NEET Biology For Respiration In Plants Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 1. RQ of fats and proteins is generally
- 1
- Less than 1
- Greater than 1
- Zero
Answer: 2. Less than 1
Question 2. The value of RQ, when the respiratory substance is poor in oxygen, is
- Zero
- Infinity
- Greater than 1
- Less than 1
Answer: 4. Less than 1
Question 3. The term protoplasmic respiration is used for the respiration of
- Fats
- Proteins
- Carbohydrates
- Organic acids
Answer: 3. Carbohydrates
Question 4. Common pathways of aerobic and anaerobic respiration is
- PPP
- Glycolysis
- TCA cycle
- ETS
Answer: 2. Glycolysis
Question 5. Anaerobic respiration in the presence of microorganisms is known as
- Pasteurization
- Decay
- Fermentation
- Putrefaction
Answer: 3. Fermentation
Question 6. The term anaerobic respiration was coined by
- Kostylchev
- Henry Beevers
- Dickens
- Cmickshank
Answer: 1. Kostylchev
respiration in plants
Question 7. In anaerobic glycolysis, a net gain of ATP is
- 2 ATP
- 6 ATP
- 8 ATP
- 1 ATP
Answer: 1. 2 ATP
Question 8. Which is not a product of fermentation?
- CO2
- H2O
- ATP
- Alcohol
Answer: 2. H2O
Question 9. The site of EMP in eukaryotes is
- Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Mitochondrial matrix
- Both 2 and 3
Answer: 2. Cytoplasm
Question 10. The pacemaker enzyme of glycolysis is
- Hexokiimse
- Hnolnsc
- Phosphofructokinase
- Pyruvate kinase
Answer: 3. Phosphofructokinase
Question 11. The number of NADH molecules produced in EMP is
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer: 2. 2
Question 12. BTS in Baeleria Lakes place at
- Cell wall
- Plasma membrane
- Nucleus
- Cytoplasm
Answer: 2. Plasma membrane
Question 13. The path of glucose breakdown to pyruvic acid was discovered by
- Embden, Meyerhof, and Parnas
- Warburg and Dickon
- Sir Hans Kreb
- Calvin
Answer: 1. Embden, Meyerhof, and Parnas
Question 14. ATPs generated by 1 NADH2 and 1 FADH2 are, respectively,
- 3,2
- 2,3
- 3. 5
- 5, 3
Answer: 1. 3,2
Question 15. The connecting link between glycolysis and the TCA cycle is
- Acetyl CoA
- OAK
- Pyruvic acid
- Citric acid
Answer: 1. Acetyl CoA
Question 16. The primary acceptor of the TCA cycle is
- OAA
- Acetyl CoA
- Citric acid
- Pyruvic acid
Answer: 1. OAA
Question 17. In the TCA cycle, how many reduced co-enzymes are produced from one acetyl CoA?
- 3 NADH2, 1 FADH2
- 2 NADH2, 1 FADH2
- 4 NADH2, 2 FADH2
- 5 NADH2, 1 FADH2
Answer: 1. 3 NADH2, 1 FADH2
Question 18. The first 5-C acid in the TCA cycle is
- Citric acid
- Succinyl CoA
- a-ketoglutaric acid
- Fumaric acid
Answer: 3. a-ketoglutaric acid
” fate of pyruvate “
Question 19. The number of total ATP generated in the TCA cycle per acetyl CoA molecule is
- 10
- 12
- 14
- 24
Answer: 2. 12
Question 20. One molecule of FADH2 upon oxidative phosphorylation yields
- 2 ATP
- 3 ATP
- 4 ATP
- 5 ATP
Answer: 1. 2 ATP
Question 21. The element required for the activation of the aconitase enzyme is.
