NEET Biology For Excretory Products And Their Elimination Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. The animals which do not actively control the osmotic condition of their body fluids are
- Osmoconformers
- Osmoregulatory
- Hyperosmotic
- Hypertonic
Answer: 1. Osmoconformers
Question 2. Which of the following can be termed as osmocon formers?
- All marine invertebrates
- Hagfish
- All freshwater invertebrates
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 2
Question 3. A freshwater fish maintains osmoregulation by
- Continuously taking in water and eliminating excess salts
- Eliminating excess of water and taking up salts from the environment
- Taking both water and salt from the environment
- Eliminating both salt and water into the environment
Answer: 2. Eliminating excess of water and taking up salts from the environment
Question 4. Which of the following means is used by freshwater organisms to prevent net gain of water or net loss of body salts?
- Contractile vacuole
- The large volume of dilute urine
- Ionocytes
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 5. Marine bony fish have body fluids hypotonic to seawater and tend to lose water from the body through
1. Gill membrane
2. Oral membrane
3. Anal membrane
- 1 only
- 1,2, and 3
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
Answer: 2. 1,2, and 3
excretion neet questions
Question 6. Divalent cations are generally eliminated in marine fish through
- Gill membrane
- Anal membrane
- Fecal matter
- Oral membrane
Answer: 3. Fecal matter
Question 7. The body fluids of sharks and coelacanths can be termed as
- Hyperosmotic and hypoionic to seawater
- Hypo-osmotic and hypoionic to seawater
- Hyperosmotic and hyperionic to seawater
- Hypo-osmotic and hyperionic to seawater
Answer: 1. Hyperosmotic and hypoionic to seawater
Question 8. Consider the following water conservation mechanisms:
1. Nasal countercurrent mechanism
2. Dependence on metabolic water
3. Highly hypertonic urine
4. Living more on a protein-rich diet
A kangaroo rat living in a desert can survive without drinking water because of
- 1, 2, and 3
- 1, 2, and 4
- 2, 3, and 4
- 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: 1. 1, 2, and 3
Question 9. Select the true statement.
- In fish, the kidney plays a major role in ammonia excretion.
- Ammonia is 100,000 times less toxic than urea.
- Sharks retain a large amount of urea in the blood as a major osmolyte to balance the osmolarity of the body fluids.
- Most terrestrial reptiles excrete ammonia.
Answer: 3. Sharks retain a large amount of urea in the blood as a major osmolyte to balance the osmolarity of the body fluids.
Question 10. One of the following can retain a large amount of urea in the blood and tissue fluid.
- Mammals including man
- Toad, frog, prawn
- Sharks, electric ray, sting ray
- Alligators, terrapins, turtles
Answer: 3. Sharks, electric ray, sting ray
Question 11. Deamination is the first step in urea formation. It means
- Reduction of ammonia
- Oxidation of ammonia
- Addition of amino group to a non-amino organic molecule
- Removal of an amino group from an amino acid
Answer: 4. Removal of an amino group from an amino acid
Question 12. Removal of metabolic waste in the form of urea is called
- Ammoniotelism
- Ureotelism
- Uricotelism
- Aminotelism
Answer: 2. Ureotelism
Question 13. Uric acid is produced by the breakdown of
- Proteins
- Amino acids
- Nucleic acids
- Starch
Answer: 3. Nucleic acids
Question 14. Guano, the fecal matter of birds contains
- Insoluble crystals of uric acid
- Insoluble crystals of urates
- Both 1 and 2
- Urea
Answer: 3. Both 1 and 2
Question 15. Flame cells (solenocytes) are excretory structures of
- Annelida
- Arthropoda
- Flatworms
- Crustaceans (prawn)
Answer: 3. Flatworms
Question 16. Antennary or green glands which are excretory and osmoregulatory organs of crustaceans consist of
- End sac
- Renal sac
- Antenna
- Lateral and transverse ducts
Answer: 1. End sac
Question 17. The kidneys not only remove the waste products from the blood but also play a very important role in maintaining
- Equilibrium of the body
- Temperature of the body
- Constant composition of the blood irrespective of the nature of the food or fluid intake
- Blood pressure constant
Answer: 3. Constant composition of the blood irrespective of the nature of the food or fluid intake
Question 18. The outer cortex of the kidney in a TS appears granular or dotted because of
- Granular cytoplasm
- The presence of a loop of Henle
- The presence of collecting ducts
- Much convoluted uriniferous tubules and Malpighian corpuscles in this region
Answer: 4. Much convoluted uriniferous tubules and Malpighian corpuscles in this region
Question 19. The concavity on the medial side of the kidney is known as
- Renal pelvis
- Hilum
- Calyces
- Pyramid
Answer: 2. Hilum
Question 20. Podocytes are associated with
- PCT part of the nephron
- Glomerulus
- Bowman’s capsule
- Loop of Henle
Answer: 3. Bowman’s capsule
Question 21. The smallest functional unit of the kidney is
- Nephron
- Collecting tubule
- Glomerulus
- Bowman’s capsule
Answer: 1. Nephron
Question 22. Henle’s loops are found in those animals that excrete hypertonic urine. One of the following does not have Henle’s loop.
