NEET Biology For Biological Classification Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Two kingdom system classification was given by
- Linnaeus
- John Ray
- Copeland
- Whittaker
Answer: 1. Linnaeus
Question 2. Which kingdom was introduced in four kingdom classifications and who proposed it?
- Protista and Copeland
- Plantae and Linnaeus
- Monera and Whittaker
- Monera and Copeland
Answer: 4. Monera and Copeland
Question 3. The kingdom system of classification is mainly based on
- Complexity of cell structure
- Mode of nutrition
- Complexity of body organization
- Ecological role
Answer: 2. Mode of nutrition
Biology MCQs with answers
Question 4. Which of the following is the major group in Monera?
- Eubacteria
- Cyanobacteria
- Archaebacteria
- All Of these
Answer: 1. Eubacteria
Question 5. Bacteria are considered primitive organisms because they
- Possess incipient nucleus
- Are small, microscopic plants, which are not seen by the naked eyes
- Cause serious diseases to human beings, domesticated animals, and crop plants
- Produce endospores which are very resistant to adverse conditions
Answer: 1. Possess incipient nucleus
biological classification
Question 6. The term “bacteria” was given by
- Koch
- Pasteur
- Ehrenberg
- Stanley
Answer: 3. Ehrenberg
Question 7. 70S ribosomes, chromatophores, circular DNA. mesosomes are found in
- All eukaryotes
- All prokaryotes
- Some prokaryotes
- Some eukaryotes and some prokaryotes
Answer: 3. Some prokaryotes
Biology MCQs with answers
Question 8. A bacterium that bears flagella all over the surface is called
- Lophotrichous
- Cephalotrichous
- Peritrichous
- Amphitrichous
Answer: 3. Peritrichous
Question 9. A distinct lipopolysaccharide wall layer is found in
- Gram-positive bacteria
- Gram-negative bacteria
- All bacteria
- Mycoplasma
Answer: 2. Gram-negative bacteria
Question 10. In bacteria, the respiratory enzymes are situated in the
- Cytoplasm
- Cell membrane
- Ribosomes
- Mitochondria
Answer: 2. Cell membrane
Question 11. The cell wall in Gram-positive bacteria is composed of
- Lipid and protein
- Murein
- Proteins only
- Cellulose and pectin
Answer: 2. Murein
Biology MCQs with answers
Question 12. Cellulose is generally absent in the cell wall of bacteria except in a few such as Acetobacter xylene and Zymosarcina. In most bacteria, it is composed of
- Chitin
- A-acetyl muramic acid
- Alternating units of A-acetyl muramic acid and N- N-acetyl glucosamine joined by 1,4 linkages.
- 1,3-linked glucose molecule
Answer: 3. Alternating units of A-acetyl muramic acid and N- N-acetyl glucosamine joined by 1,4 linkages.
Question 13. Pili represent
- Extrachromosomal genetic elements
- Protoplasmic outgrowths of donor cells
- Small flagella
- Special bacterial cilia
Answer: 2. Protoplasmic outgrowths of donor cells
Question 14. Plasmids represent
- A group of monerans
- Small parasitic organisms
- Genetic elements
- Extrachromosomal genetic elements
Answer: 4. Extrachromosomal genetic elements
Question 15. The resting spores produced by bacteria in unfavorable conditions are called
- Oldie
- Endospores
- Exospores
- Chlamydosporcs
Answer: 2. Endospores
Question 16. Conjugation in bacteria was discovered by
- Beadle and Tatum
- Zinder and Lederberg
- Griffith
- Lederberg and Tatum
Answer: 4. Lederberg and Tatum
Question 17. Genophore is the name of
- DNA of eukaryotes
- DNA of bacteria
- Genes of Drosophila
- Genes of Neurospora
Answer: 2. DNA of bacteria
Question 18. There is no alternation of generation in Rttcberirhia colt because of there is no
- Syngamy
- Reduction division
- Conjugation
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 2
Question 19. The part of the bacterial chromosome that is homologous to a genome fragment transferred from donor to recipient cell in the formation of a merozygote is known as
- Exogcnotc
- Endogcnote
- Dysgenic
- Eugenio
Answer: 2. Endogcnote
Question 20. Which of the following bacterium is associated with de-nitrification?