- Fe2+
- Mn2+
- Mg2+
- All of these
Answer: 1. Fe2+
Question 22. A characteristic feature of the ripening of some fruits (such as bananas) is a sudden increase in respiration, which is known as
- Climactic
- Photorespiration
- Anthesis
- Climacteric
Answer: 4. Climacteric
Question 23. Substrate phosphorylation in TCA occurs when
- Succinic acid changes to fumaric acid
- Fumaric acid changes to malic acid
- Succinyl CoA changes to succinic acid
- Oxalosuccinic acid changes to ketoglutaric acid
Answer: 3. Succinyl CoA changes to succinic acid
Question 24. The mineral activator needed for the enzyme isocitrate dehydrogenase of the TCA cycle is
- Fe
- Mg
- Mn
- Cu
Answer: 3. Mn
Question 25. A single turn of the Krebs cycle yields
- 1 FADH2, 2 NADH2, and 1 ATP
- 2 FADH2, 2 NADH2, and 2 ATP
- 1 FADH2, 3 NADH2, and 1 ATP
- 1 FADH2, 1 NADH2, and 1 ATP
Answer: 3. 1 FADH2, 3 NADH2, and 1 ATP
Question 26. Fumarase enzyme converts
- Succinic acid to malic acid
- Succinic acid to fumaric acid
- Fumaric acid to malic acid
- Fumaric acid to citric acid
Answer: 3. Fumaric acid to malic acid
Question 27. ETS (electron transport system) is found in
- Cytoplasm
- Mitochondrial matrix
- Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Outer mitochondrial membrane
Answer: 3. Inner mitochondrial membrane
Question 28. The number of multiprotein complexes in ETS in mitochondria is
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
Answer: 3. 5
Question 29. The complex concerned with oxidative phosphorylation in the inner mitochondrial membrane is
- Complex 4
- Complex 5
- Complex 3
- Complex 2
Answer: 2. Complex 5
Question 30. Mobile electron carriers in ETS in the mitochondrial membrane are
- PQ, PC
- CoQ, Cyt c
- PQ, Cyt c
- PC, CoQ
Answer: 2. CoQ, Cyt c
Question 31. The Proton channel is found in
- F0 of ATPase
- F1 of ATPase
- Cyt c
- CoQ
Answer: 1. F0 of ATPase
Question 32. In prokaryotic cells, the number of ATPs generated from one glucose molecule is
- 36
- 38
- 34
- 32
Answer: 2. 38
Question 33. Inhibition of sugar breakdown due to the presence of O2 under aerobic conditions is called
- Pasteur effect
- Warburg effect
- Gibbs effect
- Kutusky effect
Answer: 1. Pasteur effect
Question 34. The number of shuttles for transporting extra mitochondrial NADH, into mitochondria is
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 0
Answer: 2. 2
Question 35. Which acid of the TCA cycle is connecting the link with nitrogen metabolism?
- Succinic acid
- Malic acid
- a-ketoglutaric acid
- Citric acid
Answer: 3. a-ketoglutaric acid
Question 36. According to the chemiosmotic mechanism for ATP synthesis given by P. Mitchell, the force/factor responsible for ATP synthesis is
- Membrane potential across the membrane
- Proton motive force
- Electron motive force
- Redox potential
Answer: 2. Proton motive force
Question 37. The intermediate common to fatty acid and carbohydrate oxidation is
- Pyruvate
- Acetyl CoA
- Oxaloacetate
- Succinate
Answer: 2. Acetyl CoA
Question 38. From the oxidation of one molecule of palmitic acid (fatty acid), the number of ATP molecules gained are
- 131
- 129
- 38
- 142
Answer: 2. 129
” end product of oxidative phosphorylation “
Question 39. β-oxidation occurs in
- Pea seeds
- Gram seeds
- Wheat grains
- Cotton seeds
Answer: 4. Cotton seeds
Question 40. The number of dehydrogenations in pentose phosphate pathways is
- 2
- 1
- 3
- 4
Answer: 1. 2
Question 41. The ATP cycle was given by
- Karl Lohman
- Warburg and Lipman
- Peter Mitchel
- Fritz Lipman
Answer: 4. Fritz Lipman
Question 42. In cyanide-resistant respiration, the electrons are passed from ubiquinone to
- Cyt b
- Fe-S protein
- Flavoprotein
- FMN protein
Answer: 3. Flavoprotein
Question 43. In PPP, the net gain of ATP molecules for one glucose molecule is
- 34 ATPs
- 35 ATPs
- 36 ATPs
- 38 ATPs
Answer: 2. 35 ATPs
Question 44. A shunt to EMP or a safety valve is called
- Pentose phosphate pathways
- Cyanide resistance pathways
- ED pathway
- ETS
Answer: 1. Pentose phosphate pathways
Question 45. Which is not an important intermediate of PPP (HMS)?
