NEET Biology For Cell The Unit Of Life Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Which of the following cytoskeletal elements plays an important role in the movement of chromosomes?
- Microfilamenls
- Microtubules
- Intermediate filaments
- All of these
Answer: 2. Microtubules
Question 2. The bacterial genome or nucleoid is made up of
- A single double-stranded chromosome with histone
- UNA and histories
- single double-stranded DNA, not complexed with histone proteins, nor packed in the chromosome
- A single-stranded circular DNA
Answer: 3. single double-stranded DNA, not complexed with histone proteins, nor packed in the chromosome
Question 3. In bacterial cells. DNA is extensively looped and coiled with the help of
- Acid proteins
- Ilistories
- Basic nucleoid proteins called as polyamines
- Actin
Answer: 3. Basic nucleoid protein called as polyamines
” cell biology mcq”
Question 4. Two animal cells are interconnected by
- Plasmodesmata
- Cell wall
- Desmosomc
- Plasma membrane
Answer: 3. Desmosomc
Question 5. The type of growth shown by the primary cell wall is
- Accretionary
- Instussuceptionary
- Protoplasmic
- None, as it cannot expand or grow
Answer: 2. Instussuceptionary
Question 6. Plasmodesmata often has ER (endoplasmic reticulum) tubule called as
- Symplasm
- Desmotubulc
- Apoplasm
- Intermediate filaments
Answer: 2. Desmotubulc
Question 7. Which of the following is associated with the detoxification of drugs and muscle contraction by the release and uptake of Ca+2 ions?
- Golgi complex
- RER
- SER
- Free ribosomes
Answer: 3. SER
Question 8. The main organelle involved in the modification and routing of newly synthesized proteins to their destination is
- Chloroplast
- Mitochondria
- Lysosome
- Endoplasmic reticulum
Answer: 4. Endoplasmic reticulum
Question 9. The term endoplasmic reticulum was used by
- Keith Poter
- Thompson
- Robertson
- Keith Peter and Thompson
Answer: 1. Keith Potcr
Question 10. Ribosomes, when associated with ER, attach with their
- Smaller subunit
- Larger subunit (60S)
- BOS subunit
- Either by smaller or by larger subunits
Answer: 1. Smaller subunit
Question 11. Ribosomes are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum through
- Ribophorins
- r-RNA
- t-RNA
- Hydrophobic interaction
Answer: 1. Ribophorins
Question 12. RER is well developed in cells engaged in the synthesis of
- Nucleotides
- Proteins
- Lipids
- Secretory products
Answer: 2. Proteins
Question 13. SER is mainly found in cells actively engaged in
- Secretion activity
- Protein metabolism
- Lipid metabolism
- Catabolic activity
Answer: 3. Lipid metabolism
Question 14. Golgi apparatus/apparato reticular is specialized for all except
- Glycosidation and glycosylation of lipids and proteins
- Recycling of the plasma membrane pinched off by pinocytosis and phagocytosis
- Secretion
- Intracellular digestion
Answer: 4. Intracellular digestion
Question 15. Which of the following statements is incorrect about the Golgi apparatus?
- The sacs on the forming face (cis-face) are associated with ER.
- Golgi apparatus was studied by Camillo Golgi in the nerve cells of owls by metallic impregnation technique.
- Golgi apparatus in plants is called as dictyosome and secretes mucilage in the root cap cells.
- Golgi apparatus has no role in the modification of proinsulin.
Answer: 4. Golgi apparatus has no role in the modification of proinsulin.
Question 16. Lysosomes are formed by budding off vesicles from Golgi apparatus and contain
- Oxidizing enzymes
- 40 different acid hydrolases
- Respiratory enzymes
- Basic hydrolases
Answer: 2. 40 different acid hydrolases
Question 17. Which of the following is likely to show the absence of lysosomes?
- Cyanophyceae
- Protozoa
- Anther tapetum
- Mammalian leucocytes
Answer: 2. Protozoa
Question 18. Lysosomes were first discovered by
- Rohdin
- Pemer
- Christian de Duve
- None of these
Answer: 3. Christian de Duve
Question 19. Which of the following organelles show polymorphism?
- Golgi apparatus
- Lysosome
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
Answer: 2. Lysosome
Question 20. Autolysis is associated with
- Ribosome
- Kinetosome
- Lysosome
- Golgi apparatus
Answer: 3. Lysosome
Question 21. Which of the following organelles possess oxidases and are associated with oxidation reactions other than those of respiration?
- Spherosomcs
- Peroxisomes
- Lysosomes
- Golgi
Answer: 2. Peroxisomes
Question 22. Which of the following organelles takes part in photorespiration?
- Glyoxysome
- Peroxisome
- Dictyosome
- ER
Answer: 2. Peroxisome
Question 23. Peroxisomes contain peroxide-producing enzymes. These are found in
- Plant cells
- Animal cells
- Both (1) and (2)
- Bacteria and blue-green algae
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
Question 24. Which of the following is a peroxide-destroying enzyme present in peroxisome?
- Urate oxidase
- Catalase
- Amino acid oxidase
- Peroxidase
Answer: 2. Catalase
Question 25. Non-secretory proteins are synthesized by
- ER-bound ribosomes
- Free ribosomes
- Polysomes
- Endosomes
Answer: 2. Free ribosomes
“cell unit of life “
Question 26. Find out the incorrect statement with respect to glyoxysomes.
- It is reported from the endosperm of germinating seeds.
- They usually occur in fat-rich plant cells.
- They are associated with the glyoxylate cycle.
- They develop from mitochondria.
Answer: 4. They develop from mitochondria.
Question 27. The proper folding of proteins following synthesis is assisted by
- Polyribosomes
- Specific proteins called chaperons
- Polysomes
- Free ribosomes
Answer: 2. Specific proteins called chaperons
Question 28. Protein synthesis in an animal cell occurs
- Only on the ribosomes present in the cytosol
- Only on ribosomes attached to the nuclear envelope and ER
- On ribosomes present in the cytoplasm as well as in mitochondria
- On ribosomes present in the nucleolus as well as in the cytoplasm
Answer: 3. On ribosomes present in the cytoplasm as well as in mitochondria
Question 29. When ATP concentration is low or the respiratory chain is inhibited, the mitochondria are seen in
- Active state
- Condensed state
- Orthodox state
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 3. Orthodox state
Question 30. Mitochondria and chloroplasts are semi-autonomous as they possess
- DNA
- DNA + RNA
- DNA + RNA ribosomes
- Proteins
Answer: 3. DNA + RNA ribosomes
Question 31. Which of the following organelles is concerned with the generation of ATP through electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation?
