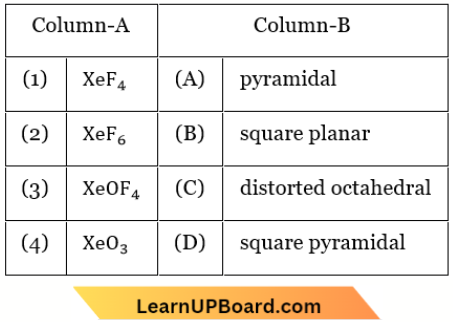
- 1-C, 2-D, 3-A, 4-B
- 1-A, 2-B, 3-C, 4-D
- 1-B, 2-C, 3-D, 4-A
- 1-B, 2-C, 3-A, 4-D
Answer: 3. 1-B, 2-C, 3-D, 4-A
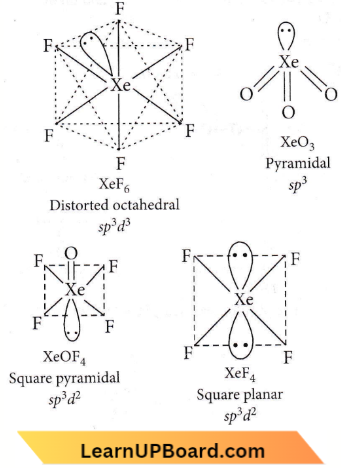
p-Block Elements NEET question bank
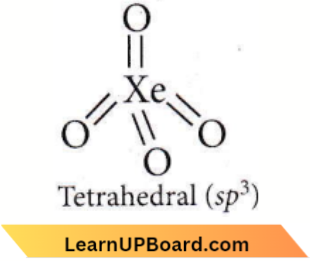
Question 86. Identify the incorrect statement, regarding the molecule Xe04.
- XeO4 molecule is square planar.
- There are four pπ – dπ bonds.
- There are four sp³ – p, σ bonds.
- XeO4 molecule is tetrahedral.
Answer: 1. XeO4 molecule is square planar.
Question 87. Which compound has a planar structure?
- \(\mathrm{XeF}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{XeOF}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{XeO}_2 \mathrm{~F}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{XeO}_4\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{XeF}_4\)
In XeF4 the ‘Xe’ atom is sp³d² hybridised, which contains tu,o lone pair orbitals and four bond pair orbitals. Therefore, the shape of XeF4 molecule is square plar.rar, with one lone pair orbital over and the other below the plane.