- NADPH2,
- Erythrose 4phosphate
- Ribulose
- Aromatic compounds
Answer: 4. Aromatic compounds
Question 46. The first step of ethyl alcohol fermentation requires
- Dehydrogenation
- Decarboxylation
- FMN
- Zn2+
Answer: 2. Decarboxylation
Question 47. Hexose monophosphate shunt is
- The pentose phosphate pathway is a set of reactions that bypasses the glycolysis and Krebs cycle routes for glucose oxidation in the cell.
- Conversion of glucose into pyruvic acid.
- The sum of all chemical transformations.
- A process by which starch is synthesized.
Answer: 1. Pentose phosphate pathway or a set of reactions that bypasses the glycolysis and Krebs cycle routes for glucose oxidation in the cell.
Question 48. The efficiency of respiration is approximately
- 45%
- 50%
- 90%
- 30%
Answer: 1. 45%
” respiration in plant”
Question 49. Cytochromes are
- Simple proteins
- S-containing proteins
- Conjugated proteins
- Cu-containing proteins
Answer: 3. Conjugated proteins
Question 50. The most appropriate reason for storing green-colored apples at low temperatures is
- The rate of photosynthesis is reduced.
- Respiration and photosynthesis are completely inhibited.
- The rate of respiration is reduced.
- The rate of photosynthesis and respiration are reduced.
Answer: 3. The rate of respiration is reduced.
Question 51. The Respiratory Quotient (RQ) is defined as
- Volume of O2/Vblume of CO2
- Volume of CO2/Volume of O2
- Volume of O2/Volume of N2
- Volume of N2/Volume of CO2
Answer: 2. Volume of CO2 /Volume of O2
Question 52. Pyruvic acid is formed during
- Krebs cycle
- Glycolysis
- Ornithine cycle
- Calvin cycle
Answer: 2. Glycolysis
Question 53. The correct sequence of electron acceptor in ATP synthesis is
- cyt, a, a3 b, c
- cyt b, c, a, a3
- cyt b, c3, a, a3
- cyt c, b, a, a3
Answer: 2. cyt b, c, a, a3
Question 54. Which one of the following contains copper besides iron?
- Cytochrome-f
- Cytochrome oxidase
- Platoquinone
- Cytochrome-C1
Answer: 2. Cytochrome oxidase
Question 55. Where does the formation of acetyl CoA from pyruvic acid take place?
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
- Cytoplasm
- Golgi body
Answer: 1. Mitochondria
Question 56. The number of ATP molecules produced by the electron transport system from Krebs cycle intermediates in a single turn is
- H
- 14
- 12
- 16
Answer: 1. H
Question 57. In anaerobic respiration, the number of ATP molecules produced are
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 8
Answer: 2. 2
Question 58. In which of the following steps of the Krebs cycle, CO2 is evolved?
- Isocitric acid → Oxalosuccinic acid
- Oxalosuccinic acid → α-ketoglutaric acid
- Succinic acid → Fumaric acid
- Malic acid → Oxaloacetic acid
Answer: 2. Oxalosuccinic acid → α-ketoglutaric acid
Question 59. Which of the following enzymes is not used in the Krebs cycle?