- Chloroplast
- Mitochondria
- Glyoxysome
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 2. Mitochondria
Question 32. F0-F1 particles are also called as
- Quantasomes
- Glyoxysome
- Parade particles
- Oxisomes
Answer: 4. Oxisomes
Question 33. Organelle rich in Manganese is
- Ribosome
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
- Nucleus
Answer: 2. Mitochondria
Question 34. The presence of DNA in mitochondria and chloroplast supports the hypothesis that
- Glycolysis occurs in both mitochondria and chloroplast
- Mitochondria and chloroplast both originated as independent free-living organisms
- ATP is produced in mitochondria as well as in chloroplast
- Mitochondria and chloroplast undergo meiosis and mitosis independent of the nucleus
Answer: 2. Mitochondria and chloroplast both originated as independent free-living organisms
Question 35. Synthesis of ATP in mitochondria takes place
- In the matrix
- In the Intracoastal space
- At the cristae
- At the outer membrane
Answer: 3. At the cristae
Question 36. Oxysomes are submicroscopic particles present on the
- Surface of the inner membrane of the mitochondrion
- Thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts
- The outer membrane of the mitochondrion
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Answer: 1. Surface of the inner membrane of the mitochondrion
Question 37. Mitochondria are not found in
- Mature WBC
- Mature RBC
- Nerve cell
- Sperm
Answer: 2. Mature RBC
Question 38. The mitochondrial DNA differs from the nuclear DNA in
- Lacking association with histones
- Being circular in nature
- Having a higher C-G ratio
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 39. Genes for cytoplasmic male sterility in plants are generally located in
- Mitochondrial genome
- Chloroplast genome
- Nuclear genome
- Cytosol
Answer: 1. Mitochondrial genome
Question 40. Chlorophyll in chloroplasts is located in
- Grana
- Pyrenoid
- Stroma
- Both grana and stroma
Answer: 1. Grana
Question 41. Which of the following organelles stores proteins?’
- Amyloplasts
- Aleuroplasts
- Plastids
- Elaioplasts (oleosomes)
Answer: 2. Aleuroplasts
Question 42. Grana in chloroplast is formed by the piling of
- Cristae
- Thylakoids
- Oxisomes
- Dictyosomes
Answer: 2. Thylakoids
Question 43. The symbiont hypothesis suggests that there are similarities between prokaryotes, mitochondria, and chloroplasts like
- Presence of circular DNA associated with histones and 70S ribosomes
- The presence of circular DNA net associated with histones and 70S ribosomes present
- 50S ribosomes and DNA
- 30S ribosomes and DNA
Answer: 2. Presence of circular DNA net associated with histones and 70S ribosomes present
Question 44. Quantasomes are found in
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
- Nucleus
- Lysosome
Answer: 2. Chloroplast
Question 45. Each quantasome contains
- 100 chlorophyll molecules
- 200 chlorophyll molecules
- 300 chlorophyll molecules
- 230 chlorophyll molecules
Answer: 4. 230 chlorophyll molecules
Question 46. Hammerling’s experiment on Acetabularia proved the role of
- Chromosomes in heredity
- Nucleus in heredity
- Nucleo-cytoplasmic ratio
- Cytoplasm in controlling differentiation
Answer: 2. Nucleus in heredity
Question 47. At certain places, the nuclear envelope is interrupted by the presence of nuclear pores which are enclosed by circular structures called as
- Perinuclear space
- Annuli
- Pore complex
- Nucleolus
Answer: 2. Annuli
Question 48. The main site for ribosomal RNA synthesis is
- Nucleus
- Nucleolus
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Nucleolus
Answer: 2. Nucleolus
Question 49. Telomeres
- Initiate RNA synthesis
- Seal ends of chromosomes
- Have guanine-rich repeats
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 4. Both (2) and (3)
Question 50. The term nucleolus was coined by
- Bowman
- Fontana
- Flemming
- Leeuwenhoek
Answer: 1. Bowman
“cell the unit of life “
Question 51. Telomerase is an enzyme that is a
- Simple protein
- RNA
- Fibonucleoprotein
- Repetitive DNA
Answer: 3. Fibonucleoprotein
Question 52. The nucleolus is produced from
- 1° constriction
- Nucleolus-organizing region of certain chromosomes
- Nuclear envelope
- ER
Answer: 2. Nucleolus-organizing region of certain chromosomes
Question 53. A cystolith is a deposit of
- Calcium citrate
- Calcium carbonate
- Silica
- Calcium oxalate
Answer: 2. Calcium carbonate
Question 54. Which of the following suggests advanced features of an organism?
- The karyotype shows a large size difference between the smallest and the largest chromosome.
- Karyotype has few metacentric chromosomes.
- Asymmetric karyotype
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 55. Tolbert is associated with which one of the following cell structures?
- Peroxisomes
- Spherosomes
- Quantasomes
- Glyoxysomes
Answer: 1. Peroxisomes
Question 56. A single mitochondrion is found in
- Flight muscles of insects
- Human sperm
- Micrasterias
- Chaos chaos
Answer: 3. Micrasterias
Question 57. The smallest cell organelle is
- Peroxisome
- Spherosome
- Ribosome
- Lysosome
Answer: 3. Spherosome
Question 58. The complex formed of centriole and kinoplasm called as
- Diplosome
- Centrosphere
- Centrosome
- Kinetosome
Answer: 3. Centrosome
Question 59. Man and mouse cells are treated with red am green fluorescent dyes separately and are made to fuse. The resultant cells when kept at 37°C, the distribution of dye on the surface of cell will be
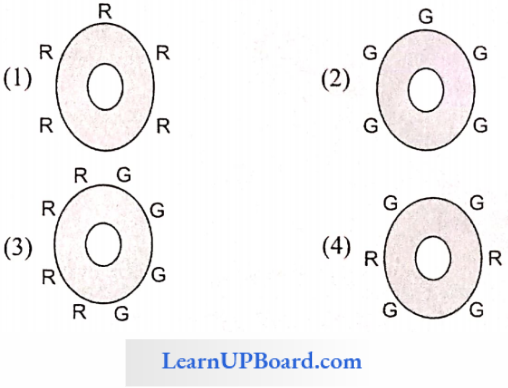
Answer: 4
“cell questions with answers “
Question 60. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) powers the movement of cilia and flagella. Adenosine triphosphatase activity is present in
- Nexin protein
- Dynein protein
- Massule
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 2. Dynein protein
Question 61 The r-RNAs of BOS ribosomes of larger subunits are
- 18S
- 23S + 5S
- 28S + 5.8S + 5S
- 16S
Answer: 3. 28S + 5.8S + 5S
Question 62. A component of the cytoskeleton is
- Microtubule
- Bone
- Chitin
- Cartilage
Answer: 1. Microtubule
Question 63. Kinetochore is the
- Fibrous granular structure within the centromere
- Surface of centromere
- Constriction near chromosome end
- End of chromosome
Answer: 2. Surface of centromere
Question 64. Who amongst the following scientists is credited with the discovery of cell and published Micrographia?
