NEET Biology For Evolution Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Following is the diagrammatic representation of Miller’s experiment. What is correct labeling? Choose the correct option.
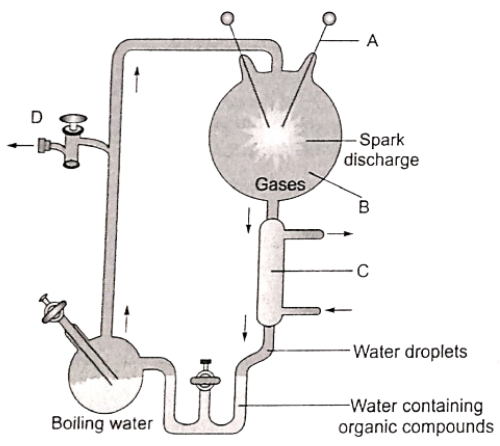
Diagrammatic representation of Miller’s experiment
A B C Ꭰ
Electrodes CH4 + NH3 + H2 + H2O Condenser Vacuum pump
Electrodes NH2 + H2o + CH4 Hot water Trap
Electrodes NH3 + CH4 Steam Trap
Electrodes NH3 + CO2 + H2 + H2O Hot water Vaccum
Answer. 1. Electrodes CH4 + NH3 + H2 + H2O Condenser Vacuum pump
Question 2. Which of the following is not true about coacervates?
- They are protein aggregates.
- They do not have lipid membrane and cannot reproduce.
- The work on coacervates was done by Oparin.
- They are protobionts with polysaccharides, proteins, and water.
Answer. 1. They are protein aggregates.
Question 3. Extraterrestrial origin of life was proposed by the theory of
- Catastrophism
- Spontaneous generation
- Special creation
- Panspermia
Answer. 4. Panspermia
Question 4. Eukaryotes developed around
- 1600 million years ago
- 459 million years ago
- 3800 million years ago
- 4200 million years ago
Answer. 1. 1600 million years ago
Question 5. Simple one-celled cyanobacteria-like organisms appeared on earth
- 5600 million years ago
- 5000 million years ago
- 4600 million years ago
- 3.3 to 3.5 billion years ago
Answer. 4. 3.3 to 3.5 billion years ago
evolution mcq
Question 6. The theory of abiogenesis or spontaneous generation was finally disapproved by
- Louis Pasteur
- A.I. Oparin
- A.R. Wallace
- Sydney Fox
Answer. 1. Louis Pasteur
Question 7. Which of the following experiments suggests that the simplest living organisms could not have originated spontaneously from non-living matter?
- Larvae could appear in decaying organic matter.
- Microbes did not appear in stored meat.
- Microbes appeared from unsterilized organic matter.
- Meat was not spoiled when heated and kept sealed in a vessel.
Answer. 4. Meat was not spoiled when heated and kept sealed in a vessel.
Question 8. The proponent of the theory of spontaneous generation was
- Louis Pasteur
- van Helmont
- Spallanzani
- Francesco Redi
Answer. 2. van Helmont
Question 9. According to the cosmozoic theory, life comes on the earth from other planets in space in the form of
- Spores
- Seeds
- Gametes
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 10. The theory that living organisms on the earth came from outer space is based on the study of
- Igneous rocks
- Sedimentary rocks
- Meteorites
- Moon soil
Answer. 3. Meteorites
Question 11. Which one of the following appeared on the earth with the coming of plants and was absent in the past?
- Carbon dioxide
- Methane
- Ammonia
- Oxygen
Answer. 4. Oxygen
Question 12. The scientist related with the theory of biogenesis and experiments with swan-necked flasks is
- van Helmont
- Louis Pasteur
- Miller
- Haeckel
Answer. 2. Louis Pasteur
Question 13. The atmosphere became oxidizing with the appearance of
- Autotrophic bacteria
- Autotrophic cyanobacteria
- Land plants
- Algae
Answer. 2. Autotrophic cyanobacteria
Question 14. Which one of the following gases was not present in free form at the time life originated on the earth?
- Ammonia
- Oxygen
- Hydrogen
- Methane
Answer. 2. Oxygen
Question 15. An experiment to prove that organic compounds were the basis of life was performed by
- Von Helmont
- Opann
- S. Miller
- Fox
Answer. 3. S. Miller
Question 16. Stanley Miller had put the Oparin-Haldane theory to test in 1953, by creating in the laboratory the probable conditions on the primitive earth. In the experiment, simple amino acids were synthesized from which of the following mixtures, as observed after 18 days?
- H2, O2, N2, and H2O
- CH2, CN, H2, and O2
- H2, NH3, CH4, and water vapor
- NH3, CH4, and O2
Answer. 3. H2, NH3, CH4, and water vapor
Question 17. The English scientist who worked on the origin of life and settled in India is
- A.I. Oparin
- J.B.S. Haldane
- Louis Pasteur
- van Helmont
Answer. 2. J.B.S. Haldane
Question 18. Which ones are the most essential for the origin of life?
- Enzymes
- Proteins
- Carbohydrates
- Nucleic acids
Answer. 4. Nucleic acids
Question 19. The Russian scientist who proposed the theory of origin of life was
- Opann
- Haldane
- Miller
- None of these
Answer. 1. Opann
Question 20. The presence of NaCl in body fluid indicates that life originated in
- Primitive ocean
- Rain-water lakes
- Salt solution
- All of these
Answer. 1. Primitive ocean
Question 21. The origin of life from non-living matter is known as
- Coaoervates
- Abiogenesis
- Biogenesis
- None of these
Answer. 2. Abiogenesis
Question 22. A.I. Oparin wrote
- Origin of Species
- Origin of Life
- Philosophic Zoologique
- The Planet
Answer. 2. Origin of Life
Question 23. The first organisms that appeared on the earth were
- Chemoheterotrophs
- Chemoautotrophs
- Photoautotrophs
- Decomposers
Answer. 1. Chemoheterotrophs
Question 24. The most important condition for the origin of life is the presence of
- Water
- Oxygen
- Nitrogen
- Carbon
Answer. 1. Water
Question 25. H.C. Urey wrote which of the following books?
- The Planets
- Origin of Life
- The Origin of Species
- None of these
Answer. 1. The Planets
Question 26. During the origin and evolution of life, key biological compounds were progressively synthesized in ocean with the help of energy obtainable from
- Lightning
- Ultraviolet light
- Lightning as well as ultraviolet light
- Combustion of certain compounds
Answer. 3. Lightning as well as ultraviolet light
Question 27. Which type of respiration probably arose first?
- Aerobic as it releases more energy
- Anaerobic as it releases more energy
- Aerobic as it is more complex
- Anaerobic as early atmosphere contained little or no oxygen
Answer. 4. Anaerobic as early atmosphere contained little or no oxygen
Question 28. Early atmosphere contained methane and other hydrocarbons. They have been now replaced by
- Nitrogen
- Oxygen
- Carbon dioxide
- Hydrogen
Answer. 3. Carbon dioxide
Question 29. According to the discovery made in 1980’s, RNA can act like enzyme to assemble new RNA molecules on RNA template. Which of the following statements is not proved by this theory?
- Coacervates may not have been the first step in the evolution of life.
- Perhaps the first macromolecule was RNA.
- Coacervates were the basis for the first cell.
- After the formation of RNA, the stability of molecule improved by surrounding RNA within a coacervate.
Answer. 3. Coacervates were the basis for the first cell.
Question 30. The aggregates of artificially produced prebiotic molecules are called
- Protobionts
- Microspheres
- Coacervates
- Prokaryotes
Answer. 1. Protobionts
Question 31. The evolutionary process giving rise to new species adapted to new habitats and ways of life is called adaptive radiation. For example,
- Darwin’s finches in Galapagos Islands
- Australian marsupials that radiated to form new species
- Wolf and Tasmanian wolf
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 32. Humming birds and hawk illustrate
- Convergent evolution
- Homology
- Adaptive radiation
- Parallel evolution
Answer. 3. Adaptive radiation
Question 33. Convergent evolution is illustrated by
- Rat and dog
- Bacterium and protozoan
- Star fish and cuttlefish
- Dog fish and whale
Answer. 4. Dog fish and whale
Question 34. All the following are examples of homologous organs, except
- Arm of man and flipper of whale
- Thorn of Bougainvillea and tendril of Cucurbit
- Eye of an octopus and eye of a mammal
- Brain of frog and man
Answer. 3. Eye of an octopus and eye of a mammal
Question 35. The homologous organs are
- Wings of pigeon and housefly
- Wings of housefly and bat
- Wings of pigeon and forelimbs of man
- Wings of butterfly, bat, and housefly
Answer. 3. Wings of pigeon and forelimbs of man
“evolution class 12 mcq “
Question 36. Anatomically and structurally different but functionally similar structures are called
- Analogous
- Divergent
- Homologous
- Convergent
Answer. 1. Analogous
Question 37. Organs that have similar origin and developmental plan but different functions are called
- Vestigial organs
- Analogous organs
- Homologous organs
- Physiological organs
Answer. 3. Homologous organs
Question 38. Find the odd one out:
- Trunk of an elephant and hand of a chimpanzee
- Ginger and sweet potato
- Wings of bat and insect
- Nails of human beings and claws of a cat
Answer. 4. Nails of human beings and claws of a cat
Question 39. The convergent evolution of two species is usually associated with
- A recent common ancestor
- Analogous organ
- Homologous organ
- Different habitat
Answer. 2. Analogous organ
Question 40. Find the odd one out with respect to evolution.
