NEET Biology For Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Which of the following structures is not supported by incomplete cartilaginous rings?
- Trachea
- Secondary bronchi
- Terminal bronchioles
- Primary bronchi
Answer: 3. Trachea
Question 2. Teacher is a straight tube extending up to the mid-thoracic cavity, which divides at the level of
- Second cervical vertebra
- Fifth cervical vertebra
- Fifth thoracic vertebra
- Fifth lumbar vertebra
Answer: 3. Fifth thoracic vertebra
Question 3. The outer pleural membrane is in close contact with
- Surface of lungs
- Thoracic cavity
- Both (1) and (2)
- Alveoli.
Answer: 2. Thoracic cavity
Question 4. The volume of air remaining in the lungs even after a forcible expiration is
- Expiratory reserve volume
- Expiratory capacity
- Residual volume
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 3. Residual volume
Question 5. The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration is
- Vital capacity
- ERV + TV + JRV
- TLC + RV
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 6. Which of the following statements is incorrect w.r.t. the mechanism of breathing?
- The movement of air into and out of the lungs is carried out by creating a pressure gradient between the lungs and the atmosphere.
- Inspiration is initiated by the contraction of the diaphragm which increases the volume of the thoracic chamber.
- The contraction of external intercostal muscles lifts up the ribs and sternum causing a decrease in the volume of the thoracic chamber.
- On average, a healthy human breathes 12-16 times/ min.
Answer: 3. The contraction of external intercostal muscles lifts up the ribs and sternum causing a decrease in the volume of the thoracic chamber.
Question 7. The thoracic cage of man is formed of
- Ribs and sternum
- Ribs, sternum, and thoracic vertebrae
- Ribs, sternum, and lumbar vertebrae
- Ribs and thoracic vertebrae
Answer: 2. Ribs, sternum, and thoracic vertebrae
Question 8. The Trachea is lined with incomplete rings of
- Fibrous cartilage
- Calcified cartilage
- Elastic cartilage
- Hyaline cartilage
Answer: 4. Hyaline cartilage
Question 9. Lungs have a large number of alveoli for
- Having a spongy texture and proper shape
- More surface area for diffusion of gases
- More space for increasing the volume of inspired air
- More nerve supply
Answer: 2. More surface area for diffusion of gases
Question 10. In mammals, ventilation movements of the lungs are governed by
- Muscular wall of lungs
- Intercostal muscles
- Diaphragm
- Diaphragm and intercostal muscles
Answer: 4. Diaphragm and intercostal muscles
Question 11. What will be the po2 and pco2 in the atmospheric air as compared to those in the alveolar air?
- Po2 lesser, pco2 higher
- Po2 higher, pco2 lesser
- Po2 higher, pco2 higher
- Po2 lesser, pco2 lesser
Answer: 2. po2 higher, pco2 lesser
” respiratory system questions”
Question 12. What is the partial pressure of oxygen and carbon dioxide in atmospheric air?
- Po2 159 mm Hg,pco20.3 mm Hg
- Po2 104 mm Hg, pco2 40 mm Hg
- Po2 40 mm Hg,pCo245 mm Hg
- Po2 95 mm Hg,/>Co2 40 mm Hg
Answer: 1. po2 159 mm Hg,pco20.3 mm Hg
Question 13. Diffusion membrane is made up of which of the following layers?
- Thin squamous epithelium of alveoli
- Basement membrane
- Endothelium of alveolar capillaries
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 14. Which of the following statements is incorrect about the transport of gases?
- About 97% of O2 is transported by RBCs in the blood.
- About 3% of O2 is carried in a dissolved state in the plasma.
- About 20-25% of CO2 is transported by RBCs.
- About 70% of carbon dioxide is carried in a dissolved state in plasma.
Answer: 4. About 70% of carbon dioxide is carried in a dissolved state in plasma.
Question 15. The binding of oxygen with hemoglobin is primarily related to which of the following factors?
- Partial pressure of CO2
- Partial pressure of O2
- Hydrogen ion concentration
- Temperature
Answer: 2. Partial pressure of O2
Question 16. Which of the following factors are favorable for the formation of oxyhemoglobin?
1. High po2, low pco2
2. Lesser H1 concentration, lower temperature
3. Low Po2, high CO2
4. High Hf, higher temperature
- 1 only
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 3 and 4
Answer: 2. 1 and 2
Question 17. Under which conditions the oxygen dissociation curve will move towards the right?
- Low po2
- High Co2
- High H+ concentration and higher temperature
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 18. Tick mark the incorrect statement.
- Every 100 mL of deoxygenated blood delivers approximately 4 mL of CO2 to the alveoli.
- Carbonic anhydrase is present in very high concentrations in RBC.
- High pco2 and low po2 in tissues help in the binding of carbon dioxide.
- CO2 is carried in hemoglobin as carboxyhemoglobin.
Answer: 4. CO2 is carried in hemoglobin as carboxyhemoglobin.
