NEET Questions On s-Block Elements
NEET Chemistry For The s Block Elements Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.
Assertion A: Metallic sodium dissolves in liquid ammonia giving a deep blue solution, which is paramagnetic.
Reason R: The deep blue solution is due to the formation of amide.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- A is true but R is false.
- A is false but R is true.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer: 1. A is true but R is false.
Sodium metal dissolves in liquid ammonia giving a deep blue solution which is conducting in nature. \(\mathrm{Na}+(x+y) \mathrm{NH}_3 \rightarrow\left[\mathrm{Na}\left(\mathrm{NH}_3\right)_x\right]^{+}+\left[e\left(\mathrm{NH}_3\right)_y\right]^{-}\)
The blue colour of the solution is due to the ammoniated electron which absorbs energy in the visible region of light and thus, imparts blue colour to the solution.
The solution is paramagnetic and on standing, slowly liberates hydrogen gas resulting in the formation of amide. \(\mathrm{Na}_{(a m)}^{+}+e^{-}+\mathrm{NH}_{3(0)} \rightarrow \mathrm{NaNH}_{2(a m)}+1 / 2 \mathrm{H}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}\)
(where ‘am’ denotes solution in ammonia.)
Question 2. Identify the incorrect statement from the following.
- Alkali metals react with water to form their hydroxides.
- The oxidation number of K in KO2 is +4.
- The ionisation enthalpy of alkali metals decreases from top to bottom in the group.
- Lithium is the strongest reducing agent among the alkali metals.
Answer: 2. The oxidation number of K in KO2 is +4.
The superoxide species (KO2) is represented as O–2, since the compound is neutral, therefore the oxidation state of potassium is +1. Remaining all the given statements are correct
Question 3. Match List-1 with List-2.
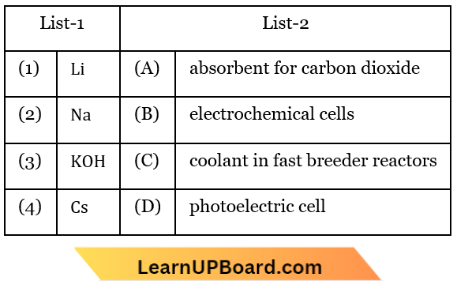
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) -(D), (2) – (A), (3) – (C), (4) – (B)
- (1) -(C), (2) – (D), (3) – (B), (4) – (A)
- (1) -(A), (2) – (C), (3) – (D), (4) – (B)
- (1) -(B), (2) – (C), (3) – (A), (4) – (D)
Answer: 4. (1) -(B), (2) – (C), (3) – (A), (4) – (D)
Question 4. Ionic mobility of which of the following alkali metal ions is lowest when the aqueous solution of their salts is put under an electric field?
- K
- Rb
- Li
- Na
Asnwer: 3. Li
The hydration enthalpy of alkali metal ions decreases with an increase in ionic sizes i.e., Li+>Na+>K>Rb+>Cs+
Hence, lithium having a maximum degree of hydration will be the least mobile.
The order of ionic mobility is \(\left.\left[\mathrm{Li}_{(a q)}\right]^{+}<\left[\mathrm{Na}_{(a q)}\right)\right]^{+}<\left[\mathrm{K}_{(a q)}\right]^{+}<\left[\mathrm{Rb}_{(a q)}\right]^{+}\)
Read and Learn More NEET MCQs with Answers
Question 5. Which one of the alkali metals, forms only, the normal oxide, 2O on heating in the air?
- Rb
- K
- Li
- Na
Answer: 3. Li
When alkali metals are heated in an atmosphere of oxygen, the alkali metals ignite and form oxides. On combustion Li forms Li2O; sodium gives the peroxide Na2O2 and potassium and rubidium give superoxide (MO2).
