NEET Biology Human Reproduction Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Temperature in scrotum necessary for sperm formation should be
- 2°C above body temperature
- 2°C below body temperature
- 8°C above body temperature
- 8°C below body temperature
Answer. 2. 2°C below body temperature
Question 2. Cryptorchidism is
- Non-development of testes
- Non-descent of testes into scrotum
- Removal of scrotum
- Breaking connection of vas deferens
Answer. 2. Non-descent of testes into scrotum
Question 3. Tubuli recti of seminiferous tubules open into
- Epididymis
- Vasa efferentia
- Vasa deferentia
- Rete testis
Answer. 4. Rete testis
Question 4. Common duct formed by the union of vas deferens and the duct of seminal vesicle is
- Urethra
- Tunica vasculosa
- Ejaculatory
- Spermatic duct
Answer. 3. Ejaculatory
Question 5. Accessory glands of male reproductive system are
- Prostate and seminal vesicles
- Prostate, Bartholin’s glands, and seminal vesicles
- Seminal vesicles and Bartholin’s glands
- Prostate, Cowper’s glands, and seminal vesicles
Answer. 4. Prostate, Cowper’s glands, and seminal vesicles
Question 6. Scrotal sacs of man are connected with the abdominal cavity by
- Inguinal canal
- Haversian canal
- Spermatic canal
- Rete testis
Answer. 1. Inguinal canal
Question 7. Sperms are stored and nourished inside
- Cowper’s gland
- Epididymis
- Seminiferous tubules
- Vasa efferentia
Answer. 2. Epididymis
Question 8. The role of the Leydig cells of testis is
- To provide nourishment to sperms
- To provide motility to sperms
- To bring about maturation of sperms
- Synthesis of testosterone hormone
Answer. 4. Synthesis of testosterone hormone
Question 9. Vas deferens arises from
- Cauda epididymis
- Caput epididymis
- Corpus epididymis
- Rete testis
Answer. 1. Cauda epididymis
Question 10. Epididymis is
- Network of sinuses between seminiferous tubules and vasa efferentia
- Intermediate structure between rete testis and vasa efferentia
- A long coiled tube between vasa efferentia and vas deferens
- Connection between vas deferens and seminal vesicle
Answer. 3. A long coiled tube between vasa efferentia and vas deferens
Question 11. Failure of testis to descend in scrotal sac is known as
- Impotency
- Castration
- Synorchidism
- Cryptorchidism
Answer. 4. Cryptorchidism
Question 12. Which of the following releases inhibin to control spermatogenesis?
- Rete testis
- Follicular cells
- Sustentacular cells
- Leydig’s cells
Answer. 3. Sustentacular cells
Question 13. Testosterone is secreted by
- Sertoli cells
- Sustentacular cells
- Both (1) and (2).
- Leydig cell or interstitial cell
Answer. 4. Leydig cell or interstitial cell
Question 14. Vas deferens starts from which part of epididymis?
- Caput epididymis
- Corpus epididymis
- Cauda epididymis
- None of these
Answer. 3. Cauda epididymis
Question 15. Rete testis is a highly anastomosing labyrinth lined by
- Simple squamous epithelium
- Cuboidal epithelium
- Columnar epithelium
- Tessalated epithelium
Answer. 2. Cuboidal epithelium
Question 16. Which of the following gland is a collection of 30-40 tubuloalveolar glands and surrounds the first part of urethra?
- Corpus spongiosum
- Corpus cavernosum
- Prostate
- Cowper’s gland
Answer. 3. Prostate
Question 17. In man, the sperms released from the testis take which of the following route to reach the urethera?
- Vasa efferentia, Bidder’s canal, uriniferous tubule
- Vasa efferentia, epididymis, vas deferens
- Vasa efferentia, Bidder’s canal, nephrostome
- Vasa efferentia, collecting tubules, and Bidder’s canal
Answer. 2. Vasa efferentia, epididymis, vas deferens
Question 18. The life span of a human sperm in male genital duct is
- 24 h
- 48 h
- 72 h
- Many weeks
Answer. 4. Many weeks
Question 19. Mesovarium is the peritoneal covering of
- Ovary
- Testis
- Kidney
- Liver
Answer. 1. Ovary
Question 20. Ostium is an aperture present in
- Ampulla part
- Fallopian funnel
- Ovisac
- Cloaca
Answer. 2. Fallopian funnel
Question 21. The lower narrow end of uterus is called
- Urethra
- Cervix
- Clitoris
- Vulva
Answer. 2. Cervix
Question 22. Which group represents the external genitalia of human female?
- Labium minora, labium majora, vagina
- Labium majora, labium minora, oviduct
- Labium minora, labium majora, cervix
- Labium majora, labium minora, clitoris
Answer. 4. Labium majora, labium minora, clitoris
Question 23. The layers of ovum from outside to inside are
- Corona radiata, zona pellucida, vitelline membrane
- Zona pellucida, corona radiata, vitelline membrane
- Vitelline membrane, zona pellucida, corona radiata
- Zona pellucida, vitelline membrane, corona radiata
Answer. 1. Corona radiata, zona pellucida, vitelline membrane
Question 24. In human females, ova are produced in
- Ovary
- Oviduct
- Uterus
- Vagina
Answer. 1. Ovary
Question 25. Hormone responsible for ovulation and development of corpus luteum is
- FSH
- LH
- LTH
- ICSH
Answer. 2. LH
Question 26. When egg is not fertilized, yellow colored corpus lutem degenerates to form
- Corpus albicans
- Corpus callosum
- Corpora bigemina
- Corpora quadrigemina
Answer. 1. Corpus albicans
Question 27. In the absence of pregnancy, corpus luteum
- Becomes active and secretes FSH and LH
- Produces a lot of oxytocin and relaxin
- Degenerates after some time
- Is maintained by progesterone
Answer. 3. Degenerates after some time
Question 28. Egg is liberated from ovary and enters the fallopian tube in
- Secondary oocyte stage
- Primary oocyte stage
- Oogonial stage
- Mature ovum stage
Answer. 1. Secondary oocyte stage
Question 29. Lower narrow end of uterus is called
- Urethra
- Cervix
- Clitoris
- Vulva
Answer. 2. Cervix
Question 30. Which one of the following is adapted for receiving the male’s penis during copulation and for serving as the birth canal during parturition?
- Cervix
- Vagina
- Fundus
- Body
Answer. 2. Vagina
Question 31. Clitoris in a human female is
- Vestigial organ
- Analogous to penis in male
- Homologous to penis in male
- None of these
Answer. 3. Homologous to penis in male
Question 32. Which of the following is not true for clitoris?
- It is the erectile part of female reproductive system.
- It ends in glans clitoridis.
- It has three erectile bodies with it.
- Its end is covered with prepuce.
Answer. 3. It has three erectile bodies with it.
