NEET Biology Photosynthesis In Higher Plants Multiple Choice Questions And Answers
Question 1. Photosynthesis is
- Anabolic, exergonic, and oxidation-reduction process
- Catabolic, exergonic, and oxidation-reduction process
- Anabolic, endergonic, and oxidation-reduction process
- Catabolic, endergonic, and oxidation-reduction process
Answer: 3. Anabolic, endergonic, and oxidation-reduction process
Question 2. At which step oxygen is used in the peroxisome?
- Glycolate to glyoxylate
- Glyoxylate to glycine
- Glycine to serine
- Serine to hydroxy pyruvate
Answer: 1. Glycolate to glyoxylate
Question 3. Who found that water is an essential requirement of photosynthesis?
- J. Priestley
- Saussure
- Helmont
- Ingen Housz
Answer: 2. Saussure
Question 4. The wavelength of PAR (photosynthetically active radiation) is
- 40-70 nm
- 400-700 mn
- 400-700Å
- 40-70 Å
Answer: 2. 400-700 mn
Question 5. The bulk fixation of carbon through photosynthesis takes place in
- Crop plants
- Tropical rain forests
- Ocean
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 3. Ocean
Question 6. Photosynthesis process was first discovered by
- Priestley
- Ingen Housz
- Engleman
- Blackman
Answer: 2. Ingen Housz
” neetprep photosynthesis “
Question 7. A tadpole-like configuration is found in
- Chlorophyll
- Carotenoids
- Phycobilins
- Anthocyanin
Answer: 1. Chlorophyll
Question 8. Choose the correct statement.
- Chlorophyll-a is soluble in petroleum ether and shows maximum absorption peaks at 453 nm and 642 nm.
- In chlorophyll-b, -CH3 replaces -CHO at 3-C of chlorophyll-a.
- Chlorophyll-b is soluble in methyl alcohol and shows maximum absorption peaks in 429 nm and 660 nm.
- For the biosynthesis of chlorophyll, the raw materials required are succinyl Co-A and glycine.
Answer: 4. For the biosynthesis of chlorophyll, raw materials required are succinyl Co-A and glycine.
Question 9. A quantasome consists of 230 chlorophyll molecules and acts as a photosynthetic unit. It was discovered by
- Park and Biggins
- Hatch and Slack
- Pelletier and Caventou
- Blackman
Answer: 1. Park and Biggins
Question 10. Chlorophyll-c is found in
- Brown algae
- Red algae
- Green algae
- Green algae and Embryophyta
Answer: 1. Brown algae
Question 11. The first step in photosynthesis is
- Excitation of chlorophyll by light
- Ionization of water
- ATP synthesis
- Production of assimilatory power
Answer: 1. Excitation of chlorophyll by light
Question 12. Electric charge separation or quantum conversion occurs at
- Antenna molecules
- Thylakoid membrane
- Reaction center
- Stroma
Answer: 3. Reaction center
Question 13. Phycobilins found in blue-green algae and red algae are/have
- Soluble in hot water
- Found in chromatophores
- Mg+2 and tail
- Lipoidal in nature
Answer: 1. Soluble in hot water
Question 14. The photo system is composed of
- Reaction center
- Light harvesting complex
- Both (1) and (2)
- Granum
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
Question 15. PS-2 is found in
- Stacked part of granum
- Non-stacked part of granum
- Stroma thylakoid
- Stroma
Answer: 1. Stacked part of granum
Question 16. Photosystem concerned with the reduction of NADP is
- PS-1
- PS-2
- Both (1) and (2)
- Quantasome
Answer: 1. PS-1
Question 17. The reaction center of Rhodobacterium was crystallized by
- Amon
- Huber etal
- Emerson
- Warburg
Answer: 2. Huber etal
Question 18. If a photosynthesizing plant releases oxygen containing more than the normal amount of 180, it is concluded that the plant has been supplied with
- C6H12O6 containing 18O
- H2O containing 18O
- CO2 containing 18O
- Oxygen in the form of ozone
Answer: 2. H2O containing 18O
Question 19. Minerals involved in the photo-oxidation of water is
- Mn, Cl, Ca
- Mg, Fe, Mn
- Mn Fe, Ca
- N, P, K
Answer: 1. Mn, Cl, Ca
Question 20. The light reaction produces assimilatory power in the form of
- ATP, NADH2
- ATP, NADPH2
- NAD
- NADP
Answer: 2. ATP, NADPH2
Question 21. The z-scheme in the thylakoid membrane is concerned with
- Reduction of NAD
- Reduction of CO2
- Electron transfer
- All of these
Answer: 3. Electron transfer
Question 22. The primary electron acceptor of PS-2 is
- Pheophytin
- Ferredoxin
- PQ
- PC
Answer: 1. Pheophytin
” photosynthesis questions”
Question 23. The absorption of radiant energy causes
- Reduction of chlorophyll
- Oxidation of chlorophyll
- Absorption of CO2
- Evolution of O2
Answer: 2. Oxidation of chlorophyll