Question 19. Carbon dioxide is carried in the blood mainly as
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Potassium bicarbonate
- Carbamino-hemoglobin
- Dissolved gas in plasma
Answer: 1. Sodium bicarbonate
Question 20.The hemoglobin of a human fetus
- Has higher affinity for oxygen than that of an adult
- Has a lower affinity for oxygen than that of an adult
- Has the same affinity for oxygen as an adult
- Has two protein sub-units instead of four
Answer: 1. Has a higher affinity for oxygen than that of an adult
Question 21. Ring-like cartilage of the larynx is known as
- Thyroid cartilage
- Arytenoid cartilage
- Cricoid cartilage
- Cartilage of Santorini
Answer: 3. Cricoid cartilage
Question 22. Which of the following prevents the collapsing of the trachea?
- Muscles
- Diaphragm
- Ribs
- Cartilaginous rings
Answer: 4. Cartilaginous rings
Question 23. The trachea is lined with incomplete rings of
- Fibrous cartilage
- Calcified cartilage
- Elastic cartilage
- Hyaline cartilage
Answer: 4. Hyaline cartilage
Question 24. The number of alveoli in the human lungs has been estimated to be approximately
- 100 million
- 300 million
- 125 million
- 300 billion
Answer: 2. 300 million
Question 25. In humans, the oblique fissure is present in
- Right lung
- Left lung
- Both of these
- None of these
Answer: 3. Both of these
Question 26. The covering of the lung is called
- Pericardium
- Perichondrium
- Pleural membrane
- Peritoneum
Answer: 3. Pleural membrane
Question 27. The terminal bronchiole is lined by
- Simple squamous epithelium
- Ciliated columnar or cuboidal epithelium
- Stratified epithelium
- Pseudostratified epithelium
Answer: 2. Ciliated columnar or cuboidal epithelium
Question 28. Which of the following muscles contracts during normal expiration?
- Internal intercostal muscles
- Diaphragm
- Abdominal muscles
- None of these
Answer: 4. None of these
Question 29. Chest movements are inconspicuous during
- Normal breathing
- Abdominal breathing
- Thoracic breathing
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 30. Tidal volume is
- The volume of air breathed in or out in one normal inspiration/expiration
- The volume of air breathed out by forced expiration alters normal inspiration
- The volume of air breathed out by forced expiration after forced inspiration
- The volume of air that remains in the lungs even after maximum expiration
Answer: 1. The volume of air breathed in or out in one normal inspiration/expiration
Question 31. Which of the following pulmonary volumes cannot be measured by spirometer directly?
- Nodal volume
- Vital capacity
- Inspiratory capacity
- Residual volume
Answer: 4. Residual volume
Question 32. Ribs move outward during respiration with
- Intercostal muscles
- Petrohyal muscles
- Pharyngeal muscles
- None of these
Answer: 1. Intercostal muscles
Question 33. Functional residual capacity (FRC) includes
1. TV
2. IRV
3. RV
4. ERV
- (1) + (3)
- (2) + (4)
- (3) + (4)
- (1) + (2) + (4)
Answer: 3. (3) + (4)
Question 34. If a person exhales forcefully by applying all his efforts, what will be the pulmonary volume inhaled by him immediately under normal conditions without applying any extra effort?
- TV + IRV
- TV only
- TV + ERV
- TV + IRV + ERV
Answer: 3. TV + ERV
Question 35. The pco2 level in the expired air under normal conditions is approximately
- 46 mm of Hg
- 100 mm of Hg
- 32 mm of Hg
- 116 mm of Hg
Answer: 3. 32 mm of Hg
Question 36. Which of the following factors will decrease oxygenation?
- High Hb
- Increased blood flow
- Anemia
- Increased blood volume
Answer: 3. Anemia
Question 37. Which statement is wrong?
- The partial pressure of CO2 (pco2) is higher in the air inside the lungs than inside the venous blood.
- The partial pressure of O2 (po2) is higher in the air inside the lungs than in the arterial blood.
- The partial pressure of CO2 (po2,) is lower inside the venous blood than in the air in the lung.
- The partial pressure of CO2 (pco2) is higher inside the venous blood than in the air.
Answer: 1. The partial pressure of CO2 (pco2) is higher in the air inside the lungs than inside the venous blood.
Question 38. The exchange of gases between alveolar air and alveolar capillaries occurs by
- Osmosis
- Active transport
- Absorption
- Diffusion
Answer: 4. Diffusion
Question 39. The amount of oxygen transported by 1L of blood under strenuous conditions is approximately
- 5 mL
- 50 mL
- 15 mL
- 150 mL
Answer: 4. 150 mL
Question 40. In alveoli, surfactant is produced by
- Type 1 pneumocyte
- Type 2 pneumocyte
- Kupflcr’s cells
- Dust cells
Answer: 2. Type 2 pneumocyte
Question 41. The combination of O2 with hemoglobin can be increased mostly by
- Increasing O2 concentration in air
- Decreasing O2 concentration in blood
- Increasing CO2 concentration in air
- Decreasing CO2 concentration in blood
Answer: 4. Decreasing CO2 concentration in blood
Question 42. The effect of CO2 concentration on the dissociation of oxyhemoglobin was explained by
- G.S. Carter
- Yapp
- William Hoar
- Christian Bohr
Answer: 4. Christian Bohr
Question 43. The oxygen hemoglobin dissociation curve will shift to the right on the decrease of
- Acidity
- Carbon dioxide concentration
- Temperature
- PH
Answer: 4. PH
Question 44. If CO2 level gels increase in the blood, it favors
- Loading of O2 in the blood
- Unloading of O2 from the blood
- Decreased availability of oxygen to tissues
- Both (1) and (3)
Answer: 2. Unloading of O2 from the blood
Question 45.If oxyhemoglobin dissociation curves are drawn for maternal and fetal hemoglobin, which of the following is true?
