NEET Biology For Anatomy Of Flowering Plants Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Tissue is the group of cells which are
- Similar in origin, but dissimilar in form and function
- Similar in origin and form, but dissimilar in function
- Similar in origin, form the, and function
- Dissimilar in origin, but similar in form and function
Answer: 3. Similar in origin, form and function
Question 2. The father of plant anatomy who also coined the term tissue is
- Marcello Malpighi
- N. Grew
- Schleiden
- Hanstein
Answer: 2. N. Grew
Question 3. Meristem is characterized by
- Isodiametric cells with cellulosic thin wall
- Absence of intercellular space and vacuole
- Absence of reserve food material, plastids, and ER
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 4. Secondary meristems are derived from
- Promeristerms
- Primary meristems
- Primary permanent tissue
- Lateral meristems
Answer: 3. Primary permanent tissue
” anatomy mcqs”
Question 5. The intercalary meristems are infact portions of
- Lateral meristems
- Secondary meristems
- Apical meristems
- Permanent tissues that become meristematic
Answer: 3. Apical meristems
Question 6. According to Haberlandt, cortex and pith are derived from
- Periblem
- Plerome
- Procambium
- Ground meristem
Answer: 4. Ground meristem
Question 7. Which one of the following theories in root is equivalent to Schmidt’s theory?
- Tunica corpus theory
- Histogen theory
- Korper-kappe theory
- Quiescent center theory
Answer: 3. Korper-kappe theory
Question 8. The plane of division in Tunica is
- Anticlinal
- Periclinal
- Both anticlinal and periclinal
- Peripheral division
Answer: 1. Anticlinal
Question 9. Root cap is derived from
- Calyptrogen
- Dermatogen
- Protoderm
- Periblem
Answer: 1. Calyptrogen
Question 10. The primary growth in Equisetum stem occurs due to the activity of
- Apical meristem
- Intercalary meristem
- Lateral meristem
- Primordial meristem
Answer: 2. Intercalary meristem
Question 11. Quiescent center in root meristem acts as
- Waiting meristems
- Reserve meristems
- Reservoir of growth hormones
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 12. The grass stem elongates by the activity of
- Apical meristem
- Intercalary meristem
- Lateral meristem
- Primordial meristem
Answer: 2. Intercalary meristem
Question 13. The term meristem was coined by
- C. Nageli
- Mittens
- Schuepp
- Schmidt
Answer: 1. C. Nageli
Question 14. The primary growth is affected by
- Primary cambium
- Apical meristems
- Cambium
- Secondary cambium
Answer: 2. Apical meristems
Question 15. The intercalary meristem is present in
- Mint
- Grasses
- Bamboo
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 16. The organization of shoot apex into tunica and corpus is determined largely on the basis of
- Regions of meristematic activity
- Planes of cell division
- Rate of shoot tip growth
- The phase of cell division
Answer: 2. Planes of cell division
Question 17. The central region of the root apex containing less active cells is known as
- Plerome
- Dermatogen
- Periblem
- Quiescent zone
Answer: 4. Quiescent zone
Question 18. The velamen of orchid root is derived from the
- Phellogen of root
- Plerome of root
- Dermatogen of root
- Periblem of root
Answer: 3. Dermatogen of root
Question 19. According to the history theory, the plerome gives rise to the
- Epidermis
- Cortex
- Pith
- Central stele
Answer: 4. Central stele
Question 20. Collenchyma differs from parenchyma in having
- Living protoplasm
- Cellulose walls
- Vacuoles
- Pectin and cellulose deposits at comers
Answer: 4. Pectin and cellulose deposits at comers
Question 21. Collenchyma is a type of mechanical tissue but it is not as efficient as sclerenchymia. However, it has certain advantages like
- It offers no resistance to the growing organs
- It has the power of growth
- It is flexible
- Though it has the power of growth, it offers no resistance to the growing organs and it is flexible
Answer: 3. It is flexible
Question 22. Walls of sclerenchyma arc
- Rigid
- Lignified
- Pectinized
- Subenzed
Answer: 2. Lignified
Question 23. Which one of the following is not a fundamental tissue?
- Parenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Chlorenchyma
- Aerenchyma
Answer: 2. Collenchyma
Question 24. Plasmodesmata maintains cell-to-cell cytoplasmic connection, and is quite common in
- Parenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Sclereids
- Sclerenchyma fibers
Answer: 1. Parenchyma
Question 25. A parenchymatous cell that stores ergastic substances is called
- Phragmoplast
- Idioblast
- Leucoplast
- Amyloplast
Answer: 2. Idioblast
Question 26. The mechanical tissue with high refractive index is
- Collenchyma
- Prosenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
- Sclereids
Answer: 1. Collenchyma
Question 27. Which one of the following acts as water storage tissue in succulent plants?
- Parenchyma
- Aerenchyma
- Angular collenchyma
- Meristem
Answer: 1. Parenchyma
Question 28. Collenchyma is absent in
- Root
- Dicot stem
- Monocots
- Both (1) and (3)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (3)
Question 29. Cell wall in dead mechanical tissue shows
- Lignified nature
- Cutinized nature
- Pectose deposition
- Hemicellulose deposition
Answer: 1. Lignified nature
Question 30. Find the correct match.
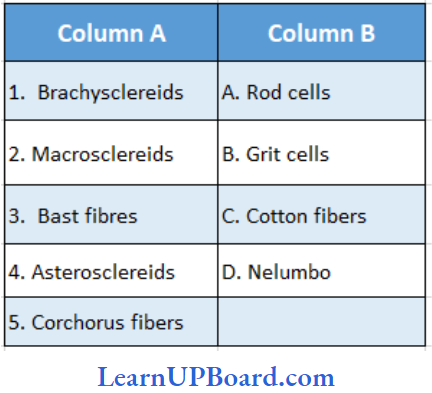
- (1) → (B), (2) → (A), (3) → (E), (4) → (C)
- (1) → (B), (2) → (A), (3) → (E), (4) → (D)
- (1) → (A), (2) → (B), (3) → (E), (4) → (D)
- (1) → (B), (2) → (A), (3) → (D), (4) →(E)
Answer: 2. (1) → (B), (2) → (A), (3) → (E), (4) → (D)
Question 31. Bordered pits are very common in
- Monocotyledons
- Gymnosperms
- Dicotyledons
- All of these
Answer: 1. Monocotyledons
Question 32. Sieve tubes are better suited for translocation because they
- Possess a broader lumen and perforated cross walls
- Are broader than longer
- Possess bordered pits
- Possess no end walls
Answer: 1. Possess a broader lumen and perforated cross walls
Question 33. The presence of lignin in a cell is a characteristic of
- Phloem
- Woody tissue
- All soft tissue
- Cork
Answer: 2. Woody tissue
Question 34. The main water-conducting element of the xylem in homozygous plants is
- Trachea
- Vessel
- Tracheid
- Xylem parenchyma
Answer: 3. Tracheid
Question 35. Vesselless angiosperms are
- Tetracentraceae
- Trochodendraceae
- Winteraceae
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 36. Centripetal and centrifugal xylems are important features of
- Root and stem, respectively
- Exarch and endarch, respectively
- Endarch and exarch, respectively
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 37. Callose plug and p-proteins are associated with
- Companion cells
- Sieve tube
- Phloem parenchyma
- Trachea
Answer: 2. Sieve tube
Question 38. Phloem parenchyma is absent in
- Dicots and few monocots
- Monocots
- Moriocots and dorsiventral leaf
- Gymnosperms
Answer: 2. Monocots
Question 39. The wood of gymnosperms is known as softwood because
- It is very soft
- It appears like a sponge
- It can be bent easily
- It does not possess vessels
Answer: 4. It does not possess vessels
Question 40. The percentage of tracheids in softwood is
- 5-10%
- 90-95%
- 15-25%
- 35-45%
Answer: 2. 90-95%
Question 41. Articulated laticifers are
- Formed by the fusion of cells
- A network-like structure
- Found in the plants which are the source of commercial rubber
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 42. Secretory tissues that secrete proteolytic enzymes are found in
- Nepenthes
- Plumbago
- Urtica
- Polygonum
Answer: 1. Nepenthes
Question 43. In plants having the longest vessel, oil glands are formed
- Lysigenously
- Schizogenously
- Schizolysigenously
- None of these
Answer: 1. Lysigenously
Question 44. In trees, the death of protoplasm is essential for a vital function such as
- Food transport
- Water transport
- Both (1) and (2)
- Stomatal movements
Answer: 2. Water transport
Question 45. The pericycle of roots is never sclerenchymatous because it
- Does not act as a mechanical tissue in roots
- Is the place of the origin of root branches
- Gives rise to root hair
- Gives rise to root hair (when the root is young) and root branches (at maturity)
Answer: 2. Is the place of the origin of root branches
Question 46. Choose the correct statement regarding pericycle in dicot root.
- It is parenchymatous.
- It gives rise to cork cambium.
- It gives rise to lateral roots.
