NEET Biology For Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. The strongest evidence in favor of DNA as genetic material comes from
- Griffith effect
- Conjugation
- Taylor’s experiment
- Cairn’s effect
Answer. 1. Griffith effect
Question 2. Molecular explanation for transformation was given by
- Griffith
- Avery, McCarty, and Macleod
- Lederberg and Tatum
- Avery and McCarty
Answer. 2. Avery, McCarty, and Macleod
Question 3. Radioactive element used to label the DNA of bacterio- phage in the Waring blender experiment of Hershey and Chase was
- S35
- p32
- N15
- C14
Answer. 2. p32
Question 4. Transforming principle in Griffith’s experiments explains
- Certain rules for auxenic culture of bacteria
- Ingredients of culture medium
- Chemical substance released by S type
- Chemical substance released by R type
Answer. 3. Chemical substance released by S type
” molecular basis of inheritance “
Question 5. Some viruses do not have DNA. This suggests that
- They are non-infective viruses
- RNA is the genetic material in these viruses
- DNA is not the genetic material
- RNA is a self-replicating molecule
Answer. 2. RNA is the genetic material in these viruses
Question 6. RNA as genetic material in plant viruses was shown by
- Hershey and Chase
- Fraenkal Conrat
- F. Griffith
- Lederberg and Tatum
Answer. 1. Hershey and Chase
Question 7. The largest biomolecule in the cell which shows autocatalytic and heterocatalytic functions is
- Protein
- RNA
- DNA
- Carbohydrate
Answer. 2. RNA
Question 8. Who gave 3D model of B-DNA?
- Watson and Crick
- Wilkins and Franklin
- F. Meischer
- Zacharis
Answer. 3. F. Meischer
Question 9. Bonding between deoxyribose and base in pyrimidine nucleoside molecule is
- 1′-1 glycosidic linkage
- 1′-6 glycosidic linkage
- 1′-9 glycosidic linkage
- 1′-4 glycosidic linkage
Answer. 1. 1′-1 glycosidic linkage
Question 10. According to the Chargaff rule, (A+T)/(G + C) values in E. coli and human beings, respectively, are
- 1.52 and 0.93
- 0.93 and 1.52
- 0.66 and 1
- Always unit in both
Answer. 1. 1.52 and 0.93
Question 11. Numbers of base pairs in one turn of B-DNA and Z-DNA are, respectively,
- 9 and 11
- 10 and 11
- 10 and 12
- 8 and 9
Answer. 3. 10 and 12
Question 12. The total amount of DNA present in the haploid genome of an organism is called its
- C-value
- Phenotype
- Genotype
- Karyotype
Answer. 1. C-value
Question 13. T (melting temperature) value of DNA is high when it contains
- A+T>G+C
- G+C>A+T
- A+T=G+C
- A +G=T+C
Answer. 2. G+C>A+T
Question 14. Select the incorrect statement regarding RNA molecule:
- It has highly reactive 2′-OH group.
- It shows high rate of mutation than DNA.
- It is genetic material in some viruses.
- It follows Chargaff’s rule.
Answer. 4. It follows Chargaff’s rule.
Question 15. The distance covered by a complete turn of DNA double helix is
- 3.4 Å
- 34 Å
- 3.6 Å
- 36 Å
Answer. 2. 34 Å
Question 16. The ratio of bases which confirms Chargaff’s rule is/are
- A +G=T+C
- G+T=A+C
- A+T=G+C
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 17. The terms cistron, recon, and muton were proposed by
- W. Ingram
- Bateson
- J. Lederberg
- S. Benzer
Answer. 4. S. Benzer
Question 18. The modern concept of gene is that it is
- A segment of DNA capable of crossing-over
- A functional unit of DNA
- A segment of DNA
- A segment of chromosome
Answer. 2. A functional unit of DNA
Question 19. DNA replication is
- Semi-conservative
- Semi-discontinuous
- Conservative and discontinuous
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 20. Semiconservative mode of DNA replication was experimentally proved in prokaryotes by
- Meselson and Stahl
- Taylor
- Jacob and Monod
- A. Kornberg
Answer. 1. Meselson and Stahl
Question 21. In Meselson and Stahl’s experiment, heavy isotope 15N was used in the form of
- NaNO,
- 15NH,CI
- KNO
- NH4NO,
Answer. 2. 15NH,CI
Question 22. If a hybrid DNA molecule labeled with 15N is allowed to replicate twice in normal culture medium, the percentage of hybrid DNA after second replication will be
- 50%
- 12.5%
- 25%
- 75%
Answer. 3. 25%
Question 23. Assuming that 50 heavy (i.e., containing N15) DNA molecules replicated twice in a medium containing N14, we expect
- 100 half and 150 light DNA molecules
- 100 half-heavy and half-light and 100 light DNA molecules
- 50 heavy and 150 light DNA molecules
- 50 heavy and 100 light DNA molecules
Answer. 2. 100 half-heavy and half-light and 100 light DNA molecules
Question 24. Semi-conservative nature of the replication of eukaryotic chromosome was experimentally demonstrated by
- Cairns
- Meselson and Stahl
- Taylor
- Hershey and Chase
Answer. 3. Taylor
Question 25. Which statement is correct for bacterial replication?