Question 6. The ease of adsorption of the hydrated alkali metal ions on an ion-exchange resins follows the order
- Li+ < K+ < Na+ < Rb+
- Rb+ < K+ < Na+ < Li+
- K+ < Na+ < Rb+ < Li+
- Na+ < Li+ < K+ < Rb+
Answer: 2. Rb+ < K+ < Na+ < Li+
The order of decreasing hydration enthalpy of alkali metal ions is: Li+ > Na+ > K+ > Rb+
Thus, the ease of adsorption of hydrated ions is in the order: Rb+< K+< Na+< Li+
s-Block Elements NEET MCQs
Question 7. The sequence of ionic mobility in aqueous solution is
- Rb+ > K+ > Cs+ > Na+
- Na+ > K+ > Rb+ > Cs+
- K+ > Na+ > Rb+ > Cs+
- Cs+ > Rb+ > K+ > Na+
Answer: 4. Cs+ > Rb+ > K+ > Na+
The smaller the size of the cation, the higher the hydration and its reflective size will increase hence mobility in an aqueous solution will decrease. Hence, the correct sequence of ionic mobility in an aqueous solution of the given cations is Cs+>Rb+>K+>Na+.
Question 8. When a substance (A) reacts with water it produces a combustible gas (B) and a solution of substance (C) in water. When another substance (D) reacts with this solution of (C), it also produces the same gas (B) on warming but (D) can produce gas (B) on reaction with dilute sulphuric acid at room temperature. Substance (A) imparts a deep golden-yellow colour to the smokeless flame of the Bunsen burner. Then (A), (B), (C) and (D) respectively are
- \(\mathrm{Ca}, \mathrm{H}_2, \mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_2, \mathrm{Sn}\)
- \(\mathrm{K}, \mathrm{H}_2, \mathrm{KOH}, \mathrm{Al}\)
- \(\mathrm{Na}, \mathrm{H}_2, \mathrm{NaOH}, \mathrm{Zn}\)
- \(\mathrm{CaC}_2, \mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_2, \mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_2, \mathrm{Fe}\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{Na}, \mathrm{H}_2, \mathrm{NaOH}, \mathrm{Zn}\)
When a substance (A) reacts with water it produces a combustible gas (B) and a solution of substance (C) in water. When another substance (D) reacts with this solution of (C), it also produces the same gas (B) on warming but (D) can produce gas (B) on reaction with dilute sulphuric acid at room temperature. Substance (A) imparts a deep golden-yellow colour to the smokeless flame of the Bunsen burner.
Only ‘Na’ imparts a golden colour to Bunsen flame, therefore, A = Na, B = H2, C = NaOH, D = Zn.
⇒ \(\underset{\text{A}}{2 \mathrm{Na}}+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \underset{\text{A}}{2 \mathrm{NaOH}}+\underset{\text{B}}{\mathrm{H}_2}\)
⇒ \(\underset{\text{D}}{\mathrm{Zn}}+\underset{\text{C}}{2 \mathrm{NaOH}} \rightarrow \mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{ZnO}_2+\underset{\text{B}}{\mathrm{H}_2}\)
⇒ \(\underset{\text{D}}{\mathrm{Zn}}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4 \text { (dil.) } \rightarrow \mathrm{ZnSO}_4+\underset{\text{B}}{\mathrm{H}_2}\)
Question 9. Which one of the following properties of alkali metals increases in magnitude as the atomic number rises?
- Ionic radius
- Melting point
- Electronegativity
- First ionization energy
Answer: 1. Ionic radius
In a group, the ionic radius increases with an increase in atomic number whereas the m.pt. decreases down in a group due to the weakening of metallic bonds. Similarly, electronegativity and ionization energy also decrease down the group.
Question 10. In the case of alkali metals, the covalent character decreases in the order
- MF > MCI > MBr > MI
- MF > MCI > Ml > MBr
- MI > MBr > MCI > MF
- MCI > MI > MBr > MF
Answer: 3. MI > MBr > MCI > MF
Alkali metals are highly electropositive and halogens are electronegative. Thus, for the halides of a given alkali metal, the covalent character decreases with an increase in the electronegativity of halogens.
