NEET Biology For Principles Of Inheritance And Variation Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. The phrase “like begets like” is best analyzed in the context of
- Forward genetics
- Reverse genetics
- Classical genetics
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 2. The term genetics was coined by
- Bateson
- Mendel
- Morgan
- Johanssen
Answer. 1. Bateson
Question 3. Which one of the following inheritance or theory is based on the blending concept and explains gemmule as the basis of inheritance?
- Preformation theory
- Pangenesis theory
- Reproductive blood theory
- Mendelian inheritance
Answer. 2. Pangenesis theory
Question 4. Mendel’s experimental plant was Pisum sativum, but he also worked and failed to find similar results on
- Tobacco and sweet pea
- Hieracium and Lablab
- Hieracium and sweet pea
- Lablab and sweet pea
Answer. 2. Hieracium and Lablab
Question 5. Predecessor/s of Mendel was/were
- Goss
- Kolreuter
- Naudin
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 6. Mendel read out and presented his paper in the seminar of Natural History Society of Brunn in
- 1857
- 1859
- 1865
- 1866
Answer. 3. 1865
” pedigree analysis questions”
Question 7. Who amongst the following found out the original paper of Mendel and got it published in Flora?
- De Vries
- Correns
- Tschermak
- Kolreuter
Answer. 1. De Vries
Question 8. Find odd one out (with respect to pea traits).
- Yellow cotyledon
- Yellow pod
- Terminal flower
- Constricted pod
Answer. 1. Yellow cotyledon
Question 9. Which one of the following Mendelian traits is present on the fifth chromosome?
- Pod shape
- Pod color
- Flowers color
- Pod position
Answer. 2. Pod color
Question 10. The recombinant phenotypic ratio in F2 obtained from pa- rental cross having genotypes TTRR x ttrr will be
- 9:3:3:1
- 3:1
- 1:2:1
- 3:3
Answer. 4. 3:3
Question 11. Heterozygous tall and red flowered pea plants are selfed and total 2000 seeds are collected. What is the total number of seeds for both heterozygous traits?
- 250
- 500
- 1250
- 750
Answer. 2. 500
Question 12. Types of gametes formed by the plant with genotype *AABbccDD will be
- 4
- 16
- 8
- 2
Answer. 4. 2
Question 13. In monohybrid cross, pure homozygous plants will be
- One
- Two
- Three
- Four
Answer. 2. Two
Question 14. Total 512 seeds are collected from the cross WwYy x WwYy. Find the number of plants produced with first dominant and second recessive trait.
- 288
- 96
- 32
- 320
Answer. 2. 96
Question 15. Which Mendelian cross can produce two genotypes and two phenotypes?
- Monohybrid cross
- Monohybrid test cross
- Incomplete dominance
- Co-dominance
Answer. 2. Monohybrid test cross
Question 16. A trihybrid cross is made between two yeasts, both with genotypes AaBbCc. What proportion of offsprings will be of genotype aabbcc?
- 0
- 1/4
- 1/16
- 1/64
Answer. 4. 1/64
Question 17. From the cross AABb x aaBb, genotypes AaBB: AaBb: Aabb: aabb are obtained in the ratio of
- 1:1:1:1
- 1:2:1:0
- 0:3:1:0
- 1:1:1:0
Answer. 2. 1:2:1:0
Question 18. In a cross between a pure tall pea plant with green pod and a pure short plant with yellow pod, how many short plants out of 16 would you expect in F2 generation?
- 9
- 4
- 3
- 1
Answer. 2. 4
Question 19. Find the correct match.
Column 1 Column 2
a. Phenotype (1) G. Shull
b. Heterosis (2) Johanssen
c. Heterozygous (3) Correns
d. Incomplete dominance (4) Bateson
- a (2), b (1), c (4), d (3)
- a (2), b (1), c (3), d (4)
- a (4), b (1), c (3), d (2)
- a (1), b (2), c (3), d (4)
Answer. 1. a (2), b (1), c (4), d (3)
Question 20. An allele is the
- Total number of genes for a trait
- Total number of genes on chromosome
- Alternative form of a gene
- Alternative form of a character
Answer. 3. Alternative form of a gene
Question 21. How many phenotypes are produced in a test cross of AaBBCC?
- Two
- Four
- Eight
- Twelve
Answer. 1. Two
Question 22. Which parental combination represents outcross?
- AA × BB
- Aa x aa
- аа х АА
- Aa x AA
Answer. 4. Aa x AA
Question 23. Which one of the following crosses would have ratio 1:1:1:1?
- TtRR x ttrr
- TTRR × ttrr
- TtRrx ttrr
- TURR × TTrr
Answer. 3. TtRrx ttrr
Question 24. When red and white flowered Mirabilis plants are crossed, all pink flowers are produced in F, generation. When F, progeny is selfed, the expected phenotypic and genotypic ratios are, respectively,
- 1:2:1 and 3:1
- 3:1 and 1:2:1
- 1:21 and 1:2:1
- 1:1 and 1:1:1
Answer. 3. 1:21 and 1:2:1
Question 25. If a character is controlled by six alleles of a gene, then the possible genotypes would be
- 21
- 729
- 64
- 42
Answer. 1. 21
Question 26. The ratio of children with blood groups A: B: AB: 0, born to a set of parents in which the mother is with blood group A and the father is with blood group B, will be
- 1:1:1:1
- 2:0:2:0
- 0:0:4:0
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 27. Possible blood groups in children from the parents with blood groups B and O are
- All B
- All O
- Both B and O
- A and B
Answer. 3. Both B and O
Question 28. Which one of the following genes influences the viability of the organisms when present in homozygous condition?
- Curly wings gene in Drosophila
- Plum eyes gene in Drosophila
- Sickle-cell gene
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
inheritance and variation mcq
Question 29. Pleiotropic genes show
- One gene one character
- One gene regulates many phenotypic characters
- Polygenic inheritance
- Multiple allelism
Answer. 2. One gene regulates many phenotypic characters
Question 30. Emasculation of flower is done when
- Stamens are mature
- Stamens are immature
- Stigma is mature
- Stigma is immature
Answer. 2. Stamens are immature
Question 31. Consider the cross AaBbCcDdEe x aaBbccddee. What proportion of the progeny will genotypically resemble the first parent?
- 1/64
- 2/64
- 4/16
- 4/46
Answer. 1. 1/64
Question 32. When only one allele of a pair is present, the condition is called
- Homozygous
- Hemizygous
- Heterozygous
- Incomplete dominance
Answer. 2. Hemizygous
Question 33. Both the alleles are independently expressed in
- Eye color in Drosophila
- Fruit color in Cucurbita
- Sickle-cell hemoglobin
- Height in tobacco
Answer. 3. Sickle-cell hemoglobin
Question 34. Reciprocal cross is
- Intraspecific hybridization
- Back cross
- Pollen grains from one variety deposited on the stigma of the contrasting variety and vice versa, in hybridization experiments
- Test cross
Answer. 3. Pollen grains from one variety deposited on the stigma of the contrasting variety and vice versa, in hybridization experiments
Question 35. Bridge between two generations which contributes equally in the heredity of the offsprings is
- Chromosome
- Somatic cells
- Sperm and egg
- Factor
Answer. 3. Sperm and egg
Question 36. Sum total of genes with all these alleles at any time in a unit of evolution is called
- Genotype
- Genome
- Gene pool
- Gene library
Answer. 3. Gene pool
Question 37. Both chromosomes as well as genes do not occur in pairs in
- Somatic cells
- Fertilized egg
- Megaspore mother cell
- Microspore
Answer. 4. Microspore
Question 38. Parallelism between factors and chromosome led to the formation of
- Cell theory
- Chromosomal theory of inheritance
- Pangenesis theory
- Pre-formation theory
Answer. 2. Chromosomal theory of inheritance
Question 39. Who observed that the behavior of chromosomes at meiosis can serve as the cellular basis of both segregation and independent assortment?
