NEET Biology Neural Control And Coordination Multiple Choice Questions Answers
Question 1. Cranial and spinal nerves can be included under
- Central nervous system
- Autonomic nervous system
- Peripheral nervous system
- Visceral nervous system
Answer: 3. Peripheral nervous system
Question 2. Odd one out w.r.t. origin.
- Astrocyte
- Microglial cells
- Oligodendrocytes
- Ependyma cells
Answer: 2. Microglial cells
Question 3. In human beings, a typical nerve cell is
- Bipolar
- Apolar
- Multipolar
- Pseudounipolar
Answer: 3. Multipolar
Question 4. The rapid movement of Na+ ions from extracellular fluid into the nerve cell leads to
- Polarization
- Depolarization
- Repolarization
- All of these
Answer: 2. Depolarization
Question 5. Depolarization is an/a
- Active process
- Passive process
- Both active and passive process
- First, it is passive and then it becomes active
Answer: 2. Passive process
” nervous system questions and answers pdf “
Question 6. If the Na+-K+ pump stops working, then
- Na+ and K+ will be in excess in extracellular fluid
- Na+ will be in excess in extracellular fluid
- K+ will be excess in intracellular fluid
- Na+ will be in excess in intracellular fluid
Answer: 4. Na+ will be in excess in intracellular fluid
Question 7. If the receptors are removed from the post-synaptic membrane, then
- Synaptic transmission will be faster
- The chemical synaptic transmission will become slow
- Chemical synaptic transmission will not occur
- Synaptic transmission will be not affected
Answer: 3. Chemical synaptic transmission will not occur
Question 8. For most excitable cells, the threshold stimulus is
- +40 mV
- -55 to -60 mV
- +60 mV
- -70 mV
Answer: 2. -55 to -60 mV
Question 9. The rate of conduction of impulse will be faster in the case of
- Myelinated nerve fibers
- Thicker nerve fibers
- Non-myelinated nerve fibers
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 2
Question 10. The synaptic cleft, an intercellular gap separating the axon tip and target neuron, is
- 10-20 nm
- 10-20 μm
- 1 dm
- 1-10 mm
Answer: 1. 10-20 nm
Question 11. Axon endings release from their synaptic vesicles a neurotransmitter substance known as
- Acetylcholine
- Acetylcholinesterase
- Inositol-3 phosphate
- Diacylglycerol
Answer: 1. Acetylcholine
Question 12. What is common about serotonin, acetylcholine, adrenaline, and noradrenaline?
- All are antidiuretic drugs.
- All are pain-relieving drugs.
- All are chemical transmitters or neurohormones.
- All are blood pressure-lowering drugs.
Answer: 3. All are chemical transmitters or neurohormones.
Question 13.In the presence of Ca2+ channel blockers, which of the following will be true?
- Neurotransmitter is released but the Na+ channel of post-synaptic neuron will not open.
- Neurotransmitter is not released but the Na+ channel of the post-synaptic neuron will open up.
- Neurotransmitter is released but the K+ channel of post-synaptic neuron opens up.
- Neither neurotransmitter is released nor the Na+ channel of post-synaptic neuron open up.
Answer: 4. Neither neurotransmitter is released nor the Na4 channel of the post-synaptic neuron opens up.
Question 14. The largest number of cell bodies of neurons in our body is found in
- Brain
- Retina
- Spinal cord
- Tongue
Answer: 1. Brain
Question 15. One of the following is not the lobe of the cerebral hemisphere.
- Parietal lobe
- Occipital lobe
- Temporal lobe
- Olfactory lobe
Answer: 4. Olfactory lobe
Question 16. A highly vascular and closely investing protective coat around the brain is known as
- Arachnoid
- Pia mater
- Dura mater
- Sub-arachnoid space
Answer: 2. Pia mater
Question 17. Corpus callosum is the link between
- Cerebellar hemispheres
- Midbrain and hindbrain
- Cerebral hemisphere
- Brain and cranium
Answer: 3. Cerebral hemisphere
Question 18. The genu and splenium in the brain are associated with
- Cerebellum
- Cerebrum
- Medulla oblongata
- Vermis
Answer: 2. Cerebrum
Question 19. Due to the presence of gyri and sulci, the surface area of the cerebral cortex almost
- Doubles
- Becomes three times
- Becomes four times
- Becomes six times
Answer: 2. Becomes three times
Question 20. Which part of the brain is involved in organizing the behavior of an organism related to its survival?
- Amygdala lobe
- Cerebral cortex
- Corpus callosum
- Hypothalamus
Answer: 4. Hypothalamus
Question 21. Which part of the limbic system converts information from short-term to long-term memory, essential in learning?
- Amygdala
- Basal ganglia
- Hippocampus
- Hypothalamus
Answer: 3. Hippocampus
Question 22. Characteristically large large-flask-shaped Purkinje cells are associated with
- Cerebral cortex
- Cerebellar cortex
- Pons
- Hypothalamus
Answer: 2. Cerebellar cortex
Question 23. Which part is involved in the movement of the head to locate and detect the source of a sound?
- Superior colliculi
- Inferior colliculi
- Pons
- Medulla oblongata
Answer: 2. Inferior colliculi
Question 24. Activities of the cerebellum are
- AH is involuntary but may involve learning in the early stage
- All are voluntary and may involve learning in their early stage
- All are voluntary and do not involve learning in their early stage
- All are involuntary and do not involve learning in their early stage
Answer: 1. AH is involuntary but may involve learning in the early stage
Question 25. Basal ganglion is a collection of subcortical nuclei in the forebrain, at the base of the cortex. A primary function of the basal ganglia is
- Sensory integration
- Short term memory
- Planning stereotyped movements
- Neuroendocrine control
Answer: 3. Planning stereotyped movements
Question 26. Which part of the brain is like a defense castle controlling moods and plays an important role in emotional behavior such as aggression and remembering fear?