- Has single ori
- Bidirectional
- Many ori and bidirectional
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 26. Prokaryotic topoisomerase is
- Helicase
- Primase
- DNA polymerase
- DNA gyrase
Answer. 4. DNA gyrase
Question 27. Kornberg enzyme is known as
- DNA polymerase I
- DNA polymerase II
- DNA polymerase 3
- RNA polymerase
Answer. 1. DNA polymerase 1
Question 28. The enzyme which has polymerizing activity in 5′ → 3′ direction but exonuclease activity in 3’→ 5′ direction only is
- RNA polymerase 3
- DNA polymerase 2
- DNA polymerase 1
- All of these
Answer. 2. DNA polymerase 2
Question 29. New strands of DNA are formed only in
- 5’3′ direction
- 3′ 5′ direction
- Both directions
- There is no specific polarity
Answer. 1. 5’3′ direction
” molecular biology mcq”
Question 30. Okazaki fragments are formed by one strand of DNA, known as
- Leading strand
- Lagging strand
- Continuous strand
- Semi-discontinuous strand
Answer. 2. Lagging strand
Question 31. DNA polymerase I is involved in
- Removal of RNA primer
- Filling of gap
- Joining of Okazaki fragments
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 32. DNA replication in the lagging strand of most eukaryotic organisms is
- Conservative and continuous
- Semi-conservative but discontinuous
- Conservative and semi-discontinuous
- Semi-conservative but continuous
Answer. 2. Semi-conservative but discontinuous
Question 33. In eukaryotes, DNA synthesis on the leading strand is catalyzed by
- DNA polymerase ε
- DNA polymerase β
- DNA polymerase β
- DNA polymerase y
Answer. 2. DNA polymerase β
Question 34. Wild type of Neurospora crassa which can synthesize all essential metabolites from raw materials is called
- Auxotroph
- Autotroph
- Prototroph
- Saprotroph
Answer. 3. Prototroph
Question 35. Find the incorrect matching:
- One gene one enzyme-Beadle and Tatum
- One gene one polypeptide-Yanofsky
- One gene one character de Vries
- One mRNA one polypeptide-Monad
Answer. 4. One mRNA one polypeptide-Monad
Question 36. Unidirectional flow of information called central dogma was given by
- F.H.C. Crick
- Temin
- Baltimore
- Dulbecco
Answer. 1. F.H.C. Crick
Question 37. The synthesis of DNA on RNA template was first observed in
- Rice dwarf virus
- Wound tumor virus
- Rous sarcoma virus
- E. coli
Answer. 3. Rous sarcoma virus
Question 38. Reverse transcriptase is
- RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
- RNA-dependent DNA polymerase
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
- DNA-dependent DNA polymerase
Answer. 2. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase
Question 39. The segment of master strand of DNA involved in transcription is called
- Sense strand
- Cistron
- Recon
- Muton
Answer. 2. Cistron
Question 40. In eukaryotes, RNAP 3 catalyzes the synthesis of
- All rRNA and tRNA
- mRNA, hnRNA, and snRNA
- 5S rRNA, tRNA, and snRNA
- 28S, 18S, and 5S rRNA
Answer. 3. 5S rRNA, tRNA, and snRNA
Question 41. Find the incorrect match (with respect to transcription by RNAP):
- Core enzyme-a2BB’
- Catalytic center-BB’
- Pribnow box-4 bp recognition site
- p (rho) factor-ATP dependent
Answer. 3. Pribnow box-4 bp recognition site
Question 42. DNA generally acts as a template for the synthesis of
- Only protein
- Only DNA
- Only RNA
- Both DNA and RNA
Answer. 4. Both DNA and RNA
Question 43. The core enzyme requires a factor for the termination of RNA synthesis at some sites. This is known as
- Sigma factor
- Rho factor
- Gamma factor
- Alpha particle
Answer. 2. Rho factor
Question 44. In which of the following organism mRNA has introns?
- Nostoe
- Rhizobium
- Chlamydomonas
- Mycoplasma
Answer. 3. Chlamydomonas
Question 45. If one strand of DNA has base sequence ATCCACGACTAG and the second strand undergoes transcription, what would be the base sequence on mRNA?
- TACGTGCTGATC
- ATCCACGACTAG
- AUCCACGACUAG
- AUGCACGACTAG
Answer. 3. AUCCACGACUAG
Question 46. During protein synthesis, amino acid gets attached to tRNA with the help of
- mRNA
- Aminoacyl synthetase
- Ribosome
- rRNA
Answer. 2. Aminoacyl synthetase
Question 47. The first amino acid in any polypeptide chain of prokaryotes is always
- Formylated methionine
- Formylated arginine
- Lysine
- Methionine
Answer. 1. Formylated methionine
Question 48. Considering that we have four nucleotides A, G, C, and T, the number of base substitutions that can occur in the amino acid codons is
- 549
- 564
- 281
- 256
Answer. 1. 549
Question 49. The termination of chain growth in protein synthesis is brought about by
- UUG, UGC, UCA
- UCG, GCG, ACC
- UAA, UAG, UGA
- UUG, UAG, UCG
Answer. 3. UAA, UAG, UGA
questions on dna
Question 50. In protein synthesis, the codon used as a start signal is
- AUG
- UGA
- GUA
- UAG, UAA
Answer. 1. AUG
Question 51. The translation step in the process of protein synthesis in which the conversion of the language of nucleic acid into that of proteins is made by a charged form of
- mRNA
- tRNA
- rRNA
- Template DNA
Answer. 2. tRNA
Question 52. Which site of a tRNA molecule forms hydrogen bonds with mRNA molecule?
- Codon
- Anticodon
- 5′ end of the tRNA molecule
- 3′ end of the tRNA molecule
Answer. 3. 5′ end of the tRNA molecule
Question 53. In eukaryotes, the initiation of polypeptide chain in protein synthesis is induced by
- Methionine
- Glycine
- Leucine
- Lysine
Answer. 1. Methionine
Question 54. The function of a nonsense codon is
- To release polypeptide chain from tRNA
- To form an unspecified amino acid
- To terminate the message of gene controlling protein synthesis
- To convert a sense DNA into nonsense DNA
Answer. 3. To terminate the message of gene controlling protein synthesis
Question 55. When the codon of mRNA is 5′-GUC-3′, then the anticodon on tRNA will be
- 5′-CAG-3′
- 3′-CAG-5′
- 3′-CUG-5′
- 3′-GAC-5′
Answer. 2. 3′-CAG-5′
Question 56. To code 50 amino acids in a polypeptide chain, what will be the minimum number of nucleotides in its cistron?