- The maternal curve will be on the right side
- The fetal curve will be on the right side
- Both will overlap each other
- It will depend upon the Pco2 level
Answer: 1. Maternal curve will be on the right side
Question 46. The reverse of the chloride shift occurs during
- Internal respiration
- External respiration
- Cellular respiration
- Anaerobic respiration
Answer: 2. External respiration
Question 47. The percentage amount of CO2 carried or transported by Hb is
- 10%
- 80%
- 70%
- 23%
Answer: 4. 23%
Question 48.In the process of transport of CO2, which phenomenon occurs between RBCs and plasma?
- Osmosis
- Adsorption
- Chloride shift
- Absorption
Answer: 3. Chloride shift
Question 49. Which of the following can be termed as the opposite of Bohr’s effect?
- Haldane’s effect
- Hamburger’s phenomenon
- Hering-Breuer reflex
- None of these
Answer: 1. Haldane’s effect
Question 50. The impulse for voluntary muscles for forced breathing starts in
- Cerebellum
- Medulla
- Vagus nerve
- Cerebrum
Answer: 4. Cerebrum
Question 51. The respiratory control center lies in
- Pons
- Medulla oblongata
- Cerebrum
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
“inspiration occurs when “
Question 52. Which of the following statements is wrong?
- The inspiratory center increases the strength of the contraction of rib muscles.
- The pneumatic center controls the switch-off point of inspiration.
- Breathing movements are caused by changes in the concentration of CO2 in the blood.
- The expiratory center lies in pons and inspiratory cen ter lies in medulla.
Answer: 4. The expiratory center lies in the pons and the inspiratory center lies in the medulla.
Question 53. Which of the following controls the switch-off point of inspiration?
- Apneustic center
- Pneumotaxic center
- Pons varolii
- Cerebrum
Answer: 2. Pneumotaxic center
Question 54. Which of the following is not possible when the pneumatic center is sending a strong signal?
- The rate of breathing increases
- Complete filling of lungs
- Decreased duration of inspiration
- Decreased duration of expiration
Answer: 2. Complete filling of lungs
Question 55. Overstretching of the lungs is prevented due to
- Bohr’s effect
- Hering-Breuer reflex
- Conditioned reflex
- Haldane’s effect
Answer: 2. Hering-Breuer reflex
Question 56. The rate and depth of respiration shall increase when
- Oxygen concentration increases
- CO2 concentration increases in alveolar air
- Bicarbonate concentration increases
- Bicarbonate concentration decreases
Answer: 2. CO2 concentration increases in alveolar air
Question 57. The “mountain sickness” in persons climbing to high altitudes without any aid of oxygen cylinders is due to
- Anemic hypoxia
- Arterial hypoxia
- Lack of sufficient amount of hemoglobin
- Lack of a sufficient number of erythrocytes
Answer: 2. Arterial hypoxia
Question 58. Cyanide poisoning will lead to
- Hypoxic hypoxia
- Histotoxic hypoxia
- Stagnant hypoxia
- Anemic hypoxia
Answer: 2. Histotoxic hypoxia
Question 59. Asthma is caused to
- Infection of trachea
- Infection of lungs
- Bleeding into the pleural cavity
- Spasm in bronchial muscles
Answer: 4. Spasm in bronchial muscles
Question 60. Which of the following is related to occupational lung disease?
- Silicosis
- Asbestosis
- Fibrosis of the upper part of the lung
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 61. The breakdown of the alveoli of the lungs resulting in the reduced surface area for gas exchange is known as
- Emphysema
- Sneezing
- Pneumonia
- Tuberculosis
Answer: 1. Emphysema
Question 62. If the thorax is injured and the pleura is damaged, the air enters the pleural cavity and the lungs are collapsed. This condition is known as
- Hyponea
- Orthopnea
- Dyspnea
- Pneumothorax
Answer: 4. Pneumothorax
Question 63. Protective respiratory blast is
- Hiccupping
- Coughing
- Sneezing
- None of these
Answer: 3. Sneezing
Question 64. Low oxygen tension in the blood causes
- Coughing
- Hiccups
- Sneezing
- Yawning
Answer: 4. Yawning
Question 65.Disorder/disease related to the bubbling of N2 in the blood resulting in pain or severe problems is
- Caisson’s disease
- Cheyne-stokes respiration
- Hypopnea
- Asthma
Answer: 1. Caisson’s disease
Question 66. With the increase in temperature, the respiratory rate will
- Increase
- Decrease rapidly
- Remain unaffected
- Decrease slowly
Answer: 1. Increase
Question 67. Which of the following gases makes the most stable combination with the hemoglobin of red blood cells?