- Azotobacter
- Rhodospirillum
- Pseudomonas
- Rhizohium
Answer: 3. Pseudomonas
Question 21. Broad-spectrum antibiotics is those which
- Acts on both pathogens and hosts
- Acts on all bacteria and viruses
- Acts on a variety of pathogenic microorganisms
- Is effective in very small amounts
Answer: 3. Acts on a variety of pathogenic microorganisms
Question 22. Bacteria that can survive in the absence of oxygen are known as
- Obligate anaerobes
- Facultative anaerobes
- Obligate aerobes
- Facultative aerobes
Answer: 2. Facultative anaerobes
Question 23. Streptomycin is produced by
- Streptomyces venezuelae
- Streptomyces griseus
- Stivptomyces cry tit re us
- Streptomyces atireofaciens
Answer: 2. Streptomyces griseus
Question 24. Food poisoning is caused by
- Clostridium tetani
- Clostridium botulinum
- Salmonella typhoid
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Answer: 2. Clostridium botulinum
Question 25. Rhizohium is a
- Symbiotic and Gram-negative bacterium
- Symbiotic and Gram-positive bacterium
- Free-living nitrogen-fixing bacterium
- Parasitic and nitrogen-fixing bacterium
Answer: 1. Symbiotic and Gram-negative bacterium
” infectious proteins are present in”
Question 26. Syphilis is caused by
- Neisseria gonorrhoeac
- Treponema pallidum
- Haemophilia pertussis
- Pasteurella pestis
Answer: 2. Treponema pallidum
Question 27. Jacob and Wollman coined the term
- Plasmid
- Episomc
- Circular DNA
- Chromosome
Answer: 2. Episomc
Biology MCQs with answers
Question 28. Branched-chain lipids occur in the cell membranes of
- Archaebacteria
- Mycoplasma
- Actinomycetes
- Streptomyces
Answer: 1. Archaebacteria
Question 29. Monerans producing conidia for reproduction belong to
- Eubacteria
- Archaebacteria
- Actinomycetes
- Mycoplasma
Answer: 3. Actinomycetes
Question 30. The smallest known monerans lacking cell wall are
- Spirochaetes
- Mycoplasmas
- Cyanobacteria
- Archaebacteria
Answer: 2. Mycoplasmas
Question 31. Cyanobacteria do not possess
- Gene recombinations
- Flagella
- Plasmids
- Lamellasomes
Answer: 2. Flagella
Question 32. Hcterocyst present in Nostoc is specialized for
- Fragmentation
- Nitrogen fixation
- Storage
- Photosynthesis
Answer: 2. Nitrogen fixation
Question 33. A cyanelle is
- A BGA associated with the human intestine
- A BGA associated with protists
- A tree-living BOA
- Any symbiotic BOA
Answer: 2. A BGA associated with protists
Question 34. “Contagium vivum fluidum” (i.e., living fluid infester) term has been given by
- Mayer
- Ivanowsky
- Beijerinck
- Bawden and Pine
Answer: 3. Beijerinck
NEET Biology MCQ
Question 35. The bacterial cell divides every one minute. It takes 15 min a cup to be one-fourth full. How much time will it take to fill the cup?
- 30 min
- 45 min
- 60 min
- 17 min
Answer: 4. 17 min
Question 36. Anaerobic monerans which are endosymbiotically associated with castles’ rumen are
- Bacillus
- Methanobacterium
- Halococcus
- Thermoacidophiles
Answer: 2. Methanobacterium
Question 37. The highly resistant nature of endospores is due to the presence of
- Dipicolinic acid and peptidoglycan in spore coat
- Peptidoglycan in exosporium
- Dipicolinic acid and Ca in cortex
- Dipicolinic acid and Ca in cell membrane
Answer: 3. Dipicolinic acid and Ca in the cortex
Question 38. Gange’s water purity is maintained by
- Bdellovibrio
- Clostridium
- Ferrobacillus
- Tolypothrix
Answer: 1. Bdellovibrio
Question 39. Find the correct match.
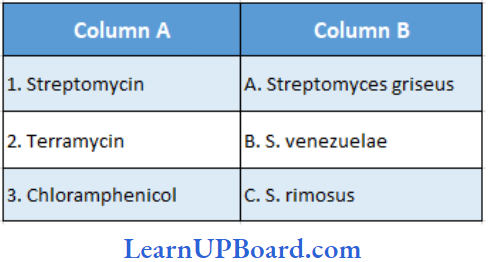
- (1) – (A), (2) – (C), (3) – (B), (4) – (D)
- (1) – (A), (2) – (B), (3) – (C), (4) – (D)
- (1) – (C), (2) – (B), (3) – (A), (4) – (D)
- (1) – (A), (2) – (B), (3) – (C), (4) – (D)
Answer: 1. (1) – (A), (2) – (C), (3) – (B), (4) – (D)
Question 40. The photosynthetic protists are
- Diatoms, euglenoids, and slime molds
- Sacrodines, dinoflagellates, and diatoms
- Euglenoids, diatoms, and dinoflagellates
- Ciliates, zooflagellates, and dinoflagellates
Answer: 3. Euglenoids, diatoms, and dinoflagellates
Question 41. Sea water glows during the night mainly due to the occurrence of
- Gonyaulax
- Noctiluca
- Euglena
- Cyclotella
Answer: 2. Noctiluca
NEET Biology MCQ
Question 42. Bivalved siliceous shells or frustules occur in
- Diatoms
- Radiolarians
- Zooflagellates
- Archaebacteria
Answer: 1. Diatoms
Question 43. Rejuvenescent spore of diatom is
- Haploid and exospores
- Diploid and statospore
- Haploid and stratosphere
- Diploid and auxospore
Answer: 4. Diploid and auxospore
Question 44. Choose the incorrect pair.