- 50
- 153
- 306
- 300
Answer. 3. 306
Question 57. An antibiotic which inhibits translation in eukaryotes is
- Chloromycetin
- Penicillin
- Puromycin
- Tetracycline
Answer. 3. Puromycin
Question 58. Find the correct match:
Column I Column II
a. Non-degenerate codon (1) GUG
b. Ambiguous codon. (2) UAG
c. Amber (3) UGG
d. Ochre (4) UGA
(5) UAA
- a (3), b (1), c (2), d (5)
- a (1), b (2), c (5), d (3)
- a (3), b (1), c(4), d (5)
- a (3), b (1), c (5), d (2)
Answer. 1. a (3), b (1), c (2), d (5)
Question 59. Triplet nature of genetic code was theoretically proposed by
- Nirenberg
- Hoagland
- Gamow
- Khorana
Answer. 3. Gamow
Question 60. Deciphering of genetic code was done by
- Nirenberg and Matthaei
- Holley and Komberg
- F.H.C. Crick
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (2)
“questions about dna “
Question 61. Genetic code consists of
- Adenine and guanine
- Guanine and cytosine
- Cytosine and uracil
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 62. A single anticodon can recognize more than one codon of mRNA. This phenomenon is termed as
- Richmond and Lang effect
- Gene flow hypothesis
- Wobble hypothesis
- Transposability
Answer. 3. Wobble hypothesis
Question 63. The term “genetic code” was given by
- Watson and Crick
- Gamow
- Beadle and Tatum
- Yanofsky
Answer. 2. Gamow
Question 64. Genetic code is called a degenerate code because
- One codon has many meanings
- More than one codon has the same meaning
- One codon has one meaning
- There are 64 codons present
Answer. 2. More than one codon has the same meaning
Question 65. Genetic code determines
- Structural pattern of organism
- The sequence of amino acids in a protein
- The number and variation of offspring
- Constancy of morphological traits
Answer. 2. The sequence of amino acids in a protein
Question 66. Khorana synthesized a biologically functional tyrosine tRNA of E. coli in 1979. It contained
- 77 nucleotide pairs
- 207 nucleotide pairs
- 312 nucleotide pairs
- 333 nucleotides only
Answer. 2. 207 nucleotide pairs
Question 67. There are 64 codons in genetic code dictionary because
- There are 64 types of tRNAs found in the cell
- There are 44 meaningless and 20 codons for amino acids
- There are 64 amino acids to be coded
- Genetic code is triplet
Answer. 4. Genetic code is triplet
Question 68. According to the operon concept, the regulatory gene regulates biochemical reaction in a cell by
- Inhibiting transcription
- Inactivating enzymes
- Inactivating substrate
- Inhibiting migration of mRNA
Answer. 1. Inhibiting transcription
Question 69. Which statement is correct for negative operon?
- Co-repressor binds with inducer.
- Co-repressor binds with repressor.
- Co-repressor does not bind with repressor.
- CAMP shows negative effect.
Answer. 2. Co-repressor binds with repressor.
Question 70. In E. coli, according to the lac operon theory, an operator gene combines with
- Inducer gene to “switch on” structural gene tran- scription
- Regulator gene to “switch on” structural gene tran- scription
- Regulatory protein to “switch off” structural gene transcription
- Regulator protein to “switch on” structural gene transcription.
Answer. 3. Regulatory protein to “switch off” structural gene transcription
Question 71. In an operon, the RNA polymerase binds to
- Regulator
- Promoter gene
- Operator gene
- Constitutive gene
Answer. 2. Promoter gene
Question 72. Find the correct match:
Column I Column II
a. Housekeeping genes (1) Histone gene
b. Luxury genes (2) snRNA genes
c. Repeated genes (3) ATPase gene
d. Pseudogenes (4) Nitrate reductase gene
- a (1), b (2), c (3), d (4)
- a (3), b (4), c (2), d (1)
- a (3), b (4), c (1), d (2)
- a (3), b (2), c (1), d (4)
Answer. 3. a (3), b (4), c (1), d (2)
Question 73. How many types of genes are identified for cancerous transformation after mutation?
- One
- Three
- Four
- Two
Answer. 4. Two
Question 74. Covalently closed circular chromosome is
- Nucleosome
- Viral chromosome
- Eukaryotic chromosome
- Bacterial chromosome
Answer. 4. Bacterial chromosome
“which one of the following is not applicable to rna “
Question 75. Idiochromosomes are
- Somatic chromosomes
- Autosomes
- Prochromosomes
- Heterosomes
Answer. 4. Heterosomes
Question 76. Non-histone chromosomal protein which forms the core or axis of chromosome is
- HMG protein
- Scaffold protein
- Regulatory protein
- All of these
Answer. 2. Scaffold protein
Question 77. Which statement is incorrect for asymmetric karyotype?
- Large difference between smallest and largest chromosome
- Small difference between smallest and largest chromosome
- It is advance type
- It is associated with zygomorphic flower
Answer. 2. Small difference between smallest and largest chromosome
Question 78. The number of base pairs in DNA helix around the octamer histone molecule is
- 140-200 bp
- 100-150 bp
- 40-67 bp
- 200-260 bp
Answer. 1. 140-200 bp
Question 79. nu-body of nucleosome consists of
- H, and H2A
- H2A and H2B
- H3 and H4
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer. 4. Both (2) and (3)
Question 80. Super-solenoid model of nucleosome has
- 10-15 nm diameter
- 100-125 nm diameter
- 300-700 Å diameter
- 300-700 nm diameter
Answer. 4. 300-700 nm diameter
Question 81. Which one of the following is used as marker chromosome?
- Monocentric chromosome
- SAT-chromosome
- Idiosome
- L-chromosome
Answer. 2. SAT-chromosome
Question 82. The Human Genome Project as megaproject was a 13 year project coordinated by the
- US Department of Energy
- National Institute of Health
- US Department of Molecular Biology
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 83. Sequencing of model organism like Caenorhabditis elegans was achieved in April, 2003, with
- 97 mbp
- 3× 109 bp
- 18 x 105 bp
- 12 mbp
Answer. 1. 97 mbp
Question 84. Percentage of protein encoding genes and transposable elements in human genome are, respectively,
- 76% and 3%
- 1% and 45%
- 20% and 24%
- 3% and 1%
Answer. 2. 1% and 45%
Question 85. SNP which is pronounced as “snips” stands for
- Small nuclear protein
- Single nucleotide particle
- Single nucleotide polymorphism
- Small nicking points
Answer. 3. Single nucleotide polymorphism
Question 86. HGP methodology which includes the identification of all genes that expressed as RNA is referred as
- RFLP
- ESTS
- VNTR
- RAPDS
Answer. 2. ESTS
Question 87. The largest human gene is located on chromosome _____ and has _______.
