NEET Biology For Morphology Of Flowering Plants Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. The most dominant plants of present-day vegetation are
- Thallophytcs
- Bryophytes
- Flowering plants
- Pteridophytes
Answer: 3. Flowering plants
Question 2. The origin of root hairs and lateral roots is, respectively,
- Exogenous and endogenous
- Endogenous and exogenous
- Both endogenously
- Both exogenously
Answer: 1. Exogenous and endogenous
Question 3. The primary growth in root is due to
- Zone of maturation
- Zone of cell division
- Zone of cell elongation
- Meristematic region
Answer: 3. Zone of cell elongation
Question 4. Root shows negative geotropic in
- Pathos
- Ficus
- A canthorhiza
- Sonneratia
Answer: 4. Sonneratia
Question 5. When adventitious root shows swelling at regular intervals for food storage, it is called
- Tubercular root
- Nodulose root
- Moniliform root
- Annulatcd root
Answer: 3. Moniliform root
” morphology of flowering plants class 11 mcq”
Question 6. Pneumatophores are generally present in
- Mangrove plants
- Xerophytes
- Hydrophytes
- Epiphytes
Answer: 1. Mangrove plants
Question 7. We often come across long rope-like structures hanging from the branches of old banyan trees. What is the morphological nature of these rope structures?
- They are branches of the shoot system
- They are prop roots
- They are tendrils
- They are special organs
Answer: 2. They are prop roots
Question 8. The underground modification of stem occurs for which one of the following functions?
- Perennation
- Storage of food
- Vegetative propagation
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 9. Find the correct match.
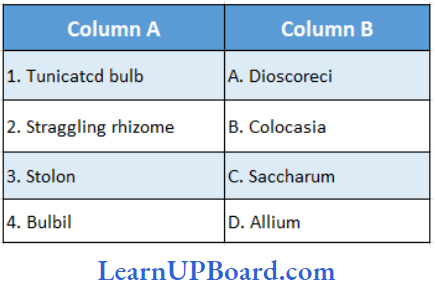
- (1) → (A), (2) → (C), (3) → (B), (4) → (D)
- (1) → (D), (2)→ (C), (3) → (B), (4)→ (A)
- (1) → (D), (2) → (C), (3) → (A), (4) → (B)
- (1) → (C), (2) → (D), (3) → (B), (4) → (A)
Answer: 2. (1) → (D), (2) → (C), (3) → (B). (4) →(A)
botany questions
Question 10. Modified stem into green, flattened branches of unlimited growth for the assimilatory function is called
- Phyllode
- Phylloblade
- Cladode
- Chylocauly
Answer: 2. Phylloblade
Question 11. The leafless stem of an onion which produces a cluster of terminal flowers is called
- Peduncle
- Floral axis
- Scape
- Rachis
Answer: 3. Scape
Question 12. The analogous structure of phylloclade is called
- Pitcher
- Phyllode
- Cladode
- Bulbil
Answer: 2. Phyllode
Question 13. Non-endospermic seed is absent in
- Soyabean
- Tulip
- Lupin
- Sunhcmp
Answer: 2. Tulip
Question 14. Which is not a modification of the stem?
- Tuber of potato
- Pitcher of Nepenthes
- Corm of Colocasia
- Rhizome of ginger
Answer: 2. Pitcher of Nepenthes
Question 15. A lateral branch with short internodes and each node bearing a rosette of leaves and tuft of roots is known as
- Sucker
- Offset
- Stolon
- Decumbent
Answer: 2. Offset
Question 16. Acaulescent habit is related to
- Allium sp.
- Iberis sp.
- Polyalthia sp.
- Palms
Answer: 1. Allium sp.
Question 17. Tripinnate compound leaf is the feature of
- Marina
- Psicliitm
- Rosa
- Mimosa
Answer: 1. Marina
Question 18. Reticulate venation is the feature of dicots but some monocots also exhibit this venation. The one following this type of venation is
- Calophyllum
- Smilax
- Eryngium
- Coraymbium
Answer: 2. Smilax
Question 19. When leaves stand at a right angle to the next upper and lower pair, then this phyllotaxy is called
- Alternate
- Opposite decussate
- Opposite superposed
- Whorled
Answer: 2. Opposite decussate
Question 20. The terminal leaflets are modified into curved hoods for climbing in
- Wild pea
- Cocklebur
- Cat’s nail
- Tiger’s nail
Answer: 3. Cat’s nail
Question 21. The duration between the development of two consecutive leaves is called
- Plastochron
- Phytochrome
- Phytron
- None of these
Answer: 1. Plastochron
Question 22. Pitcher of Nepenthes is formed from
- Leaf bases
- Lamina
- Aestivation
- Leaf apex
Answer: 2. Lamina
Question 23. The occurrence of more than one type of leaves on the same plant is known as
- Vernation
- Venation
- Aestivation
- Heterophylly
Answer: 4. Heterophylly
Question 24. The swollen petiole of Eichhornia is made up of
- Aerenchyma
- Parenchyma
- Chlorcnchyma
- Collenchyma
Answer: 1. Aerenchyma
Question 25. Inflorescence with a thick, fleshy axis and large-colored bract is
- Spathe
- Spadix
- Spikelet
- Hypanthodium
Answer: 2. Spadix
Question 26. Find the correct match
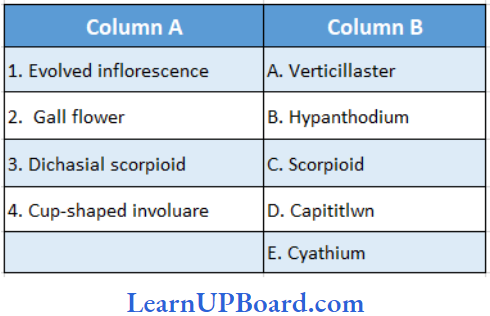
Answer: 1
Question 27. Bisexual, sessile, and bracteates flowers developing acropetally in
- Raceme
- Panicle
- Spike
- Corymb
Answer: 3. Spike
Question 28. The inflorescence of coriander is
- Umbel
- Corymb
- Typical raceme
- Umbel of umbels
Answer: 4. Umbel of umbels
Question 29. Axis of the spikelet is known as
- Rachilla
- Pedicel
- Appendage
- Rachis
Answer: 1. Rachilla
Question 30. Three types of flowers occur in the inflorescence of
- Capitalism
- Hypanthodium
- Cyathium
- Umbel
Answer: 2. Hypanthodium
Question 31. The most advanced type of inflorescence is
- Corymb
- Capitulum
- Spadix
- Polychasial cyme
Answer: 2. Capitulum
Question 32. The elongated part of the thalamus between the corolla and androecium is called
- Anthophore
- Androphore
- Gynophore
- Carpophore
Answer: 2. Androphore
Question 33. If stamens are arranged in two whorls with antipetalous outer whorls, then the condition is
- Obdiplostamenous
- Diplostamenous
- Didynamous
- Epiphyllous
Answer: 1. Obdiplostamenous
Question 34. The cohesion of stamens is shown by which one of the following conditions?