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 47. Tissues commonly known as the passport point or biological check post is characterized by
- Bulliform cells and rapids
- Cystolith and motor cells
- Casparian bands and passage cells
- Passage cells and starch
Answer: 3. Casparian bands and passage cells
Question 48. Girdling experiment is not possible in maize and sugarcane because of
- Scattered vascular bundles
- Open vascular bundles
- Closed vascular bundles
- Absence of pericycle
Answer: 1. Scattered vascular bundles
Question 49. A vascular bundle with 2: a 1 ratio of phloem and xylem is
- Collateral
- Bicollateral
- Amphivasal
- Amphicribral
Answer: 2. Bicollateral
Question 50. Root differs from the stem in having
- Parenchymatous cortex
- Pith
- Exarch xylem
- Pericycle
Answer: 3. Present on both the surfaces
“anatomy of flowering plants “
Question 51. Find the correct match
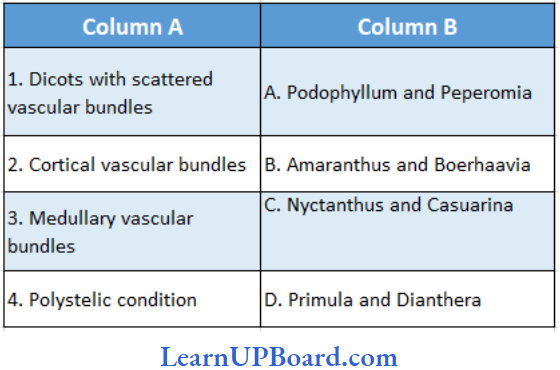
- (1) → (A), (2) → (C), (3) → (B), (4) → (D)
- (1) → (A), (2) → (B), (3) → (C), (4) → (D)
- (1) → (C), (2) → (A), (3) → (B), (4) → (D)
- (1) → (D), (2) → (B), (3) → (C), (4) → (A)
Answer: 1. (1) → (A), (2) → (C), (3) → (B), (4) → (D)
Question 52. The vascular bundles in a dicot root are
- Radial and endarch
- Conjoint and exarch
- Concentric and exarch
- Radial and exarch
Answer: 4. Radial and exarch
Question 53. A collateral vascular bundle is that
- Which has either phloem strand or xylem strand
- In which both xylem and phloem are present at the same radius
- In which both xylem and phloem are present with the xylem towards the periphery
- In which both xylem and phloem are present at different radii
Answer: 2. In which both xylem and phloem are present at the same radius
Question 54. The vascular bundles in the stems of several dicots arc conjoint, collateral, and open. In each of these bundles,
- Xylem and phloem are on the same radius with phloem towards the pith and xylem towards the pericycle without a strip of cambium between them
- Xylem and phloem are on the same radius with xylem towards the pith and phloem towards the pericycle and a strip of cambium separates the two
- Xylem completely surrounds the phloem on all sides but the two are separated by the cambium
- Phloem completely surrounds the xylem and a strip of cambium separates the two
Answer: 2. Xylem and phloem are on the same radius with xylem towards the pith and phloem towards the pericycle and a strip of cambium separates the two
Question 55. In a dicot root, with tetrarch vascular bundles, lateral roots arise from the pericycle which lies
- Opposite to phloem
- Opposite to protoxylem
- In between protoxylem and phloem
- Anywhere
Answer: 2. Opposite to protoxylem
Question 56. Which is not true for monocot stem?
- Sclerenchymatous hypodermis
- Presence of water cavity in pith
- Conjoint collateral closed vascular bundles
- Presence of bundle sheath
Answer: 2. Presence of water cavity in pith
Question 57. In leaf anatomy, phloem is directed towards
- Upper epidermis
- Lower epidermis
- The middle part of vascular bundles
- Lateral side
Answer: 2. Lower epidermis
Question 58. A leaf showing stomata and cuticle on the upper epidermis, raphides in the mesophyll and diaphragm cells, belongs to a plant that probably is a
- Mesophyte
- Floating hydrophyte
- Submerged hydrophyte
- Succulent xerophyte
Answer: 2. Floating hydrophyte
Question 59. Knots in stems are formed due to
- Bacterial infection of wounds
- Injury caused by insects
- Outgrowth of secondary tissues caused by falling of branches
- None of these
Answer: 3. Outgrowth of secondary tissues caused by falling of branches
Question 60. The vascular cambium is a meristematic layer that cuts off
- Primary xylem and primary phloem
- Xylem vessels and xylem tracheids
- Primary xylem and secondary xylem
- Secondary xylem, secondary phloem, and medullary rays
Answer: 4. Secondary xylem, secondary phloem, and medullary rays
Question 61. Balloon-like swellings formed by xylem parenchyma inside the xylem vessels through pits are
- Tracheal plug
- Tyloses
- Callose
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 62. Secondary phloem is formed by
- Procambium
- Plerome
- Vascular cambium
- Apical meristems
Answer: 3. Vascular cambium
Question 63. Derivatives of the secondary meristem in the steler region are
- Phellem and phelloderm
- Alburnum and primary phloem
- Duramen and laburnum
- Primary xylem and secondary phloem
Answer: 3. Duramen and laburnum
Question 64. Secondary medullary rays are produced by
- Fusiform initial
- Interfascicular cambium
- Phellogen
- Ray initial
Answer: 4. Ray initial
Question 65. What is the position of the oldest secondary phloem?
- Just outside the pericycle
- Just outside the vascular cambium
- Just below the pericycle
- Below the vascular cambium
Answer: 3. Just below the pericycle
Question 66. Heartwood
- Is the oldest secondary xylem ring
- Lies near pith
- Is nonfunctional
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 67. Phelloids are
- Synonyms of phellem
- Lignified cork cells
- Suberized cork cells
- Non-suberized cork cells
Answer: 4. Non-suberized cork cells
Question 68. Virgin cork is
- The first formed periderm
- A lenticellate phellem
- A non lenticellate periderm
- The last periderm
Answer: 1. The first formed periderm
Question 69. Annual rings are distinct with earlywood and latewood in the plants growing in
- Tropical region
- Temperate region
- Grassland
- Arctic region
Answer: 2. Temperate region
Question 70. As the secondary growth takes place (proceeds) in a tree, thickness of
- Heartwood increases
- Sapwood increases
- Both increases
- Both remain the same
Answer: 1. Heartwood increases
Question 71. The cork of commerce is a derivative of (or cork is formed from)
- Cork cambium (phellogen) or extra fascicular cambium
- Vascular cambium
- Fascicular cambium
- Interfascicular cambium
Answer: 1. Cork cambium (phellogen) or extra fascicular cambium
Question 72. Growth rings are well marked in trees growing in
- Simla
- Chennai
- Mumbai
- Kolkata
Answer: 1. Simla
Question 73. The youngest layer of secondary xylem in the wood of dicot plant is located
- Between pith and primary xylem
- Just outside vascular cambium
- Just inside vascular cambium
- Just inside cork cambium
Answer: 3. Just inside vascular cambium
Question 74. One cannot calculate the age of a tree by its rings if that tree is located in which of the following forests?
- Tropical deciduous
- Tropical evergreen
- Temperate deciduous
- Temperate evergreen
Answer: 2. Tropical evergreen
Question 75. When the secondary growth in thickness is initiated in a dicot root, which of the following happens first?
- Anticlinal division occurs so that cambium becomes circular.
- Parenchyma between xylem and phloem becomes meristematic.
- Cambium initial between xylem and phloem divides.
- Pericycle strands outside primary xylem divide.
Answer: 2. Parenchyma between xylem and phloem becomes meristematic.
Question 76. Abnormal secondary growth is found in
- Dracaena
- Triticum
- Helianthus
- Cucurbita
Answer: 1. Dracaena
Question 77. A tumour-like tissue of thin-walled cells developing over the wounds is called
- Tyioses
- Gall
- Cailose
- Callus
Answer: 4. Callus
Question 78. Find the incorrect matching.
- Haematoxylin—Heartwood of Haematoxylon campechianum
- Santalin—Heart wood of Pterocatpus santalimts
- Brasilin—Pith of Caesalpinia sappan
- Tannins—Heartwood of Acacia catechu (katha)
Answer: 3. Brasilin—Pith of Caesalpinia sappan
Question 79. Fibers are obtained from
- Xylem, phloem, and sclerenchyma
- Xylem, phloem, sclerenchyma, and epidermis
- Xylem, parenchyma, epidermis
- Xylem, parenchyma, endodermis
Answer: 1. Xylem, phloem, and sclerenchyma
Question 80. The quiescent center in root meristem serves as a
- Site for storage of food which is utilized during maturation
- Reservoir of growth hormones
- Reserve for the replenishment of the damaged cells of the meristem
- Region for the absorption of water
Answer: 3. Reserve for the replenishment of the damaged cells of the meristem
Question 81. The outermost primary meristem gives rise to
- Epidermis
- Procambium
- Ground meristem
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 82. Root cap regenerates or is produced from
- Calyptrogen
- Pleurome
- Periblem and histogen
- Dermatogen
Answer: 4. Dermatogen
Question 83. The tunica corpus theory was proposed by
- Schmidt
- Strasburger
- Nageli
- Hofmeister
Answer: 1. Schmidt
Question 85. Vascular cambium of the root is an example of
- Apical meristem
- Intercalary meristem
- Secondary meristem
- Root apical meristem
Answer: 3. Secondary meristem
Question 86. Vascular cambium and cork cambium are examples of
- Lateral meristem
- Apical meristem
- Elements of xylem and phloem
- Intercalary meristem
Answer: 1. Lateral meristem
Question 87. The quiescent center is found in
- Stem
- Root
- Leaves
- None of these
Answer: 2. Root
Question 88. Grass stem elongates by the activity of
- Primary meristem
- Secondary meristem
- Intercalary meristem
- Apical meristem
Answer: 3. Intercalary meristem
Question 89. The calyptrate of (the root apex forms
- Rhizoids
- Root nodule
- Root hairs
- Root cap
Answer: 4. Root cap
Question 90. Acrenchyma is found in
- Lithophytcs
- Hydrophytes
- Sciophytcs
- Xerophytes
Answer: 2. Hydrophytes
Question 91. Parenchymatous tissue is characterized by the
- Presence of uniform thickening
- Presence of thickening in the corners
- Presence of intercellular spaces
- Presence of lignified walls
Answer: 3. Presence of intercellular spaces
Question 92. The difference in the phloem of gymnosperms and angiosperms is due to
- Parenchyma
- Sieve cell
- Companion cell
- Fibers
Answer: 3. Companion cell
Question 93. Cork cambium is a
- Secondary meristem
- Apical meristem
- Intercalary meristem
- Primary meristem
Answer: 1. Secondary meristem
Question 94. The complex tissues include
- Scleroids
- Sclerenchyma
- Secretory tissues
- Collenchyma
Answer: 3. Secretory tissues
Question 95. The cell wall of xylem cells is rich in
- Lipid
- Protein
- Lignin
- Starch
Answer: 3. Lignin
Question 96. Root cap is absent in
- Lithophytes
- Hydrophytes
- Xerophytes
- Mesophytes
Answer: 2. Hydrophytes
“lenticels are present in “
Question 97. Which meristem helps in increasing girth?