- Hippocampus
- Amygdala
- Limbic system
- Thalamus
Answer: 2. Amygdala
Question 27. The link between parallel and diaconal is through
- Foramina Luschka
- Foramina Magendie
- Foramen of Monro
- Aqueduct of Sylvius
Answer: 3. Foramen of Monro
Question 28. Pallium is
- Lateral walls of the diencephalon
- Lateral walls of the cerebrum
- Floor walls of paracoel
- Roof of paracoel
Answer: 4. Roof of paracoel
Question 29. The brain stem consists of
- Medulla oblongata, pons Varolii, cerebellum
- The cerebellum, diencephalon, and midbrain
- Both 1 and 2
- Medulla, pons, midbrain
Answer: 4. Medulla, pons, midbrain
Question 30. The function of the choroid plexus is
- To produce lymph
- To produce blood
- To produce cerebrospinal fluid
- To produce endolymph
Answer: 3. To produce cerebrospinal fluid
Question 31. The pneumonitis center in the body is present in
- Heart
- Lungs
- Pons Varolii
- Medulla
Answer: 3. Pons Varolii
Question 32. One of the following transmits impulses from one side of the cerebellum to the other
- Pons Varolii
- Crura cerebri
- Corpora quadrigeminal
- Cerebellum
Answer: 1. Pons Varolii
Question 33. A branched tree-like structure present in the cerebellum is
- Arboreal
- Areole
- Arbor vitae
- Archenteron
Answer: 3. Arbor vitae
Question 34. Vermis is
- A tiny worm
- Cavity of medulla
- The small median lobe of the cerebellum in mammals
- A portion of the midbrain
Answer: 3. The small median lobe of the cerebellum in mammals
Question 35. The vomiting center is situated in
- Cerebrum
- Cerebellum
- Medulla
- Hypothalamus
Answer: 3. Medulla
Question 36. The CSF moves from the ventricle of the brain to the subarachnoid space through
- Foramina Magendie
- Foramina Luschka
- Foramen of Monro
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 2
Question 37. The end of the spinal cord is
- Cauda equina
- Foramina Luschka
- Filum terminals
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 2. Foramina Luschka
Question 38. Brachial swelling of the spinal cord extends from
- 4th cervical to the 1st thoracic vertebrae
- 1st cervical to the 4th cervical vertebrae
- 5th cervical to the 8th cervical vertebrae
- 1st thoracic to the 4th thoracic vertebrae
Answer: 1. 4th cervical to the 1st thoracic vertebrae
Question 39. Those nerves which carry impulses from the central nervous system to the muscles and glands are known as
- Sensory nerves
- Motor nerves
- Mixed nerves
- Afferent nerves
Answer: 2. Motor nerves
Question 40. The trigeminal nerve arises from the brain in the region of
- Pons varolii and divides into palatine, chorda tym-pani, and hyomandibular
- Medulla and divides into palatine, hyomandibular, and chorda tympani
- The cerebellum divides into ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular
- Pons Varolii and divides into ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular
Answer: 4. Pons Varolii divides into ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular
Question 41. The nerve related to eyeball movement, accommodation, and contraction of the pupil is
- Optic
- Auditory
- Oculomotor
- Trochlear
Answer: 3. Oculomotor
Question 42. How many pairs of cranial nerves are purely sensory?
- Five
- Four
- Six
- Three
Answer: 4. Three
Question 43. Gastric and pancreatic secretion, gastrointestinal movements, respiratory reflexes, and visceral reflexes are controlled by
- Vagus
- Abducens
- Oculomotor
- Trochlear
Answer: 1. Vagus
“nervous system questions “
Question 44. Which one of the following pairs is the motor nerve?
- Oculomotor and facial
- Vagus and trigeminal
- Optic and olfactory
- Trochlear and hypoglossal
Answer: 4. Trochlear and hypoglossal
Question 45. The lateral rectus muscle of the eye is provided with which cranial nerve?
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
Answer: 4. 6
Question 46. Paralysis of jaw muscles is due to the loss of function of which cranial nerve?
- 3
- 5
- 7
- 10
Answer: 2. 5
Question 47. Which of the following cranial nerves in man is both sensory and motor?
- Optic
- Olfactory
- Trigeminal
- Auditory
Answer: 3. Trigeminal
Question 48. Which of the following cranial nerves arc linked with taste buds?
- 7 and 3
- 9 and 2
- 4 and 8
- 7 and 9
Answer: 4. 7 and 9
Question 49. The smallest cranial nerve in the body is
- Trigeminal
- Abducens
- Ophthalmic
- Trochlear
Answer: 4. Trochlear
Question 50. The fourth cranial nerve of man is
- Abducens
- Trochlear
- Auditory
- Oculomotor
Answer: 2. Trochlear
Question 51. The spinal nerve plexus involving the 1st thoracic spinal nerve is
- Cervical plexus
- Brachial plexus
- Lumbar plexus
- Sacral plexus
Answer: 2. Brachial plexus
Question 52. The number of spinal nerves in man is
- 31
- 62
- 12
- 24
Answer: 2. 62
Question 53. What is the function of the parasympathetic nervous system?
- Acceleration of heartbeat
- Constriction of pupil
- Stimulation of sweat gland
- Contraction of erector pili
Answer: 2. Constriction of the pupil
Question 54. The ganglia that lie nearer to the tissues and away from the chain and in which preganglionic fibers terminate are known as
- Autonomic ganglion
- Collateral ganglion
- Paratonic ganglion
- None of these
Answer: 2. Collateral ganglion
Question 55. Which of the following cranial nerves is involved in the sympathetic nervous system?
- 3
- 7
- Both of these
- None of these
Answer: 4. None of these
Question 56. The neurotransmitter with the sympathetic postganglionic nerve fiber terminating at the sweat gland is
- Epinephrine
- Acetylcholine
- Adrenaline
- Both 1 and 3
Answer: 2. Acetylcholine
Question 57. Reflex action is exhibited by
- Sympathetic nerves
- Sensory nerves
- Automatic response
- Motor nerves
Answer: 3. Automatic response
Question 58. In reflex action, the reflex arc is formed by
- Brain-spinal cord-muscles
- Receptor-spinal cord-muscles
- Muscles-receptor-muscles
- Muscles-spinal cord-receptor
Answer: 2. Receptor-spinal cord-muscles
Question 59. Which one is not a reflex action?
