NEET Biology – Biotechnology: Principles and Processes
Question 1. 3′-5′ exonucleolytic degradation of DNA is performed by which enzyme?
- DNA polymerase
- Alkaline phosphatase
- DNA ligase
- RNA polymerase
Answer. 1. DNA polymerase
Question 2. The technique of gel electrophoresis was developed by
- Kary Mullis
- J.S. Chamberlain
- A. Tiselius
- F. Sanger
Answer. 3. A. Tiselius
Question 3. Which of the following dyes can be used to visualize nucleic acid after electrophoresis?
- Acridine orange
- Ethidium bromide
- Bromophenol blue
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 4. Which of the following bonds are formed by the action of DNA ligase?
- Sugar-phosphate bond
- Phosphodiester bond
- Both (1) and (2)
- Phosphate-phosphate bond
Answer. 3. Both (1) and (2)
Question 5. Who were responsible for the isolation of “methylase” kind of enzyme from E. coli in 1960’s?
- Cohen and Boyer
- Banting and Best
- Linn and Arber
- Smith and Wilcox
Answer. 3. Linn and Arber
Question 6. The specific sequence recognized by “molecular scissors” is called
- Isomer
- Isobar
- Misnomer
- Palindrome
Answer. 4. Palindrome
Question 7. When a piece of DNA is digested with Eco RI, what kind of ends are created?
- Blunt ends
- Flush ends
- Cohesive ends
- Non-staggered ends
Answer. 3. Cohesive ends
” biotechnology principles and processes “
Question 8. The sticky ends generated by the action of Eco RI on insert DNA facilitate the action of which enzyme?
- DNA polymerase
- Taq polymerase
- Alkaline phosphatase
- DNA ligase
Answer. 4. DNA ligase
Question 9. Which is incorrect with respect to DNA polymerase III?
- It requires ATP for polymerase action.
- It is required for PCR.
- It is more active than DNA polymerases I and II.
- It requires a pre-formed DNA template to work on.
Answer. 2. It is required for PCR.
Question 10. Which is not an application of modern biotechnology?
- Production of humulin
- Developing a DNA vaccine
- Gene therapy
- Production of cheese and butter
Answer. 4. Production of cheese and butter
Question 11. Which of the following cannot be related to biotechnology?
- Integration of natural science and organisms.
- Techniques to alter the chemistry of DNA.
- Introducing undesirable genes into the target organism.
- Maintenance of sterile ambience to enable the growth of only the desired microbes.
Answer. 3. Introducing undesirable genes into the target organism.
Question 12. Which of the following specific DNA sequence is responsible for initiating replication?
- Vector site
- Restriction enzymes action site
- Ori site
- Palindromic site
Answer. 3. Ori site
Question 13. Autonomously replicating, circular, extra chromosomal DNA of prokaryotic cell is called
- Satellite DNA
- Plasmid
- Recombinant DNA
- Nucleoid
Answer. 2. Plasmid
Question 14. Key tools to be involved in recombinant DNA technology are
A. Restriction enzymes
B. Polymerase enzyme
C. Ligase enzymes
D. Vectors
- (A) only
- (A) and (C) only
- (A), (B), and (C)
- (A), (B), (C), and (D)
Answer. 4. (A), (B), (C), and (D)
Question 15. The first restriction endonuclease to be discovered was
- Hind II
- Eco RI
- Bam HI
- Pst I
Answer. 1. Hind II
” short notes on biotechnology”
Question 16. Approximately, how many restriction enzymes have been isolated from the different (over 230) strains of bacteria?
- 300
- 600
- 750
- 900
Answer. 4. 900
Question 17. The conventional method for naming restriction enzymes is followed. In case of Eco RI, the “R” indicates
- Genus
- Species
- Name of the scientist
- Strain
Answer. 4. Strain
Question 18. The restriction endonuclease enzyme binds to the DNA and cuts
- Any one strand of the double helix
- Each of the two strands at specific points in their base-sugar bonds
- Each of the two strands at specific points in their base-phosphate bonds
- Each of the two strands at specific points in their sugar-phosphate backbones
Answer. 4. Each of the two strands at specific points in their sugar-phosphate backbones
Question 19. During gel electrophoresis, for the separation of DNA fragment, the
- Smallest fragment will move to the farthest point towards cathode
- Smallest fragment will move to the farthest point towards anode
- Largest fragment will move to the farthest point towards cathode
- Largest fragment will move to the farthest point towards anode
Answer. 2. Smallest fragment will move to the farthest point towards anode
Question 20. After electrophoresis, the separated DNA fragment can be visualized in ethidium bromide gel exposed to UV light. These DNA fragments appear as _________ colored bands.