- Seal’s flipper
- Bat’s wing
- Horse’s foot
- Butterfly’s wings
Answer. 4. Butterfly’s wings
Question 41. Which of the following is not vestigial organ in human beings?
- Rudimentary ear muscles, third molars (wisdom teeth), and body hair
- Coccygeal tail vertebrae and scalp muscles
- Vermiform appendix and nictitating membrane of the eye
- Ear pinna, patella, and olecranon process
Answer. 4. Ear pinna, patella, and olecranon process
Question 42. Which of the following are the vestigial organs of man?
- Hair, olecranon process, coccyx, and patella
- Coccyx, vermiform appendix, and ear muscles
- Wisdom tooth, mammary gland, coccyx, and patella
- Coccyx, hair, ear ossicles, and vermiform appendix
Answer. 2. Coccyx, vermiform appendix, and ear muscles
Question 43. Which of the following is a vestigial organ?
- Vermiform appendex
- Atlas
- Premolars
- Incisors
Answer. 1.Vermiform appendex
Question 44. Which of the following is not a vestigial organ?
- Scalp hair
- Epiglottis
- Vermiform appendix
- Wisdom tooth
Answer. 2. Epiglottis
Question 45. Archaeopteryx is a connecting link between
- Birds and reptiles
- Reptiles and mammals
- Annelids and arthropods
- Amphibians and fishes
Answer. 1. Birds and reptiles
Question 46. The recapitulation theory was put forth by
- Haeckel
- Cuvier
- Wallace
- Lamarck
Answer. 1. Haeckel
Question 47. Gill clefts and notochord appear in the embryonic development of all vertebrates from fishes to mammals. This supports the theory of
- Recapitulation
- Metamorphosis
- Biogenesis
- Abiogenesis
Answer. 1. Recapitulation
Question 48. Cycad and Ginkgo are connecting links between
- Bryophytes and pteridophytes
- Pteridophytes and gymnosperms
- Gymnosperms and angiosperms
- Thallophyla and bryophyla
Answer. 2. Pteridophytes and gymnosperms
Question 49. Which one of the following is not a living fossil?
- Peripatus
- King crab
- Archaeopteryx
- Sphenodon
Answer. 3. Archaeopteryx
Question 50. Haeckel’s biogenetic law states that
- Life originates from lifeless beings
- Course of evolution of a race is repeated in the life- history of an individual
- Progeny of an organism resembles its parents
- Life originates from pre-existing life
Answer. 2. Course of evolution of a race is repeated in the life-history of an individual
Question 51. The presence of tail and coarse hair in human baby is
- Radiation
- Atavism
- Mutation
- Crossing-over
Answer. 2. Atavism
Question 52. Origin of mammal-like reptiles occurred in
- Triassic period
- Permian period
- Jurassic period
- Tertiary period
Answer. 2. Permian period
Question 53. Excreta preserved as a fossil is called as
- Stromatolite
- Compression fossil
- Intact fossil
- Caprolite
Answer. 4. Caprolite
Question 54. Ape-like ancestors of humans appear in epoch
- Pleistocene
- Pliocene
- Miocene
- Oligocene
Answer. 2. Pliocene
Question 55. Which of the following is incorrect match?
- Devonian period-Age of fishes
- Carboniferous period-Age of amphibians
- Ordovician period-Age of invertebrates
- Cretaceous period-Age of reptiles
Answer. 4. Cretaceous period-Age of reptiles
Question 56. Mesozoic era is called the
- Age of fishes
- Age of reptiles
- Age of mammals
- Age of birds
Answer. 2. Age of reptiles
Question 57. Which one of the following is known as age of mammals?
- Mesozoic
- Palaeozoic
- Coenozoic
- Archaeozoic
Answer. 3. Coenozoic
Question 58. First mammals appeared around
- 459 million years ago
- 220 million years ago
- 1600 million years ago
- 3800 million years ago
Answer. 2. 220 million years ago
Question 59. Which of the following arrangement of periods of Mesozoic era gives a correct sequence from the earliest to the latest?
- Jurassic, Triassic, Cretaceous
- Triassic, Jurassic, Cretaceous
- Permian, Jurassic, Triassic
- Devonian, Permian, Jurassic
Answer. 2. Triassic, Jurassic, Cretaceous
Question 60. Jurassic period of Mesozoic era is characterized by which of the following?
- Gymnosperms are dominant plants and first birds appear.
- Dinosaurs become extinct and angiosperms appear.
- Flowering plants and first dinosaurs appear.
- Radiation of reptiles and origin of mammal-like reptiles.
Answer. 1. Gymnosperms are dominant plants and first birds appear.
Question 61. The flowering plants originated in which of the following periods?
- Cretaceous
- Tertiary
- Triassic
- Carboniferous
Answer. 1. Cretaceous
Question 62. Amphibia first appeared in which of the following period?
- Permian
- Carboniferous
- Devonian
- Silurian
Answer. 3. Devonian
Question 63. Permian period, during which the first most modern orders of insects appeared, occurred approximately
- 80 million years ago
- 150 million years ago
- 280 million years ago
- 550 million years ago
Answer. 3. 280 million years ago
Question 64. Dinosaurs were abundant in
- Jurassic period
- Devonian period
- Permian period
- Pleistocene period
Answer. 1. Jurassic period
Question 65. Fossils of Archaeopteryx were found from
- Jurassic rocks
- Triassic rocks
- Cretaceous rocks
- Cenozoic rocks
Answer. 3. Cretaceous rocks
“evolution neet mcqs “
Question 66. The epoch of human civilization is
- Pliocene
- Holocene
- Pleistocene
- Palaeocene
Answer. 3. Pleistocene
Question 67. Continental drift explains
- Mass extinctions
- Distribution of fossils on earth
- Geographical upheavals
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 68. Which one provides direct and solid evidence in favor of organic evolution through ages?
- Atavism
- Palaeontology
- Vestigial organs
- Galapagos island fauna
Answer. 2. Palaeontology
Question 69. The origin of seeds in the land plants was achieved about 345 million years ago in lineages recognized as ancestral to all more advanced vascular plants in
- Rhynia
- Tracheophyte ancestor
- Seed ferns
- Conifers
Answer. 3. Seed ferns
Question 70. The last major evolutionary advancement among vascular plants was the emergence of flowering plants (angio- sperms) about
- 350 million years ago
- 140 million years ago
- 1600 million years ago
- 220 million years ago
Answer. 2. 140 million years ago
Question 71. An evolutionary trend in which there is general degeneration and loss of organs is
- Progressive
- Vestigial
- Retrogressive
- Stasigenesis
Answer. 3. Retrogressive
Question 72. As horse evolved, there was progressive reduction in the number of toes. Which of the following is the correct sequence in the evolution of horse?
- Orohippus, Hyracotherium, Mesohippus, Callipus, Merychippus, Pliohippus, Equus
- Hyracotherium, Orohippus, Mesohippus, Merychippus, Pliohippus, Equus
- Orohippus, Callipus, Hyracotherium, Mesohippus, Merychippus, Pliohippus, Equus
- Hyracotherium, Mesohippus, Orohippus, Gallipus, Merychippus, Pliohippus, and Equus
Answer. 2. Hyracotherium, Orohippus, Mesohippus, Merychippus, Pliohippus, Equus
Question 73. The replacement of original hard parts or even the soft tissues of organisms by minerals is known as
- Compression
- Petrification
- Molds
- Amber
Answer. 2. Petrification
Question 74. The study of fossil plants is known as
- Palaeontology
- Palaeobotany
- Palynology
- Palaeoanatomy
Answer. 2. Palaeobotany
Question 75. Which of the following is the richest in fossil?
- Basalt
- Granite
- Lava
- Sedimentary rock
Answer. 4. Sedimentary rock
Question 76. Why do we dig fossils and study them?
- To find new fossils that have not yet been recorded.
- Fossil finding gives occupation to scientists.
- Fossils fill the gaps in the evolutionary records of animals.
- Fossils throw light on the evolution of animals of the past.
Answer. 4. Fossils throw light on the evolution of animals of the past.
Question 77. Which one of the following is used for dating archaeological specimens in wood, bones, and shells?