∴ The order of the covalent character of halides is
MI> MBr > MCI> MF
Question 11. The alkali metals form salt-like hydrides by direct synthesis at elevated temperatures. The thermal stability of these hydrides decreases in which of the following orders?
- NaH > LiH > KH > RbH > CsH
- LiH > NaH > KH > RbH > CsH
- CsH > RbH > KH > NaH > LiH
- KH > NaH > LiH > CsH > RbH
Answer: 2. LiH > NaH > KH > RbH > CsH
The ionic character of the bonds in hydrides increases from LiH to CsH due to the weakening of the M-H bond so, the thermal stability of these hydrides decreases in the order of LiH > NaH > KH > RbH > CsH.
s-Block Elements multiple choice NEET
Question 12. Which compound will show the highest lattice energy?
- RbF
- CsF
- NaF
- KF
Answer: 3. NaF
With the same anion, the smaller the size of the cation, the higher is the lattice energy. Therefore, NaF will show the highest lattice energy among the given compounds.
Question 13. Which of the alkali metal chloride (MCI) forms its dihydrate salt (MCl.2H2O) easily?
- LiCl
- CsCl
- RbCl
- KCl
Answer: 1. LiCl
LiCl is deliquescent and crystallises from aqueous solution as hydrates, LiCl.2H2O.
Question 14. Crude sodium chloride obtained by crystallisation of brine solution does not contain
- \(\mathrm{MgSO}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{MgCl}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{CaSO}_4\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{MgSO}_4\)
Crude sodium chloride, generally obtained by the crystallisation of brine solution contains sodium sulphate (Na2SO4), calcium sulphate (CaSO4), calcium chloride (CaCl2) and magnesium chloride (MgCl2) as impurities. Crude sodium chloride does not contain MgSO4
Question 15. In the Castner-Kellner cell for the production of sodium hydroxide
- Brine is electrolyzed using graphite electrodes
- Molten sodium chloride is electrolysed
- Sodium amalgam is formed at a mercury cathode
- Brine is electrolyzed with pt electrodes.
Answer: 3. Sodium amalgam is formed at a mercury cathode
In the Castner-Kellner cell, sodium amalgam is formed at the mercury cathode.
A brine solution is electrolysed using a mercury cathode and a carbon anode.
NEET practice questions s-Block Elements
Question 16. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
- Pure sodium metal dissolves in liquid ammonia to give a blue solution.
- NaOH reacts with glass to give sodium silicate.
- Aluminium reacts with excess NaOH to give Al(OH)3.
- NaHCO3 on heating gives Na2CO3.
Answer: 3. Aluminium reacts with excess NaOH to give Al(OH)3.
Al reacts with NaOH to give sodium aluminate
Question 17. In which of the following processes, fused sodium hydroxide is electrolysed at a 330 °C temperature for extraction of sodium?
- Castner’s process
- Down’s process
- Cyanide process
- Both (2) and (3).
Answer: 1. Castner’s process
In Castner’s process, sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is electroplated at a temperature of 330°C for the production of sodium metal.
Question 18. Which of the following is known as a fusion mixture?
- Mixture of Na2CO3 + NaHCO3
- \(\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{CO}_3 \cdot 10 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- Mixture of \(\mathrm{K}_2 \mathrm{CO}_3+\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{CO}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{NaHCO}_3\)
Answer: 3. Mixture of \(\mathrm{K}_2 \mathrm{CO}_3+\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{CO}_3\)
K2CO3 and Na2CO3 mixture is called a fusion mixture.
Question 19. Washing soda has a formula
- \(\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{CO}_3 \cdot 7 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{CO}_3 \cdot 10 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{CO}_3 \cdot 3 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{CO}_3\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{CO}_3 \cdot 10 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
Na2CO3.10H2O is washing soda.
NEET practice questions s-Block Elements
Question 20. The following metal ion activates many enzymes, participates in the oxidation of glucose to produce ATP and with Na, is responsible for the transmission of nerve signals.