- Closing the eyelids suddenly
- Release of saliva
- Obeying the order
- None of these
Answer: 3. Obeying the order
Question 60. Receptors of pain are
- Free nerve endings
- Merkel’sdiscs
- Meissner’s corpuscles
- Pacinian corpuscles
Answer: 1. Free nerve endings
Question 61. Krause’s end bulbs arc the skin receptors which are concerned with the sense of
- Touch
- Heat
- Cold
- Pressure
Answer: 3. Cold
Question 62. Meissner’s corpuscles are located in
- Pancreas secrete trypsinogen
- Adrenal and secrete trypsinogen
- Spleen and destroy erythrocytes
- Skin and perceive gentle pressure
Answer: 4. Skin and perceive gentle pressure
Question 63. Tactile organs at the root of the hair are
- Free nerve endings (nerve basket)
- Epidermis and dermis
- Dorsal branches of spinal nerves
- Touch corpuscles
Answer: 1. Free nerve endings (nerve basket)
Question 64. The receptors located in muscles, joints, and tendons are known as
- Exteroceptors
- Proprioceptors
- Interoceptors
- External receptors
Answer: 2. Proprioceptors
Question 65. The corpuscles lying deep in the dermis and responsible for deep pressure are known as
- Pacinian corpuscles
- Meissner’s corpuscles
- Merkel’s discs
- Ruffini’s endings
Answer: 1. Pacinian corpuscles
Question 66. White of the eye is
- Cornea
- Sclera
- Choroid
- Conjunctiva
Answer: 2. Sclera
Question 67. Pupil is regulated by
- Radial muscles
- Circular muscles
- Meridional muscles
- Radial and circular muscles
Answer: 4. Radial and circular muscles
“control and coordination questions “
Question 68. The exposed transparent region of the eyeball represents
- Fovea
- Cornea and conjuctiva
- Fibrous coat
- Cornea
Answer: 2. Cornea and conjunctiva
Question 69. Macula lutea is a part of
- Optic nerve
- Sclerotic
- Choroid
- Retina
Answer: 4. Retina
Question 70. Color to the eye is imparted by
- Lens
- Pupil
- Iris
- Vitreous humor
Answer: 3. Iris
Question 71. Eye muscles are attached with
- Sclerotic
- Cornea
- Choroid
- Retina
Answer: 1. Sclerotic
Question 72. The eye rotates in the orbit by
- Six muscles
- Three muscles
- Four muscles
- Five muscles
Answer: 1. Six muscles
Question 73. Cornea transplantation is especially successful because
- Its technique is very simple.
- The preservation of the cornea is very simple.
- Cornea has no relation with blood circulation and immunization.
- The cornea is available easily.
Answer: 3. Cornea has no relation with blood circulation and immunization.
Question 74. When the object is at a distance of more than 6 m, at that time
- Ciliary muscles arc fully contracted
- The convexity of a lens is the maximum
- Eyes are fully relaxed
- All of these
Answer: 3. Eyes arc fully relaxed
Question 75. The part of the eye which acts like a diaphragm of a photographic camera is
- Pupil
- Iris
- Lens
- Cornea
Answer: 2. Iris
Question 76. The ciliary body is located
- Near the ciliary muscles
- Near the blind spot
- Just behind the cornea
- At the junction of the iris and choroid
Answer: 4. At the junction of the iris and choroid
Question 77. Cyanopsin pigment is sensitive to
- Green color
- Red color
- Blue color
- Dim light
Answer: 3. Blue color
Question 78. The chamber between the iris and lens in the cavity of the eyeball is known as
- Vitreous chamber
- Aqueous chamber
- Posterior part of vitreous chamber
- Posterior part of an aqueous chamber
Answer: 4. Posterior part of aqueous chamber
Question 79. In old age, the vision of the eye becomes dim. It is due to
- Myopia
- Hypermetropia
- Cataract
- Astigmatism
Answer: 3. Cataract
Question 80. In hypermetropia, the image is formed
- Before the retina is corrected by a convex lens
- Behind the retina and is corrected by a convex lens
- Before the retina is corrected by the concave lens
- Behind the retina and is corrected by the concave lens
Answer: 2. Behind the retina and is corrected by a convex lens
Question 81. In presbyopia,
- The eyeball becomes short
- The lens becomes opaque
- The retina gets damaged
- Diminution of accommodation of lens due to loss of elasticity
Answer: 4. Diminution of accommodation of lens due to loss of elasticity
Question 82. In myopia, light rays from far-off objects converge
- Behind the retina
- In front of the retina
- On the retina
- In the retina
Answer: 2. In front of the retina
Question 83. The overproduction of aqueous humor results in
- Astigmatism
- Fovea centralis
- Macula lutea or yellow spot
- Glaucoma
Answer: 4. Glaucoma
Question 84. Short-sightedness or myopic vision is corrected by wearing
- Convex lenses
- Concave lenses
- Convex mirrors
- Concave mirrors
Answer: 2. Concave lenses
Question 85. During the transmission of impulse from the tympanum to the internal ear, amplification of sound waves occurs. The amplification due to the difference in the size of the tympanum and fenestra ovalis is about
- 10 times
- 22 times
- 2.2 times
- 40 times
Answer: 3. 2.2 times
Question 86. In the tympanic cavity, there is an aperture in which stapes are fitted. It is
- Foramen rotundus
- Foramen triosseum
- Foramen of Monro
- Fenestra ovalis
Answer: 4. Fenestra ovalis
Question 87. The upper aperture which puts the tympanic cavity in communication with a narrow space around the internal ear is known as
- Fenestra ovalis
- Fenestra rotundus
- Fossa ovalis
- Foramen ovale
Answer: 1. Fenestra ovalis
Question 88. Which of the following structures is not filled with endolymph?