Question 33. During spermatogenesis, meiosis occurs in
- Primary spermatocytes
- Secondary spermatocytes
- Both (1) and (2)
- Spermatogonia
Answer. 3. Both (1) and (2)
Question 34. Spermiogenesis changes
- Spermatogonium to primary spermatocytes
- Primary spermatocytes to secondary spermatocytes
- Secondary spermatocytes to spermatids
- Spermatids to sperms
Answer. 4. Spermatids to sperms
Question 35. In spermatogenesis, a primary spermatocyte produces four similar sperms while in oogenesis, a primary oocyte forms
- Four similar ova
- Three large ova and one polar body
- Two large ova and two polar bodies
- One large ova and 2-3 polar bodies
Answer. 2. Three large ova and one polar body
Question 36. Minute cells separating from ova are
- Primary oogonia
- Polar bodies
- Secondary oogonia
- Primary spermatogonia
Answer. 2. Polar bodies
Question 37. What are the diploid stages in spermatogenesis?
- Spermatogonia and spermatids
- Spermatogonia and primary spermatocytes
- Spermatogonia and primary spermatocytes
- Primary spermatocytes and secondary spermatocytes
Answer. 2. Spermatogonia and primary spermatocytes
Question 38. The extrusion of second polar body from the egg nucleus occurs
- After the entry of sperm and before the completion of fertilization
- After the completion of fertilization
- Before the entry of sperm
- Without any relation with sperm entry
Answer. 1. After the entry of sperm and before the completion of fertilization
Question 39. Spermatogenesis and sperm differentiation are under the control of
- FSH only
- LH
- Testosterone and FSH
- Parathyroid hormone
Answer. 3. Testosterone and FSH
Question 40. The middle piece of mammalian sperm possesses
- Mitochondria
- Centriole only
- Acrosome
- Parathyroid hormone
Answer. 1. Mitochondria
Question 41. A change in ovum after the penetration of sperm is
- Formation of first polar body
- Second meiosis start
- First meiosis
- Formation of second polar body
Answer. 4. Formation of second polar body
Question 42. Which of the following structures produces energy for them ability of mature sperm?
- Nucleus in head region
- Mitochondria in head region
- Axial filament in tail
- Mitochondria in middle piece
Answer. 4. Mitochondria in middle piece
Question 43. Axial filament of the sperm arises from
- Proximal centriole
- Distal centriole
- Acrosome
- Nucleus
Answer. 2. Distal centriole
Question 44. Acrosome of sperm develops from
- Mitochondria
- Golgi complex
- Ribosomes
- Centriole
Answer. 2. Golgi complex
Question 45. The phase of transformation of spermatid into sperm is called
- Spermiogenesis
- Spermateleosis
- Gametogenesis
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 46. Amoeboid sperms or tail-less, non-flagellated sperms are found in
- Earthworm
- Taenia
- Ascaris
- All of these
Answer. 3. Ascaris
Question 47. Oogenesis in a human female starts
- At puberty (8 years of age)
- At puberty (13 years of age)
- At menarche
- Before birth
Answer. 4. Before birth
Question 48. The hormone that is present in the greatest concentration in the blood during ovulation in a female is
- FSH
- LH
- Prolactin
- Progesterone
Answer. 2. LH
Question 49. In menstrual cycle of 28/29 days, ovum is released during
- Beginning of the cycle
- Middle of the cycle
- End of the cycle
- Any time during the cycle
Answer. 2. Middle of the cycle
Question 50. Loss of reproductive capacity in women after the age of 45 years is
- Menstruation
- Ageing
- Menopause
- Menarche
Answer. 3. Menopause
Question 51. The correct sequence of hormones secreted from the be- ginning of menstrual cycle is
- FSH, estrogen, progesterone
- Estrogen, FSH, progesterone
- FSH, progesterone
- Estrogen, progesterone, FSH
Answer. 1. FSH, estrogen, progesterone
Question 52. The phase of menstrual cycle in humans that lasts for 7-8 days is
- Follicular phase
- Ovulatory phase
- Luteal phase
- Menstruation
Answer. 1. Follicular phase
Question 53. Menstrual cycle occurs in
- All females
- Mammalian females
- Primate females
- Rabbits
Answer. 3. Primate females
Question 54. The withdrawal of which hormone is the immediate cause of menstruation?
- Estrogen
- FSH
- FSH-LH
- Progesterone
Answer. 4. Progesterone
Question 55. LH surge occurs during which phase of menstrual cycle?
- Menstrual phase
- Beginning of proliferative phase
- Secretory phase
- At the middle of the cycle
Answer. 4. At the middle of the cycle
Question 56. Estrous cycle is the characteristic of
- Human females
- Mammalian females
- Mammalian females other than primates
- Primate females
Answer. 3. Mammalian females other than primates
Question 57. Monoestrous animals have
- One ovulation each month
- One heat period each month
- One breeding season in a year
- One menstrual cycle each month
Answer. 3. One breeding season in a year
Question 58. Which hormone level reaches peak during the luteal phase of menstrual cycle?
- Luteinising hormone
- Progesterone
- FSH
- Estrogen
Answer. 2. Progesterone
Question 59. Menses occurs in
- Human beings only
- Old world monkeys and apes (primates)
- Every mammal
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 60. Secondary oocyte is
- Haploid
- Diploid
- Polyploid
- None of these
Answer. 1. Haploid
Question 61. Oral contraceptives check
- Ovulation
- Fertilization
- Implantation
- Entry of sperm into vagina
Answer. 1. Ovulation
Question 62. Which part of the ovary in mammals acts as an endocrine gland after ovulation?
