Surface Chemistry NEET MCQs
NEET Chemistry For Surface Chemistry Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. The correct option representing a Freundlich adsorption isotherm is
- \(\frac{x}{m}=k p^{0.3}\)
- \(\frac{x}{m}=k p^{2.5}\)
- \(\frac{x}{m}=k p^{-0.5}\)
- \(\frac{x}{m}=k p^{-1}\)
Answer: 1. \(\frac{x}{m}=k p^{0.3}\)
Freundlich adsorption isotherm equation is \(\frac{x}{m}=k p^{\frac{1}{n}}\left(1 \geq \frac{1}{n} \geq 0\right)\)
Question 2. Which one of the following characteristics is associated with adsorption?
- ΔG and ΔH are negative but ΔS is positive.
- ΔG and ΔS are negative but ΔH is positive.
- ΔG is negative but ΔH and ΔS are positive.
- ΔG, ΔH and ΔS all are negative.
Answer: 4. ΔG, ΔH and ΔS all are negative.
As the molecules of the adsorbate are held on the surface of the solid adsorbent, entropy decreases i.e., ΔS = -ve.
As ΔG=ΔH- TΔS
For the adsorption to occur, ΔG = -ve and it is possible only if ΔH= -ve
Question 3. In Freundlich adsorption isotherm, the value of 1/n is
- Between 0 and 1 in all cases
- Between 2 and 4 in all cases
- 1 In case of physical absorption
- 1 In case of chemisorption.
Answer: 1. Between 0 and 1 in all cases
Freundlich adsorption isotherm: \(\frac{x}{m}=k \cdot p^{1 / n} ; \quad 0 \leq \frac{1}{n} \leq 1\)
Read and Learn More NEET MCQs with Answers
Question 4. If x is the amount of adsorbate and m is the amount of adsorbent, which of the following relations is not related to the adsorption process?
- x/m =f(p) at constant T
- x/m =f(T) at constant p
- p =f(T) at constant (x/m)
- \(\frac{x}{m}\) = p x T
Answer: 4. \(\frac{x}{m}\) = p x T
If x is the amount of adsorbate and m is the amount of adsorbent
⇒ \(\frac{x}{m}=p \times T\) is the incorrect relation.
The correct relation is amount of absorption \(\frac{x}{m} \propto \frac{p}{T}\)
NEET questions on Surface Chemistry
Question 5. The Langmuir adsorption isotherm is deduced using the assumption
- The adsorption sites are equivalent in their ability to adsorb the particles
- The heat of adsorption varies with coverage
- The adsorbed molecules interact with each other
- The adsorption takes place in multilayers.
Answer: 1. The adsorption sites are equivalent in their ability to adsorb the particles
Langmuir adsorption isotherm is based on the assumption that every adsorption site is equivalent and that the ability of a particle to bind there is independent of whether nearby sites are occupied or not.
Question 6. A plot of log (x/m) versus log P for the adsorption of a gas on a solid gives a straight line with a slope equal to
- log k
- -log k
- n
- 1/n
Answer: 4. 1/n
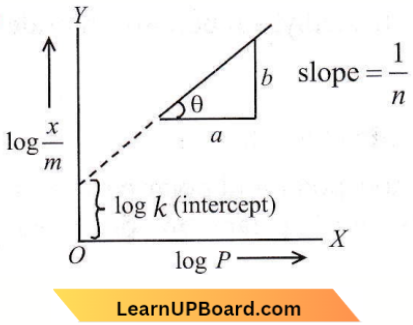
This is according to Freundlich adsorption isotherm
Question 7. Which is not correct regarding the adsorption of a gas on the surface of a solid?
- On increasing temperature, adsorption increases continuously.
- Enthalpy and entropy change is negative.
- Adsorption is more for some specific substance.
- It is a reversible reaction.
Answer: 1. On increasing temperature adsorption increases continuously.