- Lateral meristem
- Intercalary meristem
- Primary meristem
- Apical meristem
Answer: 1. Lateral meristem
Question 98. Vessels are the major conducting element mainly found in
- Xylem of angiosperms
- Xylem of gymnosperms
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these
Answer: 1. Xylem of angiosperms
Question 99. Tracheids and vessels are related to
- Xylem
- Phloem
- Both
- None of these
Answer: 1. Xylem
Question 100. Passage cells are found in
- Dicot stem
- Aerial root
- Monocot root
- Monocot stem
Answer: 3. Monocot root
Question 101. Vessels are found in
- All pteriodophyta
- All angiosperms
- Some gymnosperms
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 4. Both (2) and (3)
Question 102. Axillary bud and terminal bud are derived from the activity of
- Parenchyma
- Lateral meristem
- Apical meristem
- Intercalary meristem
Answer: 3. Apical meristem
Question 103. Cells of quiescent center arc characterized by
- Dense cytoplasm and prominent nuclei
- Light cytoplasm and small nuclei
- Dividing regularly to add to the corpus
- Dividing regularly to add to tunica
Answer: 2. Light cytoplasm and small nuclei
Question 104. Apical meristem of root is present
- Only in radicles
- Only in tap roots
- Only in adventitious roots
- In all the roots
Answer: 4. In all the roots
Question 105. Vessels occur in
- All angiosperms, all gymnosperms, and some pteridophytes
- All angiosperms and some gymnosperms
- Most angiosperms, a few gymnosperms and pteridophytes
- All pteridophytes
Answer: 3. Most angiosperms, a few gymnosperms and pteridophytes
Question 106. Which is correct?
- Tracheids are unicellular with wide lumen.
- Vessels are multicellular with wide lumen.
- Tracheids are multicellular with narrow lumen.
- Vessels are unicellular with narrow lumen.
Answer: 2. Vessels are multicellular with wide lumen.
Question 107. Which of the following are simple tissues
- Parenchyma, xylem, and phloem
- Parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma
- Parenchyma, xylem, and collenchyma
- Parenchyma, xylem, and sclerenchyma
Answer: 2. Parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma
Question 108. Diffuse porous woods are characteristics of plants growing in
- Alpine regions
- Cold winter regions
- Temperate regions
- Tropical regions
Answer: 4. Tropical regions
Question 109. Porous wood contains mainly
- Fibers
- Vessels
- Tracheids
- Solid secretions
Answer: 2. Vessels
Question 110. Bordered pits are very common in
- Monocotyledons
- Gymnosperms
- Dicotyledons
- Pteridophytes
Answer: 2. Gymnosperms
Question 111. Which of the following is known as wood?
- Primary xylem
- Secondary xylem
- Secondary phloem
- Cambium
Answer: 2. Secondary xylem
Question 112. The conducting part of phloem, according to Haberlandt (1914), is
- Hadrom
- Leptom
- Sterom
- Bark
Answer: 2. Leptom
Question 113. Epidermis in stem is produced from
- Protoderm
- Procambium
- Ground meristem
- Calyptrogen
Answer: 1. Protoderm
Question 114. Trabaculae is the transformation of
- Pericycle
- Endodermis
- Xylem
- Phloem
Answer: 2. Endodermis
Question 115. Which of the following is absent in the primary and secondary structure of stem of Pinusl
- Seive tubes
- Mucilage duct
- Companion cells
- Phloem parenchyma
Answer: 3. Companion cells
Question 116. Epiblema in roots is derived from
- Protoderm
- Procambium
- Ground meristem
- Calyptrogen
Answer: 1. Protoderm
Question 117. Procambium forms
- Only primary vascular bundles
- Only vascular cambium
- Only cork cambium
- Primary vascular bundles and vascular cambium
Answer: 1. Only primary vascular bundles
Question 118. Periblem produces
- Cortex
- Pericycle
- Vascular strand
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 1. Cortex
Question 119. Cells taking part in the conduction of sap are
- Sieve tubes
- Tracheae
- Sieve cells
- Stone cells
Answer: 2. Tracheae
Question 120. The function of vessels is
- Conduction of water and mineral
- Conduction of food
- Mechanical strength
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Conduction of water and mineral
“transverse section of monocot stem “
Question 121. Why cambium is considered as lateral meristem?
- Because it gives rise to lateral branches.
- Because it increases the girth of a plant.
- Because it increases the length of a plant.
- None of these
Answer: 2. Because it increases the girth of a plant.
Question 122. Aerenchyma is helpful in plants by
- Providing buoyancy in hydrophytes
- Promoting photosynthesis
- Giving mechanical strength to plants
- Giving flexibility to plants
Answer: 1. Providing buoyancy in hydrophytes
Question 123. The chief function of sieve tubes is
- To translocate the organic materials manufactured in the leaves
- To conduct minerals
- To transport water from root to leaves
- To help the plant in forming wood
Answer: 1. To translocate the organic materials manufactured in the leaves
Question 124. At maturity, which of the following is non-nucleated?
- Sieve cell
- Companion cell
- Palisade cell
- Cortical cell
Answer: 1. Sieve cell
Question 125. Which combination of tissues acts together to provide the support to the hypocotyl of a seedling?
- Xylem and phloem fibers
- Epidermis and parenchyma
- Xylem and parenchyma
- Epidermis and collenchyma
Answer: 4. Epidermis and collenchyma
Question 126. Senescence and death are essential in the functioning of
- Sieve tubes
- Companion cells
- Both (1) and (2)
- Xylem and sclerenchyma cells
Answer: 4. Xylem and sclerenchyma cells
Question 127. The layer of cells outside the phloem meant for giving rise to the root branches is called
- Cambium
- Corpus
- Endodermis
- Pericycle
Answer: 4. Pericycle
Question 128. The lateral roots generally originate in
- Endodermal cells lying against phloem
- Cortex
- Pericycle cells lying against protoxylem
- Cork cambium
Answer: 3. Pericycle cells lying against protoxylem
Question 129. In free floating plant, the stomata are
- Absent
- Present on upper surface
- Present on both the surfaces
- Present on lower surface
Answer: 2. Present on upper surface
Question 130. Cuticle is secreted by
- Epidermis
- Endodermis
- Both (1) and (2)
- Hypodermis
Answer: 1. Epidermis
Question 131. Which of the following do not have stomata?
- Xerophytes
- Mesophytes
- Hydrophytes
- Submerged hydrophytes
Answer: 4. Submerged hydrophytes
Question 132. Passage cells are present in
- Epidermis
- Endodermis
- Xylem
- Lenticels and hydathodes
Answer: 2. Endodermis
Question 133. Velamen tissue in orchids is found in
- Shoot
- Root
- Leaves
- Flowers
Answer: 2. Root
Question 134. Which of the following have sunken stomata?