- X, 2.4 million bases
- Y, 2400 × 103 bp
- 12, 24 × 105 bp
- X, 2400 mbp
Answer. 2. Y, 2400 × 103 bp
Question 88. The last human chromosome whose sequence was completed in May, 2006, is
- Chromosome 22
- Chromosome 14
- Chromosome 1
- Chromosomes X and Y
Answer. 1. Chromosome 22
Question 89. Sequencing the whole set of genome that contains all coding and non-coding parts is
- Expressed sequence tags
- Sequence annotation
- Microarray
- Electrophoresis
Answer. 3. Microarray
bank of biology class 12 molecular basis of inheritance
Question 90. The father of DNA fingerprinting is
- Alec Jeffreys
- Lalji Singh
- V.K. Kashyap
- E.M. Southern
Answer. 2. Lalji Singh
Question 91. Find the incorrect match:
- VNTR-11-60 bp
- SSR-15-20 bp
- Southern blotting-Nitrocellulose paper
- Western blotting-Protein
Answer. 2. SSR-15-20 bp
Question 92. The separation of DNA fragments into bands by electrophoresis is done on
- Agarose gel
- Polyacrylamide gel
- Aminobenzyloxymethyl gel
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 93. Blotting technique involves the transfer of DNA from
- Membrane to gel
- Gel to membrane
- Sol to gel
- Gel to sol
Answer. 2. Gel to membrane
Question 94. Western blot hybridization is used for
- DNA analysis
- RNA analysis
- Protein analysis
- Polysaccharide analysis
Answer. 3. Protein analysis
Question 95. In gel-electrophoresis, all DNA fragments move towards the base of the gel with variable velocities because
- DNA is positively charged
- DNA is slightly negatively charged
- DNA fragments have different molecular weights
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer. 4. Both (2) and (3)
Question 96. What are mini-satellites?
- rDNA
- VNTR
- cDNA
- SAT
Answer. 2. VNTR
Question 97. When the bands of RNA are transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane for identification, the blotting is called
- Southern blotting
- Northern blotting
- Western blotting
- Eastern blotting
Answer. 2. Northern blotting
Question 98. International Human Genome Project began in
- 1990
- 1996
- 2000
- 2001
Answer. 1. 1990
” class 12th biology molecular basis of inheritance”
Question 99. Complete genomes of which non-crop and crop plants have been sequenced?
- Datura and wheat, respectively
- Arabidopsis and maize, respectively
- Oenothera and oat, respectively
- Arabidopsis and rice, respectively
Answer. 4. Arabidopsis and rice, respectively
Question 100. According to the Human Genome Project, the percentage of introns in human genome is approximately
- 10%
- 24%
- 75%
- 99%
Answer. 2. 24%
Question 101. Find the incorrect statement:
- N-glycosidic linkage between nitrogenous base and sugar forms a nucleotide.
- 5-methyl uracil is present in DNA.
- In RNA, every nucleotide residue has additional -OH group.
- The ratio (A + T)/(G + C) is variable.
Answer. 1. N-glycosidic linkage between nitrogenous base and sugar forms a nucleotide.
Question 102. The packaging of DNA at higher level requires
- Five types of histones
- A histone octamer called nu-body
- Non-histone chromosomal proteins
- Lysine and arginine
Answer. 3. Non-histone chromosomal proteins
Question 103. Which of the following statement is not applicable for DNA replication?
- Tension is released by topoisomerase.
- In eukaryotes, DNA polymerases are of five types.
- DNA polymerase 3 is the true replicase.
- The 3′ 5′ exonuclease activity is not present in DNA polymerase 3.
Answer. 4. The 3′ 5′ exonuclease activity is not present in DNA polymerase 3.
Question 104. Match column I with column II.
Column I Column II
a. RNA (1) Translational efficiency
b. UTR (2) Smallest molecule
c. SD-sequence (3) Learning and memory
d. tRNA (4) Purine rich
- a (2), b (3), c (1), d (4)
- a (3), b (2), c (4), d (1)
- a (3), b (1), c (4), d (2)
- a (3), b (4), c (1), d (2)
Answer. 3. a (3), b (1), c (4), d (2)
Question 105. Select the correct statement from the following:
- Guanyl transferase catalyzes polyadenylation.
- Polycistronic mRNA carries codons of single protein molecule.
- In bacteria, translation begins much before mRNA is fully transcribed.
- All exons have GU at the 5′ end and AG at the 3′ end.
Answer. 3. In bacteria, translation begins much before mRNA is fully transcribed.
Question 106. Wobbling helps to maintain economy in a number of tRNA molecules because
- Genetic code is unambiguous and specific
- tRNA contains anticodons
- First two bases in the codon are specific
- Genetic message is read in open frame
Answer. 3. First two bases in the codon are specific
Question 107. When apo-repressor binds with co-repressor in tryptophan operon,
- Operator gene is “switched on”
- A complete repressor is formed
- Structural genes become functional to produce polycistronic mRNA
- Luxury genes are switched on
Answer. 2. A complete repressor is formed
Question 108. Homeodomain proteins
- Convert one body part into another
- Have tumor-forming property
- Are produced by non-coding genes
- Control gene regulation in prokaryotes
Answer. 1. Convert one body part into another
“molecular inheritance class 12 ncert “
Question 109. Select the incorrect statement:
- VNTRS are inherited from parents
- VNTRS are also called short tandem repeats
- Satellite DNA has repeating base patterns
- RAPDS are used for DNA fingerprinting
Answer. 2. VNTRS are also called short tandem repeats
Question 110. In sequence annotation,
- All expressed genes are identified
- Sequence that occurs only once in genome is tagged
- All coding and non-coding sequence are involved
- Sequencing of genes with exact location and order of known bases is done
Answer. 3. All coding and non-coding sequence are involved
Question 111. Which of the following bond is not associated with a deoxyribonucleotide?
- Phosphoester bond
- Glycosidic bond
- Phosphodiester bond
- More than one option is correct
Answer. 3. Phosphodiester bond
Question 112. RNA possess additional group at which position at the sugar which is other than DNA?
- ОН, 5′
- H, 2′
- OH, 2′
- H, 5′
Answer. 3. OH, 2′
Question 113. Hallmark of the Watson and Crick three-dimensional DNA model was based on the findings of
- Wilkins and Franklin
- Erwin Chargaff
- Hershey and Chase
- Meselson and Stahl
Answer. 2. Erwin Chargaff
Question 114. Which of the following DNA form has the maximum number of base pairs per turn?
- A-DNA
- B-DNA
- C-DNA
- Z-DNA
Answer. 4. Z-DNA
Question 115. Which of the following is a part of nu-body?
- Histone octamer
- DNA + core of nucleosome
- H, protein
- 1 3/4 turn of DNA + H, protein
Answer. 1. Histone octamer
Question 116. Choose the correct steps in the organization of eukaryotic chromosome:
- Nucleosome→ Solenoid→ Super-solenoid
- Solenoid Nucleosome→→ Chromatid
- DNA → Solenoid → Nucleosome
- Chromatin Solenoid→ Nucleosome
Answer. 1. Nucleosome→ Solenoid→ Super-solenoid
Question 117. Heterochromatin
- Is transcriptionally active
- Is densely packed
- Is replicated during early S-phase
- Stains lightly
Answer. 2. Is densely packed
Question 118. Non-histone proteins
- Are of five types
- Are involved in nucleosome formation
- Control gene expression
- Are basic proteins
Answer. 3. Control gene expression
Question 119. The number of glycosidic bonds associated with the DNA of diploid human cell is
- 6.6 × 109
- 2 × 6.6 × 10°
- 3.3 × 109
- 3.3 × 109-2
Answer. 2. 2 × 6.6 × 10°
Question 120. Choose the correct option with respect to the chemical composition of chromosome:
- DNA-40%, RNA-8.5%
- DNA-50%, Histone-40%
- RNA-1.2%, Histone-50%
- RNA-1.2%, Histone-40%
Answer. 3. RNA-1.2%, Histone-50%
Question 121. Which of the following types of bacteria were used in Griffith’s transformation experiment?