- Gynandrous
- Gynostegium
- Syngenesious
- Epipetalous
Answer: 3. Syngenesious
Question 35. The most primitive and advanced types of placentations are, respectively,
- Marginal and axile
- Superficial and axile
- Superficial and basal
- Parietal and basal
Answer: 3. Superficial and basal
Question 36. The production of flowers on old stems from dormant buds is
- Analysis
- Polycarp
- Anlhotaxy
- Cauliflory
Answer: 4. Cauliflory
Question 37. Find an incorrect match.
- Campanulate—Bell-shaped corolla
- Personate—Bilabiate corolla
- Caryophyllaceous—Butterfly-shaped corolla
Answer: 3. Personate—Bilabiate corolla
Question 38. Inferior ovary is present in
- Hypogynous flower
- Perigynous flower
- Dichogamous flower
- Epigynous flower
Answer: 4. Epigynous flower
“hypogynous flower “
Question 39. Perianth modifies into lodicules in the members which also contain
- Spikelet inflorescence
- Monocarpellary ovary
- Tetramerous flower
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 40. Vexillum is
- Posterior largest petal
- Anterior largest petal
- Found in pea family
- Permanent
Answer: 4. Permanent
Question 41. When calyx is shed with the opening of a floral bud, it is known as
- Caducous
- Deciduous
- Temporary
- Permanent
Answer: 1. Caducous
Question 42. Fruits developing from the apocarpous ovary are
- Simple fruits
- Aggregate fruits
- Composite fruits
- Pseudocarpic fruits
Answer: 2. Aggregate fruits
Question 43. Match the following.
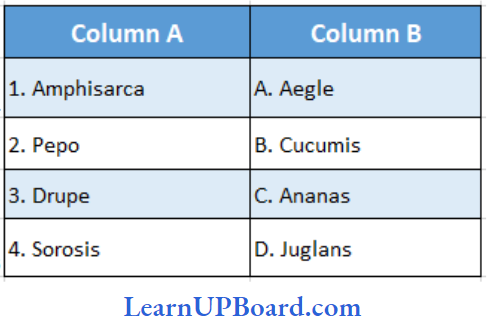
- (1) → (A), (2) → (B), (3) → (D), (4) → (C)
- (1) → (A), (2) → (B), (3) → (C), (4) → (D)
- (1) → (C), (2) → (B), (3) → (A) (4) → (D)
- (1) → (B), (2) → (A), (3) → (D), (4) → (C)
Answer: 1. (1) → (A), (2) → (B), (3)→ (D), (4) → (C)
Question 44. The presence of pappus is the characteristic of which fruit?
- Caryopsis
- Cypsella
- Scutellum
- Epiblast
Answer: 2. Cypsella
Question 45. Single shield of which of the following is an exalbuminous seed?
- Coleorhiza
- Coleoptile
- Castor seed
- Pea seed
Answer: 3. Castor seed
Question 46. Which one of the following is an exalbuminous seed?
- Wheat seed
- Maize seed
- Castor seed
- Pea seed
Answer: 4. Pea seed
Question 47. Seeds having the longest viability belong to
- Chenopodiwn
- Quercus
- Nelumbo
- Eucalyptus
Answer: 3. Nelumbo
Question 48. Find incorrect matching.
- Ancmochory—Taraxacum
- Hydrochory—Coccos
- Zoochory—Antirrhinum
- Autochory—Phlox
Answer: 3. Zoochory—Antirrhinum
Question 49. Thoms, spines, and prickles in plants work as
- Respiratory organs
- Excretory organs
- Organs of offense
- Defensive organs
Answer: 4. Defensive organs
Question 50. The presence of the tetradynamous condition and false septum, i.e., replum are the features of the family
- Solanaceae
- Brassicaceae
- Liliaceae
- Fabaccae
Answer: 2. Brassicaccaea
Question 51. The scientific name of black mustard is
- Brassica campestris
- B. rapa
- B. Juncea
- B. nigra
Answer: 4. B. nigra
Question 52. Family Leguminosae is classified into three sub-families on the basis of
- Calyx and corolla
- Symmetry of flower
- Corolla and androecium
- Corolla and carpels
Answer: 3. Corolla and Androecium
Question 53. Perigynous flowers and diadelphous conditions are found in the family
- Papilionaceae
- Caesalpinoidae
- Mimosoidae
- Solanaceae
Answer: 1. Papilionaceae
Question 54. The symbol represents which one of the following families?
- Solanaceae
- Asteraceae
- Cucurbitaceae
- Labiatae
Answer: 1. Solanaceae
Question 55. Santonin used as vermifuge is obtained from
- Artemisia
- Taraxacum
- Emilia sonchifolia
- Cantipeda orbicularis
Answer: 1. Artemisia
Question 56. The heterogamous head is with
- Ray florets only
- Disc florets only
- Neuter flowers only
- Both ray and disc florets
Answer: 4. Both ray and disc florets
Question 57. Zygomorphic flower occurs in the family which is
- Papilionaceae
- Poaceae
- Ray florets of Asteraceae
- All of these
Answer: 4. Poaceae
Question 58. The floral formula ![]() represents which one of the following groups of the family?
represents which one of the following groups of the family?
- Crotolaria and Astragalus
- Lepidium and Ibaeris
- Allium and Asparagus
- Vetiverai and Cymbopogon
Answer: 3. Allium and Asparagus
Question 59. Feathery stigma and versatile stamens are the features of the family
- Poaceae
- Umbelliferae
- Liliaceae
- Malvaceae
Answer: 1. Poaceae
Question 60. Aestivation in the Corolla
- Ascending imbricate
- Descending imbricate
- Quincuncial
- Valvate
Answer: 2. Descending imbricate
Question 61. Find the correct match.