- Iron
- Copper
- Calcium
- Potassium
Answer: 4. Potassium
Potassium ions are then the most abundant cations within cell fluids, where they activate many enzymes, participate in the oxidation of glucose to produce ATP and, with solider, are responsible for the transmission of nerve signals.
Question 21. The function of the sodium pump is a biological process operating in each and every cell of all animals. Which of the following biologically important ions is also a constituent of this pump?
- K+
- Fe2+
- Ca2+
- Mg2+
Answer: 1. K+
Question 22. Magnesium reacts with an element (X) to form an ionic compound. If the ground state electronic configuration of (X) is 1s² 2s² 2p³, the simplest formula for this compound is
- \(\mathrm{Mg}_2 X_3\)
- \(\mathrm{Mg} X_2\)
- \(\mathrm{Mg}_2 X\)
- \(\mathrm{Mg}_3 X_2\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{Mg}_3 X_2\)
Magnesium reacts with an element (X) to form an ionic compound. If the ground state electronic configuration of (X) is 1s² 2s² 2p³
The electronic configuration of X is 1s², 2s² 2p³.
So, the valency of X will be 3.
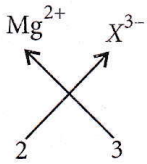
Magnesium ion = Mg2+
Formula: Mg3X2
Chemistry MCQs s-Block Elements NEET
Question 23. The electronic configuration of calcium atoms may be written as
- \([\mathrm{Ne}] 4 p^2\)
- \([\mathrm{Ar}] 4 s^2\)
- \([\mathrm{Ne}] 4 s^2\)
- \([\mathrm{Ar}] 4 p^2\)
Answer: 2. \([\mathrm{Ar}] 4 s^2\)
⇒ \({ }_{20} \mathrm{Ca} \longrightarrow 1 s^2, 2 s^2 2 p^6, 3 s^2 3 p^6, 4 s^2\)
⇒ \({ }_{18} \mathrm{Ar} \longrightarrow 1 s^2, 2 s^2 2 p^6, 3 s^2 3 p^6\)
Hence, \({ }_{20} \mathrm{Ca} \longrightarrow[\mathrm{Ar}] 4 s^2\)
Question 24. Compared with the alkaline earth metals, the alkali metals exhibit
- Smaller ionic radii
- Highest boiling points
- Greater hardness
- Lower ionization energies.
Answer: 4. Lower ionization energies.
The alkali metals are larger in size and have smaller nuclear charge thus they have lower ionization energy in comparison to alkaline earth metals.
Question 25. Which of the following atoms will have the smallest size?
- Mg
- Na
- Be
- Li
Answer: 3. Be
The atomic size decreases within a period from left to right, therefore Li > Be and Na > Mg. The size increases in a group from top to bottom. Hence, the size of Na is greater than Li. Overall order Na > Mg > Li > Be. Thus, Be has the smallest size.
Question 26. The structures of beryllium chloride in solid state and vapour phase are
- Chain in both
- Chain and dimer, respectively
- Linear in both
- Dimer and linear, respectively.
Answer: 2. Chain and dimer, respectively
In the vapour phase, BeCl2 is found in dimer form.
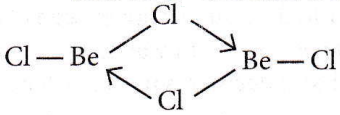
While in a solid state, it is found as a polymer (chain structure)
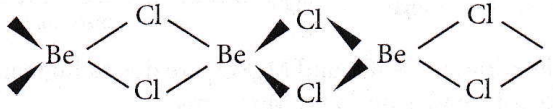
Question 27. Among the following alkaline earth metal halides one which is covalent and soluble in organic solvents is
- Beryllium chloride
- Calcium chloride
- Strontium chloride
- Magnesium chloride
Answer: 1. Beryllium chloride
Except for beryllium halides, all other halides of alkaline earth metals are ionic in nature. Beryllium halides are essentially covalent and soluble in organic solvents.
s-Block Elements quiz for NEET
Question 28. HCl was passed through a solution of CaCl2, MgCl2 and NaCl. Which of the following compound(s) crystallise(s)?
