NEET Biology For Biomolecules Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Both in cells and extracellular fluids, dibasic phosphate (HPO2-4) and monobasic phosphate (H2PO–4) act as acid-base buffers to maintain
- K+ concentration of extracellular fluid
- Na+ concentration of extracellular fluid
- Na+ concentration of cellular fluid
- H+ concentration of cellular fluid
Answer: 4. H+ concentration of cellular fluid
Question 2. All the following statements are correct except
- Mitochondria are rich in manganese.
- Molybdenum is necessary for the fixation of nitrogen catalyzed by the enzyme nitrogenase.
- Magnesium is essential for a large number of enzymes, particularly those utilizing ATP.
- Calcium and magnesium have no effect on the excitability of nerves and muscles.
Answer: 4. Calcium and magnesium have no effect on the excitability of nerves and muscles.
Question 3. The most abundant element in cell living matter is
- C
- H
- O
- N
Answer: 3. O
Question 4. Which element is/are found in cytochromes?
- Fe++ and Cu++
- Fe+++ and Mg++
- Mg++
- Cu++
Answer: 1. Fe++ and Cu++
Question 5. The concentration of Na, K, Ca in a cell in decreasing order is
- K-Na-Ca
- K-Ca-Na
- Na-K-Ca
- Ca-K-Na
Answer: 1. K-Na-Ca
Question 6. All the macromolecules are the result of the process of polymerization, a process in which repeating subunits termed monomers are bound into chains of different lengths except
- Nucleic acids
- Carbohydrates
- Lipids
- Proteins
Answer: 3. Lipids
Question 7. Raffinose has three monosaccharide units. Those are
- Glucose, pentose, and maltose
- Glucose, levulose, and galactose
- Glucose, fructose, and sucrose
- Fructose, fructose, and galactose
Answer: 2. Glucose, levulose, and galactose
Question 8. A monosaccharide is a simple polyhydroxy aldehyde or ketone molecule, which cannot be further hydrolyzed into smaller units. The number of carbon atoms in mono-saccharides vary from
- 2-8 carbons
- 2-7 carbons
- 3-6 carbons
- 3-7 carbons
Answer: 4. 3-7 carbons
Question 9. The sweetest among all naturally occurring sugars is
- Glucose
- Fructose
- Mannose
- Galactose
Answer: 2. Fructose
Question 10. Glucose is
- Aldose hexose sugar
- Ketose hexose sugar
- Pyranose pentose sugar
- Furanose pentose sugar
Answer: 1. Aldose hexose sugar
neetprep biomolecules
Question 11. Glucose is also called
- Dextrose
- Com sugar
- Grape sugar
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 12. Why sucrose and not glucose is used to preserve fruit products?
- Glucose is reactive as it has a CHO group.
- Sucrose is more common in nature.
- Sucrose is easily available and has both glucose and fructose.
- None of these
Answer: 1. Glucose is reactive as it has a CHO group.
Question 13. Honey has two sugars. They are
- Glucose and mannose
- Glucose and galactose
- Dextrose and levulose
- Dextrose and lactose
Answer: 3. Dextrose and levulose
Question 14. Which of the following is not a reducing sugar?
- Glucose
- Lactose
- Maltose
- Sucrose
Answer: 4. Sucrose
Question 15. Which of the following will yield only glucose on hydrolysis?
- Sucrose
- Lactose
- Maltose
- Raffinose
Answer: 3. Maltose
Question 16. Storing carbohydrates in the form of polysaccharides has the following advantages:
- During their formation, many molecules of water are removed from monosaccharides (dehydration synthesis), condensing the bulk to be stored.
- When necessary, polysaccharides are broken down by enzymes for the release of energy.
- Unlike small carbohydrates, polysaccharides are relatively easy to store.