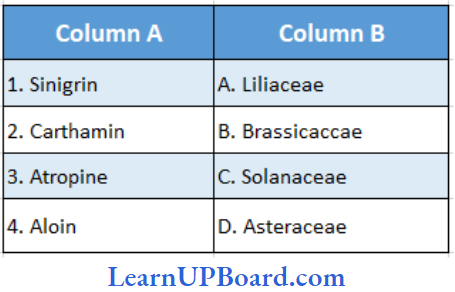
- (1) → (B), (2) → (D) (3) → (C), (4) → (A)
- (1) → (B), (2) → (D), (3) → (A), (4) → (C)
- (1) → (A), (2) → (B), (3) → (C), (4) → (D)
- (1) → (A), (2) → (B), (3) → (D), (4) → (C)
Answer: 1. (1) → (B), (2) → (D) (3) → (C), (4) → (A)
Question 62. Monoadclphous condition and pentaearpcllary ovary are present in
- China rose family
- Pea family
- Potato family
- Yucca family
Answer: 1. China Rose family
“mango and coconut develop from “
Question 63. The largest angiosperm family with an advanced type of placentation is
- Poaceae
- Asteraceae
- Cucurbitaceae
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 2. Asteraceae
Question 64. Palm oil is extracted from
- Glycin
- Gossypium
- Places
- Olea
Answer: 4. Olea
Question 65. Plants yielding colebiainc belong to the family
- Liliaceae
- Asteraceae
- Lamiaceae
- Arecaceae
Answer: 1. Liliaceae
Question 66. Indentify the wrong statement.
- A plant that bears male, female, and bisexual flowers is polygamous.
- Actinomorphic flowers can be dissected into two equal halves from any plane.
- The superior ovary is found in hypogynous flowers.
- The side of the flower towards the bract is called the posterior side.
Answer: 4. The Side of the flower towards the bract is called the posterior side.
Question 67. Compare the columns and find out the correct combination.
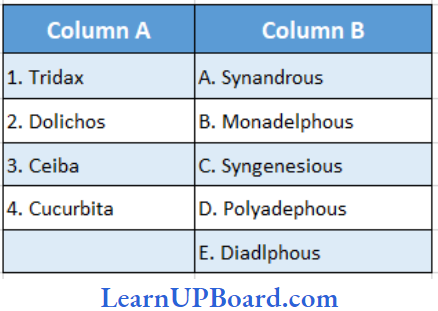
- (1) → (D), (2) → (E), (3) → (B), (4) → (A)
- (1) → (C), (2) → (E), (3) → (D), (4) → (A)
- (1) → (C), (2) → (E), (3) → (A), (4) → (D)
- (1) → (E), (2) → (C), (3) → (D), (4) → (B)
Answer: 2. (1) → (C), (2) v (E), (3) → (D), (4) → (A)
Question 68. A flower with five unequal petals has the largest posterior petal, two lateral slightly small petals, and two anterior petals partially fused to form a boat-shaped structure. Which is not correct for such a flower?
- Descending imbricate aestivation
- Odd sepal anterior
- Piston mechanism of pollination
- Many carpels
Answer: 4. Many carpels
Question 69. The staminal tube comes out of the flower in
- Pisum sativum
- Cassia fistula
- Hibiscus
- Iberis
Answer: 3. Hibiscus
Question 70 The color of the Bougainvillea flower is due to the color of its
- Corolla
- Bracts
- Calyx
- Androecium
Answer: 2. Corolla
Question 71. When pistillate and bisexual flowers develop on different plants, the condition is
- Gynodioecious
- Gymnomonoecius
- Polygamodiecius
- Polygamonoecius
Answer: 1. Gynodioecious
Question 72. Non-essential floral organs without differentiation of calyx and corolla are called
- Thalamus
- Pedicel
- Perianth
- Lodicules
Answer: 3. Perianth
Question 73. Epicalyx occurs in
- Cycas
- Power
- Nephrolepis
- China Rose
Answer: 4. China Rose
Question 74. In guava and cucurbits, the flowers are
- Hypogynous
- Epigynous
- Perigynous
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 2. Epigynous
Question 75. Synandrous condition is found in
- Sunflower
- Gourd
- Pea
- Lemon
Answer: 2. Gourd
Question 76. Floral bud is covered by
- Petals
- Anthers
- Sepals
- Stigmas
Answer: 3. Sepals
Question 77. Ovarian parts are fused, styles and stigmas free, but ovary part is unilocular with free central placentation. The plant is
- Michelia
- Nytnphaea
- Abutilon
- Dianthus
Answer: 4. Dianthus
Question 78. Replum occurs in the ovary of
- Mustard
- Pea
- Sunflower
- Lemon
Answer: 1. Mustard
Question 79. In a plant, androecium has monadelphous stamens, monoecious reniform anthers, and contorted corolla. It is
- Nerium
- Rauwolfia
- Hibiscus
- Lathyrus
Answer: 3. Hibiscus
Question 80. Pollinia occur in
- Cruciferae
- Asteraceae
- Poaceae
- Asclepiadaceae
Answer: 4. Asclepiadaceae
Question 81. Ochreate stipules occur in
- Leguminosae
- Polygonaceae
- Acanthaceae
- Malvaceae
Answer: 2. Polygonaceae
Question 82. Ovules occur along the ventral suture over a ridge in two rows in placentation
- Marginal
- Parietal
- Axile
- Free central
Answer: 1. Marginal
Question 83. Placentation found in Caryophyllaceae is
- Axile
- Basal
- Parietal
- Free central
- Marginal
Answer: 4. Free central
Question 84. Other florals develop below the base of the ovary in a flower called
- Epigynous
- Hypogynous
- Agynous
- Perigynous
Answer: 2. Hypogynous
“leaves originate from “
Question 85. An example of axile placentation is
- Marigold
- Dianthus
- Lemon
- Argemone
Answer: 3. Lemon
Question 86. Which one is monoecious?
- Marchantia
- Pinns
- Cycas
- Papaya
Answer: 2. Pinns
Question 87. Consider the following statements.
- In racemose inflorescence, the flowers are borne in a basipetal order.
- Epigynous flowers are seen in rose plants.
- In Brinjal the ovary is superior. Of these statements,
- (1) and (2) are true, but (3) is false.
- (1) and (3) are true, but (2) is false.
- (1) and (2) are false, but (3) is true.
- (2) and (3) are true, but (1) is false.
- (1) and (3) are false, but (2) is true.
Answer: 3. (1) and (2) are false, but (3) is true.