- Sutton and Boveri
- Banden and Boveri
- W. Flemming
- Boveri and Brauer
Answer. 1. Sutton and Boveri
Question 40. In a dihybrid test cross, if the parental types exceed the recombination types among the resultant progeny, it is due to
- Linkage
- Complete linkage
- Independent assortment
- Crossing-over
Answer. 1. Linkage
Question 41. In the cross involving “linked genes,” who discovered that the assortment of genes during germ cell formation is non-random in the violation of Mendel’s second law?
- Bateson and Punnet
- Morgan
- Sutton and Boveri
- Sutton
Answer. 1. Bateson and Punnet
Question 42. Test cross ratio 1:7:7:1 in sweet pea when two pairs of alleles do not show independent assortment can be obtained from parental cross which is
- BBll x bbll
- BbL1 x BBll
- BBll x bbll
- bbll x Bbll
Answer. 3. BBll x bbll
pedigree questions
Question 43. Dihybrid test cross ratio with 82% parental type and 18% recombinants type shows that genes have
- Incomplete linkage
- Complete linkage
- Independent assortment
- Double crossing-over
Answer. 4. Double crossing-over
Question 44. A dihybrid test cross ratio for two completely linked genes will be
- 1:1:1:1
- 1:1
- 1:7:7:1
- 7:1:1:7
Answer. 2. 1:1
Question 45. In a cross in Drosophila, the heterozygous member with gray body (b+) and long wings (vg+) was crossed with the one with black body and vestigial wings. The progeny had the following ratio: grey vestigial – 24; grey long- 126; black long-26; black vestigial – 124. What is the frequency of recombinants in the population?
- 15.8%
- 16.7%
- 17.5%
- 14.5%
Answer. 2. 16.7%
Question 46. An individual homozygous for genes cd is crossed with wild type and F, is crossed back with the double recessive. The appearance of the offsprings is as follows:
++ → 903
cd → 897
+d → 98
c+ → 102
The distance between genes c and d d is
- 20 map units
- 9.8 map units
- 10.2 map units
- 10 map units
Answer. 4. 10 map units
Question 47. A test cross of F, flies ++ / ab produced the following offsprings:
++/ab (R) 9
ab/ab (R) 9
+b/ab (R) 41
a+/ab (R) 41
This cross represents
- Trans configuration
- Cis configuration
- Complete linkage
- No crossing-over
Answer. 1. Trans configuration
Question 48. In rabbits, two recessive genes produce solid body color and long hair, respectively, in contrast to spotted body color and short hair, which result from dominant alleles. The results from a cross between heterozygous spotted, short-haired rabbits and solid, long-haired rabbits are as follows:
Spotted, short 48
Spotted, long 5
Solid, short 7
Solid, long 40
In terms of cross-over units, how far apart are these two genes on the chromosome?
- 48 units
- 12 units
- 40 units
- 7 units
Answer. 2. 12 units
Question 49. Assume that genes a and b are linked and show 40% re- combination. If++/++ individual is crossed with ab/ab, then types and proportions of gametes in F, will be
- ++ 20% ab 20%: +b 20%: a+ 40%
- ++ 50% ab 50%
- ++25%: ab 25%: +b 25%: a+ 25%
- ++30% ab 30% +b 20%: a+ 20%
Answer. 4. ++30% ab 30% +b 20%: a+ 20%
Question 50. Neurospora is normally pink, though an albino strain is known. If a pink (+) strain is crossed with an albino (a) strain, what would be the genotype(s) of the resulting zygote?
- ++
- aa
- +a
- +a
Answer. 3. +a
Question 51. Complete linkage is found in
- Male Drosophila
- Female silkworm
- Both (1) and (2)
- Aspergillus flavus
Answer. 3. Both (1) and (2)
Question 52. Number of linkage groups in an individual is equal to
- Number of genes
- n-number of chromosomes
- 2n number of chromosomes
- Number of autosomes
Answer. 2. n-number of chromosomes
Question 53. The bacterial and blue green algal cells contain
- Large number of linkage groups
- Only one linkage group
- Four linkage groups
- No linkage group
Answer. 2. Only one linkage group
Question 54. Find the incorrect match with respect to linkage group.
- Neurospora – 2
- Zea mays – 10
- Pisum sativum-7
- Drosophila-4
Answer. 1. Neurospora – 2
Question 55. Coupling and repulsion phenomena are concerned with
- Mutation
- Pleiotropism
- Linkage
- Crossing-over
Answer. 3. Linkage
Question 56. The exchange of chromosome segments between maternal and paternal chromatids after synapsis in meiosis is called
- Interference
- Crossing-over
- Chiasma
- Terminalization
Answer. 2. Crossing-over
Question 57. Crossing-over occurs in ______ stage.
- Leptotene
- Zygotene
- Pachytene
- Diakinesis
Answer. 3. Pachytene
Question 58. Crossing-over occurring at two-strand stage will show which one of the following types of ascospores arrangement?
- 2:4:2
- 4:4
- 2:2:2:2
- 4:2:2
Answer. 2. 4:4
Question 59. The cross-over frequencies between the genes A and B, A and C, and B and C are 6%, 15%, and 21%, respectively. What is the possible sequence of genes on chromosome?
- A, B, C
- B, A, C
- A, C, B
- Either B, A, C or C, A, B
Answer. 4. Either B, A, C or C, A, B
” monohybrid test cross ratio”
Question 60. In a linear chromosome, map distances between four loci are as follows: a-b-10, b-c-4, a-d-3, a-c-6. The expected cross-over frequency between c and d is
- 3%
- 9%
- Either 3% or 9%
- 4% to 12%
Answer. 3. Either 3% or 9%
Question 61. Mendel did not recognize the linkage phenomenon in his experiments, because
- He did not have powerful microscope
- He studied only pure plants
- There were many chromosomes to handle
- Characters he studied were located on different chromosomes
Answer. 4. Characters he studied were located on different chromosomes
Question 62. Sex-linked characters are generally
- Dominant
- Recessive
- Lethal
- Not inherited
Answer. 2. Recessive
Question 63. Which one of the following defects in man is due to sex- linked inheritance?
- Albinism
- Colorblindness
- Beri-beri
- Polydactyly
Answer. 2. Colorblindness
Question 64. A colorblind boy has 2 sisters-one colorblind and one normal. What can be the possible nature of their parents?
- Colorblind father and colorblind mother
- Normal father and colorblind mother
- Colorblind father and carrier mother
- Colorblind father and normal mother
Answer. 3. Colorblind father and carrier mother
Question 65. A normal woman, whose father had hemophilia, married a normal man. What is the chance of occurrence of hemophilia in their children?
- 25% children will be hemophilic
- 50% children will be hemophilic
- 75% children will be hemophilic
- None hemophilic but 75% will be carriers
Answer. 1. 25% children will be hemophilic
Question 66. A holandric gene is known for hypertrichosis (long hairs on ears). When a man with hairy ears marries a normal woman, what percentage of their daughters would be expected to have hairy ears?
- 100%
- 0%
- 50%
- 25%
Answer. 2. 0%
Question 67. Which one of the following trait is X-Y linked?