- Aconitase
- Decarboxylase
- Aldolase
- Fumarase
Answer: 3. Aldolase
Question 60. The end product of fermentation is
- O2,
- N2O
- H2O
- C2H5OH
Answer: 4. C2H5OH
Question 61. Gluconeogenesis is the
- Formation of glucose from other than carbohydrate
- Formation of glycogen
- Breakdown of glucose
- Formation of ammonia from glucose
Answer: 1. Formation of glucose from other than carbohydrate
Question 62. β-oxidation takes place in
- Matrix of mitochondria
- Cell cytoplasm
- Inter mitochondrial chamber
- Ribosomes
Answer: 3. Intermitochondrial chamber
Question 63. In the TCA cycle, the conversion of succinyl CoA to succinic acid requires
- Acetyl CoA+GTP + iP
- Acetyl CoA + GDP + IP
- CoA+GTP + iP
- GDP + iP
Answer: 4. GDP + iP
Question 64. Yeast is used in the formation of
- Ammonia
- Alcohol
- Curd
- Petrol
Answer: 2. Alcohol
Question 65. The equation represents fermentation
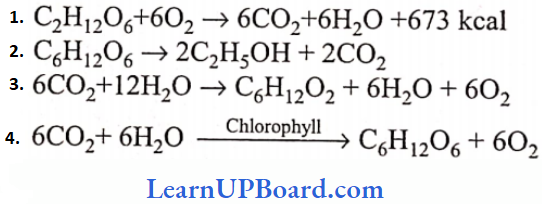
Answer: 2. C6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
Question 66. Which of the following is formed during respiration?
- O2 (oxygen)
- CO2 (carbon dioxide)
- NO2 (nitrogen dioxide)
- SO2 (sulfur dioxide)
Answer: 2. CO2 (carbon dioxide)
Question 67. The pyruvic acid formed in glycolysis is oxidized to CO2 and H2O in a cycle called
- Calvin cycle
- Hill reaction
- Starch
- Vitamins
Answer: 3. Starch
Question 68. The end product of glycolysis is
- Glucose
- Fructose
- Pyruvic acid
- Ethyl alcohol
Answer: 3. Pyruvic acid
Question 69. R.Q. is more than 1 in case of
- Fat
- Fructose
- Glucose
- Organic acid
Answer: 4. Organic acid
Question 70. The total yield in one Krebs cycle is
- 3 FADH2, 2 NADH2 1 ATP
- 2 FADH2, 2 NADH2, 2 ATP
- 2 NADH2, 1 FADH2 2ATP
- 3 NADH2, 1 FADH2, 1 ATP
Answer: 4. 3 NADH2, 1 FADH2, 1 ATP
Question 71. How much ATP will be produced during the production of 1 molecule of acetyl CoA from 1 molecule of pyruvic acid?
- 3 ATP
- 5 ATP
- 8 ATP
- 38 ATP
Answer: 1. 3 ATP
Question 72. The sequence of cytochromes is
- Cyt a, b, c, a3
- Cyt b, c, a, a3
- Cyt b, a, a3, c
- Cyt b, c, a3, a
Answer: 2. Cyt b, c, a, a3
Question 73. Cytochrome is a
- Mg pyrrole ring
- Fe porphyrin ring
- Nucleotide
- Alloy of nichrome
Answer: 2. Fe porphyrin ring
Question 74. Krebs cycle takes place in
- Mitochondrial matrix
- Cytoplasm
- Lysosome
- Nucleus
Answer: 1. Mitochondrial matrix
Question 75. Cellular respiration occurs in
- Chloroplast
- Golgi bodies
- Mitochondria
- Nucleus
Answer: 3. Mitochondria
Question 76. Maximum amount of energy/ATP is liberated on the oxidation of
- Fats
- Proteins
Answer: 1. Fats
Question 77. More CO2 is evolved than the volume of oxygen consumed when the respiratory substrate is
- Fat
- Sucrose
- Glucose
- Organic acid
Answer: 4. Organic acid
Question 78. Krebs cycle begins with the reaction [Jharkhand 2004]
- Citric acid + Acetyl CoA
- Oxaloacetic acid + Pyruvic acid
- Oxaloacetic acid + Citric acid
- Oxaloacetate + Acetyl CoA
Answer: 4. Oxaloacetate + Acetyl CoA
Question 79. Hydrolysis of fat yields
- Fatty acids
- Fatty acids and glycerol
- Mannose and glycerol
- Maltose and fatty acid
Answer: 2. Fatty acids and glycerol
Question 80. Respiratory quotient of which diet is less than unity?