- Nerium
- Mangifera
- Hydrilla
- Zea mays
Answer: 1. Nerium
Question 135. Vascular bundles in the stem of Cucurbita or Lagenaria are
- Collateral
- Bicollateral
- Radial
- Inverted
Answer: 2. Bicollateral
Question 136. The bicollateral vascular bundle is the characteristic feature of plants belonging to the family
- Cniciferae
- Liliaceae
- Cucurbitaceae
- Malvaceae
Answer: 3. Cucurbitaceae
Question 137. Passage cells occur in
- Monocot root
- Dicot root
- Monocot stem
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 138. Stomata in water lily and penstemon occur, respectively,
- Lower leaf surface and absent
- Upper leaf surface and absent
- Both leaf surfaces
- Absent in both
Answer: 2. Upper leaf surface and absent
Question 139. Root hairs are found
- In the zone of maturation
- On adventitious roots
- On the root cap
- On the apical meristem
Answer: 1. In the zone of maturation
“the endarch condition is the characteristic feature of “
Question 140. A concentric amphivasal (leptocentric) vascular bundle is one in which
- Centrally located phloem is surrounded by the xylem or xylem surrounds phloem
- Centrally located xylem is surrounded by phloem
- Xylem is flanked by phloem on the interior and exterior side only
- Phloem is flanked by the xylem on interior side only
Answer: 1. Centrally located phloem is surrounded by the xylem or xylem surrounds phloem
Question 141. Vascular bundles in which phloem is found on both the sides of xylem are called (in which of the following phloem occurs on two patches)
- Collateral
- Bicollateral (amphiphloic)
- Radial
- Amphicribral
Answer: 2. Bicollateral (amphiphloic)
Question 142. Pericycle in roots is responsible for
- The formation of lateral roots
- Providing mechanical support
- The formation of vascular bundle from cortex
- The formation of vascular bundle from endodermis
Answer: 1. The formation of lateral roots
Question 143. Monocot stem has
- Bicollateral closed vascular bundles
- Bicollateral open vascular bundles
- Collateral open vascular bundles
- Collateral closed vascular bundles
Answer: 4. Collateral closed vascular bundles
Question 144. In monocot roots, which types of vascular bundles are found?
- Collateral, conjoint, and closed
- Radial vascular bundles with exarch xylem
- Bicollateral, conjoint, and closed
- Radial vescular bundles with endarch xylem
Answer: 2. Radial vascular bundles with exarch xylem
Question 145. Exarch and polyarch vascular bundles occur in
- Monocot stem
- Monocot root
- Dicot stem
- Dicot root
Answer: 2. Monocot root
Question 146. Vascular bundles are scattered in
- Bryophytes
- Dicot root
- Dicot stem
- Monocot stem
Answer: 4. Monocot stem
Question 147. A dorsiventral leaf has
- Stomata on both sides
- Stomata on the lower surface
- Stomata on the upper surface
- No stomata
Answer: 1. Stomata on both sides
Question 148. In a leaf, vascular bundles are found in the
- Veins
- Palisade tissue
- Lower epidermis
- Upper epidermis
Answer: 1. Veins
Question 149. In a dicotyledonous stem, the sequence of tissues from the outside to the inside is
- Phellem-Pericycle-Endodermis-Phloem
- Phellem-Phloem-Endodermis-Pericycle
- Phellem-Endodermis-Pericycle-Phloem
- Pericycle-Phellem-Endodermis-Phloem
Answer: 3. Phellem-Endodermis-Pericycle-Phloem
Question 150. Hypodermis in a monocotyledonous stem is
- Parenchymatous
- Chlorenchymatous
- Collenchymatous
- Sclerenchymatous
Answer: 4. Sclerenchymatous
“plant anatomy ncert “
Question 151. In a dorsiventral leaf, protoxylem and metaxylem are located, respectively, on
- Abaxial and adaxial sides
- Adaxial and abaxial sides
- Adaxial and adaxial sides
- Abaxial and abaxial sides
Answer: 2. Adaxial and abaxial sides
Question 152. In a longitudinal section of a root, starting from the tip upward, the four zones occur in which of the following order
- Cell division, cell enlargement, cell maturation, root cap
- Cell division, cell maturation, cell enlargement, root cap
- Root cap, cell division, cell enlargement, cell maturation
- Root cap, cell division, cell maturation, cell enlargement
Answer: 3. Root cap, cell division, cell enlargement, cell maturation
Question 153. The intrafascicular cambium is situated
- Outside the vascular bundles
- In medullary rays
- Inside the vascular bundles
- In between the vascular bundles
Answer: 3. Inside the vascular bundles
Question 154. The waxy substance associated with the cell walls of cork cells is cork cells are impervious to water because of the presence of
- Cutin
- Suberin
- Lignin
- Hemicellulose
Answer: 2. Suberin
Question 155. If four radial vascular bundles are present, then the structure will be a
- Monocot stem
- Monocot root
- Dicot stem
- Dicot root
Answer: 4. Dicot root
Question 156. The functional xylem of the dicot tree is
- Sap wood
- Hard wood
- Heart wood
- Autumn wood
Answer: 1. Sap wood
Question 157. Tyloses thickenings are seen in
- Phloem cells
- Ray parenchyma only
- Collenchyma
- Ray parenchyma and xylem cells
Answer: 4. Ray parenchyma and xylem cells
Question 158. The main function of lenticel is
- Transpiration
- Guttation
- Bleeding
- Gaseous exchange
Answer: 2. Guttation
Question 159. Heart wood or duramen is the
- Outer region of secondary xylem
- Inner region of secondary xylem
- Outer region of secondary phloem
- Inner region of secondary phloem
Answer: 2. Inner region of secondary xylem
Question 160. Wood is the common name of
- Phloem
- Secondary xylem
- Cambium
- Vascular bundles
Answer: 2. Secondary xylem
Question 161. Cambium is most active in
- Pistia
- Rose
- Asparagus
- Dahlia
Answer: 1. Pistia
Question 162. Sapwood is the
- Outer functional part of secondary xylem
- Inner nonfunctional part of secondary xylem
- Outer as well as inner part of secondary xylem
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Outer functional part of secondary xylem
Question 163. The exchange of gases in old stems takes place from
- Stomata
- Hydathodes
- Lenticels
- Passage cells
Answer: 3. Lenticels
Question 164. Vascularization in plants occurs through
- Differentiation of procambium followed by primary phloem and then primary xylem
- Differentiation of procambium followed by development of xylem and phloem
- Simultaneous differentiation of procambium, xylem, and phloem
- Differentiation of procambium which is immediately followed by the development of secondary xylem and secondary phloem
Answer: 2. Differentiation of procambium followed by development of xylem and phloem
Question 165. Tyloses are
- Wound-healing secretions
- Responsible for plugging the lumen of vessels
- Special epidermal hairs covering stomata in xerophytes
- Callus secretion on sieve plates
Answer: 2. Responsible for plugging the lumen of vessels
Question 166. The removal of ring wood of tissue outside the vascular cambium from the tree trunk kill it because
- Water cannot move up
- Food does not travel down and root becomes starved
- Shoot becomes starved
- Annual rings are not produced
Answer: 2. Food does not travel down and root becomes starved
Question 167. Leaves are situated on
- Nodes
- Intemodes
- Tip
- None of these
Answer: 4. None of these
Question 168. Which of the following cell is totipotent?
- Meristem
- Sieve tube
- Collenchyma
- Xylem vessel
Answer: 1. Meristem
Question 169. Raphides are needle-like crystals of calcium oxalate which are specially found in
- Dahlia
- Pistia
- Asparagus
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Pistia
Question 170. Commercial cork is obtained from
- Mango
- Oak (Quercus suber)
- Ficus religiosa
- Pinus
Answer: 2. Oak (Quercus suber)
Question 171. Wound healing is due to
- Primary meristem
- Secondary meristem
- Ventral meristem
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Primary meristem
Question 172. Which of the following tissues is present in the leaves of Pinus to conduct water and food
- Xylem
- Phloem
- Transfussion tissue
- Conducting tissue
Answer: 3. Transfussion tissue
Question 173. Prolostelcs arc found in
- Bryophyta
- Gymnosperms
- Ptcridophyta
- Angiosperms
Answer: 3. Ptcridophyta
Question 174. The most primitive type of stele is
- Eustele
- Solenostele
- Prolostele
- Siphonostele
Answer: 3. Prolostele
Question 175. Stele consists of
- Phloem
- Xylem
- Pericycle
- All the above
Answer: 4. All the above
Question 176. The lightest wood is
- Cereus giganteus
- Ochroma lagopus
- Hardwickia binata
- Cycas
Answer: 2. Ochroma lagopus
Question 177. Inulin and raphide crystals are which type of plant products?
- Excretory
- Inorganic
- Respiratory
- Reserve material
Answer: 4. Reserve material
Question 178. Which one of the following show origin and evolution of steles
- Bryophytes
- Pteridophytes
- Gymnosperms
- Angiosperms
Answer: 2. Pteridophytes
Question 179. The stems of hydrophytic plants are soft and weak because of the poor development of
- Pith and supporting parenchyma
- Phloem and companion cells
- Xylem and supporting tissue
- Cortex and endodermis
Answer: 3. Xylem and supporting tissue
Question 180. The tunica corpus theory was proposed by
- Schmidt
- Nageli
- Hanstein
- Wolf
Answer: 1. Schmidt
Question 181. Cork cambium represents
- Secondary meristem
- Primary meristem
- Intercalary meristem
- Apical meristem
Answer: 1. Secondary meristem
Question 182. Cambium produces growth in
- Branches
- Girth
- Pith
- Cortex
Answer: 2. Girth
Question 183. Vascular bundles grow from
- Protoderm
- Periderm
- Ground meristem
- Procambium
Answer: 4. Procambium
Question 184. The tunica corpus theory is connected with
- Root apex
- Root cap
- Shoot apex
- Secondary growth
Answer: 3. Shoot apex
Question 185. Which meristem helps in increasing girth?