- Utriculus
- Tympanic cavity
- Sacculus
- Semicircular canal
Answer: 2. Tympanic cavity
Question 89. One of the following is a stirrup-shaped bone.
- Incus
- Malleus
- Stapes
- Tongue shaped
Answer: 3. Stapes
Question 90. Which part of the internal ear receives sound waves in man?
- Cochlea
- Lagena and utriculus
- Ampullae and utriculus
- None of these
Answer: 1. Cochlea
Question 91. One of the following is not a part of the membranous labyrinth.
- Semicircular canal
- Cochlear duct
- Vestibule
- Bony labyrinth
Answer: 4. Bony labyrinth
“class 11 neural control and coordination “
Question 92. The membranous labyrinth is found in
- Columella auris
- Occipitals
- Parietals
- Periotic
Answer: 4. Periotic
Question 93. The equilibrium is maintained by
- Semicircular ducts
- Ampulla
- Crista
- Cupula
Answer: 3. Crista
Question 94. The roof of scala media is called
- Reissner’s membrane
- Basilar membrane
- Tectorial membrane
- Organ of Corti
Answer: 1. Reissner’s membrane
Question 95. The tectorial membrane is found in the
- Eye of frog
- Eye of mammals
- Ear of mammals
- Tongue of frog
Answer: 3. Ear of mammals
Question 96. A molecule cannot be tasted or smelled until it has been
- Converted into protein
- Converted into transmitter
- Grouped into multimolecular complex
- Dissolved in a liquid
Answer: 4. Dissolved in a liquid
Question 97. Bowman’s glands are associated with
- Olfactory epithelium
- Taste buds
- Organ of Corti
- Vallate papillae
Answer: 1. Olfactory epithelium
Question 98.The activity of which cranial nerve can protect by warning about harmful chemicals in the air?
- 5
- 9
- 6
- 10
Answer: 1. 5
Question 99. The total number of taste buds in the human tongue is approximately
- 1000
- 10,000
- 100,000
- 50,000
Answer: 2. 10,000
Question 100. Which of the following cranial nerves is involved in causing the movement of the tongue?
- 7
- 9
- 10
- 11
Answer: 4. 11
Question 101. In right-handed individuals,
- The left cerebral hemisphere is poorly developed
- The right hemisphere is the dominant hemisphere
- The left cerebral hemisphere is the dominant hemisphere
- Both cerebral hemispheres are dominant
Answer: 3. The left cerebral hemisphere is the dominant hemisphere
Question 102. Stimulation of parasympathetic nerves is likely to produce all of the following except
- Decreased insulin secretion
- Increased exocrine pancreatic secretion
- Increased bile synthesis
- Increased gastric secretion
Answer: 1. Decreased insulin secretion
Question 103. The hypothalamus is involved in the regulation of
1. Circadian rhythm
2. Water balance
3. Respiration and heartbeat
4. Maintenance of homeostasis
5. Appetite and Satiety
Mark the correct one.
- (1), (2), (3), (4), and (5)
- (2) and (4) only
- (1), (2), (3), and (4) only
- (1), (2), and (4) only
Answer: 1. (1), (2), (3), (4), and (5)
Question 104. Which of the following do not occur during accommodation reflex?
- Contraction in ciliary muscles
- Suspensory ligaments become loose
- Decrease in radius of curvature
- Decreasing refraction
Answer: 4. Decreasing refraction
Question 105. Broca’s area (motor speech) is located in
- Frontal lobe
- Parietal lobe
- Temporal lobe
- Occipital lobe
Answer: 1. Frontal lobe
Question 106. Mark the incorrect match.
- Parkinson’s—Deficiency of dopamine disease
- Schizophrenia—Excess of dopamine
- Excess of Alzheimer’s disease—Acetylcholine
- Multiple sclerosis—Degeneration myelin sheath
Answer: 3. Excess of Alzheimer’s disease—Acetylcholine
Question 107. A person is unable to speak fluent sentences, although he has no problem understanding written or spoken words due to damage to the
- Broca’s area
- Wernicke’sarea
- Visual area
- Auditory area
Answer: 1. Broca’s area
Question 108. When the visual field of both eyes overlaps, it is called
- Binocular vision
- Monocular vision
- Stereoscopic vision
- Both 1 and 3
Answer: 1. Binocular vision
Question 109. If we accidentally focus on intense light sources such as the sun. it will damage
- Macula lutea
- Lens
- Blind spot
- Cornea
Answer: 1. Macula lutea
Question 110. If we put water in the eye. there will be blurred images due to
- Decrease in refraction as cornea forms plane surface
- Increase in refraction as cornea forms plane surface
- Decrease in refraction as cornea forms a concave surface
- Increase in refraction as cornea forms concave surface.
Answer: 1. Decrease in refraction as cornea forms plane surface
Question 111. The correct sequence of meninges from inner to outer side is
- Arachnoid → Dura mater → Pia mater
- Arachnoid → Pia mater → Dura mater
- Pia mater → Dura mater → Arachnoid
- Pia mater → Arachnoid → Dura mater
Answer: 4. Pia mater → Arachnoid → Dura mater
Question 112. The Vagus nerve is composed mainly of parasympathetic fibers. The preganglionic fibers form a network known as
- Choroid plexus
- Nervousplexus
- Auerbach’s plexus
- Brachialplexus
Answer: 3. Auerbach’s plexus
Question 113. During nerve impulse transmission, the permeability of the membrane is greater for
- Na+
- K+
- Equal for both 1 and 2
- Ca2+
Answer: 1. Na+
Question 114. In mammals, the brain center, which regulates body temperature, is situated in
- Cerebrum
- Olfactory lobe
- Cerebellum
- Medulla oblongata
Answer: 1. Cerebrum
Question 115. The junction between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of the next is called
- A joint
- A synapse
- Constant bridge
- Junction point
Answer: 2. A synapse
Question 116. Which one of the following is a motor nerve?