- Carbohydrate
- Fats
- Organic acid
- Sugar
Answer: 2. Fats
Question 81. The richest energy compound is
- Creatinine phosphate
- protein
- Carbohydrate
- Fat
Answer: 4. Fat
Question 82. The stage up to which glycolysis and fermentation are common is
- Dihydroxyacetone
- 3-Phosphoglyceraldehyde
- Pyruvate
- Glucose-6-phosphate
Answer: 3. Pyruvate
Question 83. The respiratory quotient of carbohydrate is
- Unity
- Greater than unity
- Less than unity
- Equal to five
Answer: 1. Less than unity
Question 84. During the conversion of pyruvic acid into acetyl CoA, pyruvic acid is
- Oxidized
- Reduced
- Isomerized
- Condensed
Answer: 1. Oxidized
Question 85. In the Krebs cycle,
- ADP is converted into CO2
- Pyruvic acid is converted into CO2 and H2O
- Glucose is converted into CO2
- Pyruvic acid is converted into ATP
Answer: 2. Pyruvic acid is converted into CO2 and H2O
Question 86. Incomplete breakdown of sugar in anaerobic respiration forms
- Glucose and CO2
- Alcohol and CO2
- Water and CO2
- Fructose and water
Answer: 2. Alcohol and CO2
Question 87. The significance of the Krebs cycle is the
- Synthesis of ATP
- Synthesis of amino acid
- Synthesis of chlorophyll
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 88. In plants, respiration takes place
- During day only
- During night only
- All 24 hours
- At dusk
Answer: 3. All 24-hours
Question 89. Glycolysis takes place in
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus
- Plastid
- Mitochondria
Answer: 1. Cytoplasm
Question 90. In respiration, the largest amount of energy is produced in
- Anaerobic respiration
- Krebs cycle
- Glycolysis
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Krebs cycle
Question 91. Which of the following is not an intermediate in the Krebs cycle?
- Acetic acid
- Succinyl coenzyme-A
- Malic acid
- Citric acid
Answer: 1. Acetic acid
Question 92. The pyruvic acid is formed during
- Krebs cycle
- Glycolysis
- Ornithine cycle
- Photophosphorylation
Answer: 2. Glycolysis
Question 93. The number of ATP molecules gained during aerobic respiration of 1 mole of glucose is
- 12
- 18
- 30
- 38
Answer: 4. 38
Question 94. Alcoholic fermentation takes place in the presence of
- Maltase
- Zymase
- Amylase
- Invertase
Answer: 2. Zymase
Question 95. The site of the EMP pathway in the cell is
- Peroxisome
- Cytoplasm
- Matrix of mitochondria
- The inner membrane of mitochondria
Answer: 2. Cytoplasm
Question 96. The steps of respiration are controlled by
- Substrates
- Enzymes
- Hormone
- Bile juice
Answer: 2. Enzymes
Question 97. Enzymes of the electron transport system are present in
- Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Matrix
- Intermembranous space
- Endoplasmic reticulum
Answer: 1. Inner mitochondrial membrane
Question 98. Which of the following connects glycolysis to Krebs cycle?
- Acetyl Co A
- Ribozyme
- Cytochrome oxidase
- N-acetyl glucosamine
Answer: 1. Acetyl Co A
Question 99. Pyruvic acid is the end product of
- Krebs cycle
- Electron transport system
- Photosynthesis
- Glycolysis
Answer: 4. Glycolysis
Question 100. Which of the following accepts terminal electrons during aerobic respiration?