- Lateral meristem/cambium
- Intercalary meristem
- Primary meristem
- Apical meristem
Answer: 1. Lateral meristem/cambium
Question 186. Procambium forms
- Only primary vasular bundles
- Only vascular cambiun
- Only cork cambium
- Primary vascular bundles and vascular cambium
Answer: 1. Only primary vasular bundles
Question 187. Quiescent center occurs in
- Shoot apex
- Root apex
- Both 1 and 2
- Meristematic tissue
Answer: 2. Root apex
Question 188. Intercalary meristem produces
- Secondary growth
- Primary growth
- Apical growth
- Secondary thickeing
- Secondary overgrowth
Answer: 2. Primary growth
Question 189. Histogen tissues are classified on the basis of
- Plane of division
- Type of cells they form
- Position
- Origin
Answer: 2. Type of cells they form
Question 190. Meristematic cells are characterized by
- Thin cell walls and large intercellular spaces
- Thin cell walls and no intercellular spaces
- Thick cell walls and large intercellular spaces
- Thick cell walls and small intercellular spaces
Answer: 2. Thin cell walls and no intercellular spaces
Question 191. The quiescent center is the region of root apex which is
- Actively dividing
- Water absorption area
- Inactive cells
- Root hair cells
Answer: 3. Inactive cells
Question 192. Which one of the following is not fonned from procambium?
- Xylem
- Phloem
- Intrafascicular cambium
- Interfascicular cambium
Answer: 4. Interfascicular cambium
Question 193. Which of the following is an example of secondary meristem?
- Xylem
- Phloem
- Phloem
- Cork cambium
Answer: 4. Cork cambium
Question 194. The outermost primary meristem forms
- Epidermis
- Procambium
- Ground meristem
- All the above
Answer: 1. Epidermis
Question 195. The vascular cambium of dicot stem is
- Apical meristem
- Intercalary meristem
- Local meristem
- Secondary meristem
Answer: 3. Local meristem
Question 196. The cells of quiescent center have lower concentration of
- DNA
- Proteins
- RNA
- All the above
Answer: 4. All the above
Question 197. The length of petiole increases by the activity of
- Apical meristem
- Lateral meristem
- Intercalary meristem
- All the above
Answer: 3. Intercalary meristem
Question 198. Intercalary meristem is the derivative of
- Promeristem
- Primary meristem
- Lateral meristem
- Secondary meristem
Answer: 2. Primary meristem
Question 199. Dividing cells not yet committed to become specific cell type are
- Epidermal cells
- Ground cells
- Periderm cells
- Meristem cells
Answer: 4. Meristem cells
Question 200. Shoot apical meristem occurs over the tip of
- Root
- Radicle
- Plumule
- Mesocotyl
Answer: 3. Plumule
Question 201. In dicot stems, vascular cambium is formed from
- Procambium
- Cambium
- Promeristem
- Protoderm
Answer: 1. Procambium
Question 202. Cambium is the lateral meristem that takes part in
- Intermodal growth
- Axial growth
- Growth of Branches
- Increasing girth of stem and root
Answer: 3. Growth of Branches
Question 203. Vascular tissues of the flowering plant develop from
- Dermatogen
- Periblem
- Plerome
- Phellogen
Answer: 3. Plerome
Question 204. The length of different internodes in culm of sugarcane is variable due to
- Shoot apical meristem
- Position of axillary buds
- Intercalary meristem
- Size of leaf lamina at the node below each intemode
Answer: 3. Intercalary meristem
Question 205. Lateral meristems are
- Phellogen and procambium
- Procambium and dermatogen
- Fascicular cambium and procambium
- Fascicular cambium and cork combium
Answer: 4. Fascicular cambium and cork combium
Question 206. Interfascicular cambium is
- Intercalary meristem
- Secondary meristem
- Apical meristem
- Noncalary meristem
Answer: 2. Secondary meristem
Question 207. Select the correct option.
A: Apical and intercalary meristems contribute to the growth in length while the lateral meristems bring an increase in girth in Mazie.
R: Apical and intercalary meristems always increase the height of plants
- Both A and R are true with R being the correct explanation of A.
- Both A and R are true but R is not the correct aplanation of A.
- A is true but R is false.
- A is false but R is true.
Answer: 4. A is false but R is true.
Question 208. Histogens are components of
- Secondary phellogen
- Apical meristem
- Lateral meristem
- Intercalary meristem
Answer: 2. Apical meristem
Question 209. Which one of the following is not a lateral meristem?
- Interfascicular cambium
- Phellogen
- Intercalary meristem
- Intrafascicular cambium
Answer: 3. Intercalary meristem
Question 210. Meristem that is parallel to the longitudinal axis of the plant is
- Procambium
- Intercalary meristem
- Phellogen
- Apical meristem
Answer: 3. Phellogen
Question 211. The tissue that has dead cells in the functional state is
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
- Parenchyma
- Phloem
Answer: 2. Sclerenchyma
Question 212. Albuminous cells occur in
- Xylem
- Phloem
- Cortex
- Conjunctive parenchyma
Answer: 2. Cortex
Question 213. Which group possesses vessels in its xylem?
- Pteridophytes
- Angiosperms
- Gymnosperms
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 2. Angiosperms
Question 214. The only plant cells without nucleus among the following are
- Cambium
- Xylem vessels elements
- Root hairs
- Companion cells
Answer: 2. Xylem vessels elements
Question 215. The epidermal fibers of economic importance belong to
- Cotton
- Flax
- Hemp
- Coir
Answer: 1. Cotton
Question 216. Sieve tubes arc constituent of
- Wood
- Vascular cambium
- Phcllem
- Bast
Answer: 4. Bast
Question 217. A closed collateral bundle is one where
- Xylem and phloem occur on different radii
- Collateral bundle occurs without cambium
- Xylem and phloem arc separated by cambium
- Collateral bundle occurs with cambium
Answer: 2. Collateral bundle occurs without cambium
Question 218. Anatomically, jute fibers are
- Xylem fibers
- Cortical fibers
- Pith fibers
- Phloem fibers
Answer: 4. Phloem fibers
Question 219. Jute of commerce is obtained from
- Primary phloem
- Secondary phloem
- Secondary xylem
- Primary xylem
Answer: 2. Secondary phloem
Question 220. Which is correct?
- Tracheids are unicellular with wide lumen
- Vessels are multicellular with wide lumen
- Tracheids are unicellular with narrow lumen
- Vessels are multicellular with narrow lumen
Answer: 2. Vessels are multicellular with wide lumen
Question 221. Which one of the following statements pertaining to plant structure is correct?
- Cork lacks stomata but lenticels carry out transpiration
- Passage cells help in transfer of food from cortex to phloem
- Sieve tube elements possess cytoplasm but no nuclei
- The shoot apical meristem has a quiescent center.
Answer: 3. Sieve tube elements possess cytoplasm but no nuclei
Question 222. Identify the plant tissue in which lignin is absent
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma fibers
- Sclereids
- Xylem tracheids
Answer: 1. Collenchyma
Question 223. Pith or central part of ground tissue is made of
- Collenchyma
- Parenchyma
- Chlorenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
Answer: 2. Parenchyma
Question 224. Vascular bundles having phloem on the periphery of both outer and inner cambium are
- Bicollatcral closed
- Bicollateral open
- Radial
- Biradial
Answer: 2. Bicollateral open
Question 225. Which pair has lignin in both?
- Tracheids and collenchyma
- Schlerenchyrna and sieve tube
- Schlerenchyrna and tracheids
- Parenchyma and endodermis
Answer: 3. Schlerenchyrna and tracheids
Question 226. The living part of xylem is
- Xylem tracheids
- Xylrm vessel
- Parenchyma
- Complex tissues
Answer: 3. Parenchyma
Question 227. Which is least differentiated?