- Robert Brown
- Robert Hooke
- Schleiden
- Schwann
Answer: 2. Robert Hooke
Question 65. Who was the first to observe living substances in the cells?
- Anton van Leeuwenhoek
- Alfonso Corti
- Robert Brown
- Johannes Purkinje
Answer: 1. Anton van Leeuwenhoek
Question 66. The nucleus was first observed in the cells of orchid roots in 1831 by
- Robert Brown
- Hugo von Mohl
- Schleiden
- Schwann
Answer: 2. Hugo von Mohl
Question 67. “Protoplasm is the physical basis of life” was stated by
- Purkinje
- Huxley
- Rudolf Virchow
- Schwann
Answer: 2. Huxley
Question 68. Which of the following does not show a circular DNA?
- Bacterial cell
- Nucleus
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
Answer: 2. Nucleus
Question 69. The saccules and utricles were names used for the cells by which of the following?
- Robert Brown
- Malpighii
- Purkinje
- Swanson
Answer: 4. Swanson
Question 70. The cells discovered in the thin section of cork by Robert Hooke were actually
- Cellulose
- Living cell
- Cell coat
- Cell wall
Answer: 3. Cell coat
Question 71. Most of the water found in the cell occurs in
- Cell wall
- Nucleus
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleolus
Answer: 3. Cytoplasm
Question 72. Which of the following is described as the “energy currency of the cell”?
- DNA
- RNA
- ATP
- Vitamins
Answer: 1. DNA
Question 73. Cell theory was put forward by
- Schleiden and Schwann in 1838-39
- Sutton and Boveri
- Watson and Crick
- Darwin and Wallace
Answer: 4. Darwin and Wallace
Question 74. Cell theory is applicable to all except
- Animals
- Plants
- Fungi
- Viruses
Answer: 2. Plants
Question 75. Who was the first to explain that the cells divide and new cells are formed from the pre-existing cells (Omnis cellu-la-e-celluld) in 1855?
- Louis Pasteur
- Rudolf Virchow
- Nagaii
- Robert Brown
Answer: 4. Robert Brown
Question 76. The longest cell in the human body is
- Liver cell
- Muscle cell
- Neuroglia cell
- Nerve cell
Answer: 4. Nerve cell
Question 77. What is absent in mammalian erythrocytes?
- Aerobic respiration
- Nucleus
- DNA
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 78. One of the following is an exception to the cell theory.
- Bacteria
- Prokaryotes
- Blue-green algae
- Bacteriophage
Answer: 2. Prokaryotes
Question 79. The membrane covering the vacuole is known as
- Desmosomes
- Tonoplast
- Plasmodesmata
- Tyloses
Answer: 1. Desmosomes
Question 80. Which is a non-membranous (not covered by a membrane) organelle?
- Ribosome
- Lysosome
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
Answer: 3. Mitochondria
Question 81. Which one of the following is absent in plant cell?
- Vacuole
- Cell wall
- Centrosome
- Plastids
Answer: 1. Vacuole
Question 82. Which one of the following does not have the ability to divide?
- Nerve cells
- Liver cells
- Muscle cells
- Bone marrow cells
Answer: 3. Muscle cells
Question 83. The prokaryotic cells are characterized by
- Distinct chromosome
- Absence of chromatin material
- Absence of nuclear membrane
- Distinct nuclear membrane
Answer: 1. Distinct chromosome
Question 84. Cells originate
- From pre-existing cells
- From abiotic materials
- By bacterial fermentation
- By regeneration of old cells
Answer: 1. From pre-existing cells
Question 85. Which of the following is present in both plant and animal cells?
- Primary wall
- Secondary wall
- Plasma membrane
- Plastids
Answer: 1. Primary wall
Question 86. Which of the following has a one-envelope system?
- Prokaryotic cell
- Eukaryotic cell
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these
Answer: 4. None of these
“cell biology questions “
Question 87. Small cells are metabolically active as they have
- Higher surface-area-to-volume ratio
- Higher nucleo-cytoplasmic ratio
- Glycoproteins and glycolipids
- Lower nucleo-cytoplasmic ratio
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 88. Which of the following cells do not show DNA duplication or RNA synthesis?
- Liver cells
- Muscle cells
- Nerve cells
- Mature RBCs
Answer: 1. Liver cells
Question 89. Who proposed that the cells are totipotent?
- Haberlandt
- Maheshwari
- Steward
- White
Answer: 2. Maheshwari
Question 90. The surface-to-volume ratio of a cell
- Remains constant
- Decreases with increasing size
- Increases with increasing size
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 4. Both (2) and (3)
Question 91. The cells which are capable of undergoing division and development are
- Meristematic cells
- Stem cells
- Differentiated cells
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 2. Stem cells
Question 92. The tri-lamellar model was proposed by
- J.D. Robertson
- Danielli and Davson
- Goiter and Grindell
- Singer and Nicolson
Answer: 4. Singer and Nicolson
Question 93. An animal cell differs from plant cells in not having
- Plastids
- Cell wall
- Glyoxysome
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 94. The genetic material of a bacterial cell is localized within a discrete region called as
- Nucleus
- Nucleolus
- Plasmid
- Nucleoid
Answer: 4. Nucleoid
Question 95. Which of the following is present in the prokaryotes?
- Nuclear envelope
- Golgi apparatus
- Mitochondria
- Ribosomes
Answer: 2. Ribosomes
Question 96. A Gram-negative bacteria differs from a Gram-positive bacteria in having
- Thick cell wall and is primarily made up of peptidoglycan
- A complex cell envelope made up of three layers
- The cell wall of 20-80 nm in thickness and also contains tightly bound technoid acids
- Absence of cell wall lipids
Answer: 4. Absence of cell wall lipids
Question 97. Which of the following antibiotics inhibits the cross-linking of peptidoglycan strands, thus causing the lysis of the bacterial cell?
- Penicillin
- Cephalosporin
- Chloromycetin
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 2. Cephalosporin
Question 98. The pentacyclic sterol like molecules that stabilize the bacterial cell membrane are called as
- Cholesterol
- Hopanoids
- Spectrin
- Glycophorins
Answer: 4. Glycophorins
Question 99. Glycocalyx or cell coat which functions as the cell recognition center is made up of
- Proteins
- Lipids
- Proteins and lipids
- Glycoproteins and glycolipids
Answer: 4. Glycoproteins and glycolipids
Question 100. The plasma membrane is asymmetric because
- Lipids present in the outer and inner sides of the bilayer are different.