- Molecular O2
- Molecular H2
- Molecular CO2
- NADPH2
Answer: 1. Molecular O2
Question 101. Glycolysis occurs in
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus
- Mitochondria
- Both 1 and 3
Answer: 1. Cytoplasm
Question 102. Which one of the following is the first step of glycolysis?
- Breakdown of glucose
- Phosphorylation of glucose
- Conversion of glucose into fructose
- Dehydrogenation of glucose
Answer: 2. Phosphorylation of glucose
Question 103. How many ATP molecules are released when 1 molecule of glucose is oxidized in our liver cells?
- 36
- 38
- 2
- 8
Answer: 2. 38
Question 104. The sequence of food materials consumed during starvation is
- Carbohydrates→ Fats → Proteins
- Carbohydrates → Proteins → Fats
- Proteins → Fats → Carbohydrates
- Fats → proteins → Carbohydrates
Answer: 1. Carbohydrates → Fats → Proteins
Question 105. How many ATPs are produced during the glycolysis of one molecule of glucose?
- 4
- 2
- 36
- 38
Answer: 2. 2
Question 106. The final electron acceptor in ETS is
- NAD
- FAD
- Oxygen
- Hydrogen
Answer: 3. Oxygen
Question 107. The respiratory cycle where NADH2 is produced is
- Calvin cycle
- Krebs cycle
- EMP pathway
- HMP shunt
Answer: 2. Krebs cycle
Question 108. Most of the enzymes that participate in the Krebs cycle are found in
- Matrix of mitochondria
- The inner membrane of mitochondria
- The outer membrane of mitochondria
- Stroma of chloroplast
Answer: 1. Matrix of mitochondria
Question 109. The connecting link between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle is
- Acetyl CoA
- CoQ
- Coenzyme
- CoA
Answer: 1. Acetyl CoA
Question 110. The process of oxidative phosphorylation takes place in
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplasts
- Ribosomes
- Cytoplasm
Answer: 1. Mitochondria
Question 111. Glycolysis is the conversion of
- Glucose to glycogen
- Glycogen to glucose
- Glucose to pyruvic acid
- Glucose to citric acid
Answer: 3. Glucose to pyruvic acid
Question 112. Anaerobic respiration takes place in
- Ribosome
- Nucleus
- Cytoplasm
- Vacuole
Answer: 3. Cytoplasm
Question 113. Which of the following is the product of glucose fermentation by yeast?
- C6H12O6
- C2H5OH
- (C6H10O5)n
- CH2OH
Answer: 2. C2H5OH
Question 114. Fermentation is an
- Anaerobic respiration
- Incomplete oxidation
- Excretory process
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Incomplete oxidation
Question 115. Organelles that are regarded as the house of the cell and in which oxidative reactions of the respiratory process take place are known as
- Chloroplast
- Ribosomes
- Mitochondria
- Endoplasmic reticulum
Answer: 3. Mitochondria
Question 116. In which of the following, respiration in the absence of oxygen also takes place?
- Man
- Potato
- Yeast
- Spirogyra
Answer: 3. Yeast
Question 117.CO2 is liberated during
- Ascent of sap
- Respiration
- Photosynthesis
- Transpiration
Answer: 2. Respiration
Question 118. ATP stands for which of the following?
- Adenine tetraphosphate
- Adenine triphosphate
- Adenosine diphosphate
- Adenosine triphosphate
Answer: 4. Adenosine triphosphate
Question 119. Glycolysis occurs in
- Vacuoles
- Nucleolus
- Mitochondria
- Cytoplasm
Answer: 4. Cytoplasm
Question 120. The number of ATP produced during the production of 1 molecule of acetyl CoA from 1 molecule of pyruvic acid is
- 3 ATP
- 8 ATP
- 36 ATP
- 38 ATP
Answer: 1. 3 ATP
Question 121. The energy produced by one ATP molecule is
- 7.6 kcal
- 12kcal
- 20 kcal
- 100 kcal
Answer: 1. 7.6 kcal
Question 122. Which of the following shows anaerobic respiration?