- Gonyaulax-red side
- Melos ira-golden algae
- Mycoplasma-cellulosic cell wall
- Nostoc-heterocyst
Answer: 3. Mycoplasma-cellulosic cell wall
Question 45. Leucosin (chrysolaminarin) is a carbohydrate that is stored as reserve food in case of
- Diatom
- Euglena
- Dinoflagellates
- Paramecium
Answer: 1. Diatom
Question 46. The reserved food in Euglena is
- Paramylum
- Starch
- Glycogen
- Mannitol
Answer: 1. Paramylum
Question 47. Flagellation in Euglena is
- Uniflagellation and stichonematic
- Isokont and whiplash-type
- Heterokont and whiplash-type
- Heterokont and stichonematic
Answer: 4. Heterokont and stichonematic
“euglenoids class 11 “
Question 48. A special type of red pigment present in the eyespot of Euglena and Crustacea is called
- Phycoerythrin
- Astaxanthin
- Carotene
- Xanthophyll
Answer: 2. Astaxanthin
NEET Biology MCQ
Question 49. Mixotrophic nutrition occurs in
- Paramecium
- Euglena
- Plasmodium
- Amoeba
Answer: 2. Euglena
Question 50. The paraflagellar body of Euglena helps in
- Locomotion
- Photoreception
- Reproduction
- Osmoregulation
Answer: 2. Photoreception
Question 51. The structure formed in the life cycle of cellular slime mold due to chemotactic movement is
- Pseudoplasmodium
- Swarm cells
- Macrocyst
- Capillitia
Answer: 1. Pseudoplasmodium
Question 52. Myxamoeba are formed in the life cycle of
- Physarum
- Amoeba
- Entamoeba
- Diatoms
Answer: 1. Physarum
Question 53. de Bary considered slime molds to be closely related to animals and called them
- Protozoa
- Metazoa
- Mycetozoa
- Mycotina
Answer: 3. Mycetozoa
Question 54. The difference between a red sea and red tide is that
- Red tide takes place in red sea
- Associated with cyanobacteria and protists, respectively
- One occurs by virus and the other by bacteria
- Associated with Rhodophyceae and diatoms, respectively
Answer: 2. Associated with cyanobacteria and protist, respectively
Question 55. de Bary was a leading
- Phycologist
- Mycologist
- Bryologist
- Pteridologist
Answer: 2. Mycologist
Question 56. Asexual spores of fungi (thallophytes) are commonly known as
- Oospores
- Motorsports
- Melceprcn
- Zygospores
Answer: 2. Mitosporcs
Question 57. Which one is not related to viroids?
- PSTD
- Diener
- ssRNA
- C-Jakob
Answer: 4. C-Jakob
Question 58. Which one of the following shows a haplodiplontic life cycle with four ascospores in the ascus?
- Budding yeast
- Fission yeast
- Helobial yeast
- False yeast
Answer: 1. Budding yeast
NEET Biology MCQ
Question 59. Gametangial copulation (conjugation) is common in
- Ascomycetes
- Zygomycetes
- Basidiomycetes
- Deuteromycetes
Answer: 2. Zygomycetes
Question 60. The causal agent of smallpox is
- Variola virus
- Rubella virus
- Rhino vims
- Arbo vims
Answer: 1. Variola virus
Question 61. If the thallus of an organism, for example, a fungus, is entirely converted into one or more reproductive structures, it is called as
- Eucarpic
- Holocarpic
- Holozoic
- Homothallic
Answer: 2. Holocarpic
“classification questions “
Question 62. Subterranean masses of hyphae that pass the unfavorable periods in the dormant stage are known as
- Sclerotia
- Mycelium
- Rliizomorph
- Puffballs
Answer: 3. Rliizomorph
Question 63. Asexual reproduction by aplanospore formation is the feature of
- ac fung
- Fungi imperfecti
- Conjugating fungi
- Club fungi
Answer: 3. Conjugating fungi
Question 64. Find the correct match.
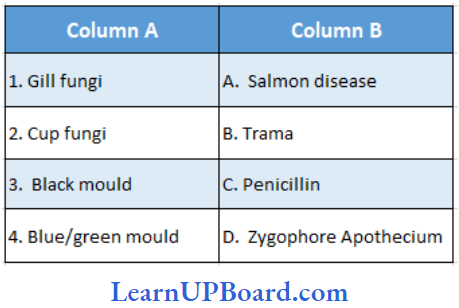
- (1) – (B), (2) – (C), (3) – (A), (4) – (E)
- (1) – (B), (2) – (E), (3) – (D), (4) – (A)
- (1) – (B), (2) – (E), (3) – (D), (4) – (C)
- (1) – (C), (2) – (C), (3) – (A), (4) – (D)
Answer: 3. (1) – (B), (2) – (E), (3) – (D), (4) – (C)
Question 65. Haploid sexual spore produced exogenously is
- Ascospore
- Oospore
- Basidiospore
- Zygospore
Answer: 3. Basidiospore
Question 66. Select the incorrectly matched pair
- Mucor mucedo-Coprophilous
- Albugo candida-Facultative parasite
- Agaricus bisporus-Edible basidiocarp
- Puccinia grafninis-Heteroecious fungi
Answer: 2. Albugo candida-Facultative parasite
Question 67. Wheat rust of crucifer is caused by
- Albugo Candida
- Sclerospora
- Phytophthora infestans
- Pythium debaryanum
Answer: 1. Albugo Candida
NEET Biology MCQ
Question 68. Coenocytic mycelium does not occur in
- Zygomycetes
- Phycomycetes
- Oomycetes
- Deuteromycetes
Answer: 4. Deuteromycetes
Question 69. Members are found in aquatic habitats and on decaying wood in moist and damp places or as obligate parasites on plants; mycelium is aseptate and coenocytic.