- CO2
- CO
- O2
- N2
Answer: 2. CO
Question 68. One of the following is not a respiratory pigment.
- Hemoglobin
- Chlorocruorin
- Hemocyanin
- Hemozoin
Answer: 4. Hemozoin
Question 69. Pneumonia can be caused by
- Bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
- Protozoan
- Fungi
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 70. Asbestosis or silicosis is characterized by the proliferation of fibrous tissue in
- Respiratory tract
- The upper part of the lung
- The lower part of the lung
- Pulmonary capillary
Answer: 2. Upper part of a lung
Question 71. The respiratory system is derived from
- Endoderm
- Mesoderm
- Ectoderm
- None of these
Answer: 1. Endoderm
Question 72. Which of the following is false?
- Blood from the right side of the heart is carried to the lungs by the pulmonary artery.
- Pleura is double covering of the kidney.
- The pancreas is both an exocrine and endocrine gland.
- Scurvy is due to vitamin C deficiency.
Answer: 2. Pleura is a double covering of the kidney.
Question 73. Pericardial fluid is secreted by
- Myocardium
- Parietal peritoneum
- Visceral peritoneum
- None of these
Answer: 3. Visceral peritoneum
Question 74. Vocal cords occur in
- Larynx
- Pharynx
- Glottis
- Bronchial tube
Answer: 1. Larynx
Question 75.Body tissues obtain oxygen from hemoglobin because of its dissociation in tissues caused by
- Low oxygen concentration and high carbon dioxide concentration
- Low oxygen concentration
- Low carbon dioxide concentration
- High carbon dioxide concentration
Answer: 4. High carbon dioxide concentration
Question 76. Lungs have a large number of alveoli for
- Having a spongy texture and proper shape
- More surface area for diffusion of gases
- More space for increasing the volume of inspired air
- More nerve supply
Answer: 2. More surface area for diffusion of gases
Question 77. Respiratory organs in scorpion are
- Gills
- Book lungs
- Skin
- Book gills
Answer: 2. Book lungs
Question 78. Which energy is consumed in breathing?
- Mechanical
- Chemical
- Bioelectrical
- Physical
Answer: 2. Chemical
Question 79. During inspiration, the diaphragm
- Relaxes
- Contracts
- Expands
- Shows no change
Answer: 2. Contracts
Question 80. In which form CO2 is carried in blood?
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Sodium carbonate
- Potassium carbonate
- Magnesium carbonate
Answer: 1. Sodium bicarbonate
Question 81. The vital capacity of the human lung is equal to
- 3500 mL
- 4800 mL
- 500 mL
- 1200 mL
Answer: 2. 4800 mL
Question 82. The type of respiration in mammals is called
- Pulmonary respiration
- Gill respiration
- Cutaneous respiration
- Tracheal respiration
Answer: 1. Pulmonary respiration
Question 83. Normal breathing is called
- Apnea
- Dyspnea
- Eupnea
- Hyperpnca
Answer: 3. Eupnea
Question 84. Mb most strongly combines with
- CO
- O2
- CO2
- O3
Answer: 1. CO
Question 85. Tissue respiration is a process by which
- Carbohydrates are synthesized
- Proteins are broken down
- Fat molecules are metabolized
- Energy is liberated
Answer: 4. Energy is liberated
Question 86. The exchange of gases in lung alveoli occurs through
- Active transport
- Osmosis
- Simple diffusion
- Passive transport
Answer: 3. Simple diffusion
Question 87. CO2 is mainly transported by
- Respiratory pigment
- Dissolution of gases
- O2 taken by tissues
- Bicarbonates
Answer: 2. Dissolution of gases
Question 88. In which form iron is present in hemoglobin?
- Ionic
- Unionic
- Fe2+
- Fe3+
Answer: 3. Fe2+
Question 89. Ventilation/respiratory control is present in
- Medulla oblongata
- Cerebellum
- Cerebrum
- Diencephalon
Answer: 1. Medulla oblongata
Question 90. Match the columns
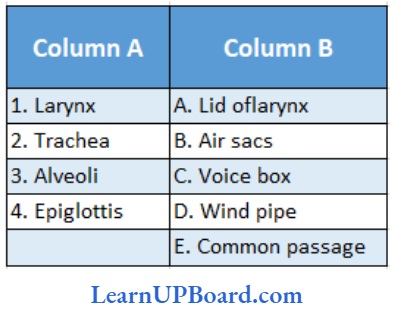
- (1) → (C), (2) → (D), (3) → 4 (B), (4) → (A)
- (1) → 4 (E), (2) → 4 (D), (3) → 4 (A), (4) → 4 (B)
- (1) → 4 (D), (2) → 4 (D), (3) → 4 (B), (4) → 4 (E)
- (1) → 4 (D), (2) → 4 (E), (3) → 4 (B), (4) → 4 (A)
Answer: 1. (1) → (C), (2) → (D), (3) → 4 (B), (4) → (A)
Question 91. The respiratory center is present in
- Cerebrum
- Hypothalamus
- Cerebellum
- Medulla oblongata
Answer: 4. Medulla oblongata
“disorders of respiratory system class 11 “
Question 92. Which of the following is shifted in chloride shift?