- Earthworms
- Rabbit
- Echinoderras
- Tapeworms
Answer: 4. Tapeworms
Question 123. It is believed that the organisms that first inhabited the earth’s surface were
- Autotrophs
- Mixotrophs
- Chemoautotrophs
- Heterotrophs
Answer: 3. Chemoautotrophs
Question 124. Pyruvic acid before combining with the oxaloacetic acid of the Krebs cycle becomes
- Citric acid
- Acetoacetic acid
- Cis-aconitic acid
- Acetyl CoA
Answer: 4. Acetyl CoA
Question 125. Anaerobic respiration takes place in
- Ribosome
- Nucleus
- Cytoplasm
- Vacuole
Answer: 3. Cytoplasm
Question 126. What is the energy coin of a cell?
- DNA
- RNA
- ATP
- Minerals
Answer: 3. ATP
Question 127. The process of oxidative phosphorylation takes place in
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplasts
- Ribosomes
- Cytoplasm
Answer: 1. Mitochondria
Question 128. RQ of which diet is less than unity?
- Carbohydrate
- Fats
- Organic acid
- Sugar
Answer: 2. Fats
Question 129. Pyruvic acid is the end product of which process?
- Krebs cycle
- Calvin cycle
- Pentose phosphate pathway
- Glycolysis
Answer: 4. Glycolysis
Question 130. 1 molecule glucose, 6 molecules of O2, and 38 ADP combine to form 6H2O, 6CO2, and
- 38 molecules of ATP
- 28 ATP
- 38 ADP
- 28 ADP
Answer: 1. 38 molecules of ATP
Question 131. The number of ATP obtained at the end of the Krebs cycle
- 2 ATP
- 4 ATP
- 8 ATP
- 38 ATP
Answer: 4. 8 ATP
Question 132. During the formation of bread, it becomes porous due to the release of CO2 by the action of
- Yeast
- Bacterial
- Virus
- Protozoans
Answer: 1. Yeast
Question 133. How many ATP molecules are produced by the aerobic oxidation of one molecule of glucose?
- 2
- 4
- 38
- 34
Answer: 3. 38
Question 134. In which one of the following do the two names refer to the same thing?
- Krebs cycle and Calvin cycle
- Tricarboxylic acid cycle and citric acid cycle
- Citric acid cycle and Calvin cycle
- Tricarboxylic acid cycle and urea cycle
Answer: 2. Tricarboxylic acid cycle and citric acid cycle
Question 135. In alcohol fermentation,
- Triosephosphate is the electron donor, while acetaldehyde is the electron acceptor.
- Triosephosphate is the electron donor, while pyruvic acid is the electron acceptor.
- There is no electron donor.
- Oxygen is the electron acceptor.
Answer: 1. Triosephosphate is the electron donor, while acetaldehyde is the electron acceptor.
Question 136. In glycolysis, during oxidation, electrons are removed by
- Molecular oxygen
- ATP
- Glyceraldehyde
- NAD+
Answer: 4. NAD+
Question 137. Aerobic respiration is how many times more useful than anaerobic respiration
- 2
- 8
- 9
- 38
Answer: 3. 9
Question 138. For the retting of jute, the fermenting microbe used is
- Helicobacter pylori
- Methanophilic bacteria
- Streptococcus lactic
- Butyric acid bacteria
Answer: 4. Butyric acid bacteria
Question 139. During which stage in the complete oxidation of glucose are the greatest number of ATP molecules formed from ADP?
- Conversion of pyruvic acid to acetyl CoA
- Electron transport chain
- Glycolysis
- Krebs cycle
Answer: 2. Electron transport chain
Question 140. The deficiencies of micronutrients affect not only the growth of plants but also vital functions such as photosynthetic and mitochondrial electron flow. Among the list given below, which group of three elements shall affect the most, both photosynthetic and mitochondrial electron transport?