- Orange
- Blue
- Silver
- Green
Answer. 1. Orange
Question 21. The procedure through which a piece of DNA is introduced in a host bacterium is called
- Cloning
- Transformation
- PCR
- Clonal selection
Answer. 2. Transformation
Question 22. After completing the transformation experiment involving the coding sequence of enzyme a-galactosidase, the recombinant colonies should
- Give blue color
- Not give blue color
- Have active α-galactosidase
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer. 2. Not give blue color
Question 23. Which of the following has the ability to transform normal cells into cancerous cells in animals?
- Agrobacterium tumifaciens
- Retroviruses
- DNA viruses
- Plasmids
Answer. 2. Retroviruses
Question 24. Which of the following is not applicable to Agrobacterium tumifaciens?
- Pathogen of several dicot plants.
- Has the ability to transform normal plant cells.
- Delivers gene of our interest.
- Ti plasmid of it is always pathogenic to plants with out any exception.
Answer. 4. Ti plasmid of it is always pathogenic to plants with out any exception.
Question 25. Insertional inactivation is related to
- Microinjection
- Gene gun
- Gel electrophoresis
- Selection of recombinants
Answer. 4. Selection of recombinants
Question 26. For transformation with recombinant DNA, the bacterial cells must first be made competent, which means
- Should increase their metabolic reactions
- Should decrease their metabolic reactions
- Increase efficiency with which DNA enters the bacterium
- Ability to divide fast
Answer. 3. Increase efficiency with which DNA enters the bacterium
Question 27. Which of the following method can be used for making the bacterial cell competent?
- Treating with specific concentration of divalent cation (Ca2+).
- Treating with specific concentration of monovalent cation (K).
- Heat shock.
- Both (1) and (3).
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (3).
“biotechnology notes “
Question 28. Which of the following techniques can be used to introduce foreign DNA into cell?
- Using disarmed pathogen
- Microinjection
- Gene gun
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 29. During heat shock, the temperature used for giving thermal shock to the bacterium is
- 82°C
- 100°C
- Liquid nitrogen
- 42°C
Answer. 4. 42°C
Question 30. Which of the following enzymes is used in case of fungus to cause the release of DNA along with other macromolecules?
- Lysozyme
- Cellulase
- Chitinase
- Amylase
Answer. 3. Chitinase
Question 31. During the isolation of DNA, the addition of which of the following causes the precipitation of purified DNA?
- Chilled ethanol
- Ribonuclease enzyme
- DNA polymerase
- Proteases
Answer. 1. Chilled ethanol
Question 32. Which of the following is the correct sequence of PCR (polymerase chain reaction)?
- Denaturation → Annealing → Extension
- Extension → Denaturation → Annealing
- Annealing → Extension → Denaturation
- Denaturation → Extension → Annealing
Answer. 1. Denaturation → Annealing → Extension
Question 33. The most commonly used bioreactor is of stirring type. The stirrer facilitates
- Temperature control
- pH control
- Oxygen availability
- Product removal
Answer. 3. Oxygen availability
Question 34. After the completion of biosynthetic stage, the separation and purification of product is called
- Upstream processing
- Downstream processing
- Modern biotechnology
- Gene amplification
Answer. 2. Downstream processing
Question 35. From isolated DNA from a cell culture with seven de- sired genes, DNA segment can be excised by molecular scissors or chemical scalpels what biotechnologists call as
- Polymerase enzymes
- DNA ligase
- Restriction enzymes
- Helicase
Answer. 3. Restriction enzymes
Question 36. All the following statements about Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer are correct but one is wrong. Which one is wrong?
- They discovered recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology, and this marks the birth of modern biotechnology.
- They first produced healthy sheep clone, a Finn Dorset lamb, Dolly, from the differentiated adult mammary cells.
- They invented genetic engineering by combining a piece of foreign DNA containing a gene from a bacterium with a bacterial plasmid using the enzyme restriction endonuclease.
- They isolated the antibiotic resistance gene by cutting out a piece of DNA from the plasmid which was responsible for conferring antibiotic resistance.
Answer. 2. They first produced healthy sheep clone, a Finn Dorset lamb, Dolly, from the differentiated adult mammary cells.