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 17. The most abundant organic compound in the biosphere is
- Lignin
- Cellulose
- Pectin
- Hemi-cellulose
Answer: 2. Cellulose
Question 18. The largest amount (90%) of cellulose amongst the natural materials is present in
- Wood
- Cotton fibers
- Rayon
- Roughage
Answer: 2. Cotton fibers
Question 19. Carbohydrates, the most abundant biomolecules on earth, are produced by
- Some bacteria, algae, and green plant cells
- Fungi, algae, and green plant cells
- All bacteria, fungi, and algae
- Viruses, fungi, and algae
Answer: 1. Some bacteria, algae, and green plant cells
Question 20. Cellulose is
- Heptopolysaccharidc
- Heteropolysaccharide branched
- Hexosan polysaccharide, unbranched
- Pentosan polysaccharide, branched
Answer: 3. Hexosan polysaccharide, unbranched
Question 21. Which of the following is added to ice creams, cosmetics, and medicines to emulsify and give a smooth texture?
- Cellulose acetate
- Cellulose nitrate
- Carboxymethyl cellulose
- Cellulose
Answer: 3. Carboxymethyl cellulose
Question 22. Cliitin is the second most abundant organic substance present in the exoskeleton of insects and crustaceans. It is a
- Protein
- Polysaccharides and the basic unit is N-acetylglucosamine
- Protein and CaCO3 deposits in it
- Lipid
Answer: 2. Polysaccharide and the basic unit is N-acetylglucosamine
Question 23. One of the following is the correct sequence of carbohydrates in the order of increasing complexity of chemical structure.
- Sucrose, starch, oligosaccharide, maltose, triose
- Triose, maltose, sucrose, oligosaccharide, starch
- Triose, glucose, maltose, oligosaccharide, starch
- Oligosaccharide, triose, starch, sucrose, maltose
Answer: 3. Triose, glucose, maltose, oligosaccharide, starch
Question 24. Which one is a carbohydrate?
- Inulin
- Raphide
- Aleurone
- Cystolith
Answer: 1. Inulin
Question 25. The center of starch grain is called hilum. It is made up of
- Protein
- Carbohydrate
- Fat
- Nitrogen
Answer: 1. Protein
Question 26. Which one is a fibrous polysaccharide?
- Starch
- Glycogen
- Cellulose
- Mucilage
Answer: 3. Cellulose
Question 27. Glucose is stored as glycogen in
- Pancreas
- Bone
- Kidney
- Liver
Answer: 4. Liver
Question 28. Which of the following yields purgative?
- Hibiscus esculentus
- Plantago ovata
- Aloe barbadensis
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 4. Both (2) and (3)
Question 29. Choose the odd one out.
- Keratin phosphate
- Hyaluronic acid
- Chondroitin sulfate
- Alginic acid
Answer: 4. Alginic acid
Question 30. A cellulose molecule is formed by the polymerization of glucose. The number of glucose molecules present in cellulose is
- 600
- 6000
- 60,000
- 60
Answer: 2. 6000
Question 31. Mucilages are polysaccharides formed from galactose and mannose. They are slimy substances. Which one of the following is not a mucilage?
- Agar
- Alginic acid
- Rayon
- Carrageenin
Answer: 3. Rayon
Question 32. Starch grains of rice are
- Dumb-bell shaped
- Simple eccentric
- Simple concentric
- Compound
Answer: 4. Compound
Question 33. Cellulose forms a major portion of the food of grazing cattle. It is
- Digested by the gut bacteria
- Digested by the animal itself
- Digested partly by animals and partly by bacteria
- Passed out undigested
Answer: 1. Digested by the gut bacteria
Question 34. The number of monosaccharide units in a polysaccharide is
- 2
- 7
- 10
- More than 10
Answer: 4. More than 10
Question 35. A bond that is formed between the aldehyde or ketone group of monosaccharide and the alcoholic group of another organic compound is known as
- Peptide bond
- Glycosidic bond
- Phosphodiester bond
- Ester bond
Answer: 2. Glycosidic bond
Question 36. Which one of the following is a saturated fatty acid?
- Oleic acid
- Linoleic acid
- Linolenic acid
- Stearic acid
Answer: 4. Stearic acid
Question 37. Which of the following is the most essential fatty acid?