- Diplococcus, R-3, and S-2 type
- Pneumococcus, T2 phage
- Streptococcus, R-2, and S-3 type
- Diplococcus, E. coli
Answer. 3. Streptococcus, R-2, and S-3 type
Question 122. The biochemical nature of transforming principle was defined by
- Griffith
- Avery, Macleod, McCarty
- Watson and Crick
- Taylor
Answer. 2. Avery, Macleod, McCarty
Question 123. In Hershey and Chase experiment, the protein of T2 phage was made radioactive by using
- S32
- p31
- S35
- p32
Answer. 3. S35
Question 124. Choose the correct option with respect to RNA.
- Presence of thymine in place of uracil.
- Absence of free 2’OH in sugar.
- Mutates at faster rate.
- Heavy using NH4Cl
Answer. 3. Mutates at faster rate.
Question 125. Semi-conservative DNA replication was proved by Messelson and Stahl, in which DNA was made
- Radioactive using N15
- Heavy using N14
- Heavy using NH4Cl
- Radioactive using 14NH,CI
Answer. 3. Heavy using NH4Cl
Question 126. During DNA replication, strand separation by breaking the H-bonds is performed by
- Topoisomerase
- Gyrase
- Helicases
- More than one option is correct
Answer. 4. More than one option is correct
Question 127. RNA primer is removed by
- DNAP-1
- DNAP-2
- DNAP-3
- Primase
Answer. 1. DNAP-1
Question 128. How many types of DNA polymerases are associated with eukaryotic cell?
- Three
- Four
- Five
- Two
Answer. 3. Five
Question 129. Which of the following acts as a substrate as well as provides energy for DNA polymerization?
- Ribonucleoside
- Deoxyribonucleoside
- Ribonucleotide
- Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate
Answer. 4. Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate
Question 130. DNA replication is
- Semi-conservative, continuous
- Conservative, continuous
- Semi-conservative, semi-discontinuous
- Semi-continuous, conservative
Answer. 3. Semi-conservative, semi-discontinuous
Question 131. Which of the following is a genetic RNA?
- mRNA
- rRNA
- hnRNA
- RNA present in plant viruses
Answer. 4. RNA present in plant viruses
Question 132. The mRNA of prokaryotes is
- Polycistronic
- Monocistronic
- Formed by splicing of hnRNA
- Carries genetic message to DNA
Answer. 1. Polycistronic
Question 133. Select the odd one out with respect to Shine Dalgarno sequence.
- 5’AGGAGGU3′
- Helps in binding of 30S ribosomal unit
- Helps in binding of 50S ribosomal unit
- Present near initiation codon
Answer. 3. Helps in binding of 50S ribosomal unit
Question 134. Which of the following type of ribosomal RNA is not present in eukaryotes?
- 18S
- 28S
- 5.8S
- 16S
Answer. 4. 16S
Question 135. Inverted L-shaped three-dimensional structure of tRNA was suggested by
- Kim and Klug
- Kuntz
- Fraenkel-Conrat
- Holley
Answer. 1. Kim and Klug
Question 136. Organisms that can complete their life cycle on minimal nutrient medium are called
- Prototrophs
- Auxotrophs
- Arginine mutants
- Citrulline mutants
Answer. 1. Prototrophs
Question 137. Find the incorrect match:
- Central dogma – F. Crick
- Reverse central dogma – Temin and Baltimore
- Split genes – Kornberg
- mRNA-Jacob and Monad
Answer. 3. Split genes – Kornberg
Question 138. Recognition sequence for transcription in prokaryotes is
- TATATAT
- TATMT
- TATAAAT
- CMT
Answer. 2. TATMT
Question 139. Transcription starts non-specifically in the absence of
- Sigma factor
- Rho factor
- Core enzyme
- DNA polymerase
Answer. 1. Sigma factor
Question 140. Tailoring of hnRNA is done by
- Snurps
- Introns
- Exons
- 18 srRNA
Answer. 1. Snurps
Question 141. Formylated methionine acts as translation initiation in
- Prokaryotes
- Eukaryotes
- Viruses
- Archaebacteria
Answer. 1. Prokaryotes
Question 142. Which of the following codons is known as ochre?
- UAG
- UGA
- UAA
- UUU
Answer. 3. UAA
Question 143. Which of the following is an ambiguous codon?
- AUG
- GUG
- UAG
- GAG
Answer. 2. GUG
Question 144. Which property of genetic code is utilized in wobble hypothesis?
- Degeneracy
- Non-overlapping
- Non-ambiguous
- Universal
Answer. 1. Degeneracy
Question 145. In the mitochondrial DNA, UGA codes for
- Chain termination
- Chain initiation
- Tryptophan
- Tyrosine
Answer. 3. Tryptophan
Question 146. The activation of amino acids during translation is done by
- Peptidyl transferase
- Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase
- Methionine
- Initiation factors
Answer. 2. Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase
Question 147. The movement of ribosome on mRNA is called
- Transcription
- Translation
- Translocation
- Protein synthesis
Answer. 3. Translocation
Question 148. The elongation factors required for prokaryotes are
- EF-Tu and EF-Ts
- eEF1
- eIF2
- eEF2
Answer. 1. EF-Tu and EF-Ts
Question 149. Which of the following inhibits the binding of aminoacyl tRNA to ribosomes?
- Neomycin
- Erythromycin
- Streptomycin
- Tetracycline
Answer. 4. Tetracycline
Question 150. The mechanism by which a gene is able to express itself in the phenotype of an organism is called
- Gene expression
- RNA synthesis
- Translocation
- Formylation
Answer. 1. Gene expression
Question 151. The genes that are constantly expressing themselves in a cell are called
- Luxury genes
- Constitutive genes
- Non-constitutive genes
- More than one option is correct
Answer. 2. Constitutive genes
Question 152. How many structural genes are present in the lac operon of E. coli?