Question 88. The ovary in hypogynous flowers is said to be
- Half inferior
- Inferior
- Superior
- None of these
Answer: 3. Superior
Question 89. Aestivation found in pea flowers is
- Twisted
- Valvate
- Imbricate
- Vexillary
Answer: 4. Vexillary
Question 90. In which of the following kinds of ovules, the embryo sac is horse-shoe shaped?
- Orthotropous ovule
- Hemitorpous ovule
- Amphitropous ovule
- Circinotropous ovule
Answer: 3. Amphitropous ovule
Question 91. Which of these is an example for a zygomorphic flower with imbricate aestivation?
- Canna
- Cassia
- Cucumber
- Calotropis
- Mustard
Answer: 2. Cassia
Question 92. Gynandrous condition means
- Adhesion of stamens and carpels
- Cohesion of stamens
- Stamens united by filaments
- Free stamens
Answer: 1. Adhesion of stamens and carpels
Question 93. Feathery stigma is called
- Plumose
- Spur
- Stylopodium
- Calyculus
Answer: 1. Plumose
Question 94. The expression “gynoecium is apocarpous” implies that
- Gynoecium comprises only one pistil which is fused with the stamens.
- Gynoecium comprises more than one carpel which are free.
- The gynoecium comprises more than one carpel which are fused.
- Gynocium comprises only one carpel which is free.
Answer: 2. Gynoecium comprises more than one carpel which are free.
Question 95. In unilocular ovary with a single ovule, the placentation is
- Basal
- Free central
- Axile
- Marginal
Answer: 1. Basal
Question 96. The technical term used for the androecium in a flower of China rose (Hibiscus rosa sinensis) is
- Diadelphous
- Polyandrous
- Polyadelphous
- Monadelphous
Answer: 4. Monadelphous
Question 97. Maize/wheat/rice grain is
- Fruit
- Seed
- Embryo
- Dried bud
Answer: 1. Fruit
Question 98. The edible part in the fruit of litchi is
- Mesocarp
- Aril
- Fleshy thalamus
- Cotyledons
Answer: 2. Aril
Question 99. In Asteraceae/sunflower, the fruit is
- Drupe
- Cypsela
- Berry
- Carcerules
Answer: 2. Cypsela
“perigynous flower “
Question 100. Wheat/rice grain is a fruit of the type
- Cypsela
- Samara
- Aliens
- Caryopsis
Answer: 4. Caryopsis
Question 101. Which one of the following is a nut?
- Walnut
- Cashewnut
- Groundnut/Areca
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 102. Which one of the following does not have a polycarpcllary ovary?
- Guava
- Coconut
- Apple
- Fig
Answer: 1. Guava
Question 103. A simple one-seeded, dry, indehiscent fruit in which the pericarp and testa are fused is
- Nut
- Achene
- Cypsela
- Caryopsis
Answer: 4. Caryopsis
Question 104. Coir of commerce is obtained from
- Endocarp of coconut
- Mesocarp of coconut
- Stem of jute
- Leaves of coconut
Answer: 1. Endocarp of coconut
Question 105. Fruit of Calotropis is
- Nut
- Follicle
- Berry
- Siliqua
Answer: 2. Follicle
Question 106. Fruit growing from hypanthium/fruit of fig is
- Sorosis
- Siliqua
- Syconus
- Samara
Answer: 3. Syconus
Question 107. Caryopsis is the fruit of
- Coconut
- Brinjal
- Tomato
- Maize/sorghum
Answer: 4. Maize/sorghum
Question 108. A false fruit is that of
- Mango
- Cashewnut
- Apple
- Brinjal
Answer: 3. Apple
Question 109. The fruit of Armona squamosal (custard apple) is
- Etaerio of berries
- Etaerio of drupes
- Hypanthodium
- Etaerio of achenes
Answer: 1. Etaerio of berries
Question 110. The edible part of apple/pear is
- Cotyledons
- Thalamus/receptacle
- Mesocarp
- Endocarp
Answer: 2. Thalamus/receptacle
Question 111. carp is stony in the fruit of
- Berry
- Pome
- Drupe
- Pepo
Answer: 3. Drupe
Question 112. The edible part of mango is
- Pericarp
- Mesocarp
- Pome
- Epicarp
Answer: 2. Mesocarp
Question 113. The edible part of coconut is
- Endocarp
- Mesocarp
- Aril
- Sced/endosperm
Answer: 4. Sced/endosperm
Question 114. Dry indehiscent single-seeded fruit formed from the carpellary syncarpous inferior ovary is
- Cremocarp
- Caryopsis
- Cypsela
- Berry
Answer: 3. Cypsela
Question 115. Pepo is a fruit of
- Crucifcrae
- Leguminosae
- Cucurbitaceae
- Liliaceae
Answer: 3. Cucurbitaceae
Question 116. Formation of fruit without fertilization is
- Apogamy
- Apospory
- Syngenesious
- Parthenocarpy
Answer: 4. Parthenocarpy
Question 117. The edible part of guava is
- Thalamus and pericarp
- Entire fruit
- Endocarp
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Thalamus and pericarp
Question 118. Aril represents the edible part in
- Litchi
- Apple
- Mango
- Banana
Answer: 1. Litchi
Question 119. Science and practice of fruit culture is
- Spermology
- Pomology
- Anthology
- Dendrology
Answer: 2. Pomology
Question 120. Syconus fruit develops from
- Catkin
- Varticillaster
- Hypanthodium
- Cyathium
Answer: 3. Hypanthodium
Question 121. Syconus is the name of
- Inflorescence
- Fruit
- Thalamus
- Ovary
Answer: 2. Fruit
Question 122. Geocarpic fruit is
- Mango
- Orange
- watermelon
- Pea nut
Answer: 4. Pea nut
Question 123. Jack fruit is
- Soros is
- Syconus
- Siliqua
- Lomentum
Answer: 1. Soros is
Question 124. Fruit of Candytuft is
- Capsule
- Follicle
- Silicula
- Pome
Answer: 3. Silicula
Question 125. Pome is a false fruit as
- Endocarp is cartilaginous
- Pericarp is inconspicuous
- Fruit is surrounded by fleshy thalamus
- All the above
Answer: 3. Fruit is surrounded by fleshy thalamus
Question 126. Schizocarpic fruit has
- Fleshy pericarp
- Origin from inflorescence
- Origin from the apocarpous pistil
- Trait of breaking up into single-seeded parts
Answer: 4. Trait of breaking up into single-seeded parts
Question 127. Select the correct combination of edible part
- Coconut—-Mesocarp
- Apple—Mesocaip
- Mango—-Endocarp
- Banana—Mesocarp-Endocarp
Answer: 4. Banana—Mesocarp-Endocarp
Question 128. Which one of the following is a true match
- Composite fruit—Pineapple
- Aggregate fruit—Pineapple
- True fruit—Apple
- False fruit—Mango
Answer: 1. Composite fruit—Pineapple
Question 129. Single-seeded fruit develops from
- Tricarpellary ovary
- Bicarpellary syncarpous ovary
- Multicarpellary syncarpous ovary
- Pistil has single ovule
Answer: 4. Pistil having single ovule
Question 130. The fruit of coconut is
- Berry
- Cypsela
- Drupe
- Cremocarp
Answer: 3. Drupe
Question 131. A composite/sorosis fruit is
- Banana
- Pineapple
- Pear
- Coconut
Answer: 2. Pineapple
Question 132. Which is the correct match for an edible part?