Question 24. The action spectrum of photosynthesis was discovered by
- Van Niel
- Engelman
- Blackman
- None of these
Answer: 2. Engelman
Question 25. The chemiosmotic theory for photophosphorylation was given by
- P-Mitchell
- Amon
- Arnold
- Anderson
Answer: 1. P-Mitchell
Question 26. PS-1 is located on
- The inner surface of the thylakoid membrane
- The outer surface of the thylakoid membrane
- Both surfaces of the thylakoid membrane
- The stroma of chloroplasts
Answer: 2. The outer surface of the thylakoid membrane
Question 27. The red drop effect was studied by
- Van Niel
- Blink
- Emerson
- Calvin
Answer: 3. Emerson
Question 28. C3 cycle (reductive pentose phosphate cycle) is basically a
- CO2 reduction cycle
- CO2 oxidation cycle
- Photochemical reaction
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 1. CO2 reduction cycle
Question 29. To reduce 1 CO2 molecule in C3 cycle, assimilatory power needed is
- 3 ATP, 2NP, DPH2
- 2 ATP, 3NADPH2
- 5 ATP, 2NADPH2
- 6.5 ATP, 2NADPH2
Answer: 1. 3ATP, 2NP, DPH2
Question 30. Q10 of light reaction is
- 1
- 2-3
- 5
- ∞
Answer: 1. 1
Question 31. CO2 acceptor and carboxylation enzyme in C3 plants are, respectively,
- PEP, PEPCO
- RuBP, RuBisCO
- OAA, RuBisCO
- 3 PGA, RuBisCO
Answer: 2. RuBP, RuBisCO
Question 32. A bifunctional enzyme is
- Phosphoglycerate kinase
- PEPCO
- RuBisCO
- Phosphoglyceraldehyde dehydrogenase
Answer: 3. RuBisCO
Question 33. Which is not a step in the Calvin cycle?
- Carboxylation
- Glycolytic reversal
- Regeneration
- Photophosphorylation
Answer: 4. Photophosphorylation
Question 34. Cyclic photophosphorylation releases
- ATP and NADPH2
- ATP, NADPH2, and oxygen
- ATP only
- NADPH2 only
Answer: 3. ATP only
Question 35. Which of the following is a copper-containing protein acting as a mobile electron carrier in the thylakoid membrane?
- Plastocyanin
- Plastoquinone
- Pheophytin
- Cytochrome b6
Answer: 1. Plastocyanin
Question 36. Reducing agents for CO2 fixation in bacterial photosynthesis is
- NADH2
- NADPH2
- FMNH2
- All of these
Answer: 1. NADH2
Question 37. A wasteful light-induced respiratory process releasing CO2 is called
- Warberg effect
- Kutusky effect
- Photorespiration
- CAM
Answer: 3. Photorespiration
Question 38. In photorespiration, release of CO2 occurs in
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
- Peroxisomes
- All of these
Answer: 1. Mitochondria
Question 39. Inhibition of photosynthesis in high concentration of O2 is called
- Warberg effect
- Kutusky effect
- Pasteur effect
- Emerson effect
Answer: 1. Warberg effect
Question 40. The substrate of photorespiration is
- OAA
- Glycolic acid
- 3-PGA
- PEP
Answer: 2. Glycolic acid
Question 41. Photorespiration occurs
- During day time
- In C3 plants
- In cooperation with chloroplasts, peroxisomes, and mitochondria
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 42. DCMU, (3,4-chlorophenyl,l-dimethyl urea, also called diuron) a potent herbicide, inhibits
- O2 evolution
- Photophosphorylation
- Both (1) and (2)
- Oxidative phosphorylation
Answer: 4. Oxidative phosphorylation
Question 43. An oxidative phosphorylation is the formation of
- NADPH2 in respiration
- NADPH2 in photosynthesis
- ATP in respiration
- ATP in photosynthesis
Answer: 3. ATP in respiration
Question 44. CO2-concentrating steps are found in
- C3 Plants
- C4 plants
- CAM plants
- Temperate plants
Answer: 2. C4 plants
Question 45. The number of carboxylations in the photosynthesis in sorghum and maize is
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer: 2. 2
Question 46. Kranz anatomy is
- Having peripheral reticulum in chloroplast
- The presence of a distinct bundle sheath
- Dimorphic chloroplast
- Large vacuoles in mesophyll cells
Answer: 2. Presence of distinct bundle sheath
Question 47. In C4 plants, the first product is
- 3-PGA
- OAA
- Malic acid
- Glutamic acid
Answer: 2. OAA
Question 48. In C4 plants, mesophyll cells and bundle sheath cells are specialized to perform, respectively,
- Light reaction and dark reaction
- Dark reaction and light reaction
- Light reaction and photorespiration
- Photorespiration and dark reaction
Answer: 1. Light reaction and dark reaction
Question 49. Low-temperature sensitivity of C4 plants are due to
- PEP synthetase
- PEPCO
- RuBisCO
- Malate dehydrogenase
Answer: 1. PEP synthetase
Question 50. The members of which of the following families show Kranz anatomy?