Adsorption is the ability of a substance to concentrate or hold gases, liquids or dissolved substances upon its surface. Solids absorb greater amounts of substances at lower temperatures. In general, adsorption decreases with an increase in temperature.
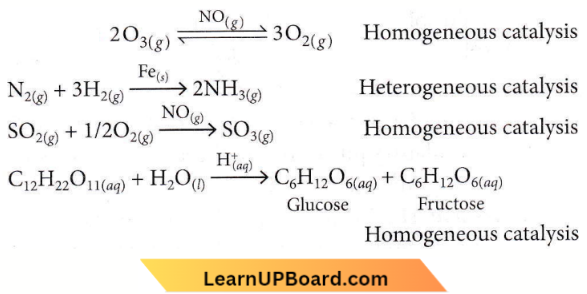
Question 8. Which one is an example of heterogeneous catalysis?
- Decomposition of ozone in the presence of nitrogen monoxide,
- Combination between dinitrogen and dihydrogen to form ammonia in the presence of finely divided iron.
- Oxidation of sulphur dioxide into sulphur trioxide in the presence of oxides of nitrogen.
- Hydrolysis of sugar catalysed by H+ ions.
Answer: 2. Combination between dinitrogen and dihydrogen to form ammonia in the presence of finely divided iron.
Question 9. The incorrect statement regarding enzymes is
- Enzymes are biocatalysts
- Like chemical catalysts enzymes reduce the activation energy of bioprocesses
- Enzymes are polysaccharides
- Enzymes are very specific for a particular reaction and substrate.
Answer: 3. Enzymes are polysaccharides
Enzymes are protein molecules of high molecular mass and form colloidal solutions in water.
Surface Chemistry multiple choice NEET
Question 10. Which one of the following statements is not correct?
- The value of the equilibrium constant is changed in the presence of a catalyst in the reaction at equilibrium.
- Enzymes catalyse mainly biochemical reactions.
- Coenzymes increase the catalytic activity of enzymes.
- The catalyst does not initiate any reaction.
Answer: 1. The value of the equilibrium constant is changed in the presence of a catalyst in the reaction at equilibrium.
Catalysts do not change the value of equilibrium constant as they affect forward as well as backward reactions equa1ly.
Question 11. Which one of the following statements is incorrect about enzyme catalysis?
- Enzymes are mostly proteinous in nature.
- Enzyme action is specific.
- Enzymes are denatured by ultraviolet rays and at high temperatures.
- Enzymes are least reactive at optimum temperature.
Answer: 4. Enzymes are least reactive at optimum temperature.
The enzyme activity rises rapidly with temperature and becomes maximum at a definite temperature, called optimum temperature.
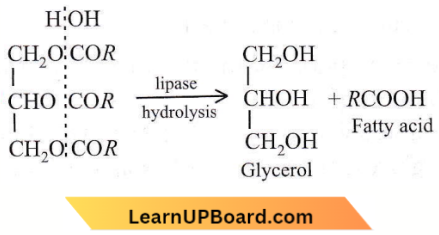
Question 12. The enzyme which hydrolyses triglycerides to fatty acids and glycerol is called
- Maltase
- Lipase
- Zymase
- Pepsin.
Answer: 2. Lipase
Question 13. According to the adsorption theory of catalysis, the speed of the reaction increases because
- The concentration of reactant molecules at the active centres of the catalyst becomes high due to adsorption
- In the process of adsorption, the activation energy of the molecules becomes large
- Adsorption produces heat which increases the speed of the reaction
- Adsorption lowers the activation energy of the reaction.
Answer: 4. Adsorption lowers the activation energy of the reaction.
Adsorption causes a decrease in surface energy which appears as heat. thus, adsorption is an exothermic process and hence lowers the activation energy of the reaction.
NEET practice questions Surface Chemistry
Question 14. A colloidal system has particles of which of the following sizes?