- Extrinsic proteins are more abundant on the inner surface than on the outer surface.
- Oligosaccharides are attached only to the external surface of lipids and proteins of a biomembrane.
- All of these
Answer: 3. Oligosaccharides are attached only to the external surface of lipids and proteins of a biomembrane
“cell structure and function mcqs “
Question 101. Components of the eukaryotic plasma membrane are
- Proteins and lipids
- Proteins and carbohydrates
- Lipids (20-79%), proteins (20-70%), oligosaccharides (1-5%), and water (20%)
- Lipids (20-70%), proteins (20-79%), carbohydrates (1-5%), and DNA
Answer: 3. Lipids (20-79%), proteins (20-70%), oligosaccharides (1-5%), and water (20%)
Question 102. The unit membrane concept was proposed by
- Danielli
- Davson
- Robertson
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 3. Robertson
Question 103. The universally accepted model of the plasma membrane is
- Lamellar model
- Unit membrane model
- Fluid mosaic model
- Overton model
Answer: 2. Unit membrane model
Question 104. According to the fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane, extrinsic proteins are
- Superficially arranged and cannot be separated easily
- Peripheral proteins are loosely connected to membranes and, therefore, can be easily removed in an aqueous medium
- Integral proteins which project beyond the lipid layer on both sides of the membrane and are considered as channel proteins
- Tightly attached to lipids and cannot be separated
Answer: 2. Peripheral proteins and are loosely connected to membranes and, therefore, can be easily removed in aqueous medium
Question 105. According to the widely accepted “fluid mosaic model,” cell membranes are semi-fluid, where lipids and integral proteins can diffuse randomly. In recent years, this model has been modified in several respects. In this regard, which of the following statements is incorrect?
- Proteins in cell membranes can travel within the lipid bilayer.
- Proteins can also undergo flip-flop movements in the lipid bilayer.
- Proteins can remain confined within certain domains of the membranes.
- Many proteins remain completely embedded within the lipid bilayer.
Answer: 4. Many proteins remain completely embedded within the lipid bilayer.
Question 106. Fluid mosaic model of cell membrane proposes
- A lipid bilayer with embedded proteins only
- A lipid bilayer with proteins on the outer surface only
- A lipid bilayer coated with proteins on both surfaces
- A lipid bilayer with proteins of two types, embedded (intrinsic) and superficial (extrinsic)
Answer: 1. A lipid bilayer with embedded proteins only
Question 107. Out of proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates present in a “cell membrane,’
- Carbohydrates are minimum
- Carbohydrates are maximum
- Lipids are minimum
- All three are in equal proportion
Answer: 1. Carbohydrates are minimum
Question 108. Carrier molecules facilitating transport across cell mem-brane are
- Proteinaceous
- Fatty acids
- Starch
- Alkaloids
Answer: 3. Starch
Question 109. “Protein icebergs in a sea of lipids” means
- Unit membrane concept
- Sandwich model
- Fluid mosaic model
- None of these
Answer: 2. Sandwich model
Question 110. Extrinsic and intrinsic proteins found in the plasma membrane are in the ratio
- 70:30
- 30:70
- 40:60
- 60:40
Answer: 4. 60:40
Question 111. The main function of the plasma membrane is to
- Store cell material
- Control all cellular activities
- Maintain cell shape and size
- Regulate the inflow and outflow of material through the cell wall
Answer: 4. Regulate the inflow and outflow of material through the cell wall
“cell questions and answers “
Question 112. The plasma membrane is more permeable to
- Polysaccharides
- Proteins
- Glycoproteins
- Phospholipids
Answer: 1. Polysaccharides
Question 113. Plasma membrane, particularly in animal cells, is elastic due to
- Lipids
- Proteins
- Carbohydrates
- None of these
Answer: 4. None of these
Question 114. In the ultrastructure of cell membrane and its functions,
- Phospholipids are more than carbohydrates for signal.
- Proteins are less than carbohydrates for fluidity.
- The amount of phospholipids is highly variable for the transport of hydrophilic molecules.
- The amount of protein is unequally distributed in the membrane for better transport.
Answer: 4. The amount of protein is unequally distributed in the membrane for better transport.
Question 115. Two basic components of the cytoskeleton are
- Actin and myosin
- Tubulin and myosin
- Tubulin and actin
- All of these
Answer: 1. Actin and myosin
Question 116. Hydrolytic enzymes are abundantly found in which cell organelles?
- Ribosome
- Lysosome
- Oxysome
- Endoplasmic reticulum
Answer: 2. Lysosome
Question 117. Which of the following is the site of lipid synthesis
- Rough ER
- Smooth ER
- Golgi bodies
- Ribosome
Answer: 2. Smooth ER
Question 118. Ribosomes are produced in
- Nucleolus
- Cytoplasm
- Mitochondria
- Golgi body
Answer: 1. Nucleolus
Question 119. Which of the following pairs lack the unit membrane
- Nucleus and ER
- Mitochondria and Chloroplast
- Ribosome and nucleolus
- Golgi body and lysosome
Answer: 3. Ribosome and nucleolus
Question 120. Golgi body is concerned with
- Respiration
- Secretion
- Excretion
- Degradation
Answer: 2. Secretion
Question 121. Which of the following occurs more than one and less than five in a chromosome?
- Chromatid
- Chromomere
- Centromere
- Telomere
Answer: 4. Telomere
Question 122. The cells without nuclei arc present in
- Vascular cambium
- Root hair
- Companion cell
- Members of the sieve tube
Answer: 4. Members of sieve tube
Question 123. A plant with a minimum number of chromosomes is
- Haplopappus gracilis
- Salix te/rasperma
- Poa
- Cynodon
Answer: 1. Haplopappus gracilis
Question 124. Heteropycnosis is exhibited by
- Autosome
- Chromatid body
- Nucleolus
- Sex chromosome
Answer: 4. Sex chromosome
Question 125. The main function of the lysosome is
- Sexual reproduction
- Extracellular digestion
- Intracellular digestion
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 4. Both (2) and (3)
Question 126. Which of the following maintains continuity between the water and lipid phases inside and outside the cells?