- Linoleic
- Linolenic
- Arachidonic
- Stearic
Answer: 1. Linoleic
Question 38. Lecithin is a
- Fatty acid
- Phospholipid with choline attached to phosphate group
- Cholesterol
- Fat
Answer: 2. Phospholipid with choline attached to a phosphate group
Question 39. Bee wax is secreted by
- Drones
- Workers
- Queen
- Hooey
Answer: 2. Workers
Question 40. Which of the following is a phospholipid?
- Lecithin
- Glycerol
- Oleic acid
- Prostaglandin
Answer: 1. Lecithin
Question 41. Keratin is a protein that has larger amount of
- Sulfur
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Phosphorous
Answer: 1. Sulfur
Question 42. Waxes are simple lipids formed by the combination of long-chain fatty acid with a long-chain monohydric alcohol. Bee wax is made up of
- Palmitic and merieyl alcohol
- Hexacosyl palmitate
- Ergosterol
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 43. Which is not a lipid?
- Lecithin
- β-keratin
- Sterol
- Wax
Answer: 2. β-keratin
Question 44. An anti-fertility steroid is
- Diosgenin
- Cortisol
- Estradiol
- Progesterone
Answer: 1. Diosgenin
Question 45. In the brain, most common types of lipids are
- Glycolipids
- Lipoproteins
- Phospholipids
- Steroids
Answer: 1. Glycolipids
Question 46. Find the odd one out
- Palmitic acid, stearic acid
- Oleic acid, linoleic acid
- Linoleic acid, oleic acid
- Tripalmitin. linolenic acid
Answer: 4. Tripalmitin. linolenic acid
Question 47. Which of the following are basic amino acids?
- Glycine and alanine
- Lysine and arginine
- Glutamic acid and aspartic acid
- Histidine and proline
Answer: 2. Lysine and arginine
Question 48. Which of the following is the simplest amino acid?
- Alanine
- Asparagine
- Glycine
- Tyrosine
Answer: 3. Glycine
Question 49. The hormone adrenaline (epinephrine) is formed from which of the following amino acids?
- Glycine
- Tyrosine
- Tryptophan
- Alanine
Answer: 2. Tyrosine
Question 50. Which of the following amino acids is involved in the formation of heme?
- Tryptophan
- Tyrosine
- Glycine
- Histidine
Answer: 3. Glycine
“biomolecules previous year questions “
Question 51. Vitamin nicotinamide as well as the plant hormone indole-3-acetic acid are fonned from
- Tryptophan
- Alanine
- Glutamic acid
- Serine
Answer: 1. Tryptophan
Question 52. On losing the carboxyl group as carbon dioxide, amino acids form biologically active
- Glucose
- Amine such as histamine
- Alcohol
- N-base
Answer: 2. Amine such as histamine
Question 53. The skin pigment melanin is formed from
- Tyrosine
- Adrenaline
- Indole-3-acetic acid
- Tryptophan
Answer: 1. Tyrosine
Question 54. Which one of the following is an alcoholic amino acid pair?
- Tyrosine and serine
- Threonine and serine
- Phenylalanine and tyrosine
- Tryptophan and phenylalanine
Answer: 2. Threonine and serine
Question 55. One of the following is not an essential amino acid?
- Tryptophan and valine
- Lysine and methionine
- Leucine and isoleucine
- None of these
Answer: 4. None of these
Question 56. One of the following amino acids does not contain sulfur.
- Tryptophan
- Methionine
- Cystine
- Cysteine
Answer: 1. Tryptophan
Question 57. One of the following is a heterocyclic amino acid.
- Proline
- Histidine
- Hydroxyproline
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 58. One of the following is a neutral amino acid.
- Arginine
- Glycine
- Glutamic acid
- Aspartic acid
Answer: 2. Glycine
Question 59. Which of the following is a non-polar amino acid?