Question 37. What is the fate of a piece of DNA which is somehow transferred into an alien organism?
- This piece of DNA would not be able to multiply itself in the progeny cells of the organism if not integrated into the genome of the organism.
- If the alien piece of DNA has become a part of the chromosome, it will replicate.
- If the alien piece of DNA is linked with the origin of replication in chromosome, it will replicate.
- All of these.
Answer. 4. All of these.
Question 38. In the year 1963, the two enzymes responsible for restricting the growth of bacteriophage in Escherichia coli were isolated. These were and, respectively.
- Ligase, restriction endonuclease
- Helicase, restriction endonuclease
- Methylase, restriction endonuclease
- DNA polymerase, restriction endonuclease
Answer. 3. Methylase, restriction endonuclease
“process of biotechnology “
Question 39. The cutting of DNA by restriction endonucleases results in fragments of DNA. These fragments are generally separated by a technique known as
- Gel-filtration chromatography
- Centrifugation
- Gel electrophoresis
- Thin-layer chromatography
Answer. 3. Gel electrophoresis
Question 40. Which of the following bacteria are known as natural genetic engineers of plants, as gene transfer is happening in nature without human interference?
- Azotobacter
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- Escherichia coli
- Rhizobium
Answer. 2. Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Question 41. The technique in which a foreign DNA is precipitated on the surface of tungsten or gold particles and shot into the target cells is known as
- Microinjection
- Chemical-mediated genetic transformation
- Electroporation
- Biolistics
Answer. 4. Biolistics
Question 42. The isolation of the genetic material in pure form-free from other macromolecules can be achieved by treating the bacterial cells/plant or animal tissues with the following enzymes, except
- Lysozyme
- Cellulase
- Chitinase
- Ligase
Answer. 4. Ligase
Question 43. Which of the following is not a recombinant protein used in medical practice?
- TPA (tissue plasminogen activator)
- Interferon (α, B, and 7)
- Vaccine (for hepatitis B)
- Heparin
Answer. 4. Heparin
Question 44. cDNA is
- Circular DNA in bacteria
- Complementary DNA
- Copy DNA
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer. 4. Both (2) and (3)
Question 45. The Noble Prize of 1978 for restriction endonuclease technology was given to
- Temin and Baltimore
- Milstein and Kohler
- Arber, Nathans, and Smith
- Holley, Khorana, and Nirenberg
Answer. 3. Arber, Nathans, and Smith
Question 46. Plasmids are used in genetic engineering because they
- Are easily available
- Are able to integrate with host chromosome
- Are able to replicate along with chromosomal DNA
- Contain DNA sequence coding for drug resistance
Answer. 3. Are able to replicate along with chromosomal DNA
Question 47. Which of the following processes and techniques are included under biotechnology?
A. In vitro fertilization leading to a test-tube baby.
B. Synthesizing gene and using it.
C. Developing DNA vaccine.
D. Correcting a defective gene.
- (B) and (D) only (3)
- (B), (C), and (D)
- (A) and (B)
- (A), (B), (C), and (D)
Answer. 4. (A), (B), (C), and (D)
Question 48. The tumor-inducing (Ti) plasmid has now been modified to a cloning vector which is no more pathogenic to plants but is still able to use mechanisms to deliver genes of our interest into a variety of plants because Ti plasmid has been modified by
- Adding tumor-forming genes
- Deleting tumor-forming genes
- Adding genes resistant to endonucleases
- Deleting endonuclease
Answer. 2. Deleting tumor-forming genes
“biotechnology principles and processes class 12 “
Question 49. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
- Plasmids have the ability to replicate within the bacterial cells independent of the control of chromosomal DNA.
- Some plasmids have only one or two copies per cell whereas others may have 15-100 copies per cell.
- Bacteriophages have the ability to replicate within the bacterial cell independent of the control of chromosomal DNA.
- Transformation is a procedure of separation and isolation of DNA fragments.
Answer. 4. Transformation is a procedure of separation and isolation of DNA fragments.
Question 50. Which of the following is the first artificial cloning vector that has two selectable markers-tetracycline (tetR) and antibiotic restriction enzymes (ampR)?
- YAC
- BAC
- pBR322
- Cosmid vectors
Answer. 3. pBR322
Question 51. Restriction endonucleases are most widely used in recombinant DNA technology. They are obtained from
- Bacteriophage
- Bacterial cells
- Plasmids
- All prokaryotic cells
Answer. 2. Bacterial cells
Question 52. All the following statements are correct about genetic engineering, but one is wrong. Which one is wrong?