- Vitelline membrane
- Graffian follicle
- Corpus luteum
- Germinal epithelium
Answer. 3. Corpus luteum
Question 63. The transparent layer found around the outer surface of a developing ovum is called
- Zona radiata
- Zona pellucida
- Theca externa
- Theca interna
Answer. 2. Zona pellucida
Question 64. Cessation of menstrual cycle is called
- Ovulation
- Puberty
- Menopause
- Implantation
Answer. 3. Menopause
Question 65. Based on the distribution of yolk, the egg of humans is
- Telolecithal
- Centrolecithal
- Microlecithal
- Alecithal
Answer. 4. Alecithal
Question 66. Egg will be having moderate amount of yolk in case of
- Sea urchin
- Starfish
- Frog
- All of these
Answer. 3. Frog
Question 67. Vitelline layer around the egg is deposited by
- Ovary
- Oviduct
- Egg itself
- Coelom
Answer. 3. Egg itself
Question 68. In bony fishes, reptiles, and birds, the cleavage pattern is
- Meroblastic centrolecithal
- Holoblastic unequal
- Meroblastic discoidal
- Holoblastic radial
Answer. 3. Meroblastic discoidal
Question 69. The eggs of insects are
- Homolecithal
- Centrolecithal
- Meiolecithal
- Telolecithal
Answer. 2. Centrolecithal
Question 70. Spiral cleavage is found in
- Coelenterates
- Annelids
- Echinodermata
- Mollusca
Answer. 2. Annelids
Question 71. Leathery eggs are found in
- Amphibians
- Reptiles
- Birds
- Mammals
Answer. 2. Reptiles
Question 72. An avian blastula is called
- Coeloblastula
- Stereoblastula
- Discoblastula
- Periblastula
Answer. 3. Stereoblastula
Question 73. When blastomeres from the outer surface are rolled in, into the interior of developing embryo, it is called
- Invagination
- Involution
- Ingression
- Delamination
Answer. 2. Involution
Question 74. After a sperm has penetrated an ovum in the process of fertilization, the entry of further sperms is prevented by
- Development of the vitelline membrane
- Development of the pigment coat
- Condensation of yolk
- Formation of fertilization membrane
Answer. 4. Formation of fertilization membrance
Question 75. Fertilization in human beings occurs in
- Fallopian tube
- Uterus
- Ampulla part of oviduct
- Isthmus part of oviduct
Answer. 3. Ampulla part of oviduct
Question 76. The function of hyaluronidase is
- To form cone of reception in egg
- To dissolve the cementing part of granulosa cells
- To release second polar body
- None of these
Answer. 2. To dissolve the cementing part of granulosa cells
Question 77. Fertilizin proteins are associated with
- Corona radiata of the ovum
- Zona pellucida of the ovum
- Acrosome of the sperm
- Tail part of the sperm
Answer. 2. Zona pellucida of the ovum
Question 78. Blastocyst comes out of slit of zona pellucida in
- Ampulla part of fallopian tube
- Isthmus part of fallopian tube
- Uterine part of fallopian tube
- Uterus
Answer. 4. Uterus
Question 79. Cervical gland starts secreting viscous mucus for filling the cervical canal to form a protective plug during pregnancy under the influence of
- FSH
- LH.
- Progesterone
- Oxytocin
Answer. 3. Progesterone
Question 80. Skeleton and muscles in a vertebrate embryo develop from
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm
- Endo-mesoderm
- Endoderm
Answer. 2. Mesoderm
Question 81. Gestation period in a man is about
- 10 weeks
- 28 weeks
- 36 weeks
- 38 weeks
Answer. 4. 38 weeks
Question 82. Umbilical cord suspends embryo in amniotic cavity and is attached to the midgut region of the embryo. In cutherians, this umbilical cord is formed of the stalk of
- Yolk sac and amnion
- Allantois and chorion
- Yolk sac and chorion
- Allantois and yolk sac
Answer. 2. Allantois and chorion
Question 83. If both the ovaries of a pregnant female are removed in the second trimester, it will lead to
- Abortion
- Slow development of fetus
- Normal development
- Premature birth
Answer. 3. Normal development
Question 84. Amniotic fluid comes out through vagina during which stage of parturition?
- Dilation stage
- Expulsion stage
- After birth stage
- None of these
Answer. 1. Dilation stage
Question 85. The placenta in mammals is formed by
- Allantois
- Amnion
- Chorion
- Both (1) and (3)
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (3)
Question 86. The placenta in man is
- Haemochorial
- Epitheliochorial
- Syndesmochorial
- Haemo-endothelial
Answer. 1. Haemochorial
Question 87. The stage of embryo development at which implantation occurs in human females is
- Morula
- Zygote
- Blastocyst
- Transient three-celled stage
Answer. 3. Blastocyst
Question 88. In ectopic pregnancy, fetus grows in
- Fundus part of uterus
- Fallopian tube
- Uterus
- Both (1) and (3)
Answer. 2. Fallopian tube
Question 89. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
- Fertilization occurs in fallopian tube.
- Fertilization is a physio-chemical process/event.
- Cleavage produces morula.
- Cleavage leads to increased mass of protoplasm.
Answer. 4. Cleavage leads to increased mass of protoplasm.
Question 90. Cortical granules are associated with
- Oogenesis
- Spermatogenesis
- Cleavage
- Fertilization
Answer. 4. Fertilization
Question 91. Termination of gastrulation is marked by
- Closure of primitive gut
- Obliteration of archenteron
- Obliteration of blastocoel
- Closure of neural tube
Answer. 3. Obliteration of blastocoel
Question 92. Onset of pregnancy
- Stimulates testosterone secretion
- Leads to degeneration ovary
- Inhibits further ovulation
- Inhibits fusion of egg and sperm nuclei
Answer. 3. Inhibits further ovulation
Question 93. Site of fertilization in a mammal is
- Ovary
- Uterus
- Vagina
- Fallopian tube
Answer. 4. Fallopian tube
Question 94. Placenta is
- Channel for providing essential requirements for growth of embryo
- Storage organ
- Conductor for nerve impulse
- Meant for protection of embryo from shocks
Answer. 1. Channel for providing essential requirements for growth of embryo
Question 95. After a sperm has penetrated an ovum, the entry of other sperms is prevented by
- Condensation of yolk
- Formation of pigment coat
- Development of vitelline
- Development of fertilization membrane
Answer. 4. Development of fertilization membrane
Question 96. Two offsprings developed in the same uterus from the fertilization of two different ova are
- Monozygotic twins
- Dizygotic twins
- Fraternal twins
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer. 4. Both (2) and (3)
Question 97. Type of parthenogenesis in the honey bee is
- Complete, thelytoky
- Incomplete, thelytoky
- Complete, arrhenotoky
- Incomplete, arrhenotoky
Answer. 4. Incomplete, arrhenotoky
Question 98. The main white fibrous cover around the testis is called
- Tunica vasculosa
- Tunica albuginea
- Tunica vaginalis
- Tunica media
Answer. 2. Tunica albuginea
Question 99. The muscles playing major role in the positioning of the testis are
- Cremaster
- Dartos
- Detrusor
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 100. Which of the following is not the part of intratesticular genital duct system?
- Rete testis
- Tubuli recti
- Vas deferens
- Vas efferens
Answer. 3. Vas deferens
Question 101. Ampulla part in the male reproductive system is related to
- Epididymis
- Vas deferens
- Fallopian tube
- Tubuli recti
Answer. 2. Vas deferens
Question 102. The inhibin hormone is released by
- Medulla
- Granulosa cells
- Theca cells
- Zona pellucida
Answer. 2. Granulosa cells
Question 103. Ostium is the aperture present in
- Oviduct
- Fallopian funnel
- Ovisac
- Cloaca
Answer. 2. Fallopian funnel
Question 104. In humans, perineum refers to the space between
- Incisor and premolar teeth
- Mouth and nostril
- Upper and lower lips
- Anus and vulva
Answer. 4. Anus and vulva
Question 105. The scrotal sac of a male mammal is homologous to which part of female genitalia?
- Vagina
- Uterus
- Clitoris
- Labia majora
Answer. 4. Labia majora
Question 106. The function of Bartholin’s gland in a female is
- To nourish the growing embryo
- To neutralize the acidity of vagina
- Secretion of fructose
- To render the vagina slimy
Answer. 4. To render the vagina slimy
Question 107. If in a sperm the proximal centriole becomes non-functional, which of the following shall not occur?
- First cleavage
- Second cleavage
- Maturation of oocyte
- Spermiogenesis
Answer. 1. First cleavage
Question 108. Which of the following plays important role in concentrating testosterone in the seminiferous tubules?
