NEET Questions On p-Block Elements
NEET Chemistry For The p Block Elements Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Taking stability as the factor, which one of the following represents the correct relationship?
- AlCl > AlCl3
- TlI > TlI3
- TICI3 > TlCl
- InI3 > InI
Answer: 2. TlI > TlI3
As we move down the group, the stability of the +3 oxidation state decreases while that of the +1 oxidation state increases. Thus, the stability order for the +1 oxidation state is Al < Ga < In< Tl and the +3 oxidation state is Al > Ga > In > TI.
Hence, the stability order is, AlC3 > AICI, TII > TlI3, TlCl > TlCl3 and InI > InI3
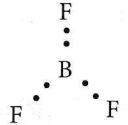
Question 2. BF3 is a planar and electron-deficient compound. Hybridization and the number of electrons around the central atom, respectively are
- sp² and 8
- sp³ and 4
- sp³ and 6
- sp² and 6
Answer: 4. sp² and 6
BF3 is a planar and electron-deficient compound. Hybridization and the number of electrons around the central atom
BF3 is a sp²-hybridised planar molecule. It forms 3σ-bonds with 3F-atoms, hence has six electrons around it.
Question 3. The correct order of atomic radii in group 13 elements is
- B < Al < In < Ga < Tl
- B < Al < Ga < In < l
- B < Ga < Al < Tl < In
- B < Ga < Al < In < Tl
Answer: 4. B < Ga < Al < In < Tl
Question 4. AlF3 is soluble in HF only in the presence of KF. It is due to the formation of
- \(\mathrm{K}_3\left[\mathrm{AlF}_3 \mathrm{H}_3\right]\)
- \(\mathrm{K}_3\left[\mathrm{AlF}_6\right]\)
- \(\mathrm{AlH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{K}\left[\mathrm{AlF}_3 \mathrm{H}\right]\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{K}_3\left[\mathrm{AlF}_6\right]\)
AlF3 is insoluble in anhydrous HF because the F– ions are not available in hydrogen-bonded HF molecules but, it becomes soluble in the presence of a small amount of KF due to the formation of complex, K3[AlF3].
⇒ \(\mathrm{AlF}_3+3 \mathrm{KF} \rightarrow \mathrm{K}_3\left[\mathrm{AlF}_6\right]\)
Read and Learn More NEET MCQs with Answers
Question 5. The stability of the +1 oxidation state among Al, Ga, In, and Tl increases in the sequence
- Al < Ga < In < Tl
- Tl < In < Ga < Al
- In < Tl < Ga < Al
- Ga < In < Al < Tl
Answer: 1. Al < Ga < In < Tl
In group 13 elements, the stability of the +3 oxidation state decreases down the group while that of the +1 oxidation state increases due to the inert pair effect. Hence, the stability of the +1 oxidation state increases in the sequence: Al <Ga<In<Tl.
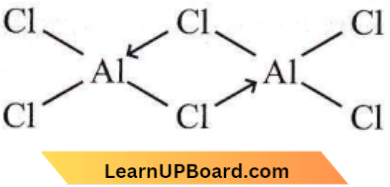
Question 6. Aluminum (3) chloride forms a dimer because aluminum
- Belongs to 3rd group
- Can have a higher coordination number
- Cannot form a trimer
- Has high ionization energy.
Answer: 2. Can have a higher coordination number
AlCl3 forms a dimer, as Al due to the presence of 3d-orbitals can expand its covalency from four to six. Also, dimerization enables Al atoms to complete their octets.
p-Block Elements NEET MCQs
Question 7. Which one of the following elements is unable to form \(\mathrm{MF}_6^{3-} \text {. }\) ion?