- Hypertrichosis
- Porcupine skin
- Cystic fibrosis
- Epidermolysis bullosa
Answer. 4. Epidermolysis bullosa
Question 68. When sex determination occurs after fertilization it is called
- Progamic
- Syngamic
- Epigamic
- Apogamic
Answer. 3. Epigamic
Question 69. XX-XY type sex determination in plants was first discovered in
- Melandrium
- Coccinia
- Sphacrocarpos
- Fragaria elatior
Answer. 3. Sphacrocarpos
Question 70. In birds, the females are
- ZZ
- Zw
- ZO
- YY
Answer. 2. Zw
Question 71. Genic balance theory was given by
- Bridges
- Morgan
- Boveri
- Muller
Answer. 1. Boveri
Question 72. According to the genic balance theory of Bridges, which is correct for AAA+ XXY condition of Drosophila?
- Supermale
- Superfemale
- Intersex
- Normal male but sterile
Answer. 3. Intersex
Question 73. Gynandromorph or sex mosaic is produced by
- Loss of X-chromosome
- Non-disjunction of Y-chromosome
- Disjunction of X-chromosome
- Disjunction of autosomes
Answer. 1. Loss of X-chromosome
Question 74. The concept of sudden genetic change which breeds true in an organism is visualized in the principle of
- Natural selection
- Heredity
- Variations
- Mutation
Answer. 4. Mutation
Question 75. Gene mutation is caused by
- Reproduction
- Linkage
- Change in the sequence of nitrogenous base
- Change in the sequence of genes in DNA
Answer. 3. Change in the sequence of nitrogenous base
Question 76. Which radiations induce the formation of thymine dimers in DNA that interfere with its replication?
- UV radiations
- X rays
- Gamma rays
- Infrared light
Answer. 1. UV radiations
Question 77. Which of the following radiations do not result in any mutational change?
- X rays
- Gamma rays
- Ultraviolet rays
- Infrared rays
Answer. 4. Infrared rays
Question 78. “Mutations can be induced by X rays” was revealed by
- Stanley Miller
- Bridges
- Muller
- Darlington
Answer. 3. Muller
Question 79. Which chemical mutagen results in deamination of bases?
- HNO2
- Base analogs
- Acridine dyes
- PEG
Answer. 1. HNO2
Question 80. “Burkitt lymphoma” in humans is due to
- Deletion
- Translocation
- Transition
- Tautomeric shift
Answer. 2. Translocation
Question 81. Bar eye character in Drosophila is due to
- Deletion
- Multiple alleles
- Duplication
- Inversion
Answer. 3. Duplication
Question 82. Find the incorrect match:
- 44+ XYY-Jacob’s syndrome
- 44+ XO – Turner’s syndrome
- 44+ XXXY — Huntington’s chorea
- 2N + 1 – Down’s syndrome
Answer. 3. 44+ XXXY — Huntington’s chorea
Question 83. Find the correct match:
Column 1 Column 2
a. 2N-1-1 (1) Trisomy
b. 2N + 1 (2) Monosomy
c. 2N + 1 + 1 (3) Nullisomy
d. 2N-2 (4) Double trisomy
(5) Double monosomy
- a (5), b (1), e (4), d (3)
- a (2), b (1), e (4), d (3)
- a (5), b (1), e (4), d (2)
- a (2), b (1), e (4), d (5)
Answer. 1. a (5), b (1), e (4), d (3)
Question 84. Syndrome due to extra 18th autosomal chromosome is known as
- Patau’s syndrome
- Edward’s syndrome
- Cri-du-chat syndrome
- Down’s syndrome
Answer. 2. Edward’s syndrome
Question 85. If gene frequency for PTC non-taster is 0.4, then what will be the number of heterozygote tasters in a population of 3000?
- 1080
- 1440
- 480
- 2520
Answer. 2. 1440
Question 86. In the given pedigree, indicate whether the shaded symbols indicate dominant or recessive allele..
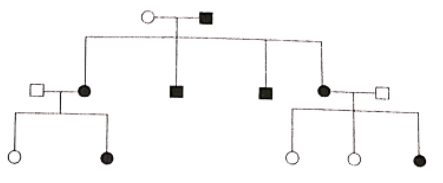
- Dominant
- Recessive
- Co-dominant
- It can be recessive or dominant both
Answer. 4. It can be recessive or dominant both
Question 87. Cystic fibrosis is due to recessive gene mutation of
- Chromosome 4
- Chromosome 7
- Chromosome 11
- X-chromosome
Answer. 2. Chromosome 7
dihybrid cross questions
Question 88. Albinism in man is caused by the absence of one enzyme necessary for the synthesis of melanin. It is
- Tyrosinase
- Lysine
- Melanase
- Luciferase
Answer. 1. Tyrosinase
Question 89. A normal woman whose father was albino marries a man who is albino. What proportion of normal and albino can be expected among the offspring?
- All albino
- 1 normal: 1 albino
- All normal
- 2 normal: 1 albino
Answer. 2. 1 normal: 1 albino
Question 90. Mark the correct statement (with respect to the Mendelian dihybrid cross where the two parents differed in two pairs of contrasting traits: seed color and seed shape).
- 3/4th of F2 plants have green seeds and 1/4th have yellow.
- Mendel cross-hybridized F, plants and got 9:3:3 : 1 phenotypic ratio.
- In F2 generation, round and wrinkled seed shape segregates just like in a monohybrid cross.
- Parental phenotypic ratio is 1:1 in F2 generation.
Answer. 3. In F2 generation, round and wrinkled seed shape segregates just like in a monohybrid cross.
Question 91. ABO blood groups in human beings are controlled by gene I. Gene I has three alleles in which
- 1A, 1B, and i produce a slightly different form of sugar
- 1B and i produce identical sugars
- 1A and 1B produce a slightly different form of sugar
- Only allele i produces sugar
Answer. 3. 1A and 1B produce a slightly different form of sugar
Question 92. Starch grain size in garden pea, flower color in 4’O clock plant, and heterozygous individual for sickle-cell anemia are examples of
- Incomplete dominance
- Non-allelic interaction
- Co-dominance
- Inter-allelic interaction
Answer. 4. Inter-allelic interaction
Question 93. Morgan carried out several dihybrid crosses in fruit fly and found that
- Loosely linked genes show low recombination
- The strength of linkage between genes of white eye and miniature wing is lower than the genes of yellow body and white eye
- Tightly linked genes show equal amount of parental and recombinant types in F2 generation
- All genes segregate independently of each other and the F2 ratio deviates very significantly from the 9:3 :3:1 ratio
Answer. 2. The strength of linkage between genes of white eye and miniature wing is lower than the genes of yellow body and white eye
Question 94. Consider the following four statements (A, B, C, and D) and select the right option for incorrect statements.
A. Mendelian experiments had large sampling size, which gave greater credibility to the data that he collected.
B. Recessive allele influences the appearance of pheno- type even in the presence of an alternative allele.
C. Multiple alleles can be found only when population studies are made.
D. In F2 generation of Mendelian monohybrid cross, the tall and dwarf traits were identical to their parental types and showed blending.
The incorrect statements are
- (A) and (C)
- (C) and (D)
- (B) and (D)
- (B) and (C)
Answer. 3. (B) and (D)
Question 95. Mr. Wilson is suffering from hypertrichosis and phenylketonuria. His father is heterozygous for phenylke- tonuria. The probability of Wilson’s sperm having one recessive autosomal allele and holandric gene is
- 1/8
- 1/16
- 1/4
- 1/2
Answer. 4. 1/2
Question 96. Select the incorrect match with respect to human genetic disorders.
Disorders Chromosome number Dominant/recessive
(1) Cystic fibrosis 7 Recessive
(2) Sickle-cell anemia 15 Recessive
(3) Phenylketonuria 12 Recessive
(4) Huntington’s chorea 4 Dominant
Answer. 2. Sickle-cell anemia 15 Recessive
Question 97. Consider the following statements (A)-(D) each with one or two blanks:
A. _______ are commonly observed in cancer cells.
B. During ________, purine is replaced by another purine.
C. Failure of ___________ after telophase stage of cell division results in an increase in whole set of chromosomes in an organism and this phenomenon is known as __________
D. In Down’s syndrome, the affected individual is short- statured with ______ round head and partially open mouth.
Which one of the following options gives the correct fill ups for the respective blank numbers from (1) to (5) in the statements?