- It is a technique for artificially and deliberately modifying DNA (genes) to suit human needs.
- It is often referred as gene splicing.
- The organism carrying the foreign genes is termed as transgenic or GMO.
- Alec Jeffrey is the father of genetic engineering.
Answer. 4. Alec Jeffrey is the father of genetic engineering.
Question 53. All the following are the properties of enzyme Taq polymerase, except
- It is thermostable DNA polymerase
- It is isolated from a bacterium, Thermus aquaticus
- It is used for the amplification of gene of interest using PCR
- It is thermostable RNA polymerase
Answer. 4. It is thermostable RNA polymerase
Question 54. Which of the following is incorrect match?
- Gene therapy: An abnormal gene is replaced by normal gene
- Cloning: Ability to multiply copies of antibiotic resistance gene in E. coli
- Restriction enzymes: Molecular scissors
- Exonucleases: Molecular glue
Answer. 4. Exonucleases: Molecular glue
Question 55. Appropriate techniques have been developed for large- scale cell culture using bioreactors for producing
- Foreign gene product
- Vaccines
- Hormones
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 56. The uptake of genes by cells in microbes and plants is termed as
- Insertional inactivation
- Transformation
- Selectable markers
- Cloning vectors
Answer. 2. Transformation
Question 57. If we ligate a foreign DNA at the BamHI site of tetracycline resistance gene in pBR322, the recombinant plasmid will
- Show ampicillin resistance only
- Show tetracycline resistance
- Will grow well on tetracycline-containing medium
- Will not grow on ampicillin-containing medium
Answer. 1. Show ampicillin resistance only
Question 58. Polyethylene glycol can help in the uptake of foreign DNA into the host cell. This type of gene transfer is called
- Electroporation
- Chemical mediated genetic transformation
- Microinjection
- Particle gun
Answer. 2. Chemical mediated genetic transformation
Question 59. The normal E. coli cells carry resistance against which of the following antibiotics?
- Ampicillin
- Chloramphenicol
- Tetracycline or kanamycin
- None of these
Answer. 4. None of these
Question 60. The isolation of genetic material from fungal cells does not involve the use of
- Agarose
- Chitinase
- Ethanol
- Water
Answer. 1. Agarose
“biotechnology process “
Question 61. In a restriction digestion experiment, the sticky ends of vector rejoined forming a circular vector without insert. Which enzyme can be used to eliminate this possibility?
- DNA ligase
- Alkaline phosphatase
- DNA polymerase
- RNA polymerase
Answer. 2. Alkaline phosphatase
Question 62. Denaturation can be achieved at which temperature during PCR?
- 72°C
- 95°C
- 40°C
- 25°C
Answer. 2. 95°C
Question 63. Choose the incorrect statement with respect to Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
- It is a Gram-negative soil bacterium.
- It produces crown gall disease in dicot plants.
- The foreign DNA is inserted at the ori site of Ti plasmid.
- Ti plasmid becomes incorporated into the plant chromosomal DNA.
Answer. 3. The foreign DNA is inserted at the ori site of Ti plasmid.
Question 64. Which is not a method for the introduction of recombinant DNA into host cells?
- Electroporation
- Biolistics
- Transfection
- Restriction digestion
Answer. 4. Restriction digestion
Question 65. The essential requirements for a gene amplification reaction are
- 20 mg of DNA template
- Forward and reverse primers
- Mg2+
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 66. Choose the incorrect statement with respect to PCR reaction:
- It requires Taq polymerase.
- It requires dNTP’s.
- It generates 2n molecules after n number of cycles.
- The optimum temperature for polymerization step is greater than or equal to 90°C.
Answer. 4. The optimum temperature for polymerization step is greater than or equal to 90°C.
Question 67. Which is not an application of PCR?
- DNA fingerprinting
- DNA foot-printing
- Detection of mutation
- Prenatal diagnosis
Answer. 2. DNA foot-printing
Question 68. Rejoining of vector molecule after restriction enzyme digestion can be avoided by
- Using different enzymes for insert and vector
- Using same enzyme for insert and vector
- Using DNA ligase immediately after digestion
- Using alkaline phosphatase on only vector
Answer. 4. Using alkaline phosphatase on only vector
biotechnology processes
Question 69. If the target gene is inserted at Sal 1 site of the recombinant, plasmid will show resistance for pBR322
- Ampicillin
- Tetracyline
- Both (1) and (2)
- Kanamycin
Answer. 1. Ampicillin
Question 70. It is theoretically possible for a gene from any organism to function in any other organism. Why is this possible?