- Ga
- Al
- B
- In
Answer: 3. B
Boron does not have vacant d-orbitals in its valence shell, so it cannot expand its covalency beyond 4 i.e., ‘B’ cannot form the ions like \(\mathrm{MF}_6^{3-} \text {. }\)
Question 8. The tendency of BF3, BCl3, and BBr3 to behave as Lewis acid decreases in the sequence
- BCl3 > BF3 > BBr3
- BBr3 > BCl3 > BF3
- BBr3 > BF3 > BCl3
- BF3 > BCl3 > BBr3
Answer: 2. BBr3 > BCl3 > BF3
The relative Lewis acid character of boron trihalides is found to follow the following order, BBr3 > BCl3 > BF3, but the expected order on the basis of electronegativity of the halogens (electronegativity of halogens decreases from F to I) should be, BF3, > BCl3 > BBr3
This anomaly is explained on the basis of the relative tendency. of the halogen atom to back donate its unutilized electrons to the vacant p-orbital of the boron atom. In BF3, boron has a vacant 2p orbital and each fluorine has fully filled unutilized 2p-orbitals.
Fluorine transfers two electrons to the vacant 2p-orbital of boron, thus forming pπ – pπ bond
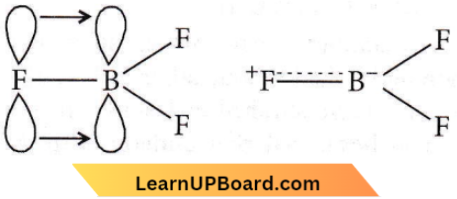
This type of bond has some double-bond character and is known as dative or back bonding. All the three bond lengths are the same. It is possible when a double bond is delocalized. The delocalization may be represented as :
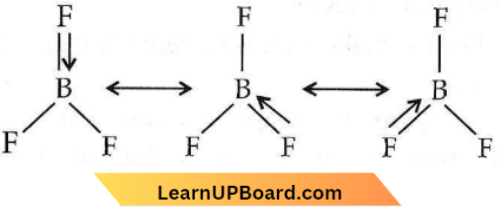
The tendency to back donate decreases from F to I as the energy level difference between B and halogen atoms increases from F to L So, the order of Lewis acid strength is BF3 < BCl3 < BBr3
Question 9. Boron compounds behave as Lewis acids, because of their
- Ionisation property
- Electron deficient nature
- Acidic nature
- Covalent nature.
Answer: 2. Electron-deficient nature
Lewis acids are those substances that can accept a pair of electrons and boron compounds usually are deficient in electrons.
Question 10. Which of the following statements is not correct about diborane?
- There are two 3-center-2-electron bonds.
- The four terminal B – H bonds are two center two-electron bonds.
- The four terminal hydrogen atoms and the two boron atoms lie in one plane.
- Both the boron atoms are sp² hybridized.
Answer: 4. Both the boron atoms are sp² hybridized.
In diborane (B2H6), each boron (B) atom uses sp³ hybrid orbitals for bonding.
p-Block Elements multiple choice NEET
Question 11. Boric acid is an acid because its molecule
- Contains replaceable H+ ion
- Gives up a proton
- Accepts OH– from water releasing a proton
- Combines with a proton from the water molecule.
Answer: 3. Accepts OH– from water releasing a proton
Boric acid behaves as a Lewis acid, by accepting a pair of electrons from the OH– ion of water thereby releasing a proton.
Question 12. Which of the following structures is similar to graphite
- B4C
- B2H6
- BN
- B
Answer: 3. BN
BN is known as inorganic graphite and has a structure similar to graphite.
Question 13. The type of hybridisation of boron in diborane is
- sp³-hybridisation
- sp²-hybridisation
- sp-hybridization
- sp³d²-hybridisation.
Answer: 1. sp³-hybridisation
Each ‘B’ atom in diborane (B2H6) is sp³-hybridised’ Of the 4-hybrid orbitals, three have one electron each, while the 4th is empty.
Two orbitals of each form o bond with two ‘H’- atoms, with one of the remaining hybrid orbital (either filled or empty), ls orbital of ‘H’ atom and one of the hybrid orbitals of other ‘B’ atom overlap to form three centered two-electron bond. So there exist two such types of three-centered bonds.
Question 14. Which of the following statements about H3BO3 is not correct?