- (3) Karyokinesis, (4) polyploidy, (5) large
- (2) Transversion, (3) cytokinesis, (4) chromosomal aberration
- (1) Chromosomal aberration, (4) polyploidy, (5) small
- (2) Transition, (3) karyokinesis, (5) large
Answer. 3. (1) Chromosomal aberration, (4) polyploidy, (5) small
Question 98. Study the given pedigree chart of a certain family and select the correct conclusion which can be drawn for the character.
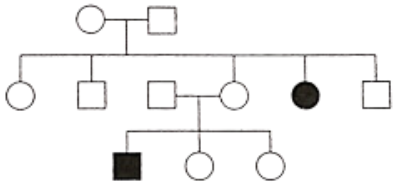
- The trait under study could be hemophilic.
- Only female parent is homozygous recessive.
- Both the parents are homozygous dominant.
- Inheritance of a condition like sickle-cell anemia as an autosomal recessive trait.
Answer. 4. Inheritance of a condition like sickle-cell anemia as an autosomal recessive trait.
” monohybrid cross ratio “
Question 99. The frequency of an autosomal dominant allele is 0.6. Calculate the frequency of recessive phenotype in a population of 10,000.
- 1200
- 4000
- 1600
- 1000
Answer. 1. 1200
Question 100. With increasing age, the linkage
- Becomes strong
- Becomes weak
- Terminates
- Remains unchanged
Answer. 1. Becomes strong
Question 101. If there were only parental combinations in F2 of a dihybrid cross, then Mendel might have discovered
- Independent assortment
- Atavism
- Linkage
- Repulsion
Answer. 3. Linkage
Question 102. Mendelian dihybrid and dihybrid with linkage are, respectively, related with how many chromosomes?
- 1 pair and 2 pair
- 2 pair and 1 pair
- 2 pair and 2 pair
- 1 pair and 1 pair
Answer. 2. 2 pair and 1 pair
Question 103. A dihybrid plant with incomplete linkage on test cross may produce how many types of plants?
- 2
- 4
- 8
- 1
Answer. 2. 4
Question 104. The number of linkage groups in a cell having 10 pairs of chromosomes are
- 5
- 10
- 15
- 20
Answer. 2. 10
Question 105. The two eukaryotic organelles responsible for cytoplasmic inheritance are
- Lysosome and mitochondria
- Chloroplasts and lysosomes
- Mitochondria and chloroplasts
- Mitochondria and Golgi complex
Answer. 3. Mitochondria and chloroplasts
Question 106. Cross-over value (COV) of genes A and B is 5% while COV of genes B and C is 15%. The possible sequence of three genes on chromosome is
- A-B-C
- C-A-B
- B-C-A
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer. 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 107. Which of the following conditions represent a case of co-dominant genes?
- A gene expresses itself, suppressing the phenotypic effect of its alleles.
- Genes those are similar in phenotypic effect when present separately, but when together interact to produce a different trait.
- Alleles, both of which interact to product a trait, which may resemble either of the parental type.
- Alleles, each of which produces an independent effect in heterozygous condition.
Answer. 4. Alleles, each of which produces an independent effect in heterozygous condition.
Question 108. A sinistral shelled female snail has Dd genotype cross with dextral shelled male having dd genotype. What type of shell will be present in the progeny?
- All dextral
- All sinistral
- 50% dextral, 50% sinistral
- None
Answer. 2. All sinistral
Question 109. In female Drosophila, the linked gene exhibits recombination during the meiosis of gamete formation, but such a recombination does not occur during the formation of sperm in male Drosophila because
- Male Drosophila is sterile
- Male Drosophila is parthenogenetic male
- No crossing-over occurs in male Drosophila
- Male Drosophila is haploid
Answer. 3. No crossing-over occurs in male Drosophila
Question 110. The condition in which only one allele of a pair is present is known as
- Homozygous
- Heterozygous
- Hemizygous
- Incomplete dominance
Answer. 3. Hemizygous
Question 111. A colorblind man marries a daughter of a colorblind father. Then in the offspring,
- All sons are colorblind
- All daughters are colorblind
- Half sons are colorblind
- No daughter is colorblind
Answer. 3. Half sons are colorblind
Question 112. A woman with normal vision marries a man with normal vision and gives birth to a colorblind son. Her husband dies and she marries a colorblind man. What is the probability of her children having the abnormality
- 50% colorblind sons + 50% colorblind daughters
- All sons colorblind and daughters carrier
- All daughters colorblind and sons normal
- 50% sons colorblind and all daughters normal
Answer. 1. 50% colorblind sons + 50% colorblind daughters
Question 113. Albinism is determined by a recessive gene in man. The presence of albinism in 50% children born to a couple proves that
- Both parents are heterozygous for albinism
- Father is homozygous normal and mother is heterozygous
- Father is homozygous for albinism but mother is heterozygous
- Both are homozygous
Answer. 3. Father is homozygous for albinism but mother is heterozygous
Question 114. A gene that shows its effect on more than one character is
- Polygene
- Pleotropic gene
- Multifactor gene
- Multiple gene
Answer. 2. Pleotropic gene
Question 115. In Drosophila, crossing-over occurs in females but not in males. Genes A and B are 10 map unit apart on chro- mosome. A female Drosophila has genotype AB/ab and a male Drosophila has genotype AB/ab. How many types of gametes are produced by female and male Drosophila, respectively?
- 4 types: 2 types
- 2 types: 2 types
- 4 types: 4 types
- 4 types: 1 type
Answer. 1. 4 types: 2 types
Question 116. In polygenic inheritance trait, which is controlled by three pairs of genes, two individuals that are heterozygous for three alleles crossed each other. Such type of cross produced phenotypic ratio
- 1:2:1
- 9:3:3:1
- 1:4:6:4:1
- 16:15 20:15:6:1
Answer. 4. 16:15 20:15:6:1
Question 117. In a cross between individuals homozygous for (a, b) and wild type (++), 700 out of 1000 individuals were of parental type. Then the distance between a and b is
- 70 map units
- 35 map units
- 30 map units
- 15 map units
Answer. 3. 30 map units
Question 118. Which of the following show linkage group in coupling phase?
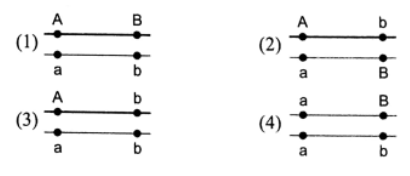
Answer. 1.

Question 119. In Drosophila, several alleles exhibit the same phenotype, e.g., W+s, W+c, W+g exhibit eye color. These alleles are called
- Pseudoalleles
- Isoalleles
- Multiple alleles
- All of the above
Answer. 2. Isoalleles
Question 120. Which statement is incorrect about linkage?
- It helps in maintaining the valuable traits of new varieties.
- It helps in forming new recombinants.
- Knowledge of linkage helps the breeder to combine all desirable traits in a single variety.
- It helps in locating genes on chromosome.
Answer. 2. It helps in maintaining the valuable traits of new varieties.