- Both MgCl2 and CaCl2
- Only NaCl
- Only MgCl2
- NaCl, MgCl2 and CaCl2
Answer: 2. Only NaCl
CaCl2 and MgCI2 are more soluble than NaCl. Thus, when HCl was passed through a solution containing CaCl2, MgCI2, and NaCl, only NaCl crystallised.
Question 29. Which of the following is an amphoteric hydroxide?
- Be(OH)2
- Sr(OH)2
- Ca(OH)2
- Mg(OH)2
Answer: 1. Be(OH)2
Be(OH)2 is amphoteric in nature as it reacts with acid and alkali.
⇒ \(\mathrm{Be}(\mathrm{OH})_2+2 \mathrm{OH}^{-} \rightarrow\left[\mathrm{Be}(\mathrm{OH})_4\right]^{2-}\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{Be}(\mathrm{OH})_2+2 \mathrm{HCl}+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow\left[\mathrm{Be}(\mathrm{OH})_4\right] \mathrm{Cl}_2\)
Question 30. Among CaH2, BeH2, BaH2, the order of ionic character is
- BeH2 < CaH2 < BaH2
- CaH2 < BeH2 < BaH2
- BeH2 < BaH2 < CaH2
- BaH2 < B2 < CaH2
Answer: 1. BeH2 < CaH2 < BaH2
BeH2 < CaH2< BaH2
On moving down the group, the metallic character of metals increases. So, the ionic character of metal hydrides increases.
Hence, BeH2 will be the least ionic
Question 31. On heating which of the following releases CO2 most easily?
- Na2CO3
- MgCO3
- CaCO3
- K2CO3
Answer: 2. MgCO3
The stability of carbonates increases down the group with an increase in the size of the metal ions. Also, the alkali metal carbonates are more stable than alkaline earth metal carbonates. Hence, MgCO3 is the least stable and it releases CO2 most easily.
⇒ \(\mathrm{MgCO}_3\)\(\underrightarrow{\Delta}\)\(\mathrm{MgO}+\mathrm{CO}_2\)
Question 32. Solubility of the alkaline earth metal sulphates in water decreases in the sequence
- Sr > Ca > Mg > Ba
- Ba > Mg > Sr > Ca
- Mg > Ca > Sr > Ba
- Ca > Sr > Ba > Mg
Answer: 3. Mg > Ca > Sr > Ba
The solubility of alkaline earth metal sulphates decreases down the group because hydration energy decreases.
Question 33. Which of the following compounds has the lowest melting point?
- CaCl2
- CaBr2
- Cal2
- CaF2
Answer: 3. Cal2
As the covalent character in the compound increases and the ionic character decreases, the melting point of the compound decreases. So, CaI2 has the highest covalent character and lowest melting point.
NEET MCQs on s-Block Elements
Question 34. Which of the following alkaline earth metal sulphates has a hydration enthalpy higher than the lattice enthalpy?
- CaSO4
- BeSO4
- BaSO4
- SrSO4
Answer: 2. BeSO4
The hydration enthalpy of BeSO4 is higher than its lattice energy. Within group 2, the hydration energy decreases down the group while lattice energy is almost the same.
Question 35. Which one of the following compounds is a peroxide?
- KO2
- BaO2
- MnO2
- NO2
Answer: 2. BaO2
BaO2 has peroxide linkage
Question 36. Property of the alkaline earth metals that increases with their atomic number
- Solubility of their hydroxides in water
- Solubility of their sulphates in water
- Ionization energy
- Electronegativity
Answer: 1. Solubility of their hydroxides in water
The solubility of an ionic compound depends on two factors:
- Lattice energy, and
- Hydration energy
In the case of alkaline earth metal hydroxides, the lattice energy decreases as we move down the group. This decrease is more than the decrease in the hydration energy down the group.
Question 37. Which of the following oxides is not expected to react with sodium hydroxide?