- O2 and CO2
- Bicarbonate ions
- CO2
- O2
Answer: 2. Bicarbonate ions
Question 93. Which one of the following is capable of carrying oxygen?
- Plasma
- Blood
- Serum
- Lymph
Answer: 2. Blood
Question 94. Bicarbonate ions can be generated in
- Lymphocytes
- Neutrophil
- Basophil
- RBCs
Answer: 4. RBCs
Question 95. Adam’s apple represents
- Cricoid cartilage
- Thyroid cartilage
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Thyroid cartilage
Question 96. The amount of oxygen which is present in 1g of Hb is
- 1.34 mL
- 13.4 mL
- 134 mL
- 20 mL
Answer: 1. 1.34 mL
Question 97. Book lungs are respiratory organs of
- Mollusca
- Mammals
- Arachnida
- Earthworm
Answer: 3. Arachnida
Question 98. The respiratory center in the brain is stimulated by
- CO2 concentration in venous blood
- O2 concentration in arterial blood
- CO2 concentration in artery blood
- O2 concentration in venous blood
Answer: 3. CO2 concentration in artery blood
Question 99. The energy currency of a cell is
- 10 AMP
- ATP
- Carbohydrates
- NAD
Answer: 2. ATP
Question 100. What can determine the percentage of oxygen earned by Hb?
- PH of blood
- Percentage of CO2
- Partial pressure of oxygen
- All of above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 101. Hamburger’s effect is also known as
- Sodium shift
- Chloride shift
- Lead shift
- None of these
Answer: 2. Chloride shift
Question 102. The correct order of structures through which the ait- passes in the body is
- Nasal cavity, larynx, trachea, bronchi air sacs
- Bronchi, nasal cavity, larynx, trachea air sacs
- Larynx bronchi, nasal cavity, trachea air sacs
- Nasal cavity, trachea, larynx, bronchi air sacs
Answer: 1. Nasal cavity, larynx, trachea, bronchi air sacs
Question 103. During inspiration,
- The diaphragm gets raised and the ribs get lowered
- Both the diaphragm and ribs get lowered
- Ribs get raised and the diaphragm gets lowered
- The diaphragm gets flattered and ribs get raised
Answer: 4. The diaphragm gets flattered and ribs get raised
Question 104. Which one of the following can respire in the absence of oxygen?
- Amoeba
- Tapeworm
- House fly
- Hydra
Answer: 2. Tapeworm
Question 105.When CO2 concentration in the blood increases, breathing becomes
- Slow and deep
- Faster and deeper
- Shallower and slow
- There is no effect on breathing
Answer: 2. Faster and deeper
Question 106. The ascent of high mountains may cause altitude sickness in men. The prime cause of this is
- Excess of CO2 in blood
- Decreased efficiency of hemoglobin
- Decreased partial pressure of oxygen
- Decreased proportion of oxygen in the air
Answer: 3. Decreased partial pressure of oxygen
Question 107. In the lungs, there is a definite exchange of ions between RBC and plasma. Removal of CO2 from blood involves
- Efflux of Cl– ions from RBC
- An influx of Cl– ions into RBC
- An influx of HCO3– ions into RBC
- Efflux of HCO3– ions from RBC
Answer: 1. Efflux of Cl ions from RBC
Question 108. Which enzyme is most abundantly found in RBC?
- Carbonic anhydrase
- Hemoglobin
- Albumin
- Thrombinasc
Answer: 1. Carbonic anhydrase
Question 109. The combination of O2 with hemoglobin can be increased mostly by
- Decreasing O2 concentration in blood
- Increasing O2 concentration in the air
- Increasing CO2 concentration in air
- Decreasing CO2 concentration in air
Answer: 2. Increasing O2 concentration in the air
Question 110. SARS is caused by the variant of
- Pneumococcus pneumonia
- Common cold coronavirus
- Asthma
- Bronchitis
Answer: 2. Common cold coronavirus
Question 111. Pleurisy is the disease of
- Liver
- Heart
- Lungs
- Kidneys
Answer: 3. Lungs
Question 112. At higher altitudes, a man suffers much from
- Cold
- Oxygen deficiency
- Higher atmospheric pressure
- Ultraviolet radiations
Answer: 2. Oxygen deficiency
Question 113. Tuberculosis in men is caused by
- Tuberculosis virus
- Streptococci
- Staphylococci
- Tuberculosis bacillus
Answer: 4. Tuberculosis bacillus
Question 114. Asthma is a respiration disease caused due to
- Infection of lungs
- Tracheal infection
- Bleeding in the pleural cavity
- Cramps in the bronchial muscles obstructing the air passage
Answer: 4. Cramps in the bronchial muscles obstructing the air passage
Question 115. The exchange of gases in lung alveoli occurs through
- Active transport
- Osmosis
- Simple diffusion
- Passive transport
Answer: 3. Simple diffusion
Question 116. Vocal cords occur in
- Pharynx
- Larynx
- Glottis
- Bronchial tube
Answer: 2. Larynx
Question 117. Adam’s apple represents
- Arytenoid cartilage of larynx
- Cricoid cartilage of larynx
- Thyroid cartilage of larynx
- All the above