Question 121. The first mutant reported by Morgan on Drosophila was
- Red eyed male
- Red eyed female
- White eyed male
- White eyed female
Answer. 3. White eyed male
Question 122. Non-ionizing radiations commonly used for inducing mutations in organisms are
- UV rays
- Beta rays
- X rays
- Gamma rays
Answer. 1. UV rays
principles of inheritance and variation class 12
Question 123. The smallest unit of genetic material which upon mutation produces a phenotypic effect is
- Sexual reproduction
- Meiosis
- Mutation
- Independent assortment
Answer. 3. Mutation
Question 124. Chemical mutagens are far more hazardous than radiations because
- Exposure to chemicals is more prevalent
- Organisms possess protection from radiation but no protection from chemicals
- Chemically induced mutations are more deleterious
- Chemicals are synthetic
Answer. 2. Organisms possess protection from radiation but no protection from chemicals
Question 125. Mutagens that are effective on DNA replication only are
- Base analogs and acridines
- Alkylating agents
- HNO2
- α and B rays
Answer. 1. Base analogs and acridines
Question 126. Haploids are preferred over diploids for mutation studies because
- Recessive mutation is expressed in F1
- Recessive mutation is expressed in F2
- Dominant phenotype is expressed
- Dominant phenotype is suppressed
Answer. 1. Recessive mutation is expressed in F1
Question 127. The type of gene mutation that involves the replacement of purine with pyrimidine or vice versa (Or) The substitution of one type of base with another type of base is
- Transduction
- Transversion
- Translocation
- Transcription
Answer. 2. Transversion
Question 128. Mutations induced by 5-bromo uracil are
- Transversional mutations
- Transitional mutations
- Frame shift mutations
- Backward mutations
Answer. 2. Transitional mutations
Question 129. Deamination of adenine and guanine by HNO, and UV rays produces
- Cytosine and uracil
- Xanthine and hypoxanthine
- Hypoxanthine and xanthine
- Xanthine and uracil
Answer. 3. Hypoxanthine and xanthine
Question 130. In a random mating population in equilibrium, which of the following brings about a change in gene frequency in a non-directional manner?
- Mutation
- Random drift
- Selection
- Migration
Answer. 2. Random drift
Question 131. Given below is the representation of a kind of chromosomal mutation:
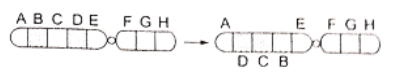
Identify the kind of mutation.
- Deletion
- Duplication
- Inversion
- Reciprocal translocation
Answer. 3. Inversion
Question 132. The “cri-du-chat” syndrome is caused by change in chromosome structure involving
- Deletion
- Duplication
- Inversion
- Translocation
Answer. 1. Deletion
Question 133. Chromosome with genes abcdefg becoming abedcfg is
- Duplication
- Deletion
- Translocation
- Inversion
Answer. 4. Inversion
Question 134. Which one of the following scientists’ names is correctly matched with the theory put forth by him?
- de Vries Natural selection
- Mendel – Theory of pangenesis
- Weismann Theory of continuity of germplasm
- Pasteur – Inheritance of acquired characters
Answer. 3. Weismann Theory of continuity of germplasm
Question 135. Which of the following is an example of substantive dis- continuous variation?
- Hairless cat
- Short legged ancon sheep
- Polydactyly in humans
- More than one option is correct.
Answer. 4. More than one option is correct.
Question 136. Find the incorrect match.
- Moist vapor theory proposed by-Pythagoras
- Theory of epigenesis-Homunculus
- Theory of pangenesis-Gemmules
- Theory of germplasm proposed by-Weismann
Answer. 2. Theory of epigenesis-Homunculus
Question 137. Which of the following genotype represents heterozygous condition?
- TT
- tt
- Tt
- RR
Answer. 3. Tt
Question 138. In garden pea plant, S. Blixt led to locate Mendel’s seven characters on chromosomes numbers
- 1, 4, 5, 7
- 1,4, 5, 6
- 4, 5, 6, 7
- 2, 3, 4, 7
Answer. 1. 1, 4, 5, 7
Question 139. Mendel selected Pisum sativum for hybridization experiments because of
- Clear contrasting characters and short life span
- Long life span and non-fertile hybrids
- Presence of unisexual flowers
- Infertile hybrids and production of large number of seeds by each plant
Answer. 1. Clear contrasting characters and short life span
Question 140. Mark the odd one (with respect to dominant trait in garden pea).
- Yellow pod
- Inflated pod
- Axial flower
- Yellow seed
Answer. 1. Yellow pod
Question 141. The transmission of genetic characters from parents to offsprings is
- Variation
- Heredity
- Blending
- Somatoplasm
Answer. 2. Heredity
Question 142. Who coined the term “allele”?
- Saunders
- Bateson
- Johannsen
- Mendel
Answer. 2. Bateson
Question 143. Which of the following trait of garden pea is present on the seventh chromosome?
- Pod shape
- Pod color
- Seed shape
- Stem height
Answer. 3. Seed shape
Question 144. Who amongst the following raised the status of Mendel’s generalizations to laws?
- Correns
- de Vries
- Tschermak
- Goss
Answer. 1. Correns
Question 145. The phenotype of F, hybrid resembles either of the two parents in
- Dominance
- Incomplete dominance
- Co-dominance
- Intermediate inheritance
Answer. 1. Dominance
Question 146. Mendel proposed the law of dominance and the law of segregation based on his observations on
- Monohybrid crosses
- Dihybrid crosses
- Test crosses
- Outcrosses
Answer. 1. Monohybrid crosses
Question 147. Which of the following phenotypic ratio was found by Mendel in the F2 generation of a dihybrid cross?
- 3:1
- 1:2:1:2:4:2:1:2:1
- 9:3:3:1
- 12:4
Answer. 3. 9:3:3:1
Question 148. Both phenotypic and genotypic ratios of F2 are the same in
- Co-dominance
- Incomplete dominance
- Outcross
- More than one option is correct
Answer. 4. More than one option is correct
Question 149. The ability of a gene to have multiple phenotypic effects is known as
- Pleiotropy
- Co-dominance
- Incomplete dominance
- Complete dominance
Answer. 1. Pleiotropy
Question 150. How many types of gametes can be produced by a dip- loid organism, if it is heterozygous for three loci?
- 6
- 4
- 9
- 3
Answer. 3. 8
Question 151. What will be the genotypic ratio in the F2 generation of a monohybrid outcross?
- 9:3:3:1
- 1:2:1
- 1:1
- 3:1
Answer. 3. 1:1
Question 152. A cross between F, hybrid and its homozygous recessive parent is called
- Outcross
- Test cross
- Monohybrid cross
- Dihybrid cross
Answer. 2. Test cross
Question 153. Select the correct option with respect to the law of independent assortment:
- It can be explained by using monohybrid cross.
- The inheritance of one character is dependent on another character.
- This law is not applicable universally.
- It was proposed by Bateson.
Answer. 3. This law is not applicable universally.
Question 154. Find the incorrect match:
- Gamete-Pure for a trait
- Co-dominance-Flower color in snapdragon
- Lethal gene-Body color in mice
- Incomplete dominance-Carl Correns
Answer. 2. Co-dominance-Flower color in snapdragon
Question 155. Select the odd one out with respect to non-allelic gene interactions:
- Epistasis
- Duplicate genes
- Incomplete dominance
- Complementary genes
Answer. 3. Incomplete dominance
Question 156. Fruit color in Cucurbita pepo is an example of
- Complementary genes
- Duplicate genes
- Dominant epistasis
- Polymeric genes demonstrated by Bateson
Answer. 3. Dominant epistasis
Question 157. Complementary genes were demonstrated by Bateson and Punnet in
- Capsella
- Lathyrus odoratus
- Antirrhinum
- Mirabilis
Answer. 2. Lathyrus odoratus
Question 158. If dominant alleles of two gene loci produce the same phenotype, whether both genes inherited separately or together, this inheritance will be
- Recessive epistasis
- Dominant epistasis
- Duplicate genes interaction
- Inhibitory genes interaction
Answer. 3. Duplicate genes interaction
Question 159. A gene which hides the action of another gene is termed as
- Co-dominant gene
- Epistatic gene
- Hypostatic gene
- Lethal gene
Answer. 2. Epistatic gene
Question 160. In polymeric gene action, the modified dihybrid phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation is
- 9:3:3:1
- 13:3
- 9:6:1
- 12:3:4
Answer. 3. 9:6:1
Question 161. Which of the following genotype of sweet pea plant is related with the production of purple colored flowers?