- Uranium-238
- Argon isotope
- Carbon-14
- Strontium-90
Answer. 3. Carbon-14
Question 78. The age of fossils was previously determined by radioactive elements. More precise and recent method which has led to the revision of evolutionary period is
- Study of carbohydrate and protein in fossils
- Study of conditions of fossilization
- Electron spin resonance and fossil DNA
- Presence of carbohydrate and protein in rocks
Answer. 3. Electron spin resonance and fossil DNA
Question 79. Fossil X is older than fossil Y. The most evident statement is
- Fossil Y has got some of the vestigial organs which are functional in X
- Fossil Y has got homologous and analogous organs of fossil X
- Fossil X is found in deeper sedimentation than fossil Y
- Fossil Y was found in better state than fossil Y
Answer. 3. Fossil X is found in deeper sedimentation than fossil Y
Question 80. The oldest fossil of modern horse is known as
- Eohippus
- Mesohippus
- Merychippus
- Equus
Answer. 1. Eohippus
Question 81. The theory of inheritance of acquired characters or the theory of use and disuse of organ was given by
- Wallace
- Lamarck
- Charles Darwin
- Hugo de Vries
Answer. 2. Lamarck
Question 82. Weissman cut the tails of new born mice generation after generation, but the tails neither disappeared nor shortened showing that
- Tail has the power of regeneration
- Mutation theory is wrong
- Lamarckism was wrong in the inheritance of acquired characters
- Tail is an essential organ
Answer. 3. Lamarckism was wrong in the inheritance of acquired characters
Question 83. A scientist kept 80 generations of Drosophila in darkness, and even after that, the flies had normal eyes. This disapproves the law of
- Natural selection
- Neo-Darwinism
- Use and disuse
- Synthetic theory
Answer. 3. Use and disuse
Question 84. Who among the following is associated with the concept of appetency?
- Lamarck
- Charles Darwin
- Wallace
- Erasmus Darwin
Answer. 1. Lamarck
Question 85. Penguin is a bird that lost the use of its wings by not flying. Such statement would express the views of
- Darwin
- Wallace
- Lamarck
- Huxley
Answer. 3. Lamarck
Question 86. The concept of appetency was given by
- Lamarck
- Darwin
- Oparin
- Haldane
Answer. 1. Lamarck
Question 87. Which of the following is the correct sequence of events in the origin of new species according to Darwinism?
- Natural selection, variation and their inheritance, survival of fittest, struggle for existence, high rate of reproduction
- High rate of reproduction, constancy in number, struggle for existence, inheritable variations, survival of fittest, natural selection
- High rate of reproduction, variations, constancy in number, struggle for existence, survival of fittest
- Variation, high rate of reproduction, constancy in number, struggle for existence, survival of fittest, natural selection
Answer. 2. High rate of reproduction, constancy in number, struggle for existence, inheritable variations, survival of fittest, natural selection
Question 88. The main drawback of Darwin’s theory of natural selection was that it could not provide satisfactory explanation of
- Survival of fittest
- Struggle for existence
- Mimicry
- Basis of variation and the mode of transmission of the variants to the next generation
Answer. 4. Basis of variation and the mode of transmission of the variants to the next generation
Question 89. According to the theory proposed by T.R. Malthus,
- Population and the existing means of subsistence increase at the same rate
- Population increases arithmetically while the existing means of subsistence increase geometrically
- Population increases geometrically while the means of subsistence increase arithmetically
- Population increases at a fast rate but the means of subsistence do not increase
Answer. 3. Population increases geometrically while the means of subsistence increase arithmetically
Question 90. Successful adaptation means
- Moving to a new means
- Producing more offsprings
- An increase in fitness
- Evolving new characteristics
Answer. 3. An increase in fitness
Question 91. Frequency of a character increases when it is
- Recessive
- Dominant
- Inheritable
- Adaptable
Answer. 4. Adaptable
Question 92. “Descent of Man and Selection in Relation to Sex” was written by
- Nicolaus Copernicus
- Darwin
- Carolus Linnaeus
- Francesco Redi
Answer. 2. Darwin
Question 93. Regarding evolution, Darwin’s explanation is that
- Certain species have “built-in” plans of evolution
- The traits used most often persist longer
- Progressive adaptations enable one species to have more offsprings
- Code determines which species should evolve
Answer. 1. Certain species have “built-in” plans of evolution
Question 94. Darwin’s theory of pangenesis proposes
- Development of useful organs and degeneration of useless organs
- Development of an organ due to will power
- Increase in organ size with age
- Every organ of the body produces minute hereditary particles called gemmules, carried through the blood from every organ and collected together into gametes
Answer. 4. Every organ of the body produces minute hereditary particles called gemmules, carried through the blood from every organ and collected together into gametes
Question 95. Which of the following theories refused Darwin’s theory of pangenesis mentioned in the book “On the Variation of Animals and Plants Under Domestication”?
- Lamarck’s theory of inheritance of acquired characters
- Weismann’s theory of germplasm
- Haeckel’s recapitulation theory
- Hugo de Vries’ mutation theory
Answer. 2. Weismann’s theory of germplasm
Question 96. Hugo de Vries’ contribution is
- Mutation theory, on the basis of his observation on the wild variety of evening primrose (Oenothera lamarckiana)
- Theory of natural selection
- Law of dominance
- Law of segregation
Answer. 1. Mutation theory, on the basis of his observation on the wild variety of evening primrose (Oenothera lamarckiana)
Question 97. Neo-Darwinism is a synthesis of theories proposed by
- Lamarck and Charles Darwin
- Charles Darwin and A.R. Wallace
- Hugo de Vries and Charles Darwin
- Charles Darwin and F. Redi
Answer. 3. Hugo de Vries and Charles Darwin
Question 98. Evolution at the genetic level due to changes in the hereditary materials at the level of population is called
- Macroevolution
- Microevolution
- Saltation
- Sports
Answer. 2. Microevolution
Question 99. Coevolution does not occur in case of
- Parasitism
- Mutualism
- Both (1) and (2)
- Commensalism
Answer. 4. Commensalism
Question 100. Which of the following statements is not applicable to the replica plate experiment of Lederberg and Lederberg?
- Mutations are actually pre-adaptive.
- Pre-adaptive mutations appear without exposure to new environment.
- The new environment induces mutations.
- The new environment only selects the pre-adaptive mutations that occurred earlier.
Answer. 3. The new environment induces mutations.
Question 101. In Lederberg’s replica plating, streptomycin-resistant strain can develop by using
- Minimal medium and streptomycin
- Complete medium and streptomycin
- Only minimal medium
- Only complete medium
Answer. 2. Complete medium and streptomycin
Question 102. Using imprints from a plate with complete medium and carrying bacterial colonies, you can select streptomycinresistant mutants and prove that such mutations do not originate as adaptation. These imprints need to be used
- On plates with and without streptomycin
- On plates with minimal medium
- Only on plates with streptomycin
- Only on plates without streptomycin
Answer. 1. On plates with and without streptomycin
Question 103. Experimental evidence for the selection of bacteria by using the replica technique was demonstrated by
- Prof. A.D. Bradshaw
- Prof. Y.D. Tyagi
- J. Lederberg and E. Lederberg
- Alfred Russel Wallace
Answer. 3. J. Lederberg and E. Lederberg
Question 104. Lederberg’s replica plating experiment suggests
- Characters are heritable
- Natural selection plays an important role in fixing a mutation of survival value
- Genes are independent entities
- Bacteria can multiply in culture medium
Answer. 2. Natural selection plays an important role in fixing a mutation of survival value
Question 105. Ultimate source of variation is
- Recombination
- Mutation
- Genetic drift
- Intermingling of two widely separated populations
Answer. 2. Mutation
Question 106. The concept of genetic drift was introduced by
- Hardy Weinberg
- Sewall Wright
- Huxley
- Hugo de Vries
Answer. 2. Sewall Wright
Question 107. Random genetic drift in a population results from
- Highly genetically variable individuals
- Large population size
- Constant low mutation rate
- Interbreeding within small populations
Answer. 4. Interbreeding within small populations
Question 108. In a small population, the increase in the frequency of a character by chance that has little adaptive value is due to
- Genetic drift
- Natural selection
- Artificial selection
- Migration
Answer. 1. Genetic drift
Question 109. Reduction in allele frequencies in a population which of- ten prevents the species from reversing its path of extinction is called
- Founder effect
- Genetic mutation
- Genetic bottleneck
- Microevolution
Answer. 3. Genetic bottleneck
Question 110. The unit of natural selection is
- Individual
- Population
- Species
- Mutation
Answer. 1. Individual
Question 111. Industrial melanism is an example of
- Neo-Lamarckism
- Natural selection
- Neo-Darwinism
- Mutation
Answer. 2. Natural selection
Question 112. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
- Industrial melanism is an example of natural selection.
- Before industrial revolution, Biston betularia with gray color was abundant.