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
Answer. 2. 3
Question 153. In lac operon, B-galactosidase enzyme is made by which lac operon of E. coli?
- lac y
- lac a
- lac z
- lac i
Answer. 3. lac z
Question 154. Inducer molecule in the lac operon of E. coli is chemically a/an
- Disaccharide
- Amino acid
- Protein
- RNA
Answer. 1. Disaccharide
Question 155. Tryptophan operon is
- Catabolic system
- Repressible system
- Inducible system
- Having three structural genes
Answer. 2. Repressible system
Question 156. Choose the correct option with respect to the chemical nature of apo-repressor and co-repressor, respectively, in trp operon?
- Protein, amino acid
- Amino acid, protein
- Lipoidal, sugary
- Sugary, lipoidal
Answer. 1. Protein, amino acid
Question 157. Gene battery model was proposed by
- Jacob and Monad
- Gamow
- H.G. Khorana
- Britten and Davidson
Answer. 4. Britten and Davidson
Question 158. An insect leg may change into antenna due to mutation in
- c-oncogene
- v-oncogene
- Homeotic genes
- Proto-oncogene
Answer. 3. Homeotic genes
Question 159. VNTRS consist of hypervariable repeat regions of DNA having a basic repeat sequence of _____ bp and flanked on both sides by ____.
- 1-6 bp, GC rich sequences
- 11-60 bp, restriction sites
- 1-6 bp, restriction sites
- 11-60 bp, ribonucleotides
Answer. 2. 11-60 bp, restriction sites
Question 160. Mark the correct match:
- Intron-VNTR
- SSR-11-60 bp
- VNTR-Microsatellite
- Minisatellite–Exon
Answer. 1. Intron-VNTR
Question 161. During DNA fingerprinting, the separation of DNA fragments is done by
- Autoradiography
- Hybridization
- Denaturation
- Electrophoresis
Answer. 4. Electrophoresis
Question 162. Sequencing the whole set of genome that contained all the coding and non-coding sequences and later assigning different regions in the sequence with functions is known as
- Sequence annotation
- PCR
- Northern blot
- Microarray
Answer. 1. Sequence annotation
Question 163. The last step of DNA fingerprinting is
- Blotting
- Autoradiography
- Hybridization
- Isolation of desired DNA
Answer. 2. Autoradiography
Question 164. DNA fingerprinting can be used
- To solve cases of disputed paternity and maternity
- For criminal identification and forensics
- For personal identification
- More than one option is correct
Answer. 4. More than one option is correct
Question 165. Human genome is said to have approximately
- 3 × 10° bp
- 3 × 106 bp
- 6.6 × 106 bp
- 3.3 × 10° bp
Answer. 1. 3 × 10° bp
Question 166. How many total number of genes are found in human genome?
- 18,000
- 30,000
- 13,000
- 4,000
Answer. 2. 30,000
Question 167. ___% of the genome codes for protein in human beings.
- 98
- 50
- 24
- <2
Answer. 4. <2
Question 168. In humans, the largest gene is present on
- Chromosome-1
- Y-chromosome
- X-chromosome
- Chromosome-7
Answer. 3. X-chromosome
Question 169. TDF gene is the smallest gene in humans with
- 231 bp
- 14 bp
- 2968 bp
- 3000 bp
Answer. 2. 14 bp
Question 170. SNP stands for
- Single nucleoside polymorphism
- Simple nucleotide polymorphism
- Single nucleotide polymorphism
- Simple nucleoside polymorphism
Answer. 3. Single nucleotide polymorphism
Question 171. Similarity in DNA and RNA is
- Both are polymers of nucleotides
- Both have similar pyrimidine
- Both have similar sugar
- Both are genetic material
Answer. 1. Both are polymers of nucleotides
Question 172. The length of one loop of B-DNA is
- 3.4 nm
- 0.34 nm
- 20 nm
- 10 nm
Answer. 1. 3.4 nm
Question 173. ATP is
- Nucleotide
- Nucleoside
- Nucleic acid
- Vitamin
Answer. 1. Nucleotide
Question 174. In three-dimensional view, the molecule of tRNA is
- L-shaped
- S-shaped
- Y-shaped
- E-shaped
Answer. 1. L-shaped
Question 175. Which of the following is initiation codon?
- UAG
- AUC
- AUG
- CCU
Answer. 3. AUG
Question 176. The method of DNA replication in which two strands of DNA separate and synthesize new strands is
- Dispersive
- Conservative
- Semi-conservative
- Non-conservative
Answer. 3. Semi-conservative
Question 177. DNA replication occurs in which stage of cell cycle?
- G, phase
- S phase
- G2 phase
- M phase
Answer. 2. S phase
Question 178. Extranuclear DNA is found in
- Lysosome and chloroplast
- Chloroplast and mitochondria
- Mitochondria and lysosome
- Golgi body and endoplasmic reticulum
Answer. 2. Chloroplast and mitochondria
Question 179. Which one of the following triplet codes is correctly matched with its specificity for an amino acid in protein synthesis or as a start or stop codon?
- UCG-Start
- UUU-Stop
- UGU – Leusine
- UAC – Tyrosine
Answer. 4. UAC – Tyrosine
Question 180. During translation initiation in prokaryotes, a GTP molecule is needed in
- Formation of formyl-met-tRNA
- Binding of 30S subunit of ribosome with mRNA
- Association of 30S mRNA with formyl-met RNA
- Association of 50S subunit of ribosome with initiation complex
Answer. 3. Association of 30S mRNA with formylmet RNA
Question 181. In recent years, DNA sequences (nucleotide sequence) of mtDNA and Y-chromosomes were considered for the study of human evolution because
- They are small and, therefore, easy to study
- They are uniparental in origin and do not take part in recombination
- Their structure is known in great detail
- They can be studied from the samples of fossil remains
Answer. 2. They are uniparental in origin and do not take part in recombination
Question 182. Degeneration of a genetic code is attributed to the
- First member of a codon
- Second member of a codon
- Entire codon
- Third member of a condon
Answer. 4. Third member of a condon
Question 183. What would happen if in a gene encoding a polypeptide of 50 amino acids, the 25th codon (UAU) is mutated to UAA?
- A polypeptide of 24 amino acids will be formed.
- Two polypeptides of 24 and 25 amino acids will be formed.
- A polypeptide of 49 amino acids will be formed.
- A polypeptide of 25 amino acids will be formed.
Answer. 1. A polypeptide of 24 amino acids will be formed.