- Compositae and Amaranthaceae
- Chenopodiaceae and Euphorbiaceae
- Gramineae
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 51. The initial CO2 acceptor in C4 plants is
- PEP
- PGA
- RuBP
- Pyruvate
Answer: 1. PEP
Question 52. Agranal chloroplasts are found in the
- Mesophyll of pea leaves
- Bundle sheath of mango leaves
- Mesophyll of maize leaves
- Bundle sheath of sugarcane leaves
Answer: 4. Bundle sheath of sugarcane leaves
stroma lamellae lacks
Question 53. The technique which has been most useful for investigating the Calvin cycle is
- Radioactive isotope technique
- Biotechnology technique
- Photometric technique
- Flashlight experimental technique
Answer: 1. Radioactive isotope technique
Question 54. Which is not true for CAM plants?
- Scotoactive opening of stomata
- Dark acidification of cytoplasm
- Separation of Hatch-Slack cycle and O3 cycle in time
- Single carboxylation
Answer: 4. Single carboxylation
Question 55. CAM pathway operates in
- Drought-escaping xerophytes
- Drought-resisting xerophytes
- Drought-enduring xerophytes
- None of these
Answer: 2. Drought-resisting xerophytes
Question 56. Photosynthesis in green algae and bacteria is, respectively,
- Oxygenic and anoxygenic
- Anoxygenic and oxygenic
- Oxygenic in both
- Anoxygenic in both
Answer: 1. Oxygenic and anoxygenic
Question 57. Law of limiting factor was given by
- Liebig
- Amon
- Blackman
- Wilstatter
Answer: 3. Blackman
Question 58. Find the odd one (with respect to double carboxylation).
- Zcamays
- Euphorbia maculala
- Piston sativum
- Amaranthus
Answer: 3. Piston sativum
Question 59. The process in which organisms do not require light and pigment and synthesize their food, utilizing energy released by the oxidation of inorganic and organic substances, is
- Photoautotrophic
- Heterotrophic
- Chemosynthesis
- Saprophytistn
Answer: 3. Chemosynthesis
Question 60. The essentiality of light in photosynthesis can be demonstrated by
- Molls half leaf experiment
- Ganong screen
- Inverted funnel experiment
- KOH solution
Answer: 2. Ganong screen
Question 61. Photochemical reactions in the chloroplasts are directly involved in the
- Fixation of carbon dioxide
- Synthesis of glucose and starch
- Formation of phosphoglyceric acid
- Photolysis of water and phosphorylation of ADP to ATP
Answer: 4. Photolysis of water and phosphorylation of ADP to ATP
Question 62. Which of the following elements are essential for the photolysis of water?
- Ca and Cl
- Mn and Cl
- Zn and I
- Cu and Fe
Answer: 2. Mn and Cl
Question 63. Which of the following is involved in the transfer of electrons in photosynthesis?
- Phytochrome
- Cytochrome
- Photohormone
- Desmosome
Answer: 2. Cytochrome
Question 64. The substrate for photorespiration is
- Glycolatc
- Glucose
- Lipid
- Sucrose
Answer: 1. Glycolatc
Question 65. In aquaria, green plants are grown for
- CO2 production
- Starch production
- O2 Production
- Increase beauty
Answer: 3. O2 Production
Question 66. A structure known as peroxisomes is associated with
- Photosynthesis
- Respiration
- Photorespiration
- Photophosphorylation
Answer: 3. Photorespiration
Question 67. In the mesophyll cells of CAM plants, CCL fixation during the day occurs through
- RuBP oxygenase
- PEP carboxylase
- RuBP carboxylase
- Both RuBP carboxylase and PEP carboxylase
Answer: 3. RuBP carboxylase
Question 68. The first electron acceptor in photosystem-1 of cyclic photophosphorylation is
- Cytochrome
- Plastocyanin
- Ferredoxin
- Plastoquinone
Answer: 3. Ferredoxin
Question 69. Kranz anatomy is found in the leaves of
- C3 plants
- C4 plants
- Both C3 and C4 plants
- None of these
Answer: 2. C4 plants
Question 70. In bacterial photosynthesis
- PS-1 is present
- PS-2 is present
- Both PS-1 and PS-2 are present
- None of these are present
Answer: 1. PS-1 is present
Question 71. Which chlorophyll molecule does not have a phytol tail?
- chl a
- chl b
- chl c
- chl d
Answer: 3. chl c
“questions about photosynthesis “
Question 72. Calvin used algae in his experiment to trace out the path of carbon. The algae used were
- Chlorella and Chlamydomonas
- Chlorella and Scenedesmus
- Chlorococcum and Chlorella
- Chlorococuum and Scenedesmus
Answer: 2. Chlorella and Scenedesmus
Question 73. Which element is essential for the photolysis of water?
- Nitrogen
- Chlorine
- Carbon
- Oxygen
Answer: 2. Chlorine
Question 74. In C4 plants, initial CO2 fixation takes place in the chloroplasts of
- Guard cells
- Mesophyll cells
- Spongy tissue
- Bundle sheath
Answer: 2. Mesophyll cells
Question 75. Which one of the following elements is required for photosynthetic oxygen evolution?