- Birds
- Mammals
- Frogs
- None of these
Answer: 3. Frogs
excretory products
Question 23. The thin segment of the descending limb of Loop of Henle is lined by
- Columnar cells
- Flat cells
- Cuboidal cells
- Pyramidal cells with characteristic brush border
Answer: 2. Flat cells
Question 24. Collecting tubes or ducts combine to form
- Duct of Bellini
- Bidder’s canal
- Columns of Bertin
- Ureter
Answer: 1. Duct of Bellini
Question 25. Brush border surface can be taken as the characteristic feature of
- PCT
- Bowman’s capsule
- Loop of Henle
- OCT
Answer: 1. PCT
Question 26. The first, and fourth portion of the descending limb is lined by
- Simple squamous epithelium
- Stratified squamous epithelium
- Cuboidal epithelium
- Columnar epithelium
Answer: 3. Cuboidal epithelium
Question 27. Which of the following statements is not true w.r.t. nephron?
- Cortical nephrons are more common.
- Cortical nephrons lack vasa recta.
- In juxtamedullary nephrons, the blood first passes through the vasa recta and then through the
capillaries of glomerulus - The glomeruli of juxtamedullary nephrons are placed close to the inner margin of the cortex.
Answer: 3. In juxtamedullary nephrons, the blood first passes through the vasa recta and then through the capillaries of the glomerulus
Question 28. Which of the following defines the net filtration pressure (NFP)?
- BCOP – (GHP + CHP)
- GHP-(BCOP + CHP)
- (BCOP + GHP) – CHP
- (GHP – CHP) + BCOP
Answer: 2. GHP-(BCOP + CHP)
Question 29. Which of the following is correct?
- The afferent arteriole is narrower than the efferent arteriole.
- An efferent venule is narrower than a vein.
- An efferent arteriole is narrower than an afferent arteriole.
- Both afferent and efferent arterioles are of the same diameter.
Answer: 3. An efferent arteriole is narrower than an afferent arteriole.
Question 30. The glomerular filtration rate is
- 125mL/min
- 180 L/day
- 1300 mL/min
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 2
Question 31. If the GFR is 125 mL/min and the renal plasma flow is 700 mL/min, the filtration fraction is
- About 6%
- About 18%
- About 12%
- About 24%
Answer: 2. About 18%
Question 32. Which of the following mechanisms will operate mainly to check variation in flow to the glomerulus in case of fluctuation in blood pressure?
- Counter current mechanism
- Myogenic mechanism
- Adam’s stroke condition
- Neurogenic mechanism
Answer: 2. Myogenic mechanism
Question 33. One of the following is impermeable to water
- PCT
- DCT
- Descending limb of Henle’s loop
- Ascending limb of Henle’s loop
Answer: 4. Ascending limb of Henle’s loop
Question 34. Active reabsorption of Na+, K+ takes place in
- DCT
- PCT
- Ascending limb of Henle’s loop
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 35. Tubular secretion helps to maintain a proper acid-base balance by removing one of the following from the blood
- H+ions and ammonia
- Uric acid
- H+ ions and urea
- Ammonia and creatinine
Answer: 1. H+ions and ammonia
Question 36. The concentration of sodium and chloride ions is the lowest
- Near the cortex
- Deep in medulla
- In the interstitial fluid
- In the middle of Henle’s loop
Answer: 1. Near the cortex
Question 37. Which statement is wrong?
- The counter-current mechanism changes the isotonic glomerular filtrate into hypertonic urine by
increasing salt concentration around the nephron and collecting the tubule. - The wall of the collecting tubule is permeable to water whereas the ascending limb is impermeable to water.
- The absorption of water in DCT is facultative.
- As the filtrate passes through the ascending limb, sodium is transported passively in an ascending thick segment.