- Simple tissues
- Parenchyma
- Circulatory tissues
- Complex tissue
Answer: 2. Parenchyma
Question 228. The term parenchyma was coined by
- Hooke
- Schleiden
- Grew
- Mcttenius
Answer: 3. Grew
Question 229. P-protein occurs in
- Sieve tube elements
- Tracheids
- Vessels
- Phloem parenchyma
Answer: 1. Sieve tube elements
Question 230. Companion cells are found in
- Epidermis
- Cambium
- Xylem
- Phloem
Answer: 4. Phloem
Question 231. The common feature in vessel elements and sieve tube elements is
- Enucleate condition
- Presence of p-protein
- Thick secondary wall
- Pores on lateral walls
Answer: 1. Enucleate condition
Question 232. In sieve elements, the possible function of P-proteins is
- Autolytic enzymes
- The sealing mechanism for wounding
- Providing energy for active translocation
- Deposition of callose on sieve plates
Answer: 2. Sealing mechanism on wounding
Question 233. The collateral conjoint vascular bundle possesses
- Xylem and phloem on alternate radii
- Phloem surrounding xylem
- Xylem surrounding phloem
- Xylem and phloem on the same radius with two groups of phloem, on the two sides of the xylem
- Xylem and phloem on the same radius with one group of phloem outside xylem
Answer: 4. Xylem and phloem on the same radius with one group of phloem outside the xylem
Question 234. Match the columns
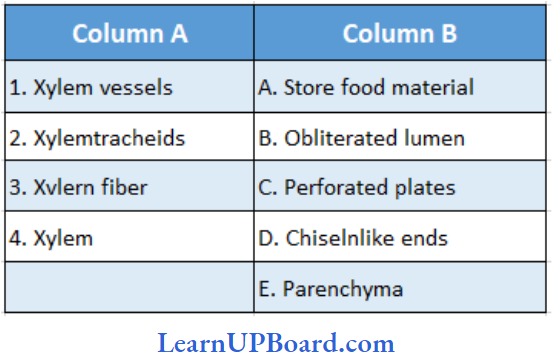
- (1) → (C), (2) → (D), (3) → (B), (4) → (A)
- (1) → (D), (2) → (C), (3) → (B), (4) → (A)
- (1) → (C), (2) → (B), (3) → (A), (4) → (D)
- (1) → (B). (2) → (A), (3) → (D), (4) → (C)
- (1) → (A), (2) → (B), (3) → (C), (4) → (D)
Answer: 1. (1) → (C), (2) → (D), (3) → (B), (4) → (A)
Question 235. Bordered pits are elongated transversely and arranged in vertical series. The pattern is known as
- Scalariform pitting
- Intervascular pitting
- Reticulate thickening
- Oblique pitting
Answer: 1. Scalariform pitting
Question 236. Trichomes take part in
- Transpiration and exchange of gases
- Protection and reduction of transpiration
- Exudation of water drops
- Desiccation
Answer: 2. Protection and reduction of transpiration
Question 237. Simple sieve plate occurs in
- Cucurbita
- Vitis
- Pyrus
- Primus
Answer: 1. Cucurbita
Question 238. Lacunate collenchyma is found in the stem of
- Leucas
- Monstera
- Cucurbita
- Sambucus
Answer: 3. Cucurbita
Question 239. Angiosperm lacking vessels is
- Mangifera
- Dillenia
- Magnolia
- Drimys
Answer: 4. Drimys
Question 240. Sclereids found in the seed coat of pulses are
- Marcrosclereids
- Brachysclereids
- Osteosclreids
- Asterosclereids
Answer: 1. Asterosclereids
Question 241. Xylem produced through centrifugal differentiation is
- Exarch
- Endarch
- Research
- Centrarch
Answer: 4. Centrarch
Question 242. What is wrong with sieve babe elements?
- Peripheral cytoplasm and large vacuole.
- The perforated end wall becomes impregnated with lignin.
- P-proteins occur evenly distributed throughout the lumen.
- Absence of nucleus at maturity.
- Tube-like structures present in longitudinal series.
Answer: 2. Perforated end wall becomes impregnated with lignin.
Question 243. Collenchyma is
- Living with no reserved food
- Living with protoplasm
- Dead and hollow
- Dead with reserve food
Answer: 2. Living with protoplasm
Question 244. Vessels and companion cells occur in
- Thallophytes
- Bryophytes
- Pteridophytes
- Angiosperms
Answer: 4. Angiosperms
Question 245. Which ones are correct?
- Uneven thickening of cell wall is characteristic of sclerenchyma
- Periblem forms cortex of stem and root
- Tracheids are chief water conducting elements in gyntno sperms
- The commercial cell is devoid of the nucleus at maturity
- Commercial cork is obtained from Quercus suber
- 2, 3, 5
- a, 4
- 2, 5
- 3, 4
- 1, 2, 3
Answer: 1. 2, 3, 5
Question 246. In a vascular bundle, the xylem shows centripetal development. It is
- Centrarch
- Mesarch
- Endarch
- Exarch
Answer: 3. Endarch
Question 247. Which pair has lignin in themselves?
- Tracheid and collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma and sieve tube
- Sclerenchyma and tracheids
- Parenchyma and endodermis
Answer: 3. Sclerenchyma and tracheids
Question 248. Parenchymatous cells filling the space and vascular tissue is are
- Ground tissues
- Epidermal tissues
- Pith
- Vascular bundles
Answer: 1. Ground tissues
Question 249. Match the column
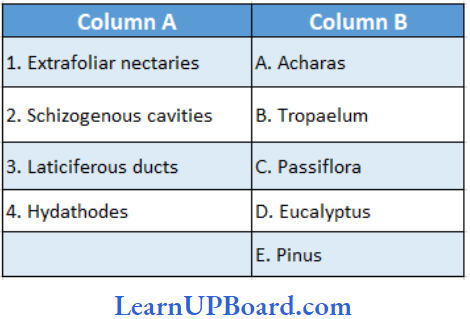
- (1) → (C), (2) →(A), (3) → (B), (4) → (D)
- (1) → (C), (2) → (E), (3) → (A), (4) → (B)
- (1) → (B), (2) → (A), (3) → (C), (4) → (D)
- (1) → (E), (2) → (B), (3) → (A), (4) → (C)
Answer: 2. (1) → (C), (2) → (E), (3) → (A), (4) → (B)
Question 250. Senescence, an active developmental cellular process in the growth and functioning of a flowering plant, is indicated in
- Annual plants
- Floral parts
- Leaf abscission
- Vessels and tracheids
Answer: 3. Leaf abscission
Question 251. Tissue cells commonly found in the fruit walls of nuts and pulp of some fruits like guava are called
- Fibers
- Sclereids
- Tracheids
- Vessels
Answer: 2. Sclereids
Question 252. At maturity, sieve plates become impregnated with
- Cellulose
- Suberin
- Callose
- Lignin
- Pectin
Answer: 3. Lignin
Question 253. Choose the correct options.
- Thread-like cytoplasmic strands, running from one cell to other are known as plasmodesmata
- The xylem and phloem constitute the vascular bundle of the stem.
- First formed, xylem elements are described as metaxylem.
- Radial bundles are mainly found in leaves.
- 1, 2 true; 3, 4 wrong
- 4 true; 1, 2, 3 wrong
- 4 true; 1, 2, 4 wrong
- 2 true; 1, 3, 4 wrong
- 1 true; 2, 3, 4 wrong
Answer: 1. 1, 2 true; 3, 4 wrong
Question 254. Which one consists of living cells?
- Vessels
- Tracheids
- Companion cells
- Sclerenchyma
Answer: 3. Companion cells
Question 255. Annular and spirally thickened conducting element that generally develops in protoxylem when root or stem is
- Widening
- Differentiating
- Maturing
- Elongating
Answer: 4. Elongating
Question 256. Which one is enucleated?
- Companion cell
- Sieve cell
- Tracheid
- Vessel
Answer: 2. Sieve cell
Question 257. Which of the following is a complex tissue?
- Parenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Xylem
- Sclerenchyma
Answer: 3. Xylem
Question 258. Compare the statements A and B.
A: Sclerenchyma cells do not have plasmodesmata
B: Cell walls of some permanent tissue are heavily lignified.
- Statement A is correct and B is wrong
- Both the statements A and B are wrong
- Both the statements A and B are correct
- Statement A is wrong and B is correct
Answer: 3. Both the statements A and B are correct
Question 259. The activity of sieve tubes is remotely controlled by the protoplasm of
- Phloem parenchyma
- Companion cells
- Phloem fibers
- Both phloem parenchyma and phloem fibers
Answer: 2. Companion cells
Question 260. Find the incorrect statement.
- Root hairs are unicellular elongations.
- Trichomes are unicellular elongations.
- Trichomes are multicellular elongations.
- Root hairs absorb water and minerals.
Answer: 1. Root hairs are unicellular elongations.
Question 261. The arrangement of the xylem in the stem is
- Endarch
- Mesarch
- Exarch
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 1. Endarch
Question 262. Which of the following is not part of the epidermal tissue system?
- Trichomes
- Companion cells
- Guard cells
- Subsidiary cells
- Root hairs
Answer: 2. Companion cells
Question 263. Which of the following statements is true?
- Collenchyma occurs in layers below epidermis.
- Xylem parenchyma cells are living, thin, walled, and lignified.
- Sclerenchyma cells are usually dead and without protoplasts.
- Companion cells are specialized sclerenchyma cells.
- Phloem fibers are generally present in primary phloem.
Answer: 3. Companion cells are specialized sclerenchyma cells.
Question 264. The transport of food material in higher plants takes place through
- Companion cells
- Sieve elements
- Tracheids
- Transfusion tissue
Answer: 2. Sieve elements
Question 265. Cotton fiber is basically a type of
- Trichome
- Scale
- Dried seed coat
- Non-glandular hair
Answer: 4. Non-glandular hair
Question 266. Heartwood is the
- Outer part of the secondary xylem
- Inner part of the secondary xylem
- The outer part of the secondary phloem
- Inner part of the secondary phloem
Answer: 2. Inner part of secondary xylem
Question 267. As the secondary growth takes place (proceeds) in a tree, thickness of
- Heartwood increases
- Sapwood increases
- Both increases
- Both remain the same
Answer: 3. Both increases
Question 268. The bark of tree commonly comprises
- All the tissue outside the vascular cambium
- All the tissue outside the cork cambium
- Only the cork
- The cork and secondary cortex
Answer: 1. All the tissue outside the vascular cambium
Question 269. A well-developed pith is found in
- Monocot root and monocot stem
- Monocot stem and dicot root
- Monocot root and dicot stem
- Dicot root and dicot stem
Answer: 3. Monocot root and dicot stem
Question 270. Cork is formed from
- Cork cambium (phellogen)
- Vascular cambium
- Phloem
- Xylem
Answer: 1. Cork cambium (phellogen)
Question 271. The function of cork cambium is to produce
- Secondary xylem and secondary phloem
- Cork and secondary cortex
- Secondary cortex and phloem
- Cork
Answer: 2. Cork and secondary cortex
Question 272. Monocot root differs from dicot root in having
- Open vascular bundles
- Scattered vascular bundles
- Well-developed pith
- Radially arranged vascular bundles
Answer: 3. Well-developed pith
Question 273. Where do the Casparian bands occur?