- Auditoty
- Abducens
- Optic nerve
- Trigeminal nerve
Answer: 2. Abducens
Question 117. NissI granules are absent in
- Axon
- Cyton
- Dendron
- Schwann cells
Answer: 1. Axon
Question 118. Which of the following is a purely motor cranial nerve?
- Olfactory
- Optic
- Abducens
- Vagus
Answer: 3. Abducens
Question 119. The trigeminal nerve in the case of frogs is
- 1 cranial nerve
- 2 cranial nerve
- 4 cranial nerve
- 5 cranial nerve
Answer: 4. 5 cranial nerve
Question 110. In the human body, muscular coordination is controlled by
- Spinal cord
- Cortex
- Cerebellum
- Cerebral hemisphere
Answer: 3. Cerebellum
Question 111. The sense of smell is controlled by
- Cerebrum
- Cerebellum
- Olfactory lobe
- Hypothalamus
Answer: 1. Cerebrum
Question 112. The third ventricle connects to lateral ventricles through
- Foramen magnum
- Foramen monro
- Foramen magnetic
- Foramen Anuschka
Answer: 2. Foramen monro
Question 113. The connection between axon and dendrite is
- Synapse
- Synapse
- Desmosome
- Tight junction
Answer: 1. Synapse
Question 114. Depolarization of axolemma during nerve conduction takes place because of
- Equal amounts of Na+ and K+ move out across axon- lemma
- Na+ move inside
- More Na+ outside
- None
Answer: 2. Na+ move inside
“questions about the nervous system “
Question 115. Which of the following statements is correct for the node of Ranvier of nerve
- Neurilemma is discontinuous.
- Myelin sheath is discontinuous.
- Both neurilemma and myelin sheath are discontinuous.
- Covered by myelin sheath.
Answer: 2. Myelin sheath is discontinuous.
Question 116. What used to be described as Nissl granules in a nerve cell are now identified as
- Cell metabolites
- Fat granules
- Ribosomes
- Mitochondria
Answer: 3. Ribosomes
Question 117. In the resting state of the neural membrane, diffusion due to concentration gradients, if allowed, would drive
- K+ and Na+ out of the cell
- Na+ into the cell
- Na+ out of the cell
- K+ into the cell
Answer: 2. Na+ into the cell
Question 118. Unidirectional transmission of a nerve impulse through nerve fibers is because
- Nerve fiber is insulated by a medullary sheath.
- The sodium pump starts operating only at the cyton and then continues into the nerve fiber.
- Neurotransmitters are released by dendrites and not by axon endings.
- Neurotransmitters are released by axon endings and not by dendrites.
Answer: 4. Neurotransmitters are released by axon endings and not by dendrites.
Question 119. Nerve cells do not possess
- Neurilemma
- Sarcolemma
- Dendrites
- Axon
Answer: 2. Sarcolemma
Question 120. Dendrites are associated with which system?
- Nervous system
- Digestive system
- Muscular system
- Blood vascular system
Answer: 1. Nervous system
Question 121. During the transmission of nerve impulses through a nerve fiber, the potential on the inner side of the plasma membrane has which type of electric charge?
- First positive, then negative, and continue to be negative
- First negative, then positive, and continue to be positive
- First positive, then negative, and again back to positive
- First negative, then positive, and again back to negative
Answer: 4. First negative, then positive, and again back to negative
Question 122. Arbor vitae is a part of
- Cerebrum
- Cerebellum
- Midbrain
- Forebrain
Answer: 2. Cerebellum
Question 123. Which has H-shaped gray matter?
- Cerebrum
- Spinal cord
- Cerebellum
- Medulla oblongata
Answer: 2. Spinal cord
Question 124. Which of the following is the part of the midbrain of the rabbit?
- Cerebrum
- Diencephalon
- Corpora quadrigemina
- None of these
Answer: 3. Corpora quadrigemina
Question 125. The function of cerebrospinal fluid does not include
- Protection of the brain and spinal cord by containing antibody
- Protection of delicate brain and spinal cord from shock
- As a medium for the excretion of waste product
- Buoyancy to brain
Answer: 1. Protection of the brain and spinal cord by containing antibody
Question 126. The third ventricle lies in
- Medulla oblongata
- Midbrain
- Diencephalon
- Cerebrum
Answer: 3. Diencephalon
Question 127. Which part of the brain is supposed to be damaged if, in an accident, a person loses control of water balance, hunger, and body temperature?
- Cerebellum
- Hypothalamus
- Medula oblongata
- Corpora quadrigemina
Answer: 2. Hypothalamus
Question 128. Column 1 lists the parts of the human brain and column 2 lists the function. Match the two columns and identify the correct choice from those given.
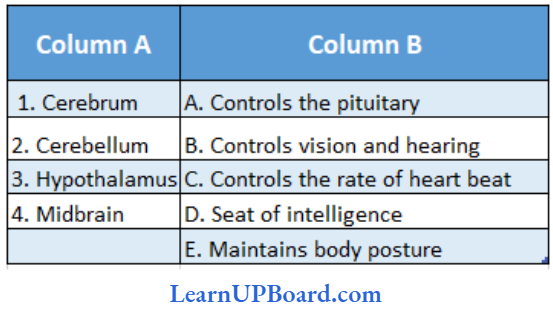
Answer: 4.
Question 129. Which of the following destroys acetylcholinesterase?
- Malathion
- CO
- KCN
- Colchicine
Answer: 1. Malathion
Question 130. Botulism affects
- Digestive system
- Blood vascular system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
Answer: 3. Nervous system
Question 131. Nor-epinephrine leads to an increase in
- Blood pressure
- Urine production
- Cellular respiration
- Release of epinephrine
Answer: 1. Blood pressure
Question 132. Injury to the vagus nerve in humans is not likely to affect
- Gastrointestinal movements
- Pancreatic secretion
- Cardiac movements
- Tongue movements
Answer: 4. Tongue movements
Question 133. In a man, the abducens nerve is injured. Which one of the following functions will be affected?