- Black-colored form of the same moth (melanic), dominant mutant carbonaria, increased after industrial revolution.
- The gray color of Biston betularia was due to dominant allele.
Answer. 4. The gray color of Biston betularia was due to dominant allele.
“evolution means fill in the blanks “
Question 113. Which one of the following phenomena supports Darwin’s concept of natural selection in organic evolution?
- Development of transgenic animals
- Production of sheep Dolly by cloning
- Prevalence of pesticide-resistant insects
- Development of organs from stem cells for organ transplantation
Answer. 3. Prevalence of pesticide-resistant insects
Question 114. When selection acts to eliminate both extremes from the array of phenotypes, the frequency of intermediate type, which is already more, is increased. This is called
- Disruptive selection
- Balancing selection
- Stabilizing selection
- Non-directional selection
Answer. 3. Stabilizing selection
Question 115. Which of the following are examples of artificial selection?
- Kohlrabi
- Cabbage
- Cauliflower
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 116. If a sub-population becomes reproductively isolated in the midst of its parent population, this mode of speciation is called
- Sympatric speciation
- Allopatric speciation
- Sibling species
- Mutation
Answer. 1. Sympatric speciation
Question 117. Reproductive isolation is
- Inability to interbreed
- Ability to interbreed
- Breeding in isolation
- Intraspecific breeding
Answer. 1. Inability to interbreed
Question 118. Which of the following is not a characteristic of true species?
- Members of a species can interbreed.
- Gene flow does not occur between the populations of a species.
- Each species is reproductively isolated from every other species.
- Variations occur amongst members of a species.
Answer. 2. Gene flow does not occur between the populations of a species.
Question 119. Mule, which is produced from the mating of male donkey and a mare (female horse), is an example of which type of reproductive isolation?
- Hybrid breakdown
- Hybrid sterility
- Hybrid inviability
- Reverse evolution
Answer. 2. Hybrid sterility
Question 120. When a hybrid produces sterile or infertile offspring, it is known as
- Hybrid sterility
- Hybrid breakdown
- Hybrid inviability
- Gametic isolation
Answer. 2. Hybrid breakdown
Question 121. Modern synthetic theory of evolution is based on
- Genetic and chromosomal mutations
- Genetic recombination and natural selection
- Reproductive isolation
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 122. Transfer of genes from one gene pool to another is
- Genetic drift
- Gene flow
- Speciation
- Mutation
Answer. 2. Gene flow
Question 123. Gene flow is
- Transfer of genes between genetically distinct but interbreeding populations
- Transfer of genes from females to males of an organism
- Transfer of genes from outside to chromosomes
- Transfer of genes from sperm to egg
Answer. 1. Transfer of genes between genetically distinct but interbreeding populations
Question 124. Gene pool of a population tends to remain stable if the population is large, without large-scale mutations, with- out migration, and with
- Random mating
- Moderate environmental changes
- Natural selection
- Reduction in predators
Answer. 1. Random mating
Question 125. Primates originated about
- 210 million years ago
- 150 million years ago
- 65 million years ago
- 36 million years ago
Answer. 3. 65 million years ago
Question 126. Anthropoid apes were ancestors of
- Monkeys
- Apes
- Homo habilis
- All the these
Answer. 4. All the these
Question 127. Which one of the following is the closest relative of man?
- Chimpanzee
- Orangutan
- Gorilla
- Gibbon
Answer. 1. Chimpanzee
Question 128. Evolution of man is believed to have taken place in
- Central America
- Australia
- Asia
- Africa
Answer. 4. Africa
Question 129. Cradle of human evolution is
- Grassland of South Africa
- Savannah of Central Africa
- Subarctic Europe
- Arabia
Answer. 2. Savannah of Central Africa
Question 130. Proconsul is ancestor of
- Apes only
- Man only
- Both (1) and (2)
- All primates
Answer. 3. Both (1) and (2)
Question 131. One thing that is not similar in great apes and man is
- Posture
- DNA content
- Protein homology
- Banding pattern of chromosome
Answer. 1. Posture
Question 132. The family to which Homo sapiens belongs is
- Pongidae
- Hylobatidae
- Hominidae
- None of these
Answer. 3. Hominidae
Question 133. The brain of Australopithecus measured
- 350-450 cm3
- 1400-1450 cm3
- 700-900 cm3
- 800-1400 cm3
Answer. 1. 350-450 cm3
Question 134. The ancestor of man who first stood erect was
- Australopithecus
- Java ape-man
- Peking man
- Cro-Magnon man
Answer. 1. Australopithecus
Question 135. The earliest man who used tools was
- Homo habilis
- Homo erectus
- Java man
- Peking man
Answer. 1. Homo habilis
Question 136. The connecting link between ape and man is
- Cro-Magnon man
- Australopithecus
- Neanderthal man
- Lemur
Answer. 2. Australopithecus
Question 137. Bipedal locomotion is advantageous because it
- Increases speed
- Reduces body weight
- Provides better support to body
- Releases forelimbs for other purposes
Answer. 4. Releases forelimbs for other purposes
Question 138. Fossils of so called Java man and Peking man belong to
- Homo sapiens
- Homo erectus
- Homo habilis
- None of these
Answer. 2. Homo erectus
Question 139. Dubois, in 1891, found the fossil of Java ape-man. It is
- Sinanthropus pekinensis
- Pithecanthropus erectus
- Homo rhodesiensis
- Homo sapiens
Answer. 2. Pithecanthropus erectus
Question 140. The smallest cranial capacity is that of the
- Modern man
- Cro-Magnon man
- Neanderthal man
- Java man
Answer. 4. Java man
Question 141. Which of the following fossil man possessed a cranial capacity almost equal to that of modern man?
- Neanderthal man
- Java ape-man
- Peking man
- Australopithecus africanus
Answer. 1. Neanderthal man
“questions about evolution “
Question 142. Fire was first used for protection and cooking by
- Java man
- Neanderthal man
- Peking man
- Cro-Magnon man
Answer. 1. Java man
Question 143. “Lucy” is the fossil of
- Australopithecus afarensis
- Homo sapiens
- Homo erectus
- Cro-Magnon man
Answer. 1. Australopithecus afarensis
Question 144. The fossils of Neanderthal were first obtained from Neander Valley in
- Germany
- Italy
- America
- France
Answer. 1. Germany
Question 145. The first evidence of ceremonial burial of dead have been found with fossils of
- Cro-Magnon man
- Java ape-man
- Neanderthal man
- Peking man
Answer. 3. Neanderthal man
Question 146. Who were the first to built hut-like structure for dwelling and buried their dead?
- Neanderthal man
- Cro-Magnon man
- Java man
- Homo sapiens sapiens
Answer. 1. Neanderthal ma
Question 147. Man (Homo) originated in
- Palaeocene
- Miocene
- Oligocene
- Pleistocene
Answer. 4. Pleistocene
Question 148. Which is correct?
- Neanderthal man is direct ancestor of humans.
- Homo erectus is direct ancestor of man.
- Cro-Magnon man was found in Ethiopia.
- Australopithecus is real ancestor of modern man.
Answer. 2. Homo erectus is direct ancestor of man.
Question 149. Cro-Magnon was
- Carnivorous
- Omnivorous
- Herbivorous
- Frugivorous
Answer. 2. Omnivorous
Question 150. Cranial capacity of Neanderthal man was
- 1400 cc
- 1300 cc
- 1200 cc
- 1100 cc
Answer. 1. 1400 cc
Question 151. Chronological sequence of evolution of the genus Homo is
- Homo habilis, H. erectus, H. sapiens neanderthalensis, H. sapiens sapiens
- Homo habilis, H. sapiens neanderthalensis, H. sapiens sapiens
- Homo erectus, H. habilis, H. sapiens sapiens, H. neanderthalensis
- H. neanderthalensis, H. erectus, H. sapiens sapiens, H. habilis
Answer. 1. Homo habilis, H. erectus, H. sapiens neanderthalensis, H. sapiens sapiens
Question 152. A common ancestry for man and great apes has been deduced from similarities in
- Proteins
- Banding pattern of chromosomes
- DNA content
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 153. In gorilla, great apes, and chimpanzee, the number of chromosomes is
- 2n = 46
- 2n=44
- 2n=48
- None of these
Answer. 3. 2n=48
Question 154. Trends in human evolution have been
- Erect posture
- Opposable thumb
- Bipedal
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 155. Colored rock-paintings were presumably first made by
- Cro-Magnon man
- Neanderthal man
- Java ape-man
- Peking man
Answer. 1. Cro-Magnon man
Question 156. The characteristics of modern man are
- Small teeth without large canines and slight curvature of vertebral column
- Flattened face without muzzle and brow ridges
- Rounded skull with downward looking foramen magnum
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 157. Which is direct ancestor of Homo sapiens?