Answer: 4. As the filtrate passes through the ascending limb, sodium is transported passively in the ascending thick segment.
excretory products and their elimination questions and answers
Question 38. Which one of the following is produced in the kidneys?
- Rennm
- Renin
- Unease
- Arginase
Answer: 2. Renin
Question 39. Angiotensin-2 increases the blood volume by
- Signaling PCT to reabsorb more NaCl and water
- Stimulating the adrenal gland to release aldosterone
- By stimulating the release of ADH
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 40. Reabsorption of Na+ is controlled by
- Vasopressin or ADH
- Aldosterone
- Renin
- Rennin
Answer: 2. Aldosterone
Question 41.When the volume of body fluid falls below normal, ADH
- Decreases permeability of distal convoluted tubule and collecting tubule
- Increases permeability of distal convoluted tubule and collecting tubule
- Has nothing to do with the permeability of convoluted tubule
- Decreases permeability of proximal convoluted tubule
Answer: 2. Increases permeability of distal convoluted tubule and collecting tubule
Question 42. The reabsorption of water in the kidneys is under the control of a hormone
- STH
- ACTH
- LH
- ADH
Answer: 4. ADH
Question 43. The yellow color of urine is due to
- Uric acid
- Urea
- Urochrome
- Melanin
Answer: 3. Urochrome
Question 44. Vitamin excreted by urine in higher vertebrates is
- A
- D
- K
- C
Answer: 4. K
Question 45. Hematuria is a disorder involving
- Loss of blood through the urine
- Loss of hemoglobin in RBC
- Loss of glucose in the urine
- Increase in the concentration of blood urea
Answer: 1. Loss of blood through the urine
Question 46. The retroperitoneal kidney is
- Kidney of fish
- Kidney covered by peritoneum on ventral side
- Kidney covered by peritoneum on the dorsal side
- Kidney uncovered by peritoneum on dorsal side.
Answer: 4. Kidney uncovered by peritoneum on the dorsal side.
Question 47. The difference between glomerular filtrate and plasma is of
- Proteins
- Potassium
- The first is white whereas the latter is yellow
- The first is yellow whereas the latter is white
Answer: 1. Proteins
Question 48. A condition of failure of the kidney to form urine is called
- Diuresis
- Hematuria
- Anuria
- Ketonuria
Answer: 3. Anuria
Question 49. Diuresis is a condition in which
- The excretory volume of urine increases
- The excretory volume of urine decreases
- The kidney fails to excrete urine
- The water balance of the body is disturbed
Answer: 1. The excretory volume of urine increases
Question 50. The presence of RBC in urine is called
- Anuria
- Hematuria
- Glycosuria
- Ketonuria
Answer: 2. Hematuria
Question 51. Ornithine cycle is related to
- Respiration
- Excretion
- Digestion
- Nutrition
Answer: 2. Excretion
Question 52. The volume of urine is regulated by
- Aldosterone
- Aldosterone and ADH
- Aldosterone, ADH and testosterone
- ADH
Answer: 2. Aldosterone and ADH
Question 53. Reabsorption of glucose from glomerular filtrate occurs in
- Collecting tube
- Loop of Henle
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Distal convoluted tubule
Answer: 3. Proximal convoluted tubule
Question 54. Patients with diabetes have glucose in their urine because
- Glucose is not absorbed from GF
- Glucose is absorbed from GF
- Glandular cells secreted glucose in GF
- The concentration of glucose is higher in GF as compared to its normal amount
Answer: 4. The Concentration of glucose is higher in GF as compared to its normal amount
Question 55. The number of pyramids in the kidney of a man is
- 4
- 6
- 8
- 12
Answer: 4. 12
Question 56. Na+ and Cl– both are removed by
- Ascending limb of Henle’s loop
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Both 1 and 2
- Descending limb of Henle’s loop
Answer: 3. Both 1 and 2
Question 57. Excretion involves a process in which
- Harmful substances are stored in cells before being eliminated
- Urine is forced out from the urinary bladder and sweat from the skin
- Harmful substances in the body are chemically changed
- Substances of no further use or those present in excessive quantities are thrown out of the body
Answer: 4. Substances of no further use or those present in excessive quantities are thrown out of the body
Question 58. Which of the following sets of animals produce the same substance as their chief excretory product?
- Camel, housefly, and snake
- Fish, pigeon, and frog
- Amoeba, ant, and antelope
- Frog, monkey, and dog
Answer: 4. Frog, monkey, and dog
Question 59. Column of Bcrtini is found in
- Liver
- Kidney
- Ovaries
- Testes
Answer: 2. Kidney
“excretory products and their elimination bank of biology “
Question 60. Which feature enables the mammalian kidney to concentrate urine in the medullary region?