- Movement of the neck
- Movement of the tongue
- Movement of the eyeball
- Swallowing
Answer: 3. Movement of the eyeball
Question 134. One of the examples of the action of the autonomous nervous system is
- Pupillary reflex
- Swallowing of food
- Peristalsis of the intestines
- Knee-jerk response
Answer: 3. Peristalsis of the intestines
Question 135. Excessive stimulation of the vagus nerve in humans may lead to
- Hoarse voice
- Peptic ulcers
- Efficient digestion of protein
- Irregular contractions of the diaphragm
Answer: 2. Peptic ulcers
Question 136. Mulch the following human spinal nerves in column 1 with 2 and choose the correct options:
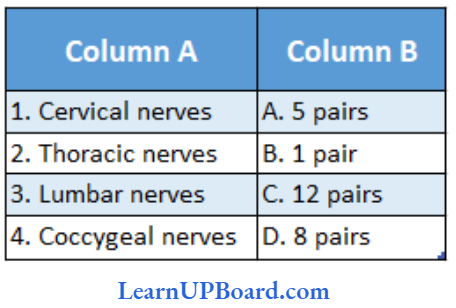
- 1→ B, 2 → D, 3 → A, 4 → C
- 1 → D, 2 → C, 3→ A, 4 → B
- 1 → D, 2 → B, 3 → A, 4 → D
- 1→ A, 2 → D, 3 → B, 4 → C
Answer: 2. 1 → D, 2 → C, 3→ A, 4 → B
Question 137. The ninth pair of cranial nerves in frog is
- Vagus
- Trigeminal
- Hypoglossal
- Glossopharyngeal
Answer: 4. Glossopharyngeal
Question 138. Which of the following is not under the control of the vagus nerve?
- Gastrointestinal movement
- Respiratory movement
- Salivation
- None of these
Answer: 3. Salivation
Question 139. Which of the following is released by the parasympathetic nervous system?
- Serotonin
- Acetylcholine
- Epinephrine
- Nor-epinephrine
Answer: 2. Acetylcholine
“questions about nervous system “
Question 140. The mandibular nerve is the branch of which cranial nerve?
- 2
- 3
- 5
- 6
Answer: 3. 5
Question 141. The Vagus nerve is composed mainly of parasympathetic fibers. The preganglionic fibers form a network in the walls of the gut. This network is known as
- Choroid plexus
- Nervous plexus
- Auerbach’s plexus
- Brachial plexus
Answer: 3. Auerbach’s plexus
Question 142. Given below is a table comparing the effects of sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system for four features (1-4). Which one feature is correctly matched?
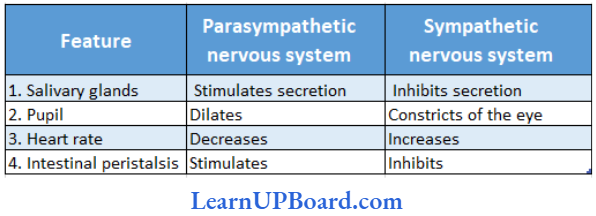
Answer: 2.
Question 143. Effect of anesthetics on the body
- Inhibits Na-K pump
- Kills nerves
- Stops brain functions
- Inactivates skin cells
Answer: 1. Inhibits Na-K pump
Question 144. A deficiency of oxygen affects mainly the
- Brain
- Skin
- Kidney
- Intestine
Answer: 1. Brain
Question 145. Neuroglial cells associated with
- Heart
- Kidney
- Brain
- Eyes
Answer: 3. Brain
Question 146. Adrenaline directly affects on
- S A node
- β-cells of Langerhans
- Dorsal root of the spinal cord
- Epithelial cells of the stomach
Answer: 1. S A node
Question 147. In which animal, nerve cell is present but brain is absent?
- Sponge
- Earthworm
- Cockroach
- Hydra
Answer: 4. Hydra
Question 148. Which of the following is the dominant intracellular anion?
- Potassium
- Chloride
- Phosphate
- Calcium
Answer: 3. Phosphate
Question 149. The nervous system develops from
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm
- Ectomesoderm
- Endomesoderm
Answer: 1. Ectoderm
Question 150. Which of the following is not correctly matched?
- Rhinencephalon—Olfaction
- Hypothalamus—Pituitary
- Cerebellum—Balance
- Medulla oblongata—Temperature regulation
Answer: 4. Medulla oblongata—Temperature regulation
Question 151. The internal carotid artery supplies blood to
- Kidney
- Liver
- Heart
- Brain
Answer: 4. Brain
Question 152. Which one of the following characters is not typical of the class Mammalia?
- Seven cervical vertebrae
- Thecodont dentition
- Alveolar lungsnerves
- Ten pairs of cranial
Answer: 4. Ten pairs of cranial
Question 153. Parkinson’s disease (characterized by tremors and progressive rigidity of limbs) is caused by the degeneration of brain neurons that are involved in movement control and make use of neurotransmitter
- Acetylcholine
- Nor-epinephrine
- Dopamine
- GABA
Answer: 3. Dopamine
Question 154. Which one of the following statements is correct?
- Neither hormones control neural activity, nor the nervous control endocrine activity
- Endocrine glands regulate neural activity, but not vice versa
- Neurons regulate endocrine activity, but not vice versa
- Endocrine glands regulate neural activity and the nervous system regulates endocrine glands
Answer: 4. Endocrine glands regulate neural activity and the nervous system regulates endocrine glands
Question 155. Which one of the following does not act as a neurotransmitter?
- Nor-epinephrine
- Cortisone
- Acetylcholine
- Epinephrine
Answer: 2. Cortisone
Question 156. Which of the following two systems are opposite in action to each other?
- Nervous, sensory
- Nervous, endocrine
- Sensory, Endocrine
- Parasympathetic, sympathetic
Answer: 4. Parasympathetic, sympathetic
Question 157. Which of the following structures is present only in the mammalian brain?