- Homo erectus
- H. sapiens neanderthalensis
- Ramapithecus
- Australopithecus
Answer. 1. Homo erectus
Question 158. Which is correct regarding the evolution of mankind?
- Homo erectus was preceded by Homo habilis.
- Australopithecus lived in Australia.
- Neanderthal man and Cro-Magnon man lived together.
- None of these.
Answer. 1. Homo erectus was preceded by Homo habilis.
Question 159. Common origin of man and chimpanzee is best shown by
- Cranial capacity
- Binocular vision
- Chromosomes
- Dental formula
Answer. 3. Chromosomes
Question 160. Who amongst the following diverged from the main line of hominid evolution about 10 million years ago?
- Gibbon
- Orangutan
- Gorilla
- Chimpanzee
Answer. 1. Gibbon
Question 161. Which is correct order in the evolutionary history of man?
- Peking man → habilis man → Neanderthal man → Cro-Magnon man
- Peking man → Heidelberg man → Neanderthal man → Cro-Magnon man
- Peking man → Neanderthal man → Homo sapiens → Heidelberg man
- Peking man → Homo sapiens → Neanderthal man → Cro-Magnon man
Answer. 2. Peking man → Heidelberg man → Neanderthal man → Cro-Magnon man
Question 162. The fossil of Cro-Magnon man was found in
- Southern France
- Northern France
- Northern Germany
- South Africa
Answer. 1. Southern France
Question 163. Dryopithecus is also called
- Parapithecus
- Proconsul
- Oreopithecus
- Pithecanthropus
Answer. 2. Proconsul
Question 164. In recent years, DNA sequences of mitochondrial DNA and V-chromosomes were considered for the study of human evolution because
- They can be studied from the sample of fossil remains
- They are small and, therefore, easy to study
- They are uniparental in origin and do not take part in recombination
- Their structure is known in greater detail
Answer. 3. They are uniparental in origin and do not take part in recombination
Question 165. Some bio-indicator plants have evolved metal tolerance, and can indicate the occurrence of specific metal deposits. The plant which is the bio-indicator of lead is
- Agrostis tenuis
- Astragalus
- Haplopappus
- Impatiens balsamina
Answer. 1. Agrostis tenuis
Question 166. A baby has been born with a small tail. It is a case of exhibiting
- Retrogressive evolution
- Mutation
- Atavism
- Metamorphosis
Answer. 3. Atavism
Question 167. In which condition gene ratio remains constant in a species?
- Gene flow
- Mutation
- Random mating
- Sexual selection
Answer. 3. Random mating
Question 168. Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution. This statement was given by
- Thedosius Dobzhansky
- Darwin
- Wallace
- Malthus
Answer. 1. Thedosius Dobzhansky
Question 169. The phrase “survival of fittest” was used by
- Charles Darwin
- Herbert Spencer
- Jean Baptiste Lamarck
- Hugo de Vries
Answer. 2. Herbert Spencer
Question 170. Degradation, aggregation, and diastrophism have resulted in
- Folding of land masses
- Raising of land masses
- Lowering of land masses
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 171. It is useful to study the origin and evolution of life because
- We learn that life cannot exist anywhere else
- We learn about the unity and diversity of living organisms
- We learn that human species has the responsibility to conserve nature
- Human species is the most evolved; so, no harm can come to us
Answer. 2. We learn about the unity and diversity of living organisms
Question 172. The role of isolation in evolution is
- Differentiation of species
- Maintenance of species
- Extermination of species
- Evolutionary divergence
Answer. 4. Evolutionary divergence
Question 173. Which of the following animals exhibit poisonous Müllerian mimicry?
- Bees
- Wasps
- Hornets
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 174. Which one of the following plants is tolerant to selenium?
- Astragalus
- Agrostis tenuis
- Impatiens balsamia
- Prosopis juliflora
Answer. 1. Astragalus
Question 175. Which one of the following animal has been extinct recently?
- Dodo
- Dinosaur
- Pterodactyla
- Mammoth
Answer. 1. Dodo
Question 176. Two bands of a population come together after a period of isolation. Speciation will have taken place if the two groups
- No longer mate
- Cannot interbreed or produce fertile offsprings
- Compete for the same food supply
- No longer intermingle
Answer. 2. Cannot interbreed or produce fertile offsprings
Question 177. Organic evolution would not have taken place if
- Individual in a population did not show genetic variation
- Individuals did not transmit the characters acquired during their lifetime to offsprings
- Somatic variations were not inherited
- Somatic variations were not transformed into genetic variations
Answer. 1. Individual in a population did not show genetic variation
Question 178. What is wrong about evolution?
- Evolution is a slow and continuous process of change.
- All diversity of organisms has arisen due to evolution.
- Evolution is due to natural selection only.
- Evolution is due to variations arising from changes in genetic material.
Answer. 3. Evolution is due to natural selection only.
Question 179. Survival due to geographic isolation is best exemplified by mammalian fauna of
- Oriental region
- Ethiopean region
- Palaearctic region
- Australian region
Answer. 4. Australian region
Question 180. Which of the following is irrelevant in the evolution of man?
- Loss of tail
- Increase in the ability to communicate with others and develop community behavior
- Protection of hand for toolmaking
- Change of diet from hard nuts and hard roots to soft food
Answer. 1. Loss of tail
Question 181. According to geological clock, if last 4800 million years = 24 h, then the appearance of animals took place
- At 18.30 h, 4600 million years ago
- At 18.30 h, 1100 million years ago
- At 13.00 h, 220 million years ago
- At 10.00 h, 1-2 million years ago
Answer. 2. At 18.30 h, 1100 million years ago
Question 182. There are two opposing views about the origin of mod- ern man. According to one view, Homo erectus in Asia were the ancestors of modern man. A study of variation in DNA, however, suggested African origin of modern man. What kind of observation on DNA variation could suggest this?
- Greater variation in Asia than in Africa
- Greater variation in Africa than in Asia
- Similar variation in Africa and Asia
- Variation only in Asia and no variation in Africa
Answer. 2. Greater variation in Africa than in Asia
Question 183. Which of the following is relatively the most accurate method for dating of fossils?
- Radiocarbon method
- Potassium-argon method
- Electron-spin resonance method
- Uranium-lead method
Answer. 3. Electron-spin resonance method
Question 184. Evolution due to genetic changes within a species is
- Microevolution
- Macroevolution
- Megaevolution
- Coevolution
Answer. 1. Microevolution
Question 185. Future human generations will be less adapted due to
- Genetic drift
- Mutation
- Natural selection
- Gene flow
Answer. 3. Natural selection
Question 186. Today, the tiger population in India has reduced. This is because
A. Tigers exist in geographically isolated population
B. Of hunting and habitat destruction
C. Of genetic drift
D. Of homogenizing effect of gene flow
Choose the correct option:
- (A) and (B) only
- (A), (B), and (C)
- (B) and (C) only
- (A), (B), (C), and (D)
Answer. 2. (A), (B), and (C)
Question 187. What molecular evidence suggests that Homo sapiens originated in Africa and then radiated out to other places?
A. Maximum variations are found in the mitochondrial DNA of Africans
B. Variations in V-chromosome
C. Similarity in skull of apes and man
D. Binocular vision
- (A) only
- A and B
- (A), (B), and (C)
- (A), (B), (C), and (D)
Answer. 2. A and B
Question 188. The eyes of first primates faced forward. All the following are advantages of these, except
- Binocular vision
- This gave the primates excellent depth perception, which enabled them to judge distances accurately when moving through the trees
- The field of vision of two eyes is different
- Binocular vision results in three-dimensional image
Answer. 3. The field of vision of two eyes is different
Question 189. As Pangaea broke apart,
- Dinosaurs became more alike
- Mammals became dominant
- Dinosaur species flourished
- World climate changed
Answer. 4. World climate changed
Question 190. The illustration shows the skull of two different mammals. Use the illustration to answer the question that follows:
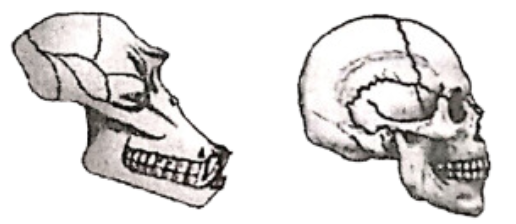
Which of the following accurately describes the differ- ences between these skulls?
- Skull (A) has more teeth than skull (B)
- Skull (A) has more brain capacity than skull (B)
- Skull (A) is of primate and skull (B) is not of a primate
- Skull (A) is the skull of an ape because of simian gap and skull (B) is the skull of human
Answer. 4. Skull (A) is the skull of an ape because of simian gap and skull (B) is the skull of human
Question 191. Which of the following is not true?
- About 15 mya, primates Oryopithecus and Ramap- ithecus existed.
- Ramapithecus was more ape-like.
- Homo erectus had a large brain around 900 cm3.