- All organisms have ribosomes.
- All organisms have the same genetic code.
- All organisms are made up of cells.
- All organisms have similar nuclei.
Answer. 2. All organisms have the same genetic code.
Question 71. If you discovered a bacterial cell that contained no restriction enzymes, which of the following would you except to happen?
- The cell would create incomplete plasmids.
- The cell would be unable to replicate its DNA.
- The cell would become an obligate parasite.
- The cell would be easily infected by bacteriophages.
Answer. 4. The cell would be easily infected by bacteriophages.
Question 72. Assume that you are trying to insert a gene into a plasmid and someone gives you a preparation of DNA cut with restriction enzyme X. The gene you wish to insert has sites on both ends for cutting by restriction enzyme Y. You have a plasmid with a single site for Y, but not for X. Your strategy should be to
- Cut the plasmid with restriction enzyme X and insert the fragments cut with Y into the plasmid
- Cut the plasmid with restriction enzyme X and insert the gene into the plasmid
- Cut the plasmid twice with restriction enzyme Y and ligate the two fragments into the plasmid cut with the same enzyme
- Cut the plasmid twice with restriction enzyme Y and ligate the two fragments onto the ends of the human DNA fragments cut with restriction enzyme X
Answer. 3. Cut the plasmid twice with restriction enzyme Y and ligate the two fragments into the plasmid cut with the same enzyme
Question 73. 1. Transform bacteria with recombinant DNA molecule.
2. Cut the plasmid DNA using restriction enzymes.
3. Extract plasmid DNA from bacterial cells.
4. Hydrogen-bond the plasmid DNA to non-plasmid DNA fragments.
5. Use ligase to seal plasmid DNA to non-plasmid DNA.
From the given list, which of the following is the most logical sequence of steps for splicing foreign DNA into a plasmid and inserting the plasmid into a bacterium?
- 4, 5, 1, 2, 3
- 3, 2, 4, 5, 1
- 3, 4, 5, 1, 2
- 2, 3, 5, 4, 1
Answer. 2. 3, 2, 4, 5, 1
Question 74. A eukaryotic gene has sticky ends produced by restriction endonuclease Eco RI. The gene is added to a mixture containing Eco RI and a bacterial plasmid that carries two genes, which make it resistant to ampicillin and tetracyline. The plasmid has one recognition site for Eco RI located in the tetracycline resistance gene. This mixture is incubated for several hours and then added to bacteria growing in nutrient broth. The bacteria are allowed to grow overnight and are streaked on a plate using a technique which produces isolated colonies that are clones of the original. Samples of these colonies are then grown in four different media: nutrient broth plus ampicillin, nutrient broth plus tetracycline, nutrient broth plus ampicillin and tetracycline, and nutrient broth containing no antibiotics.
The bacteria containing the engineered plasmid would grow in
- The ampicillin and tetracycline broth only
- The nutrient broth, the ampicillin broth, and the tetracycline broth
- The nutrient broth and the ampicillin broth only
- The nutrient broth only
Answer. 3. The nutrient broth and the ampicillin broth only
Question 75. Agrobacterium tumefaciens is used in genetic engineering for
- DNA mapping
- DNA modification
- Vector
- DNA fingerprinting
Answer. 3. Vector
Question 76. A genetically engineered bacteria used for clearing oil spills is
- Escherischia coli
- Bacillus subtilis
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- Pseudomonas putida
Answer. 4. Pseudomonas putida
Question 77. Who isolated the first restriction endonucleases?
- Temin and Baltimore
- Sanger
- Nathans and Smith
- Paul Berg
Answer. 3. Nathans and Smith
Question 78. Genetic engineering is
- Study of extra-nuclear gene
- Manipulation of genes by artificial method
- Manipulation of RNA
- Manipulation of enzymes
Answer. 2. Manipulation of genes by artificial method
Question 79. Which of the following enzymes cut the DNA molecule at specific nucleotide sequence?
- Restriction endonuclease
- DNA ligase
- RNA polymerase
- Exonuclease
Answer. 1. Restriction endonuclease
Question 80. DNA fingerprinting was invented by
- Karl Mullis
- Alec Jeffery
- Dr. Paul Berg
- Francis Collins
Answer. 2. Alec Jeffery
Question 81. Which structure is involved in genetic engineering?