- Leydig’s cells
- Sertoli cells (ABP)
- Granulosa cells
- Tubuli recti
Answer. 2. Sertoli cells (ABP)
Question 109. The fall in the number of sperms per millimeter of semen causes sterility. This is due to insufficient amount of
- Acid phosphates
- Alkaline phosphates
- Testosterone
- Hyaluronidase
Answer. 3. Testosterone
Question 110. Anestrum state is
- Non-ovulation in human female
- Suspension of menstrual cycle in human female
- Suspension of estrous cycle in non-primates
- “Period of heat” in non-primates
Answer. 3. Suspension of estrous cycle in non-primates
Question 111. The principle chemical components of yolk are
- Proteins and carbohydrates
- Proteins, phospholipids, and fats
- Proteins and vitamins
- Carbohydrates and lipids
Answer. 2. Proteins, phospholipids, and fats
Question 112. Vitelline membrane is a
- Primary egg membrane
- Secondary egg membrane
- Tertiary egg membrane
- None of these
Answer. 1. Primary egg membrane
Question 113. Which of the following around a hen’s egg is a tertiary membrane?
- Albumen
- Shell membranes
- Calcareous shell
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 114. When cleavage furrow bisects both poles of the egg passing through the animal-vegetal axis, the plane of cleavage is called
- Meridional
- Equatorial
- Vertical
- Horizontal
Answer. 1. Meridional
Question 115. Which one of the following is not a characteristic of cleavage?
- Mitotic divisions
- Increase in the synthesis of DNA
- Increase of protoplasm
- Cells of continuously smaller size
Answer. 3. Increase of protoplasm
Question 116. Right and left sides of an embryo become apparent during
- Radial cleavage
- Bilateral cleavage
- Spiral cleavage
- Biradial cleavage
Answer. 2. Bilateral cleavage
Question 117. A blastula consisting of a blastoderm of one or several layers of cells arranged around a spacious blastocoel is termed as
- Periblastula
- Coeloblastula
- Stereoblastula
- Discoblastula
Answer. 2. Coeloblastula
Question 118. The movement of micromeres over the surface of blastula, resulting in the elongation of embryo, is known as
- Divergence
- Convergence
- Involution
- Epiboly
Answer. 4. Epiboly
Question 119. Blastodisc is restricted to a small area in
- Eutherian egg
- Avian egg
- Ascaris egg
- Amphibian egg
Answer. 2. Avian egg
Question 120. Mosaic or determinate cleavage is found in
- Sponges, echinoderms, and eutherian mammals
- Cyclostomes, elasmobranchs, dipnoi, amphibian, and cephalopod molluscs
- Coelenterates
- Nematodes and amphioxus
Answer. 4. Nematodes and amphioxus
Question 121. Which of the following is involved in capacitation?
- Removal of membrane cholesterol present over acrosome
- Entry of Ca2+ into sperms
- Dilution of decapacitation factors
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 122. The function of cortical granules in the cortex of the ovum is the formation of
- Vitelline membrane
- Perivitelline membrane
- Fertilization membrane
- Plasma membrane
Answer. 3. Fertilization membrane
Question 123. The fertilization membrane is secreted because
- It checks the entry of more sperms after fertilization
- It checks the entry of antigens in ovum
- It checks syngamy
- None of these
Answer. 1. It checks the entry of more sperms after fertilization
Question 124. Which of the following is involved in slow block to the polyspermy?
- Cortical reaction
- Zona reaction
- Depolarization starting at the fertilization cone
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 125. “Cells of Rauber” are
- Trophoblast cells in contact with embryonal knob
- Cells of inner cell mass
- Cells present in the blastocoel
- Uterine epithelial cells making contact with blastocyst
Answer. 1. Trophoblast cells in contact with embryonal knob
Question 126. The part of decidua present between embryo and the lu- men of uterus is called
- Decidua basalis
- Decidua capsularis
- Decidua parietalis
- Perimetrium
Answer. 2. Decidua capsularis
Question 127. Which of the following is true regarding the first germinal layer to differentiate during embryonic development?
- Endoderm, epiblast
- Endoderm, hypoblast
- Mesoderm, epiblast
- Mesoderm, hypoblast
Answer. 1. Endoderm, epiblast
Question 128. Ontogenetically, liver and pancreas are
- Ectodermal
- Mesodermal
- Endodermal
- None of these
Answer. 3. Endodermal
Question 129. The mesoderm gives rise to all structures except
- Nervous system
- Muscular system
- Circulatory system
- Gonads
Answer. 1. Nervous system
Question 130. The effect of teratogens is maximum during
- First trimester
- Second trimester
- Third trimester
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer. 1. First trimester
Question 131. Hormone administered for hastening child birth is meant for
- Stimulating striped muscles
- Raising blood pressure
- Increasing energy availability
- Contraction of smooth muscles
Answer. 4. Contraction of smooth muscles
Question 132. Gestation period in humans is
- 10 weeks
- 28 weeks
- 32 weeks
- 38 weeks
Answer. 4. 38 weeks
Question 133. Extra-embryonic membrane amnion provides
- Cells to embryo
- Protection to embryo
- Nutrition to embryo
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer. 2. Protection to embryo
Question 134. Active in rolling of endodermal and mesodermal cells into the interior of embryo is
- Ingression
- Involution
- Inversion
- Epiboly
Answer. 2. Involution
Question 135. Gastrulation comprises
- Morphogenetic movements
- Differentiation of archenteron
- Differentiation of three germ layers
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 136. During embryonic development, which of the following organs is formed first?
- Heart
- Brain
- Neural tube
- Skin
Answer. 3. Neural tube
Question 137. Which of the following are the derivatives of endoderm?
- Muscles and blood
- Alimentary canal and respiratory organs
- Excretory and reproductive organs
- Skin and nerve cord
Answer. 2. Alimentary canal and respiratory organs
Question 138. Fetal ejection reflex in a human female is induced by
- Release of oxytocin from pituitary gland
- Pressure exerted by amniotic fluid
- Differentiation of mammary glands
- Fully developed fetus and placenta
Answer. 4. Fully developed fetus and placenta
Question 139. Find the incorrect match with respect to increase in the levels of following hormones:
- Oxytocin-Uterine contraction during labor
- Prolactin-Lactation after child birth
- Progesterone – Uterine contraction
- Luteinizing hormone – Stimulates ovulation
Answer. 3. Progesterone – Uterine contraction
Question 140. Kidneys, heart, and gonads are formed from
- Ectoderm
- Endoderm
- Inner cell mass
- Mesoderm
Answer. 4. Mesoderm
Question 141. The lytic enzyme present in semen is
- Ligase
- Estrogenase
- Androgenase
- Hyaluronidase
Answer. 4. Hyaluronidase
Question 142. Progesterone is secreted by
- Corpus aorta
- Corpus albicans
- Corpus luteum
- Corpus callosum
Answer. 3. Corpus luteum
Question 143. Which of the following causes abortion in ladies?