Answer: 4. All the above
Question 118. The respiratory center of the brain is stimulated by
- Carbon dioxide content in venous blood
- Carbon dioxide content in arterial blood
- Oxygen content in venous blood
- Oxygen content in arterial blood
Answer: 2. Carbon dioxide content in arterial blood
Question 119. Carbon dioxide entering erythrocytes reacts with water to form carbonic acid. The enzyme is
- Carbonic anhydrase
- Carboxypeptidase
- Hydrolase
- Oxidoreductase
Answer: 1. Carbonic anhydrase
Question 120. Arytenoid cartilage is found in
- Hyoid
- Sternum
- Larynx
- Nose
Answer: 3. Larynx
Question 121. At the time of expiration, the diaphragm becomes
- Oblique
- Normal
- Flattened
- Dome-shaped
Answer: 4. Dome-shaped
Question 122. The exchange of bicarbonates and chloride ions between RBC and plasma is called
- Chloride shift
- Bohr’s effect
- Haldane’s effect
- Intracellular respiration
Answer: 1. Chloride shift
Question 123.When CO2 concentration in the blood increases, breathing becomes
- There is no effect on breathing
- Slow and deep
- Faster
- Shallower and slow
Answer: 3. Faster
Question 124. If CO2 concentration increases in the blood, then breathing will
- Increases
- Decrease
- Stop
- Remain unchanged
Answer: 1. Increases
Question 125. Hering-Breuer reflex is related to the
- Effect of pH on respiratory center
- Effect of CO2 on Respiratory Center
- Effect of nerves on respiratory center
- Effect of temperature on respiratory center
Answer: 3. Effect of nerves on respiratory center
Question 126. The toxic effect of carbon monoxide is due to its greater affinity for hemoglobin as compared to oxygen
- 2 times
- 20 times
- 200 times
- 300 times
Answer: 4. 200 times
Question 127. CO2 is transported mainly by
- Plasma
- Carbonic acid
- Bicarbonate
- Carboxyhemoglobin
Answer: 3. Bicarbonate
Question 128. By which mechanism, is oxygen r, transported from the lung to cells
- Diffusion
- Facilitated diffusion
- Transpiration
- Osmosis
Answer: 1. Diffusion
Question 129. Why is CO poisonous for man?
- CO affects the nerves of the lungs.
- CO affects the diaphragm and intercostal muscles.
- CO reacts with oxygen reducing a percentage of O2 in air.
- Hemoglobin combines with CO instead of O2 and the product cannot dissociate,
Answer: 4. Hemoglobin combines with CO instead of O2 and the product cannot dissociate,
Question 130. One hemoglobin carries how many molecules of O2?
- 4
- 2
- 6
- 8
Answer: 1. 4
Question 131. The respiratory center is present in
- Cerebellum
- Cerebrum
- Medulla oblongata
- Hypothalamus
Answer: 3. Medulla oblongata
Question 132. After deep inspiration, the capacity of maximum expiration of the lung is called
- Total lung capacity
- Functional residual capacity
- Vital capacity
- Inspiratory capacity
Answer: 3. Vital capacity
Question 133. Pneumotaxic center is present in
- Cerebrum
- Cerebellum
- Medulla oblongata
- Pons Varolii
Answer: 4. Pons Varolii
Question 134. Hamburger’s shift is also known as
- Bicarbonate shift
- Chloride shift
- Potassium shift
- All of these
Answer: 2. Chloride shift
Question 135. Hemoglobin shows maximum affinity with
- Carbon monoxide
- Carbon dioxide
- Oxygen
- Ammonia
Answer: 1. Carbon monoxide
Question 136. The dissociation curve shifts to the right when
- CO2 concentration decreases
- CO2 concentration increases
- O2 concentration decrease
- Cl concentration increases
Answer: 2. CO2 concentration increases
Question 137. The epithelium of bronchioles is
- Pseudostratified and columnar
- Squamous and sensory
- Pseudostratified and sensory
- Cuboidal and columnar
Answer: 2. Squamous and sensory
Question 138. If a man from the coast goes to Everest Peak, then
- His breathing and heartbeat will increase
- His breathing and heartbeat will decrease
- His respiratory rate will decrease
- His heartbeat will decrease
Answer: 1. His breathing and heartbeat will increase
Question 139. The structure which prevents the entry of food into the windpipe is
- Gullet
- Glottis
- Tonsil
- Epiglottis
Answer: 4. Epiglottis
Question 140. In which of the following animals, respiration occurs without a respiratory organ?
- Fish
- Cockroach
- Tadpole
- Earthworm
Answer: 4. Earthworm
Question 141. Carbonic anhydrase is found in high concentrations in
- Leucocytes
- Blood plasma
- Erythrocytes
- Lymphocytes
Answer: 3. Erythrocytes
Question 142. What would happen if human blood becomes acidic (low pH)?
- The oxygen-carrying capacity of hemoglobin increases.
- The oxygen-carrying capacity of hemoglobin decreases.
- RBC count increases.
- RBC count decreases.
Answer: 2. Oxygen-carrying capacity of hemoglobin decreases.