- CcPp
- CCpp
- ccPP
- Ccpp
Answer. 1. CcPp
Question 162. Select the odd one out with respect to polygenic inheritance:
- Bell-shaped curve is obtained.
- Also called quantitative inheritance.
- Recessive alleles show cumulative effect.
- Intermediate phenotypes are more frequent.
Answer. 3. Recessive alleles show cumulative effect.
Question 163. Select the correct match (with respect to dihybrid phenotypic ratio in F2 generation):
- Recessive epistasis – 12:3:1
- Dominant epistasis-9: 3:4
- Collaborative gene-9:3:3:1
- Duplicate genes – 9:7
Answer. 3. Collaborative gene-9:3:3:1
Question 164. Skin color in man is controlled by
- Three pairs of polygenes
- Duplicate genes
- Six pairs of polygenes
- Supplementary genes
Answer. 1. Three pairs of polygenes
Question 165. Select the odd one out with respect to the chromosomal theory of inheritance.
- It was proposed by Sutton and Boveri.
- The behavior of chromosomes is parallel to the behavior of genes.
- Chromosomes and genes occur in pairs in diploid and haploid cells, respectively.
- The paired condition of both, chromosomes as well as Mendelian factors, is restored during fertilization.
Answer. 3. Chromosomes and genes occur in pairs in diploid and haploid cells, respectively.
Question 166. The term gene for Mendelian factor was coined by
- Sutton and Boveri
- Morgan
- Bateson
- Johannsen
Answer. 4. Johannsen
Question 167. Morgan used Drosophila as experimental material because
- It cannot be reared and bred under lab conditions
- A single mating produces very few offsprings
- It has large number of morphologically similar chromosomes
- It has a short life span
Answer. 4. It has a short life span
Question 168. Who carried out several dihybrid crosses in Drosophila to study genes that were sex-linked?
- Morgan
- Sutton
- Bateson
- Punnet
Answer. 1. Morgan
Question 169. Coupling and repulsion hypothesis in sweet pea plant was explained by
- Mendel
- Bateson and Punnet
- T.H. Morgan
- Sutton and Boveri
Answer. 2. Bateson and Punnet
Question 170. Find the odd one out with respect to complete linkage:
- 100% parental combinations in F2 generation.
- F2 phenotypic ratio is 3: 1 in dihybrid cross.
- Dihybrid test cross ratio is 1 : 1 in F2 generation.
- Linked genes tend to separate frequently.
Answer. 4. Linked genes tend to separate frequently.
Question 171. The condition where an individual heterozygous for two pairs of linked genes (AaBb) possesses two dominant genes on one homologous chromosome pair and two recessive on the other is said to be
- Cis-arrangement
- Trans-arrangement
- Partly cis partly trans
- More than one option is correct
Answer. 1. Cis-arrangement
Question 172. How many linkage groups are present in human male?
- 24
- 23
- 46
- 22
Answer. 1. 24
Question 173. Linkage ratio of 7:1:1:7 in case of dihybrid test cross means that there are
- 2 parental and 14 recombinant plants
- 14 parental and 2 recombinant plants
- 9 parental and 7 recombinant plants
- 8 parental and 8 recombinant plants
Answer. 2. 14 parental and 2 recombinant plants
Question 174. Find the incorrect statement with respect to chromosomal mapping:
- Crossing-over is important in locating genes on chromosome.
- Recombination frequency depends on the distance between the genes.
- Recombination frequency is inversely proportional to the distance between the genes.
- The sequences and the relative distances between various genes are graphically represented in terms of recombination frequencies.
Answer. 3. Recombination frequency is inversely proportional to the distance between the genes.
Question 175. Individuals having homomorphic sex chromosomes produce
- One type of gametes
- Two types of gametes
- No gametes
- Only one gamete in complete life span
Answer. 1. One type of gametes
Question 176. Holandric genes are present on
- X-chromosomes
- Y-chromosomes
- Sex chromosomes as well as autosomes
- Autosomes
Answer. 2. Y-chromosomes
Question 177. Mark the incorrect pair (with respect to sex determination):
- ZW-ZZ type-Fishes
- ZO-ZZ type-Birds
- XX-XO type-Dioscorea
- XX-XY type-Melandrium
Answer. 2. ZO-ZZ type-Birds
Question 178. Which of the following statement about a Barr body is incorrect?
- Observed by Barr and Bertram.
- Can be seen in neutrophils of females as drumstick.
- The number of Barr bodies is one less than the number of autosomes.
- Normal male has no Barr body.
Answer. 3. The number of Barr bodies is one less than the number of autosomes.
Question 179. In the XX-XO type of sex determination,
- Females produce only one type of eggs
- Females have only one X-chromosome
- Males have two X-chromosomes
- Males are homogametic
Answer. 1. Females produce only one type of eggs
Question 180. Select the odd one out with respect to the genic balance theory of sex determination in Drosophila:
- Y-chromosome plays no role in sex-determination.
- Given by C.B. Bridges.
- If X/A ratio is 1, super-females are produced.
- If N/A ratio is less than 0.5, super-males are produced.
Answer. 3. If X/A ratio is 1, super-females are produced.
Question 181. Environmental mechanism of sex determination is seen in
- Bonnelia
- Crepidula
- Grasshopper
- More than one option is correct
Answer. 4. More than one option is correct
Question 182. Select the odd one out with respect to hemophilia:
- X-linked dominant disorder
- Bleeder’s disease
- Criss-cross inheritance
- X-linked recessive disorder
Answer. 4. X-linked recessive disorder
Question 183. Select the correct match:
- Sex-limited trait-Colorblindness
- Sex-limited trait-Expressed in both sexes
- Sex-influenced trait-More frequent in one sex than in the other
- Sex-influenced trait-Porcupine skin
Answer. 3. Sex-influenced trait-More frequent in one sex than in the other
Question 184. If a normal man marries a girl who is a carrier of hemophilia, then
- All sons will be hemophilic
- All daughters will be hemophilic
- 75% of offsprings will be hemophilic
- 50% of sons will be hemophilic
Answer. 4. 50% of sons will be hemophilic
Question 185. Mark the odd one (with respect to genomatic mutation):
- Hypoploidy
- Tetrasomy
- Duplication
- Allopolyploidy
Answer. 3. Duplication
Question 186. Find the incorrect match:
- Somatic mutation – No evolutionary importance
- Germinal mutation – Gametic mutation
- Frame shift mutation – Gibberish mutation
- Chromosomal mutation – Transversion
Answer. 4. Chromosomal mutation – Transversion
Question 187. The substitution of a purine with another type of purine is called
- Transversion
- Transition
- Inversion
- Translocation
Answer. 2. Transition
Question 188. Inversion without involving the centromere is called
- Paracentric
- Monosomy
- Pericentric
- Tautomerization
Answer. 1. Paracentric
Question 189. Aneuploidy which results in the loss of a complete homologous pair of chromosomes is
- Trisomy
- Tetrasomy
- Nullisomy
- Euploidy
Answer. 3. Nullisomy
Question 190. Which of the following chemical is a base analog?