- CaO
- SiO2
- BeO
- B2O3
Answer: 1. CaO
CaO being a basic oxide does not react with NaOH, however, SiO2 (acidic oxide), BeO (amphoteric oxide) and B2O3 (acidic oxide) react with NaOH
Question 38. The correct order of increasing thermal stability of K2CO3, MgCO3, CaCO3 and BeCO3 is
- BeCO3 < MgCO3 < CaCO3 < K2CO3
- MgCO3 < BeCO3 < CaCO3 < K2CO3
- K2CO3 < MgCO3 < CaCO3 < BeCO3
- BeCO3 < MgCO3 < K2CO3 < CaCO3
Answer: 1. BeCO3 < MgCO3 < CaCO3 < K2CO3
In all cases, for a particular set of group 1 or group 2 compounds, the thermal stability increases down the group as the ionic radius of the cation increases, and its polarising power decreases.
Group 1 compounds tend to be more thermally stable than group 2 compounds because group 1 cation has a smaller charge and a larger ionic radius, and so, a lower polarising power, particularly when adjacent metals on the same period are compared.
Hence, the order of increasing thermal stability of K2CO3, MgCO3, CaCO3 and BeCO3 is BeCO3 < MgCO3 < CaCO3 < K2CO3
Question 39. In which of the following the hydration energy is higher than the lattice energy?
- MgSO4
- RaSO4
- SrSO4
- BaSO4
Answer: 1. MgSO4
NEET MCQs on s-Block Elements
When hydration energy exceeds lattice energy, the compound becomes soluble in water. The solubility of alkaline earth metal sulphates decreases in the order:
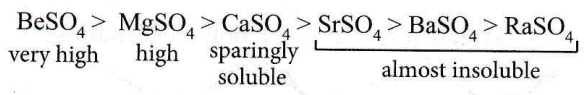
The solubilities of BeSO4 and MgSO4 are due to the high energy of solvation of smaller Be2+ and Mg2+ ions.
Question 40. The solubility in water of sulphate down the Be group is Be > Mg > Ca > Sr > Ba. This is due to
- Decreasing lattice energy
- The high heat of solvation for smaller ions like Be2+
- Increase in melting points
- Increasing molecular weight.
Answer: 2. High heat of solvation for smaller ions like Be2+
As we move down the group from BeSO4 to BaSO4 the enthalpy of hydration of the positive ion becomes smaller due to increasing in ionic size. Salts of heavier metal ions are 1ess soluble than those of lighter ions.
Question 41. All the following substances react with water. The pair that gives the same gaseous product is
- K and KO2
- Na and Na2O2
- Ca and CaH2
- Ba and BaO2
Answer: 3. Ca and CaH2
The pair which gives the same gaseous product is Ca and CaH2.
⇒ \(\mathrm{Ca}+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_2+\mathrm{H}_2\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{CaH}_2+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_2+2 \mathrm{H}_2\)
Whereas, \(\mathrm{K}\) gives \(\mathrm{H}_2\) while \(\mathrm{KO}_2\) gives \(\mathrm{O}_2\) and \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2\).
⇒ \(2 \mathrm{~K}+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{KOH}+\mathrm{H}_2\)
⇒ \(2 \mathrm{KO}_2+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{KOH}+\mathrm{O}_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2\)
Similarly, \(\mathrm{Na}\) gives \(\mathrm{H}_2\), while \(\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{O}_2\) gives \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2\).
⇒ \(2 \mathrm{Na}+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{NaOH}+\mathrm{H}_2\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{O}_2+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{NaOH}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2\)
Likewise Ba gives \(\mathrm{H}_2\) while \(\mathrm{BaO}_2\) gives \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2\).
⇒ \(\mathrm{Ba}+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{Ba}(\mathrm{OH})_2+\mathrm{H}_2\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{BaO}_2+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{Ba}(\mathrm{OH})_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2\)
Question 42. Which of the following statements is false?
- Strontium decomposes water more readily than beryllium.
- Barium carbonate melts at a higher temperature than calcium carbonate.
- Barium hydroxide is more soluble in water than magnesium hydroxide.