- Copper
- Iron
- Manganese
- Zinc
Answer: 3. Manganese
Question 76. Agranal chloroplasts occur in
- Succulents
- C3 plants
- C4 plants
- Hydrophytes
Answer: 3. C4 plants
Question 77. The wavelength of light most absorbed by chlorophyll-a during photosynthesis is
- 400 nm
- 550 nm
- 660 nm
- 700 nm
Answer: 1. 400 nm
Question 78. Which are related with photorespiration?
- Spherosome
- Lysosomes
- Glyoxysomes
- Peroxisomes
Answer: 4. Peroxisomes
Question 79. Which of the following is a C4 plant?
- Sugarcane
- Mango
- Apple
- Tomato
Answer: 1. Sugarcane
Question 80. The first stable compound formed in photosynthesis of C4 plants is
- Phosphoglyceric acid
- Strach
- Pyruvic acid
- Ribulose diphosphate
Answer: 1. Phosphoglyceric acid
Question 81. Ferredoxin is a component of
- PS-1
- PS-2
- Hill reaction
- P680
Answer: 1. PS-1
Question 82. The correct percentage of CO2 in the atmosphere is
- 0.03%
- 0.3%
- 1%
- 11%
Answer: 1. 0.03%
Question 83. Isotopes used in photosynthesis were
- C11 and P32
- C15 and P32
- C16 and P15
- C14 and O18
Answer: 4. C14 and O18
Question 84. P680 is related with
- PS-1
- PS-2
- Hill reaction
- None
Answer: 2. PS-2
Question 85. NADP reduces to NADPH2
- PS-1
- PS-2
- Calvin cycle
- Non-cyclic ETS
Answer: 4. Non-cyclic ETS
Question 86. Hills reaction was completed in
- Light
- Dark
- Both
- None
Answer: 1. Light
Question 87. Who described C4 pathway for the first time?
- Hatch and Slack
- Robert hill
- Hens Kerbs
- Melvin Kelvin
Answer: 1. Hatch and Slack
Question 88. In photosynthesis, for the synthesis of one mole of glucose number of ATP and NADPH2 required is
- 12 and 18
- 18 and 12
- 6 and 12
- 18 and 18
Answer: 2. 18 and 12
Question 89. The first acceptor of CO2 in C4 plant is
- Pyruvic acid
- Phosphoenol pyruvic
- Acetic acid
- Oxaloacetic acid
Answer: 2. Phosphoenol pyruvic
Question 90. Insectivorous plants usually survive in
- Water-rich soil
- N2-deficient soil
- N2-rich soil
- Sugar-deficient medium
Answer: 2. N2-deficient soil
Question 91. In the process of photosynthesis, water molecule breaks in
- Red drop
- Photolysis
- Phosphorylation
- Carbon assimilation
Answer: 2. Photolysis
Question 92. Who proved that oxygen evolved in photosynthesis comes from water?
- Calvin
- Mayer
- Blackman
- Ruben, Hassid, and Kamen
Answer: 4. Ruben, Hassid, and Kamen
photosynthesis in higher plants neet prep
Question 93. The process in which water splits during photosynthesis is
- Plasmolysis
- Photolysis
- hydrolysis
- Hemolysis
Answer: 2. Photolysis
Question 94. Which of the following was used during the discovery of the Calvin cycle?
- Spirogyra
- Volvox
- Chlamydomonas
- Chlorella
Answer: 4. Chlorella
Question 95. Which of the following is the maximum in chloroplast?
- RuBP carboxylase
- Hexokinase
- Phosphatase
- Nuclease
Answer: 1. RuBP carboxylase
Question 96. O2 released in the process of photosynthesis comes from
- CO2
- Water
- Sugar
- Pyruvic acid
Answer: 2. Water
Question 97. The first carbon dioxide acceptor in C4 plants is
- Phosphoenol pyruvate
- Oxaloacetic acid
- Phosphoglyceric acid
- Ribulose 1,5-diphosphate
Answer: 1. Phosphoenolpyruvate
Question 98. C4 plants are different from C3 plants with reference to the
- Type of pigments involved in photosynthesis
- The number of NADPH that arc consumed
- End product
- The substance that accepts CO2 in carbon assimilation and the first stable product
Answer: 4. The substance that accepts CO2 in carbon assimilation and the first stable product
Question 99. Calvin cycle occurs in
- Cytoplasm
- Chloroplasts
- Mitochondria
- Glyoxysoiues
Answer: 2. Chloroplasts
Question 100. Oxygen which is liberated during photosynthesis comes from
- CO2
- H2O
- Phosphoglyceric
- Chlorophyll
Answer: 2. H2O
Question 101. Which one is produced during cyclic photophosphorylation?
- ATP and NADPH2
- ATP only
- ATP and O2
- NADPH2
Answer: 2. ATP only
Question 102. A student sets up an experiment on photosynthesis as follows: He takes soda water in a glass tumbler adds chlorophyll into the contents and keeps the tumbler exposed to sunlight hoping that he has provided the necessary ingredients for photosynthesis to proceed (viz.. CO2, H2O, chlorophyll, and light). What do you think happens after, say, a few hours of exposure of light?