- Virus
- Bacteria
- Mycoplasma
- None of these
Answer. 2. Bacteria
Question 144. Accessory sexual character in female is promoted by
- Androgen
- Progesterone
- Estrogen
- Testosterone
Answer. 3. Estrogen
Question 145. Sertoli cells are found in testis. These cells are
- Nurse cell
- Reproductive cell
- Receptor cell
- None of these
Answer. 1. Nurse cell
Question 146. Cryptorchidism is a condition in which
- Testis does not descend into scrotal sac
- Sperm in not found
- Male hormones are not reactive
- Ovaries are removed
Answer. 1. Testis does not descend into scrotal sac
Question 147. The cellular layer that disintegrates and regenerates again and again in humans is
- Endometrium of uterus
- Cornea of eye
- Dermis of skin
- Endothelium of blood vessels
Answer. 1. Endometrium of uterus
Question 148. The functional maturation of sperms takes place in
- Oviduct
- Epididymis
- Vagina
- All of these
Answer. 2. Epididymis
Question 149. Surgical removal or cutting and ligation of the ends of oviduct is known as
- Tubectomy
- Oviductomy
- Castration
- Vasectomy
Answer. 1. Vasectomy
Question 150. The follicle that ruptures at the time of ovulation promptly fills with blood forming
- Corpus haemorrhagicum
- Corpus luteum
- Corpus albicans
- Corpus callosum
Answer. 1. Corpus haemorrhagicum
Question 151. In mammals, estrogens are secreted by the Graafian follicle from its
- External theca
- Internal theca
- Zona pellucida
- Corona radiata
Answer. 2. Internal theca
Question 152. Supporting cells found in the germinal epithelium of tes- tis are called
- Interstitial cells of Leydig
- Sertoli cells
- Granular cells
- Phagocytes
Answer. 2. Sertoli cells
Question 153. In mammals, the female secondary sexual characters are developed mainly by the hormone
- Relaxin
- Estrogens
- Progesterone
- Gonadotropins
Answer. 2. Estrogens
Question 154. Cryptorchidism is a condition of testes
- Unable to descend in scrotal sacs
- Unable to produce sperms
- Having been surgically removed
- Having remained undeveloped
Answer. 1. Unable to descend in scrotal sacs
Question 155. In between spermatogonia are found
- Germinal cells
- Sertoli cells
- Epithelial cells
- Lymph space
Answer. 2. Sertoli cells
Question 156. Which accessory genital gland occurs only in male mammal?
- Bartholin’s gland
- Perineal gland
- Prostate gland
- All
Answer. 3. Prostate gland
Question 157. During differentiation, the spermatids remain associated with
- Leydig’s cells
- Kupffer’s cells
- Spermatogonia
- Sertoli cell
Answer. 4. Sertoli cell
Question 158. What would happen if vasa deferentia of man are cut?
- Sperms will be non-nucleate.
- Spermatogenesis will not occur.
- Semen will be without sperms.
- Sperm will be non-motile.
Answer. 3. Semen will be without sperms.
Question 159. The Sertoli cells occur in
- Human testis
- Frog testis
- Human ovary
- Frog ovary
Answer. 1. Human testis
Question 160. Which one of the following is primary sex organ?
- Scrotum
- Penis
- Testis
- Prostrate
Answer. 3. Testis
Question 161. If somatic chromosomes’ number is 40, what shall be the chromosomal number in the cell of seminiferous tubules?
- 40
- 20
- 10
- 40 and 20
Answer. 4. 40 and 20
Question 162. Eggs are liberated from ovary in humans in the
- Secondary oocyte stage
- Primary oocyte stage
- Oogonial stage
- Mature ovum stage
Answer. 1. Secondary oocyte stage
Question 163. The Graafian follicles are found in
- Testis of mammal
- Ovary of frog
- Ovary of cockroach
- Ovary of mammals
Answer. 4. Ovary of mammals
Question 164. The site of fertilization in
- Ovary
- Uterus
- Vagina
- Fallopian tube
Answer. 4. Fallopian tube
Question 165. Endometrium is lining of
- Testis
- Urinary bladder
- Uterus
- Ureter
Answer. 3. Uterus
Question 166. A secondary sexual character is
- Breast
- Ovary
- Testis
- Thyroid
Answer. 1. Breast
Question 167. Expanded proximal part of oviduct in females is
- Uterus
- Fallopian tube
- Fimbriated funnel
- Vestibule
Answer. 3. Fimbriated funnel
Question 168. The endocrinal structure formed after ovulation (release of ovum from the Graafian follicle) is
- Corpus albicans
- Corpus callosum
- Corpus luteum
- Corpus striatum
Answer. 3. Corpus luteum
Question 169. Corpus luteum is
- Excretory
- Endocrine
- Digestive
- Reproductive
Answer. 2. Endocrine
Question 170. A female gland corresponding to the prostrate of males is
- Bartholin’s gland
- Bulbourethral gland
- Clitoris
- None
Answer. 4. None
Question 171. Progesterone is secreted by
- Corpus luteum
- Thyroid
- Thymus
- Testis
Answer. 1. Corpus luteum
Question 172. Spermatogenesis and sperm differentiation are under the control of
- FSH
- LH
- Progesterone
- Parathyroid hormone
Answer. 1. FSH
Question 173. During pregnancy, the urine of woman contains
- LH
- Progesterone
- FSH
- HCG
Answer. 4. HCG
Question 174. In the absence of pregnancy, corpus luteum
- Becomes active, secretes FSH and LH
- Produces lot of oxytocin and relaxin
- Degenerates after some time
- Is maintained by progesterone
Answer. 3. Degenerates after some time
Question 175. 10 oogonia yield 10 primary oocytes. Then how many ova are produced on the completion of oogenesis?
- 5
- 10
- 20
- 40
Answer. 2. 10
Question 176. Parturition duct in females is called
- Uterus
- Oviduct
- Vagina
- Cervix
Answer. 3. Vagina
Question 177. Which temporary endocrine gland forms in ovary after ovulation?
- Corpus callosum
- Corpus albicans
- Corpus luteum
- Corpus striatum
Answer. 3. Corpus luteum
Question 178. In mammals, the maturation of sperms take place at a temperature
- Equal to that of body
- Higher than that of body
- Lower than that of body
- At any piece of mammalian sperm
Answer. 3. Lower than that of body
Question 179. Onset of pregnancy
- Stimulates testosterone secretion
- Inhibits further ovulation
- Leads to degeneration of ovary
- Inhibits fusion of egg and sperm nuclei
Answer. 2. Inhibits further ovulation
Question 180. Graffian follicles contain
- Corpus luteum
- Corpus albicans
- Theca externa and theca interna
- Oogonial cells
Answer. 3. Theca externa and theca interna
Question 181. Bartholin’s glands occur in
- Females and help in vestibular lubrication
- Females and produce oestrogen for regulating secondary sexual characters
- Males and form liquid part of spermatic field
- Males and produce alkaline fluid for neutralizing urethral acidity
Answer. 1. Females and help in vestibular lubrication
Question 182. Which is correct?