- Cell wall
- Lecithin
- Cell vacuole
- Cell membrane of woody plants
Answer: 2. Lecithin
Question 127. The membrane surrounding cell vacuole is called
- Tonoplast
- Cell wall
- Plasma membrane
- Cell membrane
Answer: 1. Tonoplast
Question 128. The diagrammatic representation of chromosomes is known as
- Idiogram
- Karyotype
- Holotype
- Homotype
Answer: 1. Idiogram
Question 129. Thread-like structures that are composed of nuclear DNA of eukaryotic cells and are carriers of genetic information are known as chromosomes. The tenn “chromosome” was given by
- Waldeyer
- Balbiani
- Purkinje
- Sutton
Answer: 1. Waldeyer
“biology questions on cells “
Question 130. Chromosomes present in prolonged prophase in the salivary glands of Drosophila are
- Polytene chromosomes
- b-chromosomes
- Lampbrush chromosomes
- Supernumerary chromosomes
Answer: 1. Polytene chromosomes
Question 131. Chromosomes at anaphase are of various shapes due to the position of
- S and M phase
- G1 and S phase
- Centromere
- DNA
Answer: 3. Centromere
Question 132. The term “nucleosome” was given by Oudet. Olins and olins called these particles as “nu” particles. Which histone is absent in nucleosome?
- H1
- H2
- H3a
- H4
Answer: 3. H3a
Question 133. Nucleosome gives a beaded appearance to chromosomes. They help in the packing of DNA in chromosomes. A nucleosome has
- About 2 turns of DNA
- 8 histone molecules of 4 types (2 mols each of H2a, H2b, H3, and H4)
- 200 nitrogen base pairs
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 134. Salivary gland chromosomes were discovered by Balbiani (1881) from the salivary glands of larva of
- Chironomus
- Drosophila
- Silkworm
- Lac worm
Answer: 1. Chironomus
Question 135. In SAT chromosomes, SAT (satellite) is the terminal part of chromosomes beyond secondary constriction. It contains
- DNA
- RNA
- Repetitive DNA
- None of these
Answer: 3. Repetitive DNA
Question 136. Material exchange through nucleopores is facilitated by
- Lamina propria
- lipid layer
- Nucleoplasmin
- Nucleolus
Answer: 3. Nucleoplasmin
Question 137. Centriole is
- Microtubular and membranes
- Absent in Amoeba, red algae, blue-green algae, conifers, and angiosperms and is made up of peripheral triplet microtubules
- Basically locomotory and their role in spindle formation is secondary
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 138. The association of m-RNA with several ribosomes is called
- Polysome
- Informosome
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these
Answer: 1. Polysome
Question 139. The Lampbrush chromosome is found in
- Oocyte of amphibians
- The salivary gland of a mosquito
- Silk gland of silkworm
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Oocyte of amphibians
Question 140. Prokaryotic ribosomes me
- 50S
- 60s
- 70S
- 80S
Answer: 3. 70S
Question 141. Mesosomes of prokaryotes perform functions similar to
- Mitochondria
- Peroxysomes
- Lysosomes
- Ribosomes
Answer: 1. Mitochondria
Question 142. RLR is rough because of the presence of
- Volutin granules on its surface
- Ribosomes on its surface
- Lysosomes on its surface
- Mitochondria on its surface
Answer: 2. Ribosomes on its surface
Question 143. Cellular recognition is facilitated by the components of the plasma membrane. These components are generally
- Protein molecules alone
- Lipid molecules alone
- Both lipid and protein molecules
- Glycolipids and glycoproteins
Answer: 4. Glycolipids and glycoproteins
“cell biology mcqs with answers “
Question 144. Which among the following can be seen only under electron microscope?
- Chloroplast
- Ribosome
- Leucoplast
- Nucleus
Answer: 2. Ribosome
Question 145. A mature plant cell has
- Cell wall and protoplasm
- Protoplasm and vacuole
- Vacuole and cell wall
- Protoplasm cell wall and vacuole
Answer: 4. Protoplasm cell wall and vacuole
Question 146. The larger sub-unit in 80S ribosome is
- 50S
- 60S
- 40S
- 0S
Answer: 2. 60S
Question 147. Golgi bodies are absent in
- Plants
- Bacteria
- Animals
- Eukaryotic cells
Answer: 2. Bacteria
Question 148. The endoplasmic reticulum is more developed in
- Green cells
- Young cells
- Mature cells
- Bacteriophages
Answer: 2. Young cells
Question 149. Mitochondria are related to
- Prokaryotic cells
- Plasmids
- Prion
- Virus
Answer: 1. Prokaryotic cells
Question 150. The main function of lysosomes is
- Digestion
- Replication
- Translation
- Translocation
Answer: 1. Digestion
Question 151. Which of the following has a single membrane?
- Ribosome
- Peroxisome
- Nucleus
- Centrosome
Answer: 2. Peroxisome
Question 152. L-shaped chromosomes are called
- Sex-chromosomes
- Acrocentric chromosomes
- Telocentric chromosomes
- Sub-metacentric chromosomes
Answer: 4. Sub-metacentric chromosomes
“questions about cells “
Question 153. Who coined the term chromosome?
- Balbiani
- Waldeyer
- Sutton
- Purkinje
Answer: 2. Waldeyer
Question 154. A chromosome having a sub-terminal centromere is called
- Telocentric chromosome
- Acrocentric chromosome
- Metacentric chromosome
- Sub-metacentric chromosome
Answer: 2. Acrocentric chromosome
Question 155. How many types of cells are known?
- One
- Two
- Three
- Four
Answer: 2. Two
Question 156. In which of the following microorganisms, mitosis does not occur?
- Green algae
- Fungi
- Bacteria
- Higher plants
Answer: 3. Bacteria
Question 157. A mature plant cell has
- Cell wall
- Vacuole
- Protoplasm
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 158. In eukaryotic cells, the type of ribosomes is
- Only 70S
- Only 80S
- 70S and 80S both
- Only 50S
Answer: 3. 70S and 80S both
Question 159. The genetic material of prokaryotic cells is called
- Nucleus
- Nucleolus
- Nucleoid
- Centrosome
Answer: 3. Nucleoid
Question 160. Which organelle of plant cells secret polysaccharide to make cell walls?
- Golgi-bodies
- Lysosome
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
Answer: 1. Golgi-bodies
Question 161. RNA contains which of the following bases in place of thymine of DNA?
- Thymine
- Uracil
- Adenine
- None of these
Answer: 2. Uracil
Question 162. The main function of lysosomes is
- Only intracellular digestion
- Only extracellular digestion
- Both intracellular and extracellular digestions
- None
Answer: 3. Both intracellular and extracellular digestions
Question 163. A eukaryotic cell has
- Single chromatin fiber
- Definite nucleus
- Incipient nucleus
- None of these
Answer: 2. Definite nucleus
Question 164. The synthesis of lipids and proteins is associated with
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
- Lysosomes
Answer: 1. Endoplasmic reticulum
Question 165. Cell theory was proposed by
- Schleiden and Schwann
- Watson and Crick
- Darwin and Wallace
- Mendel and Morgan
Answer: 1. Schleiden and Schwann
Question 166. Which one of the following is not found in animal cell?