- Alanine
- Glutamic acid
- Serine
- None of these
Answer: 1. Alanine
Question 60. β-plated structure of protein is present in silk fibers, the protein is
- Fibroin
- Collagen
- Rayon
- Keratin
Answer: 1. Fibroin
Question 61. The keratin of hair has
- Secondary structure
- a-helical structure
- β-plated structure
- Primary structure
Answer: 2. a-helical structure
Question 62. Most of the blood proteins in our body are
- Basic
- Acidic
- Neutral
- Basic and Neutral
Answer: 2. Acidic
Question 63. The casein of milk is
- Glycoprotein
- Phosphoprotein
- Chromoprotein
- Metalloprotein
Answer: 2. Phosphoprotein
Question 64. Prolamines are
- Associated with nucleic acids
- Storage proteins
- Enzymatic protein
- Structural protein
Answer: 2. Storage proteins
Question 65. Which of the proteins is involved in the transport of organic compounds through phloem?
- Protamine
- P-Protein
- Myosin
- Glutelin
Answer: 2. P-Protein
Question 66. Cheese is a
- Globular protein
- Conjugated protein
- Denatured protein
- All of these
Answer: 3. Denatured protein
Question 67. The storage protein of wheat is
- Glutelin
- Oryzin
- Hordein
- Zein
Answer: 1. Glutelin
Question 68. The types of prolamines and glutelins found in wheat are
- Zein and Gladin
- Glutelin and hordein
- Gliadin and glutenin
- Hordein and zein
Answer: 3. Gliadin and glutenin
Question 69. Which of the following is a contractile protein?
- P-protein
- Myosin
- Albumin
- Penneases
Answer: 2. Myosin
Question 70. The storage protein found in castor oil seeds is
- Legumin
- Tuberin
- Ricin
- Leucosin
Answer: 3. Ricin
Question 71. Glycogen is stored in
- Liver and muscles
- Liver only
- Muscles only
- Pancreas
Answer: 1. Liver and muscles
“antiparallel strands of a dna molecule means that “
Question 72. Cholesterol is synthesized in
- Pancreas
- Burnner’s gland
- Spleen
- Liver
Answer: 4. Liver
Question 73. Which is a disaccharide
- Galactose
- Fructose
- Maltose
- Dextrin
Answer: 3. Maltose
Question 74. Which element is normally absent in proteins
- C
- N
- S
- P
Answer: 4. P
Question 75. Which substance is not a carbohydrate
- Starch
- Glycogen
- Wax
- Glucose
Answer: 3. Wax
Question 76. To get quick energy, one should use
- Carbohydrate
- Fats
- Vitamins
- Proteins
Answer: 1. Carbohydrate
Question 77. The protein most abundant in the human body is
- Collagen
- Myosin
- Actin
- Albumin
Answer: 1. Collagen
Question 78. Which is not a polysaccharide?
- Sucrose
- Starch
- Glycogen
- Cellulose
Answer: 1. Sucrose
Question 79. Decreasing order of amount of organic compound in animal body
- Carbohydrates, protein, fat, and nucleic acid
- Protein, fats, nucleic acid, and carbohydrate
- Protein, fats, carbohydrates, and nucleic acid
- Carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and nucleic acid
Answer: 3. Protein, fats, carbohydrates, and nucleic acid
Question 80. Characteristic feature of hemoglobin
- Reversible union with oxygen
- Red color
- Presence of Cu
- Presence of Globulin protein
Answer: 1. Reversible union with oxygen
Question 81. External coat composed of cellulose-like material occurs in
- Hemichordata
- Urochordata
- Cephalochordata
- Cyclostomata
Answer: 2. Urochordata
Question 82. Common in feathers and silk is
- Carbohydrate
- Fats
- Protein
- Nucleic acid
Answer: 3. Protein
Question 83. Monosaccharide is
- Pentose sugar
- Hexose sugar
- Only glucose
- All the above
Answer: 4. All the above
Question 84. Sugar which is found in the hemolymph of insects is called
- Maltose
- Lactose
- Trehalose
- Galactose
Answer: 3. Trehalose
Question 85. Which substance is most abundant in cells?
- Carbohydrates
- Protein
- Water
- Fats
Answer: 3. Water
Question 86. Proteins which present in protoplasm are very important because
- They provide definite shape to cell
- They function as biocatalysts
- They yield energy
- They are stored food
Answer: 2. They function as biocatalysts
Question 87. Dipeptide is
- Structure of two peptide bonds
- Two amino acids linked by one peptide bond
- The bond between one amino acid and one peptide
- None
Answer: 2. Two amino acids linked by one peptide bond
“carbohydrates question “
Question 88. Which amino acid is non-essential for the human body?