- Phycomycetes
- Ascomycetes
- Basidiomycetes
- Deuteromycetes
Answer: 1. Phycomycetes
Question 70. One of the following is a global yeast.
- Saccharomyces
- Schizosaccharomyces
- Saccharomyces
- Schizomycetes
Answer: 3. Saccharomycodes
Question 71. One of the following is a true yeast.
- Candida
- Mycoderma
- Cryptococcus
- Saccharomyces
Answer: 4. Saccharomyces
Question 72. Fungi differ from bacteria in
- Mode of nutrition
- Having NAG in cell wall
- Flagella structure
- Reserve food material as glycogen
Answer: 3. Flagella structure
Question 73. Penicillin is obtained from
- Penicillium griseofulvum
- Penicillium chrysogenum
- Penicillium camembert
- Penicillium roqueforti
Answer: 2. Penicillium chrysogenum
Question 74. Branched conidiophores are found in
- Penicillium
- Rhizopus
- Ustilago
- Saccharomyces
Answer: 1. Penicillium
Question 75. The fruiting body in Aspergillus (or Penicillium) is known as
- Cleistothecium
- Apothecium
- Perithecium
- Hysterothecium
Answer: 1. Cleistothecium
“chemosynthetic autotrophic bacteria “
Question 76. A mushroom having hallucinating properties similar to LSD is
- Morchella
- Psalliota
- Psilocybe
- Armillaria
Answer: 3. Psilocybe
Question 77. Powdery mildew of cereals is due to
- Puccinia graminis
- Claviceps purpurea
- Ustilago tritici
- Erysiphe graminicola
Answer: 4. Erysiphe graminicola
NEET Biology MCQ With Solutions
Question 78. Ergot is a product of
- Rhizopus
- Claviceps purpurea
- Aspergillus
- Sclerospora
Answer: 2. Claviceps purpurea
Question 79. The famous Irish famine is related to a disease of potatoes known as
- Late blight of potato
- Early blight of potato
- Dry rot of potato
- Potato scab
Answer: 1. Late blight of potato
Question 80. A fungus which is known as Guinea pig of the plant kingdom is
- Rhizopus
- Pythium
- Peziza
- Aspergillus
Answer: 4. Aspergillus
Question 81. A dolipore septum is a characteristic feature of
- Phycomycetes
- Ascomycetes
- Basidiomycetes
- Zygomycetes
Answer: 3. Basidiomycetes
Question 82. The fertile layer of gills is known as
- Hymenium
- Trama
- Paraphyses
- Basidia
Answer: 1. Hymenium
Question 83. An edible part of a mushroom is
- Primary mycelium
- Secondary mycelium
- Rhizomorph
- Basidiocarp
Answer: 4. Basidiocarp
Question 84. When two host species are required for the completion of a parasitic fungus life cycle, this condition is described as
- Autoecious
- Heteroecious
- Autotrophic
- Heterokaryotic
Answer: 2. Heteroecious
Question 85. Pioneer work on wheat rust was done by
- Mundkur
- Tulane
- K.C. Mehta
- Subramaniam
Answer: 3. K.C. Mehta
NEET Biology MCQ With Solutions
Question 86. The soredium is a reproductive structure of
- Ascomycetes
- Zygomycetes
- Basidiomycetes
- Lichens
Answer: 4. Lichens
Question 87. The most common chlorophycobiont in a lichen is
- Chlorella
- Trebouxia
- Gonium
- Chlamydomonas
Answer: 2. Trebouxia
Question 88. Indicators of water pollution
- E. coli
- Chlorella
- Beggiatoa
- Ulothrix
Answer: 1. E. coli
Question 89. DNA of E. coli
- ds circular
- ss circular
- ds linear
- ss linear
Answer: 1. ds circular
Question 90. Species separated by geographical barriers are called
- Allopatric
- Sympatric
- Sibling
- Endemic
Answer: 1. Allopatric
Question 91. Typhoid is caused by
- Rickettsiae
- Chlamydia
- Salmonella typhi
- Mycobacterium
Answer: 3. Salmonella typhi
Question 92. Non-symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria is
- Rhizobium
- Azospirilium
- Azotobacter
- Nitrosomonas
Answer: 3. Azotobacter
“biological questions “
Question 93. The difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes is
- ss circular DNA in prokaryotes
- Histone with prokaryotic DNA
- Operon in eukaryotes
- Membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotes
Answer: 4. Membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotes
Question 94. According to the kingdom system, blue-green algae belongs to
- Metaphyta
- Monera
- Protista
- Algae
Answer: 2. Monera
Question 95. Bacteria are essential in the carbon cycle as
- Decomposer
- Synthesizer
- Consumer
- Primary producer
Answer: 1. Decomposer
Question 96. Transduction in bacteria is can be out by
- Bacteriophage
- BGA
- Mycoplasma
- Rickettsiae
Answer: 1. BGA
NEET Biology MCQ With Solutions
Question 97. Which of the following is most used in genetic engineering?