Question 143. Dissociation of oxyhemoglobin can be promoted by
- Low blood pH
- High body temperature
- Low body temperature
- High blood pH
Answer: 2. High body temperature
Question 144. Which of the following is correct regarding respiration?
- No organism can live without respiration.
- It takes place at every time day and night.
- It involves the production of carbon dioxide and water.
- All of these.
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 145. Respiratory coefficient is
- The amount of CO2 produced to O2 absorbed.
- The amount of O2 obtained to the amount of O2 consumed.
- Always more than one.
- Always less than one.
Answer: 1. The amount of CO2 produced to O2 absorbed.
Question 146. Dyspnea is the
- Normal breathing
- Difficult breathing
- Rapid breathing
- Stage without breathing
Answer: 2. Difficult breathing
Question 147. Oxygen carrier or respiratory pigment in the blood of frogs and other vertebrates is
- Hemocyanin
- Cytochrome
- Hemoglobin
- None of these
Answer: 3. None of these
Question 148. During the transport of CO2, blood does not become acidic due to
- Neutralization of H2CO3 by Na2CO3
- Absorption by leucocytes
- Blood buffers
- Non-accumulation
Answer: 3. Blood buffers
Question 149. The respiratory center, which regulates respiration, is located in
- Cerebral peduncle
- Vagus nerve
- Pons
- Medulla oblongata
Answer: 4. Medulla oblongata
Question 150. The respiratory mechanism is controlled by
- Central nervous system
- Sympathetic nervous system
- Parasympathetic nervous system
- Autonomic nervous system
Answer: 1. Central nervous system
Question 151. Low oxygen tension in the blood causes
- Coughing
- Yawning
- Hiccupping
- Sneezing
Answer: 2. Yawning
Question 152. The oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve is
- Sigmoid
- Hyperbolic
- Straight line
- Parabolic
Answer: 1. Sigmoid
Question 153. The affinity of CO with Hb is more than oxygen by
- 2 times
- 20 times
- 200 times
- 2000 times
Answer: 3. 200 times
Question 154. The exchange of gases in the lungs is by
- Simple diffusion
- Active transport
- Passive transport
- Osmosis
Answer: 1. Simple diffusion
Question 155. The covering of the lungs is called
- Pleura
- Pericardia
- Peritoneum
- Mediastinum
Answer: 1. Pleura
Question 156. The hamburger phenomenon is also known as
- Calcium shift
- Bohr effect
- Chloride shift
- Na+-K+ pump
Answer: 3. Chloride shift
Question 157. Even when there is no air in it, the human trachea does not collapse due to the presence of %
- Bony rings
- Turgid pressure
- Chitinous rings
- Cartilaginous rings
Answer: 4. Cartilaginous rings
Question 158. The specialty common in the alveoli of the lungs and villi of the intestine in mammals is that both
- Provide a large surface area
- Have ciliated epithelium
- Are suited for diffusion of gases
- Have a rich supply of blood vessels and lymph ducts
Answer: 1. Provide a large surface area
Question 159. The movement of true vocal cords in man is controlled by cartilage
- Arytenoids
- Cricoid
- Thyroid
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 1. Arytenoids
Question 160. The presence of a large number of alveoli around alveolar ducts opening into bronchioles in mammalian lungs is
- Inefficient system of ventilation with little residual air
- Inefficient system of ventilation with a high percentage of residual air
- Efficient system of ventilation with no residual air
- Efficient system of ventilation with little residual air
Answer: 4. Efficient system of ventilation with little residual air
Question 161. The sites of gaseous exchange in the lungs are
- Tracheoles
- Alveoli
- Bronchioles
- Pulmonary chambers
Answer: 2. Alveoli
Question 162. Exposure to carbon monoxide (from coal gas) is extremely dangerous and can kill a patient because
- The compound carboxy-hemoglobin is formed with hemoglobin which can gradually clot the blood resulting in circulatory failure.
- Carboxyhemoglobin reduces the ability of blood to transport oxygen by rupturing a vast majority of erythrocytes.
- Carboxyhemoglobin greatly modifies the structure of hemoglobin, thus making it lose its affinity for oxygen.
- The compound formed, carboxy-hemoglobin does not allow RBCs to act for their respiratory function.
Answer: 2. Carboxyhemoglobin reduces the ability of blood to transport oxygen by rupturing a vast majority of erythrocytes.
Question 163. During inspiration, the diaphragm
- Relaxes to become dome-shaped
- Contracts and flattens
- Expands
- Shows no change
Answer: 2. Contracts and flattens
Question 164. Which is correct?
- Respiratory centers are not affected by CO2
- In humans, vital capacity is just double the expiratory volume.
- A human lung has 1000 alveoli.
- During inspiration, the lungs act as a suction pump.
Answer: 4. During inspiration, the lungs act as a suction pump.
Question 165. In the lungs, the air is separated from the venous blood through
- Squamous epithelium + Endothelium of blood vessel
- Squamous epithelium + Tunica externa, media, and internet of blood
- Squamous epithelium + Basement membrane + Endo thelium of blood vessels
- None of these
Answer: 3. Squamous epithelium + Basement membrane + Endo thelium of blood vessels
Question 166. Intercostal muscle arc found attached with
- Diaphragm
- Ribs
- Pleura
- Lungs
Answer: 2. Ribs
Question 167. Match the disorders given in column I with symptoms under column II. Choose the answer which gives the correct combination of alphabets with numbers.