- 5-Bromouracil
- Acridines
- Nitrous acid
- Hypoxanthine
Answer. 1. 5-Bromouracil
Question 191. Cytoplasmic male sterility in maize is due to defective
- Mitochondria
- Lysosome
- Golgi body
- Leucoplast
Answer. 1. Mitochondria
Question 192. Select the incorrect statement with respect to pedigree analysis:
- Solid symbol shows the unaffected individual.
- It is useful for genetic counselors.
- Proband is the person from which case history starts.
- It is an analysis of traits in several generations of a family.
Answer. 1. Solid symbol shows the unaffected individual.
Question 193. Which of the following abnormalities is due to X-linked recessive mutation?
- Cystic fibrosis
- Thalassaemia
- Klinefelter’s syndrome
- Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
Answer. 4. Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
Question 194. If the frequency of recessive allele is 0.3, then find out the frequency of heterozygous individuals in population?
- 42%
- 21%
- 10%
- 49%
Answer. 1. 42%
Question 195. According to Mendelism, which character is showing dominance?
- Terminal position of flower
- Green color in seed coat
- Wrinkled seeds
- Green pod color
Answer. 4. Green pod color
Question 196. Irregularity is found in Drosophila during the organ differentiation, e.g., in place of wing, long legs are formed. The gene responsible for this is
- Double dominant gene
- Homeotic gene
- Complimentary gene
- Plastid
Answer. 2. Homeotic gene
Question 197. Mendel obtained wrinkled seeds in pea due to the deposition of sugars instead of starch. It was due to which enzyme?
- Amylase
- Invertase
- Diastase
- Absence of starch branching enzyme
Answer. 4. Absence of starch branching enzyme
Question 198. A gene is said to be dominant if
- It expresses its effect only in homozygous stage
- It expresses its effect only in heterozygous condition
- It expresses its effect both in homozygous and heterozygous conditions
- It never expresses in any condition
Answer. 3. It expresses its effect both in homozygous and heterozygous conditions
Question 199. A plant of F, generation has genotype AABbCC. On selfing of this plant, what is the phenotypic ratio in F2 generation?
- 3:1
- 1:1
- 9:3:3:1
- 27:9:9:9:3:3:3:1
Answer. 1. 3:1
Question 200. In a plant, red fruit (R) is dominant over yellow fruit (r) and tallness (T) is dominant over shortness (t). If a plant with genotype RRTt is crossed with a plant with genotype rrtt, then
- All the offsprings will be tall with red fruit
- 25% will be tall with red fruit
- 50% will be tall with red fruit
- 75% will be tall with red fruit
Answer. 3. 50% will be tall with red fruit
Question 201. How many different types of gametes can be formed by F progeny resulting from the following cross: AA BB CC x aa bb cc?
- 3
- 8
- 27
- 64
Answer. 2. 8
Question 202. In order to find out the different types of gametes produced by a pea plant having genotype AaBb, it should be crossed with a plant with genotype
- AaBb
- aabb
- ААВВ
- aaBB
Answer. 2. aabb
Question 203. When a certain character is inherited only through the female parent, it probably represents the case of
- Mendelian nuclear inheritance
- Multiple plastid inheritance
- Cytoplasmic inheritance
- Incomplete dominance
Answer. 3. Cytoplasmic inheritance
Question 204. Which law would have been violated if Mendel had chosen eight characters in garden pea?
- Law of dominance
- Law of segregation
- Principle of independent assortment
- Law of purity of gametes
Answer. 3. Principle of independent assortment
Question 205. If Mendel would have studied 7 pairs of characters in a plant with 12 chromosomes instead of 14, then
- He might have not discovered independent assortment
- He might have not discovered linkage
- He might have discovered crossing-over
- He might have not observed dominance
Answer. 1. He might have not discovered independent assortment
Question 206. Plant that does not obey Mendel’s laws is
- Mirabilis jalapa
- Pisum sativum
- Cicer aeritinum
- Lberis amara
Answer. 1. Mirabilis jalapa
Question 207. In case of incomplete dominance, F2 generation has
- Genotypic ratio equal to phenotypic ratio
- Genotypic ratio 3:1
- Phenotypic ratio 3:1
- None
Answer. 1. Genotypic ratio equal to phenotypic ratio
Question 208. Genes controlling seven traits in pea studied by Mendel were actually located on
- Seven chromosomes
- Six chromosomes
- Four chromosomes
- Five chromosomes
Answer. 3. Four chromosomes
Question 209. When dominant and recessive alleles express themselves together, it is called
- Co-dominance
- Dominance
- Amphidominance
- Pseudo dominance
Answer. 1. Co-Dominance
Question 210. The nucleus of a donor embryonal cell/somatic cell is transferred to an enucleated egg cell. Then after the for- mation of organism, what shall be true?
- Organism will have extra-nuclear genes of the donor cell.
- Organism will have extra-nuclear genes of the recipient cell.
- Organism will have extra-nuclear genes of both donor and recipient cells.
- Organism will have nuclear genes of recipient cell.
Answer. 2. Organism will have extra-nuclear genes of the recipient cell.
Question 211. Genes for cytoplasmic male sterility in plants are generally located in
- Chloroplast genome
- Mitochondrial genome
- Nuclear genome
- Cytosol
Answer. 2. Mitochondrial genome
Question 212. Two crosses between the same pair of genotypes or phenotypes in which the source of the gametes is reversed in one cross is known as
- Test cross
- Reciprocal cross
- Dihybrid cross
- Reverse cross
Answer. 2. Reciprocal cross
Question 213. The genes controlling the seven pea characters studied by Mendel are known to be located on how many different chromosomes?
- Seven
- Six
- Five
- Four
Answer. 4. Four
Question 214. Extra-nuclear inheritance is a consequence of the presence of genes in
- Lysosomes and ribosomes
- Mitochondria and chloroplast
- Endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria
- Ribosomes and chloroplast
Answer. 2. Mitochondria and chloroplast
Question 215. Genes for cytoplasmic male sterility in plants are generally located in
- Nuclear genome
- Chloroplast genome
- Cytosol
- Mitochondrial genome
Answer. 4. Mitochondrial genome
Question 216. Sickle-cell anemia is
- Characterized by elongated sickle-like RBCs with a nucleus
- An autosomal linked dominant trait
- Caused by substitution of valine by glutamic acid in the beta globin chain of hemoglobin
- Caused by a change in a single base pair of DNA
Answer. 4. Caused by a change in a single base pair of DNA
Question 217. Study the pedigree chart given.
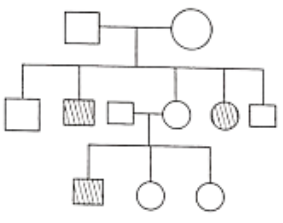
What does it show?
- Inheritance of a recessive sex-linked disease like hemophilia.
- Inheritance of a sex-linked inborn error of metabo- lism like phenylketonuria.
- Inheritance of a condition like phenylketonuria as an autosomal recessive trait.
- The pedigree chart is wrong as this is not possible.
Answer. 3. Inheritance of a condition like phenylketonuria as an autosomal recessive trait.
Question 218. The most popularly known blood grouping is the ABO grouping. It is named ABO and not ABC, because “O” in it refers to having
- No antigens A and B on RBCs
- Other antigens besides A and B on RBCs
- Over-dominance of this type on the genes for A and B types
- One antibody only-either anti-A or anti-B-on the RBCs
Answer. 1. No antigens A and B on RBCs
Question 219. Select the incorrect statement from the following:
- Baldness is a sex-limited trait.
- Linkage is an exception to the principle of independent assortment in heredity.
- Galactosemia is an inborn error of metabolism.
- Small population size results in random genetic drift in a population.
Answer. 1. Baldness is a sex-limited trait.