- Menstrual cycle is present in all mammals.
- Menstrual cycle is present in all primates.
- Estrous cycle occurs in all mammals.
- Most mammals are ovoviviparous.
Answer. 2. Menstrual cycle is present in all primates.
Question 183. Yellow corpus luteum occurs in mammals in
- Heart to initiate heartbeat
- Skin to function as pain receptor
- Brain and connects cerebral hemisphere
- Ovary for secretion of progesterone
Answer. 4. Ovary for secretion of progesterone
Question 184. Human sperm was discovered by
- Leeuwenhoek
- Aristotle
- Graaf
- Pander
Answer. 1. Leeuwenhoek
Question 185. Corpus luteum secretes
- LH
- Estrogen
- Progesterone
- FSH
Answer. 3. Progesterone
Question 186. In case of non-fertilization, corpus luteum
- Stops secreting progesterone
- Changes to corpus albicans
- Starts producing progesterone
- None of the above
Answer. 2. Changes to corpus albicans
Question 187. Correct sequence of hormone secretion from the beginning of menstruation is
- FSH, progesterone, estrogen
- Estrogen, FSH, progesterone
- FSH, estrogen, progesterone
- Esterogen, progesterone, FSH
Answer. 3. FSH, estrogen, progesterone
Question 188. Graafian follicle contains
- Many oocytes
- Many sperms
- A single oocyte
- Site for egg fertilization
Answer. 3. A single oocyte
Question 189. Progesterone level falls leading to
- Gestation
- Menopause
- Lactation
- Menstruation
Answer. 4. Menstruatioin
Question 190. Head of epididymis present at the head of testis is
- Caput epididymis
- Cauda epidiymis
- Vas deferens
- Gubernaculum
Answer. 1. Caput epididymis
Question 191. Human female reaches menopause at the age of about
- 25 years
- 35 years
- 50 years
- 70 years
Answer. 3. 50 years
Question 192. Glands secreting male sex hormone are
- Leydig cells
- Seminiferous tubules
- Vasa deferentia
- Testes
Answer. 4. Testes
Question 193. Estrogen is secreted by
- Corpus luteum
- Graafian follicle
- Germinal epithelium of ovary
- Pituitary
Answer. 2. Graafian follicle
Question 194. Testes descent into scrotum in mammals for
- Spermatogenesis
- Fertilization
- Development of sex organs
- Development of visceral organs
Answer. 1. Spermatogenesis
Question 195. The phase of menstrual cycle in humans that lasts for 7-8 days is
- Follicular phase
- Ovulatory phase
- Luteal phase
- Menstruation
Answer. 1. Follicular phase
Question 196. Menstruation is caused by
- Increase in FSH level
- Fall in oxytocin level
- Fall in progesterone level
- Increase in oestrogen level
Answer. 3. Fall in progesterone level
Question 197. In the urinogenital system, one of the following part is present in males and not in females:
- Urethra
- Fallopian tube
- Vagina
- Vas deferens
Answer. 4. Vas deferens
Question 188. Number of sperms formed from four spermatocytes is
- 4
- 1
- 16
- 32
Answer. 3. 16
Question 199. In human females, ova are produced in
- Ovarian follicles
- Oviduct
- Uterus
- Vagina
Answer. 1. Ovarian follicles
Question 200. Which is correctly matched in a normal menstrual cycle?
- Endometrium regenerates-5 to 10 days
- Release of egg- 5th day
- Endometrium secretes nutrients for implantation – 11 to 18 days
- Rise in progesterone level – 1 to 15 days
Answer. 1. Endometrium regenerates-5 to 10 days
Question 201. Spermatogonia develop into the
- Ovary
- Ovum
- Sperm
- Zygote
Answer. 3. sperm
Question 202. Spermatogonia develop through division
- Amitosis
- Mitosis
- Meiosis 1
- Meiosis 2
Answer. 2. Mitosis
Question 203. Graafian follicles occur in
- Ovary
- Testis
- Egg
- Sperm
Answer. 1. Ovary
Question 204. Ovulation occurs in and on
- Ovary
- About 14th day
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these
Answer. 3. Both (1) and (2)
Question 205. Blastopore occurs in
- Gastrula
- Blastula
- Blastocoel
- Morula
Answer. 1. Gastrula
Question 206. Mesoderm is formed through invagination of
- Ectoderm
- Endoderm
- Inner mass of cells
- Primitive streak
Answer. 4. Primitive streak
Question 207. Secretion of which structure uterus for implantation?
- Ovary
- Corpus luteum
- Pituitary gland
- Ovarian follicle
Answer. 2. Corpus luteum
Question 208. Energy center of sperm is
- Head
- Middle piece
- Entire sperm
- Tail
Answer. 2. Middle piece
Question 209. Fusion of sperm and ovum is
- Amphimixis
- Regeneration
- Fertilization
- None of the above
Answer. 3. Fertilization
Question 210. Embryo at 16-celled stage is called
- Morula
- Blastula
- Blastomere
- Gastrula
Answer. 1. Morula
Question 211. Layers of ovum from outside to inside are
- Corona radiata, zona pellucida, vitelline membrane
- Zona pellucida, corona radiata, vitelline membrane
- Vitelline membrane, zona pellucida, corona radiata
- Zona pellucida, vitelline membrane, corona radiata
Answer. 1. Corona radiata, zona pellucida, vitelline membrane
Question 212. Which layer of embryo is formed first?
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm
- Endoderm
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer. 3. Endoderm
Question 213. In which phase of cell division are oogonia arrested?
- Anaphase 2
- Anaphase 1
- Interphase
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer. 2. Anaphase 1
Question 214. Capacitation of sperms occurs in
- Female genital tract
- Vagina
- Vas efferens
- Vas deferens
Answer. 1. Female genital tract
Question 215. Fertilization of ovum occurs in
- Fimbriae of oviduct
- Isthmus of oviduct
- Ampulla of oviduct
- None of the above
Answer. 3. Ampulla of oviduct
Question 216. Function of the Sertoli cells is controlled by
- Estrogen
- FSH
- Testosterone
- ACTH
Answer. 2. FSH
Question 217. Corpus spongiosum occurs in
- Ovary
- Penis
- Egg
- Sperm
Answer. 2. Penis
Question 218. Cytoplasm of ovum does not possess
- Golgi complex
- Mitochondria
- Centrosome
- Ribosomes
Answer. 3. Centrosome
Question 219. Which of the following provides nutrition to maturing sperms?