- Rapid removal of sodium ions from medullary tissues.
- Maintaining a high osmotic pressure in the tissues between the tubules.
- High oxidative metabolism of medullary cells.
- Rapid flow of blood through the medulla.
Answer: 2. Maintaining a high osmotic pressure in the tissues between the tubules.
Question 61. In the kidney of the rabbit, the loop of Henle is the part of
- Collecting duct
- Glomerulus
- Uriniferous tubule
- Bowman’s capsule
Answer: 3. Uriniferous tubule
Question 62. In the kidney, the foundation of urine involves the following processes arranged as
- Reabsorption, filtration, and secretion
- Glomerular filtration, selective reabsorption, and tubular secretion
- Filtration, secretion, and reabsorption
- Secretion, absorption, and filtration
Answer: 2. Glomerular filtration, selective reabsorption, and tubular secretion
Question 63. A severe fall in blood pressure disturbs the function of the kidneys and reduces
- Reabsorption of useful substances
- Glomerular filtration
- Secretion of nitrogenous waste
- Renal filtration
Answer: 2. Glomerular filtration
Question 64. In a glomerulus,
- Afferent capillaries are thicker than efferent capillaries
- Afferent arteriole is thicker than efferent arteriole
- Afferent arteriole is thinner than efferent arteriole
- Afferent capillaries are thinner than efferent capillaries
Answer: 2. Afferent arteriole is thicker than efferent arteriole
Question 65. High blood pressure is maintained in glomeruli than in other capillaries because
- The variability of the diameters of arterioles causes higher resistance to blood flowing out of the glomeruli than that flowing out of the capillaries
- Glomerulus has lower hydrostatic pressure than capillary
- Capillary has a lesser diameter than glomerulus
- All the above
Answer: 1. The variability of the diameters of arterioles causes higher resistance to blood flowing out of the glomeruli than that flowing out of the capillaries
Question 66. Ultrafiltration occurs in a glomerulus when
- Osmotic pressure exceeds hydrostatic pressure
- Hydrostatic pressure exceeds osmotic pressure
- Colloidal osmotic pressure plus capsular pressure remains less than glomerular hydrostatic pressure
- Capsular hydrostatic pressure exceeds glomerular hydrostatic pressure
Answer: 3. Colloidal osmotic pressure plus capsular pressure remain less than glomerular hydrostatic pressure
Question 67. Workers in deep mines usually suffer from dehydration because
- Water is lost due to defecation
- Water is lost due to evaporation
- Water is lost along with salts in the form of sweat
- Water is lost in the form of urine
Answer: 3. Water is lost along with salts in the form of sweat
Question 68. Aquatic animals are mostly ammonotclic because the Excretion of ammonia requires large amounts of water
- Excretion of ammonia requires a large amount of water which is available to these animals
- Ammonia helps in checking the inflow of water into the body
- They get less light
- Water contains less nitrogen
Answer: 1. Excretion of ammonia requires a large amount of water which is available to these animals
Question 69. Aldosterone stimulates the reabsorption of
- Keto acids
- Glucose
- K+ ions
- Na+ ions
Answer: 4. Na+ ions
Question 70. The glomerular filtration rate would be decreased by
- An increase in the renal blood flow
- Compression of the renal capsule
- An increase in the afferent arteriolar pressure
- Constriction of the efferent arteriole
Answer: 2. Compression of the renal capsule
Question 71. In which part of the excretory system of mammals can you first use the term “urine” for contained fluid?
- Urinary bladder
- Collecting tubule
- Bowman’s capsule
- Loop of Henle
Answer: 2. Collecting tubule
Question 72. In public urinals, the urine on standing gives a pungent smell due to
- Conversion of uric acid into ammonia by ornithine cycle
- Conversion of both urea and uric acid into ammonia
- Conversion of urea into ammonia by bacteria
- None of these
Answer: 3. Conversion of urea into ammonia by bacteria
Question 73. A person who is starving, that is, not having food, water, and beverages, will have
- Less urea in his urine
- Less fat in his urine
- More glucose in his blood
- More urea in his blood
Answer: 1. Less urea in his urine
Question 74. What is the “renal threshold”?
- The highest concentration of substances up to which it is totally reabsorbed from glomerular filtrate.
- At which all the substances are reabsorbed.
- At which the filtration of a substance starts.
- At which no substance is filtered in the glomerulus.