- Tomato—Thalamus
- Maize—Cotyledons
- Guava—Mesocarp
- Date—Mesocarp
Answer: 4. Date—Mesocarp
Question 133. The edible part of the Banana is
- Epicarp
- Epicarp and mesocarp
- Mesocarp and less developed endocarp
- Endocarp and less developed mesocarp
Answer: 3. Mesocarp and less developed endocarp
Question 134. Coir is obtained from
- Fruit of Cocos nucifera
- Seed of Cocos nucifera
- Stem of Cocos nucifera
- Leaves of Cocos nucifera
Answer: 1. Fruit of Cocos nucifera
” morphology of flowering plants class 11 ncert”
Question 135. The edible part of mulberry is
- Thalamus
- Perianth
- Rachis
- Ripened ovary
Answer: 2. Perianth
Question 136. Spines on the rind of jackfruit represent
- Styles
- Carpels
- Stigmas
- Bracts
Answer: 3. Stigmas
Question 137. Which one is a composite fruit?
- Pen
- Strawberry
- Calotmpis
- Jackfruit
Answer: 4. Jackfruit
Question 138. Fruit developed (rom bicarpelley syncarpous ovary having a false septum is
- Achenc
- Siliqua
- Capsule
- Berry
Answer: 2. Siliqua
Question 139. Berries, drupes, and pomes are
- Aggregate fruits
- Composite fruits
- Simple dry fruits
- Simple succulent fruits
Answer: 4. Simple succulent fruits
Question 140. Aril is
- Outgrowth of integument
- Persistent nucellus
- An outgrowth of funicle which grows around the ovule
- Outgrowth from micropyle
Answer: 3. Outgrowth of funicle which grows around the ovule
Question 141. The nature of fruit developing from a flower depends upon the type of
- Gynoecium
- Androccium
- Pollination
- Fertilization
Answer: 1. Gynoecium
Question 142. Juicy hair-like structures observed in lemon develop from
- Exocarp
- Mesocarp
- Endocarp
- Mesocaip and endocarp
Answer: 3. Endocarp
Question 143. Fruit formed from an inflorescence is
- Simple fruit
- Pseudocarp
- Composite fruit
- Aggregate fruit
Answer: 2. Pseudocarp
Question 144. The most important edible plant food is
- Roots
- Stems
- Leaves
- Fruits
Answer: 4. Fruits
Question 145. Fruits have fructose for
- Attracting animals for seed dispersal
- Fruit ripening
- Maturation of seeds
- Nourishment of embryo
Answer: 1. Attracting animals for seed dispersal
Question 146. Fruit of elephant apple (Dillenia indica)
- Balausta
- Pcpo
- Amphisarca
- Berry
Answer: 3. Amphisarca
Question 147. Dry indehiscent fruit is
- Caryopsis
- Follicle
- Capsule
- Pod
Answer: 1. Caryopsis
“pneumatophores are “
Question 148. In sorosis type of composite fruits, the edible part is
- Cotyledons
- Fleshy thalamus
- Perianth and peduncle
- Endosperm
Answer: 3. Perianth and peduncle
Question 149. The fruit developed from a single ovary is
- Composite
- Simple fruit
- Aggregate fruit
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Simple fruit
Question 150. Drupes are called stony fruits as they have
- Hard endocarp
- Hard mesocarp
- Hard epicarp
- Hard epicarp and hard mesocarp
- Hard mesocarp and hard endocarp
Answer: 1. Hard endocarp
Question 151. Dorsiventral dehiscence occurs in fruits
- Legume
- Follicle
- Sikiqua
- Capsule
- (1) and (2)
- (2) and (3)
- (2) and (4)
- (1) and (3)
Answer: 4. (1) and (3)
Question 152. The edible part of fleshy fruit is
- Parenchymatous pulp
- Soft seeds
- Collenchymatous rind
- Sclerenchymatous endocarp
Answer: 1. Parenchymatous pulp
Question 153. Which is correct for Anacardium occidentals
- The upper part is edible
- The upper part is false fruit
- The seed is the edible part of the fruit
- The upper part is true fruit
Answer: 3. Seed is the edible part of the fruit
Question 154. Which one is a true fruit?