- Epidermis
- Endodermis
- Pericyle
- Phloem
Answer: 2. Endodermis
Question 274. Growth/annual rings are formed by the actively of
- Cambium
- Xylem
- Phloem
- Both xylem and phloem
Answer: 1. Cambium
Question 275. Tyloses occur in
- Secondary xylem
- Secondary phloem
- Callus tissue
- Cork cells
Answer: 1. Secondary xylem
Question 276. The exchange of gases between air and internal tissue of older corky stem takes place through
- Sieve tube
- Pits
- Stomata
- Lenticels
Answer: 4. Lenticels
Question 277. In roots, lateral branches grow from
- Epiblema
- Pericycle
- Cortex
- Endodermis
Answer: 2. Pericycle
Question 278. Sunken stomata occur in
- Mesophytes
- Xerophytes
- Hygrophytes
- Hydrophytes
Answer: 2. Xerophytes
Question 279. Mesophyll is differentiated into palisade and spongy tissues in
- Extremely xerophytic leaves
- Hydrophytic leaves
- Monocot leaves
- Dicot leaves
Answer: 4. Dicot leaves
Question 280. Builiform or motor cells occur in
- The upper epidermis of Dicot Leaves
- Upper epidermis of monocot leaves
- Lower epidermis of monocot leaves
- Lower epidermis of dicot leases
Answer: 2. Upper epidermis of monocot leaves
Question 281. Poyureh and exarch conditions is found in
- Monocot stem
- Monocot root
- Dicot stem
- Dicot root
Answer: 2. Monoeot root
Question 282. Meristem present in a vascular bundle is
- Fnscicular/Intrafascicular cambium
- Intrafascicular cambium
- Phellogcn
- Procambium
Answer: 1. Fnscicular/Intrafascicular cambium
Question 283. Fusiform initials produce
- Vascular rays
- Primary phloem
- Trachearv elements
- Ray parenchyma
Answer: 3. Trachearv elements
Question 284. The outer lighter colored/album region of snood is
- Autumn wood
- Spring wood
- Heart wood
- Sap wood
Answer: 4. Sap wood
Question 285. In monocots
- Leaves have reticulate venation
- Stems annual rings
- Seeds have tsvo storage organs
- Stems have scattered conducting strands
Answer: 4. Stems have scattered conducting strands
Question 286. Cork cambium is also called
- Phelloderm
- Phcllem
- Periderm
- Phellogcn
Answer: 4. Phellogcn
Question 287. Periderm is produced by
- Vascular cambium
- Fascicular cambium
- Phellogcn
- Intrafascicular cambium
Answer: 3. Phellogcn
Question 288. Common features between lenticels and hydathodes are
- They allow the exchange of gases
- They always remain closed
- There is no regulation of their opening and closing
- They occur on the same organ of the plant
Answer: 1. They allow the exchange of gases
Question 289. Endodermis of dicot stem
- Bundle sheath
- Starch sheath
- Mesophyll
- water channel
Answer: 2. Starch sheath
Question 290. Endodermis is a part of
- Medulla
- Stele
- Cortex
- Exodermis
Answer: 3. Cortex
Question 291. The functional xylem of the dicot tree is
- Sapwood
- Autumn wood
- Heartwood
- Hardwood
Answer: 1. Sapwood
Question 292. Tyloses are thickenings seen in
- Ray parenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Phloem cells
- Ray parenchyma and xylem cells
Answer: 4. Ray parenchyma and xylem cells
Question 293. Casparian strips contain
- Cutin
- Pectin
- Suberin
- Wax
Answer: 3. Suberin
Question 294. A monocot showing secondary growth is
- Coconut
- Sugarcane
- Mazie
- Yucca
Answer: 4. Yucca
Question 295. Scattered vascular bundles occur in
- Pteridophytes
- Gymnosperms
- Monocots
- Dicots
- Bryophytes
Answer: 3. Dicots
Question 296. The vascular cambium of the stem is
- Primary meristem
- Partly primary and partly secondary
- Secondary meristem
- Intercalary meristem
Answer: 2. Partly primary and partly secondary
Question 297. Growth rings are formed by the activity of
- Extrastelar cambium
- Intrastelar cambium
- Interstellar cambium
- Both 2 and 3
Answer: 4. Both 2 and 3
Question 298. The Inner darker, harder portion of the secondary xylem that cannot conduct water in older dicot stems is called
- Alburnum
- Bast
- Duramen
- Wood
Answer: 3. Duramen
Question 299. Epiblema is the name of the epidermis of
- Leaf
- Stem
- Dicot root
- Both dicot and monocot roots
Answer: 4. Both dicot and monocot roots
Question 300. Choose the correct combination of labeling of the lattice
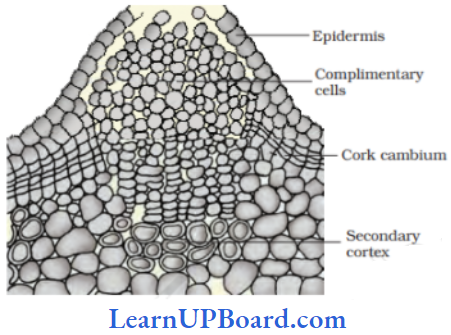
- 1 → pore, 2 → complementary cells, 3 → cork, 4 → cork cambium, 5 → secondary cortex
- 1 → pore, 2 → secondary cortex, 3 → cork, 4 → cork cambium, 5 → complementary cells
- 1 → pore, 2 —> cork cambium, 3 → secondary cortex, 4 → cork, 5 → complementary cells
- 1 → pore, 2 → cork, 3 → complementary cells, 4 → cork cambium, 5 → secondary cortex
- 1 → pore, 2 → cork, 3 → cork cambium, 4 → secondary cortex, 5 → complementary cells
Answer: 1. 1 → pore, 2 → complementary cells, 3 → cork, 4 → cork cambium, 5 → secondary cortex
Question 301. The correct sequence of layers from outside to inside of a typical monocot root is
- Epiblema, endodermis, cortex, pericycle
- Pericycle, cortex, endodermis, epiblema
- Epiblema, cortex, endodermis, pericycle
- Epiblema, pericycle, cortex, endodermis
Answer: 3. Epiblema, cortex, endodermis, pericycle
Question 302. (A): All the endodermal cells of a root do not contain casparian thickenings on their radial walls and transverse walls.
(R): Passage cells are found in endodermis.
- Both (A) and (R) are true. (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
- Both (A) and (R) are true. (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- (A) is true but (R) is false.
- (A) is false but (R) is true.
Answer: 4. (A) is false but (R) is true.
Question 303. Identify the correct order of components with reference to their arrangement from outside to inner side in a woody dicot stem
- Secondary cortex
- Autumn wood
- Secondary phloem
- Phellum
- 2,3, 1,4
- 4, 1, 3, 2
- 1,2, 4, 3
Answer: 2. 4, 1, 3, 2
Question 304. Palisade parenchyma is present on both sides in
- Ncrium
- Eucalyptus
- Wheat
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 305. Tyloses are balloon-like ingrowths in vessels developed from the adjoining
- Parenchyma through pits in vessel wall
- Parenchyma through general surface of vessel wall
- Fibers through the general surface of the vessel wall
- Fibers through pits in vessel wall
Answer: 1. Parenchyma through pits in the vessel wall
Question 306. Casparian thickenings occur in the cells of
- Pcricyclc of stem
- Endodcrmis of stem
- Pcricyclc of root
- Endodcrmis of root
Answer: 4. Endodcrmis of root
Question 307. Large, nearly empty, colorless cells present on the upper surface of grass a leaf are
- Accessory cells
- Bulliform cells
- Palisade parenchyma
- Spongy parenchyma
- Passage cells
Answer: 2. Bulliform cells
Question 308. Which of the following is/are not true?
- Cork cambium is otherwise called phellogen.
- Cork is otherwise called Phellem.
- The secondary cortex is otherwise called the periderm.
- Cork cambium, cork, and secondary cortex are collectively called phelloderm.
- (2) and (4) only
- (2) and (3) only
- (3) and (2) only
- (2) and (2) only
- (1) and (4) only
Answer: 3. (3) and (2) only
Question 309. The collateral open vascular bundles and eustele are found in
- Dicot root
- Dicot stem
- Monocot stem
- Monocot root
Answer: 2. Dicot stem
Question 310. Radial vascular bundles occur in
- Dicot root
- Monocot root
- All roots
- Dicot stem
Answer: 3. All roots
“anatomy ncert “
Question 311. Vascular cabium produces
- Secondary xylem and secondary phloem
- Secondary xylem only
- Secondary phloem only
- Primary xylem and primary phloem
Answer: 1. Secondary xylem and secondary phloem
Question 312. Phellogen is also known as?
- Vascular cambium
- Periderm
- Cork cambium
- Apical cambium
Answer: 3. Cork cambium
Question 313. Which one is/are not true?
- Cork cambium is called phellogen.
- Cork is called phellogen.
- The secondary cortex is called the periderm.