- Plastid
- Plasmid
- Codon
- None
Answer. 2. Plasmid
Question 82. Which of the following is the example of chemical scissors?
- Eco RI
- HindIII
- Bam I
- All of the above
Answer. 4. All of the above
Question 83. Restriction endonucleases are used in genetic engineering because
- They can degrade harmful proteins
- They can join DNA fragments
- They can cut DNA at variable sites
- They can cut DNA at specific base sequences
Answer. 4. They can cut DNA at specific base sequences
Question 84. Chimeric DNA is
- DNA which contains uracil
- DNA synthesized from RNA
- Recombinant DNA
- DNA which contains single strand
Answer. 3. Recombinant DNA
Question 85. A piece of nucleic acid used to find out a gene by forming hybrid with it is called
- cDNA
- DNA probe
- Sticky end
- Blunt end
Answer. 2. DNA probe
Question 86. Which of the following is the example of direct gene transfer?
- Microinjection
- Electroporation
- Particle gun
- All the above
Answer. 4. All the above
Question 87. How many copies of DNA sample are produced in PCR technique after 6 cycles?
- 4
- 32
- 16
- 64
Answer. 3. 16
Question 88. The basic procedure involved in the synthesis of recombinant DNA molecule is depicted. The mistake in the cedure is procedure is
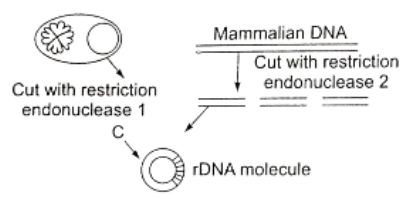
- Enzyme polymerase is not included
- The mammalian DNA is shown double stranded
- Only one fragment is inserted
- Two different restriction enzymes are used
Answer. 4. Two different restriction enzymes are used
Question 89. Western blotting is used for the identification of
- DNA
- RNA
- Protein
- All the above
Answer. 3. Protein
Question 90. In rDNA technique, which of the following technique is not used in introducing DNA into host cell?
- Transduction
- Conjugation
- Transformation
- Electroporation
Answer. 2. Conjugation
Question 91. Which of the following techniques are used in analyzing restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP)?
(a) Electrophoresis
(b) Electroporation
(c) Methylation
(d) Restriction digestion
- (a) and (c)
- (c) and (d)
- (a) and (d)
- (b) and (d)
Answer. 3. (a) and (d)
Question 92. Restriction enzymes are
- Not always required in genetic engineering
- Essential tool in genetic engineering
- Nucleases that cleave DNA at specific sites
- (2) and (3) both
Answer. 4. (2) and (3) both
Question 93. The function of restriction endonuclease enzyme is
- It is useful in genetic engineering
- It protects the bacterial DNA against foreign DNA
- It is helpful in transcription
- It is helpful in protein synthesis
Answer. 2. It protects the bacterial DNA against foreign DNA
Question 94. A bacterium modifies its DNA by adding methyl groups to the DNA. It does so to
- Clone its DNA
- Be able to transcribe many genes simultaneously
- Turn its gene on
- Protect its DNA from its own restriction enzyme
Answer. 4. Protect its DNA from its own restriction enzyme
Question 95. Plasmid has been used as vector because
- It is circular DNA which has capacity to join eukaryotic DNA
- It can move between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
- Both ends show replication
- It has antibiotic resistance gene
Answer. 1. It is circular DNA which has capacity to join eukaryotic DNA
Question 96. Which of the following cuts the DNA from specific places?
- Restriction endonuclease (Eco RI)
- Ligase
- Exonuclease
- Alkaline phosphate
Answer. 1. Restriction endonuclease (Eco RI)
Question 97. The manipulation of DNA in genetic engineering becomes possible due to the discovery of
- Restriction endonuclease
- DNA ligase
- Transcriptase
- Primase
Answer. 1. Restriction endonuclease
Question 98. Restriction enzymes
- Are endonucleases which cleave DNA at specific sites
- Make DNA complementary to an existing DNA or RNA
- Cut or join DNA fragments
- Are required in vector-less direct gene transfer
Answer. 1. Are endonucleases which cleave DNA at specific sites
Question 99. DNA fingerprinting refers to
- Techniques used for the identification of fingerprints of individuals
- Molecular analysis of profiles of DNA samples
- Analysis of DNA samples using imprinting devices
- Techniques used for molecular analysis of different specimens of DNA
Answer. 2. Molecular analysis of profiles of DNA samples
Question 100. Restriction endonucleases
- Are synthesized by bacteria as part of their defense compound
- Are present in mammalian cells for degradation of DNA when the cell dies
- Are used in genetic engineering for ligating two DNA molecules
- Are used for in vitro DNA synthesis
Answer. 1. Are synthesized by bacteria as part of their defense compound
Question 101. What is the first step in the Southern blot technique?