Question 184. During transcription, the DNA site at which RNA polymerase binds is called
- Promoter
- Regulator
- Receptor
- Enhancer
Answer. 1. Promoter
Question 185. Which one of the following is a chain growth polymer?
- Starch
- Nucleic acid
- Polystyrene
- Protein
Answer. 3. Polystyrene
Question 186. The correct statement in respect of protein hemoglobin is that it
- Functions as a catalyst for biological reactions
- Maintains blood sugar level
- Acts as an oxygen carrier in the blood
- Forms antibodies and offers resistance to diseases
Answer. 3. Acts as an oxygen carrier in the blood
Question 187. The number of chiral carbons in B-D-(+) glucose is
- Five
- Six
- Three
- Four
Answer. 1. Five
Question 188. The helical structure of proteins is stabilized by
- Dipeptide bonds
- Hydrogen bonds
- Ether bonds
- Peptide bonds
Answer. 2. Hydrogen bonds
Question 189. During transcription, if the nucleotide sequence of the DNA strand that is being coded is ATACG, then the nucleotide sequence in the mRNA would be
- TATGC
- TCTGG
- UAUGC
- UATGC
Answer. 3. UAUGC
Question 190. Which of the following ratio is generally constant for a given species?
- (A+G)/(C+T)
- (T+C)/(G+A)
- (G+C)/(A+T)
- (A+C)/(T+G)
Answer. 3. (G+C)/(A+T)
Question 191. Which form of RNA has a structure resembling cloverleaf?
- rRNA
- hnRNA
- mRNA
- tRNA
Answer. 4. tRNA
Question 192. After mutation at a genetic locus, the character of an organism changes due to the change in
- protein structure
- DNA replication
- protein synthesis pattern
- RNA transcription pattern
Answer. 1. protein structure
Question 193. During replication of a bacterial chromosome, DNA synthesis starts from a replication origin site and
- RNA primers are involved
- Is facilitated by telomerase
- Moves in one direction of the site
- Moves in bidirectional way
Answer. 4. Moves in bidirectional way
Question 194. A sequence of how many nucleotides in messenger RNA makes a codon for an amino acid?
- Three
- Four
- One
- Two
Answer. 1. Three
Question 195. Which one of the following pairs is correctly matched with regard to the codon and the amino acid coded by it?
- UUU-Valine
- AAA-Lysine
- AUG-Cysteine
- CCC-Alanine
Answer. 2. AAA-Lysine
Question 196. DNA is present in
- Chromosomes and dictyosome
- Chloroplast and lysosomes
- Mitochondria and chloroplasts
- Mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum
Answer. 3. Mitochondria and chloroplasts
Question 197. Which of the following is the simplest amino acid?
- Alanine
- Asparagine
- Glycine
- Tyrosine
Answer. 3. Glycine
Question 198. Enzymes, vitamins, and hormones can be classified into a single category of biological chemicals, because all of these
- Are exclusively synthesized in the body of a living organism as at present
- Enhance oxidative metabolism
- Are conjugated proteins
- Help in regulating metabolism
Answer. 4. Help in regulating metabolism
Question 199. Which one of the following makes use of RNA as a template to synthesize DNA?
- DNA dependant RNA polymerase
- DNA polymerase
- Reverse transcriptase
- RNA polymerase
Answer. 3. Reverse transcriptase
Question 200. Nucleotides are building blocks of nucleic acids. Each nucleotide is a composite molecule formed by
- Base-sugar-OH
- Base-sugar-phosphate
- Sugar-phosphate
- Base-sugar-phosphate
Answer. 2. Base-sugar-phosphate
Question 201. Protein synthesis in an animal cell occurs
- On ribosomes present in cytoplasm as well as in mitochondria
- On ribosomes present in the nucleolus as well as in cytoplasm
- Only on ribosomes attached to the nuclear envelope and endoplasmic reticulum
- Only on the ribosomes present in cytosol
Answer. 1. On ribosomes present in cytoplasm as well as in mitochondria
Question 202. Which one of the following hydrolyzes internal phosphodiester bonds in a polynucleotide chain?
- Lipase
- Protease
- Exonuclease
- Endonuclease
Answer. 4. Endonuclease
Question 203. Carbohydrates, the most abundant biomolecules on earth, are produced by
- Some bacteria, algae, and green plant cells
- All bacteria, fungi, and algae
- Fungi, algae, and green plants cells
- Viruses, fungi, and bacteria
Answer. 1. Some bacteria, algae, and green plant cells
Question 204. The production of a human protein in bacteria by genetic engineering is possible because
- Bacterial cell can carry out the RNA splicing reactions
- The mechanism of gene regulation is identical in humans and bacteria
- The human chromosome can replicate in bacterial cell
- The genetic code is universal
Answer. 4. The genetic code is universal
Question 205. During transcription, holoenzyme RNA polymerase binds to a DNA sequence and the DNA assumes a saddle-like structure at that point. What is that sequence called?
- CAAT box
- GGTT box
- AAAT box
- TATA box
Answer. 4. TATA box
Question 206. Which functional group participates in disulfide bond formation in proteins?
- Thioether
- Thiol
- Thioester
- Thiolactone
Answer. 2. Thiol
Question 207. Bond between phosphate and sugar in a nucleotide is
- H-bond
- Covalent bond
- Phosphodiester bond
- Sulfide bond
Answer. 2. Covalent bond
Question 208. Which of the following is formed in nucleolus?
- rRNA
- tRNA
- mRNA
- DNA
Answer. 1. rRNA
Question 209. Ribosomes are composed of
- DNA + Protein
- DNA
- RNA + Protein
- RNA + DNA
Answer. 3. RNA + Protein
Question 210. DNA probes are copied from the messenger RNA molecules with the help of
- Restriction enzymes
- Reverse transcriptase
- DNA polymerase
- Adenosine deaminase
Answer. 2. Reverse transcriptase
Question 211. Which one of the following statement is true for protein synthesis (translation)?
- Amino acids are directly recognized by mRNA.
- The third base of the codon is less specific.
- Only one codon codes for an amino acid.
- Every tRNA molecule has more than one amino acid attachment site.
Answer. 2. The third base of the codon is less specific.
Question 212. Which antibiotic inhibits interaction between tRNA and mRNA during bacterial protein synthesis?