- It has a layer structure in which planar BO3 units are joined by hydrogen bonds.
- It does not act as a proton donor but acts as a Lewis acid by accepting hydroxyl ions.
- It is a strong tribasic acid.
- It is prepared by acidifying an aqueous solution of borax.
Answer: 3. It is a strong tribasic acid.
H3BO3 is a weak monobasic acid. \(\mathrm{B}(\mathrm{OH})_3+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \longrightarrow\left[\mathrm{B}(\mathrm{OH})_4\right]^{-}+\mathrm{H}^{+}\)
Question 15. Which of the following is an incorrect statement?
- SnF4 is ionic in nature.
- PbF4 is covalent in nature.
- SiCl4 is easily hydrolyzed.
- GeX4(X = F, Cl, Br, I) is more stable than GeX2.
Answer: 2. PbF4 is covalent in nature.
Generally, the halides of group-4 elements are covalent in nature. PbF4 and SnF4 are exceptions which are ionic in nature.
NEET practice questions p-Block Elements
Question 16. Which of the following species is not stable?
- [SiCl6]2-
- [SiF6]2-
- [GeCl6]2-
- [Sn(OH)6]2-
Answer: 1. [SiCl6]2-
[SiCl6]2- is not stable due to steric hindrance by large-sized Cl atoms.
Question 17. It is because of the inability of ns² electrons of the valence shell to participate in bonding that
- Sn2+ is oxidizing while Pb4+ is reducing
- Sn2++ and Pb2+ are both oxidizing and reducing
- Sn4+ is reducing while Pb4+ is oxidizing
- Sn2+ is reducing while Pb4+ is oxidizing.
Answer: 4. Sn2+ is reducing while Pb4+ is oxidizing.
The inertness of s-subshell electrons towards bond formation is known as the inert pair effect. This effect increases down the group thus, for Sn, the +4 oxidation state is more stable whereas, for Pb, the +2 oxidation state is more stable, i.e., Sn2+ is reducing while Pb4+ is oxidizing.
Question 18. Which of the following oxidation states is the most characteristic of lead and tin respectively?
- +2, +4
- +4, +4
- +2, +2
- +4, +2
Answer: 1. +2, +4
When ns² electrons of the outermost shell do not participate in bonding then these ns² electrons are called inert pair and the effect is called the inert pair effect. Due to this inert pair effect, Ge, Sn, and Pb of group 14 have a tendency to form Loth +a and +2 ions.
Now the inert pair effect increases down the group, hence the stability of M2+ ions increases, and M4+ ions decrease down the group. For this reason, Pb2+ is more stable than Pb4+ and Sn4+ is more stable than Sn2+
Question 19. Carbon and silicon belong to the (4) group. The maximum coordination number of carbon in commonly occurring compounds is 4, whereas that of silicon is 6. This is due to
- Availability of low lying d-orbitals in silicon
- The large size of the silicon
- More electropositive nature of silicon
- Both (2) and (3).
Answer: 1. Availability of low-lying d-orbitals in silicon
Carbon and silicon belong to the (4) group. The maximum coordination number of carbon in commonly occurring compounds is 4, whereas that of silicon is 6.
Carbon has no d-orbitals, while silicon contains d-orbitals in its valence shell which can be used for bonding purposes.
NEET practice questions p-Block Elements
Question 20. Match List-1 with List-2
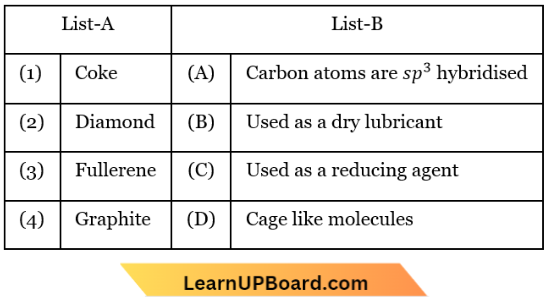
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) – (C), (2) – (1), (3) – (D), (4) – (B)
- (1) – (C), (2) – (D), (3) – (A), (4) – (B)
- (1) – (B), (2) – (D), (3) – (A), (4) – (C)
- (1) – (D), (2) – (A), (3) – (B), (4) – (C)
Answer: 1. (1) – (C), (2) – (1), (3) – (D), (4) – (B)
Question 21. Choose the correct statement.