- Glycine
- Phenylalanine
- Arginine
- Methionine
Answer: 1. Glycine
Question 89. In which form, the extra sugars is stored in the body?
- Glucose monosaccharide
- Sucrose disaccharide
- Glycogen polysaccharide
- Fatty acid and glycerol
Answer: 3. Glycogen polysaccharide
Question 90. Products of protein catabolism are
- NH3, CO2, and urea
- Urea, CO2, and NH
- Urea, NH3, and uric acid
- Urea, NH3, alanine, and creatine
Answer: 1. NH3, CO2, and urea
Question 91. Galactosemia disease in children can be prevented if they are provided
- Milkless food
- Proteinaceous milk
- More milk
- Vitamin-less milk
Answer: 1. Milkless food
Question 92. Glycogen is
- Polymer of amino acids
- Polymer of fatty acids
- Unsaturated fats
- Polymer of glucose
Answer: 4. Polymer of glucose
Question 93. Carbohydrate is
- Polymer of fatty acids
- Polymer of amino acids
- Polyhydroxy aldehyde or ketone
- None
Answer: 3. Polyhydroxy aldehyde or ketone
Question 94. In which form, food is stored in the animal body?
- Glucose
- Glycogen
- Cellulose
- ATP
Answer: 2. Glycogen
Question 95. Which compound produces more than twice the amount of energy as compared to carbohydrates?
- Protein
- Fats
- Vitamins
- Glucose
Answer: 2. Fats
Question 96. What is the normal ratio of sugar in human blood?
- 0.01%
- 0.1%
- 1%
- 0.18%
Answer: 2. 0.1%
Question 97. Carbohydrates are stored in mammals as
- Glucose in liver
- Glycogen in muscles and spleen
- Lactic acid in muscles
- Glycogen in liver and muscles
Answer: 4. Glycogen in the liver and muscles
Question 98. Carbohydrate metabolism is controlled by
- Parathormone
- Insulin
- Glucose
- Vitamin B12
Answer: 2. Insulin
Question 99. Fattiness is due to the excess of
- Connective tissue
- Blood
- Muscular tissue
- Adipose tissue
Answer: 4. Adipose tissue
Question 100. Which one of the following is polysaccharide?
- Sucrose
- Lactose
- Glycogen
- Glucose
Answer: 3. Glycogen
Question 101. A starving person will first use
- Fats
- Glycogen
- Blood
- Muscle protein
Answer: 2. Glycogen
Question 102. Units of proteins that unite in long chains to form proteins are called
- Sugar
- Purines
- Pyrimidines
- Amino acids
Answer: 4. Amino acids
Question 103. Milk protein is
- Lactogen
- Myosin
- Casein
- Pepsin
Answer: 3. Casein
Question 104. Chemically, enzymes are
- Fats
- Carbohydrates
- Hydrocarbons
- Proteins
Answer: 4. Proteins
Question 105. Long-chain molecules of fatty acids are formed by
- Polymerization of two carbon compounds
- Decomposition of fats
- Polymerization of glycogen
- Conversion of glycogen
Answer: 1. Polymerization of two carbon compounds
Question 106. Most simple amino acid is
- Tyrosine
- Lysine
- Glycine
- Aspartic acid
Answer: 3. Glycine
Question 107. Fats in the body are formed when
- Glycogen is formed from glucose
- Sugar level become stable in the blood
- Extra glycogen storage in the liver and muscles is stopped
- All of them
Answer: 3. Extra glycogen storage in liver and muscles is stopped
Question 108. For body growth and repair, one needs
- Carbohydrates
- Fats
- Protein
- Vitamins
Answer: 3. Protein
Question 109. In India, the best source for proteins in herbivorous persons is
- Pulses
- Potato
- Egg
- Meat
Answer: 1. Pulses
Question 110. Proteins are conducted in the body in the form of
- Amino acids
- Natural protein
- Enzymes
- Nucleic acids
Answer: 1. Amino acids
Question 111. Which is sweet in taste, but is not sugar?