- The brain capacities of Homo habilis were between 650 cm3 and 800 cm3.
Answer. 2. Ramapithecus was more ape-like.
Question 192. Who were the first to use hides to protect their body and buried their dead?
- Neanderthal man
- Homo erectus
- Cro-Magnon man
- Homo habilis
Answer. 1. Neanderthal man
Question 193. Modern Homo sapiens arose
- Near East and Central Asia between 100,000 and 40,000 years ago
- During ice age between 75,000 and 10,000 years ago
- About 10,000 years ago
- About 18,000 years ago
Answer. 2. During ice age between 75,000 and 10,000 years ago
Question 194. The most apparent change during the evolutionary history of Homo sapiens is traced in
- Loss of body hair
- Walking upright
- Shortening of the jaws
- Remarkable increase in the brain size
Answer. 4. Remarkable increase in the brain size
Question 195. The first human-like being-the hominid-was called
- Australopithecus
- Homo erectus
- Homo habilis
- Homo sapiens
Answer. 3. Homo habilis
Question 196. The most advanced theory of origin of life is that of
- Catastrophic
- Haldane and Oparin
- Cosmozoic
- Spontaneous
Answer. 2. Haldane and Oparin
Question 197. Possible early source of energy was
- Chlorophyll
- CO2
- UV radiations and lightning
- Green plants
Answer. 3. UV radiations and lightning
Question 198. Swan-necked flask experiment was performed by
- Louis Pasteur
- Robert Koch
- Francisco Redi
- Aristotle
Answer. 1. Louis Pasteur
Question 199. Spark discharge apparatus for testing the chemical origin of life was designed by
- Urey and Miller
- Jacob and Monod
- Oparin and Haldane
- Dixon and Joly
Answer. 1. Urey and Miller
Question 200. Which is the most important for the origin of life?
- Oxygen
- Water
- Nitrogen
- Carbon
Answer. 2. Water
Question 201. Theory of spontaneous generation was supported by
- Van Helmont
- Redi
- Spallanzani
- Pasteur
Answer. 1. Van Helmont
Question 202. One of the greatest advocates of the theory of special creation was
- C. Darwin
- Aristotle
- Father Saurez
- Huxley
Answer. 3. Father Saurez
Question 203. A compound important in prebiotic evolution was
- SO2
- YCH1
- SO3
- NO
Answer. 2. YCH1
Question 204. Which ones are the most essential for the origin of life?
- Enzymes
- Proteins
- Carbohydrates
- Nucleic acids
Answer. 4. Nucleic acids
Question 205. Approximate age of earth (in million years) is
- 3600
- 4600
- 7200
- 6000
Answer. 2. 4600
Question 206. According to the theory of abiogenesis, life originates from
- Non-living
- Spontaneously
- Chemicals
- Other planets
Answer. 1. Non-living
Question 207. Abiogenesis is
- Origin of life from non-living organisms
- Origin of microbes from living organisms
- Spontaneous
- Origin of microbes and viruses
Answer. 3. Spontaneous
Question 208. Experimental proof that organic compounds formed the basis of evolution was given by
- Oparin
- Pasteur
- Miller and Urey
- Spallanzani
Answer. 3. Miller and Urey
Question 209. Which of the following has been basic to the origin of life?
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Nucleic acids
- Nucleoproteins
Answer. 3. Nucleic acids
Question 210. Coacervates were experimentally produced by
- Oparin and Sidney Fox
- Fischer and Huxley
- Jacob and Monod
- Urey and Miller
Answer. 1. Oparin and Sidney Fox
Question 211. Who disapproved abiogenesis for the first time?
- Lamarck
- F. Redi
- Pasteur
- Darwin
Answer. 2. F. Redi
Question 212. Which experiment suggests that simplest living organ- isms could not have originated spontaneously from non- living matter?
- Microbes did not appear in stored meat.
- Microbes appeared from unsterilized organic matter.
- Larvae could appear in decaying organic matter.
- Meat was not spoiled when heated and kept in sealed vessel.
Answer. 4. Meat was not spoiled when heated and kept in sealed vessel.
Question 213. The origin of life from pre-existing life is propounded by
- Biogenesis theory
- Abiogenesis theory
- Special creation theory
- Extra terrestrial theory
Answer. 1. Biogenesis theory
Question 214. Extra terrestrial origin of life was proposed by the theory of
- Catastrophism
- Spontaneous generation
- Special creation
- Panspermia
Answer. 4. Panspermia
Question 215. Stanley Miller’s experiment supports
- Abiogenesis
- Biogenesis
- Pangenesis
- Chemical theory
Answer. 4. Chemical theory
Question 216. Cyanobacteria originated on earth about
- 4.3-4.8 billion years ago
- 3.3-3.8 billion years ago
- 2.3-2.8 billion years ago
- 1.3-1.8 billion years ago
Answer. 2. 3.3-3.8 billion years ago
Question 217. Coacervates belong to the category of
- Protozoans
- Molecular aggregates
- Molecular aggregates surrounded by lipid mem- brane
- Cyanobacteria
Answer. 2. Molecular aggregates
Question 218. The oldest fossil record of blue-green algae is 2.9 billion years old. It is
- Stromatolites
- Archaeopteryx
- Archaeopterix
- Chlamydomonas
Answer. 3. Archaeopterix
Question 219. First life consisted of
- Provirus
- Virus
- Bacteria
- Protovirus
Answer. 4. Protovirus
Question 220. Which of the following amino acids was not found to be synthesized in Miller’s experiment?
- Alanine
- Glycine
- Aspartic acid
- Glutamic acid
Answer. 4. Glutamic acid
Question 221. Miller and Urey performed an experiment to prove the origin of life. They took gases ammonia and hydrogen along with
- N2 and H2O
- CH4 and N2
- H2O and CH4
- CO2 and NH3
Answer. 3. H2O and CH4
Question 222. The term “hot dilute soup” was given by
- Haldane
- Urey
- Oparin
- None of the above
Answer. 1. Haldane
Question 223. Coacervates are
- Protein aggregates
- Protein and lipid aggregates
- Chemical aggregates
- Protobionts with polysaccharides, proteins, and water
Answer. 4. Protobionts with polysaccharides, proteins, and water
Question 224. The concept of chemical evolution of life is based on
- Effect of solar radiations on chemicals
- Interaction of water, air, and clay under intense heat
- Combination of chemicals under hot moist environment conditions
- Crystallization of chemicals
Answer. 3. Combination of chemicals under hot moist environment conditions
Question 225. The living form resulting from the final stage of chemical evolution of life is called
- Prebiont
- Protobiont
- Protenoid
- Probiont
Answer. 2. Protobiont
Question 226. Scientists believe that life on earth originated by
- Spontaneous generation
- Chemical evolution/abiogenesis
- Special creation
- Extra terrestrial transfer
Answer. 2. Chemical evolution/abiogenesis
Question 227. Which of the following was formed in S. Miller’s experiment?
- Microspheres
- Nucleic acids
- Amino acids
- UV radiations
Answer. 3. Amino acids
Question 228. S.L. Miller’s closed flask contained
- CH4
- NH, and water vapors
- H2
- All the above
Answer. 4. All the above
Question 229. Microspheres possessed a membrane of
- Lipid and protein
- Lipid
- Carbohydrates
- Fats
Answer. 2. Lipid
Question 230. Which is incorrect about protobionts in the abiogenic origin of life?
- They were partially isolated from surroundings.
- They could maintain an internal environment.
- They were able to reproduce.
- They could separate combination of molecules from the surroundings.
Answer. 3. They were able to reproduce.
Question 231. Origin of life occurred in
- Precambrian
- Coenozoic
- Palaeozoic
- Mesozoic
Answer. 1. Precambrian
Question 232. In their experiment to prove the origin of life, Miller and Urey took gases
- Methane, ethane, hydrogen, ammonia
- Methane, ethane, ammonia, water vapors
- Methane, ethane, ammonia, water vapors
- Ammonia, water vapors, butane, hydrogen
Answer. 3. Methane, ethane, ammonia, water vapors
Question 233. Miller performed experiment to prove abiogenetic molecular evolution of life. Which molecule was not present in Miller’s experiment?
- Water
- Methane
- Oxygen
- Ammonia
Answer. 3. Oxygen
Question 234. Which is incorrect?