- Diamond and graphite have a two-dimensional network.
- Diamond is covalent and graphite is ionic.
- Diamond is sp³ hybridized and graphite is sp² hybridized.
- Both diamond and graphite are used as lubricants.
Answer: 3. Diamond is sp³ hybridized and graphite is sp² hybridized.
In diamond, each carbon atom undergoes sp³ hybridization and is linked to four other carbon atoms by using hybridized orbitals in a tetrahedral fashion. In graphite, each carbon atom in a hexagonal ring undergoes sp² hybridization and makes three sigma bonds with three neighboring carbon atoms. The fourth electron forms a π-bond.
Question 22. Which of the following does not show electrical conduction?
- Diamond
- Graphite
- Potassium
- Sodium
Answer: 1. Diamond
Except for diamonds other three conduct electricity. Potassium and sodium are metallic conductors, while graphite is a non-metallic conductor.
Question 23. The percentage of lead in lead pencils is
- 80
- 20
- Zero
- 70
Answer: 3. Zero
The lead pencil contains graphite and clay. It does not contain lead.
Question 24. In graphite, electrons are
- Localized on each C-atom
- Localized on every third C-atom
- Spread out between the structure
- Present in antibonding orbital.
Answer: 3. Spread out between the structure
In graphite, each carbon atom undergoes sp²-hybridisation and is covalently bonded to three other .urbor. atoms by single bonds. The fourth electron forms π-bond. The electrons are delocalized over the whole sheet.
i.e., electrons are spread out between the structure.
Chemistry MCQs p-Block Elements NEET
Question 25. Which of the following types of forces bind together the carbon atoms in a diamond?
- Ionic
- Covalent
- Dipolar
- VanderWaals
Answer: 2. Covalent
In diamond, each carbon atom is sp³ hybridized and thus, forms covalent bonds with four other carbon atoms lying at the corners of a regular tetrahedron.
Question 26. Which of the following is an insulator?
- Graphite
- Aluminium
- Diamond
- Silicon
Answer: 3. Diamond
All the above are conductors except diamond. Diamond is an insulator.
Question 27. Identify the correct statements from the following:
- CO2(g) is used as a refrigerant for ice cream and frozen food.
- The structure of C60 contains twelve six-carbon rings and twenty-five carbon rings.
- ZSM-5, a type of zeolite, is used to convert alcohol into gasoline.
- CO is a colorless and odorless gas.
- (1), (2), and (3) only
- (1) and (3) only
- (2) and (3) only
- (3) and (4) only
Answer: 4. (3) and (4) only
- Solid CO2 (dry ice) is used as a refrigerant for ice cream and frozen food.
- The structure of C60 contains twenty-six-membered rings and twelve five-membered rings.
- 3 and 4 are correct statements
Question 28. Which of the following compounds is used in cosmetic surgery?
- Silica
- Silicates
- Silicones
- Zeolites
Answer: 3. Silicones
Silicones being biocompatible are used in surgical and cosmetic Plants.
Question 29. Which of these is not a monomer for a high molecular mass silicone polymer?
- Me3SiCl
- PhSiCl3
- MeSiCl3
- Me2SiCl3
Answer: 1. Me3SiCl
It can form only dimer.
p-Block Elements quiz for NEET
Question 30. The basic structural unit of silicates is
- \(\mathrm{SiO}_3^{2-}\)
- \(\mathrm{SiO}_4^{2-}\)
- \(\mathrm{SiO}^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{SiO}_4^{4-}\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{SiO}_4^{4-}\)
SiO4-4 orthosilicate is the basic unit of silicates.
Question 31. Which statement is wrong?
- Beryl is an example of cyclic silicate.