- Corpus luteum
- Corpus striatum
- Corpus fibrosum
- Corpuscallosum
Answer: 4. Corpuscallosum
Question 158. You are watching a horror movie and you notice your heart is beating fast and your mouth is dry. It is because of
- Fight and flight response
- Autonomic nervous system
- Sympathetic nervous system
- Both 1 and 3
Answer: 2. Autonomic nervous system
Question 159. Tongue is under the control of
- Trigeminal
- Facial
- Autonomic system
- Glossopharyngeal
Answer: 4. Glossopharyngeal
Question 160. The number of cranial nerves in frogs is
- 10
- 12
- 10 pairs
- 12 pairs
Answer: 3. 10 pairs
Question 161. Intercellular communication in multicellular organisms occurs through
- Nervous system only
- Digestive system only
- Respiratory system only
- Both the nervous and endocrine systems
Answer: 4. Both the nervous and endocrine systems
Question 162. Which of the following substances leads to the inhibition of the central nervous system?
- Glycine
- GABA
- Nor-epinephrine
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 2
Question 163. Which one of the following pairs of structures distinguishes a nerve cell from other types of cells?
- Vacuoles and fibers
- Flagellum and medullary sheath
- Nucleus and mitochondria
- Perikaryon and dendrites
Answer: 4. Perikaryon and dendrites
Question 164. The fifth cranial nerve of a frog is called
- Optic nerve
- Vagus
- Trigeminal
- Ophthalmic
Answer: 3. Trigeminal
Question 165. If the dorsal root of the spinal cord is broken down, then its effect is
- No effect on impulse
- Impulse is transmitted fast
- Impulse is transmitted but slowly
- No impulse is transmitted from the receptor
Answer: 4. No impulse is transmitted from the receptor
Question 166. The acetylcholinesterase enzyme splits acetylcholine into
- Acetone and choline
- Acetic acid and choline
- Amino acid and choline
- Aspartic acid and acetylcholine
Answer: 2. Acetic acid and choline
Question 167. The olfactory area is present in :
- Frontal lobe
- Parietal lobe
- Temporal lobe
- Occipital lobe
Answer: 3. Temporal lobe
Question 168. Somesthetic or post-central area is responsible for
- Initiation of motor impulses for voluntary muscles
- Initiation of motor impulses for involuntary muscles
- Perception of pain, touch, and temperature
- Coordination of speech
Answer: 3. Perception of pain, touch, and temperature
Question 169. Dilation of the pupil of the human eye is caused by
- Parathormone
- Sympathetic
- Parasympathetic nerve system
- Autonomic nervous
Answer: 2. Sympathetic
Question 170. The nerve impulse is generated when nerve cell undergoes
- Depolarization
- Repolarization
- Hyperpolarization
- Pscudopolarization
Answer: 1. Depolarization
Question 171. Nerve impulse initiates with the movements of
- K+
- Na+
- Ca2+
- Mg2+
Answer: 2. Na+
Question 172. Which part of the brain controls intellectual ability?
- Frontal lobe
- Parietal lobe
- Temporal lobe
- Occipital lobe
Answer: 1. Frontal lobe
Question 173. The occipital lobe is connected with
- Smell
- Vision
- Speech
- Hearing
Answer: 2. Vision
Question 174. A: The imbalance in the concentration of Na+, K+, and proteins generates resting potential. R: To maintain the unequal distribution of Na+ and K+, the neurons use electrical energy.
- Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- (A) is a true statement, but (R) is false.
- Both (A) and (R) are false.
Answer: 2. Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Question 175. During the conduction of nerve impulses, the action potential is the result of the movement of
- Na+ from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid
- Na+ from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
- Na+ toward both directions
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Na+ from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
Question 176. Which of the damaged cells cannot be repaired?
- Liver cells
- Brain cells
- Bone cells
- Epidermal cells
Answer: 2. Brain cells
Question 177. The 4 cranial nerve is
- Facial
- Trochlear
- Olfactory
- Oculomotor
Answer: 2. Trochlear
Question 178. Adrenaline is equivalent to which neurotransmitter?
- GABA
- Serotonin
- Epinephrine
- Nor-epinephrine
Answer: 3. Epinephrine
Question 179. All sensory pathways to the cerebral cortex synapse at
- Pons
- Thalamus
- Cerebellum
- Hypothalamus
Answer: 1. Pons
Question 180. A man is admitted to a hospital. He is suffering from an abnormally low body temperature, loss of appetite, and extreme thirst. His brain scan would probably show a tumor in
- Pons
- Cerebellum
- Hypothalamus
- Medulla oblongata
Answer: 3. Hypothalamus
Question 181. The nerve centers which control the body temperature and the urge to eat are contained in
- Pons
- Thalamus
- Cerebellum
- Hypothalamus
Answer: 4. Hypothalamus
Question 182. The optic lobes in humans are represented by corpora
- Bigemina
- Arenacea
- Striata
- Quadrigemina
Answer: 4. Quadrigemina
Question 183. In a medullated nerve fiber, the conduction of impulses is faster due to the presence of
- Pericytes
- Nissl granules
- Endoneurium and Epineurium
- Myelin sheath and node of Ranvier
Answer: 4. Myelin sheath and node of Ranvier
Question 184. Which of the following is not an effect of the sympathetic nervous system?
- Dilation of the pupil
- Inhibition of peristalsis
- Elevation of blood pressure
- Stimulation of saliva secretion
Answer: 4. Stimulation of saliva secretion
Question 185. When a neuron is in a resting state, i.e., not conducting any impulse, the axonal membrane is
- Comparatively more permeable to Na+ ions and nearly impermeable to K+ ions
- Equally permeable to both Na+ and K+ ions
- Impermeable to both Na+ and K+ ions
- Comparatively more permeable to K+ ions and nearly impermeable to Na+ ions
Answer: 4. Comparatively more permeable to K+ ions and nearly impermeable to Na+ ions
Question 186. The human hindbrain comprises three parts, one of which is
- Corpus callosum
- Cerebellum
- Hypothalamus
- Spinal cord
Answer: 2. Cerebellum
Question 187. Diagrammatic cross-section of a single loop of human cochlea
Which one of the following options correctly represents the names of the three different parts?