- Walnut
- Areca nut
- Cashew nut
- Ground nut
Answer: 3. Cashew nut
Question 155. The edible part in sorosis fruit is
- Perianth
- Perianth + Sepals
- Placenta
- Perianth + Placenta
Answer: 4. Perianth + Placenta
Question 156. Pineapple (ananas) fruit develops from
- A cluster of flowers borne compactly on a common axis
- Multilocular monocarpellary flower
- Unilocular polycarpelley flower
- Mulitpistillate syncarpous flower
Answer: 1. Cluster of flowers borne compactly on a common axis
Question 157. Seedless fruit in Banana is produced by
- Parthenogenesis
- Asexual reproduction
- Triploidy
- Cross-pollination
Answer: 2. Asexual reproduction
“sunken stomata is found in “
Question 158. Banana is
- Cremocarap
- Parthenocarpic berry
- Drupe
- Capsule
Answer: 2. Parthenocarpic berry
Question 159. A fruit that has a fleshy mesocarp and stony endocarp is
- Pome
- Berry
- Pepo
- Drupe
Answer: 4. Drupe
Question 160. Match the column
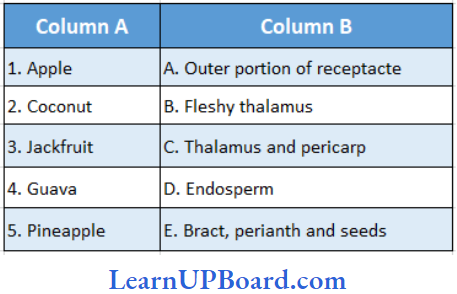
- (1) → (E), (2) → (C), (3) → (A), (4) → (D), (5) → (B)
- (1) → (B), (2) → (C), (3) → (A), (4) → (E), (5) → (D)
- (1) → (B), (2) → (D), (3) → (E), (4) → (C), (5) → (A)
- (1) → (B), (2) → (B) (C), (3) → (D), (4) → (E), (5)→ (A)
- (1) → (E), (2) → (D), (3) → (C), (4) → (B), (5) → (A)
Answer: 3. (1)→ (B), (2) → (D), (3) → (E), (4) → (C), (5) → (A)
Question 161. Lomentumn is
- Achenial fruit
- Schizocarpic fruit
- Composite fruit
- Syconus fruit
Answer: 2. Schizocarpic fruit
Question 162. The pericarp and placenta are edible parts of simple fleshy berry fruit
- Tomato
- Jack fruit
- Banana
- Date palm
Answer: 1. Tomato
Question 163. The edible part in the fruit of Hesperidium is
- Endocarp
- Mesocarp
- Juicy hairs
- Pericarp
Answer: 3. Juicy hairs
Question 164. Dried fruit used in making a musical instrument is
- Snake gourd
- Bitter gourd
- Bottle gourd
- All the above
Answer: 3. Bottle gourd
Question 165. Geocarpic fruits are formed in
- Watermelon
- Onion
- Carrot
- Groundnut
Answer: 4. Groundnut
Question 166. A single flower with multiple ovaries is called
- Simple fruit
- Aggregate fruit
- Composite fruit
- False fruit
Answer: 2. Aggregate fruit
Question 167. Arrange the fruits in descending order of the chambers of the ovary they develop.
- Carcerulus
- Schizocarp
- Cremocarp
- Regma
- 2, 1, 4, 3
- 1, 4, 3, 2
- 2, 4, 3, 1
- 2, 3, 1, 4
Answer: 1. 2, 1, 4, 3
Question 168. Which of the following fruits is chambered, developed from the inferior ovary, and has seeds with succulent testa?
- Orange
- Cucumber
- Pomegranate
- Guava
Answer: 3. Pomegranate
Question 169. The fleshy receptacle of the syconus of fig encloses a number of
- Berries
- Accents
- Mericarps
- Samaras
Answer: 2. Achencs
Question 170. Find out the correct statements.
- Seeds of peas are exalbuminous.
- The fruit of the peach is a drupe.
- Seeds of tomato are albuminous.
- The fruit of coconut is berry.
- 1,2, 3
- 1,2
- 2,4
- 1,3
Answer: 2. 1,2
Question 171. In which plant the fruit is a drupe, the seed coat is thin, the embryo is inconspicuous, and the endosperm is edible?
- Groundnut
- Apple
- Wheat
- Coconut
Answer: 4. Coconut
Question 172. In the drupe of coconut, the mesocarp is
- Stony
- Fleshy
- Fibrous
- Watery
Answer: 3. Fibrous
Question 173. Which statements are correct?
- A fruit developing from inflorescence composite fruit
- The mesocarp is edible in Apple
- Gynobasic style occurs in Ocimum
- Hypanthodium occurs in Euphorbia species
- 1, 4 correct
- 1, 3 correct
- 1, 2 correct
- 2, 4 correct
- 2, 3, 4 correct
Answer: 2. 1, 3 correct
Question 174. Cotyledons and testa are, respectively, edible in
- Walnut and tamarind
- French bean and coconut
- Cashew nut and litchi
- Groundnut and pomegranate
Answer: 4. Groundnut and pomegranate
Question 175. Which is the correct answer to assertion (a) and reason (r).
- Assertion (A): In syconus-type fruit, the achenes formed are fewer than the total number of flowers in the inflorescence.
- Reason (r): Upper and middle flowers do not develop into fruits
- Both (A) and (R) are correct with (R) being a correct explanation of (A).
- Both (A) and (R) are correct with (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- (A) is true but (R) is false.
- (A) is false but (R) is true.
Answer: 1. Both (A) and (R) are correct with (R) being a correct explanation of (A).
Question 176. Which of the following fruits is parthenocarpic?
- Mango
- Lemon
- Banana
- Apple
Answer: 3. Banana
Question 177. Which is multicellular and splits longitudinally along dorsal sutures?
- Septicidal
- Gram
- Loculicidal
- Septifragal
Answer: 3. Loculicidal
Question 178. Bracts, perianth, and seeds are edible parts of
- Cocos nucifera
- Mangifera indica
- Argemone Mexicana
- Artocarpus heterophyllus
Answer: 4. Cocos nucifera
Question 179. In coconut fruit, the hard shell is
- Endocarp
- Fused structure of mesocarp and endocarp
- Fused structure of epicarp and mesocarp
- Epicarp
Answer: 1. Endocarp
Question 180. Which one is not a false fruit?
- Apple
- Mango
- Strawberry
- Cashewnut
Answer: 2. Mango
Question 181. The scientific name of banana is
- Musa paradisiacal
- Musa superba
- Musa textilis
- Hibiscus mutabilis
Answer: 1. Musa paradisiac
Question 182. Mechanical injury of seed coat to break dormancy is called
- Scarification
- Stratification
- Impaction
- Compaction
Answer: 1. Scarification
Question 183. A seed which does not require oxygen for germination is
- Pea
- Rice
- Typha
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 4. Both (2) and (3)
Question 184. The outermost layer of the endosperm of maize grain is
- Epidermis
- Pericarp
- Tunica
- Alcurone
Answer: 4. Alcurone
Question 185. Oil is stored in the endosperm of
- Groundnut
- Soybean
- Coconut
- Cashewnut
Answer: 3. Coconut
Question 186. Micropyle occurs in
- Ovary
- Seeds
- Ovule
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 4. Both (2) and (3)
Question 187. Shield-shaped cotyledon/scutellum occurs in
- Maize/sorghum
- Gram
- Pea
- Cucumber
Answer: 1. Maize/sorghum
Question 188. A method of breaking dormancy and allowing ample absorption of water is
- Stratification
- Scarification
- Vernalization
- Devernalizatiou
Answer: 2. Scarification
Question 189. During seed germination, the seed coat ruptures due to
- Differentiation of cotyledons
- Massive glycolysis in endosperm cotyledons
- Massive imbibition of water
- A sudden increase in cell division
Answer: 3. Massive imbibition of water
Question 190. Hormone group responsible for breaking seed dormancy
- ABA
- Cytokinin
- Auxin
- Gibberellin
- 1, 3
- 1, 2, 4
- 2, 3, 4
- 1,2,4
Answer: 3. 2, 3, 4
Question 191. In some halophytes, seeds germinate with fruits while attached to the parent plant.