Answer: 1. The highest concentration of substances up to which it is totally reabsorbed from glomerular filtrate.
Question 75.The glomerular filtrate contains
- Blood minus cells
- Blood minus cells and proteins
- Plasma minus cells and proteins
- Blood minus proteins
Answer: 2. Blood minus cells and proteins
Question 76. Which of the following terms refers to painful urination?
- Enuresis
- Dysuria
- Anuria
- Ketosis
Answer: 2. Dysuria
Question 77. In diabetes mellitus, the patient drinks more water as there is urinary loss of
- Protein
- Salt
- Insulin
- Glucose
Answer: 4. Glucose
Question 78. A patient who excretes a large quantity of sodium in urine has
- Diseased adrenal cortex
- Diseased adrenal medulla
- Diseased parathyroid
- Diseased thymus
Answer: 1. Diseased adrenal cortex
Question 79. A kidney stone is
- Deposition of sand in kidney
- Blockage by fats
- Blockage by proteins
- A salt such as oxalate crystallizes in the pelvis
Answer: 4. A salt such as oxalate crystallized in the pelvis
Question 80. Glycosuria is the term used for
- Loss of glucose in the urine
- Loss of blood in the urine
- Loss of salts in the urine
- None of these
Answer: 1. Loss of glucose in the urine
Question 81. Part not belonging to the uriniferous tubule is
- Glomerulus
- Henle’s
- Distal convoluted tubule
- Collecting duct
Answer: 4. Collecting duct
Question 82. Which pair is correct?
- Sweat—Temperature regulation
- Saliva—Sense of food taste
- Sebum—Sexual attraction
- Humerus—Hind leg
Answer: 1. Sweat—Temperature regulation
Question 83. Malpighian corpuscles are present in
- Cortex
- Medulla
- Germinal cells
- None of them
Answer: 1. Cortex
Question 84. In rabbits and humans, the kidney is
- Metanephric
- Mesonephric
- Pronephric
- Opisthonephric
Answer: 1. Metanephric
Question 85. Brush border is characteristic of
- Neck of nephron
- Collecting tube
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- All the above
Answer: 3. Proximal convoluted tubule
Question 86. The difference between glomerular filtrate and plasma is of
- Proteins
- Potassium
- The first is white whereas the latter is yellow
- The first is yellow whereas the latter is white
Answer: 1. Proteins
Question 87. Nitrogenous waste products are eliminated mainly as
- Urea in tadpoles and ammonia in adult frog
- Ammonia in tadpoles and urea in adult frog
- Urea in both tadpole and adult frog
- Urea in tadpoles and uric acid in adult frog
Answer: 2. Ammonia in tadpoles and urea in adult frog
Question 88. Reabsorption of useful substances from glomerular filtrate occurs in
- Collecting tube
- Loop of Henle
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Distal convoluted tubule
Answer: 3. Proximal convoluted tubule
Question 89. ADH controls the water permeability of
- Collecting tube (distal part)
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Distal convoluted tubule (distal part)
- All the above
Answer: 3. Distal convoluted tubule (distal part)
Question 90. What will happen if one kidney is removed from the body of a human being?
- Death due to poisoning
- Uremia and death
- Stoppage of urination
- Nothing, the person will survive and remain normal kidney will become hypertrophied.
Answer: 4. Nothing, the person will survive and remain normal kidney will become hypertrophied.
Question 91. The total filtrate formed in 24 h in the human kidney is
- 1.8 L
- 8.0 L
- 18 L
- 180 L
Answer: 4. 180 L
Question 92. Ammonia is converted into urea in
- Heart
- Spleen
- Liver
- Brain
Answer: 3. Liver
Question 93. Which vitamin is excreted out in high quantity through urine in man?
- Vitamin C
- VitaminB
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin K
Answer: 1. Vitamin C
Question 94. If the afferent arteriole diameter is less than the efferent arteriole, then what happens?
- No effect
- Ultrafiltration reaction is slow.
- Ultrafiltration is not possible.
- Ultrafiltration will stop and tubular secretion will start.
Answer: 3. Ultrafiltration is not possible.
Question 95. The concentration of urine depends upon which organ?