- E. coli and Agrobacterium
- Mycobacteria and Salmonella
- Aspergillus
- Penicillium
Answer: 1. E. coli and Agrobacterium
Question 98. Modem fanners can increase the yield of paddy up to 50% by the use of
- Cyanobacteria
- Rhizobium
- Cyanobacteria in Azolla pinnata
- Fann yard manure
Answer: 3. Cyanobacteria in Azolla pinnata
Question 99. Koch’s postulates are not applicable to
- Mycobacterium leprae
- Tuberculosis
- Pneumonia
- Cholera
Answer: 1. Mycobacterium leprae
Question 100. Plant-pathogenic bacteria are mostly
- Gram-positive, non-spore-forming
- Gram-negative non-spore-forming
- Gram negative spore fonning
- Gram negative spore fonning
Answer: 2. Gram-negative non-spore-forming
Question 101. Anabaena is associated with Azolla’s
- Stem
- Leaves
- Roots
- Flowers
Answer: 2. Leaves
Question 102. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria convert
- N2 → NH3
- NH+4+ → Nitrates
- NO2 →NO3
- NO3 →N2
Answer: 1. N2 → NH3
Question 103. The main reason of water blooms in rivers, lakes, sea, etc., is
- Brown algae and green algae
- Cyanobacteria and dinoflagellates
- Eichornia
- Fishes
Answer: 2. Cyanobacteria and dinoflagellates
Question 104. Azolla is used in the cultivation of
- Maize
- Sorghum
- Wheat
- Rice
Answer: 4. Rice
Question 105. Which one produces gas by decomposing the gobar (dung) in gobar gas?
- Fungus
- Virus
- Methanogenic
- Algae
Answer: 3. Methanogenic
Question 106. Maximum photosynthesis takes place by
- Phytoplankton
- Zooplankton
- Marsh plants
- Woody plants
Answer: 1. Phytoplankton
NEET Biology MCQ With Solutions
Question 107. The genetic material of prokaryotic cells is
- Non-historic double-stranded DNA
- Historic double-stranded DNA
- Histone and DNA both arc absent
- Histone without DNA
Answer: 1. Non-historic double-stranded DNA
Question 108. Diatomaceous earth is used as a heat insulator in boilers and steam pipes because the cell wall of diatom is
- Composed of Iron
- Composed of Silicon dioxide
- Conductor of heat
- Bad conductor of heat
Answer: 4. Bad conductor of heat
Question 109. One of the free-living anaerobic nitrogen-fixer is
- Beijernickia
- Rhodospirillum
- Rhizobiitm
- Azotobacter
Answer: 2. Rhodospirillum
Question 110. Some hyperthermophilic organisms that grow in highly acidic (pH = 2) habitats belong to the two groups
- Eubacteria and archaea
- Cyanobacteria and diatoms
- Protists and mosses
- Liverworts and yeasts
Answer: 1. Eubacteria and archaea
Question 111. Bacteria can be considered to be a plant because
- Some of the bacteria are photosynthetic
- Some of the bacteria have chlorophyll
- Some of the bacteria can make their own food
- Bacteria have cell wall
Answer: 4. Bacteria have cell wall
Question 112. The major component of the bacterial cell wall is a polymer called
- Chitin
- Xytan
- Cellulose
- Peptidoglycan
Answer: 4. Peptidoglycan
Question 113. Oxytetracycline is produced by
- Mycoplasma
- Actinomycetes
- Cyanobacteria
- Eubacteria
Answer: 2. Actinomycetes
Question 114. Cyanobacteria existed years ago.
- 2.9 billion
- 3.4 billion
- 1 million
- 44 thousand
Answer: 2. 3.4 billion
Question 115. Which of the following is non-symbiotic, anaerobic, non-photosynthetic nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
- Clostridium
- Nos toe
- Anabaena
- Azotobacter
Answer: 1. Clostridium
NEET Biology MCQ With Solutions
Question 116. Bacterial cells include all except
- Nuclear material without membrane
- Cell wall of murein
- DNA compounds with histones
- Ribosomes
Answer: 3. DNA compound with histones
Question 117. The pigment phycocyanin and phycoerythrin are present in
- Bacillariophyceae
- Archaebacteria
- Eubacteria
- Cyanobacteria
Answer: 4. Cyanobacteria
Question 118. Barophilic prokaryotes
- Grow slowly in highly alkaline frozen lakes at high altitudes.
- Occur in water containing high concentrations of barium hydroxide.
- Grow and multiply in deep marine sediments.
- Readily grow and divide in seawater enriched in any soluble salt of barium.
Answer: 3. Grow and multiply in deep marine sediments.