- Vivipary
- Halophytosis
- Monocarpic
- Vernalisation
- Seismonasty
Answer: 1. Vivipary
Question 192. Mitochondria produce more energy during
- Formation of seed
- Seed maturation
- Dormant seed
- Seed germination
Answer: 4. Seed germination
Question 193. Which one is endospermous?
- Cajanus cajan
- Helianthus annus
- Ricinus communis
- Ravenala madagascariensis
Answer: 3. Ricinus communis
Question 194. Embryo of sunflower has
- One cotyledon
- Two cotyledons
- Many cotyledons
- No cotyledon
Answer: 2. Two cotyledons
Question 195. Non-albuminous seeds occur in
- Maize
- Wheat
- Rice
- Vallisneria
Answer: 4. Vallisneria
Question 196. In pulses, protein is stored in
- Cotyledons
- Endosperm
- Pericarp
- Seed coat
Answer: 1. Cotyledons
Question 197. The aleurone layer of maize grain is specially rich in
- Proteins
- Starch
- Lipid
- Auxins
Answer: 1. Proteins
Question 198. Which of the following is an oil seed plant?
- Sunflower
- Hibiscus
- Marigold
- Rose
Answer: 1. Sunflower
Question 199. Which one is monocot albuminous seed?
- Maize
- Wheat
- Rice
- All the above
Answer: 4. All the above
Question 200. In groundnut, oil is stored in
- Embryo axis
- Endosperm
- Cotyledons
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Cotyledons
Question 201. Assign the seeds to their respective categories.
- Maize
- Mustard
- Pea
- Endospermic
- Non endospermic
- 1 4, 2 4, 3 5, 2 4
- 1 4, 2 5, 3 5
- 4 5, 2 5, 3 4
- 1 5, 2 4, 3 5
Answer: 2. 1 4, 2 5, 3 5
Question 202. In pea, castor, and maize, the number of cotyledons are, respectively,
- One, two, and two
- Two, two, and one
- Two, one, and two
- One, two, and one
Answer: 2. Two, two, and one
Question 203. Which one does not exhibit seed dormancy?
- Phaseolus
- Rhizophora
- Cassis
- Xanthium
Answer: 2. Rhizophora
Question 204. Which one yields castor oil?
- Sesamum indicum
- Cocos nucifera
- Ricinus communis
- Brassica campesteris
Answer: 3. Ricinus communis
Question 205. Dry fruit “Chilgoza” is
- Fruit of Cycas
- Seed of Cycas
- Fruit of Pinus gerardiana
- Seed of Pinus gerardiana
Answer: 4. Seed of Pinus gerardiana
Question 206. Why is vivipary an undesirable character for annual crop plants?
- It reduces the vigor of the plant.
- It adversely affects the fertility of plants.
- The seeds exhibit long dormancy.
- The seeds cannot be stored under normal conditions for next season.
Answer: 4. The seeds cannot be stored under normal conditions for next season.
Question 207. A dicot plant lacking cotyledons is
- Cuscuta
- Santalum
- Lodoicea
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Cuscuta
Question 208. Seed of castor is
- Non-endospermic exalbuminous
- Endospermic albuminous
- Endospermic exalbuminous
- Non-endospermic albuminous
Answer: 2. Endospermic albuminous
Question 209. In cereal grains, a single cotyledon is represented by
- Coleoptile
- Coleorhiza
- Scutellum
- Prophyll
Answer: 3. Scutellum
Question 210. The edible part of the paddy is
- Endosperm
- Cotyledons
- Fruit
- Endosperm and embryo
Answer: 4. Endosperm and embryo
Question 211. The point of attachment of the stalk with the seed is
- Hilum
- Micropyle
- Tegmen
- Plumule
Answer: 1. Hilum
Question 212. In maize grain, plumule is covered by a protective sheath called
- Scutellum
- Coleorrhiza
- Coleoptile
- Tegmen
Answer: 3. Coleoptile
Question 213. Match the columns.
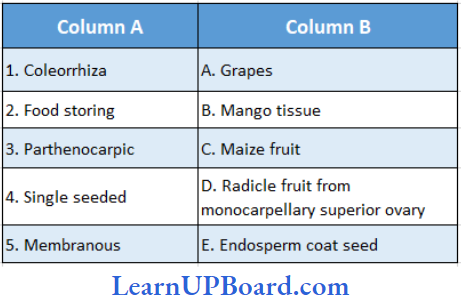
- (1) → (A), (2) → (C), (3) → (B), (4) → (E), (5) → (D)
- (1) →(D), (2) → (E), (3) → (A), (4) → (B), (5) → (C)
- (1) → (C), (2) → (A), (3) → (D), (4) → (B), (5) → (E)
- (1) → (4), (2) → (B), (3) → (E), (4) → (A), (5) → (C)
- (1) →(5), (2) → (A), (3) → (C), (4) → (D), (5) → (B)
Answer: 2. (1) → (D), (2) → (E), (3) → (A), (4) → (B), (5) → (C)
Question 214. In monocotyledonous seeds, the endosperm is separated from the embryo by a distinct layer off
- Testa
- Tegmen
- Aleurone layer
- Scutellum
- Coleoptile
Answer: 4. Coleoptile
Question 215. Scutellum of maize is
- Cotyledonary
- Endosperm
- Tegmen
- Testa
Answer: 1. Cotyledonary
Question 216. Identify the characters of the plant where the eight-nucleate embryo sac was first studied by Strasburger.
- Micropyle, chalaza, and funiculus in the same vertical line
- Both unisexual and bisexual flowers on the same plant
- Filiform apparatus conducts food from endosperm to egg apparatus
- Long funiculus coils like watch spring around the ovule.
- 1, 2, and 3
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 4
- 1 and 3
Answer: 2. 1 and 2
Question 217. Find the correct answers endosperm.
- Mazie
- Onion
- Rice
- Bean
- 1, 2, and 3
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
Answer: 1. 1, 2, and 3
Question 218. Find the correct answer: For germination of angiosperm seeds
- On hydration, the seed germinates showing increased enzyme activity.
- The respiration rate of germinating seed increases along- with an increase in enzymatic activity.
- The increase in respiratory rate continues till senescence.