- Photosynthesis will take place and glucose will be produced.
- Photosynthesis will take place and starch will be produced which turn the mixture turbid.
- Photosynthesis will not take place because CO2 dissolved in soda water escapes into the atmosphere.
- Photosynthesis will not take place because intact chloroplasts are needed for the process.
Answer: 4. Photosynthesis will not take place because intact chloroplasts are needed for the process.
Question 103. The first reaction in photorespiration is
- Carboxylation
- Decarboxylation
- Oxygenation
- Phosphorylation
Answer: 3. Oxygenation
Question 104. The law of limiting factors, in photosynthesis, was given by
- R. Hill
- Calvin
- Blackman
- Amon
Answer: 3. Blackman
Question 105. Carbon dioxide acceptor in C3 plants is
- PEP
- RuDP
- PGA
- NADP
Answer: 2. RuDP
Question 106. Insectivorous plants grow in soils which are deficient in
- Nitrogen
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Carbohydrate
Answer: 1. Nitrogen
Question 107. Quantasomcs are found in
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
- Lysosome
- Endoplasmic reticulum
Answer: 2. Chloroplast
Question 108. During photosynthesis,
- O2 evolved comes from CO2
- ATP is formed
- ATP is not formed
- Water is required as a medium but it does not take part in photosynthesis
Answer: 2. ATP is formed
Question 109. Cu is present in
- Plasmaletnma
- Plastoquinone
- Plastocyanin
- Ferrcdoxin
Answer: 3. Plastocyanin
Question 110. In which of the following, oxygen does not evolve during photosynthesis?
- Photosynthetic red algae
- Photosynthetic green algae
- Photosynthetic blue-green algae
- Photosynthetic bacteria
Answer: 4. Photosynthetic bacteria
Question 111. In the process of photosynthesis,
- O2 is taken and CO2 is evolved
- O2 is taken and CO2 is not evolved
- CO2 is taken and O2 is evolved
- CO2 is taken and NO2 is evolved
Answer: 3. CO2 is taken and O2 is evolved
Question 112. Cuscuta is a
- Parasitic plant
- Symbiotic plant
- Predator
- Decomposer
Answer: 1. Parasitic plant
Question 113. In photosynthesis, there is
- Reduction of H2O
- Oxidation of H2O
- Oxidation of CO2
- Oxidation of NO2
Answer: 2. Oxidation of H2O
Question 114. In case of C4 plants, the acceptor of CO2 is
- Phosphoglyceraldehyde
- Ribulose monophosphate
- Phosphoenol pyruvate
- Ribulose diphosphate
Answer: 3. Phosphoenolpyruvate
Question 115. The first step in the light reaction of photosynthesis is
- Formation of ATP
- Ionization of water
- Attachment of CO2 to a pentose sugar
- Excitement of electron of chlorophyll by a photon of light
Answer: 4. Excitement of electron of chlorophyll by a photon of light
Question 116. Sugarcane shows high efficiency for CO2 fixation because of
- Calvin cycle
- Hatch and Slack cycle
- TCA cycle
- Greater sunlight
Answer: 2. Hatch and Slack cycle
Question 117. The source of CO2 for photosynthesis during day in CAM plants is
- 3-PGA
- Malic acid
- Oxaloacetic acid
- Pyruvate
Answer: 2. Malic acid
Question 118. Chlorophyll has in its center.
- Iron
- Magnesium
- Copper
- Sulfur
Answer: 2. Magnesium
Question 119. Calvin cycle of C4 plants operates in
- Grana of mesophyll chloroplasts
- Stroma of chloroplasts in mesophyll cells
- Bundle sheath cells chloroplasts
- Wrong statements wrong
Answer: 3. Bundle sheath cells chloroplasts
Question 120. Photorespiration takes place in
- Chloroplast, mitochondria
- Mitochondria, peroxisome
- Bundle sheath chloroplasts
- Chloroplast, peroxisome, mitochondria
Answer: 4. Chloroplast, peroxisome, mitochondria
Question 121. Which one is false about Kranz’s anatomy?
- Bundle sheath cells have large chloroplast and less developed grana.
- Mesophyll cells have large chloroplast and more developed grana.
- It is found in triplex, sugarcane, and maize.
- Plants having it have better photosynthesizing power than C3 plants.
Answer: 2. Mesophyll cells have large chloroplast and more developed grana.
Question 122. Who discovered that CO2 is taken in and O2 is released by green plants?
- Meyer
- Ijugen Housz
- Senebier
- Priestly
Answer: 4. Priestly
Question 123. Primitive photosynthetic plants utilize solar energy by
- Cyclic photophosphorylation
- Z-scheme
- Both (1) and (2)
- Calvin cycle
Answer: 1. Cyclic photophosphorylation
Question 124. Which one of the following is a wasteful process?