Question 119. Teichoic acid is present in
- Gram-positive bacteria
- Gram-negative bacteria
- Spirochaete
- Actinomycetes
Answer: 2. Gram-negative bacteria
Question 120. For the retting of jute, the fermenting microbe used is
- Helicobacter pylori
- Mesophilic bacteria
- Streptococcus lactic
- Butyric acid bacteria
Answer: 4. Butyric acid bacteria
Question 121. The free-living aerobic nitrogen-fixing bacterium is
- Azotobacter
- Rhizobium
- Clostridium
- Anabaena
Answer: 1. Azotobacter
Question 122. Cyanobacteria is
- Nitrogen-fixing free-living photosynthetic organism.
- Symbiotic mycorrhizae
- Photosynthetic algae
- Saprophytic fungus
Answer: 1. Nitrogen-fixing free-living photosynthetic organism.
Question 123. Genetic elements that may be present inside as well as extrachromosomal entities are
- Episomes
- Mesosomes
- Oxysomes
- Autosomes
Answer: 1. Episomes
Question 124. The bacterial cell wall is made up of
- Cellulose
- Hemicellulose
- Both (1) and (2)
- Peptidoglycan
- Glycogen
Answer: 4. Glycogen
Question 125. The most widely used bioweapon is
- Bacillus subtilis
- Pseudomonas putida
- Bacillus anthracis
- None above
Answer: 3. Bacillus anthracis
NEET MCQ
Question 126. A bacterial cell divides once every minute and it takes one hour to fill a cup. How much time will it take to fill half the cup?
- 30 minutes
- 60 minutes
- 29 minutes
- 59 minutes
Answer: 4. 59 minutes
“chlamydomonas belongs to which kingdom “
Question 127. Bacteria is pathogenic due to
- Mitochondria
- Cell membrane
- Cell wall
- Nucleic acid
Answer: 4. Nucleic acid
Question 128. Which of the following is a non-pathogenic bacteria of the colon?
- Escherichia coli
- Balantidium coli
- Entamoeba coli
- Enterohius vermicularis
Answer: 2. Balantidium coli
Question 129. Treponema pallidum is
- The causative agent of syphilis
- The example of the spirochaete bacterium
- The causative agent of sexually transmitted disease
- All are correct
Answer: 4. All are correct
Question 130. Which of the following is correct?
- Bacteria are only autotrophic.
- Bacteria are only heterotrophic.
- Most are heterotrophic but few are autotrophic.
- Most bacteria are autotrophic but few are heterotrophic.
Answer: 3. Most are heterotrophic but few are autotrophic.
Question 131. WIDAL test is performed as the diagnostic value in
- Tuberculosis
- Typhoid
- Cholera
- Tetanus
Answer: 2. Typhoid
Question 132. The two bacteria found to be very useful in genetic engineering experiments are
- Nitrosomonas and Klebsiella
- Escherichia and Agrobacterium
- Nitrobacter and Azotobacter
- Rhizobium and Diplococcus
Answer: 2. Escherichia and Agrobacterium
Question 133. Pili of bacteria are useful for
- Locomotion
- Sexual contacts
- Asexual reproduction
- Transformation
- Feeding
Answer: 2. Sexual contacts
Question 134. The bacterium (Clostridium botulinum) that causes botulism is
- An obligate aerobe
- A facultative anaerobe
- An obligate anaerobe
- A facultative aerobe
Answer: 3. An obligate anaerobe
Question 135. In prokaryotes, what helps in anaerobic respiration?
- Mitochondria
- Folds of plasma membrane
- Ribosomes
- Cell wall
Answer: 2. Folds of plasma membrane
Question 136. Blue-green algae such as Nostoc and Anabaena can photosynthesize due to the presence of
- Heterocysts
- Akinetes
- Chromatophores
- Leghemoglobin
Answer: 3. Chromatophores
NEET MCQ
Question 137. The exceptional feature of blue-green algae which is the basis of their studies is
- Aplanospores
- Sclcrodia
- Heterocysts
- Haplospores
Answer: 3. Heterocysts
Question 138. Crown galls are caused in plants due to the infection of
- Insects
- Virus
- Bacteria
- Fungi
Answer: 3. Bacteria
Question 139. Curing often leaves is brought about by the activity of
- Fungi
- Bacteria
- Mycorrhizae
- Viruses
Answer: 2. Bacteria
Question 140. In prokaryotes, chromatophores are
- Specialized granules are responsible for the coloration of cells.
- Structures are responsible for organizing the shape of the organism.
- Inclusion bodies lie free inside the cells for carrying out various metabolic activities.
- Internal membrane systems may become extensive and complex in phtosythesis bacteria.
Answer: 4. Internal membrane systems that may become extensive and complex in photosynthesis bacteria.
Question 141. Which one of the following pathogens causes canker disease?
- Meloidogyne incognita
- Anguina tritici
- Xanthornonas citri
- Pseudomonas rubilineans
- Phytophthora infestans
Answer: 3. Pseudomonas rubilineans
Question 142. Find out the pairs that are correctly matched.