- Starch
- Saccharine
- Lactose
- Protein
Answer: 2. Saccharine
Question 112. The formation of protein can be considered as
- Dehydration synthesis
- Dehydration analysis
- Hydration synthesis
- Hydration analysis
Answer: 1. Dehydration synthesis
Question 113. Translocation of sugars in flowering plants occurs in the form of
- Glucose
- Sucrose
- Fructose
- Maltose
Answer: 2. Sucrose
Question 114. Sucrose is composed of
- Glucose and fructose
- Glucose and glycogen
- Two molecules of glucose
- Glycogen and fructose
Answer: 1. Glucose and fructose
Question 115. Which of the following amino acid is essential?
- Alanine
- Glycine
- Tryptophan
- Tyrosine
Answer: 3. Tryptophan
Question 116. Which of the following disaccharides will give two molecules of glucose on hydrolysis?
- Maltose
- Sucrose
- Lactose
- None
Answer: 1. Maltose
Question 117. Which is the most structural part of the body?
- Protein
- Carbohydrates
- Lipid
- Nucleic acid
Answer: 1. Protein
Question 118. Which of the following sugar is found in ATP?
- Deoxyribose
- Ribose
- Trehalose
- Glucose
Answer: 2. Ribose
“questions on carbohydrates “
Question 119. Deficiency of protein leads to
- Rickets
- Scurvy
- Kwashiorkor
- Carotenemia
Answer: 3. Kwashiorkor
Question 120. Lactose is composed of
- Glucose + Galactose
- Glucose + Fructose
- Glucose + Glucose
- Glucose + mannose
Answer: 1. Glucose + Galactose
Question 121. The true statement for cellulose molecules is
- β-1′-4″ linkage, unbranched
- β-1′-4″ linkage, branched
- β-1′-4″ linkage, branched
- β-1′-6″ linkage, unbranched
Answer: 1. β-1′-4″ linkage, unbranched
Question 122. Contractile protein is
- Actin
- Myosin
- Troponin
- Tropomyosin
Answer: 1. Actin
Question 123. Variations in proteins are due to
- Sequence of amino acids
- Number of amino acids
- R-group
- None
Answer: 1. Sequence of amino acids
Question 124. The antibodies are
- γ-globulins
- Albumins
- Vitamins
- Sugar
Answer: 1. γ-globulins
Question 125. Which of the following does not contain metal?
- Glycoproteins
- Ferritin
- Cytochromes
- Chromoproteins
Answer: 1. Glycoproteins
Question 126. Which protein is found in the maximum amount?
- Catalase
- Zinc carbonic anhydrase
- Transferase
- RuBisCO
Answer: 4. RuBisCO
Question 127. Proteoglycan in cartilages, which is part of polysaccharide. is
- Chondroitin
- Ossein
- Casein
- Cartilage
Answer: 1. Chondroitin
Question 128. In the genetic code dictionary, how many codons are used to code for all the 20 essential amino acids?
- 20
- 64
- 61
- 60
Answer: 3. 61
Question 129. Enzyme concerned with the transfer of electrons is
- Hydrolase
- Dehydrogenase
- Transaminase
- Protease
Answer: 2. Dehydrogenase
Question 130. At which pH, enzymes of lysosomes are usually active?
- 5
- 7
- 8
- At any pH
Answer: 3. 8
Question 131. Enzymes are made up of
- Edible proteins
- Proteins
- Nitrogen-containing carbohydrates
- Carbohydrates
Answer: 4. Carbohydrates
Question 132. Hydrolytic enzymes, which act on low pH are called as
- Protease
- α-Amylase
- Hydrolases
- Peroxidase
Answer: 2. α-Amylase
Question 133. Enzymes, vitamins, and hormones can be classified into a single category of biological chemicals because all of these
- Enhance oxidative metabolism
- Are conjugated proteins
- Are exclusively synthesized in the body of a living organism
- Help in regulating metabolism
Answer: 1. Enhance oxidative metabolism
Question 134. Which of the following statements regarding enzyme inhibition is correct?