- Nucleus
- Golgi bodies
- Chloroplast
- Mitochondria
Answer: 3. Chloroplast
Question 167. Unit membrane consists of
- Lipid + Sugar + Lipid
- Protein + Lipid + Protein
- Lipid + Protein + Lipid
- Protein
Answer: 2. Protein + Lipid + Protein
Question 168. The principal constituents of chromosomes are
- DNA +Protein
- DNA
- RNA
- RNA
Answer: 1. DNA +Protein
Question 169. The shape of the chromosome is determined by
- Telomere
- Centromere
- Chromomere
- Centrosome
Answer: 2. Centromere
Question 170. In a bacterial cell, the respiratory enzymes are found in
- Mitochondria
- Chondriosome
- Mesosome
- Centrosome
Answer: 3. Mesosome
Question 171. The cell wall of Spirogyra is made up of
- Cellulose
- Suberin
- Lignin
- Chitin
Answer: 1. Cellulose
Question 172. The main function of the Golgi complex is
- Translocation
- Phosphorylation
- Glyco-oxidation
- Fermentation
Answer: 1. Translocation
Question 173. In cell division, spindle fibers are made up of protein
- Myoglobin
- Tubulin
- Albumin
- Myosin
Answer: 2. Tubulin
Question 174. Choose the incorrect match.
- Nucleus—RNA
- Lysosome—Protein synthesis
- Mitochondria—Respiration
- Cytoskeleton—Microtubules
Answer: 2. Lysosome—Protein synthesis
Question 175. Rough endoplasmic reticulum is associated with
- Fat synthesis
- Steroid synthesis
- Protein synthesis
- All of these
Answer: 3. Protein synthesis
Question 176. The resolving power of an electron microscope is
- 10
- 105
- 1005
- 10005
Answer: 2. 105
“cell the unit of life bank of biology “
Question 177. The number of barr bodies in XXXXY is
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer: 3. 3
Question 178. The study related to the structure and function of a cell is called as
- Physiology
- Cell Biology
- Histology
- Cytology
Answer: 2. Cell biology
Question 179. The fluid mosaic model was given by
- Knoll and Ruska
- Singer and Ruska
- Singer and Nicolson
- Bateson and Punnet
Answer: 3. Singer and Nicolson
Question 180. The characteristic of blue-green algae is
- DNA without histone
- Nucleus absent
- Nuclear membrane absent
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 181. The cell wall of a cell is removed. The remaining is called
- Etioplast
- Aleuroplast
- Amyloplast
- Protoplast
Answer: 4. Protoplast
Question 182. The movement against the concentration gradient is called
- Osmosis
- Active transport
- Diffusion
- Passive transport
Answer: 2. Active transport
Question 183. Which one is present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
- Ribosome
- Mitochondria
- ER
- Nucleus
Answer: 1. Ribosome
Question 184. Centromere is also called
- Chromomere
- Secondary constriction
- Primary constriction
- Chromonema
Answer: 3. Primary constriction
Question 185. In Singer and Nicolson’s model of the plasma membrane, the extrinsic proteins are
- Tightly associated with intrinsic protein and can be easily separated
- Loosely associated with intrinsic protein
- Loosely associated with intrinsic protein and can be easily separated
- Loosely associated with intrinsic protein and cannot be easily separated
Answer: 3. Loosely associated with intrinsic protein and can be easily separated
Question 186. Ribosomes are associated with
- RNA synthesis
- Protein synthesis
- Enzyme mobilization
- DNA synthesis
Answer: 2. Protein synthesis
Question 187. Which organelle is not found in an animal cell?
- Peroxisome
- Ribosome
- Lysosome
- None of these
Answer: 4. None of these
Question 188. Actin fiber is present in
- Cilia
- Flagella
- Carbohydrate
- Microfilaments
Answer: 4. Microfilaments
Question 189. Meiosis can be observed in
- Tapetal cells
- Megaspores
- Micropores
- Spore mother cells
Answer: 4. Spore mother cells
Question 190. Carrier proteins are involved in
- Transport of enzymes
- Water transport
- Active transport of ions
- Passive transport of gases
Answer: 3. Active transport of ions
Question 191. The recent model for plasma membrane proposed by Singer and Nicolson is
- Molecular lipid model
- Lamellar model
- Unit membrane model
- Fluid mosaic model
Answer: 4. Fluid mosaic model
Question 192. The function of mitochondria is
- Excretion
- Respiration
- Digestion
- Excretion and respiration
Answer: 2. Respiration
Question 193. The term basal body is associated with the development of
- Cilia and flagella
- Cell plate
- Phragmoplast
- Kinetochore
Answer: 1. Cilia and flagella
Question 194. The Golgi body originates form
- Lysosome
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Mitochondria
- Cell membrane
Answer: 2. Endoplasmic reticulum
Question 195. Lipid molecules in the plasma membrane are arranged in which manner?
- Scattered
- Series
- Alternate
- Head parallel
Answer: 4. Head parallel
Question 196. The structure of the nuclear membrane helps in
- Organization of the spindle
- Synapsis of homologous chromosome
- Nucleo-cytoplasmic exchange of material
- Anaphasic separation of daughter chromosome
Answer: 3. Nucleo-cytoplasmic exchange of material
Question 197. Hydrolytic enzymes are stored in
- Golgi bodies
- Lysosomes
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Mitochondria
Answer: 2. Lysosomes
Question 198. Ribosomes may be also called
- Microsome
- Dictyosomes
- Ribonucleoprotein
- Oxysomes
Answer: 3. Ribonucleoprotein
Question 199. Genes are present in
- Chromosomes
- Lamellae
- Plasma membrane
- Mesosomes
Answer: 1. Chromosomes
Question 200. The chromosome showing an L-shaped structure by the presence of a centromere is termed as
- Acentric
- Metacentric
- Sub-metacentric
- Telocentric
Answer: 3. Sub-metacentric
Question 201. Who coined the term “cell”?
- Purkinje
- Robert Brown
- Robert Hooke
- Hugo von Mold
Answer: 3. Robert Hooke
Question 202. Chromosome having centromere in its middle is called
- Acrocentric
- Telocentric
- Metacentric
- Submetacentric
Answer: 3. Metacentric
Question 203. Single membrane-bound organelle is
- Lysosome
- Plastid
- Nucleus
- Mitochondria
Answer: 1. Lysosome
Question 204. Which of the following does not possess a lipoproteinaceous membrane?