- The secondary cambium, cork, and secondary cortex are collectively called phelloderm.
- (1) and (4) only
- (1) and (2) only
- (2) and (3) only
- (2) and (4) only
- (1) and (2) only
Answer: 1. (1) and (4) only
Question 314. The cambium ring consists of
- Interfascicular cambium
- Intrafascicular cambium
- Both (1) and (2)
- Phelloderm
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
Question 315. Endodcrmis takes part in
- Providing protection
- Preventing water loss from the stele
- Maintaining rigidity
- All the above
Answer: 2. Preventing water loss from stele
Question 316. In autumn and winter, cambium produces
- Sapwood
- Heartwood
- Early wood
- Latewood
Answer: 4. Latewood
Question 317. The cells of grass leaves which help minimize cuticular transpiration are
- Bulliform cells
- Guard cells
- Subsidiary cells
- Endodermal cells
Answer: 1. Bulliform cells
Question 318. Cork cambium is
- Primary meristem
- Apical meristem
- Secondary meristem
- Intercalary meristem
Answer: 3. Secondary meristem
Question 319. Secondary growth is best observed in
- Teak and pine
- Deodar and fem
- Wheat and maidenhair fem
- Sugarcane and sunflower
Answer: 1. Teak and pine
Question 320. Passage cells are thin-walled cells found in
- Phloem elements serve as entry points
- Testa of seeds for emergence of embryonal axis
- The central area of style for the passage of pollen tube
- Endodermis of roots to facilitate rapid transport of water from cortex to pericycle
Answer: 4. Endodermis of roots to facilitate rapid transport of water from cortex to pericycle
Question 321. Find out the correct and incorrect statements.
- In dicot root, the vascular bundles are collateral and endarch
- The innermost layer of the cortex in a dicot root is the endodermis
- In dicot root, phloem and xylem bundles are separated by conjunctive tissue
- (1) true, (2), (3) false
- (2) true, (1), (3) false
- (1) false, (2),(3) true
- (2) false, (1), (3) true
- (3) true, (1), (2) false
Answer: 3. (1) false, (2), (3) true
Question 322. The closing layers of lenticels show the deposition of
- Cutin
- Lignin
- Pectin
- Suberin
Answer: 4. Suberin
Question 323. What differentiates a dicot leaf from a monocot leaf?
- Stomata only on the upper side
- Differentiation of palisade and spongy parenchyma
- Parallel venation
- Stomata on the upper and lower sides
Answer: 2. Differentiation of palisade and spongy parenchyma
Question 324. Cellular layers from the outside to the inside in old dicot stems are
- Epidermis, phellem, phellogen, phelloderm
- Epidermis, hypodermis, cortex, endodermis
- Epidermis, phellogen, phellem, endodermis
- Epidermis, hypodermis, phellogen, phelloderm
Answer: 1. Epidermis, phellem, phellogen, phelloderm
Question 325. Older resin-clogged central secondary xylem and younger outer secondary xylem are, respectively, known as
- Alburnum and duramen
- Duramen and alburnum
- Autumn wood and springwood
- Spring-wood and autumn-wood
Answer: 2. Duramen and alburnum
Question 326. Which character is not associated with plants where Shull studied inbreeding depression while Miller and Letham extracted a hormone from its seeds?
- Atactostele in stem
- Bundle sheath in leaf
- Chromosome number 30 in endosperm
- Medulla absent in root
Answer: 4. Medulla absent in root
Question 327. The condition found in the roots of a plant having assimilatory submerged roots and spongy petioles
- Tetrarch
- Triarch
- Monarch
- Mature stem
Answer: 3. Monarch
Question 328. The cuticle is absent in
Mesophytes
Young roots
Leaves
Mature stem
Answer: 2. Young roots
Question 329. In an annual ring, the light-colored part is
- Heartwood
- Sapwood
- Early wood
- Latewood
Answer: 3. Earlywood
Question 330. What is true about heartwood?
- It does not help in water conduction.
- It is also called alburnum.
- It is dark in color but is very soft.
- It has tracheary elements which are filled with tannins, resins, etc.
- 2, 3, 4
- 1, 2, 3
- 2, 4
- 1, 4
Answer: 4. 1, 4
Question 331. Pith parenchyma generally lacks
- Vacuole
- Chloroplasts
- Mitochondria
- Nucleus
Answer: 2. Chloroplasts
Question 332. Tctrarch bundles occur in the
- Leaf of Ciccr arietinum
- Leaf of Pisum sativum
- The root of Ciccr arietinwn
- Root of Zcamays
Answer: 3. Root of Ciccr arietinwn
Question 333. Which is not part of periderm?
- Phellogen
- Cork
- Secondary cortex
- Wood
Answer: 4. Wood
Question 334. Lenticels arc patches of
- Loose cells in leaves
- Loose cells on bark for aeration
- Subsidiary cells of stomata
- Cells for respiration of epiphytes
Answer: 2. Loose cells on bark for aeration
Question 335. Conjoint and closed vascular bundles with no phloem parenchyma are observed in
- Monocot stem
- Dicot stem
- Monocot root
- Dicot root
Answer: 1. Monocot stem
Question 336. Match the column and choose the correct combination
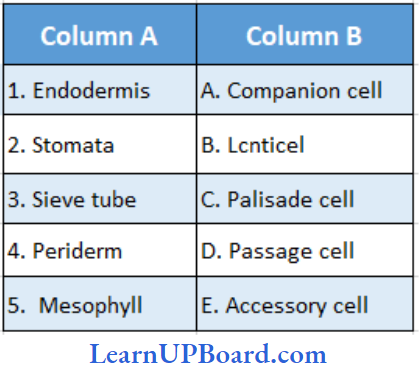
- (1) → (D), (2) → (E), (3) → (B), (4) → (A), (5) → (C)
- (1) → (E), (2) → (C), (3) → (A), (4) → (B), (5) → (D)
- (1) → (B), (2) → (E), (3) → (C), (4) → (D), (5) → (A)
- (1) → (D), (2) → (E), (3) → (A), (4) → (B), (5) → (C)
- (1) → (D), (2) → (B), (3) → (E), (4) → (C), (5) → (A)
Answer: 4. (1) → (D), (2) → (B), (3) → (E), (4) → (C), (5) → (A)
Question 337. In barley stem, vascular bundles are
- Open and scattered
- Closed and scattered
- Closed and radial
- Open and in a ring
Answer: 2. Closed and scattered
Question 338. Palisade parenchyma is absent in the leaves of
- Gram
- Soyabean
- Sorghum
- Mustard
Answer: 3. Sorghum
Question 339. Anatomically, a fairly old dicotyledonous root is distinguished from dicotyledonous stem by the
- Position of protoxylem
- Absence of secondary xylem
- Absence of secondary phloem
- Presence of cortex
Answer: 1. Position of protoxylem
Question 340. Arrange the following in the order of their location from periphery to center in the entire dicotyledonous plant body.
- Fusiform cells
- Trichoblasts
- Collocytes
- Tylosis
- 2, 3, 1, 4
- 1, 2, 3, 4
- 4, 1, 2, 3
- 3, 2, 1, 2
Answer: 1. 2, 3, 1, 4
Question 341. The vascular bundle of monocot is
- Scattered
- Closed
- Endarch
- All the above
Answer: 4. All the above
Question 342. The structure absent in monocot is
- Sieve tubes
- Pith
- Cambium
- Vessels
Answer: 3. Cambium
Question 343. Which of the following is not correct?
- Early wood is characterized by a large number of xylary elements.
- Latewood is characterized by a large number of xylary elements.
- Early wood is characterized by vessels with narrower cavities.
- Latewood is characterized by vessels with narrower cavities.
Answer: 2. Latewood is characterized by a large number of xylary elements.
Question 344. Medullary rays are made up of
- Fibers
- Tracheids
- Sclerencyma cells
- Parenchymatous cells
Answer: 4. Parenchymatous cells
Question 345. Heartwood differs from sapwood in
- The absence of vessels and parenchyma
- Having dead and non-conducting elements
- Being susceptible to pests and pathogens
- The presence of rays and fibers
Answer: 2. Having dead and non-conducting elements
Question 346. Ground tissue includes
- All tissues external to endodermis
- All tissues except the epidermis and vascular bundles
- Epidermis and cortex
- All tissues internal to endodermis
Answer: 2. All tissues except the epidermis and vascular bundles
Question 347. The cork cambium, cork, and secondary cortex are, collectively, called
- Phelloderm
- Phellogen
- Periderm
- Phellem
Answer: 3. Periderm
Question 348. The common bottle cork is a product of
- Phellogen
- Xylem
- Vascular cambium
- Dermatogen
Answer: 1. Phellogen
Question 349. Closed vascular bundles lack
- Conjunctive tissue
- Cambium
- Pith
- Ground tissue
Answer: 2. Cambium
Question 350. Water-containing cavities in vascular bundles are found in
- Maize
- Cycas
- Finns
- Sunflower
Answer: 1. Maize
Question 351. Companion cells are closely associated with
- Vessel elements
- Trichomes
- Guard cells
- Sieve elements
Answer: 4. Sieve elements
Question 352. As compared to a dicot root, a monocot root has
- More abundant secondary xylem
- Many xylem bundles
- Inconspicuous annual rings
- Relatively thicker periderm
Answer: 2. Relatively thicker periderm