- Non-competitive inhibition of an enzyme can be overcome by adding a large amount of substrate.
- Competitive inhibition is seen when a substrate competes with an enzyme for binding to an inhibitor protein.
- Competitive inhibition is seen when the substrate and the inhibitor compete for the active site on the enzyme.
- Non-competitive inhibitors often bind to the enzyme irreversibly.
Answer: 2. Competitive inhibition is seen when a substrate competes with an enzyme for binding to an inhibitor protein.
Question 135. The catalytic efficiency of two different enzymes can be compared by
- KM value
- pH optimum value
- Formation of the product
- The molecular size of the enzyme
Answer: 3. Formation of the product
Question 136. The graph given shows the effect of substrate concentration on the rate of reaction of the enzyme green-gram-phosphatase. What does the graph indicate?
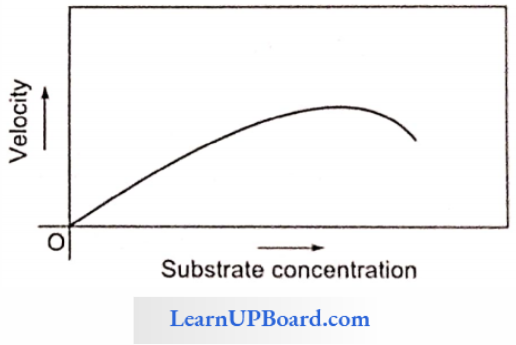
- The rate of enzyme reaction is directly proportional to the substrate concentration.
- Presence of an enzyme inhibitor in the reaction mixture.
- Formation of an enzyme-substrate complex.
- At higher substrate concentrations, the pH increases.
Answer: 4. At higher substrate concentrations, the pH increases.
“protein part of enzyme is known as “
Question 137. An organic substance bound to an enzyme and essential for its activity is called
- Apoenzyme
- Isoenzyme
- Coenzyme
- Holoenzyme
Answer: 3. Coenzyme
Question 138. Shows the conservation of a substrate into the product by an enzyme. In which one of the four options (1-4).
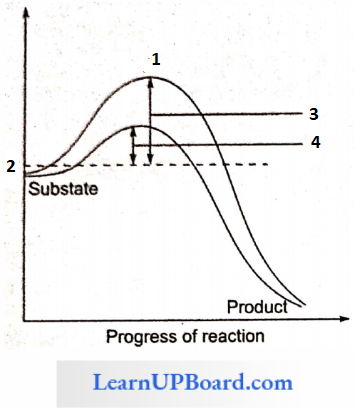
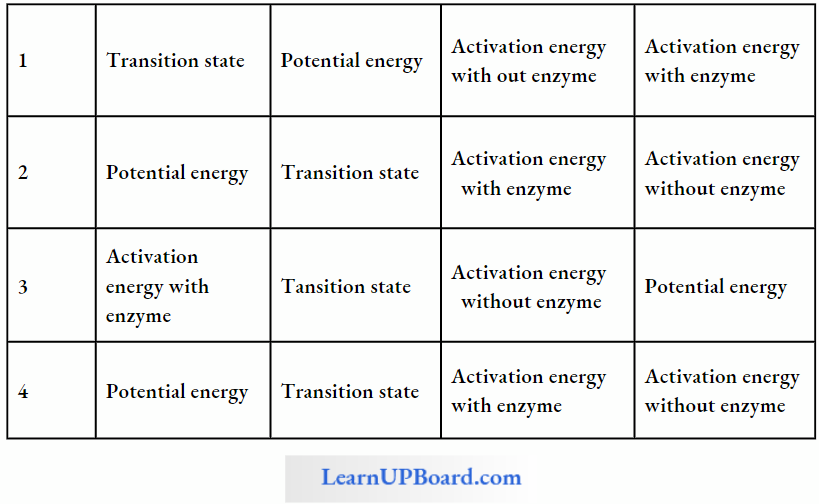
Answer: 1
Question 139. Three of the following statements about enzymes are correct which one is wrong?
- Enzymes are denatured at high temperatures but in the c era in exceptional organisms they are effective even a: temperatures 80-90°C.