- Lysosomes
- Lomasomes
- Ribosomes
- Sphaerosomes
Answer: 3. Ribosomes
Question 205. Centrosome is not present in
- Cells of higher plants
- Cells of lower plants
- Cells of higher animals
- Cells of lower animals
Answer: 1. Cells of higher plants
Question 206. The site of protein synthesis is
- Ribosome
- SER
- Golgi bodies
- Lysosomc
Answer: 1. Ribosome
Question 207. To study the living cells without staining, which of the following microscopes can be used?
- SEM
- Florescent
- Phase contrast
- TEM
Answer: 3. Phase contrast
Question 208. Molecular biology is the study of
- Structure, function, and cell reproduction
- Physicochemical studies of biomolecules
- Studying tissues under a microscope
- Metabolic activity of life
Answer: 2. Physicochemical studies of biomolecules
Question 209. The sub-cellular components can be separated by
- Paper chromatography
- Autoradiography
- Gel electrophoresis
- Differential and density gradient centrifugation
Answer: 4. Differential and density gradient centrifugation
Question 210. The chromosome separation during metaphase can be best studied by
- Phase contrast microscope
- TEM
- X-ray technique
- Scanning electron microscope
Answer: 1. Phase contrast microscope
Question 211. The technique of chromatography was developed by
- Wilkins
- George Gey
- Tswett
- Zemicks
Answer: 3. Tswett
Question 212. Which of the following dye is used for staining cell organelle, and mitochondria?
- Janus Green
- Safranin
- Azure B
- Crystal violet
Answer: 1. Janus Green
Question 213. In the fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane,
- Upper layer is non-polar and hydrophilic
- Polar layer is hydrophobic
- Phospholipids form a bimolecular layer in the middle part
- Proteins form a middle layer
Answer: 3. Phospholipids form a bimolecular layer in the middle part
Question 214. According to the widely accepted “fluid mosaic model,” cell membranes are semi-fluid, where lipids and integral proteins can diffuse randomly. In recent years, this model has been modified in several respects. In this regard, which of the following statements is incorrect?
- Proteins can also undergo flip-flop movements in the lipid bilayer.
- Many proteins remain completely embedded within the lipid bilayer.
- Proteins in cell membranes can travel within the lipid bilayer.
- Proteins can remain confined within certain domains of the membranes.
Answer: 1. Proteins can also undergo flip-flop movements in the lipid bilayer.
Question 215. Which one of the following is not a constituent of cell membrane?
- Cholesterol
- Glycolipids
- Proline
- Phospholipids
Answer: 3. Proline
Question 216. The main organelle involved in the modification and rout¬ing of newly synthesized proteins to their destination is
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Lysosomc
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
Answer: 1. Endoplasmic reticulum
Question 217. Chlorophyll in chloroplasts is located in
- Grana
- Pyrcnoid
- Stroma
- Both grana and stroma
Answer: 1. Grana
Question 218. Which of the following statements regarding mitochondrial membrane is not correct?
- The outer membrane resembles a sieve.
- The outer membrane is permeable to all kinds of molecules.
- The enzymes of the electron transfer chain are embedded in the outer membrane.
- The inner membrane is highly convoluted forming a series of infoldings.
Answer: 3. The enzymes of the electron transfer chain are embedded in the outer membrane
Question 219. Polysome is formed by
- A ribosome with several subunits
- Ribosomes attached to each other in a linear arrangement
- Several ribosomes attached to a single mRNA
- Many ribosomes attached to a strand of endoplasmic reticulum
Answer: 3. Several ribosomes attached to a single mRNA
Question 220. Vacuole in a plant cell
- Lacks membrane and contains air
- Lacks membrane and contains water and excretory substances
- Is membrane-bound and contains storage proteins and lipids
- Is membrane-bound and contains water and excretory substances
Answer: 4. Is membrane-bound and contains water and excretory substances
Question 221. In germinating seeds, fatty acids are degraded exclusively in the
- Peroxisomes
- Mitochondria
- Proplastids
- Glyoxysomes
Answer: 4. Glyoxysomes
Question 222. Keeping in view the fluid mosaic model for the structure of cell membrane, which one of the following statements is correct with respect to the movement of lipids and proteins from one lipid monolayer to the other (described as -flip-flop movement)?
- While proteins can flip-flop, lipids cannot.
- Neither lipids nor proteins can flip-flop.
- Both lipids and proteins can flip-flop.
- While lipids can rarely flip-flop, proteins cannot.
Answer: 4. While lipids can rarely flip-flop, proteins cannot.
Question 223. Three of the following statements regarding cell organelles are correct while one is wrong. Which one is wrong?
- Lysosomes are double-membraned vesicles budded off from the Golgi apparatus and contain digestive enzymes.
- The endoplasmic reticulum consists of a network of membranous tubules and helps in transport, synthesis, and secretion.
- Leucoplasts are bound by two membranes that lack pigment but contain their own DNA and protein-synthesizing machinery.
- Spharosomes are single membrane bonds and are associated with the synthesis and storage of lipids.
Answer: 1. Lysomes are double-membraned vesicles budded off from the Golgi apparatus and contain digestive enzymes.
Question 224. In which one of the following would you expect to find glyoxysomes?
- Endosperm of wheat
- Endosperm of castor
- Palisade cells in leaf
- Root hairs
Answer: 2. Endosperm of castor
Question 225. Which of the following statements regarding cilia is not correct?
- Cilia contain an outer layer of nine doublet microtubules surrounding two single microtubules.
- The organized beating of cilia is controlled by fluxes of Ca2+ across the membrane.
- Cilia are hair-like cellular appendages.
- Microtubules of cilia are composed of tubulin.
Answer: 2. The organized beating of cilia is controlled by fluxes of Ca2+ across the membrane.
Question 226. The contractile protein of skeletal muscle involving ATPase activity is
- Actinin
- Toponin
- Tropomyosin
- Myosin
Answer: 4. Myosin
Question 227. Select the wrong statement from the following:
- Both chloroplasts and mitochondria contain an inner and outer membrane.
- Both chloroplast and mitochondria have an internal compartment, the thylakoid space bounded by the thylakoid membrane.
- Both chloroplasts and mitochondria contain DNA.
- The chloroplasts are generally much larger than mitochondria.
Answer: 2. Both chloroplast and mitochondria have an internal compartment, the thylakoid space bounded by the thylakoid membrane.