- Bowman’s capsule
- Length of Henle’s loop
- PCT
- Network of capillaries arising from glomerulus
Answer: 2. Length of Henle’s loop
Question 96. Conversion of ammonia to urea is done by
- Ornithine cycle
- Arginine cycle
- Fumaric cycle
- Citrulline cycle
Answer: 1. Ornithine cycle
Question 97. The movement of ions against the concentration gradient will be
- Active transport
- Osmosis
- Diffusion
- All of these
Answer: 1. Active transport
Question 98. If Henle’s loop were absent from mammalian nephron, which of the following is to be expected
- There will be no urine formation
- There will be hardly any change in the quality and quantity of urine formed
- The urine will be more concentrated
- The urine will be more dilute
Answer: 4. The urine will be more dilute
Question 99. The correct order of excretory organs in cockroaches, earthworms, and rabbits is, respectively,
- Skin, Malpighi tubules, kidney
- Malpighi tubules, kidney
- Nephridia, Malpighi tubules, kidney
- Nephridia, kidney, green gland
Answer: 2. Malpighi tubules, kidney
Question 100. The net pressure gradient that causes the fluid to filter out of the glomeruli into the glomeruli into the capsule is
- 20 mm Hg
- 50 mm Hg
- 75 mm Hg
- 30 mm Hg
Answer: 1. 20 mm Hg
Question 101. Which one of the following blood vessels in mammals contains the least amount of urea?
- Hepatic portal vein
- Hepatic vein
- Dorsal aorta
- Renal vein
Answer: 4. Renal vein
Question 102. A person who is on a long hunger strike and is surviving only on water will have
- Less urea in his urine
- More sodium in his urine
- Less amino acids in his urine
- More glucose in his blood
Answer: 1. Less urea in his urine
Question 103. Water reabsorption in the distal parts of kidney tubules is regulated by
- STH
- TSH
- ADH
- MSH
Answer: 3. ADH
Question 104. Due to insufficient filtration in the How man’s capsule, all are likely to happen except
- Accumulation of fluid in the body
- Increase in blood pressure
- Increase in blood urea level
- Loss of glucose through urine
Answer: 4. Loss of glucose through urine
Question 105. The appearance of albumin in the urine is most likely due to
- Increase in blood pressure
- Decrease in the blood osmotic pressure
- Damage to the Malpighian corpuscles
- Damage to the proximal convoluted tubules
Answer: 3. Damage to the Malpighian corpuscles
Question 106. Urinary excretion of Na is regulated by
- Anterior pituitary
- Posterior pituitary
- Adrenal cortex
- Adrenal medulla
Answer: 3. Adrenal cortex
Question 107. Kidney crystals are solid clusters of
- Calcium nitrate and uric acid
- Phosphate and uric acid
- Calcium carbonate and uric acid
- Calcium metabisulphite and uric acid
Answer: 2. Phosphate and uric acid
Question 108. The yellow color of the urine of vertebrates is due to
- Cholesterol
- Urochrome
- Uric acid
- Melanin
Answer: 2. Urochrome
Question 109. Which one of the four parts mentioned below does not constitute a part of a single uriniferous tubule
- Bowman’s capsule
- Distal convoluted tubule
- Loop of Henle
- Collecting duct
Answer: 4. Collecting duct
Question 110. Diuresis is a specific pathological condition that leads to
- Increased volume of urine excretion
- Decreased volume of urine excretion
- Increased glucose excretion
- Decreased electrolyte concentration
Answer: 1. Increased volume of urine excretion
Question 111. Which one of the following pairs of waste substances is removed from blood in the ornithine cycle?
- CO2 and urea
- Ammonia and urea
- CO2 and ammonia
- Urea and sodium salt
Answer: 3. CO2 and ammonia
Question 112. The term hematuria is used to describe
- Internal bleeding
- Blood in urine
- Blood cancer
- Blood poisoning
Answer: 2. Blood in urine
Question 113. In the kidney, the formation of urine involves the following processes arranged as
- Glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and tubular secretion
- Reabsorption, filtration, and secretion
- Secretion, absorption, and filtration
- Filtration, secretion, and reabsorption
Answer: 1. Glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and tubular secretion
Question 114. An advantage of excreting nitrogenous wastes in the form of uric acid is that
- Uric acid can be excreted in almost solid form
- The formation of uric acid requires a great deal of energy
- Uric acid is the first metabolic breakdown product of acids
- Uric acid may be excreted through the lungs
Answer: 1. Uric acid can be excreted in almost solid form
Question 115. If Hetile’s loop were absent from mammalian nephron, which of the following is to be expected?
- The urine will be more in volume.
- There will be no urine formation.
- There will be hardly any change in the quality and quantity of urine formed.
- The urine will be more concentrated.
Answer: 1. The urine will be more in volume.