- Mg2SiO4 is orthosilicate.
- The basic structural unit in silicates is the SiO4 tetrahedron.
- Feldspars are not aluminosilicates.
Answer: 4. Feldspars are not aluminosilicates.
Feldspars are three-dimensional aluminosilicates.
Question 32. Name the two types of the structure of silicate in which one oxygen atom of [SiO4]4- is shared.
- Linear chain silicate
- Sheet silicate
- Borosilicate
- Three dimensional
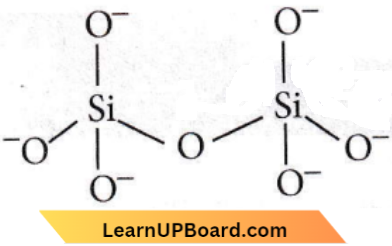
Answer: 3. Pyrosilicate
Borosilicate contains two units of SiO44- joined along a corner containing oxygen-atom
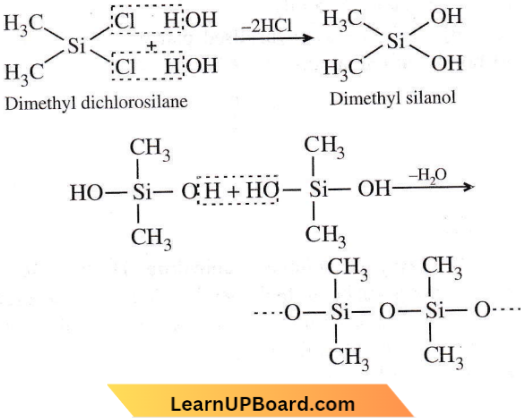
Question 33. The straight-chain polymer is formed by
- Hydrolysis of CH3SiCl3 followed by condensation polymerization
- Hydrolysis of (CH3)4Si by addition polymerisation
- Hydrolysis of (CH3)2SiCl2 followed by condensation polymerisation
- Hydrolysis of (CH3)3SiCl followed
Answer: 3. Hydrolysis of (CH3)2SiCl2 followed by condensation polymerization
Hydrolysis of substituted chlorosilanes yields corresponding silanols which undergo polymerization. Out of the given chlorosilanes, only (CH3)2SiCl2 will give linear polymer on hydrolysis followed by polymerisation.
Question 34. Which of the following anions is present in the chain structure of silicates?
- \(\left(\mathrm{Si}_2 \mathrm{O}_5^{2-}\right)_n\)
- \(\left(\mathrm{SiO}_3^{2-}\right)_n\)
- \(\mathrm{SiO}_4^{4-}\)
- \(\mathrm{Si}_2 \mathrm{O}_7^{6-}\)
Answer: 2. \(\left(\mathrm{SiO}_3^{2-}\right)_n\)
Chain silicates are formed by sharing two oxygen atoms by each tetrahedron. Anions of chain silicate have two general formula
- \(\left(\mathrm{SiO}_3\right)_n^{2 n-}\)
- \(\left(\mathrm{Si}_4 \mathrm{O}_{11}\right)_n^{6 n-}\)
NEET MCQs on p-Block Elements
Question 35. Which one of the following statements about the zeolite is false?
- They are used as cation exchangers.
- They have an open structure which enables them to take up small molecules.
- Zeolites are aluminosilicates having a three-dimensional network.
- Some of the SiO44- units are replaced by AlO45- and AlO69- ions in zeolites.
Answer: 4. Some of the SiO44- units are replaced by AlO45- and AlO69- ions in zeolites.
In zeolites, some of the Si4+ ions may be replaced by Al3+ ions. This results in an unbalanced anionic charge To maintain electrical neutrality, positive ions must be introduced.
p-Block Elements NEET question bank
Question 36. The substance used as a smoke screen in warfare is
- SiCl4
- PH3
- PCl5
- Acetylene.
Answer: 1. SiCl4
SiCl4 gets hydrolysed in moist air and gives white fumes which are used as a smoke screen in warfare.