Question 220. If selfing occurs in the plant having genotype RrYy, then the ratio of genotypes RRYY, RrYY, RRYY, RrYy will be
- 1:2:2:4
- 1:2:2:1
- 1:1:1:1
- 2:2:2:1
Answer. 1. 1:2:2:4
Question 221. What ratio is expected in offsprings if father is colorblind and mother’s father was colorblind?
- 50% daughters are colorblind.
- All sons are colorblind.
- All daughters colorblind.
- All sons are normal.
Answer. 1. 50% daughters are colorblind.
Question 222. Independent assortment of genes does not take place when
- Genes are located on homologous chromosomes
- Genes are linked and located on the same chromosome
- Genes are located on non-homologous chromosomes
- All the above
Answer. 2. Genes are linked and located on the same chromosome
Question 223. What is true for monoclonal antibodies?
- These antibodies are obtained from one parent and for one antigen.
- These are obtained from different parents and for one antigen.
- These are obtained from one parent and for many antigens.
- These are obtained from many parents and for many antigens.
Answer. 2. These are obtained from different parents and for one antigen.
Question 224. Ratio of complementary genes is
- 9:3:4
- 12:3:1
- 9:3:3:4
- 9:7
Answer. 4. 9:7
Question 225. Genes A and B are linked. What shall be the genotype of progeny in a cross bet: AB/ab and ab/ab?
- AAbb and aabb
- AaBb and aabb
- AABB and aabb
- None
Answer. 2. AaBb and aabb
Question 226. Two non-allelic genes produce new phenotype when present together but fail to do so independently. Then it is called
- Epistasis
- Polygene
- Non-complimentary gene
- Complimentary gene
Answer. 4. Complimentary gene
Question 227. Male XX and female XY sometimes occur due to
- Deletion
- Transfer of segments in X and Y chromosomes
- Aneuploidy
- Hormonal imbalance.
Answer. 2. Transfer of segments in X and Y chromosomes
Question 228. Which of the following is the example of pleiotropic gene?
- Hemophilia
- Thalassemia
- Sickle-cell anemia
- Colorblindness
Answer. 3. Sickle-cell anemia
Question 229. Pattern baldness, moustaches, and beard in human males are examples of
- Sex-linked traits
- Sex-limited traits
- Sex-differentiating traits
- Sex-determining traits
Answer. 2. Sex-limited traits
Question 230. When a cluster of genes show linkage behavior they
- Do not show a chromosome map
- Show recombination during meiosis
- Do not show independent assortment
- Induce cell division
Answer. 3. Do not show independent assortment
Question 231. Genetic map is one that
- Establishes sites of genes on a chromosome
- Establishes various stages in gene evolution
- Shows the stage during cell division
- Shows the distribution of various species in a region
Answer. 1. Establishes sites of genes on a chromosome
Question 232. One of the genes present exclusively on the X-chromo- some in humans is concerned with
- Baldness
- Red green colorblindness
- Facial hair/moustaches in males
- Night blindness
Answer. 2. Red green colorblindness
Question 233. The recessive genes located on the X-chromosome in humans are always
- Expressed in females
- Lethal
- Sub-lethal
- Expressed in males
Answer. 4. Expressed in males
Question 234. Lack of independent assortment of two genes A and B in fruit fly Drosophila is due to
- Crossing-over
- Repulsion
- Recombination
- Linkage
Answer. 4. Linkage
Question 235. A normal woman whose father was colorblind is married to a normal man. The sons would be
- All colorblind
- 75% colorblind
- 50% colorblind
- All normal
Answer. 3. 50% colorblind
Question 236. If father shows normal genotype and mother shows a carrier trait for hemophilia,
- All female children will be carrier
- A male child has 50% chances of active disease
- A female child has 50% chances of active disease
- All female children will be colorblind
Answer. 2. A male child has 50% chances of active disease
Question 237. Which of the following is not a hereditary disease?
- Hemophilia
- Cretinism
- Cystic fibrosis
- Thalassemia
Answer. 2. Cretinism
Question 238. A woman with normal vision, but whose father was colorblind, marries a colorblind man. Suppose that the fourth child of this couple was a boy. This boy
- Must have normal color vision
- May be colorblind or may have normal vision
- Will be partially colorblind since he is heterozygous for the colorblind mutant allele
- Must be colorblind
Answer. 2. May be colorblind or may have normal vision
Question 239. Hemophilia is more commonly seen in human males than in human females because
- This disease is due to a Y-linked recessive mutation
- This disease is due to an X-linked recessive mutation
- This disease is due to an X-linked dominant mutation
- A greater proportion of girls die in infancy
Answer. 2. This disease is due to an X-linked recessive mutation
Question 240. A man and a woman, who do not show any apparent signs of a certain inherited disease, have seven children (2 daughters and 5 sons). Three of the sons suffer from the given disease but none of the daughters are affected. Which of the following mode of inheritance do you sug- gest for this disease?
- Sex-limited recessive
- Autosomal dominant
- Sex-linked recessive
- Sex-linked dominant
Answer. 3. Sex-linked recessive
Question 241. Grain color in wheat is determined by three pairs of polygenes. Following cross AABBCC (dark color) * aabbcc (light color), in F2 generation, what proportion of the progeny is likely to resemble either parent?
- None
- Less than 5%
- One-third
- Half
Answer. 2. Less than 5%
Question 242. The genotype of a plant showing dominant phenotype can be determined by
- Test cross
- Dihybrid cross
- Pedigree analysis
- Back cross
Answer. 1. Test cross
Question 243. ABO blood groups in humans are controlled by gene I. It has three alleles-IA, IB, and i. Since there are three different alleles, six different genotypes are possible. How many phenotypes can occur?
- Three
- One
- Four
- Two
Answer. 3. Four
Question 244. Select the correct statement from the ones given with respect to dihybrid cross?
- Tightly linked genes on the same chromosome show higher recombinations.
- Genes far apart on the same chromosome show very few recombinations.
- Genes loosely linked on the same chromosome show similar recombinations as the tightly linked ones.
- Tightly linked genes on the same chromosome show very few recombinations.
Answer. 4. Tightly linked genes on the same chromosome show very few recombinations.
Question 245. Hexaploid wheat developed through
- Hybridomas
- Chromosome doubling
- Hybridization
- Hybridization and chromosome doubling
Answer. 4. Hybridization and chromosome doubling
Question 246. Breeding is possible between two members of
- Genus
- Family
- Order
- Species
Answer. 4. Species
Question 247. In which one of the following combinations, (1)-(4), of the number of chromosomes is the present day hexaploid wheat correctly represented?
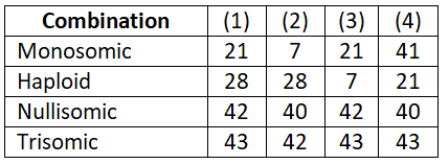
Answer. 4. Trisomic 41 21 40 43
Question 248. In a mutational event, when adenine is replaced by guanine, it is a case of
- Frameshift mutation
- Transcription
- Transition
- Transversion
Answer. 4. Transversion
Question 249. A normal-visioned man whose father was colorblind marries a woman whose father was also colorblind. They have their first child as a daughter. What are the chances that this child would be colorblind?
- Zero percent
- 25%
- 50%
- 100%
Answer. 1. Zero percent
Question 250. F2 generation in a Mendelian cross showed that both genotypic and phenotypic ratios are same as 1:21. It represents a case of
- Dihybrid cross
- Monohybrid cross with complete dominance
- Monohybrid cross with incomplete dominance
- Co-dominance
Answer. 3. Monohybrid cross with incomplete dominance 4. Co-dominance
Question 251. A certain road accident patient with unknown blood group needs immediate blood transfusion. His one doctor friend at once offers his blood. What was the blood group of the donor?
- Blood group AB
- Blood group O
- Blood group A
- Blood group B
Answer. 2. Blood group O