Question 116. A condition of the failure of the kidney to form urine is called
- Deamination
- Entropy
- Anuria
- None of these
Answer: 3. Anuria
Question 117. Which of the following is the characteristic of a metanephric kidney?
- Hypotonic urine production
- Excess secretion of uric acid
- Loop of Henle
- Hormone production
Answer: 3. Loop of Henle
Question 118. The hormone secreted by the kidney is
- Gastrin
- Secretin
- Erythropoietin
- Aldosterone
Answer: 3. Erythropoietin
Question 119. Which of the following are uricotelic animals?
- Rolm and frog
- Lizard and crow
- Camel and frog
- Earthworm and eagle
Answer: 2. Lizard and crow,
Question 120.Marine teleosts. undergoing putrefaction, emit a sharp characteristic foul odor, which is due to the production of
- Trimethylamine
- Hydrogen sulfide
- Ammonia
- Lactic Acid
Answer: 1. Trimethylamine
Question 121. Freshwater bony fishes maintain water balance by
- Excreting a hypotonic urine
- Excreting salt across their gills
- Drinking a small amount of water
- Excreting wastes in the form of uric acid
Answer: 1. Excreting a hypotonic urine
Question 122. Which is mismatched?
- Bowman’s capsule—Glomerular Alteration
- PCT—Absorption of Na+ and K+
- DCT—Absorption of glucose
- None of these
Answer: 3. DCT—Absorption of glucose
Question 123. Loop of Henle is associated with
- Excretory system
- Respiratory system
- Reproductive system
- Digestive system
Answer: 1. Excretory system
Question 124. The complete reabsorption of glucose takes place in
- Collecting tubule
- Distal tubule
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Henle loop
Answer: 3. Proximal convoluted tubule
Question 125. Which of the following is the metabolic waste of protein metabolism?
- NH3, urea, and CO2
- Urea, oxygen, and N2
- Urea, ammonia, and alanine
- Urea, ammonia, and creatinine
Answer: 1. NH3, urea, and CO2
Question 126. Glomerular filtrate contains
- Blood without blood cells and proteins
- Plasma without sugar
- Blood with proteins but without cells
- Blood without urea
Answer: 1. Blood without blood cells and proteins
Question 127. Glomerular hydrostatic pressure is present in
- Tubule of kidney
- Bowman’s capsule
- Glomerulus or uriniferous tubule
- Malpighian tubule
Answer: 3. Glomerulus or uriniferous tubule
Question 128. Diuresis is a condition which is characterized by
- Increase in urine volume
- Increased sugar excretion
- Decrease in urine volume
- Decrease in ionic balance
Answer: 1. Increase in urine volume
Question 129. A liquid which collects in the cavity of Bowman’s capsule is
- Blood plasma minus blood proteins
- Glycogen and water
- Urea, glycogen, and water
- Urea
Answer: 1. Blood plasma minus blood proteins
Question 130. The mammalian kidney resembles the contractile vacuole of Amoeba in the excretion of
- Glucose
- Excess water
- Urea
- Ammonia
Answer: 2. Excess water
Question 131. ADH acts on the
- Collecting tubule of the kidney
- Loop of Henle
- Collecting ducts of tests
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Collecting tubule of kidney
Question 132. Enzyme “renin” is secreted by
- Cells of stomach
- Cells of intestine
- Cortical cells of the kidney
- Cells of juxtaglomerular apparatus of kidney
Answer: 4. Cells of the juxtaglomerular apparatus of the kidney
Question 133. Absorption of Na+ and K+ ions does not occur in
- Bowman’s capsule
- Loop of Henle
- Distal convoluted tubule
- Proximal convoluted tubule
Answer: 1. Bowman’s capsule
Question 134. Urea synthesis takes place in
- Urinary bladder
- Alimentary canal
- Liver
- Kidney
Answer: 3. Liver
Question 135. Glycosuria is the condition
- In which a man eats more sugar
- In which a man excretes sugar in urine
- In which sugar is excreted in feces
- A man has low sugar levels in the blood
Answer: 2. In which a man excretes sugar in urine
Question 136. Find the incorrect statement regarding the mechanism of urine formation in man.
- Tubular secretion takes place in the PCT.
- Aldosterone induces greater reabsorption of sodium.
- The counter-current systems contribute to diluting the urine.
- The glomerular filtration rate is about 125 mL/min.
Answer: 3. The counter-current systems contribute to diluting the urine.