- The rate of enzymatic activity increases.
- (1), (2), (3)
- (1) and (2)
- (2) and (4)
- (1) and (3)
Answer: 2. (1) and (2)
Question 219. Pre-chilling treatment to break seed dormancy is
- Scarification
- Vernalization
- Impaction
- Stratification
Answer: 4. Stratification
Question 220. Endosperm is consumed by the developing embryo in
- Coconut
- Pea
- Maize
- Castor
Answer: 2. Castor
Question 221. Embryo axis above the cotyledon is known as
- Plypocotyl
- Funicle
- Epicotyl
- Raphe
Answer: 3. Epicotyl
Question 222. Scutellum is the seed leaf of
- Gymnosperms
- Dictos
- Pteridophytes
- Monocots
Answer: 4. Monocots
Question 223. An example of a seed with endosperm, perisperm, and caruncle is
- Castor
- Coffee
- Lily
- Colton
Answer: 1. Castor
Question 224. Match the following
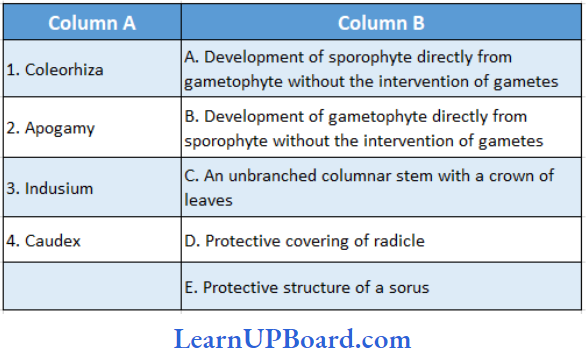
- (1) → (E), (2) → (B), (3) → (D), (4) → (A)
- (1) → (C), (2) → (E), (3) → (B), (4) → (D)
- (1) → (D), (2) → (A), (3) → (E), (4) → (C)
- (1) → (B), (2) → (C), (3) → (A), (4)→ (E)
Answer: 3. (1) → (D), (2) → (A), (3)→ (E), (4) → (C)
Question 225. Residual persistent nucellus is known as
- Peri sperm
- Integument
- Pericarp
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Peri sperm
Question 226. Non-endospermic seeds are found in
- Barley
- Castor
- Bean
- Wheat
Answer: 3. Bean
Question 227. In hypogeal germination, plumule comes out of the ground due to the elongation of
- Hypocotyl
- Epicotyl
- Cotyledons
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 2. Epicotyl
Question 228. A large shield-shaped cotyledon found in some monocotyledonous seeds is
- Aleurone layer
- Coleorhiza
- Scutellum
- Hilum
- Coleoptile
Answer: 3. Scutellum
Question 229. Seed develops from
- Embryo
- Ovule
- Embryo sac
- Ovary
Answer: 2. Ovule
Question 230. Keel is the characteristic of the flower of
- Cassia
- Calotropis
- Bean
- Gulmohur
Answer: 3. Bean
Question 231. Seeds of Ruellia tuberose are disseminated by
- Censer mechanism
- Parachute mechanism
- Jaculator mechanism
- Explosive mechanism
Answer: 3. Jaculator mechanism
Question 232. Clematis and Narvelia are dispersed by air with the help of
- Persistent inflated calyx
- Persistent hairy styles
- Hair
- Wings
Answer: 2. Persistent hairy styles
Question 233. The censer mechanism of seed dispersal is found in
- Papaveraceae
- Liliaceae
- Leguminosae
- Rosaceae
Answer: 1. Papaveraceae
Question 234. In which plant only two curved hooks are formed on seeds?
- Xanthium
- Martynia
- Tribulus
- Ricinus
Answer: 2. Martynia
Question 235. Birds disseminate seeds by
- Eating fruit and passing the seeds unharmed through excreta at places
- Their feathers
- Carrying seeds in their beaks
- Eating fruits and digesting fruit contents in their alimentary canal.
Answer: 1. Eating fruit and passing the seeds unharmed through excreta at places
Question 236. Pappus occurs in Compositae for
- Air pollination
- Aar dispersal
- Insect pollination
- Animal dispersal
Answer: 2. Aar dispersal
Question 237. Bright-colored fleshy fruits are dispersed by
- Air
- Insects
- Water
- Birds
Answer: 4. Birds
Question 238. Which one of the following statements is correct?
- In tomato, fruit is a capsule.
- Seeds of orchids have oil-rich endosperm.
- Placentation in primose is basal.
- Flower of tulip is a modified shoot
Answer: 4. Flower of tulip is a modified shoot
Question 239. The correct floral formula of chilli is

Answer: 2
Question 240. Flowers are zygomorphic in
- Mustard
- Gulmohur
- Tomato
- Darura
Answer: 2. Gulmohur
Question 241. The ovary is half inferior in the flower of
- Peach
- Cucumber
- Cotton
- Guava
Answer: 1. Peach
Question 242. A drupe develops in
- Mango
- Wheat
- Pea
- Tomato
Answer: 1. Mango
Question 243. Placentation in tomato and lemon is
- Free central
- Marginal
- Axile
- Parietal
Answer: 3. Axile
Question 244. How many plants in the list given below have composite fruits that develop from an inflorescence?
- Five
- Two
- Three
- Four
Answer: 3. Three
Question 245. Phyllode is present in
- Euphorbia
- Australian Acacia
- Opimtia
- Asparagus
Answer: 2. Australian Acacia
Question 246. The coconut water and the edible part of the coconut are equivalent to
- Endocarp
- Mesocarp
- Embryo
- Endosperm
Answer: 4. Endosperm
Question 247. The cymose inflorescence is present in
- Sesbania
- Trifolium
- Brassica
- Solatium
Answer: 4. Solatium
Question 248. Vexillary aestivation is the characteristic of the family
- Astcrnccnc
- Solanaceae
- Brassicaceae
- Fabaceae
Answer: 4. Fabaceae
Question 249. The gynoecium consists of many free pistils in flowers of
- Tomato
- Papaver
- Michelia
- Aloe
Answer: 3. Michelia
Question 250. How many plants in the list given below have marginal placentation? Mustard, gram, tulip, Asparagus, arhar, sun hemp, chili, colchicine, onion, moong, pea, tobacco, lupin
- Four
- Five
- Six
- Three
Answer: 3. Six
Question 251. Cuscuta is an example of
- Ectoparasitism
- Brood parasitism
- Predation
- Endoparasitism
Answer: 1. Ectoparasitism