- Beryllium hydroxide is more basic than barium hydroxide.
Answer: 4. Beryllium hydroxide is more basic than barium hydroxide.
Beryllium hydroxide although amphoteric, is however less basic than barium hydroxide.
Question 43. In context with beryllium, which one of the following statements is incorrect?
- It is rendered passive by nitric acid.
- It forms Be2C.
- Its salts rarely hydrolyse.
- Its hydride is electron-deficient and polymeric.
Answer: 3. Its salts rarely hydrolyse.
Due to the very small size of Be2+, beryllium salts are readily hydrolysed because of high hydration energy. \(\mathrm{BeCl}_2+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{Be}(\mathrm{OH})_2+2 \mathrm{HCl}\)
Question 44. The suspension of slaked lime in water is known as
- Lime water
- Quicklime
- Milk of lime
- Aqueous solution of slaked lime.
Answer: 3. Milk of lime
⇒ \(\underset{\text { Quick lime }}{\mathrm{CaO}}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \longrightarrow \underset{\text { Slaked lime }}{\mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_2+\text { Heat }}\)
This process is known as slaking of lime. The paste of lime in water (i.e., suspension) is called milk of lime while the filtered and clear solution is known as lime water.
NEET questions on s-Block Elements
Question 45. The product obtained as a result of a reaction of nitrogen with CaC2 is
- CaCN3
- Ca2CN
- Ca(CN)2
- CaCN
Answer: 3. Ca(CN)2
Read Ca(CN)2 as CaCN2
⇒ \(\mathrm{CaC}_2+\mathrm{N}_2 \longrightarrow \underset{\text{Slaked lime}}{\mathrm{CaCN}_2}+\mathrm{C}\)
Question 46. Which one of the following is present as an active ingredient in bleaching powder for bleaching action?
- CaOCl2
- Ca(OCl)2
- CaO2Cl
- CaCl2
Answer: 2. Ca(OCl)2
The active ingredient in bleaching powder for bleaching action is Ca(OCl)2.
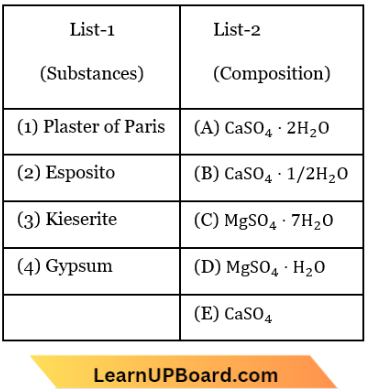
Question 47. Match List-1 with List-2 for the compositions of substances and select the correct answer using the code given:
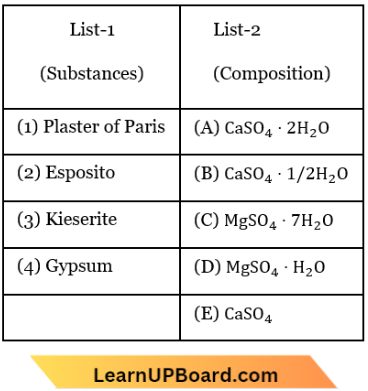
- (1)-(C), (2)-(D), (3)-(A), (4)-(B)
- (1)-(B), (2)-(C), (3)-(D), (4)-(A)
- (1)-(A), (2)-(B), (3)-(C), (4)-(E)
- (1)-(D), (2)-(C), (3)-(B), (4)-(A)
Answer: 2. (1)-(B), (2)-(C), (3)-(D), (4)-(A)
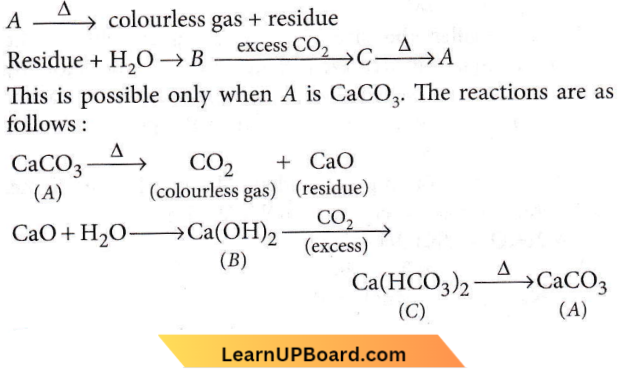
Question 48. The compound A on heating gives a colourless gas and a residue that is dissolved in water to obtain B. Excess of CO2 is bubbled through an aqueous solution of B, and C is formed which is recovered in the solid form. Solid C on gentle heating gives back A. The compound is
- CaCO3
- Na2CO3
- K2CO3
- CaSO4•2H2O
Answer: 1. CaCO3
The compound A on heating gives a colourless gas and a residue that is dissolved in water to obtain B. Excess of CO2 is bubbled through an aqueous solution of B, and C is formed which is recovered in the solid form. Solid C on gentle heating gives back A.