- Enzymes are highly specific.
- Most enzymes are proteins but some are lipids.
- Enzymes require optimum pH for maximal activity.
Answer: 3. Most enzymes are proteins but some are lipids.
Question 140. DNA or RNA segment tagged with a radioactive molecule is called
- Vector
- Probe
- Clone
- Plasmid
Answer: 2. Probe
Question 141. The main area of various types of activities
- Plasma membrane
- Mitochondrion
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus
Answer: 3. Cytoplasm
Question 142. Given it is the diagrammatic representation of one of the categories of small molecular weight organic compounds in the thing tissues. Identify the category shown and the one blank component “X“ in it.
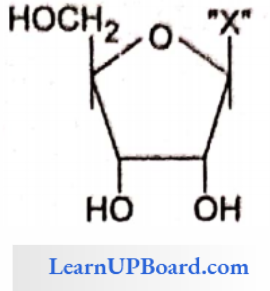
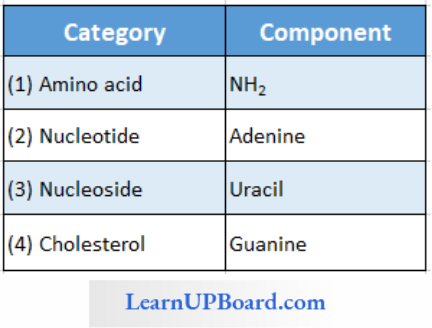
Answer: 3
Question 143. Which one out of 1-4 given below correctly represents the structural formula of the basic amino acid?
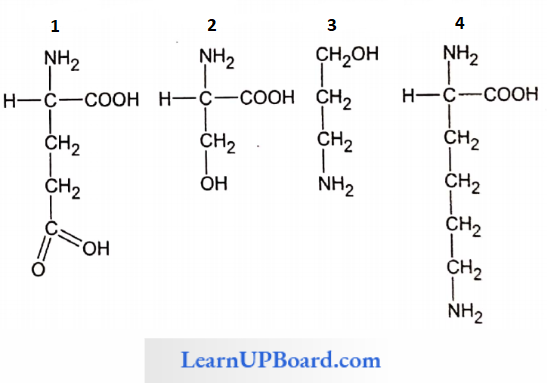
- 4
- 1
- 2
- 3
Answer: 1. 4
Question 144. Which one of the following biomolecules is correctly characterized?
- Lecithin—A phosphorylated glyceride found in the cell membrane
- Palmitic acid—An unsaturated fatty acid with 18 carbon atoms
- Adenylic acid—Adenosine with a glucose phosphate molecule
- Alanine amino acid—Contains an amino group and an acidic group anywhere in the molecule
Answer: 1. Lecithin—A phosphorylated glyceride found in the cell membrane
Question 145. A phosphoglyceride is always made up of
- Only an unsaturated fatty acid is esterified to a glycerol molecule to which a phosphate group is also attached.
- A saturated or unsaturated fatty acid is esterified to a glycerol molecule to which a phosphate group is also attached.
- A saturated or unsaturated fatty acid is esterified to a phosphate group which is also attached to a glycerol molecule.
- Only a saturated fatty acid is esterified to a glycerol molecule to which a phosphate group is also attached.
Answer: 2. A saturated or unsaturated fatty acid esterified to a glycerol molecule to which a phosphate group is also attached.
Question 146. The essential chemical components of many enzymes are
- Nucleic acids
- Carbohydrates
- Vitamins
- Proteins
Answer: 3. Vitamins
Question 147. The transition state structure of the substrate formed during an enzymatic reaction is
- Permanent but unstable
- Transient and unstable
- Permanent and stable
- Transient but stable
Answer: 2. Transient and unstable
Question 148. The most abundant intracellular cation is
- Ca++
- H+
- K+
- Na+
Answer: 3. K+
Question 149. Macromolecules chitin is a
- Phosphorus-containing polysaccharide
- Sulfur-containing polysaccharide
- Simple polysaccharide
- Nitrogen-containing polysaccharide
Answer: 4. Nitrogen-containing polysaccharide