- Denaturation of DNA on the gel for hybridization with specific probe.
- Production of a group of genetically identical cells.
- Digestion of DNA by restriction enzyme.
- Isolation of DNA from a nucleated cell such as the one from the scene of crime.
Answer. 1. Denaturation of DNA on the gel for hybridization with specific probe.
Question 102. Which of the following is not produced by E. coli in lactose?
- B-galactosidase
- Thiogalactoside transacetylase
- Lactose dehydrogenase
- Lactose permease
Answer. 3. Lactose dehydrogenase
Question 103. The technique of transferring DNA fragment separated on agarose gel to a synthetic membrane such as nitrocellulose is known as
- Northern blotting
- Southern blotting
- Western blotting
- Dot blotting
Answer. 2. Southern blotting
Question 104. The production of a human protein in bacteria in genetic engineering is possible because
- Bacterial cell can carry out RNA splicing reactions
- The mechanism of gene regulation is identical in humans and bacteria
- Human chromosome can replicate in bacterial cell
- Genetic code is universal
Answer. 4. Genetic code is universal
Question 105. Electroporation procedure involves
- Fast passage of food through sieve pores in phloem elements with the help of electric stimulation
- Opening of stomatal pores during night by artificial light
- Making transient pores in the cell membrane to introduce gene constructs
- Purification of saline water with the help of a membrane system
Answer. 3. Making transient pores in the cell membrane to introduce gene constructs
Question 106. The total number of nitrogenous bases in human genome is estimated to be about
- 3.5 million
- 35 thousand
- 35 million
- 3.1 billion
Answer. 4. 3.1 billion
Question 107. Two microbes found to be very useful in genetic engineering are
- Escherichia coli and Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- Vibro cholerae and a tailed bacteriophage
- Diplococcus sp. and Pseudomonas sp.
- Crown gall bacterium and Caenorhabdits elegans
Answer. 1. Escherichia coli and Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Question 108. Restriction endonuclease
- Cuts the DNA molecule randomly
- Cuts the DNA molecule at specific sites
- Restricts the synthesis of DNA inside the nucleus
- Synthesizes DNA
Answer. 2. Cuts the DNA molecule at specific sites
Question 109. The restriction enzyme Eco RI has the property of
- Endonuclease activity
- Exonuclease activity
- Ligation activity
- Correcting the topology of replicating DNA
Answer. 1. Endonuclease activity
Question 110. DNA ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the
- Splitting of DNA threads into small bits
- Joining of the fragments of DNA
- Denaturation of DNA
- Synthesis of DNA
Answer. 2. Joining of the fragments of DNA
Question 111. More advancement in genetic engineering is due to
- Restriction endonuclease
- Reverse transcriptase
- Protease
- Zymase
Answer. 1. Restriction endonuclease
Question 112. The function of PCR is
- Translation
- Transcription
- DNA amplification
- None of these
Answer. 3. DNA amplification
Question 113. Which of the following is used as the best genetic vector?
- Bacillus thuriengenesis
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- Pseudomonas putida
- All of these
Answer. 2. Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Question 114. The transfer of protein from electrophoretic gel to nitrocellulose membrane is known as
- Transferase
- Northern blotting
- Western blotting
- Southern blotting
Answer. 3. Western blotting
Question 115. DNA fingerprinting was first discovered by
- Alec Jeffery
- Cark Mullis
- C. Milstein
- Dr. Paul Berg
Answer. 1. Alec Jeffery
Question 116. Which of the following enzyme is used to join DNA fragments?