- Photorespiration
- Respiration
- Photosynthesis
- ETS
Answer: 1. Photorespiration
Question 125. DCMU
- Inhibits PS-1
- Inhibits PS-2
- Destroys chloroplast
- Inhibits oxidative phosphorylation
Answer: 2. Inhibits PS-2
Question 126. NH3 releases from
- Photorespiration
- Dark respiration
- CAM
- All of these
Answer: 1. Photorespiration
Question 127. Photosystem 1 and Photosystem 2 are found in the
- Stroma of chloroplast
- Grana of chloroplast
- Ma trix of mitochondria
- The inner membrane of mitochondria
Answer: 2. Grana of chloroplast
Question 128. A cell organelle essential for photorespiration is
- Ribosome
- Dictyosome
- Peroxisome
- Cilyoxisome
Answer: 3. Peroxisome
Question 129. In which of the following the rate of transpiration is high?
- CAM Plant
- C3 plants
- C3 and C4
- C4 plants
Answer: 2. C3 plants
Question 130. Of which cell organelle is grana a part?
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
- Aleurone grain
- Starch grain
Answer: 2. Chloroplast
Question 131. The substrate of photorespiration is
- Glycolate
- Glucose
- Pyruvic acid
- Acetyl COA
Answer: 1. Glycolate
Question 132. The maximum light absorbed by the chlorophyll-a is at the wavelength of
- 460 nm
- 500 nm
- 600 nm
- 660 nm
Answer: 1. 460 nm
Question 133. During photosynthesis, oxygen is evolved from
- H2S
- H2O
- CO2
- HCO3
Answer: 2. H2O
Question 134. Which of the following acts as an electron carrier in both photosynthesis and respiration?
- Ferredoxin
- Phytochrome
- Cytochrome
- Cryptochrome
Answer: 3. Cytochrome
Question 135. The photosynthetic unit is
- Glyoxysome
- Spherosome
- Microsome
- Quanasome
Answer: 4. Quanasome
Question 136. Warburg effect is related with
- Concentration of O2
- Concentration of N
- Concentration of H2
- Concentration of Cilyoxisome
Answer: 1. Concentration of O2
Question 137. Stroma is the ground substance of
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Mitochondria
- Nucleolus
- Chloroplast
Answer: 4. Chloroplast
Question 138. Which of the following peroxisomes in plants are associated?
- Photorespiration
- Photosynthesis
- Photoperiodism
- Phototropism
Answer: 1. Photorespiration
Question 139. In C3 plants, the first stable product of photosynthesis is
- Malic acid
- Oxaloacetic acid
- Phosphoglyceric acid (PGA)
- Phosphoglyceraldehyde (PGAL)
Answer: 3. Phosphoglyceric acid (PGA)
Question 140. The process of taking CO2 by plants and releasing O2 is known as
- Photosynthesis
- Endosmosis
- Transpiration
- Respiration
Answer: 1. Photosynthesis
Question 141. Which of the colors of light is mostly absorbed by chlorophyll-a?
- Green
- Red
- Blue
- Infrared
Answer: 3. Blue
Question 142. In photosynthesis, ATP is synthesized during
- Cyclic photophosphorylation
- Non-cyclic photophosphorylation
- Both (1) and (2)
- In the photolysis of water
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
Question 143. Which of the following elements is essential for the photolysis of water?
- Fe
- Mg
- Mn
- Cu
Answer: 3. Mn
Question 144. Peroxisomes are concerned with
- Respiration
- Photorespiration
- Photosynthesis
- Flowering
Answer: 2. Photorespiration
Question 145. The reduction process of CO2 and ATP formation in plants has a relationship. In this reaction, ATP is
- Formed
- Utilized
- Not utilized
- None of these
Answer: 2. Utilized
Question 146. ATP synthesis during photosynthesis is termed as
- Phosphorylation
- Oxidative phosphorylation
- Photophosphorylation
- Photorespiration
Answer: 3. Photophosphorylation
Question 147. Which of the following is used during the discovery of Calvin?
- Spirogyra
- Volvox
- Chlamydomonas
- Chlorella
Answer: 4. Chlorella
Question 148. The primary receptor of CO2 in photosynthesis is
- Phosphoric acid
- Ribulose phosphate
- Glucose
- Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate
Answer: 4. Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate
Question 149. In sugarcane plants, 14CO2 is fixed in malic acid, in which the enzyme that fixes CO2 is
- Ribulose biphosphate carboxylase
- Phosphoenol pyruvic acid carboxylase (PEP-case)
- Ribulose phosphate kinase
- Fructose phosphatase
Answer: 2. Phosphoenol pyruvic acid carboxylase (PEP-case)
Question 150. Photorespiration in C3 plants starts from
- Phosphoglycerate
- Glycerate
- Glycine
- Phosphoglycolate
Answer: 4. Phosphoglycolate
Question 151. The substrate of photorespiration is
- Glycolate
- Glucose
- Pyruvic acid
- Acetyl CoA
Answer: 1. Glycolate
Question 152. Tracer elements are
- Micro-elements
- Macro-elements
- Radio-isotopes
- Vitamins
Answer: 3. Radio-isotopes
Question 153. Choose the correct match. Bladderwort, sundew, Venus flytrap
- Nepenthes, Dionaea, Drosera
- Nepenthes, Utricularia, Vanda
- Utricularia. Drosera, Dionaea
- Dionaea, Trapa, Vanda
Answer: 3. Utricularia. Drosera, Dionaea
Question 154. Which of the following is wrong in relation to photorespiration?