Question 228. The telomeres of eukaryotic chromosomes consist of short sequences of
- Cytosine-rich repeats
- Adenine-rich repeats
- Guanine-rich repeats
- Thymine-rich repeats
Answer: 3. Guanine-rich repeats
Question 229. If you are provided with root tips of onion in your class and are asked to count the chromosomes, which of the following stages can your most conveniently look into
- Telophase
- Anaphase
- Prophase
- Metaphase
Answer: 4. Metaphase
Question 230. Protein synthesis in an animal cell occurs
- On ribosomes present in the cytoplasm as well as in mitochondria
- On ribosomes present in the nucleolus as well as in the cytoplasm
- Only on ribosomes attached to the nuclear envelope and endoplasmic reticulum
- Only on the ribosomes present in cytosol
Answer: 1. On ribosomes present in the cytoplasm as well as in mitochondria
Question 231. Telomerase is an enzyme that is a
- RNA
- Ribonucleoprotein
- Repetitive DNA
- Simple protein
Answer: 1. RNA
Question 232. The length of DNA molecule greatly exceeds the dimensions of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. How is the DNA accommodated?
- Deletion of non-essential genes
- Supper-coiling in nucleosomes
- DNase digestion
- Through the elimination of repetitive DNA
Answer: 2. Supper-coiling in nucleosomes
Question 233. Centromere is required for
- Movement of chromosomes towards poles
- Cytoplasmic cleavage
- Crossing over
- Transcription
- During entire prophase
Answer: 1. Movement of chromosomes toward poles
Question 234. Plasmodesmata are
- Connections between adjacent cells
- Lignified cemented layers between cells
- Locomotory structures
- Membranes connecting the nucleus with plasmalemma
Answer: 1. Connections between adjacent cells
Question 235. Middle lamella is composed mainly of
- Phosphoglycerides
- Hemicellulose
- Muramic acid
- Calcium pectate
Answer: 4. Calcium pectate
Question 236. Cytoskeleton is made up of
- Proteinaceous filaments
- Calcium carbonate granules
- Callose deposits
- Cellulosic microfibrils
Answer: 1. Proteinaceous filaments
Question 237. The cell junctions called tight, adhering, and gap junctions are found in
- Neural tissue
- Muscular tissue
- Connective tissue
- Epithelial tissue
Answer: 4. Epithelial tissue
Question 238. There is no DNA in
- Hair root
- An enucleated ovum
- Mature RBCs
- A mature spermatozoa
Answer: 3. Mature RBCs
Question 239. A student wishes to study the cell structure under a light microscope having 10X eyepiece and 45X objective. He should illuminate the object which one of the following colors of light so as to get the best possible resolution.
- Yellow
- Green
- Red
- Blue
Answer: 3. Red
Question 240. A major breakthrough in the studies of cells came with the development of the electron microscope. This is because
- Electron beams can pass through thick materials, whereas light microscopy requires thin section.
- The electron microscope is more powerful than the light microscope as it uses a beam of electrons that have wavelengths much longer than that of photons.
- The resolution power of the electron microscope is much higher than that of the light microscope.
- The resolving power of the electron microscope is 200-350 nm as compared to 0.1-0.2 nm for the light microscope.
Answer: 3. The resolving power of the electron microscope is 200-350 nm as compared to 0.1-0.2 nm for the light microscope.
Question 241. The main area of various types of activities of a cell is
- Plasma membrane
- Mitochondrion
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus
Answer: 3. Cytoplasm
Question 242. Carrier ions such as Na+ facilitate the absorption of substances such as
- Amino acids and glucose
- Glucose and fatty acids
- Fatty acids and glycerol
- Fructose and some amino acids
Answer: 4. Fructose and some amino acids
Question 243. The plasma membrane consists mainly of
- Phospholipids embedded in a protein bilayer
- Proteins embedded in a phospholipid bilayer
- Proteins embedded in a polymer of glucose molecules
- Proteins embedded in a carbohydrate bilayer
Answer: 2. Proteins embedded in a phospholipid bilayer
Question 244. An elaborate network of filamentous proteinaceous structures present in the cytoplasm which helps in the maintenance of cell shape is called
Endoplasmic reticulum
- Plasmalemma
- Cytoskeleton
- Thylakoid
Answer: 3. Cytoskeleton
Question 245. Identify the components labeled A, B, C, and D from the list (1) to (8) given along with.
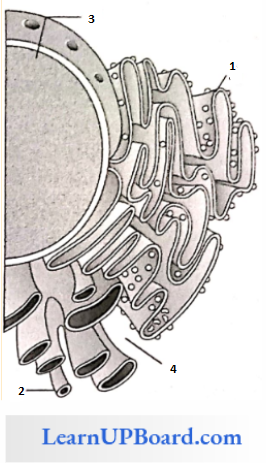
Components:
- Cristae of mitochondria
- Inner membrane of mitochondria
- Cytoplasm
- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum
- Mitochondrial matrix
- Cell vacuole
- Nucleus
The correct components are:
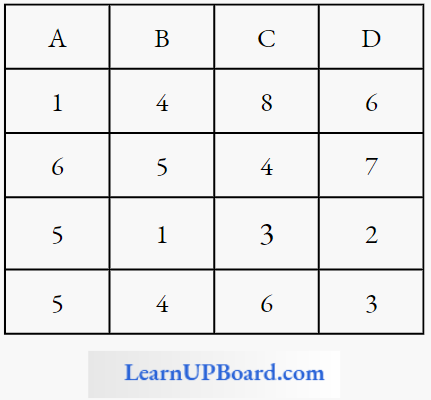
Answer: 4
Question 246. What is true about ribosomes?
- These are composed of ribonucleic acid and proteins.
- These are found only in eukaryotic cells.
- These are self-splicing introns of some RNAs.
- The prokaryotic ribosomes are 80 S, where “S” stands for sedimentation coefficient.
Answer: 1. These are composed of ribonucleic acid and proteins.
Question 247. Select the correct statement from the following regarding cell membranes.
- Proteins make up 60 to 70% of the cell membrane.
- Lipids are arranged in a bilayer with polar heads toward the inner part.
- Fluid mosaic model of cell membrane was proposed by Singer and Nicolson.
- Na+ and K ions move across cell
Answer: 3. Fluid mosaic model of cell membrane was proposed by Singer and Nicolson.
Question 248. The correct sequence of cell organelles during photorespiration is
- Chloroplast—Rough endoplasmic reticulum—Dictyosomes
- Chloroplast—Mitochondria—Peroxisome
- Chloroplast—Vacuole—Peroxisome
- Chloroplast—Golgi bodies—Mitochondria
Answer: 2. Chloroplast—Mitochondria—Peroxisome