- Terminase
- Endonuclease
- Ligase
- DNA polymerase
Answer. 3. Ligase
Question 117. Restriction endonucleases are enzymes which
- Make cuts at specific positions within the DNA molecule
- Recognize a specific nucleotide sequence for binding of DNA ligase
- Restrict the action of enzyme DNA polymerase
- Remove nucleotides from the ends of the DNA molecule
Answer. 1. Make cuts at specific positions within the DNA molecule
Question 118. Satellite DNA is a useful tool in
- Organ transplantation
- Sex determination
- Forensic science
- Genetic engineering
Answer. 3. Forensic science
Question 119. PCR and restriction fragment length polymorphism are the methods for
- Genetic transformation
- DNA sequencing
- Genetic fingerprinting
- Study of enzymes
Answer. 3. Genetic fingerprinting
Question 120. Which one is a true statement regarding DNA polymerase used in PCR?
- It serves as a selectable marker.
- It is isolated from a virus.
- It remains active at high temperature.
- It is used to ligate introduced DNA in recipient cells.
Answer. 3. It remains active at high temperature.
Question 121. For transformation, microparticles coated with DNA to be bombarded with gene gun are made up of
- Platinum or zinc
- Silicon or platinum
- Gold or tungsten
- Silver or platinum
Answer. 3. Gold or tungsten
Question 122. A single strand of nucleic acid tagged with a radioactive molecule is called
- Selectable marker
- Plasmid
- Probe
- Vector
Answer. 3. Probe
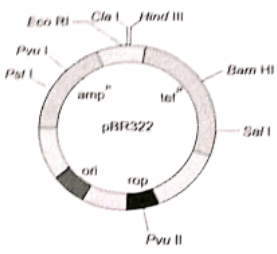
Question 123. The following figure is the diagrammatic representation of the E. coli vector PBR 322. Which one of the given options correctly identifies its certain component(s)?
- rop-reduced osmotic pressure
- Hind III, Eco RI-selectable markers
- ampR, tetR-antibiotic resistance genes
- ori-original restriction enzyme
Answer. 3. ampR, tetR-antibiotic resistance genes
Question 124. Which one of the following is a case of wrong matching?
- Vector DNA: Site for tRNA synthesis
- Micropropagation: In vitro production of plants in large numbers
- Callus: Unorganized mass of cells produced in tissue culture
- Somatic hybridization: Fusion of two diverse cells
Answer. 1. Vector DNA: Site for tRNA synthesis
Question 125. Biolistics (gene gun) is suitable for
- Disarming pathogen vectors
- Transformation of plant cells
- Constructing recombinant DNA by joining with vectors
- DNA fingerprinting
Answer. 3. Constructing recombinant DNA by joining with vectors
Question 126. In genetic engineering, the antibiotics are used
- As selectable markers
- To select healthy vectors
- As sequences from where replication starts
- To keep the cultures free of infection
Answer. 1. As selectable markers
Question 127. What is it that forms the basis of DNA fingerprinting?
- The relative proportions of purines and pyrimidines in DNA.
- The relative difference in the DNA occurrence in blood, skin, and saliva.
- The relative amount of DNA in the ridges and grooves of fingerprints.
- Satellite DNA occurring as highly repeated short DNA segments.
Answer. 4. Satellite DNA occurring as highly repeated short DNA segments.
Question 128. The following figure shows three steps (A)-(C) of PCR. Select the option giving correct identification together with what it represents?

Options:
- B-Denaturation at a temperature of about 98°C separating the two DNA strands
- A-Denaturation at a temperature of about 50°C
- C-Extension in the presence of heat stable DNA polymerase
- A-Annealing with two sets of primers
Answer. 3. C-Extension in the presence of heat stable DNA polymerase
Question 129. Which one of the following represents a palindromic sequence in DNA?
- 5′-GAATTC-3′; 3′- CTTAAG-5′
- 5′-CCATCC-3′; 3′-GAATCC-5′
- 5′-CATTAG-3′; 3′-GATAAC-5′
- 5′-GATACC-3′; 3′-CCTAAG-5′
Answer. 1. 5′-GAATTC-3′; 3′- CTTAAG-5′
Question 130. DNA fragments generated by restriction endonucleases in a chemical reaction can be separated by
- Polymerase chain reaction
- Electrophoresis
- Restriction mapping
- Centrifugation
Answer. 2. Electrophoresis
Question 131. The colonies of recombinant bacteria appear white in contrast to the blue colonies of non-recombinant bacteria because of
- Insertional inactivation of alpha-galactosidase in non-recombinant bacteria
- Insertional inactivation of alpha-galactosidase in recombinant bacteria
- Inactivation of glycosidase enzyme in recombinant bacteria
- Non-recombinant bacteria containing beta-galactosidase
Answer. 4. Non-recombinant bacteria containing beta-galactosidase