Question 137. If 1L of water is introduced into human blood, then
- BMR increases
- BMR decreases
- RBC collapses and urine production increases
- RBC collapses and urine production decreases
Answer: 3. RBC collapses and urine production increases
Question 138. In which of the following organisms, the excretory organs are correctly stated?
- Human—Kidneys, sebaceous glands, and tear glands
- Earthworm—Pharyngeal, integumentary, and septal nephridia
- Cockroach—Malpighian tubules and enteric caeca
- Frog—Kidneys, skin, and buccal epithelium
Answer: 3. Cockroach—Malpighian tubules and enteric caeca
Question 139. Urea synthesis takes place primarily in the liver because
- Enzyme arginase is present in the liver only.
- NH3 and CO2 are present in the liver only.
- Hormone ADH is found in the liver only.
- A kidney is smaller than a liver.
Answer: 1. Enzyme arginase is present in the liver only.
Question 140. Which one of the following correctly explains the function of a specific part of a human nephron?
- Podocytes: Create minute spaces (slit pores) for the filtration of blood into the Bowman’s capsule.
- Henle’s loop: Most reabsorption of the major substances from the glomerular filtrate.
- Distal convoluted tubule: Reabsorption of Kh ions into the surrounding blood capillaries.
- Afferent arteriole: carries the blood away from the glomerular towards the renal vein.
Answer: 1. Podocytes: Create minute spaces (slit pores) for the filtration of blood into the Bowman’s capsule.
Question 141. The uricotelic mode of passing out nitrogenous wastes is found in
- Reptiles and bird
- Birds and annelids
- Amphibians and reptiles
- Insects and amphibians
Answer: 1. Reptiles and bird
Question 142. Ureters act as urogenital ducts in
- Male humans
- Female humans
- Both male and female frogs
- Male frogs
Answer: 4. Male frogs
Question 143. The maximum amount of electrolytes and water (70-80%) from the glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed in which part of the nephron?
- Distal convoluted tubule
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Descending limb of the loop of Henle
- Ascending limb of the loop of Henle
Answer: 2. Proximal convoluted tubule
Question 144. Which one of the following options gives the correct categorization of six animals according to the type of nitrogenous wastes (A, B, C) they give out?
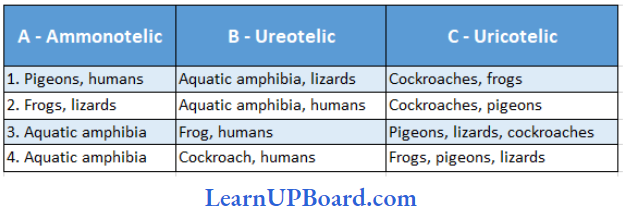
Answer: 3
Question 145. A fall in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) activates
- Juxtaglomerular cells release renin
- Adrenal cortex to release aldosterone
- The adrenal medulla releases adrenaline
- Posterior pituitary to release vasopressin
Answer: 1. Juxtaglomerular cells release renin
Question 146. Which one of the following characteristics is common both in humans and adult frogs?
- Four-chambered heart
- Internal fertilization
- Nucleated RBCs
- Ureotelic mode of excretion
Answer: 4. Ureotelic mode of excretion
Question 147. Human urinary system with structures labeled A-D. Select the option which correctly identifies them and gives their characteristics and/or functions.
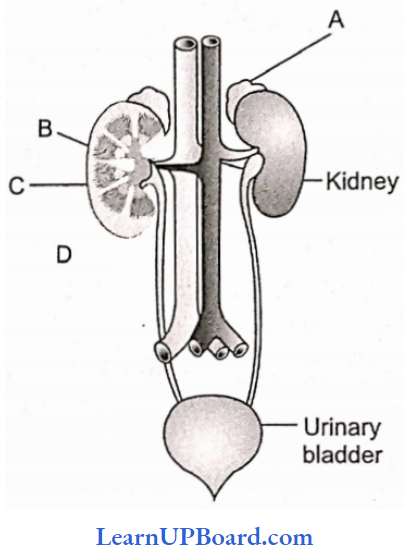
- B → Pelvis → Broad, funnel-shaped space inner to the hilum, directly connected to the loop of Henle.
- C → Medulla → The inner zone of the kidney and contains complete nephrons.
- D → Cortex → The outer part of the kidney and does not contain any part of nephrons.
- A → Adrenal gland → Located at the anterior part of the kidney. Secretes catecholamine which stimulates glycogen breakdown.
Answer: 4. A → Adrenal gland → Located at the anterior part of the kidney. Secretes catecholamine which stimulates glycogen breakdown.