- J.B.S Haldane Law of continuity of germplasm
- Louis Pasteur – Germ theory of disease and immunology
- de Vries – Mutation theory
- Lemaitre – Big bang theory
Answer. 1. Lemaitre – Big bang theory
Question 235. Fossils are studied for
- Tracing evolutionary history of organisms
- Studying extinct organisms
- Filling gaps in our study
- Providing jobs to scientists
Answer. 2. Studying extinct organisms
Question 236. The theory “ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny” was proposed by
- Mendel
- Haeckel
- Erasmus
- Weismann
Answer. 2. Haeckel
Question 237. Monkeys and some lower groups have certain blood groups which are
- Identical to those of man
- Identical to those of anthropod apes
- Identical to those of anthropod apes
- Somewhat similar to white persons
- Not identical to those of man
Answer. 1. Identical to those of man
Question 238. Organic evolution is change in
- Single individual
- A few members of population
- Major portion of population
- Entire population
Answer. 3. Major portion of population
Question 239. Heart is four-chambered in
- Amphibia
- Fishes
- Mammals
- Reptiles
Answer. 3. Mammals
Question 240. Homologous organs are
- Human eyes and squid eyes
- Gills of fish and lungs of man
- Hands of man and wings of bat
- Leaf of moss and frond of fern
Answer. 3. Hands of man and wings of bat
Question 241. Coal has been mainly formed by
- Bryophytes
- Pteridophytes/pteridosperms
- Angiosperms
- Algae
Answer. 2. Pteridophytes/pteridosperms
Question 242. Darwin’s finches provide evidence of evolution from
- Anatomy
- Morphology
- Biogeography
- All the above
Answer. 3. Biogeography
Question 243. Which one is not vestigial in humans?
- Third molar
- Coccyx
- Segmental abdominal muscles
- Finger nails
Answer. 4. Finger nails
Question 244. Vestigial pelvic girdle and bone remnants of hind limbs nare characteristic of
- Whale
- Dolphin
- Shark
- Seal
Answer. 1. Whale
Question 245. The sequence in the evolution of horse was
- Equus, Eohippus, Mesohippus, Merychippus
- Eohippus, Mesohippus, Merychippus, Equus
- Mesohippus, Eohippus, Equus, Mesohippus
- Merychippus, Mesohippus, Eohippus, Equus
Answer. 2. Eohippus, Mesohippus, Merychippus, Equus
Question 246. Origin of life occurred in
- Carboniferous
- Cambrian
- Pre-Cambrian
- Ordovician
Answer. 3. Pre-Cambrian
Question 247. The age of evolution of man is measured by
- Electron microscope
- Chemical reaction
- Radioactive dating
- Ultraviolet radiation
Answer. 2. Chemical reaction
Question 248. Modern birds rose in
- Palaeozoic
- Coenozoic
- Mesozoic
- Archaeozoic
Answer. 1. Palaeozoic
Question 249. Tasmanian wolf is a marsupial while wolf is a placental mammal. This shows
- Convergent evolution
- Divergent evolution
- Parallelism
- Inheritance of acquired characters
Answer. 2. Divergent evolution
Question 250. Pioneers in the field of organic evolution were
- Darwin, Lamarck, Landsteiner, and de Vries
- Darwin, de Vries, Lamarck, Huxley
- Lamarck, Landsteiner, Malthus, de Vries
- Landsteiner, de Vries, Malthus, Darwin
Answer. 2. Darwin, de Vries, Lamarck, Huxley
Question 251. Occurrence of higher number of endemic species in South America and Australia is due to
- Retrogressive evolution
- Continental separation
- These species have become extinct from other regions
- Absence of terrestrial links between these places
Answer. 1. Retrogressive evolution
Question 252. Similarities between organisms of different genotypes is due to
- Convergent evolution
- Divergent evolution
- Microevolution
- Macroevolution
Answer. 3. Microevolution
Question 253. Which of the following is not atavistic in humans?
- Tail in some babies
- Enlarged canines
- Six fingers
- Dense body hair
Answer. 2. Enlarged canines
Question 254. Which are not homologous?
- Forearms of humans and fins of fishes
- Wings of bat and insects
- Fins of fishes and flippers of whales
- Human forearms, bat’s wings, and flippers of whale
Answer. 2. Wings of bat and insects
Question 255. The presence of tail and coarse hair in human baby is
- Radiation
- Atavism
- Mutation
- Crossing-over
Answer. 2. Atavism
Question 256. The unit of evolution is
- Population
- Species
- Individual
- Subspecies
Answer. 1. Population
Question 257. The possibility of occurrence of coal in an area is determined by the study of
- Microfossils
- Ecology
- Economic botany
- Mining contents
Answer. 1. Microfossils
Question 258. Darwin’s finches occur in
- Australia
- Galapagos Islands
- Siberia
- India
Answer. 2. Galapagos Islands
Question 259. Evolution does not occur in case of
- Parasitism
- Mutualism
- Both (1) and (2)
- Commensalism
Answer. 4. Commensalism
Question 260. Ancestral amphibians were tetrapods that evolved during
- Carboniferous period
- Cretaceous period
- Jurassic period
- Devonian period
Answer. 4. Devonian period
Question 261. Interacting populations are
- Symbiotic
- Mutualistic
- Parasitic
- Coevolved
Answer. 4. Coevolved
Question 262. Archaeopteryx, toothed fossil bird, occurred during
- Jurassic
- Triassic
- Cretaceous
- Permian
Answer. 2. Triassic
Question 263. Mesozoic era is known as golden age of
- Fishes
- Amphibians
- Reptiles
- Molluscs
Answer. 3. Reptiles
Question 264. Continental drift explains
- Mass extinctions
- Distribution of fossils on earth
- Geographical upheavals
- All the above
Answer. 4. All the above
Question 265. Reptilian feature of Archaeopteryx is
- U-shaped furcula
- Beak
- Abdominal ribs
- Feathers
Answer. 3. Abdominal ribs
Question 266. Archaeopteryx is the connecting link between
- Fishes and amphibians
- Amphibians and birds
- Amphibians and reptiles
- Reptiles and birds
Answer. 4. Reptiles and birds
Question 267. Which is not vestigial in man?
- Tail vertebrae
- Nails
- Nictitating membrane
- Vermiform appendix
Answer. 2. Nails
Question 268. The development of adaptations along parallel lines in unrelated groups of animals is
- Adaptive convergence
- Adaptive radiation
- Adaptive divergence
- Adaptive induction
Answer. 1. Adaptive convergence
Question 269. Which of the following is vestigial in humans?
- Mammary glands in males
- Knee bones
- Nictitating membrane
- Ear pinna
Answer. 3. Nictitating membrane
Question 270. Which is a pair of vestigial organs?
- Coccyx and intercostal muscles
- Coccyx and auricular muscles
- Facial hairs in ladies
- Coccyx and premolars
Answer. 2. Coccyx and auricular muscles
Question 271. Which of the following is used for dating archaeological specimens such as bones, shells, and wood?
- 3 H
- 14 C
- 121 I
- 32 P
Answer. 2. 14 C
Question 272. Convergent evolution is illustrated by
- Rat and dog
- Bacterium and protozoan
- Starfish and cuttlefish
- Dogfish and whale
Answer. 4. Dogfish and whale
Question 273. Which one correctly describes homologous structures?
- Organs with anatomical similarities but performing different functions
- Organs with anatomical similarities but performing different functions
- Organs that have no function now but had an important function in ancestors
- Organs appearing only in embryonic stage and disappearing later in the adult
Answer. 1. Organs with anatomical similarities but performing different functions
Question 274. The early-stage human embryo distinctly possesses
- Gills
- Gill slits
- External ear (pinna)
- Eye brows
Answer. 2. Gill slits
Question 275. Mesozoic era was dominated by
- Birds
- Fishes
- Reptiles
- Mammals
Answer. 3. Reptiles
Question 276. The age of fossils was previously determined by radioactive elements. More precise recent method which has led to the revision of evolutionary periods is
- Study of carbohydrates and proteins in fossils
- Study of conditions of fossilization
- Electron spin resonance and fossil DNA
- Presence of carbohydrates and proteins in rocks
Answer. 3. Electron spin resonance and fossil DNA
Question 277. The flippers of seal are modified
- Hindlimbs
- Forelimbs
- Fins
- Gills
Answer. 2. Forelimbs
Question 278. Potato and sweet potato have edible parts that are
- Homologous
- Analogous
- Recent introductions
- Two species of the same genus
Answer. 2. Analogous
Question 279. The classical example of adaptive radiation during the formation of new species is
- Marsupials of Australia
- Darwin’s finches
- Giant tortoise
- All the above
Answer. 4. All the above
Question 280. Mammals such as whale, dolphin, bat, monkey, and horse have some common characters but also show conspicuous differences. This is due to the phenomenon of
- Divergence
- Convergence
- Genetic drift
- Normalization
Answer. 1. Divergence
Question 281. Which of the following pairs of structures is homologous?
- Wings of grasshopper and forelimbs of flying squirrel
- Tentacles of Hydra and arms of starfish
- Forelimbs of a bat and forelegs of a horse
- Wings of a bird and wings of a moth
Answer. 3. Forelimbs of a bat and forelegs of a horse
Question 282. Which is relatively the most accurate method of dating of fossils?