- D: Sensory hair cells, A: Endolymph, B: Tectorial membrane
- A: Perilymph, B: Tectorial membrane, C: Endolymph
- B: Tectorial membrane, C: Perilymph, D: Secretory cells
- C: Endolymph, D: Sensory hair cells, A: Serum
Answer: 2. A: Perilymph, B: Tectorial membrane, C: Endolymph
Question 188. Which one of the following is the correct difference between rod cells and cone cells of our retina?
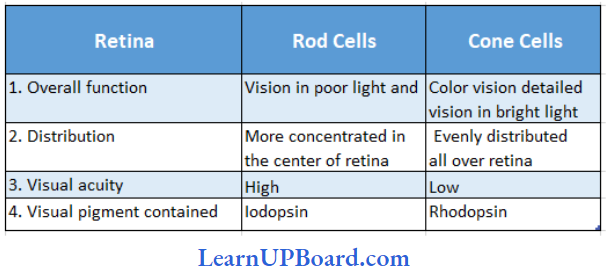
Answer: 1
Question 189. A coma transplant in humans is almost never rejected. This is because
- It is composed of enucleated cells
- It is a non-living layer
- Its cells are least penetrable by bacteria
- It has no blood supply
Answer: 4. It has no blood supply
Question 190. Static equilibrium is maintained by
- Utriculus
- Sacculus
- Both of these
- Semicircular canals
Answer: 3. Both of these
Question 191. Organ of Corti helps in
- Maintaining equilibrium
- Formation of wax
- Hearing
- All of these
Answer: 3. Hearing
Question 192. Eustachian tube connects
- Pharynx to the middle ear
- Middle ear to external ear
- Left ventricle to right ventricle
- Left atrium to right atrium
Answer: 1. Pharynx to middle ear
Question 193. Which organ of the rabbit is concerned with equilibrium?
- Cochlea
- Ear ossicles
- Eustachian ducts
- Semicircular canals
Answer: 4. Semicircular canals
Question 194. Bowman’s glands are found in
- Olfactory epithelium
- External auditory canal
- Cortical nephrons only
- Juxtamedullary nephrons
Answer: 1. Olfactory epithelium
Question 195. The correct order of arrangement of ear ossicles starting from the tympanum is
- Incus, malleus, stapes
- Malleus, incus, stapes
- Stapes, malleus, incus
- Incus, stapes, malleus
Answer: 2. Malleus, incus, stapes
Question 196. In the following abnormalities of the eyes, which one is a serious condition that leads to blindness?
- Myopia
- Glaucoma
- Presbyopia
- Astigmatism
- Hypermetropia
Answer: 2. Glaucoma
Question 197. The lens and cornea do not have a blood supply. So the nutrients are supplied by
- Retina
- Eyelash
- Blind spot
- Aqueous humor
Answer: 4. Aqueous humor
Question 198. Which part of the human ear plays no role in hearing as such but is otherwise very much required?
- Organ of Corti
- Vestibular apparatus
- Ear ossicles
- Eustachian tube
Answer: 2. Vestibular apparatus
Question 199. Select the answer that correctly matches the endocrine gland with the hormone it secretes and its function/deficiency symptom.
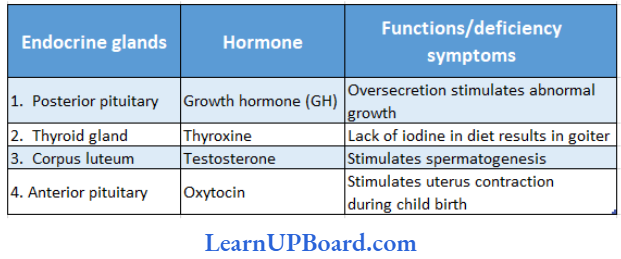
Answer: 2.
Question 200. Parts A, B, C, and D of the human eye. Select the option which gives correct identification along with its functions/characteristics.:
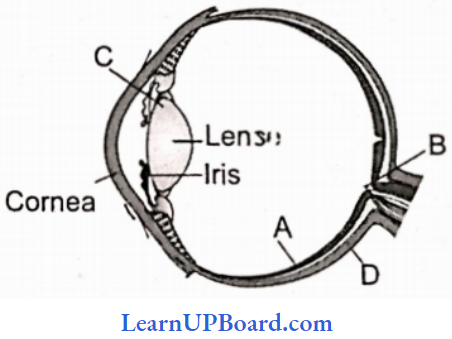
- B—Blind spot—Has only a few rods and cones.
- C—Aqueous chamber—Reflects the light which does not pass through the lens.
- D—Choroid—Its anterior part forms the ciliary body.
- A—Retina—Contains photoreceptors: rods and cones.
Answer: 4. A—Retina—Contains photoreceptors: rods and cones.
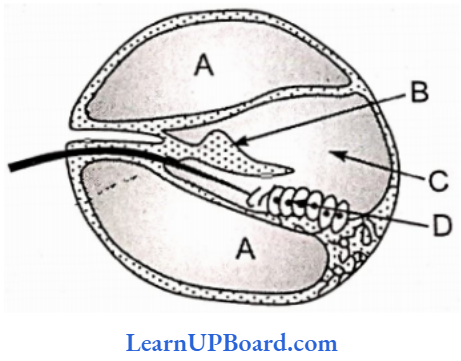
Question 201. Axon terminal and synapse. Identify correctly at least two of A-D.
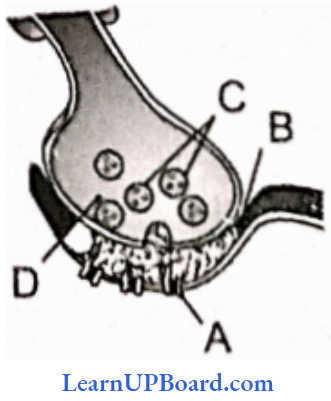
- B – Synaptic connection, D – K+
- A – Neurotransmitter, B – Synaptic cleft
- C – Neurotransmitter, D – Ca++
- A – Receptor, C – Synaptic vesicles
Answer: 4. A – Receptor, C – Synaptic vesicles