- It occurs is chloroplasts.
- It occurs in the daytime only.
- It is a characteristic of C4 plants.
- It is a characteristic of C3 plants.
Answer: 3. It is a characteristic of C3 plants.
Question 155. Photosynthetic active radiation (PAR) represents the following range of wavelengths.
- 400-700 nm
- 500-600 nm
- 450-950 nm
- 340-150 nm
Answer: 1. 400-700 nm
Question 156. In C3 plants, the first stable product of photosynthesis during the dark reaction is
- Phosphoglyceraldehyde
- Malic acid
- Oxaloacetic acid
- 3-Phosphoglyceric acid
Answer: 4. 3-Phosphoglyceric acid
Question 157. Plants adapted to low light intensity have
- Leaves modified to spines
- Large photosynthetic unit size than the sun plants
- Higher rate of CO2 fixation than the sun plants
- More extended root system
Answer: 2. Larger photosynthetic unit size than the sun plants
Question 158. In chloroplast, chlorophyll is present in the
- Stroma
- Outer membrane
- Inner membrane
- Thylakoids
Answer: 4. Thylakoids
Question 159. Which one of the following categories of organisms do not evolve oxygen during photosynthesis?
- Red algae
- Photosynthetic bacteria
- C4 plants with Kranz anatomy
- Blue-green algae
Answer: 2. Photosynthetic bacteria
Question 160. Which pair is wrong?
- C3 plant—Maize
- Calvin cycle—PGA
- Hatch-Slack cycle—OAA
- C4 plant—Kranz anatomy
Answer: 1. C4 plant—Maize
Question 161. Photosynthesis in C4 plants is relatively less limited by atmospheric CO2 levels because
- Four carbon acids are the primary initial CO2 fixation products
- The primary fixation CO2 is mediated via PEP carboxylase
- Effective pumping of CO2 into bundle sheath cells
- RuBisCO in C4 plants has a higher affinity for CO2
Answer: 3. Effective pumping of CO2 into bundle sheath cells
Question 162. Chlorophyll in chloroplasts is located in
- Grana
- Pyrcnoid
- Stroma
- Both grana and stroma
Answer: 1. Grana
Question 163. As compared to a C3 plant, how many additional molecules of ATP are needed for the net production of one molecule of hexose sugar by C4 plants?
- Two
- Six
- Zero
- Twelve
Answer: 4. Twelve
Question 164. Carbohydrates, the most abundant biomolecules on earth, are produced by
- All bacteria, fungi, and algae
- Fungi, algae, and green plant cells
- Some bacteria, algae, and green plant cells
- Viruses, fungi, and bacteria
Answer: 3. Some bacteria, algae, and green plant cells
Question 165. The deficiencies of micronutrients not only affect the growth of plants but also vital functions such as photo-synthetic and mitochondrial electron flow. Among the list given below, which group of three elements shall affect the most both photosynthetic and mitochondrial electron transport?
- Cu, Mn, Fe
- Co, Ni, Mo
- Mn, Co, Ca
- Ca, K, Na
Answer: 1. Cu, Mn, Fe
Question 166. The chemiosmotic theory of ATP synthesis in chloroplasts and mitochondria is based on
- Proton gradient
- Accumulation of K ions
- Accumulation of Na ions
- Membrane potential
Answer: 1. Proton gradient
Question 167. Photosynthetic active radiation (PAR) has the following range of wavelengths
- 400-700 nm
- 450-920 nm
- 340-450 nm
- 500-600 nm
Answer: 1. 400-700 nm
Question 168. In the light reaction of photosynthesis, oxygen comes from
- Water
- CO2
- Soil
- Atmosphere
Answer: 1. Water
Question 169. The product of light reaction of photosynthesis is
- Carbohydrate
- ATP
- NADP and O2
- NADPH2, ATP, and O2
Answer: 4. NADPH2, ATP, and O2
Question 170. In photosystem-1, the first electron acceptor is
- Plastocyanin
- An iron-sulfur protein
- Ferredoxin
- Cytochrome
Answer: 2. An iron-sulfur protein
Question 171. The translocation of organic solutes in sieve tube members is supported by
- Mass How involving a carrier and ATP
- Cytoplasmic streaming
- Root pressure and transpiration pull
- P-protein
Answer: 1. Mass How involving a carrier and ATP
Question 172. During photorespiration, the oxygen-consuming reaction(s) occur(s) in the
- Grana of chloroplasts and peroxisomes
- Stroma of chloroplasts
- Stroma of chloroplasts and mitochondria
- Stroma of chloroplasts and peroxisomes
Answer: 4. Stroma of chloroplasts and peroxisomes
Question 173. The first acceptor of electrons from an excited chlorophyll molecule of photosystem-2 is
- Quinone
- Cytochrome
- Iron-sulfur protein
- Ferredoxin
Answer: 1. Quinone
Question 174. In the leaves of C4 plants, malic acid formation during CO2 fixation occurs in the cells of
- Epidermis
- Mesophyll
- Bundle sheath
- Phloem
Answer: 2. Mesophyll
Question 175. In leaves of C4 plants, malic acid synthesis during CO2 fixation occurs in
- Bundle sheath
- Guard cells
- Epidermal cells
- Mesophyll cells
Answer: 4. Mesophyll cells
Question 176. The C4 plants are photosynthetically more efficient then C3 plants because
- The CO2 efflux is not prevented.