- 10-9 m to 10-12 m
- 10-6 m to 10-9 m
- 10-4 m to 10-10 m
- 10-5 m to 10-7 m
Answer: 2. 10-6 m to 10-9 m
The particle size of colloids lies in the range of 10-6 m to 10-9 m. Particles themselves are invisible even under the most powerful microscope.
Question 15. Pumice stone is an example of
- Solid sol
- Foam
- Sol
- Gel.
Answer: 1. Solid sol
Pumice stone is an example of a solid sol in which the dispersed phase is gas and the dispersion medium is solid.
Question 16. Given below are two statements:
Statement-1: In the coagulation of a negative sol, the flocculating power of the three given ions is in the order: \(\mathrm{Al}^{3+}>\mathrm{Ba}^{2+}>\mathrm{Na}^{+}\)
Statement-2: In the coagulation of a positive sol, the flocculating power of the three given salts is in the order: \(\mathrm{NaCl}>\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4>\mathrm{Na}_3 \mathrm{PO}_4\)
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
- Both statement-1 and statement-2 are correct.
- Both statement-1 and statement-2 are incorrect.
- Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect.
- Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct.
Answer: 3. Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect.
In the coagulation of a positive sol, the flocculating power is in the order: \(\mathrm{PO}_4^{3-}>\mathrm{SO}_4^{2-}>\mathrm{Cl}^{-}\) or, \(\mathrm{NaCl}<\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4<\mathrm{Na}_3 \mathrm{PO}_4\)
Question 17. The right option for the statement “Tyndall effect is exhibited by” is
- Urea solution
- NaCl solution
- Glucose solution
- Starch solution.
Answer: 4. Starch solution.
As the starch solution is a colloidal solution hence it exhibits the Tyndall effect. NaCl, urea and glucose form a true solution.
Chemistry MCQs Surface Chemistry NEET
Question 18. Measuring zeta potential is useful in determining which property of colloidal solution?
- Viscosity
- Solubility
- Stability of the colloidal particles
- Size of the colloidal particles
Answer: 3. Stability of the colloidal particles
Measuring, zeta potential is useful in determining the stability of the colloidal particles.
Question 19. Which mixture of the solutions will lead to the formation of negatively charged colloidal [AgI]I-1 sol?
- 50 mL of 0.1 M AgNO3 + 50 mL of 0.1 M KI
- 50 mL of 1 M AgNO3 + 50 mL of 1.5 M KI
- 50 mL of 1 M AgNO3 + 50 mL of 2 M KI
- 50 mL of 2 M AgNO3 + 50 mL of 1.5 M KI
Answer: 2. 50 mL of 1 M AgNO3 + 50 mL of 1.5 M KI
If the colloidal sol of AgI is prepared by adding KI solution to AgNO3 till KI is in slight excess, iodide ion (I–) will be adsorbed on the surface of AgI thereby, giving a negative charge to the sol.
⇒ \(\mathrm{AgI}+\underset{(\text { From } \mathrm{KI})}{\mathrm{I}^{-}} \longrightarrow \underset{\text { Negative sol }}{\mathrm{AgI}: \mathrm{I}^{-}}\)
Question 20. On which of the following properties does the coagulating power of an ion depend?
- The magnitude of the charge on the ion alone
- The size of the ion alone
- Both the magnitude and sign of the charge on the ion
- The sign of charge on the ion alone
Answer: 3. Both the magnitude and sign of the charge on the ion
According to the Hardy-Schulze rule, the coagulating power of an electrolyte depends on both the magnitude and sign of the charge of the effective ion or electrolyte.
Question 21. The coagulation values in millimoles per litre of the electrolytes used for the coagulation of As2S3 are given below:
- (NaCl) = 52,
- (BaCl2) = 0.69,
- (MgSO4) = 0.22
The correct order of their coagulating power is
- 1 > 2 > 3
- 2 > 1 > 3
- 3 > 2 > 1
- 3 > 1 > 2
Answer: 3. 3 > 2 > 1
Coagulating power \(\propto \frac{1}{\text { Coagulation value }}\)
The lower the coagulation value, the higher is the coagulating power so, the correct order is: \(\underset{3} {\mathrm{MgSO}_4}>\underset{2} {\mathrm{BaCl}_2}>\underset{1}{\mathrm{NaCl}}\)
Surface Chemistry quiz for NEET
Question 22. Fog is a colloidal solution of
- Solid in gas
- Gas in gas
- Liquid in gas
- Gas in liquid.