- Radiocarbon method
- Potassium-argon method
- Electron spin-resonance method
- Uranium-lead method
Answer. 3. Electron spin-resonance method
Question 283. What is the correct arrangement of periods of Paleozoic era in ascending order in geological time scale?
- Cambrian Devonian → Ordovician → Silurian → Carboniferous → Permian
- Cambrian Ordovician → Silurian → Devonian → Carboniferous → Permian
- Cambrian Ordovician → Devonian → Silurian → Carboniferous → Permian
- Silurian→ Devonian → Cambrian → Ordovician → Permian → Carboniferous
Answer. 2. Cambrian Ordovician→ Silurian → Devonian →Carboniferous → Permian
Question 284. An important evidence in favor of organic evolution is the occurrence of
- Homologous and analogous organs
- Homologous and vestigial organs
- Analogous and vestigial organs
- Homologous organs only
Answer. 1. Homologous and analogous organs
Question 285. Jurassic period of Mesozoic era is characterized by
- Flowering plants and first dinosaurs appear
- Gymnosperms are dominant plants and first birds appear
- Radiation of reptiles and angiosperms appear
- Dinosaurs become extinct and angiosperms appear
Answer. 2. Gymnosperms are dominant plants and first birds appear
Question 286. Evolutionary history of an organism is known as
- Ontogeny
- Phylogeny
- Ancestry
- Palaeontology
Answer. 2. Phylogeny
Question 287. Duck-billed platypus is connecting link between
- Echinodermata and Chordata
- Arthropoda and Mollusca
- Reptilia and Mammalia
- Reptilia and Aves
Answer. 3. Reptilia and Mammalia
Question 288. Tendrils of Cucurbita and thorns of Bougainvillea are
- Homologous organs
- Analogous organs
- Vestigial organs
- Atavistic divergence
Answer. 1. Homologous organs
Question 289. Parallelism is due to
- Adaptive divergence
- Adaptive convergence
- Adaptive convergence of unrelated species
- Adaptive convergence of closely related species
Answer. 4. Adaptive convergence of closely related species
Question 290. Which one is correct?
- There is no evidence of presence of gills in mammalian embryos.
- Ontogeny repeats phylogeny.
- All plant and animal cells are totipotent.
- Stem cells are specialized cells.
Answer. 2. Ontogeny repeats phylogeny.
Question 291. Finches of Galapagos provide evidence for
- Retrogressive evolution
- Special creation
- Biogeographical evolution
- Evolution due to mutation
Answer. 3. Biogeographical evolution
Question 292. Two species of different genealogy show resemblance due to similar adaptation. The phenomenon is
- Convergent evolution
- Divergent evolution
- Microevolution
- Coevolution
Answer. 1. Convergent evolution
Question 293. Adaptive radiation is
- Evolution of different species from a common ancestor
- Adaptation due to geographical isolation
- Migration of members of a species to different geographical areas
- Power of adaptation of an individual to a variety of environments
Answer. 1. Evolution of different species from a common ancestor
Question 294. What is common to whale, seal, and shark?
- Homoiothermy
- Seasonal migration
- Thick subcutaneous fat
- Convergent evolution
Answer. 4. Convergent evolution
Question 295. Life has existed on earth for the last
- 2.3 billion years
- 3.9 billion years
- 4.3 billion years
- 5.0 billion years
Answer. 2. 3.9 billion years
Question 296. Darwin’s finches show
- Adaptive radiation
- Parallel evolution
- Homology
- Natural selection
Answer. 1. Adaptive radiation
Question 297. Connecting link between Annelida and Mollusca is
- Nautilus
- Neopilina
- Glochidium
- Veliger larva
Answer. 2. Neopilina
Question 298. Which period is largely associated with the extinction of dinosaurs and increase in flowering plants and reptiles?
- Triassic
- Jurassic
- Cretaceous
- Permian
Answer. 3. Cretaceous
Question 299. Tachyglossus is connecting link between
- Reptiles and mammals
- Reptiles and birds
- Amphibians and reptiles
- Birds and mammals
Answer. 1. Reptiles and mammals
Question 300. Phylogeny is
- Evolutionary history
- Small body mass
- Group of phyla
- Smaller extremities
Answer. 1. Evolutionary history
Question 301. As per Allen’s rule, mammals of cold regions conserve body heat through
- Larger body mass
- Life history
- Longer extremities
- Genetics of animals
Answer. 4. Genetics of animals
Question 302. Peripatus is connecting link between
- Porifera and coelenterata
- Ctenophora and Platyhelminthes
- Mollusca and Echinodermata
- Annelida and Arthropoda
Answer. 4. Annelida and Arthropoda
Question 303. A living connecting link that provides evidence of organic evolution is
- Sphenodon between reptiles and birds
- Archaeopteryx between reptiles and birds
- Lung fishes between pisces and reptiles
- Duck-billed platypus between reptiles and mammals
Answer. 4. Duck-billed platypus between reptiles and mammals
Question 304. After the Industrial Revolution, melanic moths survived because
- They had black color
- They had gray body color
- They shifted to different habitat
- They reproduced vigorously
Answer. 1. They had black color
Question 305. Vesitiges of girdles are found in
- Rattle snake
- Krait
- Cobra
- Python
Answer. 4. Python
Question 306. An evolutionary pattern characterized by a rapid increase in the number of kinds of closely related species is called
- Divergent evolution
- Convergent evolution
- Adaptive radiation
- Parallel evolution
Answer. 3. Adaptive radiation
Question 307. The first seed plants appeared in
- Cretaceous era
- Carboniferous era
- Devonian era
- Silurian era
Answer. 2. Carboniferous era
Question 308. Given are four statements (a)-(d) with one or two blanks. Select the option which fills up the blanks in two statements.
(a) Wings of butterfly and birds look alike and are the result of _______ evolution.
(b) Miller showed that CH4, H2, NH3, and ______ when exposed to electric discharge in a flask resulted in the formation of _______ evidence of evolution.
(c) Vermiform appendix is a _______ organ and ________.
(d) According to Darwin, evolution took place due to _______ and ______of the fittest.
- (d)-(1) small variations, (2) survival; (a)-(1) convergent
- (a)-(1) convergent; (b)-(1) oxygen, (2) nucleolides
- (b)-(1) water vapors, (2) amino acids; (c)-(1) rudimentary, (2) anatomical
- (c)-(1) vestigial, (2) anatomical; (d)-(1) mutations, (2) multiplication
Answer. 1. (d)-(1) small variations, (2) survival; (a)-(1) convergent
Question 309. What was the most significant trend in the evolution of modern man (Homo sapiens) from his ancestors?
- Binocular vision
- Increasing cranial capacity
- Upright posture
- Shortening of jaws
Answer. 2. Increasing cranial capacity
Question 310. Which one of the following options gives one correct ex- ample each of convergent evolution and divergent evolution?
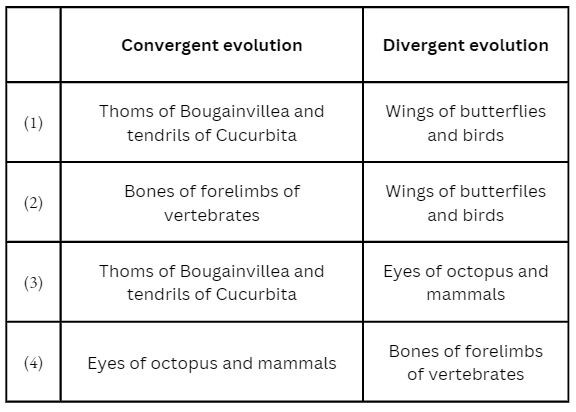
Answer. 4. Eyes of octopus and mammals Bones of forelimbs of vertebrates
Question 311. The extinct human who lived 1,00,000 to 40,000 years ago, in Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa, with short stature, heavy eyebrows, retreating foreheads, large jaws with heavy teeth, stocky bodies, a lumbering gait, and stooped posture was
- Neanderthal human
- Cro-Magnon human
- Ramapithecus
- Homo habilis
Answer. 1. Neanderthal human
Question 312. Evolution of different species in a given area starting from a point and spreading to other geographical areas is known as
- Nutrition
- Migration
- Divergent evolution
- Adaptive radiation
Answer. 4. Adaptive radiation
Question 313. The process by which organisms with different evolutionary history evolve similar phenotypic adaptations in response to a common environmental challenge is called
- Convergent evolution
- Non-random evolution
- Adaptive radiation
- Natural selection
Answer. 1. Convergent evolution
Question 314. Variation in gene frequencies within populations can occur by chance rather than by natural selection. This is referred to as
- Genetic drift
- Random mating
- Genetic load
- Genetic flow
Answer. 1. Genetic drift
Question 315. According to Darwin, the organic evolution is due to
- Interspecific competition
- Competition within closely related species
- Reduced feeding efficiency in one species due to the presence of interfering species
- Intraspecific competition
Answer. 1. Interspecific competition