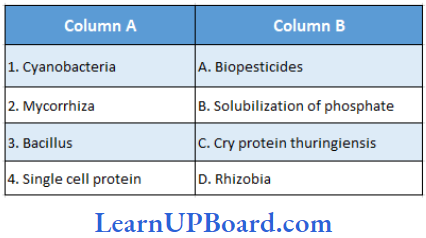
- (1) and (B)
- (2) and (C)
- (3) and (C)
- (4) and (C)
- (2) and (D)
Answer: 3. (3) and (C)
Question 143. Which one of the following statements about mycoplasma is wrong?
- They are pleomophic
- They are sensitive to penicillin
- They cause diseases in plants
- They are called PPLO
Answer: 2. They are sensitive to penicillin.
Question 144. The presence of a cluster of polar flagella is termed as
- Monotrichous
- Amphitriehous
- Lophotrichous
- Peritrichous
Answer: 3. Lophotrichous
Question 145. Some bacteria can also live in the absence of oxygen. These are
- Obligate aerobes
- Facultative aerobes
- Obligate anerobes
- Facultative anerobes
Answer: 1. Obligate aerobes
Question 146. What are the infoldings of the plasma membrane called in prokaryotes that store respiratory pigments?
- Glyoxysomes
- Oxysomes
- Mesosomes
- Cristae
Answer: 2. Oxysomes
Question 147. Plasmid is
- Small extract chromosomal circular self-replicating DNA that can carry genes into the host organism
- Bacteriophage
- DNA found in mitochondria
- DNA incorporated in bacteria
Answer: 4. DNA incorporated in bacteria
Question 148. The difference between Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria is in their
- Cell membrane
- Cell wall
- Ribosome
- Mitochondria
Answer: 4. Mitochondria
NEET MCQ
Question 149. The cell wall of a bacterium is made up of
- Cellulose
- Hemicellulose
- Lignin
- Peptidoglycan
- Glycogen
Answer: 2. Hemicellulose
Question 150. Which of the following Monerans lack cell walls?
- Actinomycetes
- Photosynthetic bacteria
- Eubacteria
- None above
Answer: 1. Actinomycetes
Question 151. Bacteria can live under sub-zero temperatures for
- More than 1000 years
- 100-1000 years
- Few years
- Few days
Answer: 1. More than 1000 years
Question 152. A set of bacterial diseases is
- Diptheria, leprosy, and plague
- Malaria, mumps, and polio
- Cholera, typhoid, and mumps
- Tetanus, TB, and malaria
Answer: 1. Diptheria, leprosy, and plague
Question 153. In prokaryotes, genetic recombination can occur during
- Transduction
- Transformation
- Conjugation
- All of these
Answer: 1. Transduction
Question 154. Thermococcus, Methanococcus, and Methanobacterium exemplify
- Archaebacteria that contain protein homologous to eukaryotic core histones.
- Archaebacteria that lack anarchist ones resemble those found in eukaryotes but whose DNA is negatively supercoiled.
- Bacteria whose DNA is relaxed or positively supercoiled but which have a cytoskeleton as well as mitochondria.
- Bacteria that contain a cytoskeleton and ribosomes.
Answer: 4. Bacteria that contain a cytoskeleton and ribosomes.
Question 155. Which one of the following is not characteristic of Gram-positive bacteria?
- Cell wall is smooth.
- Mesosomes are distinctively prominent.
- The basal body of the flagellum contains two rings.
- An outer membrane is present.
- The Murein content of cell wall is 70-80%.
Answer: 5. Murein content of cell wall is 70-80%.
Question 156. Pathogenicity of bacteria causing tuberculosis and lep¬rosy is due to
- Cholesterol
- Ergosterol
- Prostaglandins
- Glycerol
- Wax-D
Answer: 1. Cholesterol
NEET MCQ
Question 157. Bacterial leaf blight of rice is caused by a species of
- Xanthomonas
- Pseudomonas
- Alternaria
- Engine
Answer: 2. Pseudomonas
Question 158. Streptomyces griseus gives which of these antibiotics?
- Chloramphenicol
- Streptomycin
- Tetracycline
- Penicillin
Answer: 1. Chloramphenicol
Question 159. Indirect transfer of genetic material from one bacterium to another through bacteriophage is
- Transduction
- Transcription
- Conjugation
- Translation
- Transformation
Answer: 4. Transtation
Question 160. The bacterial brown rot of potatoes is caused by
- Xanthomonas citri
- Escherichia coli
- Agrobacterium tumofaciens
- Psuedomonas solanacearum
- Salmonella typhosa
Answer: 2. Escherichia coli
Question 161. Which of the following is a bacterial disease?
- Red rust of tea
- Citrus canker
- Red rot of sugarcane
- Late blight of potato
Answer: 2. Citrus canker
NEET Biology practice mcq questions with solution
Question 162. Shorter generation time of E. coli compared to eukaryotes may be explained on the basis of
- Shape
- Large surface and volume ratio
- Presence of cell wall
- Cell wall is smooth
- Absence of organelles
Answer: 2. Large surface and volume ratio
Question 163. Division in a bacteria cell is carried out through
- Multiple fission
- Binary fission
- Budding
- Plasmotomy
Answer: 3. Budding
Question 164. Antibiotic resistance genes are present on
- Plastid
- DNA
- Plasmid
- RNA
Answer: 3. DNA
Question 165. Cyanobacteria is a member of
- Fungi
- Protozoa
- Monera
- Pteridophytes
Answer: 2. Protozoa
Question 166. The Gram-negative bacteria detect and respond to the chemicals in their surroundings by
- Muramic acid
- Lipopolysaccharide
- Volutin granules
- Porins
Answer: 2. Lipopolysaccharide
NEET Biology practice mcq questions with solution
Question 167. Which of the following is not bacteria?