- They have more chloroplasts
- The CO2 compensation point is more.
- CO2 generated during photorespiration is trapped and recycled through PEP carboxylase
Answer: 2. They have more chloroplasts
Question 177. Electrons from the excited chlorophyll molecule of photosystem 2 are accepted first by
- Quinone
- Ferredoxin
- Cytochrome-b
- Cytochrome-f
Answer: 1. Quinone
Question 178. Stroma in the chloroplasts of higher plant contains
- Chlorophyll
- Light-independent reaction enzymes
- Light-independent reaction enzymes
- Ribosomes
Answer: 3. Light-independent reaction enzymes
Question 179. Oxygenic photosynthesis occurs in
- Chlorohium
- Chromatium
- Oscillatoria
- Rhodospirillum
Answer: 3. Oscillatoria
Question 180. Cyclic photophosphorylation results in the formation of
- ATP
- NADPH
- ATP and NADPH
- ATP, NADPH, and O2
Answer: 1. ATP
Question 181. PGA as the first CO2 fixation product was discovered in the photosynthesis of
- Angiosperm
- Alga
- Bryophyte
- Gymnosperm
Answer: 2. Alga
Question 182. C4 plants are more efficient in photosynthesis than C3 plants due to
- Presence of thin cuticle
- Lower rate of photorespiration
- Higher leaf area
- The presence of larger number of chloroplasts in the leaf cells
Answer: 2. Lower rate of photorespiration
Question 183. Kranz anatomy is one of the characteristics of the leaves of
- What
- Sugarcane
- Mustard
- Potato
Answer: 2. Sugarcane
Question 184. Study the pathway given. In which of the following options, correct words for all the three blanks A, B, and C are indicated?
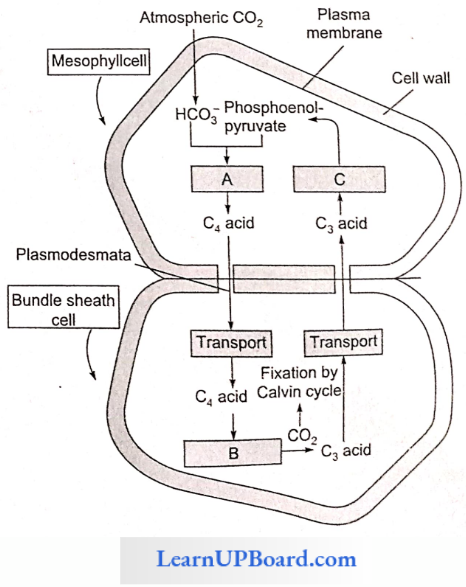
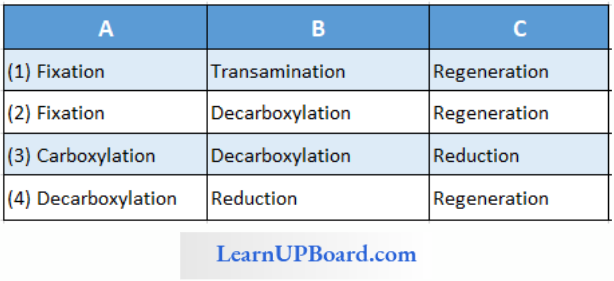
Answer: 2
Question 185. Read the following four statements, A, B, C, and D, and select the right option having both correct statements
- Z scheme of light reaction takes place in the presence of PS-1 only.
- Only PS-1 is functional in cyclic photophosphorylation.
- Cyclic photophosphorylation results in the synthesis of ATP and NADPH2.
- Stroma lamellae lack PS-2 as well as NADP.
- A and B
- B and C
- C and D
- B and D
Answer: 4. B and D
Question 186. A process that makes an important difference between C3 and C4 plants is
- Glycolysis
- Photosynthesis
- Photorespiration
- Transpiration
Answer: 3. Photorespiration
Question 187. Which one of the following organisms is correctly matched with its three characteristics?
- Pea: C3 pathway, Endospermic seed, Vexillary aestivation
- Tomato: Twisted aestivation, Axile placentation, Berry
- Onion: Bulb, Imbricate aestivation, Axile placentation
- Maize: C3 pathway, Closed vascular bundles, Scutellum
Answer: 3. Onion: Bulb, Imbricate aestivation, Axile placentation