- Cu, Mn Fe
- Co, Ni, Mo
- Mn Co, Ca
- Ca, K, Na
Answer: 1. Cu, Mn Fe
Question 141. The chemiosmotic theory of ATP synthesis in the chloro- plast and mitochondria is based on
- Proton gradient
- Accumulation of K ions
- Accumulation of Na ions
- Membrane potential
Answer: 1. Proton gradient
Question 142. Respiration is which type of process?
- Catabolic
- Metabolic
- Anabolic
- None
Answer: 1. Catabolic
Question 143. RQ is represented by
- O2 /CO2
- CO2 /O2 ,
- V2 /(V2 -V)
- O2 taken in
Answer: 2. CO2 /O,
Question 144. Which is the site of the Krebs cycle?
- Chloroplast
- Golgi body
- Mitochondria
- Endoplasmic reticulum
Answer: 3. Mitochondria
Question 145. The curing of tea leaves is brought about by the activity of
- Viruses
- Fungi
- Bacteria
- Mycorrhiza
Answer: 3. Bacteria
Question 146. Which of the following statements regarding mitochondrial membrane is NOT correct?
- The inner membrane is highly convoluted forming a series of infolding.
- The outer membrane resembles a sieve.
- The outer membrane is permeable to all kinds of molecules.
- The enzymes of the electron transfer chain are embedded in the outer membrane.
Answer: 4. The enzymes of the electron transfer chain are embedded in the outer membrane.
Question 147. How many ATP molecules could maximally be generated from one molecule of glucose, if the complete oxidation of one mole of glucose to C02 and H20 yields 686 kcal and the useful chemical energy available in the high energy phosphate bond of 1 mole of ATP is 2 kcal?
- 57
- 2
- 30
- 28
Answer: 1. 57
Question 148. The overall goal of glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport system is the formation of
- Nucleic acids
- ATP in small stepwise units
- ATP in one large oxidation reaction
- Sugars
Answer: 2. ATP in small stepwise units
Question 149. All enzymes of the TCA cycle are located in the mitochondrial matrix except one which is located in the iimer mitochondrial membrane in eukaryotes and cytosol in prokaryotes. This enzyme is
- Succinate dehydrogenase
- Lactate dehydrogenase
- Isocitrate dehydrogenase
- Malate dehydrogenase
Answer: 1. Succinate dehydrogenase
Question 150. Which one of the following mammalian cells is not capable of metabolizing glucose to carbon dioxide aerobically?
- Red blood cells
- White blood cells
- Unstriated muscle cells
- Liver cells
Answer: 1. Red blood cells
Question 151. A competitive inhibitor of succinic dehydrogenase is
- μ-ketoglutarate
- Malate
- Malonate
- Oxaloacetate
Answer: 3. Malonate
Question 152. The chemiosmotic coupling hypothesis of oxidative phosphorylation proposes that adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is formed because
- A proton gradient forms across the inner membrane
- There is a change in the permeability of the inner mitochondrial membrane towards adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
- Hich-energy bonds are formed in mitochondrial proteins
- ADP is pumped out of the matrix into the intermembrane space
Answer: 1. A proton gradient forms across the inner membrane
Question 153. The energy-releasing process in which the substrate is oxidized without an external electron acceptor is called
- Aerobic respiration
- Glycolysis
- Fermentation
- Photorespiration
Answer: 3. Fermentation
Question 154. In germinating seeds, fatty acids are degraded exclusively in the
- Peroxisomes
- Mitochondria
- Proplastids
- Glyoxysomes
Answer: 4. Glyoxysomes
Question 155. The energy-releasing metabolic process in which the substrate is oxidized without an external electron acceptor is called(Pre)
- Aerobic respiration
- Photorespiration
- Glycolysis
- Fermentation
Answer: 4. Fermentation