- Methanogens
- Diatoms
- Archaebacteria
- Blue-green algae
Answer: 2. Diatoms
Question 168. A bacterium is capable of withstanding extreme heat, dryness, and toxic chemicals. This indicates that it is probably able to form
- A thick peptidoglycan wall
- Endospores
- Endotoxins
- Endogenous buds
Answer: 3. Endotoxins
Question 169. The vector for plague is
- Anopheles
- Aedes
- Xenopsylla
- Culex
Answer: 2. Aedes
Question 170. Lung tuberculosis is caused by
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Escherichia coli
Answer: 2. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Question 171. An example for symbiotic bacteria is
- Erwinia amylovora
- Rhizobium leguminosarum
- Xanthomonas campestris
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Answer: 3. Xanthomonas campestris
Question 172. Non-pathogenic bacteria found in our vermiform appendix is
- Entamoeba histolytica
- Shigella
- Escherichia coli
- Ascaris
Answer: 1. Entamoeba histolytica
Question 173. Which one of the following organisms possesses characteristics of plant and an animal?
- Euglena
- Bacteria
- Mycoplasma
- Paramoecium
2. Bacteria
Question 174. The scientist who coined the term Protista to include both plant and animal-like unicellular organisms was
- Robert Koch
- E.F. Haeckel
- L. Pasteur
- Joseph Lister
Answer: 1. Robert Koch
Question 175. Protista includes
- Protozoa, algae, and fungi
- Algae, Bryophyta, bacteria, and fungi
- Fungi, slime molds, and vascular plants
- Protozoa, bacteria, algae, and Bryophyta
Answer: 2. Algae, Bryophyta, bacteria, and fungi
Question 176. Slime molds belong to the kingdom
- Monera
- Protista
- Plantae
- Animalia
Answer: 1. Monera
Question 177. Which protist reproduces both by binary fission and conjugation?
- Amoeba
- Paramecium
- Euglena
- Monocytes
Answer: 2. Paramecium
Question 178. Total parasites belong to a protozoan group
- Sporozoa
- Ciliata
- Sarcodina
- Zooflagellata
Answer: 2. Ciliata
Question 179. Protozoan protists respire through
- Pseudopodia
- Contractile vacuole
- Mitochondria
- General surface
Answer: 1. Pseudopodia
Question 180. Which one is not a protozoan protist?
- Plasmodium vivax
- Paramecium caudatum
- Enterobius vermiclaris
- Trypanosoma gambiense
Answer: 2. Paramecium caudatum
Question 181. Protozoan protists are differentiated on the basis of
- Nuclei
- Size
- Shape
- Locomotory structures
Answer: 3. Shape
Question 182. Endoparasitic protistan protozoans belong to
- Sporozoa
- Ciliata
- Sarcodina
- Mastigophora
Answer: 4. Mastigophora
Question 183. Protozoans found commensal in the human colon is
- Entamoeba coli
- P. vivax
- A. aegypti
- All of these
Answer: 1. Entamoeba coli
Question 184. The primary grouping of protozoan protists is based on
- Locomotor organelles
- Size and shape
- Mode of feeding
- Mode of reproduction
Answer: 1. Locomotor organelles
Question 185. Protozoans are able to live efficiently due to their
- Motility
- Rapid reproduction
- Ability to manufacture food
- Specialized organelles
Answer: 1. Motility
Question 186. Protista contains
- Euglena, dinoflagellates, and yeast
- Amoeba, paramecium, hydra
- Euglena, paramecium, mushroom
- Amoeba, paramecium, and dinoflagellates
Answer: 4. Amoeba, paramecium, and dinoflagellates
Question 187. The cyanobacteria are also referred to as
- Golden algae
- Slime molds
- Blue-green algae
- Protists
Answer: 3. Blue-green algae
Question 188. Which one of the following does not differ in E. coli and Chlamydomonas
- Chromosomal organization
- Cell wall
- Cell membrane
- Ribosomes
Answer: 3. Cell membrane
Question 189. The nuclear membrane is absent in
- Agaricus
- Volvox
- Nostoc
- Penicillium
Answer: 3. Nostoc
Question 190. Maximum nutritional diversity is found in the group
- Animalia
- Monera
- Plantae
- Fungi
Answer: 2. Monera
Question 191. The most abundant prokaryotes helpful to humans in making curd from milk and in the production of antibiotics are the ones categorized as
- Archaebacteria
- Chemosynthetic autotrophs
- Heterotrophic bacteria
- Cyanobacteria
Answer: 3. Heterotrophic bacteria