- Erthromycin
- Neomycin
- Streptomysin
- Tetracycline
Answer. 2. Tetracycline
Question 213. Amino acid sequence in protein synthesis is decided by the sequence of
- tRNA
- mRNA
- cDNA
- rRNA
Answer. 2. mRNA
Question 214. “One gene one enzyme” hypothesis was postulated by
- R. Franklin
- Hershay and Chase
- A. Garrod
- Beadle and Tatum
Answer. 4. Beadle and Tatum
Question 215. One turn of the helix in a B-form DNA is approximately
- 20 nm
- 0.34 nm
- 3.4 nm
- 2 nm
Answer. 3. 3.4 nm
Question 216. “Antiparallel strands of a DNA molecule” means that
- One strand turns anticlockwise
- The phosphate groups of two DNA strands, at their ends, share the same position
- The phosphate groups at the start of two DNA strands are in opposite positions (pole)
- One strand turns clockwise
Answer. 3. The phosphate groups at the start of two DNA strands are in opposite positions (pole)
Question 217. During protein synthesis in an organism, at one point, the process comes to a halt. Select the group of three codons from the following from which any one of the three can bring about this halt.
- UUU, UCC, UAU
- UUC, UUA, UAC
- UAG, UGA, UAA
- UUG, UCA, UCG
Answer. 3. UAG, UGA, UAA
Question 218. Thymine is
- 5-Methyluracil
- 4-Methyluracil
- 3-Methyluracil
- 1-Methyluracil
Answer. 1. 5-Methyluracil
Question 219. The molecular basis of organ differentiation depends on modulation in transcription by
- RNA polymerase
- Ribosome
- Transcription factor
- Anticodon
Answer. 3. Transcription factor
Question 220. The Okazaki fragments in DNA chain growth
- Result in transcription
- Polymerize in the 3′ to 5′ direction and from replication fork
- Prove semi-conservative nature of DNA replication
- Polymerize in the 5′ to 3′ direction and explain 3′ to 5′ DNA replication
Answer. 4. Polymerize in the 5′ to 3′ direction and explain 3′ to 5′ DNA replication
Question 221. The two polynucleotide chains in DNA are
- Parallel
- Discontinuous
- Antiparallel
- Semi-conservative
Answer. 3. Antiparallel
Question 222. About 98% mass of every living organism is composed of just six elements including carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and
- Phosphorous and sulfur
- Sulfur and magnesium
- Magnesium and sodium
- Calcium and phosphorus
Answer. 1. Phosphorous and sulfur
Question 223. A plant requires magnesium for
- Holding cells together
- Protein synthesis
- Chlorophyll synthesis
- Cell wall development
Answer. 3. Chlorophyll synthesis
Question 224. Polysome is formed by
- A ribosome with several subunits
- Ribosomes attached to each other in a linear arrangement
- Several ribosomes attached to a single mRNA
- Many ribosomes attached to a strand of endoplasmic reticulum
Answer. 3. Several ribosomes attached to a single mRNA
Question 225. Which one of the following pairs of nitrogenous bases of nucleic acids is wrongly matched with the category mentioned against it?
- Guanine, adenine—Purines
- Adenine, thymine—Purines
- Thymine, uracil—Pyrimidines
- Uracil, cytosine—Pyrimidines
Answer. 2. Adenine, thymine Purines
Question 226. In the DNA molecule,
- The proportion of adenine in relation to thymine varies with the organism
- There are two strands which run antiparallel one in 5′, 3′ direction and the other in 3′, 5′ direction
- The total amount of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides is not always equal
- There are two strands which run parallel in the 5′, 3′ direction
Answer. 2. There are two strands which run antiparallel one in 5′, 3′ direction and the other in 3′, 5′ direction
Question 227. Which one of the following pairs of codons is correctly matched with their function or the signal for the particular amino acid?
- AUG, ACG-Start/methionine
- UUA, UCA-Leucine
- GUU, GCU-Alanine
- UAG, UGA-Stop
Answer. 4. UAG, UGA-Stop
Question 228. What is not true for genetic code?
- It is unambiguous.
- A codon in mRNA is read in a non-contiguous fashion.
- It is nearly universal.
- It is degenerate.
Answer. 2. A codon in mRNA is read in a non-contiguous fashion.
Question 229. The removal of introns and joining the exons in a defined order in a transcription unit is called
- Capping
- Splicing
- Tailing
- Transformation
Answer. 2. Splicing
Question 230. Semi-conservative replication of DNA was first demonstrated in
- Salmonella typhimurium
- Drosophila melanogaster
- Escherichia coli
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
Answer. 3. Escherichia coli
Question 231. Whose experiments cracked the DNA and discovered unequivocally that a genetic code is a “triplet”?
- Beadle and Tatum
- Nirenberg and Mathaei
- Hershey and Chase
- Morgan and Strutevant
Answer. 2. Nirenberg and Mathaei
Question 232. If one strand of DNA has nitrogenous base sequence as ATCTG, what would be the complementary RNA strand sequence?
- UAGAC
- AACTG
- ATCGU
- TTAGU
Answer. 1. UAGAC
Question 233. The removal of RNA polymerase III from nucleoplasm will affect the synthesis of
- hnRNA
- mRNA
- rRNA
- tRNA
Answer. 4. tRNA
Question 234. Which one of the following is not a part of a transcription unit in DNA?
- A terminator
- A promoter
- The structural gene
- The inducer
Answer. 4. The inducer
Question 235. A certain road accident patient with unknown blood group needs immediate blood transfusion. His one doctor friend at once offers his blood. What was the blood group of the donor?
- Blood group AB
- Blood group O
- Blood group A
- Blood group B
Answer. 2. Blood group O
Question 236. The removal of introns and the joining of exons in a de- fined order during transcription is called
- Inducing
- Slicing
- Splicing
- Looping
Answer. 3. Splicing
Question 237. The diagram shows an important concept in the genetic implication of DNA. Fill in the blanks A to C.
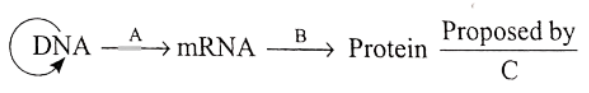
- A-translation; B-transcription; C-Erevin Chargaff
- A transcription; B-translation; C-Francis Crick
- A-translation; B-extension C; -Rosalind Franklin
- A-transcription; B-replication; C-James Watson
Answer. 2. A transcription; B-translation; C-Francis Crick
Question 238. Which enzyme/s will be produced in a cell in which there is a nonsense mutation in the lac Y gene?
- Lactose permease
- Transacetylase
- Lactose permease and transacetylase
- β-Galactosidase
Answer. 4. β-Galactosidase