Answer: 3. Liquid in gas
Fog is an example of aerosol in which the dispersed phase is liquid and the dispersion medium is gas.
Question 23. Which property of colloidal solution is independent of charge on the colloidal particles?
- Electroosmosis
- Tyndall effect
- Coagulation
- Electrophoresis
Answer: 2. Coagulation
Tyndall effect is the scattering of light by colloidal particles which is independent of the charge on them.
Question 24. The protecting power of lyophilic colloidal sol is expressed in terms of
- Coagulation Value
- Gold Number
- Critical Micelle Concentration
- Oxidation Number.
Answer: 2. Gold Number
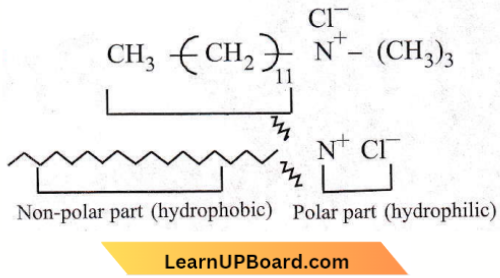
Question 25. Which one of the following forms micelles in an aqueous solution above a certain concentration?
- Dodecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride
- Glucose
- Urea
- Pyridinium chloride
Answer: 1. Dodecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride
NEET MCQs on Surface Chemistry
Question 26. Position of non-polar and polar parts in micelle
- Polar at the outer surface but non-polar at the inner surface
- Polar at the inner surface non-polar at the outer surface
- Distributed over all the surface
- Are present in the surface only.
Answer: 1. Polar at the outer surface but non-polar at the inner surface
Micelles are the clusters or aggregates formed in solution by association of colloids. Usually, such molecules have a lyophobic group and a lyophilic group. The long hydrocarbon is the lyophobic portion which tries to recede away from the solvent water and the ionisable lyophitic group which tends to go into water resulting in ions.
As the concentration is increased the lyophobic parts receding away from the solvent approach each other and form a cluster. Thus, the lyophobic ends are in the interior and lyophilic groups projecting outward in contact with the solvent.
Question 27. Which one of the following methods is commonly used method for the destruction of colloids?
- Dialysis
- Condensation
- Filtration by animal membrane
- By adding electrolyte
Answer: 4. By adding electrolyte
By adding electrolytes the colloidal particles are precipitated. The electrolytes neutralise the charge of colloids leading to their coagulation and thus, destroying the colloid.
NEET MCQs on Surface Chemistry
Question 28. At the critical micelle concentration (CMC) the surfactant molecules
- Associate
- Dissociate
- Decompose
- Become Completely Soluble.
Answer: 1. Associate
The soap concentration at which micelles (spherical colloid molecules) first appear is called critical micelle concentration (CMC). At this condition, the surfactant molecules associate with each other
Question 29. The ability of an anion, to bring about coagulation of a given colloid, depends upon
- The magnitude of the charge
- Both magnitude and charge
- Its charge only
- Sign of the charge alone.
Answer: 2. Both magnitude and charge
Both magnitudes of charge and the nature of charge affect the coagulation of a given colloid. The greater the magnitude of the charge, the quicker will be the coagulation.
Surface Chemistry NEET question bank
Question 30. When a few typical solutes are separated by a particular selective membrane such as protein particles, or blood corpuscles, this process is called
- Transpiration
- Endosmosis
- Dialysis
- Diffusion.
Answer: 3. Dialysis
Dialysis is the process of separating the particles of colloids from the particles of crystalloids by means of diffusion through a selective membrane placed in water.