- Leydig cell
- Scrotum
- Epididymis
- Sertoli cells
Answer. 4. Sertoli cells
Question 220. LH and FSH are collectively called
- Oxytocin
- Somatotropins
- Gonadotropins
- Luteotropins
Answer. 3. Gonadotropins
Question 221. Mammalian blastula is known as
- Trophoderm
- Blastocyst
- Fetal blastula
- Oedema
Answer. 2. Blastocyst
Question 222. Acrosome of sperm contains
- Hydrolytic enzymes
- DNA
- Fructose
- Mitochondria
Answer. 1. Hydrolytic enzymes
Question 223. Radial cleavage is found in
- Tunicates
- Protozoans
- Coelenterates
- Annelids
Answer. 3. Coelenterates
Question 224. Cavity formed during gastrulation is
- Primitive gut
- Gastrocoel
- Archenteron
- All of the above
Answer. 2. Gastrocoel
Question 225. Menstrual phase is followed by
- Luteal phase
- Follicular phase
- Fertilization
- Implantation
Answer. 2. Follicular phase
Question 226. If for some reason, the vasa efferentia in the human re-productive system get blocked, the gametes will not be transported from
- Testes to epididymis
- Epididymis to vas deferens
- Ovary to uterus
- Vagina to uterus
Answer. 1. Testes to epididymis
Question 227. The testes in humans are situated outside the abdominal cavity inside a pouch called scrotum. The purpose served is for
- Maintaining the scrotal temperature lower than the internal body temperature
- Escaping any possible compression by the visceral organs
- Providing more space for the growth of epididymis
- Providing a secondary sexual feature for exhibiting the male sex
Answer. 1. Maintaining the scrotal temperature lower than the internal body temperature
Question 228. The figure given depicts a diagrammatic sectional view of the human female reproductive system. Which set of three parts out of I-VI have been correctly identified?
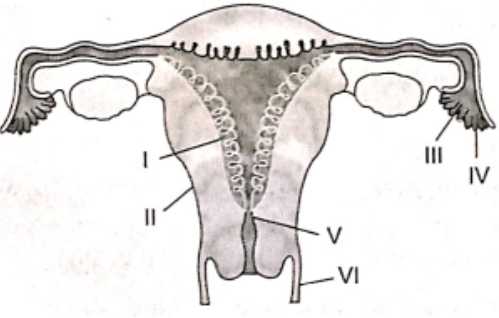
- (2) endometrium, (3) infundibulum, (4) fimbriae
- (3) infundibulum, (4) fimbriae, (5) cervix
- (4) oviducal funnel, (5) uterus, (6) cervix
- (1) perimetrium, (2) myometrium, (3) fallopian tube
Answer. 2. (3) infundibulum, (4) fimbriae, (5) cervix
Question 229. Singnals for parturition originate from
- Oxytocin released from maternal pituitary
- Placenta only
- Fully developed fetus only
- Both placenta as well as fully developed fetus
Answer. 4. Both placenta as well as fully developed fetus
Question 230. The secretory phase in the human menstrual cycle is also called
- Luteal phase and lasts for about 6 days
- Follicular phase and lasts for about 6 days
- Luteal phase and lasts for about 13 days
- Follicular phase and lasts for about 13 days
Answer. 3. Luteal phase and lasts for about 13 days
Question 231. Human placenta is
- Haemochorial
- Syndesmochorial
- Yolk sac
- Haemo-endothelial
Answer. 1. Haemochorial
Question 232. Human eggs are
- Alecithal
- Microlecithal
- Mesolecithal
- Macrolecithal
Answer. 1. Alecithal
Question 233. Human egg has
- One Y-chromosome
- One X-chromosome
- Two Y-chromosomes
- One X-chromosome and one Y-chromosome
Answer. 2. One X-chromosome and one Y-chromosome
Question 234. Fertilizins are emitted by
- Immature eggs
- Mature eggs
- Sperms
- Polar bodies
Answer. 2. Mature eggs
Question 235. During cleavage, what is true about embryo?
- Nucleocytoplasmic ratio remains unchanged
- Size does not increase
- There is less consumption of oxygen
- The division is like meiosis
Answer. 2. Size does not increase
Question 236. At the end of first meiotic division, male germ cell differentiates into
- Secondary spermatocyte
- Primary spermatocyte
- Spermatogonium
- Spermatid
Answer. 1. Secondary spermatocyte
Question 237. A mature sperm has
- A pair of flagella
- A nucleus, an acrosome, and a centriole
- A nucleus, an acrosome, a pair of centrioles
- A nucleus, an acrosome, a pair of centrioles and a tail
Answer. 4. A nucleus, an acrosome, a pair of centrioles and a tail
Question 238. Ovulation occurs under the influence of
- LH
- FSH
- Estrogen
- Progesterone
Answer. 1. LH
Question 239. Part of sperm involved in penetrating egg membrane is
- Tail
- Acrosome
- Allosome
- Autosome
Answer. 2. Acrosome
Question 240. Type of cleavage in an egg is determined by
- Amount and distribution of yolk
- Number of egg membranes
- Size and location of nucleus
- Shape and size of sperm
Answer. 1. Amount and distribution of yolk
Question 241. Fertilization is fusion of
- Diploid spermatozoan with diploid ovum to form diploid zygote
- Haploid spermatozoan with diploid ovum to from diploid zygote
- Diploid spermatozoan with haploid ovum to form diploid zygote
- Haploid spermatozoan with haploid ovum to form diploid zygote
Answer. 4. Haploid spermatozoan with haploid ovum to form diploid zygote
Question 242. Correct sequence in development is
- Fertilization → Zygote → Cleavage → Morula → Blastula → Gastrula
- Fertilization → Zygote → Blastula → Morula → Cleavage → Gastrula
- Fertilization → Cleavage → Morula → Zygote → Blastula → Gastrula
- Cleavage Zygote Fertilization → Morula → Blastula → Gastrula
Answer. 1. Fertilization → Zygote → Cleavage → Morula → Blastula → Gastrula
Question 243. Middle piece of mammalian sperm contains
- Nucleus
- Vacuoles
- Mitochondria
- Centriole
Answer. 3. Mitochondria
Question 244. Immediately after ovulation, the mammalian egg is covered by a membrane called
- Chorion
- Zona pellucida
- Corona raidata
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer. 4. Both (2) and (3)
Question 245. Cleavage in the fertilized egg of humans
- Starts in uterus
- Is meroblastic
- Starts when egg is in fallopian tube
- Is discoidal
Answer. 3. Starts when egg is in fallopian tube
Question 246. Polar body is produced during the formation of
- Sperm
- Secondary oocyte
- Oogonium
- Spermatocytes
Answer. 2. Secondary oocyte
Question 247. The head of mature mammalian sperm is made of
- An acrosome
- Elongated nucleus covered by acrosome
- Two centrioles and an axial filament
- Nucleus, acrosome, cytoplasm, and mitochondrial sheath
Answer. 2. Elongated nucleus covered by acrosome
Question 248. Oocyte is liberated from ovary under the influence of LH, after completing
- Mitosis and before liberating polar bodies
- Meiosis 1 and before liberating second polar bodies
- Meiosis
- Meiosis 2 after the release of the first polar body
Answer. 3. Meiosis
Question 249. Which cell division is found during cleavage?