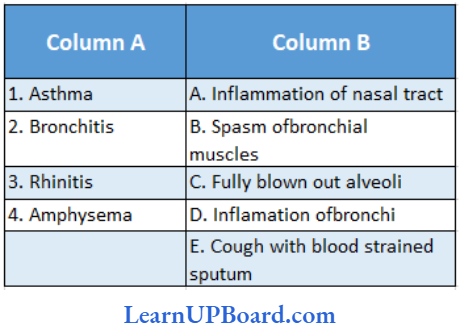
- A = 4, B=2, C = 5, D = 1
- A= 5, B = 3, C = 2, D = 1
- A= 3, B = 1, C = 5, D = 4
- A = 2, B = 4, C = 1, D = 3
Answer: 4. A = 2, B = 4, C = 1, D = 3
“initial bronchioles “
Question 168. In the lungs, there is a definite exchange of ions between RBC and plasma. Removal of CO2 from blood involves
- The influx of Cl– ions into RBC
- The influx of HCO3– tons into RBC
- Efflux of Cl ions from RBC
- Efflux of HCO3– ions from RBC
Answer: 4. Efflux of HCO3– ions from RBC
Question 169. Which one of the following statements is incorrect?
- The presence of non-respiratory air sacs increases the efficiency of respiration in birds.
- In insects, circulating body fluids serve to distribute oxygen to tissues.
- The principle of countercurrent flow facilitates efficient respiration in the gills of fish.
- The residual air in the lungs slightly decreases the efficiency of respiration in mammals.
Answer: 2. In insects, circulating body fluids serve to distribute oxygen to tissues.
Question 170. Consider the following statements:
1. Carbonic anhydrase is present in the erythrocytes
2. In erythrocytes, carbon dioxide combines with water and is transported.
- Statement A is correct and is responsible for Statement B.
- Statement A is not correct, but statement B is correct.
- Both statements A and B are wrong,
- Statement A is correct, but not involved in statement
Answer: 1. Statement A is correct and is responsible for Statement B.
Question 171. Carboxyhemoglobin complex results due to this pollutant?
- CO2
- CO
- H2CO3
- SO2
Answer: 2. CO2
Question 172. Listed below are four respiratory capacities (a-d) and four jumbled respiratory volumes of a normal human adult. Respiratory capacities Respiratory volumes
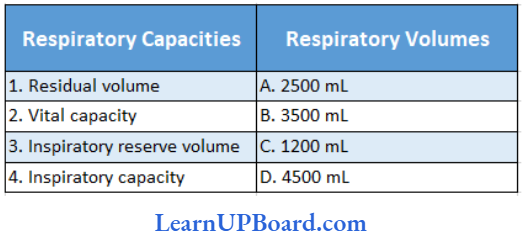
Which one of the following is the correct matching of capacities and volumes?
- 4500 mL, B.3500mL
- 2500 mL, C. 4500mL
- 1200 mL, D.2500mL
- 3500 mL, A. 1200mL
Answer: 4. 3500 mL, A. 1200mL
Question 173. What is true about RBCs in humans?
- They do not cany CO2 at all.
- They cany about 20-25% of CO-,
- They transport 99.5% of O2.
- They transport about 80% oxygen only and the rest 20% of it is transported in a dissolved state in blood plasma.
Answer: 2. They cany about 20-25% of CO-,
Question 174. Which one of the following is the correct statement for respiration in humans?
- Neural signals from the pneumotoxic center in the pons region of the brain can increase the duration of inspiration.
- Workers in grinding and stone-breaking industries may suffer from lung fibrosis.
- About 90% of carbon dioxide (CO2) is carried by hemoglobin as carbamino-hemoglobin.
- Cigarette smoking may lead to inflammation of the bronchi.
Answer: 2. Workers in grinding and stone-breaking industries may suffer from lung fibrosis.
Question 175. The human respiratory system with labels A, B, C, and D. Select the option that gives correct identification and main function and/or characteristic.
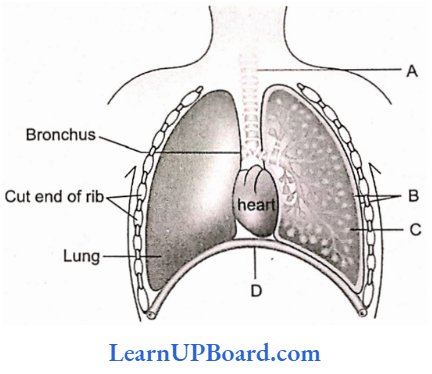
- B—Pleural membrane—Surrounds ribs on both sides to provide cushion against rubbing.
- C—Alveoli—Thin-walled vascular bag-like structures for the exchange of gases.
- D—The lower end of the lungs—Diaphragm pulls it down during inspiration.
- A—Trachea—Long tube supported by complete cartilaginous rings for conducting inspired air
Answer: 2. C—Alveoli—Thin-walled vascular bag-like structures for the exchange of gases.