The reactions can be summarised as follows:
Question 49. Which of the following represents calcium chlorite?
- Ca(ClO3)2
- Ca(ClO2)2
- CaClO2
- Ca(ClO4)2
Answer: 2. Ca(ClO2)2
Since the valency of calcium is 2 and a chlorite ion is CIO–2, therefore calcium chlorite is Ca(ClO2)2.
NEET questions on s-Block Elements
Question 50. Identify the correct statement.
- Plaster of Paris can be obtained by hydration of gypsum.
- Plaster of Paris is obtained by partial oxidation of gypsum.
- Gypsum contains a lower percentage of calcium than Plaster of Paris.
- Gypsum is obtained by heating Plaster of Paris.
Answer: 3. Gypsum contains a lower percentage of calcium than Plaster of Paris.
Gypsum is CaSO4.2H2O and plaster of Paris is (CaSO4)2.H2O. Therefore, gypsum contains a lower percentage of calcium than Plaster of Paris.
Question 51. Bleaching powder is obtained by the action of chlorine gas and
- Dilute solution of Ca(OH)2
- Concentrated solution of Ca(OH)2
- Dry CaO
- Dry-slaked lime.
Answer: 4. Dry slaked lime.
Cl2 gas reacts with dry slaked lime, Ca(OH)2 to give bleaching powder.
⇒ \(\mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_2+\mathrm{Cl}_2\) \(\underrightarrow{\Delta}\) \(\mathrm{CaOCl}_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
Question 52. Which one of the following statements is correct?
- The bone in the human body is an inert and unchanging substance.
- Mg plays roles in neuromuscular function and interneuronal transmission.
- The daily requirement of Mg and Ca in the human body is estimated to be 0.2-0.3 g.
- All enzymes that utilise ATP in phosphate transfer require Ca as the cofactor.
Answer: 3. The daily requirement of Mg and Ca in the human body is estimated to be 0.2-0.3 g.
Bones are not the inert and unchanging substances. Calcium plays an important role in neuromuscular function and interneuronal transmission.
All enzymes that utilise ATP in phosphate transfer require magnesium as the cofactor.
Question 53. Enzymes that utilize ATP in phosphate transfer require an alkaline earth metal (M) as the cofactor. M is
- Sr
- Be
- Mg
- Ca
Answer: 3. Mg
All enzymes that utilise ATP in phosphate transfer require magnesium as the cofactor
NEET practice questions s-Block Elements
Question 54. Which of the following statements is false?
- Ca2+ ions are not important in maintaining the regular beating of the heart.
- Mg2+ ions are important in the green parts of the plants.
- Mg2+ ions form a complex with ATP.
- Ca2+ ions are important in blood clotting.
Answer: 1. Ca2+ ions are not important in maintaining the regular beating of the heart.
Ca2+ ions are required to trigger the contraction of muscles and to maintain the regular beating of the heart
Question 55. Which of the following metal ions play an important role in muscle contraction?
- K+
- Na+
- Mg2+
- Ca2+
Answer: 4. Ca2+
Calcium is an essential element for the contraction of muscles.