- Amitosis
- Mitosis
- Closed mitosis
- Meiosis
Answer. 2. Mitosis
Question 250. 10 oogonia yield 10 primary oocytes. Then how many ova are produced on the completion of oogenesis?
- 5
- 10
- 20
- 40
Answer. 2. 10
Question 251. At the time of fertilization, sperm head enters in the egg from
- Anywhere
- Animal pole
- Vegetal pole
- Lateral side of egg
Answer. 3. Vegetal pole
Question 252. In which stage of development the embryonic cells form the germinal layers by the movement?
- Morula
- Blastula
- Gastrula
- Nerula
Answer. 2. Blastula
Question 253. In mammals, eggs are microlecithal and isolecithal because these are
- Oviparou
- Viviparous
- Ovoviviparous
- None of these
Answer. 2. Viviparous
Question 254. Which of the following is not correct for gastrulation?
- Archenteron is formed.
- All germinal layers are formed.
- Morphogenetic movements.
- Some blastomeres and blastocoel degenerate.
Answer. 4. Some blastomeres and blastocoel degenerate.
Question 255. At which stage of spermatogenesis, sperms acquire their whole structural maturity and they contain a haploid nucleus and other organs?
- Spermiogenesis
- Growth phase
- Multiplication phase
- Maturation phase
Answer. 1. Spermiogenesis
Question 256. Sperm enters from which part of egg?
- Anywhere in unfertilized egg from vegetal pole
- From animal pole in unfertilized egg
- In unfertilized egg from vegetal pole
- None
Answer. 2. From animal pole in unfertilized egg
Question 257. Completion of gastrulation is indicated by
- Obliteration of archenterone
- Obliteration of blastocoel
- Closing of blastopore
- Closing of neural tube
Answer. 2. Closing of neural tube
Question 258. In mammals, egg is fertilized in
- Ovary
- Fallopian tube
- Uterus
- Vagina
Answer. 2. Fallopian tube
Question 259. What is formed at the time of gastrulation?
- Gills
- Heart
- Myotome
- Archenteron
Answer. 4. Archenteron
Question 260. Which part of spermatid forms the acrosomes of sperm?
- Mitochondria
- Golgi body
- Nucleus
- Lysosome
Answer. 2. Golgi body
Question 261. How many sperms are formed by one primary spermatocyte?
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
Answer. 1. 4
Question 262. The chemical in ovum which attracts sperms is
- Fertilizin
- Antifertilizin
- Agglutinin
- Thrombin
Answer. 1. Fertilizin
Question 263. Which of the following organ is differentiated first during development?
- Heart
- Skin
- Brain
- Neural tube
Answer. 3. Brain
Question 264. In a vertebrate, which germ layer forms the skeletal muscles?
- Ectoderm
- Endoderm
- Mesoderm
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer. 3. Mesoderm
Question 265. Which layer develops first during embryonic development?
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm
- Endoderm
- Both (1) and (3)
Answer. 3. Endoderm
Question 266. The whole nervous system including neuron in a frog and other vertebrates is derived from
- Ectoderm
- Endoderm
- Mesoderm
- All of these
Answer. 1. Ectoderm
Question 267. In a sperm, the mitochondria occurs
- In tail
- In acrosome
- In middle piece
- In head
Answer. 3. In middile piece
Question 268. Which set of enzymes is found in the acrosome of mammalian spermatozoa?
- Hyaluronidase, corona penetrating enzyme (CPE)
- Hyaluronidase, CPE, zona lysine
- Hyaluronidase, CPE, peptidase
- Hyaluronidase only
Answer. 2. Hyaluronidase, CPE, zona lysine
Question 269. Fixing up of blastocyst in the wall of the uterus is known as
- Fertilization
- Implantation
- Impregnation
- Placentation
Answer. 2. Implantation
Question 270. The type of placenta found in human beings is
- Diffuse
- Zonary
- Cotyledonary
- Discoidal
Answer. 4. Discoidal
Question 271. The number of fetal membranes in a man is
- 1
- 3
- 4
- 0
Answer. 3. 4
Question 272. Placenta in human beings is formed by
- Amnion
- Chorion
- Allantois
- Allantois, chorion, and uterine wall
Answer. 4. Allantois, chorion, and uterine wall
Question 273. The phenomenon of nuclear fusion of sperm and egg is known as
- Karyogamy
- Parthenogenesis
- Vitellogenesis
- Oogenesis
Answer. 1.
Question 274. Arrchenteron cavity is found in
- Blastula
- Gastrula
- Morula
- Planula
Answer. 2. Gastrula
Question 275. Mammalian placenta originates from
- Allantois and chorion
- Yolk sac
- Allantois
- Amnion
Answer. 1. Allantois and chorion
Question 276. What is true for cleavage?
- Size of cell increases.
- Size of embryo increases.
- Size of cell decreases.
- Size of embryo decreases.
Answer. 3. Size of cell increases.
Question 277. A blastopore is found in
- Blastula and is the opening of blastocoel
- Gastrula and is the opening of blastocoel
- Blastula and is the opening of archenteron
- Gastrula and is the opening of archenteron
Answer. 4. Gastrula and is the opening of archenteron
Question 278. The extraembryonic membranes of mammalian embryo are derived from
- Trophoblast
- Follicle cells
- Formative cells
- Inner cell mass
Answer. 1. Trophoblast
Question 279. Find out the wrong statement:
- In mammals, allantois is not excretory in function.
- Amnion is the outer layer containing amniotic fluid that acts as shock absorber to the soft embryo.
- Yolk sac is a fetal membrane that helps in the nourishment of the embryo in general.
- Chorio-allantoic membrane develops villi and contributes much to the development of placenta.
Answer. 2. Amnion is the outer layer containing amniotic fluid that acts as shock absorber to the soft embryo.
Question 280. The woman who consumed the drug thalidomide for relief from vomiting during early months of pregnancy gave birth to children with
- Harelip
- No spleem
- Extra fingers and toes
- Underdeveloped limbs
Answer. 4. Underdeveloped limbs
Question 281. The chemical substance released by activated spermatozoa that acts on the ground substance of the follicle cells is known as
- Relaxin
- Teratogen
- Progesterone
- Hyaluronidase
Answer. 4. Hyaluronidase
Question 282. Menstrual flow occurs due to lack of
- FSH
- Oxytocin
- Vasopressin
- Progesterone
Answer. 4. Progesterone
Question 283. What is the correct sequence of sperm formation?
- Spermatogonia, spermatocyte, spermatozoa, spermatid
- Spermatogonia, spermatozoa, spermatocyte, spermatid
- Spermatogonia, spermatocyte, spermatid, spermatozoa
- Spermatid, spermatocyte, spermatogonia, spermatozoa
Answer. 3. Spermatogonia, spermatocyte, spermatid, spermatozoa
Question 284. Which one of the following is not the function of placenta? It
- Secretes estrogen
- Facilitates removal of carbon dioxide and waste material from embryo
- Secretes oxytocin during parturition
- Facilitates supply of oxygen and nutrients to embryo
Answer. 3. Secretes oxytocin during parturition
